Employees Reactions to Organizational Change
|
|
|
- Juliet Atkins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Employees reactions to change are influenced by a number of factors. It is reasonable to expect employees to react since the process of change involves going from the known to the unknown, and when employees react, it is important to distinguish between the symptoms of their reactions and the causes behind them. Employees Reactions to Organizational Change By Cynthia Wittig Literature indicates that a high proportion of change initiatives are unsuccessful (Beer & Nohria, 2000). Researchers generally agree that employee resistance is one of the leading causes for the failure of change initiatives (Bovey & Hede, 2001b; Waldersee & Griffiths, 1996). Such findings indicate that change agents focusing on employee reactions including resistance and acceptance during organizational change is of utmost importance to the success of the initiative. In response, this paper provides a model that illustrates the process of how employees reactions to change are formed. Employees Reactions to Organizational Change Employees reactions to change are influenced by a number of factors. It is reasonable to expect employees to react since the process of change involves going from the known to the unknown, and when employees react, it is important to distinguish between the symptoms of their reactions and the causes behind them (Bovey & Hede, 2001b). Following is an analysis of three factors that research strongly identifies as influencing employees reactions to change: employees emotions and cognitions, communication, and employees participation in decision making. Evidence suggests that these factors explain much of employees reactions, arguably more than other factors present during organizational change. Although these factors are closely related and can even be considered interwoven in many ways, each factor contributes individual and important information. Employees Emotions and Cognitions Many change efforts fail since change agents underestimate the importance of the individual, cognitive-affective nature of change (Ertuk, 2008), and emotions and cognition are closely intertwined (Pessoa, 2008). The following separate yet interrelated aspects of emotions and cognitions impact employees reactions to organizational change: emotional intelligence, irrational thoughts, defense mechanisms, and employee attitudes. Emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence (EI) is the capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships (Vakola, Tsaousis, & Nikolaou, 2004). The role of EI in employees reactions to change is important because individuals with high levels of EI experience more career success, feel less job insecurity, are more effective in team leadership and performance, are more adaptable to stressful events, and exhibit better coping strategies than those with low EI levels (Vakola, Tsaousis, & Nikolaou, 2004). Irrational thoughts. Research indicates that irrational ideas are significantly and positively correlated with employees resistance to change. Individuals tend to have automatic thoughts that incorporate what has been described as faulty, irrational, or crooked thinking (Bovey & Hede, 2001a). During change, employees create their own interpretations of what is going to happen, Employees Reactions to Organizational Change 23
2 how others perceive them, and what others are thinking or intending (Bovey & Hede, 2001a). Defense mechanisms. Defense mechanisms arise involuntarily in response to perceptions of danger and are adopted to alleviate anxiety (Bovey & Hede, 2001b). According to Bovey and Hede (2001b), employees who are unconsciously inclined to use maladaptive defenses are more likely to resist change. Employees with a tendency to unconsciously adopt adaptive defenses are less likely to resist change. Employee attitudes. Vakola, Tsaousis, and Nikolaou (2004) identified multiple studies in which employees positive attitudes toward change were vital in achieving successful organizational change initiatives. Several factors impact employees attitudes toward change, specifically gender, tenure, educational attainment, and social systems (Vakola, Tsaousis, & Nikolaou, 2004; Oreg, 2006). Stanley, Meyer, and Topolnytsky (2005) identified that a relationship exists between employees cynical attitudes and resistance. Communication The vital importance of communication during the change process has been empirically demonstrated and generally agreed upon among theorists (Lewis, 2006). Since the success of organizational change initiatives lies in the reaction of employees, it is crucial to communicate to employees information about the change to positively influence their reactions. Poorly managed change communication can result in resistance and exaggerating negative aspects of the change. Effective communication reduces employees uncertainty, and a negative correlation exists between uncertainty and employees willingness to accept change (Elving, 2005). The amount and quality of information that is communicated to employees can influence how employees react (Wanberg & Banas, 2000). Such evidence acknowledges that communi cation is a key factor, and its importance cannot be understated in impacting employees reactions. Processes of Communication. There are several communication processes that impact employees reactions, including frequency, mode, content, and flow of communication. Gray and Laidlaw (2002) argued that the more embedded these processes are within management, the more effective the outcomes are because they enhance the quality of working relationships, harmony, and trust. Social accounting. Social accounting influences the quality of the communication and, therefore, impacts employees reactions. According to Lines (2005), social accounting is defined as the process used for explaining the reasons for the decision to those affected by the decision. Successful social accounting leads to a positive influence on the likelihood of implementation success (Lines, 2005). Leader-member exchange. An aspect of communication that impacts employees resistance is the leader-member exchange (LMX) relationship, or the quality of relationships between employees and their supervisors. Employees with high quality LMX accept change more readily than employees with lower quality LMX, arguably due to increased access to information, assistance, and involvement in decision making (Farr-Wharton & Brunetto, 2007). Employee Participation in Decision Making One specific method of communication that strongly impacts employees reactions is employee participation in decision making (PDM). PDM is a process in which influence or decision making is shared between superiors and their subordinates (Bordia, Hobman, Jones, Gallois, & Callan, 2004). The structural characteristics of PDM initiatives impact the degree to which the initiative affects employees reactions (Dachler & Wilpert, 1978). Positive effects. Key attributes of PDM, such as open communication, expressing new ideas, shared vision, common direction, mutual respect, and trust, are also suggested as the key elements in managing change (Erturk, 2008). Participation is positively associated with employees perceptions of fairness, which is vital for acceptance of change and commitment to organizational goals (Bordia, Hobman, Jones, Gallois, & Callan, 2004). Type of change decision. The type of change decision presented in PDM initiatives impacts the resulting influence on employees reactions to the change initiative. The positive effects of PDM on employees seem to be greater when tactical decisions (the what and how to change) rather than strategic decisions (the if of the change) must be made (Sagie & Koslowsky, 1994). Spectrum of Employees Reactions to Organizational Change The above literature review strongly supports that a number of factors impact employees reactions to change. Throughout the remainder of this paper, a model of the process of how employees reactions to change are formed is proposed, supported by three propositions. The author also demonstrates application of this model in practice to increase employees acceptance of change. Several theories support that distinct phases are encountered throughout the process of initiating change (Lewin, 1951). However, based on both the author s experience with change initiatives in the travel industry and scientific literature, the argument that change does not occur in distinct phases is provided. Rather, change occurs as a flow of processes and endeavors that is not static. This perspective does not undermine the importance of Lewin s theory of freezing and unfreezing each stage, but suggests that these states are not identifiably distinct. Therefore, considering a model of change that represents a non-static, dynamic flow of processes is imperative. Employees Reactions to Change: and Many researchers have reported findings in terms that suggest employee acceptance and resistance are concrete milestones that 24 OD PRACTITIONER Vol. 44 No
3 Figure 1: Spectrum of Employees Reactions to Organizational Change Mild reaction can be attained, and that once attained, remain attained. Phrases such as eliminate employee resistance (Jones & Smith, 2001) and gain employee acceptance (Sigler, 1999) may indicate that organizations can reach these milestones in change initiatives in the same manner; for example, that the organization may achieve the goals of completing the initiative in the number of days allotted (the project is either completed in less or more than the days allotted). However, this is not the case in the author s experience. Rather, the line in employees reactions to organizational change between resistance and acceptance is often blurred. To enable change agents to identify employees acceptance and resistance, it is important to operationalize definitions of reactions to change. is a multidimensional attitude toward change, comprising affective (feelings toward the change), cognitive (evaluations of worth and benefit of the change), and behavioral (intention to act against the change) components (Oreg, 2006). Each of these dimensions can be characterized as ranging from acceptance to resistance. When these three dimensions are considered in the aggregate, the result is the employees overall acceptance or resistance to change. The author experienced change initiatives in two unrelated organizations that through juxtaposition illustrate the complexity of employees reactions. In Organization A, employees were mildly accepting of the organizational change and passively gave into the changes. In Organization B, employees were strongly accepting of the change and actively demonstrated their support by embracing the changes and initiating actions aligned with the initiative. One could argue that both Organization A and Organization B achieved employee acceptance of the change. However, with such different levels of acceptance in Organization A (mild acceptance) and Organization B (strong acceptance), stating that each organization achieved the same level of employee acceptance is hardly plausible. Herein lays the framework of the Spectrum of Employees Reactions to Organizational Change (SEROC), as illustrated in Figure 1. The fundamental concept of the SEROC is that different degrees and intensities of employee reactions to change exist. Employees reactions, as defined by the employees level of resistance and acceptance, are polar opposites on a spectrum, and neutral or indifferent reactions that are mild in strength are found in the middle of the spectrum. Employees are always located on the spectrum, and their location is determined by the strength of their reaction. The scale of the spectrum is considered both ordinal and cardinal. An employee who is twice as accepting of (or resistant to) the change is on the spectrum twice as far from neutral. Since there is no zero of reactions to change, neutral or indifferent is considered zero, or equilibrium. When analyzing employees location on the spectrum, one must consider that reactions to change are relative, and, therefore, one must recall the operational definitions of reactions to change. P1: One cannot achieve minimal resistance or attain maximum acceptance as concrete milestones. Rather, employees reactions to organizational change, as defined by the employees level of resistance and acceptance, are represented by polar opposites on a spectrum, and neutral reactions that are mild in strength are represented in the middle of the spectrum. Traversing the spectrum As employees levels of acceptance and resistance fluctuate during the change initiative, the employees location on the spectrum moves from one end to the other. Factors and events that impact employees reactions affect employees locations on the spectrum and are represented on the SEROC by vectors exhibiting the same properties as vectors found in mathematical contexts, as illustrated in Figure 2 (next page). Vectors originate at the neutral point, and vectors vary in direction (pointing toward the acceptance or resistance end of the spectrum) and magnitude (large magnitudes indicate very influential factors and small magnitudes indicate mildly influential factors) depending on the factors of change they represent. The employees position on the spectrum is determined by the overall sum of the vectors. Although factors (represented by vectors on the spectrum) actively change employees levels of resistance and acceptance, change agents passiveness also impacts employees reactions. In the author s experience, when change agents fail to introduce new factors to elicit employee acceptance of change, the intensity of the employees acceptance of change dwindles and they begin to resist the change. To illustrate this phenomenon on the SEROC, without the introduction of vectors to continually move employees toward the acceptance polar end of the spectrum, employees return to the neutral position on the spectrum as time passes. As employees continually regress toward neutral, it becomes increasingly easier for them to become located on the resistance section of the spectrum. Employees Reactions to Organizational Change 25
4 Figure 2: Vectors represent factors that influence employees reactions to change Vector representing a factor that strongly increases employees resistance to change. Vector representing a factor that increases employees resistance to change. P2: Factors and events that impact employees resistance to change are represented on the spectrum as vectors of varying magnitudes and directions. The effect of all factors (represented by the sum of all vectors) is the employees level of acceptance or resistance to change. To illustrate the application of SEROC, return to the author s experience of Organization A, in which employees were mildly accepting of a change initiative to restructure organizational roles. Examination of the employees initial reactions indicated most employees resisted the change. They feared for their job security and lacked trust in management. A small group of employees, however, accepted this change because they saw opportunity for promotion. Despite their acceptance of the change, the employees were partially hesitant to accept the change and mildly resisted because they perceived that their jobs may be eliminated. Overall, the employees on the organizational level reacted to the change with somewhat strong resistance, as shown in Figure 3. Later in the course of the change, change agents created a PDM initiative in which employees concerns were addressed and the employees felt they had contributed to the outcome of the initiative. On the SEROC, the PDM initiative is represented by a vector that moves the organization toward the acceptance end of the spectrum. Because the PDM accounted for a great deal of acceptance in the employees, the vector is of a large magnitude (see Figure 4, next page). Subsequently in the course of the initiative, the change agents failed to provide employees with sufficient communication regarding a new policy, despite otherwise effective communication. Therefore, the employees acceptance of the change started to diminish and employees returned toward the resistance end of the spectrum. Because this factor only slightly increased employees resistance, ineffective communication processes are represented by a vector with a small magnitude positioned toward the resistance end of the spectrum. After the two aforementioned factors occurred and impacted employees reactions, the employees still mildly accepted the change. This mild acceptance of the change is represented by the sum of the Figure 3: An illustration of an organization s reaction to change (mildly resistant reaction) Key Individual employees Organization (Aggregate of Individual Employees) Mild reaction 26 OD PRACTITIONER Vol. 44 No
5 Figure 4: An illustration of an organization s employees reactions to change (mildly accepting), based on two factors that are present in the change Vector representing a factor that strongly increases employees acceptance to change (a successful PDM initiative). Vector representing a factor that mildly increases employees resistance to change (ineffective communications). Overall mildly accepting reaction two vectors, which both originated at neutral on the spectrum, as shown in Figure 4. As the process described above continued and factors were continually introduced to employees, their reactions to change fluctuated and the employees location on the spectrum traversed the length of the spectrum. Mutually Exclusive Examining the relationship between resistance to and acceptance of change is important to fully understand the SEROC. The former example illustrates that employees can react with both resistance and acceptance (Harding, 2005). This concept is logical because situations rarely exist with purely positive outcomes or purely negative outcomes. Rather, almost all situations present both positive and negative outcomes. Therefore, it is expected that even employees who are very accepting of change exhibit resistance as a result of identifying negative aspects of the change. Consequently, the argument can be made that acceptance and resistance are not mutually exclusive and employees exhibit both of these reactions. When responding to the question, did the employees accept or reject the change initiative?, change agents should usually state that the employees partially accepted and partially rejected the change initiative. P3: Employees react to organizational change with both micro-levels of resistance and acceptance. Employees overall reaction is dependent on which reaction (resistance or acceptance) is stronger. Application Change initiatives are dynamic, and factors continually arise that affect employee s reactions. As a result, employees reactions are consistently fluctuating and never stagnant. Employees reactions to organizational change must be considered in the moment rather than over the span of the entire initiative (Lewin, 1951). As change agents progress through the process of the change initiative, it is important that they continually assess the employees reactions to change, diagnose the causes for their reactions (both negative and positive causes), address the employees concerns, and repeat the process. When applied to the SEROC model, the latter process translates to identifying where the employees are located on the spectrum, diagnosing the reasons that determine their location on the spectrum, addressing the employees concerns to initiate a factor (represented by a vector) that moves the employees toward the acceptance end of the spectrum, and repeating the sequence. Continually monitoring employees reactions is especially important because evidence exists that change initiatives fail due to the lack of attention to human factors in the long run (Eilam & Shamir, 2005). Limitations Despite the model of SEROC being based in scientific literature, the model does possess certain limitations. First, one could argue that this two dimension model over-simplifies the highly complex nature of employees reactions because in reality there can be n-dimensions. Factors that impact employees reactions do not have additive properties like one-dimensional vectors in the SEROC, but rather, the factors interact in a multiplicative, multidimensional manner that makes employees reactions complex. Second, although this model is based in empirical evidence, being tested in authentic settings during organizational change initiatives would validate the model. Despite these limitations, the SEROC model does present a unique lens through which to view employees reactions to change that should not be disregarded. Conclusions Organizational change is necessary for businesses to remain competitive in today s market. To successfully implement change initiatives, change agents must understand that the role of employees is highly important, and employees reactions to change are influenced by a number of factors, including employees emotions and cognitions, communication, and participation in decision making. Change agents can apply the Spectrum of Employees Reactions to Organizational Change as a unique model that illustrates how employees react to change. This model is based in the concept that the degree of employees acceptance of or resistance is an important factor that change agents should examine. Overall, this paper provides OD practitioners important information about employees reactions to change, and organizations will benefit from further research in this field. Employees Reactions to Organizational Change 27
6 References Beer, M., & Nohria, N. (2000). Cracking the code of change. Harvard Business Review, 782, Bordia, P., Hobman, E., Jones, E., Gallois, C., & Callan, V. (2004). Uncertainty during organizational change: Types, consequences, and management strategies. Journal of Business and Psychology, 18(4), Bovey, W., & Hede, A. (2001a). to organizational change: The role of cognitive and affective processes. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 22(8), Bovey, W., & Hede, A. (2001b). to organizational change: The role of cognitive and affective processes. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 16(7), Dachler, H., & Wilpert, B. (1978). Conceptual dimensions and boundaries of participation in organizations: A critical evaluation. Administrative Science Quarterly, 23, Eilam, G., & Shamir, B. (2005). Organizational change and self-concept threats: A theoretical perspective and a case study. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 41(4), Elving, W. J. (2005). The role of communication in organizational change. Corporate Communications, 10(2), Erturk, A. (2008). A trust-based approach to promote employees openness to organizational change in Turkey. International Journal of Manpower, 29(5), Farr-Wharton, R., & Brunetto, Y. (2007). Organizational relationship quality and service employee acceptance of change in SMEs: A social exchange perspective. Journal of Management & Organization, 13(2), Gray, J., & Laidlaw H. (2002). Part-time employment and communication satisfaction in an Australian retail organization. Employee Relations, 24(2), Harding, N. (2005). The inception of the national health service: A daily managerial accomplishment. Journal of Health Organization and Management, 19(3), Jones, D. R., & Smith, M. J. (2001). Implementation of new technology. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, 2( ), Lewin, K. (1951). Field theory in social science. New York, NY: Harper & Row. Lewis, L. (2006). Employee perspectives on implementation communication as predictors of perceptions of success and resistance. Western Journal of Communication, 70(1), Lines, R. (2005). How social accounts and participation during change affect organizational learning. Journal of Workplace Learning, 17(3), Oreg, S. (2006). Personality, context, and resistance to organizational change. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 15(1), Pessoa, L. (2008). On the relationship between emotion and cognition. Nature Reviews: Neuroscience, 9, Sagie, A., & Koslowsky, M. (1994). Organizational attitudes and behaviors as a function of participation in strategic and tactical change decisions: An application of path goal theory. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 15(1), Sigler, J. (1999). Systems thinking: Organizational and social systems. Futurics, 23(1), Stanley, D. J., Meyer, J. P., & Topolnytsky, L. (2005). Employee cynicism and resistance to organizational change. Cynthia Wittig, Montclair State University MBA Graduate Student concentrating in MIS, specializes in the travel industry, where her diverse business experiences and education background contribute to her unique perspective on OD applications. Her business experiences have reinforced that change is a vital part of organizational growth, and therefore, she investigated employee reactions to organizational change and devised a relevant dynamic model. She can be reached at wittigcynthia@ gmail.com. Journal of Business and Psychology, 19(4), Vakola, M., Tsaousis, I., & Nikolaou, I. (2004). The role of emotional intelligence and personality variables on attitudes toward organizational change. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 19(2), Waldersee, R., & Griffiths, A. (1996). The changing face of organizational change. Working Papers of Centre of Corporate Change, Australian Graduate School of Management, 065. Wanberg, C. R., & Banas, J. T. (2000). Predictors and outcomes of openness to changes in a reorganizing workplace. The Journal of Applied Psychology, 85(1), OD PRACTITIONER Vol. 44 No
Approaches to Managing Organizational Change
 VOLUME 12, NUMBER 1, 2010 Approaches to Managing Organizational Change Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Much has been written about the nature of change and the best methods to manage
VOLUME 12, NUMBER 1, 2010 Approaches to Managing Organizational Change Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Much has been written about the nature of change and the best methods to manage
THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE ON TEAM CREATIVITY, JOB SATISFACTION, ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT, AND WORK PERFORMANCE
 THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE ON TEAM CREATIVITY, JOB SATISFACTION, ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT, AND WORK PERFORMANCE Angela Shin-yih Chen National Chung-Hsing University, Taiwan, ROC [email protected]
THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE ON TEAM CREATIVITY, JOB SATISFACTION, ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT, AND WORK PERFORMANCE Angela Shin-yih Chen National Chung-Hsing University, Taiwan, ROC [email protected]
TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION
 TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION Ecaterina Livia TATAR Lecturer, Regional Department of Defense Resources Management Studies, Brasov, Romania The magnitude and challenges
TRAINING AND EDUCATION IN THE SERVICE OF MILITARY TRANSFORMATION Ecaterina Livia TATAR Lecturer, Regional Department of Defense Resources Management Studies, Brasov, Romania The magnitude and challenges
FRAMEWORK OF CHANGE MANAGEMENT
 FRAMEWORK OF CHANGE MANAGEMENT Andrea MATKÓ 1, Krisztina DAJNOKI 2, Zsolt BAKSI 3, Tímea TAKÁCS 4 1 University of Debrecen, Hungary, [email protected] 2 University of Debrecen, Hungary, [email protected]
FRAMEWORK OF CHANGE MANAGEMENT Andrea MATKÓ 1, Krisztina DAJNOKI 2, Zsolt BAKSI 3, Tímea TAKÁCS 4 1 University of Debrecen, Hungary, [email protected] 2 University of Debrecen, Hungary, [email protected]
Effect of Organizational Change on Employee Job Involvement: Mediating Role of Communication, Emotions and Psychological Contract
 Information Management and Business Review Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 178-184, Sep 2011 (ISSN 2220-3796) Effect of Organizational Change on Employee Job Involvement: Mediating Role of Communication, Emotions and
Information Management and Business Review Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 178-184, Sep 2011 (ISSN 2220-3796) Effect of Organizational Change on Employee Job Involvement: Mediating Role of Communication, Emotions and
The Role of Rewards and Recognition in Customer-oriented Citizenship Behaviors
 The Role of Rewards and Recognition in Customer-oriented Citizenship Behaviors Scott A. Jeffrey Monmouth University Guillermo Wilches-Alzate University of Waterloo January 6, 2009 1 Introduction Customer
The Role of Rewards and Recognition in Customer-oriented Citizenship Behaviors Scott A. Jeffrey Monmouth University Guillermo Wilches-Alzate University of Waterloo January 6, 2009 1 Introduction Customer
ITSM Solution Projects Need Organisational Change Management
 ITSM Solution Projects Need Organisational Change Management Karen Ferris, Macanta Consulting ABSTRACT This document explores the need for organisational change management (OCM) as an integral part of
ITSM Solution Projects Need Organisational Change Management Karen Ferris, Macanta Consulting ABSTRACT This document explores the need for organisational change management (OCM) as an integral part of
CHAPTER 6 HUMAN RESOURCES CLIMATE SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 HUMAN RESOURCES CLIMATE SYSTEM 6.0 Introduction An organisation's success is determined by the competencies and motivation of the employees. Sincere and capable employees are the assets of any
CHAPTER 6 HUMAN RESOURCES CLIMATE SYSTEM 6.0 Introduction An organisation's success is determined by the competencies and motivation of the employees. Sincere and capable employees are the assets of any
CPD an emotional rollercoaster
 CPD an emotional rollercoaster Aims: To raise awareness of the emotional aspects of change management (which are often ignored) and to introduce Fisher s transition curve to describe how mandatory CPD
CPD an emotional rollercoaster Aims: To raise awareness of the emotional aspects of change management (which are often ignored) and to introduce Fisher s transition curve to describe how mandatory CPD
Employee Work Passion Connecting the Dots
 PE R S PECTIVE S Employee Work Passion: Volume 3 Employee Work Passion Connecting the Dots By Drea Zigarmi, Dobie Houson, David Witt, and Jim Diehl For years, researchers, organizations, and leaders have
PE R S PECTIVE S Employee Work Passion: Volume 3 Employee Work Passion Connecting the Dots By Drea Zigarmi, Dobie Houson, David Witt, and Jim Diehl For years, researchers, organizations, and leaders have
To Promote Job Involvement via Talent Management
 To Promote Job Involvement via Talent Management Malikeh Beheshtifar Management Department, Islamic AZAD University, Rafsanjan Branch, Iran Tel : +98-913-343-0417 E-mail: [email protected] Abstract
To Promote Job Involvement via Talent Management Malikeh Beheshtifar Management Department, Islamic AZAD University, Rafsanjan Branch, Iran Tel : +98-913-343-0417 E-mail: [email protected] Abstract
The Success Profile for Shared Services and Centres of Expertise
 1 The Success Profile for Shared Services and Centres of Expertise Contents Role and models 3 Great minds think alike 4 Five factors that make the difference 5 Five factors in action 7 What can we take
1 The Success Profile for Shared Services and Centres of Expertise Contents Role and models 3 Great minds think alike 4 Five factors that make the difference 5 Five factors in action 7 What can we take
Revista Economica 65:3 (2013) LEADING EMPLOYEES THROUGH CHANGE THE ROLE OF INTERNAL MARKETING
 LEADING EMPLOYEES THROUGH CHANGE THE ROLE OF INTERNAL MARKETING RĂDULESCU Violeta 1, VOSLOBAN Raluca Ioana 2, STOICA Ivona 3 1,2 The Bucharest University of Economic Studies 3 Romanian American University
LEADING EMPLOYEES THROUGH CHANGE THE ROLE OF INTERNAL MARKETING RĂDULESCU Violeta 1, VOSLOBAN Raluca Ioana 2, STOICA Ivona 3 1,2 The Bucharest University of Economic Studies 3 Romanian American University
Transformational Leadership in Technology Post-Adoption Period: A Motivational Factor for Acquiring Technology Enhancement Information
 Transformational Leadership in Technology Post-Adoption Period: A Motivational Factor for Acquiring Technology Enhancement Information Kirill M. Yurov University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Information
Transformational Leadership in Technology Post-Adoption Period: A Motivational Factor for Acquiring Technology Enhancement Information Kirill M. Yurov University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Information
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT
 RESEARCH RESULTS CLIENT RESEARCH RESULTS BY: JAZMINE BOATMAN CONSULTANT, CABER REALIZATION RESULTS: Trainees reported a 90 percent improvement in the number of leaders displaying positive leadership behaviors
RESEARCH RESULTS CLIENT RESEARCH RESULTS BY: JAZMINE BOATMAN CONSULTANT, CABER REALIZATION RESULTS: Trainees reported a 90 percent improvement in the number of leaders displaying positive leadership behaviors
English Summary 1. cognitively-loaded test and a non-cognitive test, the latter often comprised of the five-factor model of
 English Summary 1 Both cognitive and non-cognitive predictors are important with regard to predicting performance. Testing to select students in higher education or personnel in organizations is often
English Summary 1 Both cognitive and non-cognitive predictors are important with regard to predicting performance. Testing to select students in higher education or personnel in organizations is often
BPMJ 7,3. The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available at http://www.emerald-library.com/ft
 The research register for this journal is available at http://wwwmcbupcom/research_registers The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available at http://wwwemerald-librarycom/ft BPMJ
The research register for this journal is available at http://wwwmcbupcom/research_registers The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available at http://wwwemerald-librarycom/ft BPMJ
Migration Planning guidance information documents change ManageMent Best Practices October 7, 2011
 Migration Planning guidance information documents change ManageMent Best Practices October 7, 2011 Table Of Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Change Management Approach... 1 2.1 Change Management Objectives...
Migration Planning guidance information documents change ManageMent Best Practices October 7, 2011 Table Of Contents 1. Purpose... 1 2. Change Management Approach... 1 2.1 Change Management Objectives...
Seven Principles of Change:
 Managing Change, LLC Identifying Intangible Assets to Produce Tangible Results Toll Free: 877-880-0217 Seven Principles of Change: Excerpt from the new book, Change Management: the people side of change
Managing Change, LLC Identifying Intangible Assets to Produce Tangible Results Toll Free: 877-880-0217 Seven Principles of Change: Excerpt from the new book, Change Management: the people side of change
Gestalt Therapy A GUIDE TO COUNSELLING THERAPIES (DVD) Published by: J & S Garrett Pty Ltd ACN 068 751 440
 Gestalt Therapy A GUIDE TO COUNSELLING THERAPIES (DVD) Published by: J & S Garrett Pty Ltd ACN 068 751 440 All Case Histories in this text are presented as examples only and any comparison which might
Gestalt Therapy A GUIDE TO COUNSELLING THERAPIES (DVD) Published by: J & S Garrett Pty Ltd ACN 068 751 440 All Case Histories in this text are presented as examples only and any comparison which might
How To Understand The Relationship Between Organization And Performance
 Organizational Behavior and Development Michael Beer Harvard University Organizational studies is a fragmented field. Its foundations are the disciplines of Psychology, Sociology, and Economics and applied
Organizational Behavior and Development Michael Beer Harvard University Organizational studies is a fragmented field. Its foundations are the disciplines of Psychology, Sociology, and Economics and applied
Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions
 Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions MBA 608: Interpersonal Leadership and Managing Organizational Behavior (3 credits) This course provides rising stars learning opportunities to take the next
Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions MBA 608: Interpersonal Leadership and Managing Organizational Behavior (3 credits) This course provides rising stars learning opportunities to take the next
How often do projects fail? According to
 Vol. 40, No. 2, March April 2010, pp. 159 162 issn 0092-2102 eissn 1526-551X 10 4002 0159 informs doi 10.1287/inte.1090.0473 2010 INFORMS People Skills: Ensuring Project Success A Change Management Perspective
Vol. 40, No. 2, March April 2010, pp. 159 162 issn 0092-2102 eissn 1526-551X 10 4002 0159 informs doi 10.1287/inte.1090.0473 2010 INFORMS People Skills: Ensuring Project Success A Change Management Perspective
Treatment Planning. The Key to Effective Client Documentation. Adapted from OFMQ s 2002 provider training.
 Treatment Planning The Key to Effective Client Documentation Adapted from OFMQ s 2002 provider training. 1 Models Medical Model Diagnosis Psych Eval Problems Symptoms Psycho/Social/Behavioral Model Diagnosis
Treatment Planning The Key to Effective Client Documentation Adapted from OFMQ s 2002 provider training. 1 Models Medical Model Diagnosis Psych Eval Problems Symptoms Psycho/Social/Behavioral Model Diagnosis
Change Management. PG page 1
 Change Management PG page 1 Change Management Objectives Become skilled at change management and the necessary elements for successful change management. Identify the stages of change that people and organization
Change Management PG page 1 Change Management Objectives Become skilled at change management and the necessary elements for successful change management. Identify the stages of change that people and organization
Selecting Change Agents: Exploring Traits and Skills in a Simulated Environment
 Journal of Change Management Vol. 7, Nos 3 4, 291 313, September December 2007 Selecting Change Agents: Exploring Traits and Skills in a Simulated Environment IOANNIS NIKOLAOU, ATHANASIOS GOURAS, MARIA
Journal of Change Management Vol. 7, Nos 3 4, 291 313, September December 2007 Selecting Change Agents: Exploring Traits and Skills in a Simulated Environment IOANNIS NIKOLAOU, ATHANASIOS GOURAS, MARIA
Kent State University Graduate Programs Office: Professional MBA Leadership & Organizational Change (MIS 64160)
 Kent State University Graduate Programs Office: Professional MBA Leadership & Organizational Change (MIS 64160) August-December, 2013 Course Leadership & Organizational Change course (3 credit hour) is
Kent State University Graduate Programs Office: Professional MBA Leadership & Organizational Change (MIS 64160) August-December, 2013 Course Leadership & Organizational Change course (3 credit hour) is
HAMPTON UNIVERSITY ONLINE Hampton University School of Business PhD in Business Administration
 Program Overview The PhD in Business Leadership and Administration is designed for professionals located nation wide who desire an advanced degree in business to excel in their careers. In addition, the
Program Overview The PhD in Business Leadership and Administration is designed for professionals located nation wide who desire an advanced degree in business to excel in their careers. In addition, the
Expectancy Value Theory: Motivating Healthcare Workers
 Expectancy Value Theory: Motivating Healthcare Workers Stefania De Simone Researcher in Organizational Behavior Institute for Research on Innovation and Services for Development National Research Council
Expectancy Value Theory: Motivating Healthcare Workers Stefania De Simone Researcher in Organizational Behavior Institute for Research on Innovation and Services for Development National Research Council
PSYCHOLOGY AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 PSYCHOLOGY AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT Human aspects of the project management Ver 1.0 2 360 Degree Approach of IT Infrastructure Projects PSYCHOLOGY AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT Abstract Project Management usually
PSYCHOLOGY AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT Human aspects of the project management Ver 1.0 2 360 Degree Approach of IT Infrastructure Projects PSYCHOLOGY AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT Abstract Project Management usually
LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2011-13 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4.
 LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2011-13 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4. Statistics for Management 5. Business Communication 6. Managerial Economics
LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2011-13 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4. Statistics for Management 5. Business Communication 6. Managerial Economics
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE
 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This course focuses on the external and internal environment
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This course focuses on the external and internal environment
Factors of Adolescent Self-Concept: Mass Mediated, Peer, and Family Communication. David J. Feliciano. University of West Florida
 Running head: FACTORS OF ADOLESCENT SELF-CONCEPT 1 Factors of Adolescent Self-Concept: Mass Mediated, Peer, and Family Communication David J. Feliciano University of West Florida FACTORS OF ADOLESCENT
Running head: FACTORS OF ADOLESCENT SELF-CONCEPT 1 Factors of Adolescent Self-Concept: Mass Mediated, Peer, and Family Communication David J. Feliciano University of West Florida FACTORS OF ADOLESCENT
CHAPTER 4: PREJUDICE AND DISCRIMINATION
 CHAPTER 4: PREJUDICE AND DISCRIMINATION CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 4 introduces you to the related concepts of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination. The chapter begins with definitions of these three
CHAPTER 4: PREJUDICE AND DISCRIMINATION CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 4 introduces you to the related concepts of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination. The chapter begins with definitions of these three
Objective and strategic talent management approaches to increasing human resources results
 Romanian Journal of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Hypnosis Volume 2, Issue 1, January March 2015 Theoretical Paper Objective and strategic talent management approaches to increasing human resources
Romanian Journal of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Hypnosis Volume 2, Issue 1, January March 2015 Theoretical Paper Objective and strategic talent management approaches to increasing human resources
Leader Succession and Collective Efficacy: Conditions that Create Continuity in Transition
 Versland, T. M., Quintana, E., & Malloy, J. (2014). Leader succession and collective efficacy: Conditions that create continuity in transition. The Researcher, 26(1), 3-7. Leader Succession and Collective
Versland, T. M., Quintana, E., & Malloy, J. (2014). Leader succession and collective efficacy: Conditions that create continuity in transition. The Researcher, 26(1), 3-7. Leader Succession and Collective
Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology)
 Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) Objectives The program aims to enable graduate students to analyze, to carry on the research projects,
Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) Objectives The program aims to enable graduate students to analyze, to carry on the research projects,
Simulations, Games and Experiential Learning Techniques:, Volume 1, 1974
 EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING: CONCEPTUALIZATION AND DEFINITION 1 by J. Duane Hoover Texas Tech University Experiential learning is a highly qualitative concept, and cannot be received as a rigidly defined theory
EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING: CONCEPTUALIZATION AND DEFINITION 1 by J. Duane Hoover Texas Tech University Experiential learning is a highly qualitative concept, and cannot be received as a rigidly defined theory
Pitfalls and Best Practices in Performance Management Overview
 Pitfalls and Best Practices in Performance Management Overview Introduction This article describes common pitfalls that undermine performance management initiatives, and best practices that address those
Pitfalls and Best Practices in Performance Management Overview Introduction This article describes common pitfalls that undermine performance management initiatives, and best practices that address those
J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., 5(5)220-226, 2015 2015, TextRoad Publication
 2015, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4274 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Evaluation of the Impact of Change Management Dimensions on Increasing Organizational
2015, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4274 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Evaluation of the Impact of Change Management Dimensions on Increasing Organizational
Recent Research on Leader- Member Exchange: Development, Measurement, and Context. Robert C. Liden University of Illinois at Chicago
 Recent Research on Leader- Member Exchange: Development, Measurement, and Context Robert C. Liden University of Illinois at Chicago Introduction Definition of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Relationship
Recent Research on Leader- Member Exchange: Development, Measurement, and Context Robert C. Liden University of Illinois at Chicago Introduction Definition of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Relationship
A Whole-Person/Systemic Approach to Organization Change Management. By Jeff Dooley, copyright 1998
 A Whole-Person/Systemic Approach to Organization Change Management By Jeff Dooley, copyright 1998 Over the past few decades large-scale organization change has become a way of life in American business.
A Whole-Person/Systemic Approach to Organization Change Management By Jeff Dooley, copyright 1998 Over the past few decades large-scale organization change has become a way of life in American business.
Turnover on Information Security Professionals: Findings from Korea
 HyeWon Yoo, TaeSung Kim 169 Turnover on Information Security Professionals: Findings from Korea HyeWon Yoo *, TaeSung Kim Department of Management Information Systems College of Business, Chungbuk National
HyeWon Yoo, TaeSung Kim 169 Turnover on Information Security Professionals: Findings from Korea HyeWon Yoo *, TaeSung Kim Department of Management Information Systems College of Business, Chungbuk National
Customer Engagement: An Important Concept for Marketing and Service Management Research
 Customer Engagement: An Important Concept for Marketing and Service Management Research In today s highly dynamic and interactive business environment, the role of customer engagement in co-creating interactive
Customer Engagement: An Important Concept for Marketing and Service Management Research In today s highly dynamic and interactive business environment, the role of customer engagement in co-creating interactive
How To Treat An Addiction With Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Part 1 An Overview Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a general classification of psycho therapy, based on social learning theory, which emphasizes how our thinking interacts
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Part 1 An Overview Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a general classification of psycho therapy, based on social learning theory, which emphasizes how our thinking interacts
HR Maintenance: A Vital Factor to Promote Job Commitment
 Abstract HR Maintenance: A Vital Factor to Promote Job Commitment Malikeh Beheshtifar Management Department, Rafsanjan Branch, Islamic AZAD University, Iran Email: [email protected] Mojtaba Safarian
Abstract HR Maintenance: A Vital Factor to Promote Job Commitment Malikeh Beheshtifar Management Department, Rafsanjan Branch, Islamic AZAD University, Iran Email: [email protected] Mojtaba Safarian
Strategic Leadership and
 Chapter 11 Strategic Leadership and Change Management Chapter 11 Learning Outcomes Discuss the role of strategic leadership in the strategic management process. Describe the relevance of analyzing the
Chapter 11 Strategic Leadership and Change Management Chapter 11 Learning Outcomes Discuss the role of strategic leadership in the strategic management process. Describe the relevance of analyzing the
Management & Marketing 1. Introduction
 EVALUATING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN BANKING SERVICES Irina BENA Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania Piata Romana no. 6, sector 1, Bucharest e-mail: [email protected] Abstract. New, competitive
EVALUATING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN BANKING SERVICES Irina BENA Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania Piata Romana no. 6, sector 1, Bucharest e-mail: [email protected] Abstract. New, competitive
Component Wise Comparison of the Degree of Organizational Commitment.
 Component Wise Comparison of the Degree of Organizational Commitment. MOHAMMAD TUFAIL Lecturer, AWKUM, Buner Campus. Email: [email protected] NAVEED FAROOQ Assistant Professor, AWKUM, Pabbi Campus Abstract
Component Wise Comparison of the Degree of Organizational Commitment. MOHAMMAD TUFAIL Lecturer, AWKUM, Buner Campus. Email: [email protected] NAVEED FAROOQ Assistant Professor, AWKUM, Pabbi Campus Abstract
You can t get to where you re going until you leave where you ve been.
 You can t get to where you re going until you leave where you ve been. The great thing in this world is not so much where we are, but in what direction we are moving. ~Oliver W. Holmes 1 The Three Phases
You can t get to where you re going until you leave where you ve been. The great thing in this world is not so much where we are, but in what direction we are moving. ~Oliver W. Holmes 1 The Three Phases
Organizational Change Management: A Test of the Effectiveness of a Communication Plan
 Communication Research Reports Vol. 28, No. 1, January March 2011, pp. 62 73 Organizational Change Management: A Test of the Effectiveness of a Communication Plan Cynthia B. Torppa & Keith L. Smith In
Communication Research Reports Vol. 28, No. 1, January March 2011, pp. 62 73 Organizational Change Management: A Test of the Effectiveness of a Communication Plan Cynthia B. Torppa & Keith L. Smith In
The Association of Change Management Professionals
 The Association of Change Management Professionals Statement of Change Management Scope, Knowledge Areas, and Process Groups March 31, 2012 Introduction The Association of Change Management Professionals
The Association of Change Management Professionals Statement of Change Management Scope, Knowledge Areas, and Process Groups March 31, 2012 Introduction The Association of Change Management Professionals
An integrative framework for leading strategic and organizational change
 part i An integrative framework for leading strategic and organizational change There is a great deal of literature on change. Unfortunately, the literature is fragmented and requires both scholars and
part i An integrative framework for leading strategic and organizational change There is a great deal of literature on change. Unfortunately, the literature is fragmented and requires both scholars and
A Study on Customer Orientation as Mediator between Emotional Intelligence and Service Performance in Banks
 International Journal of Business and Management Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 8028, ISSN (Print): 2319 801X Volume 2 Issue 5 ǁ May. 2013ǁ PP.60-66 A Study on Customer Orientation as Mediator between Emotional
International Journal of Business and Management Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 8028, ISSN (Print): 2319 801X Volume 2 Issue 5 ǁ May. 2013ǁ PP.60-66 A Study on Customer Orientation as Mediator between Emotional
Basic Concepts in Research and Data Analysis
 Basic Concepts in Research and Data Analysis Introduction: A Common Language for Researchers...2 Steps to Follow When Conducting Research...3 The Research Question... 3 The Hypothesis... 4 Defining the
Basic Concepts in Research and Data Analysis Introduction: A Common Language for Researchers...2 Steps to Follow When Conducting Research...3 The Research Question... 3 The Hypothesis... 4 Defining the
PHILOSOPHY, MISSION AND GOALS STATEMENT
 PHILOSOPHY, MISSION AND GOALS STATEMENT The associate degree nursing program is an integral part of Heartland Community College and derives its philosophy from the mission and goals of the college. The
PHILOSOPHY, MISSION AND GOALS STATEMENT The associate degree nursing program is an integral part of Heartland Community College and derives its philosophy from the mission and goals of the college. The
Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Human Synergistics Circumplex Model By: Eric Klisz, M.A. Organizational Development Specialist
 Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Human Synergistics Circumplex Model By: Eric Klisz, M.A. Organizational Development Specialist The following crosswalk is designed to compare and contrast the theoretical
Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Human Synergistics Circumplex Model By: Eric Klisz, M.A. Organizational Development Specialist The following crosswalk is designed to compare and contrast the theoretical
Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions
 Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions MBA 608: Interpersonal Leadership and Managing Organizational Behavior (3 credits) This course provides rising stars learning opportunities to take the next
Executive Leadership MBA Course Descriptions MBA 608: Interpersonal Leadership and Managing Organizational Behavior (3 credits) This course provides rising stars learning opportunities to take the next
Analysis of Bayesian Dynamic Linear Models
 Analysis of Bayesian Dynamic Linear Models Emily M. Casleton December 17, 2010 1 Introduction The main purpose of this project is to explore the Bayesian analysis of Dynamic Linear Models (DLMs). The main
Analysis of Bayesian Dynamic Linear Models Emily M. Casleton December 17, 2010 1 Introduction The main purpose of this project is to explore the Bayesian analysis of Dynamic Linear Models (DLMs). The main
Measuring Quality in Graduate Education: A Balanced Scorecard Approach
 Measuring Quality in Graduate Education: A Balanced Scorecard Approach Dr. S. Kim Sokoya Professor of Management Associate Dean, Graduate and Executive Education Jones College of Business Middle Tennessee
Measuring Quality in Graduate Education: A Balanced Scorecard Approach Dr. S. Kim Sokoya Professor of Management Associate Dean, Graduate and Executive Education Jones College of Business Middle Tennessee
Project Management for Development Organizations
 Project Management for Development Organizations Doing the Right Projects, Doing the Projects Right The Skills of a Project Manager Managerial Skills The evolution of development projects has changed the
Project Management for Development Organizations Doing the Right Projects, Doing the Projects Right The Skills of a Project Manager Managerial Skills The evolution of development projects has changed the
THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
 THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY Information Booklet for Applicants Director: Barry H. Cohen, Ph.D Telephone: 212-998-7815
THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY Information Booklet for Applicants Director: Barry H. Cohen, Ph.D Telephone: 212-998-7815
A new direction for Delta Pacific: A case study
 ABSTRACT A new direction for Delta Pacific: A case study Maureen Hannay Troy University Time in the classroom is largely spent providing students with theories, concepts and models. Exams frequently consist
ABSTRACT A new direction for Delta Pacific: A case study Maureen Hannay Troy University Time in the classroom is largely spent providing students with theories, concepts and models. Exams frequently consist
Change Management in Project Work Survey Results
 Change Management in Project Work Survey Results Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Survey and Participants 2 3. Change Management 6 4. Impact of Change Management on Project Effectiveness 12 5. Communications
Change Management in Project Work Survey Results Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Survey and Participants 2 3. Change Management 6 4. Impact of Change Management on Project Effectiveness 12 5. Communications
Change Management Is A Behavioral Competency You Can Develop
 Change Management Is A Behavioral Competency You Can Develop Hinda K. Sterling Herbert L. Selesnick & Sterling Selesnick, INC Change Management Is A Behavioral Competency You Can Develop This article is
Change Management Is A Behavioral Competency You Can Develop Hinda K. Sterling Herbert L. Selesnick & Sterling Selesnick, INC Change Management Is A Behavioral Competency You Can Develop This article is
Please see current textbook prices at www.rcgc.bncollege.com
 PSY101: GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY SYLLABUS LECTURE HOURS/CREDITS: 3/3 CATALOG DESCRIPTION Prerequisite: RDG099 Introduction to College Reading III This is an introduction to the study of behavior. The scientific
PSY101: GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY SYLLABUS LECTURE HOURS/CREDITS: 3/3 CATALOG DESCRIPTION Prerequisite: RDG099 Introduction to College Reading III This is an introduction to the study of behavior. The scientific
The Relationship of Paternalistic Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Upward Communication
 The Relationship of Paternalistic Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Upward Communication Chu Paoching, Assistant professor of Department of Creative Fashion Design
The Relationship of Paternalistic Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Upward Communication Chu Paoching, Assistant professor of Department of Creative Fashion Design
Develop «D» Execution & Change Management
 Develop «D» Execution & Change Management Dr. Abdurrahman Baş Fall 2013 www.abdurrahmanbas.com Contents Three Core Processes of Execution Forces for Change Principles of Change Five Activities Contributing
Develop «D» Execution & Change Management Dr. Abdurrahman Baş Fall 2013 www.abdurrahmanbas.com Contents Three Core Processes of Execution Forces for Change Principles of Change Five Activities Contributing
Behavioral Aspects of Dollar Cost Averaging
 Behavioral Aspects of Dollar Cost Averaging By Scott A. MacKillop, President, Frontier Asset Management, LLC The Traditional View Dollar-cost averaging is used by many financial advisors to help their
Behavioral Aspects of Dollar Cost Averaging By Scott A. MacKillop, President, Frontier Asset Management, LLC The Traditional View Dollar-cost averaging is used by many financial advisors to help their
Transformational Leadership and Organizational Effectiveness in Recreational Sports/Fitness Programs The Sport Journal
 United States Sports Academy - "America's Sports University" The Sport Journal - ISSN: 1543-9518 Transformational Leadership and Organizational Effectiveness in Recreational Sports/Fitness Programs Submitted
United States Sports Academy - "America's Sports University" The Sport Journal - ISSN: 1543-9518 Transformational Leadership and Organizational Effectiveness in Recreational Sports/Fitness Programs Submitted
Psychology (MA) Program Requirements 36 credits are required for the Master's Degree in Psychology as follows:
 Psychology (MA) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: Carla Marquez-Lewis CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: Carla Marquez-Lewis, [email protected]
Psychology (MA) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: Carla Marquez-Lewis CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: Carla Marquez-Lewis, [email protected]
CHANGE MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS An Introduction to Managing Change
 CORPORATE LEADERSHIP COUNCIL JUNE 2008 CHANGE MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS An Introduction to Managing Change CORPORATE LEADERSHIP COUNCIL PAGE 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions of Change Management...Page 3
CORPORATE LEADERSHIP COUNCIL JUNE 2008 CHANGE MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS An Introduction to Managing Change CORPORATE LEADERSHIP COUNCIL PAGE 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions of Change Management...Page 3
CHANGE MANAGEMENT FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ICT APPLICATIONS IN NIGERIAN CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY
 Journal of Physical Science and Innovation ISSN: 2277-0119 Volume 6, No. 1, 2014 CHANGE MANAGEMENT FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ICT APPLICATIONS IN NIGERIAN CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY Abdullahi Y. Waziri and Kherun
Journal of Physical Science and Innovation ISSN: 2277-0119 Volume 6, No. 1, 2014 CHANGE MANAGEMENT FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ICT APPLICATIONS IN NIGERIAN CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY Abdullahi Y. Waziri and Kherun
ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE PROCESS STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL CHANGE
 ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE PROCESS STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL CHANGE Ph. D Ramona Petrescu University of Craiova Faculty of Economics Craiova, Romania Abstract: Organizational change is a planned effort to improve
ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE PROCESS STEPS TO A SUCCESSFUL CHANGE Ph. D Ramona Petrescu University of Craiova Faculty of Economics Craiova, Romania Abstract: Organizational change is a planned effort to improve
Copyrighted material SUMMARY
 Source: E.C.A. Kaarsemaker (2006). Employee ownership and human resource management: a theoretical and empirical treatise with a digression on the Dutch context. Doctoral Dissertation, Radboud University
Source: E.C.A. Kaarsemaker (2006). Employee ownership and human resource management: a theoretical and empirical treatise with a digression on the Dutch context. Doctoral Dissertation, Radboud University
Leadership Guide. DALE CARNEGIE DIGITAL Presents. Manage Change Effectively
 Leadership Guide DALE CARNEGIE DIGITAL Presents Manage Change Effectively Introduction MANAGE CHANGE EFFECTIVELY Organizations today operate in an environment of rapid, continuous change. Changes engage
Leadership Guide DALE CARNEGIE DIGITAL Presents Manage Change Effectively Introduction MANAGE CHANGE EFFECTIVELY Organizations today operate in an environment of rapid, continuous change. Changes engage
Management of Change and Organizational Development. Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter
 Management of Change and Organizational Development Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter Meaning of Change Change may be defined as a variation in the
Management of Change and Organizational Development Batch: FO_J11_01 Subject: Management CS Foundation Programme The ICSI Ahmedabad Chapter Meaning of Change Change may be defined as a variation in the
Encouraging Effective Performance Management Systems
 Encouraging Effective Performance Management Systems Alison Carr, PhD candidate, Shaker Consulting Group Kelsey Kline, PhD, Organizational Development and Talent Management Consultant A White Paper prepared
Encouraging Effective Performance Management Systems Alison Carr, PhD candidate, Shaker Consulting Group Kelsey Kline, PhD, Organizational Development and Talent Management Consultant A White Paper prepared
Save from: www.uotiq.org/dep-cs. University of Technology Computer Science Department. 4 th Class Management Information Systems (MIS)
 Save from: www.uotiq.org/dep-cs University of Technology Computer Science Department 4 th Class Management Information Systems (MIS) استاذ المادة: د.علياء عبداالله Reference book: "Management Information
Save from: www.uotiq.org/dep-cs University of Technology Computer Science Department 4 th Class Management Information Systems (MIS) استاذ المادة: د.علياء عبداالله Reference book: "Management Information
Implication of Change Management on Organizational Effectiveness
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 2 Pages \ 2167-2174 2015 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 ABSTRACT Implication of Change Management on Organizational
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 2 Pages \ 2167-2174 2015 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 ABSTRACT Implication of Change Management on Organizational
Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos. Understanding Organizational Barriers
 Select Strategy www.selectstrategy.com 1 877 HR ASSET 1 877 472 7738 Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos Understanding Organizational Barriers Restructuring initiatives have become
Select Strategy www.selectstrategy.com 1 877 HR ASSET 1 877 472 7738 Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos Understanding Organizational Barriers Restructuring initiatives have become
Organizational Change and Anxiety: Developing an Instrument for the 5Rs Model
 Universal Journal of Management 3(3): 122-126, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/ujm.2015.030304 http://www.hrpub.org Organizational Change and Anxiety: Developing an Instrument for the 5Rs Model Ameenah Musaed Aldosari
Universal Journal of Management 3(3): 122-126, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/ujm.2015.030304 http://www.hrpub.org Organizational Change and Anxiety: Developing an Instrument for the 5Rs Model Ameenah Musaed Aldosari
ADVANCED DIPLOMA IN COUNSELLING AND PSYCHOLOGY
 ACC School of Counselling & Psychology Pte Ltd www.acc.edu.sg Tel: (65) 6339-5411 9 Penang Road #13-22 Park Mall SC Singapore 238459 1) Introduction to the programme ADVANCED DIPLOMA IN COUNSELLING AND
ACC School of Counselling & Psychology Pte Ltd www.acc.edu.sg Tel: (65) 6339-5411 9 Penang Road #13-22 Park Mall SC Singapore 238459 1) Introduction to the programme ADVANCED DIPLOMA IN COUNSELLING AND
Resistance to Change: The Moderating Effects of Leader-Member Exchange and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy
 Journal of Advanced Management Science Vol. 4, No. 1, January 2016 Resistance to Change: The Moderating Effects of Leader-Member Exchange and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy Nur Izzah Mohd Radzi and Rozhan
Journal of Advanced Management Science Vol. 4, No. 1, January 2016 Resistance to Change: The Moderating Effects of Leader-Member Exchange and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy Nur Izzah Mohd Radzi and Rozhan
INTERNAL CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND THE LINK TO CUSTOMER LOYALTY
 INTERNAL CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND THE LINK TO CUSTOMER LOYALTY by Bruce R. Hammond, Ph.D., Executive Consultant, AchieveGlobal Opening the email, the customer service representative carefully reviewed
INTERNAL CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND THE LINK TO CUSTOMER LOYALTY by Bruce R. Hammond, Ph.D., Executive Consultant, AchieveGlobal Opening the email, the customer service representative carefully reviewed
The Three Lenses ORGANIZATION. Managerial Psychology Fall, 2006 John S. Carroll. Strategic Design Lens. Political Lens.
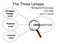 The Three Lenses Strategic Design Lens Managerial Psychology Fall, 2006 John S. Carroll Political Lens ORGANIZATION Cultural Lens Goals For Today Introduce the idea that organizations are a context for
The Three Lenses Strategic Design Lens Managerial Psychology Fall, 2006 John S. Carroll Political Lens ORGANIZATION Cultural Lens Goals For Today Introduce the idea that organizations are a context for
An Overview of the Developmental Stages in Children's Drawings
 Marilyn Zurmuehlen Working Papers in Art Education ISSN: 2326-7070 (Print) ISSN: 2326-7062 (Online) Volume 2 Issue 1 (1983) pps. 2-7 An Overview of the Developmental Stages in Children's Drawings Hufford
Marilyn Zurmuehlen Working Papers in Art Education ISSN: 2326-7070 (Print) ISSN: 2326-7062 (Online) Volume 2 Issue 1 (1983) pps. 2-7 An Overview of the Developmental Stages in Children's Drawings Hufford
THE LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENT THAT ILLUMINATES LEADER EFFECTIVENESS
 THE LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENT THAT ILLUMINATES LEADER EFFECTIVENESS CONNECTING PATTERNS OF ACTION WITH HABITS OF THOUGHT The Leadership Circle Profile (LCP) is a true breakthrough among 360 degree profiles.
THE LEADERSHIP ASSESSMENT THAT ILLUMINATES LEADER EFFECTIVENESS CONNECTING PATTERNS OF ACTION WITH HABITS OF THOUGHT The Leadership Circle Profile (LCP) is a true breakthrough among 360 degree profiles.
The Effect of Virtual Community Participation on Online Purchase Intention: A Conceptual Model
 The Effect of Virtual Community Participation on Online Purchase Intention: A Conceptual Model Hazliza Haron, Mohammed A. Razzaque, The University of New South Wales Abstract Online social networking refers
The Effect of Virtual Community Participation on Online Purchase Intention: A Conceptual Model Hazliza Haron, Mohammed A. Razzaque, The University of New South Wales Abstract Online social networking refers
