Windows Socket Programming & IPv6 Translation Middleware
|
|
|
- Imogene Hubbard
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Windows Socket Programming IPv6 Translation Middleware Dr. Whai-En Chen VoIP and IPv6 Laboratory Research Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiao Tung University TEL:
2 Outline Introduction to Socket/WinSock Programming IPv4 WinSock Programming IPv6 WinSock Programming IPv6 Translation Middleware- Socket-layer Translator Conclusions 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 2
3 Introduction What is Windows Sockets? - An Open Interface for Network Programming under Microsoft Windows What are its Benefits? - an open standard - source code portability - support dynamic linking What is its Future? -WinSock /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 3
4 Windows Sockets 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 4
5 BSD Socket APIs accept() bind() closesocket() connect() getpeername() getsockname() getsockopt() htonl() htons() inet_addr() inet_ntoa() ioctlsocket() listen() ntohl() ntohs() recv() recvfrom() select() send() sendto() setsockopt() shutdown() socket() gethostname() gethostbyaddr() gethostbyname() getprotobyname() getprotobynumber() getservbyname() getservbyport() 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 5
6 Winsock APIs WSAAsyncGetHostByAddr() WSAAsyncGetHostByName() WSAAsyncGetProtoByName() WSAAsyncGetProtoByNumber() WSAAsyncGetServByName() WSAAsyncGetServByPort() WSAAsyncSelect() WSACancelAsyncRequest() WSACancelBlockingCall() WSACleanup() WSAGetLastError() WSAIsBlocking() WSASetBlockingHook() WSASetLastError() WSAStartup() WSAUnhookBlockingHook() 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 6
7 Windows Sockets 2.0 Architecture WinSock 2 Application WinSock 2 Application WinSock 2 API Transport Functions Name Space Functions The WinSock 2 DLL WS2_32.DLL (32 bit) WinSock 2 Transport SPI WinSock 2 Name Space SPI Transport Service Provider Transport Service Provider Name Space Service Provider Name Space Service Provider 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 7
8 Compatibility of Winsock WinSock 2 Application WinSock 1.1 Application WinSock 1.1 API WINSOCK.DLL (16 bit) WSOCK32.DLL (32 bit) WinSock 2 API WS2_32.DLL (32 bit) WinSock 2 SPI TCP/IP Transport Service Provider TCP/IP-based Namespace Service Provider e.g. DNS 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 8
9 Winsock and OSI Model 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 9
10 Client/Server Model Client-Server Model Client and Server Association - protocol ( same for both Clint and server sockets ) - client IP address - client port number - server IP address - server port number 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 10
11 Client/Server Programming(1) TCP Client TCP Server socket connect socket accept bind listen send recv data data recv send close/ closesocket close/ closesocket 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 11
12 Client/Server Programming(2) UDP Client UDP Server socket socket sendto recvfrom data data bind recvfrom sendto close/ closesocket close/ closesocket 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 12
13 IPv4 Socket Programming
14 Network Program Sketch Open a socket Name the socket Associate with another socket Send and receive between sockets Close the socket 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 14
15 Open a Socket 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 15
16 Name the Socket What s in a Socket Name? - protocol, port number and IP address bind( ) int PASCAL FAR bind ( SOCKET s, /*an unbound socket */ struct sockaddr FAR *addr, /*local port and IP addr */ int namelen); /*addr structure length*/ S : socket handle addr : pointer to a socket address structure (always a sockaddr_in data structure for TCP/IP) namelen: length of socket structure pointed to by addr (always 4 for TCP/IP) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 16
17 Name the Socket sockaddr Structure struct stockaddr { u_short sa_family; /*address family*/ char sa_data[14]; /*undefined*/ }; sa_family : address family sa_data: address structure data area defined according to address family value 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 17
18 Name the Socket sockaddr_in Structure structure sockaddr_in { short sin_family; /* address family (PF_INET) */ u_short sin_port; /* port (service) number */ struct in_addr sin_addr; /* IP address (32-bit) */ char sin_zero[8]; /*<unused filler>*/ }; sin_family : address family sin_port : 16-bit port number in network order sine_addr : 32-bit Internet address in network order 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 18
19 Associate with Another Socket Protocol ( same for both client and server sockets) client IP address client port number server IP address server port number 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 19
20 Associate with Another Socket 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 20
21 Associate with Another Socket How a Server Prepares for an Association listen() int PASCAL FAR listen ( SOCKET s, /* a named, unconnected socket */ int backlog) ; /* pending connect queue length */ s: socket handle to a named socket ( bind() called), but not yet connected backlog: length of the pending connection queue ( not the same as the number of accepted connections) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 21
22 Associate with Another Socket How a Client Initiate an Association connect() int PASCAL FAR connect (SOCKET s, /*an unconnected socket */ struct sockaddr FAR *addr, /*remote port and IP addr */ int namelen ); /* addr structure length */ s: socket handle addr: pointer to socket address structure (always a sockaddr_in structure for TCP/IP) namelen: length of structure pointed to by addr (always 4 for TCP/IP) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 22
23 Associate with Another Socket How a Server Completes an Association accept() SOCKET PASCAL FAR accept (SOCKET s, /*a listening socket*/ struct sockaddr FAR *addr, /*name of incoming socket*/ int FAR *addrlen); s: socket handle addr: pointer to socket address structure ( always a sockaddr_in structure for TCP/IP) addrlen: length of socket structure that addr points to ( always 4 for TCP/IP) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 23
24 Send and Receiver between Sockets Sending Data on a Connected Socket send() int PASCAL FAR send (SOCKET s, /*associated socket*/ const char FAR *buf, /*buffer with outgoing data*/ int len, /*bytes to send*/ int flags ); /*option flags*/ s: socket handle buf: pointer to a buffer that contains application data to send len: length of data (in bytes) to send flags: flags to affect the send ( MSG_OOB, MSG_DONTROUTE) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 24
25 Send and Receiver between Sockets Sending Data on an Unconnected Socket sendto() int PASCAL FAR sendto (SOCKET s, /*a valid socket */ const char FAR *buf, /*buffer with outgoing data */ int len, /*bytes to send */ int flags, /*option flags */ struct sockaddr FAR *to, /*remote socket name */ int tolen ); /*length of sockaddr */ to: pointer to socket structure (always a sockaddr_in for TCP/IP) that contains destination address and port number ( socket name) tolen: length of socket structure pointed to by to ( always 4 for TCP/IP) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 25
26 Send and Receiver between Sockets Receiving Data recv() int PASCAL FAR recv (SOCKET s, /*associated socket*/ char FAR *buf, /*buffer with outgoing data*/ int len, /*bytes to send */ int flags ); /*option flags */ recvform() int PASCAL FAR recvform (SOCKET s, /*a valid socket*/ char FAR *buf, /*buffer with outgoing data*/ int len, /*bytes to send */ int flags ); /*option flags */ struct sockaddr FAR *from, /*remote socket name */ int fromlen ); /*length of sockaddr */ 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 26
27 Send and Receiver between Sockets s: socket handle buf: pointer to a buffer that contains application data to send len: length of data (in bytes) to send flags: flags to affect the send ( MSG_OOB, MSG_DONTROUTE) from: pointer to socket structure ( always a sockaddr_in for TCP/IP) that contains source address and port number ( socket name) fromlen: length of socket structure pointed to by from ( always 4 for TCP/IP) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 27
28 Other Useful Socket Functions Byte Ordering Functions ntohs(), ntohl() htons(), htonl() Address Translation Functions inet_addr()- 串 32 IP inet_nota()- 32 IP 串 Name Resolution gethostbyaddr()- 利 host 來 host 料 gethostbyname()- 利 host 來 host 料 hostent 料 WSAStartup() and WSACleanup() 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 28
29 hostent 料 struct hostent { char FAR * h_name; char FAR * FAR * h_aliases; short h_addrtype; short h_length; char FAR * FAR * h_addr_list; } linked-list 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 29
30 Byte Ordering Function Increasing memory address Little-endian byte order: Address A+1 Address A High-order byte low-order byte MSB 16bit value LSB Big-endian byte order: High-order byte low-order byte Address A Address A+1 Increasing memory address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 30
31 IPv4 Example for Daytime Server (Connection-oriented) oriented) int main(int argc, char **argv) { int listenfd, connfd; struct sockaddr_in servaddr; char buff[maxline]; time_t ticks; listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero(servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any); servaddr.sin_port = htons(13); /* daytime server */ bind(listenfd, (SA *) servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 31
32 IPv4 Example for Daytime Server (Connection-oriented) oriented) listen(listenfd, LISTENQ); for ( ; ; ) { connfd = accept(listenfd, (SA *) NULL, NULL); ticks = time(null); snprintf(buff, sizeof(buff), "%.24s\r\n", ctime(ticks)); write(connfd, buff, strlen(buff)); } } Close(connfd); 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 32
33 IPv4 Example for Daytime Client (Connection-oriented) oriented) int main(int argc, char **argv) { int sockfd, n; char recvline[maxline + 1]; struct sockaddr_in servaddr; if (argc!= 2) err_quit("usage: a.out <IPaddress>"); if ( (sockfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) err_sys("socket error"); bzero(servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_port = htons(13); /* daytime server */ if (inet_pton(af_inet, argv[1], servaddr.sin_addr) <= 0) err_quit("inet_pton error for %s", argv[1]); 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 33
34 IPv4 Example for Daytime Client (Connection-oriented) oriented) if (connect(sockfd, (SA *) servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)) < 0) err_sys("connect error"); } while ( (n = read(sockfd, recvline, MAXLINE)) > 0) { recvline[n] = 0; /* null terminate */ if (fputs(recvline, stdout) == EOF) err_sys("fputs error"); } if (n < 0) err_sys("read error"); exit(0); 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 34
35 IPv6 Socket Programming
36 IPv4 IPv4 IPv6 IPv4 IPv6 度 不 不 Socket API Socket API 料 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 36
37 IPv4/IPv6 度 不 數 IPv4, 32 度 IPv6, 128 度 32 bits IPv4 IPv6 128 bits 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 37
38 New Solutions for Applications IPv4 AP IPv6 AP V4/v6 Protocol-independent Application TCP/UDP TCP/UDPv6 TCP/UDP TCP/UDPv6 IPv4 IPv6 IPv4 IPv6 Layer 1 and 2 Layer 1 and /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 38
39 不 Socket API ( ) Server socket open a socket bind bind local address to the socket listen listen on a port accept wait for the connection read/write if TCP recvfrom/sendto if UDP Client socket open a socket connect connect to a server read/write if TCP recvfrom/sendto if UDP 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 39
40 IP Socket API 參 數 IP 數 IPv4 數 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 40
41 API 料 Socket 參 數 IPv4 IPv6 AF_INET AF_INET6 PF_INET PF_INET6 IN_ADDR_ANY inaddr6_any 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 41
42 API 料 料 IPv4 in_addr IPv6 in6_addr sockaddr sockaddr_in6 sockaddr_in sockaddr_in6 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 42
43 IPv4 Socket Address Structure Struct in_addr{ in_addr_t s_addr; /*32bit IPv4 address*/ }; /*network byte ordered*/ struct sockaddr_in { uint8_t sin_len; /* length of structure(16) */ sa_family_t sin_family; /* AF_INET */ in_port_t sin_port; /* 16bit TCP or UDP port number */ /*network byte ordered*/ struct in_addr sin_addr; /* 32bit IPv4 address */ /*network byte ordered*/ char sin_zero[8]; /* unused */ }; /* included in <netinet/in.h> */ 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 43
44 IPv6 Socket Address Structure Struct in6_addr{ uint8_t s6_addr[16]; /*128bit IPv6 address*/ }; /*network byte ordered*/ #define SIN6_LEN /* required for compile-time tests */ struct sockaddr_in6 { uint8_t sin6_len; /* length of structure(24) */ sa_family_t sin6_family; /* AF_INET6*/ in_port_t sin6_port; /* Transport layer port# */ /*network byte ordered*/ uint32_t sin6_flowinfo; /* priority flow label */ /*network byte ordered*/ struct in6_addr sin6_addr; /* IPv6 address */ /*network byte ordered*/ }; /* included in <netinet/in.h> */ 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 44
45 API 料 料 參 數 IPv4 sin_len sin_family sin_port sin_addr IPv6 sin6_len sin6_family sin6_port sin6_addr s_addr s6_addr 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 45
46 API 料 Name-to_address Functions Address conversion Functions IPv4 inet_aton() inet_addr() inet_ntoa() gethostbyname() gethostbyaddr() IPv6 inet_pton() inet_ntop() getipnodebyname() getipnodebyaddr() getnameinfo() getaddrinfo() 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 46
47 Data Structure Comparison AF independent struct sockaddr IPv4 dependent struct in_addr struct sockaddr_in Name resolving struct hostent IPv4 AF independent struct sockaddr_storage IPv6 dependent struct in6_addr struct sockaddr_in6 Name resolving struct addrinfo IPv6 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 47
48 Definitions and Function Calls Address FamilyProtocol Family AF_INET6 PF_INET6 for IPv6 No changes to transport socket APIs socket(), connect(), bind() Name resolving AF dependent functions are obsolete New AF independent functions gethostbyname() and gethostbyaddr()- IPv4-only getaddrinfo() and getnameinfo()- IPv4 IPv6 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 48
49 getaddrinfo() getnameinfo() Convert strings storing address and service into sockaddr structure getaddrinfo( www,hint,res); Options are specified in hint hint is an addrinfo structure Results are returned as a linked-list, each list node contains a sockaddr structure freeaddrinfo() to free returned linked-list freeaddrinfo(res); getnameinfo() converts from sockaddr into strings storing address and service getnameinfo(sa,name,sizeof(name),srv,sizeof(srv),0); 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 49
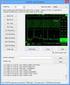
50 Introduction to Checkv4.exe Provided by Microsoft Identifies potential problems in codes and makes recommendations Identifies most trivial problems Successfully checks presence of IPv4 specified code. e.g. gethostbyname(), struct sockaddr_in, and so on. Gives some false alert Identifies parameters in comment Results from Checkv4.exe About 200 lines for CCL/ITRI SkinUA 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 50
51 Checkv4.exe (Partial Results) 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 51
52 Comparison of socket address structure
53 Socket address structure pass. bind, connect, sendto accept, recvfrom, getsockname, getpeername 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 53
54 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 54
55 NTPOCCL SIP User Agent (UA) SIP-based VoIP phone running on Windows Support H.263 Video codec Support G.711u/G.711a/G.723/G.729 Audio codec Support registration Support authentication 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 55
56 Structure of SIP UA UI UAProfile CallManager MediaManager UACore cclrtp Codec SDP siptx WaveIO SIP RTP Transport 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 56
57 Component Relationship of LAB 117 CallManager UI Function Call Windows Event CallManager Function Call MediaManager Function Call Callback Function UACore 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 57
58 GUI Problem IP Address control Is IPv4 specified Do not accept domain name Use Edit control instead 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 58
59 Get Local Address (1/2) Old method: gethostbyname() Gethostbyname() on local hostname Does getaddrinfo() on local hostname works? Not works on Windows XP Works on Windows /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 59
60 Get Local Address (2 of 2) Make use of IPHelper functions Presented in Windows from Windows 98 A Windows-only solution Works on both windows XP and 2003 Function name: GetAdaptersAddresses() 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 60
61 Parsing URI with IPv6 IPv6 address in URI Some parser assume semicolon will be used only to separate IP and Port Modify parsing algorithm to deal with IPv6 address. URI in SIP header may contains IPv6 address INVITE IP6 addrtype IPv6 address in SDP c=in IP6 FE80:60::2 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 61
62 Goal of Porting SIP UA to IPv6 Goal of Porting SIP UA to IPv6 Provide IPv6 communication to Users (a long-term solution) SIP UA should accept SIP URI that contains IPv6 literal address (specified in RFC 3261) SIP UA should correctly handle IPv6 addresses in SIP/SDP header fields SIP UA should operate with other IPv6 SIP UAs (KPhone and LinPhone) and SIP servers (IPtel and Partysip). 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 62
63 Modifications for SIP User Agent Auto IPv4/IPv6 negotiation requires modification in listening thread part and rewrite working flow of calling The IP version is the same as the IP address that user choose SIP UA will use either IPv4 or IPv6 at the same time. Lower part in protocol stack should check an extra parameter that specifies address family 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 63
64 Modifications for SIP User Agent (cont.) IPv6 address Literal format has scope-id E.g. fe80::201:2ff:fe85:37ed%3 Used by linked-local address Identify the same address on different interface Scope-id must be specified when connecting to sites using link-local address An extra parameter in data structure to keep this 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 64
65 Modifications for SIP User Agent (cont.) SIP URI may contain IPv6 address E.g. Rewrite parser to ensure correctly dealing with colon Since IPv6 address are longer than IPv4 address, GUI components related to address should be modified Avoid using IPAddressControl that supports IPv4 address only 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 65
66 Results Changes 500+ out of 100,000+ lines in 150 files About 300 lines are not identified by checkv4.exe SIP UA supports IPv4 or IPv6 communication IPv6 address in SIP URI IPv6 address in GUI and form Modifications in SIP UA Transport handle different IP versions GUI handle IPv6 address CallManager URI parsing/generating 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 66
67 Modification Summary Module name UACore siptx sip sdp rtp transport cclrtp MediaManager UI UAProfile Modified files Total: 39 files 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 67
68 SIPv6 User Agent 2 Click right botton 1 Double-click 4 Next Page /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 68
69 SIPv6 User Agent IPv6 IPv User Settings 2. User IP Address Global Unicast IPv6 Address 2001:238:f88:131:2e0:18ff:feea:f IPv4 路 6to4 Prefix 2002::/ Next Page 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 69
70 SIPv6 User Agent Server Settings 2. Use Proxy 3. Registration 若 IPv6 SIP IPv6 3 4 Next Page 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 70
71 SIPv6 User Agent LAB 117 SIPv6 User Agent Codec 參 數 Codec Settings 2. Codec Active Codecs 3. Use Video 若 不 4. 4 Next Page /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 71
72 ( SIP URI) SIP URI ( SIP:7221@3ffe:3600:1::1) 3. List 4-6. Load SIP URI OK Next Page /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 72
73 Dial /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 73
74 LAB SIPv6 User Agent (UA) Using Using IPv6 IPv6 Addresses Addresses 4. SIPv6 UA RTP INVITE OK 3.7 ACK IPv6 Network (Showroom) 2. Dual-stack Router Tunneling 3.2 INVITE OK 3.8 ACK 4. RTP 例 Internet (IPv4) SIP Signaling (IPv6) SIP Signaling (Tunnel) Dual-stack Router 3.3 INVITE OK 3.9 ACK 4. RTP IPv6 Network (NCTU VoIP Lab) SIPv6 UA 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 74
75 p SIP Messages over LAB 117 IPv6 IPv6 address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 75
76 p LAB 117 RTP Stream over IPv6 IPv6 address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 76
77 Interoperability Testing Testing with 2 Linux SIP-based phone Kphone 3.2 with IPv6 (patched by iptel) Linphone (claimed as IPv6 enabled) Environment Windows XP SP1 Redhat linux 9.0 Partysip IPv6 SIP proxy Iptel IPv6-enabled SIP server 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 77
78 Interoperability Testing Results To IPv6 SIP proxy Item Register on iptel Register on partysip Call UA through partysip proxy server Result Succeed Succeed Succeed 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 78
79 Interoperability Testing Results To IPv6 SIP UA To From Kphone Linphone SkinUA KPhone OK SIP ok SIP ok Linphone SIP ok OK SIP ok OK SIP ok OK SkinUA Linphone KPhone can not accept URI containing IPv6 Literal address in URI. 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 79
80 IPv6 Translation Mechanism- Bump-In In-the-API
81 IPv6 API Data structure SIP-based VoIP User Agent 例 200 行 Socket API 料 600 行 數 IPv6 不 易 數 v4/v6 BIA 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 81
82 來 行 BIA Function Mapper Name Resolver Address Mapper ALG Manager FTP-ALG BIA : Windows XP SP1 理 : Intel Celeron 2GHz : 128 MB : 20GB : Microsoft Visual C : Microsoft Platform SDK February 2003 BIA 行 Windows XP/ /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 82
83 Name Resolving: Translate IPv6 address to IPv4 address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 83
84 Socket-layer Translator Result 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 84
85 Using IPv4 to Browse Without Socket-layer Translator LAB /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 85
86 Conclusions In this course, you can learn the following techniques IPv4 Windows Socket Programming IPv6 Windows Socket Programming IPv4/IPv6 Domain Name Resolution You can try to do following advanced topics. Writing IPv4/IPv6 compatible programs Porting IPv4 applications to IPv6 version Writing ALG on Socket-layer Translator Writing IPv6 Test tools on SIPv6 Analyzer 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 86
87 References Microsoft Platform SDK MSDN Library VC /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 87
88 References [1] RFC Network Address Translation - Protocol Translation G. Tsirtsis P. Srisuresh 2000/2 [2] RFC-2765 Stateless IP/ICMP Translator (SIIT) Nordmark, E. 2000/2 [3] RFC-2767 Bump-In-the-Stack K. Tsuchiya H. Higuchi Y. Atarashi 2000/2 [4] RFC-3338 Bump-In-the-API S. Lee M-K. Shin Y-J. Kim E. Nordmark A. Durand 2002/10 [5] IPv6 Guide for Windows Sockets Applications MSDN Library 2003/2 sp?frame=true [6] How to upgrade WinSock application to support IPv6 Makoto Ookawa 2003/7 [7] RFC-2893 Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers R. Gilligan E. Nordmark 2000/8 [8] Hitachi Toolnet6, e.htm [9] IPv6 禮 ISBN /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 88
89 Appendix
90 IPv4 Header LAB /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 90
91 IPv6 Header LAB /12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 91
92 IPv4 Address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 92
93 IPv6 Address 2004/12/24 Speaker: Whai-En Chen 93
Porting applications & DNS issues. socket interface extensions for IPv6. Eva M. Castro. ecastro@dit.upm.es. dit. Porting applications & DNS issues UPM
 socket interface extensions for IPv6 Eva M. Castro ecastro@.upm.es Contents * Introduction * Porting IPv4 applications to IPv6, using socket interface extensions to IPv6. Data structures Conversion functions
socket interface extensions for IPv6 Eva M. Castro ecastro@.upm.es Contents * Introduction * Porting IPv4 applications to IPv6, using socket interface extensions to IPv6. Data structures Conversion functions
IPv4/IPv6 Transition for SIP VoIP Applications
 IPv4/IPv6 Transition for SIP VoIP Applications Dr. Whai-En Chen Research Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. TEL: +886-3-5731924 FAX: +886-3-5716929
IPv4/IPv6 Transition for SIP VoIP Applications Dr. Whai-En Chen Research Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. TEL: +886-3-5731924 FAX: +886-3-5716929
Socket Programming. Srinidhi Varadarajan
 Socket Programming Srinidhi Varadarajan Client-server paradigm Client: initiates contact with server ( speaks first ) typically requests service from server, for Web, client is implemented in browser;
Socket Programming Srinidhi Varadarajan Client-server paradigm Client: initiates contact with server ( speaks first ) typically requests service from server, for Web, client is implemented in browser;
Socket Programming. Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
 Socket Programming Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Background Demultiplexing Convert host-to-host packet delivery service into a process-to-process communication channel
Socket Programming Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Background Demultiplexing Convert host-to-host packet delivery service into a process-to-process communication channel
Socket Programming. Request. Reply. Figure 1. Client-Server paradigm
 Socket Programming 1. Introduction In the classic client-server model, the client sends out requests to the server, and the server does some processing with the request(s) received, and returns a reply
Socket Programming 1. Introduction In the classic client-server model, the client sends out requests to the server, and the server does some processing with the request(s) received, and returns a reply
陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 計 算 機 中 心 資 訊 網 路 組 組 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 工 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 340
 Advanced Issues- Wireless VoIP, IPv6 and Security 陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 計 算 機 中 心 資 訊 網 路 組 組 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 工 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 340 Outline Wireless VoIP IPv6 Solutions and Transition
Advanced Issues- Wireless VoIP, IPv6 and Security 陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 計 算 機 中 心 資 訊 網 路 組 組 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 工 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 340 Outline Wireless VoIP IPv6 Solutions and Transition
Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information
 Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information Keywords: sockets, client-server, network programming-socket functions, OSI layering, byte-ordering Outline: 1.) Introduction
Introduction to Socket Programming Part I : TCP Clients, Servers; Host information Keywords: sockets, client-server, network programming-socket functions, OSI layering, byte-ordering Outline: 1.) Introduction
NS3 Lab 1 TCP/IP Network Programming in C
 NS3 Lab 1 TCP/IP Network Programming in C Dr Colin Perkins School of Computing Science University of Glasgow http://csperkins.org/teaching/ns3/ 13/14 January 2015 Introduction The laboratory exercises
NS3 Lab 1 TCP/IP Network Programming in C Dr Colin Perkins School of Computing Science University of Glasgow http://csperkins.org/teaching/ns3/ 13/14 January 2015 Introduction The laboratory exercises
Unix Network Programming
 Introduction to Computer Networks Polly Huang EE NTU http://cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~phuang phuang@cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw Unix Network Programming The socket struct and data handling System calls Based on Beej's Guide
Introduction to Computer Networks Polly Huang EE NTU http://cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~phuang phuang@cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw Unix Network Programming The socket struct and data handling System calls Based on Beej's Guide
Tutorial on Socket Programming
 Tutorial on Socket Programming Computer Networks - CSC 458 Department of Computer Science Seyed Hossein Mortazavi (Slides are mainly from Monia Ghobadi, and Amin Tootoonchian, ) 1 Outline Client- server
Tutorial on Socket Programming Computer Networks - CSC 458 Department of Computer Science Seyed Hossein Mortazavi (Slides are mainly from Monia Ghobadi, and Amin Tootoonchian, ) 1 Outline Client- server
INTRODUCTION UNIX NETWORK PROGRAMMING Vol 1, Third Edition by Richard Stevens
 INTRODUCTION UNIX NETWORK PROGRAMMING Vol 1, Third Edition by Richard Stevens Read: Chapters 1,2, 3, 4 Communications Client Example: Ex: TCP/IP Server Telnet client on local machine to Telnet server on
INTRODUCTION UNIX NETWORK PROGRAMMING Vol 1, Third Edition by Richard Stevens Read: Chapters 1,2, 3, 4 Communications Client Example: Ex: TCP/IP Server Telnet client on local machine to Telnet server on
CSE 333 SECTION 6. Networking and sockets
 CSE 333 SECTION 6 Networking and sockets Goals for Today Overview of IP addresses Look at the IP address structures in C/C++ Overview of DNS Write your own (short!) program to do the domain name IP address
CSE 333 SECTION 6 Networking and sockets Goals for Today Overview of IP addresses Look at the IP address structures in C/C++ Overview of DNS Write your own (short!) program to do the domain name IP address
Client / Server Programming with TCP/IP Sockets
 Client / Server Programming with TCP/IP Sockets Author: Rajinder Yadav Date: Sept 9, 2007 Revision: Mar 11, 2008 Web: http://devmentor.org Email: rajinder@devmentor.org Table of Content Networks... 2 Diagram
Client / Server Programming with TCP/IP Sockets Author: Rajinder Yadav Date: Sept 9, 2007 Revision: Mar 11, 2008 Web: http://devmentor.org Email: rajinder@devmentor.org Table of Content Networks... 2 Diagram
TCP/IP - Socket Programming
 TCP/IP - Socket Programming jrb@socket.to.me Jim Binkley 1 sockets - overview sockets simple client - server model look at tcpclient/tcpserver.c look at udpclient/udpserver.c tcp/udp contrasts normal master/slave
TCP/IP - Socket Programming jrb@socket.to.me Jim Binkley 1 sockets - overview sockets simple client - server model look at tcpclient/tcpserver.c look at udpclient/udpserver.c tcp/udp contrasts normal master/slave
Introduction to Socket programming using C
 Introduction to Socket programming using C Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Vinay Narasimhamurthy S0677790@sms.ed.ac.uk CLIENT SERVER MODEL Sockets are
Introduction to Socket programming using C Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Vinay Narasimhamurthy S0677790@sms.ed.ac.uk CLIENT SERVER MODEL Sockets are
Implementing Network Software
 Implementing Network Software Outline Sockets Example Process Models Message Buffers Spring 2007 CSE 30264 1 Sockets Application Programming Interface (API) Socket interface socket : point where an application
Implementing Network Software Outline Sockets Example Process Models Message Buffers Spring 2007 CSE 30264 1 Sockets Application Programming Interface (API) Socket interface socket : point where an application
IPv6 Enabling CIFS/SMB Applications
 IPv6 Enabling CIFS/SMB Applications 2010 Storage Developers Conference Santa Clara Dr David Holder CEng FIET MIEEE david.holder@erion.co.uk http://www.erion.co.uk Background Erion David Holder Over twelve
IPv6 Enabling CIFS/SMB Applications 2010 Storage Developers Conference Santa Clara Dr David Holder CEng FIET MIEEE david.holder@erion.co.uk http://www.erion.co.uk Background Erion David Holder Over twelve
Network Programming with Sockets. Anatomy of an Internet Connection
 Network Programming with Sockets Anatomy of an Internet Connection Client socket address 128.2.194.242:51213 socket address 208.216.181.15:80 Client Connection socket pair (128.2.194.242:51213, 208.216.181.15:80)
Network Programming with Sockets Anatomy of an Internet Connection Client socket address 128.2.194.242:51213 socket address 208.216.181.15:80 Client Connection socket pair (128.2.194.242:51213, 208.216.181.15:80)
Programming guidelines on transition to IPv6
 Programming guidelines on transition to IPv6 Tomás P. de Miguel and Eva M. Castro tmiguel@dit.upm.es eva@gsyc.escet.urjc.es Department of Telematic Systems Engineering (DIT) Technical University of Madrid
Programming guidelines on transition to IPv6 Tomás P. de Miguel and Eva M. Castro tmiguel@dit.upm.es eva@gsyc.escet.urjc.es Department of Telematic Systems Engineering (DIT) Technical University of Madrid
Elementary Name and Address. Conversions
 Elementary Name and Address Domain name system Conversions gethostbyname Function RES_USE_INET6 resolver option gethostbyname2 Function and IPv6 support gethostbyaddr Function uname and gethostname Functions
Elementary Name and Address Domain name system Conversions gethostbyname Function RES_USE_INET6 resolver option gethostbyname2 Function and IPv6 support gethostbyaddr Function uname and gethostname Functions
Porting and Deploying VoIP to IPv6: Lessons Learned
 Porting and Deploying VoIP to IPv6: Lessons Learned Marc Blanchet Simon Perreault Viagénie http://www.viagenie.ca Presented at ClueCon, Chicago, August 2008 ANNOUNCEMENT Freeswitch now supports IPv6. IPv6
Porting and Deploying VoIP to IPv6: Lessons Learned Marc Blanchet Simon Perreault Viagénie http://www.viagenie.ca Presented at ClueCon, Chicago, August 2008 ANNOUNCEMENT Freeswitch now supports IPv6. IPv6
Software changes for Website and Application IPv6 Readiness
 Software changes for Website and Application IPv6 Readiness Ahmed Abu-Abed, P.Eng. Tamkien Systems ahmed@tamkien.com 1 Agenda Introduction Enabling Website IPv6 and Forum Certification Intro to Socket
Software changes for Website and Application IPv6 Readiness Ahmed Abu-Abed, P.Eng. Tamkien Systems ahmed@tamkien.com 1 Agenda Introduction Enabling Website IPv6 and Forum Certification Intro to Socket
UNIX. Sockets. mgr inż. Marcin Borkowski
 UNIX Sockets Introduction to Sockets Interprocess Communication channel: descriptor based two way communication can connect processes on different machines Three most typical socket types (colloquial names):
UNIX Sockets Introduction to Sockets Interprocess Communication channel: descriptor based two way communication can connect processes on different machines Three most typical socket types (colloquial names):
ELEN 602: Computer Communications and Networking. Socket Programming Basics
 1 ELEN 602: Computer Communications and Networking Socket Programming Basics A. Introduction In the classic client-server model, the client sends out requests to the server, and the server does some processing
1 ELEN 602: Computer Communications and Networking Socket Programming Basics A. Introduction In the classic client-server model, the client sends out requests to the server, and the server does some processing
VMCI Sockets Programming Guide VMware ESX/ESXi 4.x VMware Workstation 7.x VMware Server 2.0
 VMware ESX/ESXi 4.x VMware Workstation 7.x VMware Server 2.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition.
VMware ESX/ESXi 4.x VMware Workstation 7.x VMware Server 2.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition.
Elementary Name and Address Conversions
 Elementary Name and Address Conversions Domain name system gethostbyname Function RES_USE_INET6 resolver option gethostbyname2 Function and IPv6 support gethostbyaddr Function uname and gethostname Functions
Elementary Name and Address Conversions Domain name system gethostbyname Function RES_USE_INET6 resolver option gethostbyname2 Function and IPv6 support gethostbyaddr Function uname and gethostname Functions
Socket Programming in C/C++
 September 24, 2004 Contact Info Mani Radhakrishnan Office 4224 SEL email mradhakr @ cs. uic. edu Office Hours Tuesday 1-4 PM Introduction Sockets are a protocol independent method of creating a connection
September 24, 2004 Contact Info Mani Radhakrishnan Office 4224 SEL email mradhakr @ cs. uic. edu Office Hours Tuesday 1-4 PM Introduction Sockets are a protocol independent method of creating a connection
Communication Networks. Introduction & Socket Programming Yuval Rochman
 Communication Networks Introduction & Socket Programming Yuval Rochman Administration Staff Lecturer: Prof. Hanoch Levy hanoch AT cs tau Office hours: by appointment Teaching Assistant: Yuval Rochman yuvalroc
Communication Networks Introduction & Socket Programming Yuval Rochman Administration Staff Lecturer: Prof. Hanoch Levy hanoch AT cs tau Office hours: by appointment Teaching Assistant: Yuval Rochman yuvalroc
Name and Address Conversions
 11 Name and Address Conversions 11.1 Introduction All the examples so far in this text have used numeric addresses for the hosts (e.g., 206.6.226.33) and numeric port numbers to identify the servers (e.g.,
11 Name and Address Conversions 11.1 Introduction All the examples so far in this text have used numeric addresses for the hosts (e.g., 206.6.226.33) and numeric port numbers to identify the servers (e.g.,
Concurrent Server Design Alternatives
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ Advanced Socket Programming Wenyuan Xu Concurrent Server Design Alternatives Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Ref:
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ Advanced Socket Programming Wenyuan Xu Concurrent Server Design Alternatives Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Ref:
BSD Sockets Interface Programmer s Guide
 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer s Guide Edition 6 B2355-90136 HP 9000 Networking E0497 Printed in: United States Copyright 1997 Hewlett-Packard Company. Legal Notices The information in this document
BSD Sockets Interface Programmer s Guide Edition 6 B2355-90136 HP 9000 Networking E0497 Printed in: United States Copyright 1997 Hewlett-Packard Company. Legal Notices The information in this document
Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part
 Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part Overview The goal of this lab is to familiarize yourself with application level programming with sockets, specifically stream or TCP sockets, by implementing a client/server
Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part Overview The goal of this lab is to familiarize yourself with application level programming with sockets, specifically stream or TCP sockets, by implementing a client/server
Lecture 7: Introduction to Sockets
 Lecture 7: Introduction to Sockets References for Lecture 7: 1) Unix Network Programming, W.R. Stevens, 1990,Prentice-Hall, Chapter 6. 2) Unix Network Programming, W.R. Stevens, 1998,Prentice-Hall, Volume
Lecture 7: Introduction to Sockets References for Lecture 7: 1) Unix Network Programming, W.R. Stevens, 1990,Prentice-Hall, Chapter 6. 2) Unix Network Programming, W.R. Stevens, 1998,Prentice-Hall, Volume
IT304 Experiment 2 To understand the concept of IPC, Pipes, Signals, Multi-Threading and Multiprocessing in the context of networking.
 Aim: IT304 Experiment 2 To understand the concept of IPC, Pipes, Signals, Multi-Threading and Multiprocessing in the context of networking. Other Objective of this lab session is to learn how to do socket
Aim: IT304 Experiment 2 To understand the concept of IPC, Pipes, Signals, Multi-Threading and Multiprocessing in the context of networking. Other Objective of this lab session is to learn how to do socket
Review of Previous Lecture
 Review of Previous Lecture Principles of app layer protocols clients and servers app requirements Web and HTTP FTP Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and K. Ross Announcement All got partners and
Review of Previous Lecture Principles of app layer protocols clients and servers app requirements Web and HTTP FTP Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and K. Ross Announcement All got partners and
Hostnames. HOSTS.TXT was a bottleneck. Once there was HOSTS.TXT. CSCE515 Computer Network Programming. Hierarchical Organization of DNS
 Hostnames CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ Address Conversion Function and DNS RFC 1034, RFC 1035 Wenyuan Xu http://www.cse..edu/~wyxu/ce515f07.html Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Hostnames CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming ------ Address Conversion Function and DNS RFC 1034, RFC 1035 Wenyuan Xu http://www.cse..edu/~wyxu/ce515f07.html Department of Computer Science and Engineering
IPv6/IPv4 Translation for SIP Applications- Socket-Layer Translator and SIPv6 Translator
 IPv6/IPv4 Translation for SIP Applications- Socket-Layer Translator and SIPv6 Translator Whai-En Chen Research Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiao
IPv6/IPv4 Translation for SIP Applications- Socket-Layer Translator and SIPv6 Translator Whai-En Chen Research Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiao
Porting and Running Asterisk to IPv6
 Porting and Running Asterisk to IPv6 Presented at APRICOT, Bali, Feb 28 th 2007 Marc Blanchet Viagénie http://www.viagenie.ca Credentials 20+ years in IP networking and Unix, with 10 years on IPv6... IP
Porting and Running Asterisk to IPv6 Presented at APRICOT, Bali, Feb 28 th 2007 Marc Blanchet Viagénie http://www.viagenie.ca Credentials 20+ years in IP networking and Unix, with 10 years on IPv6... IP
Application Architecture
 A Course on Internetworking & Network-based Applications CS 6/75995 Internet-based Applications & Systems Design Kent State University Dept. of Science LECT-2 LECT-02, S-1 2 Application Architecture Today
A Course on Internetworking & Network-based Applications CS 6/75995 Internet-based Applications & Systems Design Kent State University Dept. of Science LECT-2 LECT-02, S-1 2 Application Architecture Today
Domain Name System (1)! gethostbyname (2)! gethostbyaddr (2)!
 Lecture 5 Overview Last Lecture Socket Options and elementary UDP sockets This Lecture Name and address conversions & IPv6 Source: Chapter 11 Next Lecture Multicast Source: Chapter 12 1 Domain Name System
Lecture 5 Overview Last Lecture Socket Options and elementary UDP sockets This Lecture Name and address conversions & IPv6 Source: Chapter 11 Next Lecture Multicast Source: Chapter 12 1 Domain Name System
IBM i Version 7.2. Programming Socket programming IBM
 IBM i Version 7.2 Programming Socket programming IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Programming Socket programming IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices
IBM i Version 7.2 Programming Socket programming IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Programming Socket programming IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices
ICT SEcurity BASICS. Course: Software Defined Radio. Angelo Liguori. SP4TE lab. angelo.liguori@uniroma3.it
 Course: Software Defined Radio ICT SEcurity BASICS Angelo Liguori angelo.liguori@uniroma3.it SP4TE lab 1 Simple Timing Covert Channel Unintended information about data gets leaked through observing the
Course: Software Defined Radio ICT SEcurity BASICS Angelo Liguori angelo.liguori@uniroma3.it SP4TE lab 1 Simple Timing Covert Channel Unintended information about data gets leaked through observing the
Mike Saywell and Tim Chown University of Southampton, UK ms@ecs.soton.ac.uk, tjc@ecs.soton.ac.uk Global IPv6 Summit, Madrid, 12 th May 2003
 Mike Saywell and Tim Chown University of Southampton, UK ms@ecs.soton.ac.uk, tjc@ecs.soton.ac.uk Global IPv6 Summit, Madrid, 12 th May 2003 IPv6 s primary advantage is address space Global addresses re-enable
Mike Saywell and Tim Chown University of Southampton, UK ms@ecs.soton.ac.uk, tjc@ecs.soton.ac.uk Global IPv6 Summit, Madrid, 12 th May 2003 IPv6 s primary advantage is address space Global addresses re-enable
Best practices in IPv6 enabled networking software development. <mauro@deepspace6.net>
 Best practices in IPv6 enabled networking software development 1 The IPv6 Protocol 1 New version of the Internet Protocol Devised by IETF to replace IPv4 It solves all the problems of IPv4 Address space
Best practices in IPv6 enabled networking software development 1 The IPv6 Protocol 1 New version of the Internet Protocol Devised by IETF to replace IPv4 It solves all the problems of IPv4 Address space
A Client-Server Transaction. Systemprogrammering 2006 Föreläsning 8 Network Programming. Hardware Org of a Network Host.
 Systemprogrammering 2006 Föreläsning 8 Network Programming Topics -server programming model A -Server Transaction Every network application is based on the client-server model: A server process and one
Systemprogrammering 2006 Föreläsning 8 Network Programming Topics -server programming model A -Server Transaction Every network application is based on the client-server model: A server process and one
Writing Client/Server Programs in C Using Sockets (A Tutorial) Part I. Session 5958. Greg Granger grgran@sas. sas.com. SAS/C & C++ Support
 Writing Client/Server Programs in C Using Sockets (A Tutorial) Part I Session 5958 Greg Granger grgran@sas sas.com SAS Slide 1 Feb. 1998 SAS/C & C++ Support SAS Institute Part I: Socket Programming Overview
Writing Client/Server Programs in C Using Sockets (A Tutorial) Part I Session 5958 Greg Granger grgran@sas sas.com SAS Slide 1 Feb. 1998 SAS/C & C++ Support SAS Institute Part I: Socket Programming Overview
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENT AND ONLINE EXERCISE FOR TEACHING AND DEVELOPMENT OF A SERVER USING SOCKET PROGRAMMING IN C
 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENT AND ONLINE EXERCISE FOR TEACHING AND DEVELOPMENT OF A SERVER USING SOCKET PROGRAMMING IN C Elena Ruiz Gonzalez University of Patras University of Granada ERASMUS STUDENT:147 1/100
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENT AND ONLINE EXERCISE FOR TEACHING AND DEVELOPMENT OF A SERVER USING SOCKET PROGRAMMING IN C Elena Ruiz Gonzalez University of Patras University of Granada ERASMUS STUDENT:147 1/100
Networks class CS144 Introduction to Computer Networking Goal: Teach the concepts underlying networks Prerequisites:
 CS144 Introduction to Computer Networking Instructors: Philip Levis and David Mazières CAs: Juan Batiz-Benet, Behram Mistree, Hariny Murli, Matt Sparks, and Tony Wu Section Leader: Aki Kobashi cs144-staff@scs.stanford.edu
CS144 Introduction to Computer Networking Instructors: Philip Levis and David Mazières CAs: Juan Batiz-Benet, Behram Mistree, Hariny Murli, Matt Sparks, and Tony Wu Section Leader: Aki Kobashi cs144-staff@scs.stanford.edu
M06 (31-May-2001) Requirements and guidelines for distributed laboratories application migration WP 3
 3URMHFW1XPEHU 3URMHFW7LWOH 'HOLYHUDEOH7\SH,67 /DERUDWRULHV2YHU1H[W *HQHUDWLRQ1HWZRUNV 3±SXEOLF &(&'HOLYHUDEOH1XPEHU &RQWUDFWXDO'DWHRI'HOLYHU\WRWKH &(& $FWXDO'DWHRI'HOLYHU\WRWKH&(& 7LWOHRI'HOLYHUDEOH :RUNSDFNDJHFRQWULEXWLQJWRWKH
3URMHFW1XPEHU 3URMHFW7LWOH 'HOLYHUDEOH7\SH,67 /DERUDWRULHV2YHU1H[W *HQHUDWLRQ1HWZRUNV 3±SXEOLF &(&'HOLYHUDEOH1XPEHU &RQWUDFWXDO'DWHRI'HOLYHU\WRWKH &(& $FWXDO'DWHRI'HOLYHU\WRWKH&(& 7LWOHRI'HOLYHUDEOH :RUNSDFNDJHFRQWULEXWLQJWRWKH
Network Programming with Sockets. Process Management in UNIX
 Network Programming with Sockets This section is a brief introduction to the basics of networking programming using the BSD Socket interface on the Unix Operating System. Processes in Unix Sockets Stream
Network Programming with Sockets This section is a brief introduction to the basics of networking programming using the BSD Socket interface on the Unix Operating System. Processes in Unix Sockets Stream
sys socketcall: Network systems calls on Linux
 sys socketcall: Network systems calls on Linux Daniel Noé April 9, 2008 The method used by Linux for system calls is explored in detail in Understanding the Linux Kernel. However, the book does not adequately
sys socketcall: Network systems calls on Linux Daniel Noé April 9, 2008 The method used by Linux for system calls is explored in detail in Understanding the Linux Kernel. However, the book does not adequately
Session NM059. TCP/IP Programming on VMS. Geoff Bryant Process Software
 Session NM059 TCP/IP Programming on VMS Geoff Bryant Process Software Course Roadmap Slide 160 NM055 (11:00-12:00) Important Terms and Concepts TCP/IP and Client/Server Model Sockets and TLI Client/Server
Session NM059 TCP/IP Programming on VMS Geoff Bryant Process Software Course Roadmap Slide 160 NM055 (11:00-12:00) Important Terms and Concepts TCP/IP and Client/Server Model Sockets and TLI Client/Server
An Overview of IPv6 CHAPTER
 56982_CH02I 12/12/97 3:29 PM Page 23 2 CHAPTER 2 An Overview of IPv6 This second chapter is meant to provide a general overview of the IPv6 protocol and of the way network layer protocols operate. These
56982_CH02I 12/12/97 3:29 PM Page 23 2 CHAPTER 2 An Overview of IPv6 This second chapter is meant to provide a general overview of the IPv6 protocol and of the way network layer protocols operate. These
A Client Server Transaction. Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd
 A Client Server Transaction Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd 4. Client handles response Client process 1. Client sends request 3. Server sends response
A Client Server Transaction Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 18 th Lecture, Nov. 3 rd 4. Client handles response Client process 1. Client sends request 3. Server sends response
Beej's Guide to Network Programming
 Beej's Guide to Network Programming Using Internet Sockets Brian Beej Jorgensen Hall beej@beej.us Version 3.0.21 June 8, 2016 Copyright 2015 Brian Beej Jorgensen Hall Thanks to everyone who has helped
Beej's Guide to Network Programming Using Internet Sockets Brian Beej Jorgensen Hall beej@beej.us Version 3.0.21 June 8, 2016 Copyright 2015 Brian Beej Jorgensen Hall Thanks to everyone who has helped
UNIX Sockets. COS 461 Precept 1
 UNIX Sockets COS 461 Precept 1 Clients and Servers Client program Running on end host Requests service E.g., Web browser Server program Running on end host Provides service E.g., Web server GET /index.html
UNIX Sockets COS 461 Precept 1 Clients and Servers Client program Running on end host Requests service E.g., Web browser Server program Running on end host Provides service E.g., Web server GET /index.html
KATRAGADDA INNOVATIVE TRUST FOR EDUCATION NETWORK PROGRAMMING. Notes prepared by D. Teja Santosh, Assistant Professor, KPES, Shabad, R.R. District.
 KATRAGADDA INNOVATIVE TRUST FOR EDUCATION NETWORK PROGRAMMING 2 P age N E T W O R K P R O G R A M M I N G INTRODUCTION UNIT-I Introduction and TCP/IP When writing programs that communicate across a computer
KATRAGADDA INNOVATIVE TRUST FOR EDUCATION NETWORK PROGRAMMING 2 P age N E T W O R K P R O G R A M M I N G INTRODUCTION UNIT-I Introduction and TCP/IP When writing programs that communicate across a computer
Chapter 10 Session Initiation Protocol. Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University
 Chapter 10 Session Initiation Protocol Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 12.1 An Overview of SIP 12.2 SIP-based GPRS Push
Chapter 10 Session Initiation Protocol Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 12.1 An Overview of SIP 12.2 SIP-based GPRS Push
The POSIX Socket API
 The POSIX Giovanni Agosta Piattaforme Software per la Rete Modulo 2 G. Agosta The POSIX Outline Sockets & TCP Connections 1 Sockets & TCP Connections 2 3 4 G. Agosta The POSIX TCP Connections Preliminaries
The POSIX Giovanni Agosta Piattaforme Software per la Rete Modulo 2 G. Agosta The POSIX Outline Sockets & TCP Connections 1 Sockets & TCP Connections 2 3 4 G. Agosta The POSIX TCP Connections Preliminaries
Computer Networks Network architecture
 Computer Networks Network architecture Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York - Networks are like onions - They stink? - Yes, no, they have layers Shrek and Donkey 1 Introduction
Computer Networks Network architecture Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York - Networks are like onions - They stink? - Yes, no, they have layers Shrek and Donkey 1 Introduction
Programmation Systèmes Cours 9 UNIX Domain Sockets
 Programmation Systèmes Cours 9 UNIX Domain Sockets Stefano Zacchiroli zack@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot 2013 2014 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1314/progsyst/
Programmation Systèmes Cours 9 UNIX Domain Sockets Stefano Zacchiroli zack@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot 2013 2014 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1314/progsyst/
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets
 Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
This tutorial has been designed for everyone interested in learning the data exchange features of Unix Sockets.
 About the Tutorial Sockets are communication points on the same or different computers to exchange data. Sockets are supported by Unix, Windows, Mac, and many other operating systems. The tutorial provides
About the Tutorial Sockets are communication points on the same or different computers to exchange data. Sockets are supported by Unix, Windows, Mac, and many other operating systems. The tutorial provides
Generalised Socket Addresses for Unix Squeak 3.9 11
 Generalised Socket Addresses for Unix Squeak 3.9 11 Ian Piumarta 2007 06 08 This document describes several new SocketPlugin primitives that allow IPv6 (and arbitrary future other) address formats to be
Generalised Socket Addresses for Unix Squeak 3.9 11 Ian Piumarta 2007 06 08 This document describes several new SocketPlugin primitives that allow IPv6 (and arbitrary future other) address formats to be
Overview. Socket Programming. Using Ports to Identify Services. UNIX Socket API. Knowing What Port Number To Use. Socket: End Point of Communication
 Overview Socket Programming EE 122: Intro to Communication Networks Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel Killebrew, Jorge Ortiz Socket Programming: how applications use the network Sockets are a C-language
Overview Socket Programming EE 122: Intro to Communication Networks Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel Killebrew, Jorge Ortiz Socket Programming: how applications use the network Sockets are a C-language
2057-15. First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring
 2057-15 First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring 7-25 September 2009 TCP/IP Networking Abhaya S. Induruwa Department
2057-15 First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring 7-25 September 2009 TCP/IP Networking Abhaya S. Induruwa Department
Programming with TCP/IP Best Practices
 Programming with TCP/IP Best Practices Matt Muggeridge TCP/IP for OpenVMS Engineering "Be liberal in what you accept, and conservative in what you send" Source: RFC 1122, section 1.2.2 [Braden, 1989a]
Programming with TCP/IP Best Practices Matt Muggeridge TCP/IP for OpenVMS Engineering "Be liberal in what you accept, and conservative in what you send" Source: RFC 1122, section 1.2.2 [Braden, 1989a]
Writing a C-based Client/Server
 Working the Socket Writing a C-based Client/Server Consider for a moment having the massive power of different computers all simultaneously trying to compute a problem for you -- and still being legal!
Working the Socket Writing a C-based Client/Server Consider for a moment having the massive power of different computers all simultaneously trying to compute a problem for you -- and still being legal!
Building Applications With Sockets
 C C Building Applications With Sockets Topics & Goals: Sockets mechanism & its use App layer design & implementation principles Building applications using sockets D Sockets: Unifying Transport API Simplify
C C Building Applications With Sockets Topics & Goals: Sockets mechanism & its use App layer design & implementation principles Building applications using sockets D Sockets: Unifying Transport API Simplify
gianluca.verin verin@libero. @libero.itit Vicenza.linux.it\LinuxCafe 1
 gianluca.verin verin@libero. @libero.itit Vicenza.linux.it\LinuxCafe 1 Agenda IPv6 Basics Connecting to 6Bone Why do we need IPv6? IPv6 Introduction-Transition IPv6 and open source community Future applications
gianluca.verin verin@libero. @libero.itit Vicenza.linux.it\LinuxCafe 1 Agenda IPv6 Basics Connecting to 6Bone Why do we need IPv6? IPv6 Introduction-Transition IPv6 and open source community Future applications
Network Programming. Chapter 11. 11.1 The Client-Server Programming Model
 Chapter 11 Network Programming Network applications are everywhere. Any time you browse the Web, send an email message, or pop up an X window, you are using a network application. Interestingly, all network
Chapter 11 Network Programming Network applications are everywhere. Any time you browse the Web, send an email message, or pop up an X window, you are using a network application. Interestingly, all network
Moving Grid Systems into the IPv6 Era
 Moving Grid Systems into the IPv6 Era Sheng JIANG, Piers O Hanlon, Peter Kirstein Department of Computer Science University College London Gower Street, WC1E 6BT London, United Kingdom {S.Jiang, P.Ohanlon,
Moving Grid Systems into the IPv6 Era Sheng JIANG, Piers O Hanlon, Peter Kirstein Department of Computer Science University College London Gower Street, WC1E 6BT London, United Kingdom {S.Jiang, P.Ohanlon,
NTP VoIP Platform: A SIP VoIP Platform and Its Services
 NTP VoIP Platform: A SIP VoIP Platform and Its Services Speaker: Dr. Chai-Hien Gan National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan Email: chgan@csie.nctu.edu.tw Date: 2006/05/02 1 Outline Introduction NTP VoIP
NTP VoIP Platform: A SIP VoIP Platform and Its Services Speaker: Dr. Chai-Hien Gan National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan Email: chgan@csie.nctu.edu.tw Date: 2006/05/02 1 Outline Introduction NTP VoIP
Carnegie Mellon. Internetworking. 15-213: Introduc0on to Computer Systems 19 th Lecture, Oct. 28, 2010. Instructors: Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron
 Internetworking 15-213: Introduc0on to Computer Systems 19 th Lecture, Oct. 28, 2010 Instructors: Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 A Client- Server Transac8on 4. Client handles response Client process
Internetworking 15-213: Introduc0on to Computer Systems 19 th Lecture, Oct. 28, 2010 Instructors: Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 A Client- Server Transac8on 4. Client handles response Client process
Computer Networks/DV2 Lab
 Computer Networks/DV2 Lab Room: BB 219 Additional Information: http://ti.uni-due.de/ti/en/education/teaching/ss13/netlab Equipment for each group: - 1 Server computer (OS: Windows Server 2008 Standard)
Computer Networks/DV2 Lab Room: BB 219 Additional Information: http://ti.uni-due.de/ti/en/education/teaching/ss13/netlab Equipment for each group: - 1 Server computer (OS: Windows Server 2008 Standard)
DNS Domain Name System
 Domain Name System DNS Domain Name System The domain name system is usually used to translate a host name into an IP address Domain names comprise a hierarchy so that names are unique, yet easy to remember.
Domain Name System DNS Domain Name System The domain name system is usually used to translate a host name into an IP address Domain names comprise a hierarchy so that names are unique, yet easy to remember.
Networks. Inter-process Communication. Pipes. Inter-process Communication
 Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
System calls. Problem: How to access resources other than CPU
 System calls Problem: How to access resources other than CPU - Disk, network, terminal, other processes - CPU prohibits instructions that would access devices - Only privileged OS kernel can access devices
System calls Problem: How to access resources other than CPU - Disk, network, terminal, other processes - CPU prohibits instructions that would access devices - Only privileged OS kernel can access devices
Aculab digital network access cards
 Aculab digital network access cards Adding and Using IPv6 Capabilities Guide Revision 1.0.2 PROPRIETARY INFORMATION Aculab Plc makes every effort to ensure that the information in this document is correct
Aculab digital network access cards Adding and Using IPv6 Capabilities Guide Revision 1.0.2 PROPRIETARY INFORMATION Aculab Plc makes every effort to ensure that the information in this document is correct
TCP/IP Sockets in C. Practical Guide for Programmers
 TCP/IP Sockets in C Practical Guide for Programmers The Morgan Kaufmann Practical Guides Series Series Editor: Michael J. Donahoo TCP/IP Sockets in C: Practical Guide for Programmers Michael J. Donahoo
TCP/IP Sockets in C Practical Guide for Programmers The Morgan Kaufmann Practical Guides Series Series Editor: Michael J. Donahoo TCP/IP Sockets in C: Practical Guide for Programmers Michael J. Donahoo
point to point and point to multi point calls over IP
 Helsinki University of Technology Department of Electrical and Communications Engineering Jarkko Kneckt point to point and point to multi point calls over IP Helsinki 27.11.2001 Supervisor: Instructor:
Helsinki University of Technology Department of Electrical and Communications Engineering Jarkko Kneckt point to point and point to multi point calls over IP Helsinki 27.11.2001 Supervisor: Instructor:
VoIP telephony over internet
 VoIP telephony over internet Yatindra Nath Singh, Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh India. http://home.iitk.ac.in/~ynsingh MOOC on M4D (c)
VoIP telephony over internet Yatindra Nath Singh, Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh India. http://home.iitk.ac.in/~ynsingh MOOC on M4D (c)
VoIP LAB. 陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 所 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 訊 工 程 研 究 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 255
 SIP Traversal over NAT 陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 所 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 訊 工 程 研 究 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 255 Outline Introduction to SIP and NAT NAT Problem Definition NAT Solutions on NTP VoIP
SIP Traversal over NAT 陳 懷 恩 博 士 助 理 教 授 兼 所 長 國 立 宜 蘭 大 學 資 訊 工 程 研 究 所 Email: wechen@niu.edu.tw TEL: 03-9357400 # 255 Outline Introduction to SIP and NAT NAT Problem Definition NAT Solutions on NTP VoIP
Asterisk with IPv6: Seamless and Ubiquitous VoIP
 Asterisk with IPv6: Seamless and Ubiquitous VoIP Marc Blanchet Viagénie marc.blanchet@viagenie.ca http://www.viagenie.ca Presented at Voice Peering Forum, Miami, March 2007 Credentials 20+ years in IP
Asterisk with IPv6: Seamless and Ubiquitous VoIP Marc Blanchet Viagénie marc.blanchet@viagenie.ca http://www.viagenie.ca Presented at Voice Peering Forum, Miami, March 2007 Credentials 20+ years in IP
NAT TCP SIP ALG Support
 The feature allows embedded messages of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) passing through a device that is configured with Network Address Translation (NAT) to be translated and encoded back to the
The feature allows embedded messages of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) passing through a device that is configured with Network Address Translation (NAT) to be translated and encoded back to the
Giving credit where credit is due
 JDEP 284H Foundations of Computer Systems Internetworking Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based on slides created by Drs. Bryant
JDEP 284H Foundations of Computer Systems Internetworking Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based on slides created by Drs. Bryant
What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking. Course Outline. Lecture 1 Outline. Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.
 What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu CSG150 Understand the basic principles of networking: Description of existing networks, and networking mechanisms
What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu CSG150 Understand the basic principles of networking: Description of existing networks, and networking mechanisms
Application Notes for Avaya IP Office 7.0 Integration with Skype Connect R2.0 Issue 1.0
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Avaya IP Office 7.0 Integration with Skype Connect R2.0 Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application Notes describe the steps to configure an Avaya
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Avaya IP Office 7.0 Integration with Skype Connect R2.0 Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application Notes describe the steps to configure an Avaya
Programming With Sockets 2
 Programming With Sockets 2 This chapter presents the socket interface and illustrates them with sample programs. The programs demonstrate the Internet domain sockets. What Are Sockets page 12 Socket Tutorial
Programming With Sockets 2 This chapter presents the socket interface and illustrates them with sample programs. The programs demonstrate the Internet domain sockets. What Are Sockets page 12 Socket Tutorial
Special Module on Media Processing and Communication
 Special Module on Media Processing and Communication Multimedia Communication Fundamentals Dayalbagh Educational Institute (DEI) Dayalbagh Agra PHM 961 Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IITD) New Delhi
Special Module on Media Processing and Communication Multimedia Communication Fundamentals Dayalbagh Educational Institute (DEI) Dayalbagh Agra PHM 961 Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IITD) New Delhi
How will the Migration from IPv4 to IPv6 Impact Voice and Visual Communication?
 How will the Migration from IPv4 to IPv6 Impact Voice and Visual Communication? Nick Hawkins Director, Technology Consulting Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved. Agenda Introduction & standards Requirements
How will the Migration from IPv4 to IPv6 Impact Voice and Visual Communication? Nick Hawkins Director, Technology Consulting Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved. Agenda Introduction & standards Requirements
Application Notes for Configuring Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 and Avaya IP Office PSTN Call Routing - Issue 1.0
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 and Avaya IP Office PSTN Call Routing - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 and Avaya IP Office PSTN Call Routing - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Time Warner ITSP Setup Guide
 October 14 Time Warner ITSP Setup Guide Author: Zultys Technical Support This configuration guide was created to assist knowledgeable vendors with configuring the Zultys MX Phone System with Time Warner
October 14 Time Warner ITSP Setup Guide Author: Zultys Technical Support This configuration guide was created to assist knowledgeable vendors with configuring the Zultys MX Phone System with Time Warner
SMTP-32 Library. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Dynamic Link Library for Microsoft Windows. Version 5.2
 SMTP-32 Library Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Dynamic Link Library for Microsoft Windows Version 5.2 Copyright 1994-2003 by Distinct Corporation All rights reserved Table of Contents 1 Overview... 5 1.1
SMTP-32 Library Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Dynamic Link Library for Microsoft Windows Version 5.2 Copyright 1994-2003 by Distinct Corporation All rights reserved Table of Contents 1 Overview... 5 1.1
Monitoring Forefront TMG
 Monitoring Forefront TMG eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced
Monitoring Forefront TMG eg Enterprise v6 Restricted Rights Legend The information contained in this document is confidential and subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced
How To Understand The Purpose Of A Sip Aware Firewall/Alg (Sip) With An Alg (Sip) And An Algen (S Ip) (Alg) (Siph) (Network) (Ip) (Lib
 NetVanta Unified Communications Technical Note The Purpose of a SIP-Aware Firewall/ALG Introduction This technical note will explore the purpose of a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-aware firewall/application
NetVanta Unified Communications Technical Note The Purpose of a SIP-Aware Firewall/ALG Introduction This technical note will explore the purpose of a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-aware firewall/application
Limi Kalita / (IJCSIT) International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, Vol. 5 (3), 2014, 4802-4807. Socket Programming
 Socket Programming Limi Kalita M.Tech Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Assam Down Town University, Guwahati, India. Abstract: The aim of the paper is to introduce sockets, its deployment
Socket Programming Limi Kalita M.Tech Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Assam Down Town University, Guwahati, India. Abstract: The aim of the paper is to introduce sockets, its deployment
RPG Does TCP/IP (Socket Progamming in RPG IV)
 RPG Does TCP/IP (Socket Progamming in RPG IV) Presented by Scott Klement http://www.scottklement.com 2007-2015, Scott Klement There are 10 types of people in the world. Those who understand binary, and
RPG Does TCP/IP (Socket Progamming in RPG IV) Presented by Scott Klement http://www.scottklement.com 2007-2015, Scott Klement There are 10 types of people in the world. Those who understand binary, and
Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets. An interface between application and network
 Socket programming Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Socket API introduced in BSD4.1 UNIX, 1981 explicitly created, used, released by apps client/server
Socket programming Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Socket API introduced in BSD4.1 UNIX, 1981 explicitly created, used, released by apps client/server
