Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources
|
|
|
- Pamela Dorsey
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 3: Updates on Overactive Bladder Treatments Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB) is a defined as urinary urgency (except in the absence of sensory input), with or without urge incontinence, usually with frequency and nocturia and in the absence of a known pathologic condition (uncommon) that may cause similar symptoms (e.g., urinary tract infection). When inadequately treated, OAB has a significant detrimental effect on patients quality of life including bothersome symptoms, inferior health-related quality of life, and higher rates of depression, anxiety, and insomnia due to nocturia and the fear of enuresis. The first-line treatment for OAB is nonpharmacologic management, consisting of lifestyle modifications, behavioral therapies (e.g., bladder and/or pelvic floor muscle training) and other toilet scheduling regimens. Anti-incontinence devices and supportive interventions are adjunctive or used to manage residual OAB symptoms. If these measures do not adequately control symptoms, pharmacotherapy with antimuscarinic medications is initiated. Antimuscarinic agents, currently the mainstay of OAB pharmacotherapy, include oxybutynin, solifenacin, darifenacin, tolterodine, trospium, and fesoterodine. These agents are available in a variety of dosage forms, ranging from transdermal patches and topical gels to oral medications (immediate-release and extended-release formulations). Still, many patients do not achieve adequate symptom relief or experience intolerable medication-related adverse events from the currently available medications. Fortunately, new treatment options for OAB with different mechanisms of action are now available. In addition, other agents, including a novel pharmacologic class of medications, are in various stages of development; the manufacturer of one of these medications has filed a New Drug Application for U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. Antimuscarinic Agents Oxybutynin Dosage Forms One of the first antimuscarinic agents, oxybutynin is available for administration via transdermal patch or topical gel in addition to oral forms. Like the transdermal patch formulation, the oxybutynin topical gel avoids first-pass liver metabolism of oxybutynin to the active metabolite 2011 by the American Pharmacists Association. All rights reserved.
2 N-desethyloxybutynin. This approach produces lower concentrations of the active metabolite, which (like the parent medication) has anticholinergic effects. Benefits of this characteristic include lower rates of the adverse anticholinergic effects of dry mouth and constipation compared with non-transdermal forms of oxybutynin, especially immediate-release oxybutynin. In contrast to the transdermal patch form of oxybutynin, the rates of local skin reactions to the gel are lower due to elimination of the patch delivery system. These improvements in tolerability are achieved while retaining the effectiveness of the oral and patch forms. Nevertheless, the same contraindications and precautions applicable to other antimuscarinics apply to the gel formulation of oxybutynin. Flexible Dosing Strategy for Antimuscarinics OAB symptoms have a variable, subjective effect on different patients. In consultation with the prescribing physician, patients have the opportunity to request increases or decreases of their medication to determine the dose that achieves the optimal balance between effectiveness and tolerability of adverse effects. In fact, this flexible dosing regimen approach has been shown to improve OAB urgency and other symptoms. Antimuscarinics that are available in multiple strengths (i.e., darifenacin, solifenacin, oxybutynin extended-release, and tolterodine), enable dose titration to patient response and therefore are candidates for flexible dosing. Patients using this approach must be cognitively intact and committed, must understand the principles of dose titration, and must be willing to assume a central role in requesting and accepting dose changes in consultation with their physician. In preparation, these patients are counseled on what to expect regarding drug effectiveness and adverse effects. They are informed of available drug strengths and encouraged to discuss the planned dose titration with their care provider. Starting with the lowest recommended dose, patients are informed that a dose increase may be needed. If intolerable adverse effects occur, patients can request a dose decrease without concern about resistance from their physician. Regardless of some improvement in the risk-tobenefit ratio using this strategy, the same contraindications and precautions apply. Antimuscarinics Alone or Combined With an α-adrenergic Antagonist for Men Historically, antimuscarinic drugs were avoided in men with OAB symptoms and benign prostatic obstruction (BPO). This precaution was due to concern about the risk of acute urinary retention characterized by worsening voiding lower urinary tract symptoms, uncomfortable or painful effort to urinate without success, and abdominal pressure/bloating. However, recent research in this population concluded that antimuscarinic monotherapy is safe and effective in decreasing OAB symptoms and improving quality of life in men with OAB storage lower urinary
3 tract symptoms ( see OAB Lexicon) due to primary bladder conditions (e.g., detrusor overactivity), with minimal or no voiding lower urinary tract symptoms. Conversely, antimuscarinic monotherapy is not recommended for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) without obstruction. Nor should this approach be used in men with baseline post-void residual urine volume greater than 200 ml or clinically significant bladder outlet obstruction, history of acute urinary retention due to BPH, high serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA), or low urine flow rate (as determined by urodynamic measurement). Antimuscarinic therapy may be added to α-adrenergic antagonist treatment in men with BPO and predominant OAB symptoms due to a concomitant or secondary bladder condition (e.g., BPH) or when these storage symptoms persist despite relief of voiding symptoms with an α-adrenergic antagonist alone or in combination or monotherapy with a 5-α-reductase inhibitor. However, concomitant therapy of an antimuscarinic and an α-adrenergic antagonist is not recommended for the treatment of BPH or in men with OAB symptoms with no significant bladder voiding lower urinary tract symptoms or significant bladder outlet obstruction. While the effectiveness and safety of the combined therapy does not appear to be affected by prostate size or PSA level, further research is needed to determine the effect of antimuscarinics in men with larger prostate glands or higher PSA levels. Also in need of investigation is whether criteria composed of these parameters would better identify suitable candidates for combined therapy. Therefore, while these parameters may help to guide treatment strategy, treatment should be chosen according to individual patient response. Post-void residual urine volume should be assessed before and after an antimuscarinic is started, especially during the first month of therapy. OAB Lexicon Term Voiding lower urinary tract symptoms Storage lower urinary tract symptoms BPH BPO BTX-A Definition Slow or intermittent urinary stream, splitting or spraying, hesitancy, straining, terminal dribble Urinary urgency, frequency, nocturia, urinary incontinence Benign prostatic hyperplasia BPH with bladder outlet obstruction OnabotulinumtoxinA, recently FDA-approved OAB treatment, for injection
4 OnabotulinumtoxinA The FDA recently approved onabotulinumtoxina (BTX-A) for injection to treat urinary incontinence due to detrusor overactivity associated with neurologic conditions such as poststroke, spinal cord injury, and multiple sclerosis in adults inadequately controlled or intolerant of an anticholinergic medication. Two double-blind, randomized controlled trials demonstrated a significant reduction in urinary incontinence episodes and increased bladder capacity in patients who received BTX-A. Cure rates of up to 38% have been achieved after a single intradetrusor injection administered under local or general anesthesia. Although BTX-A has been shown to be effective in controlling urologic symptoms in idiopathic OAB, it is not FDA-approved for this indication at this time. BTX-A achieves its therapeutic effects in OAB by inhibiting acetylcholine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) release at the parasympathetic presynaptic nerve terminal. The duration of BTX-A effects is approximately 9 months; repeated injections may be necessary. BTX-A does not produce anticholinergic symptoms. The most common adverse effects with BTX-A bladder injection are urinary tract infection and urinary retention. Therefore, intermittent self-catheterization may be necessary to empty the bladder in individuals who develop urinary retention and who are willing and able to perform this procedure. BTX-A has a boxed warning for the possible and potentially life-threatening distant spread of toxin effect. In addition to contraindications and precautions with other forms of BTX-A used, intradetrusor administration is contraindicated with acute urinary tract infection or urinary retention. Furthermore, BTX-A should be administered only with caution in individuals with urinary retention and only with monitoring of post-void residual urine volume in those who do not catheterize routinely, particularly patients with multiple sclerosis. BTX-A should be administered with caution due to its relatively invasive administration, lack of direct comparative trials with antimuscarinic drugs, and the uncommon but serious risk of distant spread of toxin indicated by the following signs and symptoms: breathing problems, chest pain or tightness, rapid irregular pulse, dysphagia, speech problems, unusual weakness, numbness, or eye problems. Hence, the use of this agent should be restricted to patients who are inadequately controlled with nonsurgical, nonpharmacologic, and antimuscarinic therapy. β 3 -Adrenoceptor Agonists A new class of drugs, β 3 -adrenoceptor agonists, is demonstrating viability for the treatment of OAB. These agents improve OAB symptoms by selectively binding and activating β 3 - adrenoceptors on the detrusor muscle and perhaps by additional mechanisms. Mirabegron is the most highly developed agent in this new class of drugs. Two Phase 3 randomized controlled trials demonstrated that mirabegron significantly decreased the mean
5 micturition frequency and number of urinary incontinence episodes, while improving quality of life in patients with OAB. Mirabegron was well tolerated with a small number of adverse events. However, it should be noted that possible adverse effects with long-term use have not been studied. The most common medication-related adverse effects that exceeded those observed with placebo in Phase 3 studies were headache, nasopharyngitis, dry mouth, and urinary tract infection (approximately 3% each). Anticholinergic adverse effects are reported to occur much less often than with antimuscarinic medications. In August 2011, the manufacturer of mirabegron submitted a New Drug Application to the FDA. In addition to the anticipated indication as a first-line pharmacotherapeutic agent for OAB, mirabegron may serve as an alternative in patients intolerant of antimuscarinic anticholinergic effects and as a primary or secondary treatment for patients with cognitive impairment, poorly controlled or severe gastroesophageal reflux disease, closed-angle glaucoma, constipation, and vision disorders, and for patients in whom antimuscarinic agents should be avoided. Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors have been shown to relax the prostate and bladder neck, likely by increasing the concentration of nitric oxide in smooth muscle. A small number of randomized controlled trials consistently showed that treatment with sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil improved lower urinary tract OAB storage symptoms as well as voiding symptoms in men with BPH. Conversely, the only randomized controlled trial of an investigational PDE-5 inhibitor, UK , in men with OAB but no bladder outlet obstruction found no difference in improvement in urgency episodes, frequency, nocturnal frequency, mean voided volume, or incontinence episode frequency compared with placebo. Only one small study of this treatment included women, and while the results for all participants showed improved urologic outcomes, the investigators did not distinguish the findings by the sex of the participants. The most common medication-related adverse events observed with PDE-5 inhibitors are headache, flushing, dyspepsia, nasopharyngitis, and diarrhea. The use of these agents is contraindicated with concomitant therapy with nitrates and nitrites, and there are many precautions for their use including ischemic heart disease and heart failure.
6 Case Study Larry Smith, a 68-year-old man who visits the pharmacy today, requests an over-the-counter (OTC) medication for troublesome, sudden strong urges to urinate. When you ask about additional symptoms, Mr. Smith reports that his symptoms began about 3 years ago with difficulty starting the urine stream, feeling that his bladder is never empty, and a weak stream. Then his symptoms worsened with sudden urges to urinate and frequent urination during the day and night, which began about 1 year ago. He states that the new symptoms bother him much more than his initial symptoms. Mr. Smith states that his physician diagnosed him as having an overactive bladder and he has been practicing the lifestyle modifications and behavioral therapies as his physician recommended. However, he has not experienced much relief from his symptoms. After checking the pharmacy record for Mr. Smith s current medications, you ask him about any other prescription or OTC products he uses. Mr. Smith currently takes tamsulosin 0.4 mg after dinner for benign prostatic hyperplasia with obstruction (BPO), metoprolol 50 mg twice daily for hypertension, isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablet 60 mg daily, nitroglycerin 0.4 mg sublingual every 5 minutes up to 3 doses as needed for chest pain, artificial tears 1 to 2 drops in both eyes 3 to 4 times daily for dry eyes, lovastatin 40 mg with each evening meal for high cholesterol, and aspirin 81 mg daily for heart protection. He knows of no other health problems. Mr. Smith quit smoking cigarettes 25 years ago. He drinks 1 to 3 alcoholic beverages on holidays but rarely during the rest of the year. You review his medications to be sure that the OAB symptoms are not related to his medications and identify none that could contribute to his OAB. Therefore, you refer him to see his primary care physician for further treatment. Mr. Smith asks whether there is any medication you can suggest that he can discuss with his physician to relieve these OAB symptoms. Mr. Smith indicates that his physician is concerned that prescribing medication for OAB can cause his kidneys to stop working, and he does not want to take that chance. You explain that while you agree there is some risk for adverse effects, most people are at low risk for this effect and assure him that his risk can be determined from his medical history and some simple urinary tract tests. You tell Mr. Smith that you will send a summary of your discussion and treatment information to his physician.
7 Answer to Question #1 1. Which of the following medication changes do you recommend the physician consider in treating Mr. Smith s OAB symptoms? a. Add an antimuscarinic. b. Replace tamsulosin with an antimuscarinic medication. c. Add sildenafil. d. Replace tamsulosin with sildenafil. The correct answer is a. The use of an antimuscarinic agent in men with BPH with known or uncertain bladder outlet obstruction was formerly considered a relative contraindication due to risks of worsening urinary retention symptoms and acute urinary retention and renal failure. More recently, it has been shown that OAB storage symptoms such as urgency, frequency, nocturia, and urinary incontinence refractory to treatment with an α-adrenergic antagonist or 5-αreductase inhibitor can be safely and effectively improved by an antimuscarinic medication. Answer b is incorrect because treatment with an antimuscarinic alone would not decrease urethral muscle sphincter tone as does tamsulosin. Therefore, the voiding symptoms of bladder outlet obstruction such as hesitancy, dribbling after urinating, and others would not be adequately managed. Answers c and d are incorrect because there is no evidence that sildenafil alone or in combination with an α-adrenergic antagonist is effective in treating OAB symptoms. There is evidence from several randomized controlled trials that PDE-5 inhibitors such as sildenafil can decrease both OAB storage symptoms and voiding symptoms of BPH. However, one recent study of an investigational PDE-5 inhibitor in patients with OAB showed no significant symptom improvement.
8 Answer to Question #2 One month later, Mr. Smith tells you his physician started him on oxybutynin gel once daily (verified in his pharmacy record), and his urinary symptoms are much improved. Case Question #2: 2. What symptom of potential acute urinary retention should Mr. Smith be counseled to monitor? a. Diarrhea. b. Abdominal cramping. c. Inability to urinate. d. Priapism. The correct answer is c. Acute urinary retention results in patients being unable to urinate or experiencing pain or discomfort when attempting to urinate. They may feel abdominal pressure, bloating, and/or voiding symptoms of slow or intermittent urinary stream, splitting or spraying, hesitancy, straining, and a terminal dribble. Answers a, b, and d are incorrect because diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and priapism are not established symptoms of acute urinary retention.
9 Answer to Question #3 Mr. Smith asks if there are any other drugs to treat OAB. You tell him that there are oral formulations of antimuscarinic agents, but that they frequently cause constipation and dry mouth which many patients find intolerable. Case Question #3: 3. Which of the following medications currently available is least likely to cause intolerable anticholinergic effects? a. Solifenacin. b. Oxybutynin extended-release. c. OnabotulinumtoxinA (BTX-A). d. Tolterodine extended-release. The correct answer is c. BTX-A, unlike the other choices, is not an antimuscarinic agent, a class associated with multi-organ anticholinergic activity. The most common adverse effects of BTX-A are urinary tract infection and urinary retention. Answers a, b, and d are incorrect. All three are antimuscarinic medications and associated with multi-organ anticholinergic effects including the gastrointestinal tract. While the extendedrelease forms are associated with relatively low rates of adverse anticholinergic effects compared with oxybutynin immediate-release tablets, many patients report anticholinergic effects including dry mouth and constipation, and drug discontinuation due to these adverse effects is common.
10 Answer to Question #4 You inform Mr. Smith that there is a new option, BTX-A, that is injected into the bladder wall. It does not have anticholinergic side effects. You explain its benefits and risks, particularly the warning about the potentially life-threatening spread of the agent s toxin effect. Case Question #4: 4. For what potential adverse effect of intradetrusor injection of BTX-A should patients be instructed to immediately contact their physician? a. Headache. b. Sensitivity to light. c. Dysphagia. d. Diarrhea. The correct answer is c. BTX-A has a boxed warning for the possible and potentially lifethreatening distant spread of toxin effect; dysphagia, the most common severe adverse reaction due to toxin spread, can be fatal. For this reason, dysphagia is included in the boxed warning. Patients who experience this symptom should immediately contact their physician. Answers a and b are incorrect because, while they are adverse effects related to BTX-A injection, they generally do not require medical attention. If they persist, worsen, or are bothersome, the patient may contact the physician for management recommendations. Answer d is incorrect because it is an uncommon adverse effect and generally does not require medical attention.
11 Fast Facts About Antimuscarinic Agents Antimuscarinic agents improve bladder capacity by reducing detrusor activity. Individual patient response to antimuscarinic agents is highly variable. The full benefits of antimuscarinic therapy may not be realized for several weeks after initiation of therapy. Successive trials with different antimuscarinic agents may be required to maximize effectiveness. Sources Lackner T, Reed K. Understanding the impact of overactive bladder from a patient perspective. Pharmacy Today. 2009;15(6): Resources Botox [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan; August Carr LK. Botulinum toxin A should not be first-line therapy for overactive bladder. Can Urol Assoc J. 2011;5: Chapple C, Wyndaele JJ, Van Kerrebroeck P, et al. Dose-ranging study of once-daily mirabegron (YM178), a novel selective β 3 -adrenoceptor agonist, in patients with overactive bladder (OAB) [abstract 774]. Eur Urol. 2010;9(2 suppl):249. Chapple CR, Yamaguchi O, Ridder A, et al. Clinical proof of concept study (Blossom) shows novel β 3 -adrenoceptor agonist YM178 is effective and well tolerated in the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder [abstract 674]. Eur Urol. 2008;7(3 suppl):239. Dmochowski RR, Peters KM, Morrow JD, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of flexible-dose fesoterodine in subjects with overactive bladder. Urology. 2010;75:62 8. Giuliano FA, Lamb J, Crossland A, et al. A placebo-controlled exploratory study investigating the efficacy and safety of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor UK-369,003 for the treatment of men with storage lower urinary tract symptoms associated with a clinical diagnosis of overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2010;106: Herschorn S, Swift S, Guan Z, et al. Comparison of fesoterodine and tolterodine extended release for the treatment of overactive bladder: a head-to-head placebo-controlled trial. BJU Int. 2009;105:58 66.
12 Kanai A, Wyndaele JJ, Andersson KE, et al. Researching bladder afferents determining the effects of β 3 -adrenergic receptor agonists and botulinum toxin type-a. Neurourol Urodynam. 2011;30: Kaplan SA, Roehrborn CG, Abrams P, et al. Antimuscarinics for treatment of storage lower urinary tract symptoms in men: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65: Kaplan SA, Schneider T, Foote JE, et al. Superior efficacy of fesoterodine over tolterodine extended release with rapid onset: a prospective, head-to-head, placebo-controlled trial. BJU Int. 2010;107: Kennelly MJ. A comparative review of oxybutynin chloride formulations: pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy in overactive bladder. Rev Urol. 2010;12:12 9. Khullar V, Cambromero J, Stroberg P, et al. The efficacy and tolerability of mirabegron in patients with overactive bladder: results from a European-Australian phase III trial [abstract 886]. Eur Urol. 2011;10(2 suppl): Kuo HC, Liao CH, Chung SD. Adverse events of intravesical botulinum toxin A injections for idiopathic detrusor overactivity: risk factors and influence on treatment outcome. Eur Urol. 2010;58: McVary KT, Monnig W, Camps JL Jr., et al. Sildenafil citrate improves erectile function and urinary symptoms in men with erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, double-blind trial. J Urol. 2007;177: McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Kaminetsky JC, et al. Tadalafil relieves lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2007;177: Michel MC, Ochodnicky P, Homma Y, et al. β-adrenoceptor agonist effects in experimental models of bladder dysfunction. Pharmacol Ther. 2011;131:40 9. Nitti V, Herschorn S, Auerbach S, et al. The efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with overactive bladder syndrome results of a North-American phase III trial [abstract 885]. Eur Urol. 2011;10(2 suppl):278.
13 Roehrborn CG, McVary KT, Elion-Mboussa A, et al. Tadalafil administered once daily for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a dose finding study. J Urol. 2008;180: Schmid DM, Sauermann P, Werner M, et al. Experience with 100 cases treated with botulinum- A toxin injections in the detrusor muscle for idiopathic overactive bladder syndrome refractory to anticholinergics. J Urol. 2006;176: Stief CG, Porst H, Neuser D, et al. A randomised, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy of twice-daily vardenafil in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2008;53: Tyagi P, Tyagi V. Mirabegron, a β 3 -adrenergic receptor agonist for the potential treatment of urinary frequency, urinary incontinence or urgency associated with overactive bladder. IDrugs. 2010;13: Tyagi P, Tyagi V, Chancellor M. Mirabegron: a safety review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011;10: Vella M, Cardozo L. Review of fesoterodine. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011;10:805 8.
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
April 12, 2013 Mandy C. Leonard, Pharm.D., BCPS Department of Pharmacy
 April 12, 2013 Mandy C. Leonard, Pharm.D., BCPS Department of Pharmacy Describe when medications are used for urinary incontinence (UI) Review medications used in UI including mechanism of action, key
April 12, 2013 Mandy C. Leonard, Pharm.D., BCPS Department of Pharmacy Describe when medications are used for urinary incontinence (UI) Review medications used in UI including mechanism of action, key
London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013
 London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013 Summary Mirabegron is first of a new class of drug, beta-3-adrenoceptor agonists, for the treatment
London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013 Summary Mirabegron is first of a new class of drug, beta-3-adrenoceptor agonists, for the treatment
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
Suffolk PCT Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report
 Suffolk PCT Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report This drug has been reviewed because it is a product that may be prescribed in primary care. Medicine Fesoterodine (Toviaz, Pfizer) Document
Suffolk PCT Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report This drug has been reviewed because it is a product that may be prescribed in primary care. Medicine Fesoterodine (Toviaz, Pfizer) Document
OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS:
 2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
mirabegron 25mg and 50mg prolonged-release tablets (Betmiga ) SMC No. (862/13) Astellas Pharma Ltd
 mirabegron 25mg and 50mg prolonged-release tablets (Betmiga ) SMC No. (862/13) Astellas Pharma Ltd 05 April 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
mirabegron 25mg and 50mg prolonged-release tablets (Betmiga ) SMC No. (862/13) Astellas Pharma Ltd 05 April 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care
 A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Prescribing Pathway for Drug Treatment for Overactive Bladder.
 East Surrey CCG, Guildford & Waverley CCG, North West Surrey CCG, Surrey Downs CCG, Surrey Heath CCG, North East Hampshire & Farnham CCG, Crawley CCG, Horsham & Mid-Sussex CCG - Prescribing Clinical Network
East Surrey CCG, Guildford & Waverley CCG, North West Surrey CCG, Surrey Downs CCG, Surrey Heath CCG, North East Hampshire & Farnham CCG, Crawley CCG, Horsham & Mid-Sussex CCG - Prescribing Clinical Network
Treatments for Overactive Bladder
 Treatments for Overactive Bladder Patient Information Author ID: SA Leaflet Number: Gyn 051 Name of Leaflet: Treatments for overactive bladder Date Produced: October 2014 Review Date: October 2016 Treatment
Treatments for Overactive Bladder Patient Information Author ID: SA Leaflet Number: Gyn 051 Name of Leaflet: Treatments for overactive bladder Date Produced: October 2014 Review Date: October 2016 Treatment
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources
 Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review
 Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
Pharmacological management of overactive bladder syndrome
 Pharmacological management of overactive bladder syndrome Bardsley, A. Postprint deposited in Curve January 2016 Original citation: Bardsley, A. (2014) Pharmacological management of overactive bladder
Pharmacological management of overactive bladder syndrome Bardsley, A. Postprint deposited in Curve January 2016 Original citation: Bardsley, A. (2014) Pharmacological management of overactive bladder
1/07/2014 HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER NORMAL BLADDER FUNCTION CAUSES OF URINARY INCONTINENCE HISTORY RISK FACTORS
 HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER Judith Goh AO MBBS(Qld) FRANZCOG CU PhD Urogynaecologist Griffith University Greenslopes Private Hospital, Brisbane Pindara Private Hospital,
HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER Judith Goh AO MBBS(Qld) FRANZCOG CU PhD Urogynaecologist Griffith University Greenslopes Private Hospital, Brisbane Pindara Private Hospital,
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials with Antimuscarinic Drugs for Overactive Bladder
 european urology 54 (2008) 740 764 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Review Neuro-urology A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
european urology 54 (2008) 740 764 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Review Neuro-urology A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
OAB (Overactive Bladder)
 OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
Management of refractory OAB conditions
 Management of refractory OAB conditions Neurotoxins and Neuromodulation Gary E. Lemack, M.D. Professor of Urology and Neurology Program Director in Urology UT-Southwestern Medical Center Overactive bladder
Management of refractory OAB conditions Neurotoxins and Neuromodulation Gary E. Lemack, M.D. Professor of Urology and Neurology Program Director in Urology UT-Southwestern Medical Center Overactive bladder
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OAB): Guidelines for prescribing. (CLINICAL GUIDELINE NO.)
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OAB): Guidelines for prescribing. (CLINICAL GUIDELINE NO.) Document Reference Number: Ratified By: Ratified: (s) Reviewed: Next Review : Responsibility for Review: Contributors:
Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OAB): Guidelines for prescribing. (CLINICAL GUIDELINE NO.) Document Reference Number: Ratified By: Ratified: (s) Reviewed: Next Review : Responsibility for Review: Contributors:
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence. A Review of the Research for Women
 Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
MEDICAL THERAPY OF ED Ian Eardley
 MEDICAL THERAPY OF ED Ian Eardley Erectile Dysfunction Plan of treatment Regardless of the aetiology of the ED, most men will benefit from oral therapy. If oral therapy fails, then more invasive options
MEDICAL THERAPY OF ED Ian Eardley Erectile Dysfunction Plan of treatment Regardless of the aetiology of the ED, most men will benefit from oral therapy. If oral therapy fails, then more invasive options
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men
 Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University
 Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Saint Mary s Hospital. Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit. Overactive Bladder. Information for Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to. women, and is a serious condition that can lead to. significant lifestyle changes.
 Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms
 THE OVERACTIVE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE BLADDER MEDICAL JOURNAL The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms Jassim Mohammad Alkhazraji*, Ban
THE OVERACTIVE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE BLADDER MEDICAL JOURNAL The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms Jassim Mohammad Alkhazraji*, Ban
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd
 botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service
 Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service This search summary contains the results of a literature search undertaken by the Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service librarians in; January 2012 All
Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service This search summary contains the results of a literature search undertaken by the Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service librarians in; January 2012 All
ORIGINAL PAPER. Introduction
 ORIGINAL PAPER Mirabegron for the treatment of overactive bladder: a prespecified pooled efficacy analysis and pooled safety analysis of three randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III studies
ORIGINAL PAPER Mirabegron for the treatment of overactive bladder: a prespecified pooled efficacy analysis and pooled safety analysis of three randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III studies
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition
 A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds
 Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Lifestyle changes. Pelvic floor muscle training
 Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP
 CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects?
 Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Faculty Disclosure. Objectives. Spectrum of Voiding Dysfunction. Types of Incontinence/Etiology. Urinary Incontinence Symptom Definitions
 Faculty Disclosure Strategies to Improve Adherence and Clinical Management of Overactive Bladder: Prevalence of OAB and Impact on Quality of Life Dr. Saffel has no actual or potential conflicts of interest
Faculty Disclosure Strategies to Improve Adherence and Clinical Management of Overactive Bladder: Prevalence of OAB and Impact on Quality of Life Dr. Saffel has no actual or potential conflicts of interest
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Conservative treatment
 Urgency urinary incontinence (UUI)/overactive bladder (OAB) treatment includes conservative management, medication and third- line treatment. Conservative treatment Conservative management includes lifestyle
Urgency urinary incontinence (UUI)/overactive bladder (OAB) treatment includes conservative management, medication and third- line treatment. Conservative treatment Conservative management includes lifestyle
Overactive Bladder New Antimuscarinics for Treatment
 Urology Overactive Bladder New Antimuscarinics for Treatment a report by Karl-Erik Andersson, MD, PhD Professor and Chairman, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary Antimuscarinics
Urology Overactive Bladder New Antimuscarinics for Treatment a report by Karl-Erik Andersson, MD, PhD Professor and Chairman, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary Antimuscarinics
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Emergency Room Treatment of Psychosis
 OVERVIEW The term Lewy body dementias (LBD) represents two clinical entities dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson s disease dementia (PDD). While the temporal sequence of symptoms is different
OVERVIEW The term Lewy body dementias (LBD) represents two clinical entities dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson s disease dementia (PDD). While the temporal sequence of symptoms is different
Dr Eva Fong. Urologist Auckland
 Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
Fecal incontinence (Encopresis) It is the fecal incontinence condition observed in children with chronic constipation over 1-2 years.
 WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS. Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center. Bladder Dysfunction
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
BJUI. A review of adherence to drug therapy in patients with overactive bladder
 2008 BJU International. No claim to original US government works Mini-review Article ADHERENCE TO DRUG THERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH OAB BASRA et al. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL A review of adherence to drug therapy
2008 BJU International. No claim to original US government works Mini-review Article ADHERENCE TO DRUG THERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH OAB BASRA et al. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL A review of adherence to drug therapy
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance
 Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
CONSENT FORM 12/19/08
 12/19/08 1001 University Place Evanston, Illinois 60201 www.northshore.org CONSENT FORM Phone (224) 364-7100 Fax (847) 570-8011 Intravesical Alkalized Lidocaine for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder
12/19/08 1001 University Place Evanston, Illinois 60201 www.northshore.org CONSENT FORM Phone (224) 364-7100 Fax (847) 570-8011 Intravesical Alkalized Lidocaine for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder
THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT
 THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT Prof. Junizaf, SpOG(K) Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
THE ROLE OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER TREATMENT Prof. Junizaf, SpOG(K) Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
Urinary Incontinence 9/17/2015. Conflict of Interest. Objectives. None
 Urinary Incontinence Karla Reinhart DNP, FNP-C, ARNP October, 2015 Conflict of Interest None Objectives Acquire knowledge of A & P of micturition, as well as pertinent pathologies for male and female incontinence
Urinary Incontinence Karla Reinhart DNP, FNP-C, ARNP October, 2015 Conflict of Interest None Objectives Acquire knowledge of A & P of micturition, as well as pertinent pathologies for male and female incontinence
Enuresis BOWEL AND BLADDER CONTROL. Voiding disorders. Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting
 Enuresis Why does my child have damp pants? Douglas E. Coplen Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting Division of Pediatric Urology Washington University School
Enuresis Why does my child have damp pants? Douglas E. Coplen Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting Division of Pediatric Urology Washington University School
Advances in Medical Treatment for Urinary Incontinence. Dr. BC Tong Geriatrician, PMH Hon Treasurer, HKCS
 Advances in Medical Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Dr. BC Tong Geriatrician, PMH Hon Treasurer, HKCS Urinary incontinence The complaint of any involuntary leakage of urine (which is objectively demonstrable
Advances in Medical Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Dr. BC Tong Geriatrician, PMH Hon Treasurer, HKCS Urinary incontinence The complaint of any involuntary leakage of urine (which is objectively demonstrable
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse. Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB)
 OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
Disclosure. Recent Advances in the Management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive Bladder: Definition. Learning Objectives. Overactive Bladder
 Disclosure Recent Advances in the Management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Astellas Regional Advisory Board Honorarium for talk Dharm Singh, MD, FACS Chief of Urology Campbellton Regional Hospital, New Brunswick
Disclosure Recent Advances in the Management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Astellas Regional Advisory Board Honorarium for talk Dharm Singh, MD, FACS Chief of Urology Campbellton Regional Hospital, New Brunswick
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
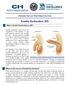 Information from your Patient Aligned Care Team What is Erectile Dysfunction or ED? Erectile dysfunction (also known as impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having
Information from your Patient Aligned Care Team What is Erectile Dysfunction or ED? Erectile dysfunction (also known as impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having
Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU
 FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
 The Pharmacologic Management of Idiopathic Overactive Bladder in Primary Care Pamela I. Ellsworth, MD CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this article on overactive bladder,
The Pharmacologic Management of Idiopathic Overactive Bladder in Primary Care Pamela I. Ellsworth, MD CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this article on overactive bladder,
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients Dissatisfied With Overactive Bladder Medication
 Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female)
 Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
The overactive bladder and bladder retraining
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Abstral Prescriber and Pharmacist Guide
 Abstral Prescriber and Pharmacist Guide fentanyl citrate sublingual tablets Introduction The Abstral Prescriber and Pharmacist Guide is designed to support healthcare professionals in the diagnosis of
Abstral Prescriber and Pharmacist Guide fentanyl citrate sublingual tablets Introduction The Abstral Prescriber and Pharmacist Guide is designed to support healthcare professionals in the diagnosis of
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Overactive Bladder Epidemiology and Management. Mr Nick Nicholas MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist Hillingdon Hospital
 Overactive Bladder Epidemiology and Management Mr Nick Nicholas MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist Hillingdon Hospital Definitions Overactive bladder (OAB) 1 detrusor overactivity suspected to be the cause
Overactive Bladder Epidemiology and Management Mr Nick Nicholas MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist Hillingdon Hospital Definitions Overactive bladder (OAB) 1 detrusor overactivity suspected to be the cause
Medication for Overactive Bladder
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Medication for Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What medication is available for overactive bladder? There are two types of medication
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Medication for Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What medication is available for overactive bladder? There are two types of medication
Current medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms/bph: do we have a standard?
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Current medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms/bph: do we have a standard? João Silva a,b,c, Carlos Martins Silva a,b,c, and Francisco Cruz a,b,c Purpose of review The
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Current medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms/bph: do we have a standard? João Silva a,b,c, Carlos Martins Silva a,b,c, and Francisco Cruz a,b,c Purpose of review The
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology
 Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
