The choice for quality ECG arrhythmia monitoring
|
|
|
- Cody Cobb
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GE Healthcare EK-Pro The choice for quality ECG arrhythmia monitoring David A. Sitzman, MSEE. Mikko Kaski, MSAM. Ian Rowlandson, MSBE. Tarja Sivonen, RN. Olli Väisänen, MD, PhD. Clinical care environments rely heavily on technology to facilitate patient care and increase efficiency. One such technology is the computerized arrhythmia analysis utilized in patient monitoring systems. This article presents the latest enhancements in GE Healthcare s EK-Pro arrhythmia detection algorithm. EK-PRO ADVANCING SIMULTANEOUS, MULTI-LEAD ARRHYTHMIA MONITORING FOR OVER THREE DECADES EK-Pro, an advanced software algorithm, is the result of more than three decades of development, design and testing. EK-Pro can simultaneously process up to five independent ECG leads for arrhythmia detection and up to 12 ECG leads for morphology analysis. The reason for analyzing multiple leads is quite simple. Unless cardiac monitors can acquire and analyze lead data that faithfully represents several different views of the heart, there is a very real risk of failure to detect clinically significant cardiac events. Conversely, because artifacts are often not evident in all leads, it is important to allow the algorithm to continue to recognize the patient s normal rhythm even when substantial artifact is present. Consider some of the important clinical benefits provided by the simultaneous analysis of three or more leads. Event Notification. By analyzing data from the inferior, anterior, and lateral walls of the heart, multi-lead algorithms can detect cardiac events that might otherwise go unnoticed. Artifact Discrimination. Simultaneous multi-lead analysis enables algorithms to better distinguish extraneous, random signals from true beats. Such artifacts can frequently cause lesser systems to exhibit faulty beat detection and interpretation, which then most often result in false and nuisance alarms. Uninterrupted Monitoring. Simultaneous, multi-lead analysis provides redundancy, so that monitoring can continue in the event of a contact failure. While such electrode issues should always be corrected at the first opportunity, it is important that arrhythmia algorithms be able to handle such failures so that the analysis function continues uninterrupted. Single and sometimes even dual-lead systems cannot provide this safety benefit. Multi-Lead ST Analysis. ST-segment monitoring has become a valuable tool clinicians can use for real-time assessment of myocardial ischemia in patients with unstable angina 1, patients treated with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) 2, and patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with thrombolytics 3. In addition, a consensus statement 4 by the ST-Segment Monitoring Practice Guideline International Working Group recommends using ST-segment monitoring in patients with chest pain that prompts emergency department visits, in patients after cardiac surgery, and in patients at risk for postoperative cardiac complications after non-cardiac surgery. Since cardiac ischemia can often be localized to specific areas of the myocardium, there is a clear need to use an ST analysis algorithm that processes multiple leads representing the inferior, anterior, and lateral views of the heart. The American Hospital Association for many years has likewise affirmed the need for simultaneous multi-lead arrhythmia analysis 5, and the technologies at the core of EK-Pro have been meeting that need for over three decades. In today s demanding care environments, a high-quality arrhythmia analysis algorithm should provide nothing less.
2 CLINICAL BENEFITS OF MULTI-LEAD ARRHYTHMIA MONITORING Multi-lead monitoring for arrhythmias has a variety of documented clinical benefits, as illustrated by these examples: Continuous monitoring when it counts. Some algorithms simply stop analyzing when they encounter artifacts. EK-Pro continues monitoring via leads that still exhibit good signal quality. Below is an example of a patient with postoperative cardiac standstill after heart surgery. Prior to the event the patient felt pain resulting in significant artifact in a majority of the leads. If this patient would have been monitored with an algorithm that did not continue monitoring in leads with good signal quality, this event may not have been detected. I II I II Figure 1. Cardiac standstill and artifact Detecting arrhythmias in different leads. The leads that best show normal rhythms are not always the same leads that best show an arrhythmia event. This example shows a significant change in morphology in leads I and III, but not in leads II and V. Figure 3. Duration of QRS during arrhythmia differs from lead to lead Finding the Best Lead. Some algorithms are configured to use a single best lead for the duration of monitoring. However, arrhythmias can often cause that best lead to exhibit low QRS amplitude or morphologies that are hard to distinguish. The example in Figure 4 show the importance of analyzing multiple leads and not just the best one or two. During arrhythmia there is low amplitude in leads I and V and relatively normal amplitude in leads II and III. II I I II Figure 2. A patient with ventricular tachycardia. More consistent and accurate interval measurements Measurements of QRS duration and QT interval can be different in the various leads. Thus, the American Heart Association recommends using global versus lead-specific measurements for consistency and accuracy 6. In the arrhythmia event in Figure 3, the QRS duration is relatively narrow in leads I and V, but significantly wider in leads II and III. Since QRS duration is a key feature in beat interpretation and arrhythmia detection, the importance of using multiply leads to obtain an accurate measurement is clear. Figure 4. Low amplitude and changes in beat morphology during arrhythmia events. ACCURATE DETECTION OF VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Continuous development of the EK-Pro has achieved excellent performance for the relatively narrow beat morphologies common to ventricular tachycardia in pediatric patients a factor that frequently pose a challenge to algorithms designed primarily for adult patients. To verify this accuracy, the EK-Pro algorithm was evaluated on waveform data representing 100 pediatric patients from the cardiac units of several pediatric hospitals. The ECG recordings in this proprietary GE database were selected by the hospitals as representative of patients having arrhythmias that were the especially challenging for monitors to detect. Results for the detection of ventricular tachycardia are shown in Table 1. Auth Alarm Type Total Events Events Detected VTACH (long run) VTACH (short run) Table 1. Results for the detection of ventricular tachycardia in 100 pediatric patients from a database enriched with challenging arrhythmias
3 SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia that results in hospitalization in the United States 7. To aid clinicians in developing an effective patient management plan that may prevent atrial fibrillation from becoming chronic, 8 the EK-Pro algorithm also provides analysis for the detection and trending of this arrhythmia. In addition, supraventricular tachyarrhythmias are a common cause of morbidity after cardiac surgery. They may decrease diastolic filling and cardiac output and increase myocardial oxygen consumption, resulting in hypotension and myocardial ischemia. These arrhythmias may also cause a dramatic increase in pulmonary pressures, especially in patients with diastolic dysfunction. The latest version of EKPro supports the detection of three supraventricular tachyarrhythmias: Supraventricular tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Frequent supraventricular beats Table 2 shows the performance of the algorithm in detecting atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia in publically available 9 MIT databases for arrhythmia 10, atrial fibrillation 11 and supraventricular arrhythmia 12. Alarm Type Total Events Sensitivity AFIB % SVT 43 93% Table 2. Measured sensitivity for the detection of atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. MISSING BEAT EK-Pro also supports the detection of missing beats. As an example, a missing beat may indicate second decree AV block from which especially type II may progress rapidly to a complete heart blockage and sudden cardiac death. Detecting a missing beat early can help in identifying the patients who potentially benefit from an implanted pacemaker. FALSE ALARM RATES Since 2012, ECRI Institute has placed clinical alarm hazards at the top of their list of Top 10 Health Technology Hazards 13. In clinical devices that monitor ECG, it is acknowledged that alerts for arrhythmias are responsible for the majority of ECG-related alarms. To ensure high levels of performance, every major version of the EK-Pro algorithm is extensively evaluated using proprietary ECG waveform data collected from multiple clinical units. This commitment to thorough evaluation, a hallmark of the EK-Pro algorithm, means that test results accurately reflect actual clinical performance. Examples of the very low false alarm rates provided by the EK-Pro algorithm are shown in Tables 3-5. Alarm Type ASYSTOLE 1 per 254 hours 1 per 2367 hours VTACH 1 per 38 hours VT > 2 1 per 8 hours Table 4. Measured false alarms from EK-Pro V13 in 7100 hours of Holter recordings collected from 284 patients. The data is notable for high levels of artifact. 14 Alarm Type ASYSTOLE 1 per 64 hours 1 per 1600 hours VTACH 1 per 106 hours VT > 2 1 per 15 hours Table 5. Measured false alarms from EK-Pro V13 in 4800 hours of multi-lead data collected from 200 ICU patients including 48 with pacemakers and LVADs. The data was collected from a GE customer hospital. ADVANCED TECHNOLOGIES USED BY THE EK-PRO ALGORITHM The EK-Pro algorithm takes advantage of several special advanced processing techniques that help contribute to its high performance levels. Continuous Correlation causes the incoming multi-lead waveforms to be continuously compared to the beat templates as part of the QRS detection process. This method greatly improves beat detection and recognition in the presence of interfering noise or artifact and is extremely advantageous amid the challenging signal conditions encountered in the clinical setting. Incremental Template Updating is a process by which the multilead waveform templates used for beat classification and measurement accurately track subtle, progressive changes in beat shapes. With this technology, automated measurements can be made consistently and accurately, since waveform artifact is effectively minimized in the waveform templates by this updating process. Contextual Analysis enables the algorithm to use information gained from neighboring beats, both before and after the beat undergoing analysis, for its identification of arrhythmia events. This allows the algorithm to consider the beats in the patient s rhythm in a manner highly similar to that used by a clinician. Configurability for neonatal and pediatric patients allows each of the aforementioned techniques to be automatically adapted for the unique waveform features presented by neonatal and pediatric patients. In addition, certain criteria for QRS detection and arrhythmia alarms are adjusted to account for the normally higher heart rates and narrower QRS widths associated with younger patient populations. Alarm ASYSTOLE 1 per 75 hours 1 per 571 hours VTACH 1 per 75 hours VT > 2 1 per 8 hours Table 3. Measured false alarms from EK-Pro V13 in 8000 hours of monitoring data from a telemetry environment notable for its noisy data conditions. The data was collected from a GE customer hospital.
4 NOTES ON OTHER PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENTS It is common for device manufacturers to test and evaluate arrhythmia detection algorithms on commercially available collections of recorded ECG signals. The two most common of these collections are frequently referred to as the MIT/BIH 15 and AHA databases 16. These databases consist of two-channel Holter recordings and make possible a convenient method for estimating and comparing the performance of arrhythmia detection algorithms. Unfortunately, standard testing that uses these two test databases reflects only 61 total hours of monitoring time for both databases combined. This stands in stark contrast to the more than 2000 hours of clinical evaluation that is applied to each major release of the EK-Pro algorithm. The minimum performance specification for EK-Pro algorithm for these databases is provided in Table 6. However, it is extremely important to understand that these databases should never be considered a gold standard by which the arrhythmia algorithm should be judged. As noted by the American Heart Association, There are problems, however, with these databases, as all ECG patterns are not included. Specifically, the AHA database includes ventricular abnormalities only and excludes abnormalities such as supraventricular arrhythmias and atrioventricular block that are clinically important in the acute myocardial infarction setting 17 Because of the limited scope of these databases, they can provide only a partial estimate of how accurately algorithms can really detect ventricular arrhythmias in actual care environments. Also noted by the American Heart Association, These databases are also collections of rhythms recorded primarily for the evaluation of diagnostic algorithms of ambulatory ECG systems under environmental conditions and with methods that differ significantly from those used, for example, in the coronary care unit. Errors may be significant. 17 It is inappropriate to assume that algorithm performance as measured on Holter databases will accurately predict the performance in acute patient monitoring. It is for these reasons the EK-Pro algorithm is always extensively tested and validated on ECG data from clinical care units, and not simply on convenient databases. AHA/MIT QRS Detection Sensitivity >97.5% QRS Positive Predictivity >97.5% VEB Detection Sensitivity >90% VEB Positive Predictivity >90% Table 6. The EK-Pro algorithm exceeds these performance specifications on AHA and MIT databases. CONCLUSIONS GE Healthcare has more than three decades of experience in developing and testing simultaneous, multi-lead arrhythmia monitoring algorithms. While the user is reminded to always refer to the User Manual that accompanies the ECG monitor for detailed arrhythmia monitoring instructions, cautions, and warnings, GE Healthcare has presented here the some of the key advantages of the latest EK-Pro algorithm. This vital technology can help improve detection of cardiac events that might otherwise go unnoticed. It delivers reliable and accurate ST monitoring, helps to reduce false alarm rates and helps to assure uninterrupted monitoring. Building on this core technology, the latest version of the EK-Pro algorithm provides improved detection of narrow complex ventricular tachycardia especially with pediatric patients and brings new technology to the detection of supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. REFERENCES 1. Langer, A. et al. ST segment shift in unstable angina: pathophysiology and association with coronary anatomy and hospital outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 13, (1989). 2. Krucoff, M. W. et al. Stability of multilead ST-segment fingerprints over time after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty and its usefulness in detecting reocclusion. Am J Cardiol. 61, (1988). 3. Drew, B. J. and Tisdale, L. A. ST-segment monitoring for coronary artery reocclusion following thrombolytic therapy and coronary angioplasty: identification of optimal bedside monitoring leads. Am J Crit Care. 2, (1993). 4. Drew, B. J. and Krucoff, M. W. for the ST-Segment Monitoring Practice Guidelines International Working Group. Multilead STsegment monitoring in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a consensus statement for healthcare professionals. Am J Crit Care. 8, (1999). 5. Mirvis, D. M. et al. Instrumentation and practice standards for electrocardiographic monitoring in special care units. A report for health professionals by a Task Force of the Council on Clinical Cardiology. American Heart Association 79, (February 1989). 6. Kligfield, P., et al. (2007). Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram. Part I: The Electrocardiogram and Its Technology. A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society. Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation. 7. Baily, D. et al. Hospitalizations for arrhythmias in the United States: Importance of atrial fibrillation, (abstr.) J Am Coll Cardiol. 19, 41A (1992). 8. Franz, M. R. et al. Electrical remodeling of the human atrium: Similar effects in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 30, , (1997). 9. Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PCh, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng C-K, Stanley HE. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 101(23):e215-e220 Circulation Electronic Pages; 2000 (June 13) Moody GB, Mark RG. The impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database. IEEE Eng in Med and Biol 20(3):45-50 (May-June 2001). (PMID: ) 11. Moody GB, Mark RG. A new method for detecting atrial fibrillation using R-R intervals. Computers in Cardiology. 10: (1983) Greenwald SD. Improved detection and classification of arrhythmias in noise-corrupted electrocardiograms using contextual information. Ph.D. thesis, Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology, ECRI Institute. Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for Health Devices, Vol 42, Issue 11, Nov Young, B & Brodnick, D & Rowlandson, I. (1993). Performance characteristics of a real-time arrhythmia analysis program on different databases. Journal of electrocardiology, 26 Suppl. 15. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Beth Israel Hospital Arrhythmia Database. 16. The American Heart Association Database of Evaluation of Ventricular Arrhythmia Detectors. 17. Mirvis, D. M. et al.
5 Imagination at work General Electric Company All rights reserved. GE, GE Monogram and imagination at work are trademarks of General Electric Company. All patient examples presented in this document are real events from hospital collected with GE Patient Monitor running EK Pro V13. Pictures drawn by GE. GE Healthcare, a division of General Electric Company JB22468XX(3) 1/15
The new generation in ECG interpretation
 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
510(k) Summary May 7, 2012
 510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
Bringing Order Out of Chaos
 Bringing Order Out of Chaos Life Care Solutions GE Healthcare Introduction Alarm management strategies that incorporate training, best clinical practices and sophisticated technology may help reduce alarm
Bringing Order Out of Chaos Life Care Solutions GE Healthcare Introduction Alarm management strategies that incorporate training, best clinical practices and sophisticated technology may help reduce alarm
GE Healthcare. Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system
 GE Healthcare Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system Each year, sudden cardiac death claims the lives of millions of people globally. Among the most compelling challenges facing clinicians today
GE Healthcare Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system Each year, sudden cardiac death claims the lives of millions of people globally. Among the most compelling challenges facing clinicians today
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Marquette 12SL Algorithm. Connected Clinical Excellence
 Marquette 12SL Algorithm Connected Clinical Excellence Clinical decision support for your ECG Since its introduction in 1980 the Marquette TM 12SL ECG analysis program has been consistently refined and
Marquette 12SL Algorithm Connected Clinical Excellence Clinical decision support for your ECG Since its introduction in 1980 the Marquette TM 12SL ECG analysis program has been consistently refined and
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Podcast with Dr. Kossick
 Podcast with Dr. Kossick Interviewed by Western Carolina University Graduate Anesthesia Student Kristin Andrejco From the Head of the Bed main@fromtheheadofthebed.com December 5, 2014 (33 min) EKG Lead
Podcast with Dr. Kossick Interviewed by Western Carolina University Graduate Anesthesia Student Kristin Andrejco From the Head of the Bed main@fromtheheadofthebed.com December 5, 2014 (33 min) EKG Lead
ST Segment Monitoring. IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note
 ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
GE Healthcare. The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System
 GE Healthcare The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System Cardiac technology. Innovation to advance care. Success in today s healthcare environment requires your
GE Healthcare The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System Cardiac technology. Innovation to advance care. Success in today s healthcare environment requires your
GE Healthcare. Rest assured. MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system
 GE Healthcare Rest assured MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system Since 1965, GE has introduced on-going innovation, which has profoundly impacted healthcare delivery, clinical guidelines and ECG standards.
GE Healthcare Rest assured MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system Since 1965, GE has introduced on-going innovation, which has profoundly impacted healthcare delivery, clinical guidelines and ECG standards.
Enterprise i MARS. Connecting hearts and minds. GE imagination at work. Full Disclosure Holter with Patient Monitoring System
 MARS Enterprise i Full Disclosure Holter with Patient Monitoring System Connecting hearts and minds GE imagination at work Powering a new standard of cardiac care A suite of diagnostic tools within reach
MARS Enterprise i Full Disclosure Holter with Patient Monitoring System Connecting hearts and minds GE imagination at work Powering a new standard of cardiac care A suite of diagnostic tools within reach
Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model
 Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model Daming Wei Graduate School of Information System The University of Aizu, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan A b s
Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model Daming Wei Graduate School of Information System The University of Aizu, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan A b s
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
Analysis of Patient Monitor Alarms in Adult Intensive Care Units --- University of California, San Francisco April 25, 2013 Patricia Harris, RN, PhD
 Analysis of Patient Monitor Alarms in Adult Intensive Care Units --- University of California, San Francisco April 25, 2013 Patricia Harris, RN, PhD **** AAMI/HTSI National Alarm Coalition UCSF GE Healthcare
Analysis of Patient Monitor Alarms in Adult Intensive Care Units --- University of California, San Francisco April 25, 2013 Patricia Harris, RN, PhD **** AAMI/HTSI National Alarm Coalition UCSF GE Healthcare
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Detection of Heart Diseases by Mathematical Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Using Phonocardiogram Signals
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
GE Healthcare. Dash 3000, 4000 & 5000. High-acuity mobile patient monitoring
 GE Healthcare Dash 3000, 4000 & 5000 High-acuity mobile patient monitoring The promise of flexibility. In healthcare, every patient s situation is unique. To deliver personalized, quality care, you require
GE Healthcare Dash 3000, 4000 & 5000 High-acuity mobile patient monitoring The promise of flexibility. In healthcare, every patient s situation is unique. To deliver personalized, quality care, you require
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias
 Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE - Telemetry
 Introduction CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE - Telemetry The purpose of the guideline is to establish evidence-informed criteria for telemetry monitoring, outline nursing assessment parameters and provide
Introduction CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE - Telemetry The purpose of the guideline is to establish evidence-informed criteria for telemetry monitoring, outline nursing assessment parameters and provide
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC. BLS Changes
 ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
GE Healthcare CASE. Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing. Connecting hearts and minds.
 GE Healthcare CASE Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing Connecting hearts and minds. Stressing better outcomes. Proven clinical excellence. Productivity-enhancing applications and features. Expanded
GE Healthcare CASE Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing Connecting hearts and minds. Stressing better outcomes. Proven clinical excellence. Productivity-enhancing applications and features. Expanded
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
Signal-averaged electrocardiography late potentials
 SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements
 Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
An Innovative Wireless Cardiac Rhythm Management (icrm) System
 An Innovative Wireless Cardiac Rhythm Management (icrm) System Gabriel E. Arrobo, Calvin A. Perumalla, Stanley B. Hanke, Thomas P. Ketterl, Peter J. Fabri, and Richard D. Gitlin Department of Electrical
An Innovative Wireless Cardiac Rhythm Management (icrm) System Gabriel E. Arrobo, Calvin A. Perumalla, Stanley B. Hanke, Thomas P. Ketterl, Peter J. Fabri, and Richard D. Gitlin Department of Electrical
Remote cardiology consultation service The Heart Center model Kjell Nikus, MD, PhD Specialist in cardiology 9.4.2013
 Remote cardiology consultation service The Heart Center model Kjell Nikus, MD, PhD Specialist in cardiology 9.4.2013 Challenges in health care Increase in health care expenditure >> GDP More effective
Remote cardiology consultation service The Heart Center model Kjell Nikus, MD, PhD Specialist in cardiology 9.4.2013 Challenges in health care Increase in health care expenditure >> GDP More effective
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
Policy & Procedures. I.D. Number: 1142
 Policy & Procedures Title: CARDIAC (ECG) MONITORING I.D. Number: 1142 Authorization: [X] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Date Revised: November 2012 Date Effective: October 2004 Scope: SHR - Acute
Policy & Procedures Title: CARDIAC (ECG) MONITORING I.D. Number: 1142 Authorization: [X] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Date Revised: November 2012 Date Effective: October 2004 Scope: SHR - Acute
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
GE Healthcare. MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital
 GE Healthcare MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital smart. MAC 2000 Complex hospital environments demand simple solutions. Equipment that simply works, every time. Technology that
GE Healthcare MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital smart. MAC 2000 Complex hospital environments demand simple solutions. Equipment that simply works, every time. Technology that
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
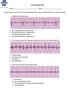 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY
 BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Frequency Prioritised Queuing in Real-Time Electrocardiograph Systems
 Frequency Prioritised Queuing in Real-Time Electrocardiograph Systems Omar Hashmi, Sandun Kodituwakku and Salman Durrani School of Engineering, CECS, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia.
Frequency Prioritised Queuing in Real-Time Electrocardiograph Systems Omar Hashmi, Sandun Kodituwakku and Salman Durrani School of Engineering, CECS, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia.
Design and Evaluation of A Novel Wireless Three-pad ECG System for Generating Conventional 12-lead Signals
 Design and Evaluation of A Novel Wireless Three-pad ECG System for Generating Conventional 12-lead Signals Huasong Cao, Haoming Li, Leo Stocco and Victor C. M. Leung Department of Electrical and Computer
Design and Evaluation of A Novel Wireless Three-pad ECG System for Generating Conventional 12-lead Signals Huasong Cao, Haoming Li, Leo Stocco and Victor C. M. Leung Department of Electrical and Computer
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
GE Healthcare CASE. Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing. Connecting hearts and minds.
 GE Healthcare CASE Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing Connecting hearts and minds. Stressing better outcomes. Proven clinical excellence. Productivity-enhancing applications and features. Expanded
GE Healthcare CASE Cardiac Assessment System for Exercise Testing Connecting hearts and minds. Stressing better outcomes. Proven clinical excellence. Productivity-enhancing applications and features. Expanded
Medical Tourism - The Role of Intervals inCardiovascular Cancer
 Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Time Critical Interventions MO-51 / 1 Hour Faculty: Matthew Strehlow, MD, FACEP Monday, 10/26/2015 / 3:30 PM - 4:20 PM The treatment of congestive heart failure (CHF)
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Time Critical Interventions MO-51 / 1 Hour Faculty: Matthew Strehlow, MD, FACEP Monday, 10/26/2015 / 3:30 PM - 4:20 PM The treatment of congestive heart failure (CHF)
ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005
 ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005 Introduction: The purpose of this document is to outline the equivalent biphasic protocols specific to
ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005 Introduction: The purpose of this document is to outline the equivalent biphasic protocols specific to
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
Iam truly honored to join the ranks of esteemed past
 CE CELEBRATING THE 100TH BIRTHDAY OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM: LESSONS LEARNED FROM RESEARCH IN CARDIAC MONITORING By Barbara J. Drew, RN, PhD. From the Department of Physiological Nursing, University of
CE CELEBRATING THE 100TH BIRTHDAY OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM: LESSONS LEARNED FROM RESEARCH IN CARDIAC MONITORING By Barbara J. Drew, RN, PhD. From the Department of Physiological Nursing, University of
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
The Impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database
 The Impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database Digital Vision History, Lessons Learned, and Its Influence on Current and Future Databases George B. Moody and Roger G. Mark Harvard-MIT Division of Health
The Impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database Digital Vision History, Lessons Learned, and Its Influence on Current and Future Databases George B. Moody and Roger G. Mark Harvard-MIT Division of Health
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
ACUTE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TREATMENT IN THE SURGICAL PATIENT
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Portable, cordless, single-channel ECG Monitor HCG-801-E
 Portable, cordless, single-channel ECG Monitor HCG-801-E Screening & Self -Monitoring of cardiac events Compact - Cordless - Simple operation Fast - Discrete Records about 30 seconds heart rhythm and waveform
Portable, cordless, single-channel ECG Monitor HCG-801-E Screening & Self -Monitoring of cardiac events Compact - Cordless - Simple operation Fast - Discrete Records about 30 seconds heart rhythm and waveform
CardioSoft * Diagnostic System
 GE Healthcare CardioSoft * Diagnostic System Connecting Hearts and Minds Clinically connected. Simply smart. CardioSoft Diagnostic System from GE Healthcare is more than a software program it is a data
GE Healthcare CardioSoft * Diagnostic System Connecting Hearts and Minds Clinically connected. Simply smart. CardioSoft Diagnostic System from GE Healthcare is more than a software program it is a data
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Osama Jarkas. in Chest Pain Patients. STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015
 STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015 PROJECT TITLE: Analysis of ECG Exercise Stress Testing and Framingham Risk Score in Chest Pain Patients PRIMARY SUPERVISOR NAME: Dr. Edward Tan DEPARTMENT:
STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015 PROJECT TITLE: Analysis of ECG Exercise Stress Testing and Framingham Risk Score in Chest Pain Patients PRIMARY SUPERVISOR NAME: Dr. Edward Tan DEPARTMENT:
REFERRAL HOSPITAL. The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO
 REFERRAL HOSPITAL The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO Time to Treatment is critical for STEMI patients For patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), percutaneous coronary
REFERRAL HOSPITAL The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO Time to Treatment is critical for STEMI patients For patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), percutaneous coronary
ST. JUDE MEDICAL: ST MONITORING. A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo
 ST. JUDE MEDICAL: ST MONITORING A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science
ST. JUDE MEDICAL: ST MONITORING A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science
ECG Anomaly Detection via Time Series Analysis
 ECG Anomaly Detection via Time Series Analysis Mooi Choo Chuah, Fen Fu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Lehigh University chuah@cse.lehigh.edu, fef25@lehigh.edu Abstract Recently, wireless
ECG Anomaly Detection via Time Series Analysis Mooi Choo Chuah, Fen Fu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Lehigh University chuah@cse.lehigh.edu, fef25@lehigh.edu Abstract Recently, wireless
Connecting Remote Cardiac Monitoring Issues with Care Areas
 Connecting Remote Cardiac Monitoring Issues with Care Areas ABSTRACT Patients in noncritical settings may have underlying cardiac conditions or demonstrate unexpected symptoms and condition changes that
Connecting Remote Cardiac Monitoring Issues with Care Areas ABSTRACT Patients in noncritical settings may have underlying cardiac conditions or demonstrate unexpected symptoms and condition changes that
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
4/7/2015. Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door. Chicago, circa 1999. Objectives. No disclosures, no conflicts
 Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s
 EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics
 Biomedical Research 2011; 22 (3): 333-337 Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics Venkatesh G Department of Physiology, Sri Siddhartha Medical
Biomedical Research 2011; 22 (3): 333-337 Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics Venkatesh G Department of Physiology, Sri Siddhartha Medical
Introduction. Planned surgical procedures
 Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
CASE STUDY. Bayleigh s Heart Disease. Written by Mark Stephenson, DVM Case Managed & Co-Written by Sonya Gordon, DVM, DVSc, DACVIM-CA
 CASE STUDY Bayleigh s Heart Disease Written by Mark Stephenson, DVM Case Managed & Co-Written by Sonya Gordon, DVM, DVSc, DACVIM-CA Patient Information PATIENT: Bayleigh PET OWNER: Ms. K. BREED: Irish
CASE STUDY Bayleigh s Heart Disease Written by Mark Stephenson, DVM Case Managed & Co-Written by Sonya Gordon, DVM, DVSc, DACVIM-CA Patient Information PATIENT: Bayleigh PET OWNER: Ms. K. BREED: Irish
CARDIOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 CARDIOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES PGY-1 Core Medicine Rotation The trainee will have the opportunity to develop clinical skills, the ability to analyze patients problems, and make treatment plans
CARDIOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES PGY-1 Core Medicine Rotation The trainee will have the opportunity to develop clinical skills, the ability to analyze patients problems, and make treatment plans
Natural History of Early Repolarization in the Inferior Leads
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Natural History of Early Repolarization in the Inferior Leads Ricardo Stein, M.D., Karim Sallam, M.D., Chandana Adhikarla, M.D., Madhavi Boga, M.D., Alexander D. Wood, B.Sc., and Victor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Natural History of Early Repolarization in the Inferior Leads Ricardo Stein, M.D., Karim Sallam, M.D., Chandana Adhikarla, M.D., Madhavi Boga, M.D., Alexander D. Wood, B.Sc., and Victor
Lead avr: The Neglected Lead
 Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
National Clinical. Respiratory
 * Posted with the Permission and Approval of the American Association for Respiratory Care. 2013, All Rights Reserved. Respiratory National Clinical Respiratory therapists adjust and respond to alarms
* Posted with the Permission and Approval of the American Association for Respiratory Care. 2013, All Rights Reserved. Respiratory National Clinical Respiratory therapists adjust and respond to alarms
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate. Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology
 Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
A MOBILE-PHONE ECG DETECTION KIT AND CLOUD MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
 A MOBILE-PHONE ECG DETECTION KIT AND CLOUD MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 1,2 SHUN-PING LIN, 2 WEN-HSU SUNG, 3 TERRY B. J. KUO, 2 JIN-JONG CHEN 1 Office of Research and Development, China University of Science and
A MOBILE-PHONE ECG DETECTION KIT AND CLOUD MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 1,2 SHUN-PING LIN, 2 WEN-HSU SUNG, 3 TERRY B. J. KUO, 2 JIN-JONG CHEN 1 Office of Research and Development, China University of Science and
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
Electrocardiographic Body Surface Mapping
 Electrocardiographic Body Surface Mapping Policy Number: 2.02.23 Last Review: 4/2016 Origination: 10/2009 Next Review: 10/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Electrocardiographic Body Surface Mapping Policy Number: 2.02.23 Last Review: 4/2016 Origination: 10/2009 Next Review: 10/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout.
 Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Evaluation of a direct access cardiac arrhythmia monitoring service
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2012, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 70 75 10.5603/CJ.2012.0010 Copyright 2012 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Evaluation of a direct access cardiac arrhythmia monitoring service David
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2012, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 70 75 10.5603/CJ.2012.0010 Copyright 2012 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Evaluation of a direct access cardiac arrhythmia monitoring service David
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
X Series Extensive Capabilities
 X Series Extensive Capabilities for Patient Transport Transporting Patients throughout the Hospital Requires the Right Equipment Full Featured yet Compact When transporting critically ill patients, you
X Series Extensive Capabilities for Patient Transport Transporting Patients throughout the Hospital Requires the Right Equipment Full Featured yet Compact When transporting critically ill patients, you
