Impact of Endoscopic Versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest Techniques on Outcomes After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
|
|
|
- Elvin Marshall
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SURGERY: The Annals of Thoracic Surgery CME Program is located online at To take the CME activity related to this article, you must have either an STS member or an individual non-member subscription to the journal. Impact of Endoscopic Versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest Techniques on Outcomes After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Maral Ouzounian, MD, Ansar Hassan, MD, PhD, Karen J. Buth, MS, Celeste MacPherson, RN, Idris M. Ali, MD, Gregory M. Hirsch, MD, and Imtiaz S. Ali, MD Division of Cardiac Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada Background. Endoscopic saphenous vein harvest (EVH) decreases leg wound infections and improves cosmesis after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Recent data, however, suggest that EVH may be associated with reduced graft patency rates. The objective of this study is to assess the effect of EVH on short-term and midterm outcomes after CABG. Methods. Data were prospectively collected on all first-time isolated CABG and combined valve/cabg with saphenous vein graft between 1998 and 2007 at a single center. Patients having traditional open vein harvest (OVH) were compared with patients having EVH. Multivariate models were used to examine the risk-adjusted impact of EVH on postoperative leg infection, composite in-hospital adverse events, and individual and composite midterm adverse events. Results. The study included 5,825 patients, of whom 2,004 (34.4%) had EVH. Patients having EVH were more likely to have ejection fraction less than 50% (32.0% versus 29.3%, p 0.04), recent myocardial infarction (24.2% versus 18.3%, p < ), and left main disease (26.0% versus 22.1%, p ). Median follow-up was 2.6 years. After risk adjustment, EVH was associated with reduced rates of leg infection (odds ratio 0.48, p 0.003) but had no association with either in-hospital (odds ratio 0.93, p 0.56) or midterm adverse outcomes (hazard ratio 0.93, p 0.22). Endoscopic saphenous vein harvest was associated with reduced readmission to hospital for unstable angina (odds ratio 0.74, p 0.01). Conclusions. Endoscopic saphenous vein harvest is associated with a lower rate of leg infection and is not an independent predictor of in-hospital or midterm adverse outcomes. Endoscopic saphenous vein harvest is a safe alternative to OVH for patients undergoing CABG with saphenous vein. (Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89:403 9) 2010 by The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Autologous saphenous vein remains the most commonly used conduit for coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Minimally invasive endoscopic vein harvest (EVH) techniques have been developed to decrease vein harvest morbidity. Compared with traditional open vein harvest (OVH), several studies have reported decreased wound related complications, improved patient satisfaction, shorter hospital stay, and reduced postoperative pain at the harvest site with EVH [1-11]. Despite these reported benefits, uptake of EVH among surgeons has been variable. Criticism of this technique centers on the risk of injury at the time of harvest with its potential detrimental effect on vein graft patency and clinical outcomes. While 6-month angiographic patency rates were found to be similar after EVH and OVH [12] and veins harvested by either technique had similar histology [7, 13], analysis of the Project of Ex-Vivo Vein Accepted for publication Sept 28, Address correspondence to Dr Imtiaz Ali, Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre, 1796 Summer St, Room 2263, Halifax, Nova Scotia, B3H 3A7, Canada; imtiaz.ali@dal.ca. Graft Engineering via Transfection (PREVENT IV) trial demonstrated EVH to be an independent predictor of vein graft failure at 1 year [14, 15], and endothelial injury has been observed after EVH [16]. The midterm safety and efficacy of EVH are unknown. Studies to date have had small sample sizes with limited follow-up and were not adequately powered to assess intermediate-term clinical outcomes. Given the paucity of clinical data available, it was the objective of this study to assess the impact of EVH on short-term and midterm clinical outcomes after CABG. We hypothesized that EVH would lead to reduced graft patency and worse mid-term outcomes. Material and Methods Study Sample All patients who underwent first-time isolated CABG or combined valve/cabg with the use of a saphenous vein graft at the Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia, between June 1, 1998, and May 31, 2007, were identified through the Maritime Heart Center 2010 by The Society of Thoracic Surgeons /10/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc doi: /j.athoracsur
2 404 OUZOUNIAN ET AL Ann Thorac Surg IMPACT OF EVH VS OVH ON CABG OUTCOME 2010;89:403 9 Table 1. Baseline and Intraoperative Characteristics Variable OVH (n 3,821) EVH (n 2,004) p Value Baseline characteristics Age, years, mean (SD) 66.2 (10.4) 66.7 (10.1) 0.08 Sex, female, % Hypertension, % Diabetes mellitus, % Dyslipidemia, % Smoking history, % Ejection fraction %, % Recent myocardial infarction, % Left main disease, % Urgent/emergent, % Body mass index , % Cerebrovascular disease, % Peripheral vascular disease, % Renal failure, % Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, % Intraoperative characteristics Total distal 2.97 (0.92) 3.12 (0.94) anastomoses, n, mean (SD) Vein graft 1.94 (0.83) 2.03 (0.84) anastomoses, n, mean (SD) Clamp time, minutes, 66 (31 101) 71 (32 110) median (IQR) Pump time, minutes, 106 (61 151) 108 (63 153) 0.29 median (IQR) Inotrope leaving operating room, % Intra-aortic balloon pump inserted, % EVH endoscopic saphenous vein harvest; range; OVH open vein harvest. IQR interquartile Cardiac Surgery Registry (MHCCSR). Patients with previous CABG surgery were excluded, as were cases in which both EVH and OVH techniques were used for vein harvesting. Approval from the Institutional Research Ethics Board was obtained before the study, and the Board waived the need for patient consent. Endoscopic Versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest Patients undergoing CABG or combined valve/cabg with EVH and OVH were differentiated from each other in the MHCCSR as of the start of the study period. The OVH was performed by either a continuous, longitudinal incision, or through multiple smaller incisions (open, bridging technique) under direct vision. An experienced surgeon or nurse practitioner performed EVH using the Guidant Vasoview system (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA) with sealed carbon dioxide insufflation. The vein was harvested through a subcutaneous tunnel with endoscopic bipolar cautery scissors to divide side branches. Surgeons were at liberty to choose EVH or OVH for each case. Factors influencing their decision may have included availability of equipment and skilled vein harvesting personnel, time constraints, and preconceptions regarding the safety and efficacy of either technique. Patients receiving veins using both EVH and OVH were excluded, and conversions from EVH to OVH were classified as EVH. Data Collection and Variable Definitions The MHCCSR is a detailed clinical registry that has prospectively collected perioperative data on all patients undergoing cardiac surgery at the Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre from March 1, 1995, until the present. For the purposes of tracking midterm survival and readmission to hospital, clinical data from the MHCCSR are linked to administrative data from Vital Statistics and the Canadian Institute for Health Information discharge abstract databases. A subgroup of cases from June 1, 1998, through September 30, 2005, was included in the link to administrative data, allowing a minimum of 6 months of follow-up. Several baseline demographic and clinical variables were considered: age, sex, body mass index greater than 35, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, smoking history (any tobacco use in the past), cerebrovascular disease (history of transient ischemic attack, cerebrovascular accident, cerebrovascular surgery, or carotid disease), peripheral vascular disease (history of aneurysm or occlusive vascular disease, or both), renal insufficiency (preoperative serum creatinine greater than 176 mol/l [1.99 mg/dl]), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, ejection fraction less than 50%, recent myocardial infarction (within 21 days preceding surgery), left main disease (more than 50% stenosis), and operative urgency (emer- Table 2. Crude In-Hospital Outcomes Outcome OVH (n 3,821) EVH (n 2,004) p Value In-hospital mortality, % Perioperative myocardial infarction, % Reoperation, % Permanent stroke, % Deep sternal wound infection, % Sepsis, % In-hospital composite a,% Leg infection, % a In-hospital composite includes in-hospital mortality, perioperative myocardial infarction, reoperation, permanent stroke, deep sternal wound infection, and sepsis. EVH endoscopic saphenous vein harvest; OVH open vein harvest.
3 Ann Thorac Surg OUZOUNIAN ET AL 2010;89:403 9 IMPACT OF EVH VS OVH ON CABG OUTCOME 405 Fig 1. Risk-adjusted effect (adjusted for preoperative variables in Table 1) of endoscopic saphenous vein harvest (EVH) on short-term and midterm adverse outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. (HR hazard ratio; OR odds ratio; OVH open vein harvest.) gent or urgent versus elective). Intraoperative variables of interest included the number of bypasses, cross-clamp and bypass times, need for an intra-aortic balloon pump, and whether the patient left the operating room on intravenous inotropic therapy. The short-term outcomes of interest included leg infections (leg incision site opened with excision of tissue, positive wound cultures, or treatment with antibiotics), in-hospital mortality, and a composite outcome consisting of in-hospital mortality, perioperative myocardial infarction (documented by electrocardiogram or biochemical changes), reoperation before discharge from hospital, permanent or disabling stroke, deep sternal wound infection, and sepsis (requires positive blood cultures). The midterm outcomes were all-cause mortality; readmission to hospital for cardiac catheterization, repeat revascularization, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, or heart failure; and a composite outcome consisting of all-cause mortality and readmission to hospital for a cardiac cause. Statistical Analysis Patients who underwent CABG or combined valve/ CABG surgery with EVH were compared with patients undergoing OVH using t tests and Kruskal-Wallis tests for continuous variables and 2 tests for categorical variables. The association of clinical characteristics with each outcome was assessed univariately, and relevant variables with 2 p values less than 0.20 were included in fully adjusted multivariable models; additional variables deemed clinically important were included in the models regardless of univariate p value. Logistic regression was used to examine the association of EVH with leg infections and the in-hospital composite outcome after fully adjusting for clinically relevant preoperative variables. Predictive accuracy of each logistic model was assessed by the receiver operating characteristics curve. The association between EVH and the intermediate individual and composite outcomes of interest was analyzed by Cox proportional hazards models fully adjusted for preoperative variables. Observations were censored at the date of last known follow-up, the time of death, or at the time of readmission to hospital for cardiac catheterization, repeat revascularization, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, or heart failure. To assess the proportional hazards assumption, a time-dependent covariate was created for each predictor as a function of survival time, and tests of proportionality were applied. For variables that did not satisfy the assumption of proportional hazards, timedependent covariates were included in the models. All analyses were performed using SAS version 8.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Authors had full access to all data and take responsibility for the integrity of data. All authors have read and agree with the contents of the article as written. Results A total of 5,825 patients formed the final study population. Of these, 2,004 (34.4%) underwent CABG or combined valve/cabg with EVH. The mean age of patients in this study was years, and 25.7% were female. A subgroup of 4,365 cases was available for linkage with administrative data and midterm analysis. Median follow-up time for patients discharged from hospital alive was 2.6 years (interquartile range, 1.0 to 4.6), and a total of 12,960 person-years of follow-up was available for analysis. Clinical Characteristics The baseline characteristics of patients who underwent CABG or combined valve/cabg with EVH or OVH are shown in Table 1. Compared with patients undergoing surgery with OVH, patients undergoing surgery with EVH were more likely to have ejection fraction less than 50% (32.0% versus 29.3%, p 0.04), recent myocardial infarction (24.2% versus 18.3%, p ), left main disease (26.0% versus 22.1%, p ), and dyslipidemia (91.1% versus 85.7 %, p ). Intraoperatively, patients undergoing CABG with EVH received a slightly greater mean number of distal anastomoses (3.12 versus 2.97, p ) and had longer median cross-clamp times (71 versus 66 minutes, p ; Table 1). Table 3. Risk-Adjusted Effect of Endoscopic Saphenous Vein Harvest on Midterm Outcomes Outcome Hazard Ratio (95% CI) p Value All-cause mortality 0.98 ( ) 0.85 Cardiac catheterization 0.83 ( ) 0.12 Repeat revascularization 0.90 ( ) 0.62 Unstable angina 0.74 ( ) 0.01 Myocardial infarction 0.95 ( ) 0.73 Heart failure 0.96 ( ) 0.71 Midterm composite a 0.93 ( ) 0.22 a Midterm composite includes all-cause mortality or readmission to hospital for cardiac catheterization, repeat revascularization, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, or heart failure. CI confidence interval.
4 406 OUZOUNIAN ET AL Ann Thorac Surg IMPACT OF EVH VS OVH ON CABG OUTCOME 2010;89:403 9 Fig 2. Risk-adjusted freedom from cardiac readmission or mortality. (EVH endoscopic saphenous vein harvest; OVH open vein harvest.) Clinical Outcomes Patients undergoing CABG or combined valve/cabg with EVH had similar rates of in-hospital mortality (3.2% versus 4.0%, p 0.16) and the in-hospital composite outcome (12.2 % versus 11.8%, p 0.68) when compared with patients undergoing surgery with OVH (see Table 2). The rate of postoperative leg wound infections was significantly lower in the EVH group (1.1% versus 2.2%, p 0.003; Table 2). After adjusting for baseline covariates, EVH remained associated with reduced leg infections (odds ratio [OR] 0.48, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.30 to 0.77), but did not emerge as an independent predictor of either inhospital mortality or morbidity (OR 0.95, 95% CI: 0.80 to 1.13; Fig 1). Furthermore, EVH was not associated with the midterm composite outcome (hazard ratio 0.93, 95% CI: 0.83 to 1.05; Fig 1). As shown in Figure 2, patients undergoing surgery with EVH and OVH had similar midterm freedom from death or readmission to hospital for a cardiac cause. Endoscopic vein harvest was found to be associated with a reduced rate of readmission to hospital for unstable angina (hazard ratio 0.74, 95% CI: 0.58 to 0.94), but not for myocardial infarction or the other components of the midterm composite outcome (Table 3). The adjusted curves demonstrating improved freedom from unstable angina in patients undergoing surgery with EVH are shown in Figure 3. Comment This is a large observational study examining midterm clinical outcomes of patients undergoing CABG or combined valve/cabg surgery with open or endoscopically harvested saphenous vein. We found no negative association between EVH and short-term and midterm adverse outcomes. Consistent with previous reports, EVH was associated with a reduced incidence of leg wound infections. It was also associated with a reduced rate of readmission to hospital for unstable angina. Minimally invasive endoscopic harvest techniques are used in 80% of cardiac surgery centers, and the consen- Fig 3. Risk-adjusted freedom from unstable angina. (EVH endoscopic saphenous vein harvest; OVH open vein harvest.)
5 Ann Thorac Surg OUZOUNIAN ET AL 2010;89:403 9 IMPACT OF EVH VS OVH ON CABG OUTCOME 407 sus panel of the International Society of Minimally Invasive Cardiothoracic Surgery recommends EVH as the standard of care for patients requiring saphenous vein grafts for coronary revascularization [10]. The short-term benefits of EVH are well documented. A meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials reported a significant reduction in wound infection using an endoscopic technique (OR 0.22, 95% CI: 0.14 to 0.37, p ), for a number needed to treat of 14 [3]. The International Society of Minimally Invasive Cardiothoracic Surgery consensus group reviewed 36 randomized and nonrandomized trials and found a 69% reduction in the risk of wound complications by EVH (OR 0.31, 95% CI: 0.23 to 0.41) [11]. Noninfective wound healing disturbances of hematoma, edema, skin necrosis, wound dehiscence, drainage, and seroma are also significantly reduced with EVH [17]. Several studies have demonstrated improved quality of life indices, including postoperative length of stay, time to mobilization, and patient satisfaction [4, 6, 7]. Finally, an economic analysis has reported EVH to be more cost effective than OVH [18]. In contrast to the abundant evidence demonstrating improved short-term and wound-related outcomes after EVH, there is a paucity of data regarding graft patency or clinical outcomes after open or minimally invasive saphenous vein harvest. Yun and colleagues [12] randomized 200 patients to EVH or OVH and reported 6-month overall occlusion rates of 21.7% for EVH and 17.6% for OVH (OR 1.15, p 0.63). In contrast, the PREVENT IV multicenter CABG trial assessed 1-year patency rates in more than 4,000 saphenous vein grafts and found EVH to be an independent predictor of graft failure as compared with OVH (OR 1.35, p 0.001) [15]. In this trial, the harvest technique used was left to the discretion of the surgeon, and details regarding the EVH technique were not specified. Macroscopic, histologic, and functional quality of veins harvested by EVH and OVH has been reported. Surgeon-assessed macroscopic quality was reviewed in a meta-analysis of 32 trials, and does not differ between veins harvested by EVH or OVH [19]. Histologic quality as assessed by light and scanning electron microscopy also does not differ between the two techniques [4]. One recent study reported damaged endothelium after EVH; however, the clinical sequelae of these structural and functional changes are unclear [16]. In addition, the majority of studies examining the functional characteristics of venous grafts, including cytokine levels, expression of adhesion molecules, vascular reactivity, and endothelial function found no difference between open and endoscopic techniques [20-24]. Along with potential injury to the vessel wall at the time of harvest, Brown and colleagues [25] observed that residual luminal clot is common if EVH is performed without systemic heparinization therapy, or with sealed carbon dioxide insufflation. The clinical impact of these observations remains to be determined. Five-year freedom from death, myocardial infarction, or recurrent angina has been reported by Allen and colleagues [26] and was similar between the two groups (75% versus 74%, p 0.85); however, the number of patients in each group of this randomized study was small (EVH, n 54; OVH, n 58). More recently, in a secondary analysis of the PREVENT IV trial, Lopes and colleagues [14] found an association of EVH with higher rates of vein graft failure and adverse clinical outcomes including higher mortality. The purpose of the trial was to assess ex vivo treatment of vein grafts with the E2F transcription factor decoy, edifoligide. It was conducted at 107 sites between 2002 and 2003, and the percentage of cases performed with EVH differed greatly across centers. The variability in experience levels and technique between centers and the overall low number of cases per institution should be considered when interpreting these findings. Despite the lack of angiographic data in our study, we included all patients undergoing CABG with a vein graft at a single institution during the study period. In this study, we found no association between EVH and midterm freedom from death, and/or readmission to hospital for cardiac catheterization, repeat revascularization, acute coronary syndromes, or heart failure. We did find an association of EVH with reduced readmission to hospital for unstable angina and a trend towards improved freedom from the composite outcome. Although these observations are interesting, there is little biological rationale for improved outcomes after EVH, and the presence of unmeasured confounders may account for these findings. It is reassuring, however, that there is no trend towards harm and suggests that although subtle changes to the venous conduit may be identified after endoscopic harvest, these may not translate to clinically relevant adverse outcomes. This study has certain limitations. Despite considering a wide array of clinical predictors of EVH in our analyses, our study was observational in nature, thus allowing for bias from unmeasured confounders. In addition, the decision to use endoscopic or open technique was largely dependent on surgeon s preference and the availability of trained assistants facile with the EVH technique. This may have introduced a selection bias as to which patients received a particular harvest technique. Finally, the lack of angiographic patency data should be noted, as a difference in graft patency may clinically manifest later than the duration of our study. We were reassured, however, by a hazard ratio of 0.93 and no evidence of divergence of the event-free survival curves in Figure 2. Despite these limitations, this study provides valuable data that have been largely lacking regarding the midterm safety of EVH. Further studies reporting 5- and 10-year clinical outcomes are necessary. In conclusion, patients undergoing CABG or combined valve/cabg surgery with EVH presented with worse systolic function and more recent myocardial infarction. After adjusting for baseline differences, no independent association between EVH and short-term or midterm adverse outcomes was found. Endoscopic saphenous vein harvest was associated with reduced readmission to hospital for acute coronary syndromes. Consistent with previous reports, EVH was found to be protective against postoperative leg wound infections. Endoscopic saphe-
6 408 OUZOUNIAN ET AL Ann Thorac Surg IMPACT OF EVH VS OVH ON CABG OUTCOME 2010;89:403 9 nous vein harvest is a safe alternative to OVH for patients undergoing CABG with saphenous vein. References 1. Allen KB, Griffith GL, Heimansohn DA, et al. Endoscopic versus traditional saphenous vein harvesting: a prospective, randomized trial. Ann Thorac Surg 1998;66: Allen KB, Heimansohn DA, Robison RJ, et al. Risk factors for leg wound complications following endoscopic versus traditional saphenous vein harvesting. Heart Surg Forum 2000;3: Athanasiou T, Aziz O, Skapinakis P, et al. Leg wound infection after coronary artery bypass grafting: a metaanalysis comparing minimally invasive versus conventional vein harvesting. Ann Thorac Surg 2003;76: Aziz O, Athanasiou T, Darzi A. Minimally invasive conduit harvesting: a systematic review. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2006;29: Bitondo JM, Daggett WM, Torchiana DF, et al. Endoscopic versus open saphenous vein harvest: a comparison of postoperative wound complications. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73: Bonde P, Graham AN, MacGowan SW. Endoscopic vein harvest: advantages and limitations. Ann Thorac Surg 2004; 77: Kiaii B, Moon BC, Massel D, et al. A prospective randomized trial of endoscopic versus conventional harvesting of the saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002;123: Patel AN, Hebeler RF, Hamman BL, et al. Prospective analysis of endoscopic vein harvesting. Am J Surg 2001;182: Puskas JD, Wright CE, Miller PK, et al. A randomized trial of endoscopic versus open saphenous vein harvest in coronary bypass surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;68: Allen KB, Cheng D, Cohn W, et al. Endoscopic vascular harvest in coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a consensus statement of the International Society of Minimally Invasive Cardiothoracic Surgery (ISMICS) Innovat Technol Tech Cardiothorac Vasc Surg 2005;1: Cheng D, Allen KB, Cohn W, et al. Endoscopic vascular harvest in coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a metaanalysis of randomized trials and controlled trials. Innovat Technol Tech Cardiothorac Vasc Surg 2005;1: Yun KL, Wu Y, Aharonian V, et al. Randomized trial of endoscopic versus open vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: six-month patency rates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005;129: Griffith GL, Allen KB, Waller BF, et al. Endoscopic and traditional saphenous vein harvest: a histologic comparison. Ann Thorac Surg 2000;69: Lopes RD, Hafley GE, Allen KB, et al. Endoscopic versus open vein-graft harvesting in coronary-artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2009;361: Magee MJ, Alexander JH, Hafley G, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft failure after on-pump and off-pump coronary artery bypass: findings from PREVENT IV. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;85: Rousou LJ, Taylor KB, Lu XG, et al. Saphenous vein conduits harvested by endoscopic technique exhibit structural and functional damage. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87: Athanasiou T, Aziz O, Al-Ruzzeh S, et al. Are wound healing disturbances and length of hospital stay reduced with minimally invasive vein harvest? A meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2004;26: Rao C, Aziz O, Deeba S, et al. Is minimally invasive harvesting of the great saphenous vein for coronary artery bypass surgery a cost-effective technique? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;135: Aziz O, Athanasiou T, Panesar SS, et al. Does minimally invasive vein harvesting technique affect the quality of the conduit for coronary revascularization? Ann Thorac Surg 2005;80: Alrawi SJ, Balaya F, Raju R, Cunningham JN, Acinapura AJ. A comparative study of endothelial cell injury during open and endoscopic saphenectomy: an electron microscopic evaluation. Heart Surg Forum 2001;4: Alrawi SJ, Raju R, Satheesan R, Cunningham JN, Acinapaura AJ. Interleukin-1, interleukin-2 and interleukin-10 expression in different techniques of saphenous vein harvesting. Heart Surg Forum 2001;4: Alrawi SJ, Samee M, Raju R, Shirazian D, Acinapura AJ, Cunningham JN. Intercellular and vascular cell adhesion molecule levels in endoscopic and open saphenous vein harvesting for coronary artery bypass surgery. Heart Surg Forum 2000;3: Nowicki M, Buczkowski P, Miskowiak B, Konwerska A, Ostalska-Nowicka D, Dyszkiewicz W. Immunocytochemical study on endothelial integrity of saphenous vein grafts harvested by minimally invasive surgery with the use of vascular mayo stripers. A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2004;27: O Regan DJ, Borland JA, Chester AH, Pennell DJ, Yacoub M, Pepper JR. Assessment of human long saphenous vein function with minimally invasive harvesting with the Mayo stripper. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1997;12: Brown EN, Kon ZN, Tran R, et al. Strategies to reduce intraluminal clot formation in endoscopically harvested saphenous veins. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;134: Allen KB, Heimansohn DA, Robison RJ, Schier JJ, Griffith GL, Fitzgerald EB. Influence of endoscopic versus traditional saphenectomy on event-free survival: five-year follow-up of a prospective randomized trial. Heart Surg Forum 2003;6:E INVITED COMMENTARY Minimally invasive harvesting (MIVH) of the great saphenous vein for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) has been shown to reduce patient-related morbidity in the postoperative period as compared with conventional vein harvesting (CVH), and can be considered to be a cost-effective option. Although the effect of MIVH on patient morbidity from wound-related complications has been extensively investigated in the literature, the effect on the quality of the harvested conduit is less clear [1, 2]. However, before attempting this comparison, it is important to consider the characteristics that would be expected of a high-quality conduit, namely its macroscopic appearance, histologic quality (with particular regard to endothelial continuity), functional characteristics, and mid-term and long-term patency [3]. The ultimate measure of quality of a conduit used for CABG is its longterm patency reassuring an optimal clinical outcome based on freedom from cardiovascular events avoiding disability, which can compromise a patient s quality of life. In their observational study, Ouzounian and colleagues [4] have demonstrated this effect. This is an important finding that also counteracts the recently published article from Lopes and colleagues [5], which concluded that it may be an increased risk of worse out by The Society of Thoracic Surgeons /10/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc doi: /j.athoracsur
Endoskopische Venenentnahme der V. saphena in der koronaren Bypasschirurgie - Aktuelle Datenlage - Dr. med. Stefanie Reutter
 Endoskopische Venenentnahme der V. saphena in der koronaren Bypasschirurgie - Aktuelle Datenlage - Dr. med. Stefanie Reutter Endoskopische Venenentnahme (EVH) - Einführung 1979 Tevaearai und Kollegen haben
Endoskopische Venenentnahme der V. saphena in der koronaren Bypasschirurgie - Aktuelle Datenlage - Dr. med. Stefanie Reutter Endoskopische Venenentnahme (EVH) - Einführung 1979 Tevaearai und Kollegen haben
Endoscopic vs open saphenous vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: A leg-related morbidity and histological comparison
 Endoscopic vs open saphenous vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: A leg-related morbidity and histological comparison Radim Brat a, Jaroslav Horacek b, Jiri Sieja a Aims. The aim of this study
Endoscopic vs open saphenous vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: A leg-related morbidity and histological comparison Radim Brat a, Jaroslav Horacek b, Jiri Sieja a Aims. The aim of this study
Endoscopic versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest in Patients Undergoing CABG, an Angiographically Measured Graft Patency Comparison
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Endoscopic versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest in Patients Undergoing CABG,
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Endoscopic versus Open Saphenous Vein Harvest in Patients Undergoing CABG,
Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
Measure #257 (NQF 1519): Statin Therapy at Discharge after Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
The descriptive analysis of Endoscopic versus Traditional Open Vein Harvest. Technique for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: report of 1974 Cases
 The descriptive analysis of Endoscopic versus Traditional Open Vein Harvest Technique for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: report of 1974 Cases Authors: Mohammad Hassan NEZAFATI, MD (1) Pouya NEZAFATI
The descriptive analysis of Endoscopic versus Traditional Open Vein Harvest Technique for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: report of 1974 Cases Authors: Mohammad Hassan NEZAFATI, MD (1) Pouya NEZAFATI
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT
 Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial
 Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial Connie N. Hess, MD, MHS, Stefan James, MD, PhD, Renato D. Lopes, MD, PhD, Daniel M. Wojdyla,
Apixaban Plus Mono vs. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the APPRAISE-2 Trial Connie N. Hess, MD, MHS, Stefan James, MD, PhD, Renato D. Lopes, MD, PhD, Daniel M. Wojdyla,
Endoscopic Vessel Harvesting: Using Advancements and Best Practices To Enhance Conduit Quality
 Endoscopic Vessel Harvesting: Using Advancements and Best Practices To Enhance Conduit Quality Bershinsky, J Matt, PA-C; Bitondo, Jerene M, PA-C; Brennan, Teresa, PA-C, MPAS; Causey, Keith, PA-C; DeMara,
Endoscopic Vessel Harvesting: Using Advancements and Best Practices To Enhance Conduit Quality Bershinsky, J Matt, PA-C; Bitondo, Jerene M, PA-C; Brennan, Teresa, PA-C, MPAS; Causey, Keith, PA-C; DeMara,
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease
 Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Cardiac Rehabilitation The Best Medicine for Your CAD Patients. James A. Stone
 James A. Stone BPHE, BA, MSc, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAACVPR, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, University of Calgary Total Cardiology, Calgary Acknowledgements and Disclosures Acknowledgements Jacques Genest
James A. Stone BPHE, BA, MSc, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAACVPR, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, University of Calgary Total Cardiology, Calgary Acknowledgements and Disclosures Acknowledgements Jacques Genest
PRECOMBAT Trial. Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf of the PRECOMBAT Investigators
 Premier of Randomized Comparison of Bypass Surgery versus Angioplasty Using Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in Patients with Left Main Coronary Artery Disease PRECOMBAT Trial Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf
Premier of Randomized Comparison of Bypass Surgery versus Angioplasty Using Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in Patients with Left Main Coronary Artery Disease PRECOMBAT Trial Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf
Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting
 Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine Seoul, Korea AMC, 2004 Background
Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine Seoul, Korea AMC, 2004 Background
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting
 Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Denominator Statement: Cardiac surgery patients with no evidence of prior infection.
 Last Updated: Version 4.3b NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form CMS/The Joint Commission: Suspended (Effective immediately beginning with July 1, 2014 discharges)
Last Updated: Version 4.3b NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form CMS/The Joint Commission: Suspended (Effective immediately beginning with July 1, 2014 discharges)
Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease What is Cardiac Rehabilitation? Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive exercise, education, and behavior modification
Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease What is Cardiac Rehabilitation? Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive exercise, education, and behavior modification
06 Validation of risk prediction model
 HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 2003-06 06 Validation of risk prediction model PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 2007 Background Participants: All HA hospitals via
HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 2003-06 06 Validation of risk prediction model PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 2007 Background Participants: All HA hospitals via
Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease
 Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
January 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 1, Pages: 1693-1700, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/1693
 Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir January 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 1, Pages: 1693-1700, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/1693 Clinicopathological comparisons of open vein harvesting
Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir January 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 1, Pages: 1693-1700, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/1693 Clinicopathological comparisons of open vein harvesting
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY Investigators
 Second Generation Drug-Eluting Stents Implantation Followed by Six Versus Twelve-Month - Dual Antiplatelet Therapy - The SECURITY Randomized Clinical Trial Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY
Second Generation Drug-Eluting Stents Implantation Followed by Six Versus Twelve-Month - Dual Antiplatelet Therapy - The SECURITY Randomized Clinical Trial Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY
HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 2003-05
 HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 23-5 5 PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 26 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Background HA AP target 2/3, coordinated by PCI Working
HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 23-5 5 PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 26 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Background HA AP target 2/3, coordinated by PCI Working
Results of streamlined regional ambulance transport and subsequent treatment of acute abdominal aortic aneurysm
 CHAPTER 6 Results of streamlined regional ambulance transport and subsequent treatment of acute abdominal aortic aneurysm JW Haveman, A Karliczek, ELG Verhoeven, IFJ Tielliu, R de Vos, JH Zwaveling, JJAM
CHAPTER 6 Results of streamlined regional ambulance transport and subsequent treatment of acute abdominal aortic aneurysm JW Haveman, A Karliczek, ELG Verhoeven, IFJ Tielliu, R de Vos, JH Zwaveling, JJAM
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery
 Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Objectives. Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery. History
 Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery Kimberly Boddicker, MD FACC Essentia Health Heart and Vascular Center 27 th Heart and Vascular Conference May 13, 2011 Objectives Summarize
Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification for Noncardiac Surgery Kimberly Boddicker, MD FACC Essentia Health Heart and Vascular Center 27 th Heart and Vascular Conference May 13, 2011 Objectives Summarize
Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care
 Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care Michelle A. Albert MD MPH Treacy S. Silbaugh B.S, John Z. Ayanian MD MPP, Ann Lovett RN
Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care Michelle A. Albert MD MPH Treacy S. Silbaugh B.S, John Z. Ayanian MD MPP, Ann Lovett RN
The return of myocardial ischemia after coronary artery
 Occurrence and Risk Factors for Reintervention After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Joseph F. Sabik III, MD; Eugene H. Blackstone, MD; A. Marc Gillinov, MD; Nicholas G. Smedira, MD; Bruce W. Lytle, MD
Occurrence and Risk Factors for Reintervention After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Joseph F. Sabik III, MD; Eugene H. Blackstone, MD; A. Marc Gillinov, MD; Nicholas G. Smedira, MD; Bruce W. Lytle, MD
Alexander Chernyavskiy 1, Alexander Volkov 1, Oleg Lavrenyuk 1, Igor Terekhov 1 and Yulia Kareva 1,2*
 Chernyavskiy et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2015) 10:163 DOI 10.1186/s13019-015-0353-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative results of endoscopic and open methods of vein harvesting for coronary artery
Chernyavskiy et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2015) 10:163 DOI 10.1186/s13019-015-0353-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative results of endoscopic and open methods of vein harvesting for coronary artery
Investor News. Not intended for U.S. and UK media
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Transcatheter Mitral Valve-in-Valve and Valve-in-Ring Implantations. Danny Dvir, MD On behalf of VIVID registry investigators
 Transcatheter Mitral Valve-in-Valve and Valve-in-Ring Implantations Danny Dvir, MD On behalf of VIVID registry investigators Introduction Bioprosthetic valves are increasingly implanted in open-heart surgeries.
Transcatheter Mitral Valve-in-Valve and Valve-in-Ring Implantations Danny Dvir, MD On behalf of VIVID registry investigators Introduction Bioprosthetic valves are increasingly implanted in open-heart surgeries.
Antiplatelet and anticoagulation treatment of patients undergoing carotid and peripheral artery angioplasty
 Round Table: Antithrombotic therapy beyond ACS Antiplatelet and anticoagulation treatment of patients undergoing carotid and peripheral artery angioplasty M. Matsagkas, MD, PhD, EBSQ-Vasc Associate Professor
Round Table: Antithrombotic therapy beyond ACS Antiplatelet and anticoagulation treatment of patients undergoing carotid and peripheral artery angioplasty M. Matsagkas, MD, PhD, EBSQ-Vasc Associate Professor
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99)
 CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery
 Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
Zhongmin Li, PhD University of California, Davis School of Medicine Zhongmin.li@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu
 Zhongmin Li, PhD University of California, Davis School of Medicine Zhongmin.li@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu 1 Health care quality and transparency of care and outcomes AHRQ s IQI and PSIs State initiatives Multiple
Zhongmin Li, PhD University of California, Davis School of Medicine Zhongmin.li@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu 1 Health care quality and transparency of care and outcomes AHRQ s IQI and PSIs State initiatives Multiple
Stroke: Major Public Health Burden. Stroke: Major Public Health Burden. Stroke: Major Public Health Burden 5/21/2012
 Faculty Prevention Sharon Ewer, RN, BSN, CNRN Stroke Program Coordinator Baptist Health Montgomery, Alabama Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Monday, May 21, 2012 2:00 4:00 p.m. Central Time Produced
Faculty Prevention Sharon Ewer, RN, BSN, CNRN Stroke Program Coordinator Baptist Health Montgomery, Alabama Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Monday, May 21, 2012 2:00 4:00 p.m. Central Time Produced
Health Economic Evaluations of Endoscopic Vein Harvesting Compared to Open Vein Harvesting for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
 Medicine with Industrial Specialization Medical Market Access Aalborg University Fall 2011 Health Economic Evaluations of Endoscopic Vein Harvesting Compared to Open Vein Harvesting for Coronary Artery
Medicine with Industrial Specialization Medical Market Access Aalborg University Fall 2011 Health Economic Evaluations of Endoscopic Vein Harvesting Compared to Open Vein Harvesting for Coronary Artery
Specialty Excellence Award and America s 100 Best Hospitals for Specialty Care 2013-2014 Methodology Contents
 Specialty Excellence Award and America s 100 Best Hospitals for Specialty Care 2013-2014 Methodology Contents Introduction... 2 Specialty Excellence Award Determination... 3 America s 100 Best Hospitals
Specialty Excellence Award and America s 100 Best Hospitals for Specialty Care 2013-2014 Methodology Contents Introduction... 2 Specialty Excellence Award Determination... 3 America s 100 Best Hospitals
Description of the OECD Health Care Quality Indicators as well as indicator-specific information
 Appendix 1. Description of the OECD Health Care Quality Indicators as well as indicator-specific information The numbers after the indicator name refer to the report(s) by OECD and/or THL where the data
Appendix 1. Description of the OECD Health Care Quality Indicators as well as indicator-specific information The numbers after the indicator name refer to the report(s) by OECD and/or THL where the data
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) with one or more risk factors
 News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions
 Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions Your Guide to EXPRESS Critical Illness Insurance Definitions This guide to critical illness definitions will help you understand the illnesses
Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions Your Guide to EXPRESS Critical Illness Insurance Definitions This guide to critical illness definitions will help you understand the illnesses
ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS WITH CORONARY STENTS FOR NON CARDIAC SURGERY. Dr. Mahesh Vakamudi. Professor and Head
 ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS WITH CORONARY STENTS FOR NON CARDIAC SURGERY Dr. Mahesh Vakamudi Professor and Head Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Sri Ramachandra University INTRODUCTION
ANESTHESIA FOR PATIENTS WITH CORONARY STENTS FOR NON CARDIAC SURGERY Dr. Mahesh Vakamudi Professor and Head Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Sri Ramachandra University INTRODUCTION
Tips for surviving the analysis of survival data. Philip Twumasi-Ankrah, PhD
 Tips for surviving the analysis of survival data Philip Twumasi-Ankrah, PhD Big picture In medical research and many other areas of research, we often confront continuous, ordinal or dichotomous outcomes
Tips for surviving the analysis of survival data Philip Twumasi-Ankrah, PhD Big picture In medical research and many other areas of research, we often confront continuous, ordinal or dichotomous outcomes
California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01
 California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01 1256.01. (a) The Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Pilot Program is hereby established in the department. The purpose of the pilot program
California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01 1256.01. (a) The Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Pilot Program is hereby established in the department. The purpose of the pilot program
COMMON METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES FOR CER IN BIG DATA
 COMMON METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES FOR CER IN BIG DATA Harvard Medical School and Harvard School of Public Health sharon@hcp.med.harvard.edu December 2013 1 / 16 OUTLINE UNCERTAINTY AND SELECTIVE INFERENCE 1
COMMON METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES FOR CER IN BIG DATA Harvard Medical School and Harvard School of Public Health sharon@hcp.med.harvard.edu December 2013 1 / 16 OUTLINE UNCERTAINTY AND SELECTIVE INFERENCE 1
The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland. Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs
 The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs Heart Disease Heart Disease is the leading cause of death
The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs Heart Disease Heart Disease is the leading cause of death
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome. Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9
 Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins
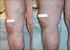 Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
Steven J. Yakubov, MD FACC For the CoreValve US Clinical Investigators
 Long-Term Outcomes Using a Self- Expanding Bioprosthesis in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis Deemed Extreme Risk for Surgery: Two-Year Results From the CoreValve US Pivotal Trial Steven J. Yakubov,
Long-Term Outcomes Using a Self- Expanding Bioprosthesis in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis Deemed Extreme Risk for Surgery: Two-Year Results From the CoreValve US Pivotal Trial Steven J. Yakubov,
PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS IN CARDIAC SURGERY
 PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS IN CARDIAC SURGERY Past,, and Future PAST 1965 first class of Physician Assistants graduated from Duke University Research revealed geographic maldistribution of primary care providers
PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS IN CARDIAC SURGERY Past,, and Future PAST 1965 first class of Physician Assistants graduated from Duke University Research revealed geographic maldistribution of primary care providers
Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Number 84 Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus Summary Overview Clinical
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Number 84 Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus Summary Overview Clinical
How can registries contribute to guidelines? Nicolas DANCHIN, HEGP, Paris
 How can registries contribute to guidelines? Nicolas DANCHIN, HEGP, Paris Pros and cons of registers Prospective randomised trials constitute the cornerstone of "evidence-based" medicine, and they therefore
How can registries contribute to guidelines? Nicolas DANCHIN, HEGP, Paris Pros and cons of registers Prospective randomised trials constitute the cornerstone of "evidence-based" medicine, and they therefore
Hot Line Session at European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2014:
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Hot Line Session at European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2014: Once-Daily
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Hot Line Session at European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2014: Once-Daily
Majestic Trial 12 Month Results
 Majestic Trial 12 Month Results S.Müller-Hülsbeck, MD, EBIR, FCIRSE, FICA ACADEMIC HOSPITALS Flensburg of Kiel University Ev.-Luth. Diakonissenanstalt zu Flensburg Knuthstraße 1, 24939 FLENSBURG Dept.
Majestic Trial 12 Month Results S.Müller-Hülsbeck, MD, EBIR, FCIRSE, FICA ACADEMIC HOSPITALS Flensburg of Kiel University Ev.-Luth. Diakonissenanstalt zu Flensburg Knuthstraße 1, 24939 FLENSBURG Dept.
Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators
 Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators Shaikha Al Naimi Doctor of Pharmacy Student College of Pharmacy Qatar University
Journal Club: Niacin in Patients with Low HDL Cholesterol Levels Receiving Intensive Statin Therapy by the AIM-HIGH Investigators Shaikha Al Naimi Doctor of Pharmacy Student College of Pharmacy Qatar University
Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation Steven J Feldhaus, MD, FACS 2015 Cardiac Symposium September 18, 2015 Stages of Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal (Intermittent) Persistent (Continuous)
Atrial Fibrillation Surgeons Role in Atrial Fibrillation Steven J Feldhaus, MD, FACS 2015 Cardiac Symposium September 18, 2015 Stages of Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal (Intermittent) Persistent (Continuous)
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
ECG may be indicated for patients with cardiovascular risk factors
 eappendix A. Summary for Preoperative ECG American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association, 2007 A1 2002 A2 European Society of Cardiology and European Society of Anaesthesiology, 2009 A3 Improvement,
eappendix A. Summary for Preoperative ECG American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association, 2007 A1 2002 A2 European Society of Cardiology and European Society of Anaesthesiology, 2009 A3 Improvement,
CARDIA 288 MONTH FOLLOW-UP SUPPLEMENTAL FORM (FORM B) HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: INTERVIEWER ID FY288BIVID2. Page 1 of 6 FY288BH4CN
 HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: 2 8 8 0 H FY288BH4CN Has the participant indicated any of the following reasons for being admitted overnight for this case? 1. Suspected or confirmed problems with the heart, circulation,
HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: 2 8 8 0 H FY288BH4CN Has the participant indicated any of the following reasons for being admitted overnight for this case? 1. Suspected or confirmed problems with the heart, circulation,
After acute myocardial infarction, diabetes CARDIAC OUTCOMES AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS
 CARDIAC OUTCOMES AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS By Deborah Chyun, RN, PhD, Viola Vaccarino, MD, PhD, Jaime Murillo, MD, Lawrence H. Young, MD, and Harlan M. Krumholz,
CARDIAC OUTCOMES AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS By Deborah Chyun, RN, PhD, Viola Vaccarino, MD, PhD, Jaime Murillo, MD, Lawrence H. Young, MD, and Harlan M. Krumholz,
Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are at high
 Long-Term Outcome of Renal Transplant Recipients in the United States After Coronary Revascularization Procedures Charles A. Herzog, MD; Jennie Z. Ma, PhD; Allan J. Collins, MD Background Retrospective
Long-Term Outcome of Renal Transplant Recipients in the United States After Coronary Revascularization Procedures Charles A. Herzog, MD; Jennie Z. Ma, PhD; Allan J. Collins, MD Background Retrospective
Department of Pharmacy, Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Medical Center, San Francisco 94115, California, USA
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 33-38 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evaluation of Glycemic Control with a Pharmacist-Managed Post-Cardiothoracic Surgery Insulin Protocol
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 33-38 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evaluation of Glycemic Control with a Pharmacist-Managed Post-Cardiothoracic Surgery Insulin Protocol
Mitral Valve Repair versus Replacement for Severe Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation. Michael Acker, MD For the CTSN Investigators AHA November 2013
 Mitral Valve Repair versus Replacement for Severe Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Michael Acker, MD For the CTSN Investigators AHA November 2013 Acknowledgements Supported by U01 HL088942 Cardiothoracic
Mitral Valve Repair versus Replacement for Severe Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Michael Acker, MD For the CTSN Investigators AHA November 2013 Acknowledgements Supported by U01 HL088942 Cardiothoracic
RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department
 RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department Sohil Pothiawala FAMS (EM), MRCSEd (A&E), M.Med (EM), MBBS Consultant Dept. of Emergency Medicine Singapore General Hospital
RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department Sohil Pothiawala FAMS (EM), MRCSEd (A&E), M.Med (EM), MBBS Consultant Dept. of Emergency Medicine Singapore General Hospital
Cardiac Assessment for Renal Transplantation: Pre-Operative Clearance is Only the Tip of the Iceberg
 Cardiac Assessment for Renal Transplantation: Pre-Operative Clearance is Only the Tip of the Iceberg 2 nd Annual Duke Renal Transplant Symposium March 1, 2014 Durham, NC Joseph G. Rogers, M.D. Associate
Cardiac Assessment for Renal Transplantation: Pre-Operative Clearance is Only the Tip of the Iceberg 2 nd Annual Duke Renal Transplant Symposium March 1, 2014 Durham, NC Joseph G. Rogers, M.D. Associate
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES
 FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IMPACT ON RACIAL AND ETHNIC DISPARITIES Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics
The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand
 The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand Guidelines on Support Facilities for Coronary Angiography and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) including Guidelines on the Performance of Procedures
The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand Guidelines on Support Facilities for Coronary Angiography and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) including Guidelines on the Performance of Procedures
Hormones and cardiovascular disease, what the Danish Nurse Cohort learned us
 Hormones and cardiovascular disease, what the Danish Nurse Cohort learned us Ellen Løkkegaard, Clinical Associate Professor, Ph.d. Dept. Obstetrics and Gynecology. Hillerød Hospital, University of Copenhagen
Hormones and cardiovascular disease, what the Danish Nurse Cohort learned us Ellen Løkkegaard, Clinical Associate Professor, Ph.d. Dept. Obstetrics and Gynecology. Hillerød Hospital, University of Copenhagen
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance
 Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance Strong. Reliable. Trustworthy. Forward-thinking. Extra help on the road to recovery Surviving a critical illness can be very challenging financially Few of us
Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance Strong. Reliable. Trustworthy. Forward-thinking. Extra help on the road to recovery Surviving a critical illness can be very challenging financially Few of us
Cardiac Rehabilitation: Strategies Approaching 2020
 ACC Banff 2015 Cardiac Rehabilitation: Strategies Approaching 2020 James A. Stone BPHE, BA, MSc, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAACVPR, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, University of Calgary Libin Cardiovascular
ACC Banff 2015 Cardiac Rehabilitation: Strategies Approaching 2020 James A. Stone BPHE, BA, MSc, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAACVPR, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, University of Calgary Libin Cardiovascular
Declaratory Ruling 2005-1 Replaces Declaratory Ruling 97-2
 Declaratory Ruling 2005-1 Replaces Declaratory Ruling 97-2 RE: The permitted role of unlicensed surgical assistants ( assistants ) in taking of the saphenous vein during coronary artery bypass graft (
Declaratory Ruling 2005-1 Replaces Declaratory Ruling 97-2 RE: The permitted role of unlicensed surgical assistants ( assistants ) in taking of the saphenous vein during coronary artery bypass graft (
Elevated heart rate at twelve months after heart transplantation is an independent predictor of long term mortality
 Elevated heart rate at twelve months after heart transplantation is an independent predictor of long term mortality C. Tomas, MA Castel, E Roig, I. Vallejos, C. Plata, F. Pérez-Villa Cardiology Department,
Elevated heart rate at twelve months after heart transplantation is an independent predictor of long term mortality C. Tomas, MA Castel, E Roig, I. Vallejos, C. Plata, F. Pérez-Villa Cardiology Department,
8-9-2012. In hospital diabetes care background and challenges. Duality of interest. One of the goals may be...
 In hospital diabetes care background and challenges Duality of interest Nothing to disclose within the framework of this presentation My own fasting BG is 4.6 mmol/l, HbA1c 5.4% Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel
In hospital diabetes care background and challenges Duality of interest Nothing to disclose within the framework of this presentation My own fasting BG is 4.6 mmol/l, HbA1c 5.4% Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY
 INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES
 ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES 1.0 Quality of Health Services: Access to Surgery Priorities for Action Acute Care Access to Surgery Reduce the wait time for surgical procedures. 1.1 Wait
ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES 1.0 Quality of Health Services: Access to Surgery Priorities for Action Acute Care Access to Surgery Reduce the wait time for surgical procedures. 1.1 Wait
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
INFORMED CONSENT FOR SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY
 INFORMED CONSENT FOR SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about your Sleeve Gastrectomy including the risks and benefits, as well as alternative treatments.
INFORMED CONSENT FOR SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about your Sleeve Gastrectomy including the risks and benefits, as well as alternative treatments.
PHARMACOLOGICAL Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation STROKE RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES Vs. BLEEDING RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES.
 PHARMACOLOGICAL Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation STROKE RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES Vs. BLEEDING RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES. Hossam Bahy, MD (1992 2012), 19 tools have been identified 11 stroke scores 1
PHARMACOLOGICAL Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation STROKE RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES Vs. BLEEDING RISK ASSESSMENT SCORES. Hossam Bahy, MD (1992 2012), 19 tools have been identified 11 stroke scores 1
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE 2011; DOI: 10.
 FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE 2011; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMSA1107913 Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD, 1 Jerry Avorn, MD, 1 Robert J. Glynn,
FULL COVERAGE FOR PREVENTIVE MEDICATIONS AFTER MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE 2011; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMSA1107913 Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD, 1 Jerry Avorn, MD, 1 Robert J. Glynn,
The clinical outcome after coronary bypass surgery: a 30-year follow-up study
 European Heart Journal (2009) 30, 453 458 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn530 CLINICAL RESEARCH Coronary heart disease The clinical outcome after coronary bypass surgery: a 30-year follow-up study Ron T. van
European Heart Journal (2009) 30, 453 458 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn530 CLINICAL RESEARCH Coronary heart disease The clinical outcome after coronary bypass surgery: a 30-year follow-up study Ron T. van
A list of FDA-approved testosterone products can be found by searching for testosterone at http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/.
 FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke
FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke
Long-Term Effect of Dual Antiplatelet Treatment after Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
 366 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-Term Effect of Dual Antiplatelet Treatment after Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Jose Lopez, M.D.,* Carlos Morales, M.D.,* Pablo Avanzas,
366 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-Term Effect of Dual Antiplatelet Treatment after Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Jose Lopez, M.D.,* Carlos Morales, M.D.,* Pablo Avanzas,
Hemodialysis catheter infection
 Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
LEADERS: 5-Year Follow-up
 LEADERS: -Year Follow-up from a Prospective, Randomized Trial of Biolimus A9-eluting Stents with a Biodegradable Polymer vs. Sirolimus-eluting Stents with a Durable Polymer : Final Report of the LEADERS
LEADERS: -Year Follow-up from a Prospective, Randomized Trial of Biolimus A9-eluting Stents with a Biodegradable Polymer vs. Sirolimus-eluting Stents with a Durable Polymer : Final Report of the LEADERS
Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient?
 Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient? --- NIRS-IVUS TVC Imaging Adds Additional Information for the Heart Team Dr. Luis Tami Memorial Regional Hospital
Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient? --- NIRS-IVUS TVC Imaging Adds Additional Information for the Heart Team Dr. Luis Tami Memorial Regional Hospital
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
Overview. Total Joint Replacement in the U.S. KP National Total Joint Registry EMR Tools and Outcome Assessment: A Model for Vascular Surgery?
 KP National Total Joint Registry EMR Tools and Outcome Assessment: A Model for Vascular Surgery? Liz Paxton Director of Surgical Outcomes and Analysis Overview KP Total Joint Replacement Registry Background
KP National Total Joint Registry EMR Tools and Outcome Assessment: A Model for Vascular Surgery? Liz Paxton Director of Surgical Outcomes and Analysis Overview KP Total Joint Replacement Registry Background
Randomized trials versus observational studies
 Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
Open Ventral Hernia Repair
 Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Atherosclerosis of the aorta. Artur Evangelista
 Atherosclerosis of the aorta Artur Evangelista Atherosclerosis of the aorta Diagnosis Classification Prevalence Risk factors Marker of generalized atherosclerosis Risk of embolism Therapy Diagnosis Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis of the aorta Artur Evangelista Atherosclerosis of the aorta Diagnosis Classification Prevalence Risk factors Marker of generalized atherosclerosis Risk of embolism Therapy Diagnosis Atherosclerosis
Protocol. Cardiac Rehabilitation in the Outpatient Setting
 Protocol Cardiac Rehabilitation in the Outpatient Setting (80308) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 09/15 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 07/07, 07/08, 05/09, 05/10, 05/11, 05/12,
Protocol Cardiac Rehabilitation in the Outpatient Setting (80308) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 09/15 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 07/07, 07/08, 05/09, 05/10, 05/11, 05/12,
European system for cardiac operative risk evaluation (EuroSCORE) q
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 16 (1999) 9±13 European system for cardiac operative risk evaluation (EuroSCORE) q S.A.M. Nashef*, F. Roques, P. Michel, E. Gauducheau, S. Lemeshow, R. Salamon,
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 16 (1999) 9±13 European system for cardiac operative risk evaluation (EuroSCORE) q S.A.M. Nashef*, F. Roques, P. Michel, E. Gauducheau, S. Lemeshow, R. Salamon,
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Summary HTA. HTA-Report Summary. Introduction
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Antioxidative vitamines for prevention of cardiovascular disease for patients after renal transplantation and patients with chronic renal failure Schnell-Inderst P, Kossmann
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Antioxidative vitamines for prevention of cardiovascular disease for patients after renal transplantation and patients with chronic renal failure Schnell-Inderst P, Kossmann
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements
 Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
 FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Dov B. Millstone, Anthony V. Perruccio, Elizabeth M. Badley, Y. Raja Rampersaud Dalla Lana School
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Dov B. Millstone, Anthony V. Perruccio, Elizabeth M. Badley, Y. Raja Rampersaud Dalla Lana School
Heart Center Packages
 Heart Center Packages For more information and appointments, Please contact The Heart Center of Excellence at the American Hospital Dubai Tel: +971-4-377-6571 Email: heartcenter@ahdubai.com www.ahdubai.com
Heart Center Packages For more information and appointments, Please contact The Heart Center of Excellence at the American Hospital Dubai Tel: +971-4-377-6571 Email: heartcenter@ahdubai.com www.ahdubai.com
