22 Digestive System. Taft College Human Physiology
|
|
|
- Lillian Tucker
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 22 Digestive System Taft College Human Physiology
2 Functions of the Digestive System (4 Basic Functions of Digestion) 1. Ingestion - food intake. 2. Digestion - process of reducing foods to their constituent building blocks from larger molecules to smaller ones that may be absorbed and used by the body. a. mechanical or physical digestion - ex. - chewing b. chemical digestion ex. Digestive enzymes (catalysts) 3. Absorption - taking in the nutrients that have been broken down. 4. Defecation or egestion - elimination of unabsorbed residues of the digestive process.
3 Components of the Digestive System 1. Alimentary Tract - tube with various modifications from mouth to anus. All digestion occurs in the tube. All absorption occurs from this tube. Within wall of tract is smooth muscle that serves to propel foods = peristalsis 2. Accessory organs - structures that lie outside of the alimentary tract. These organs empty secretions into the digestive tract by way of ducts. The secretions are necessary for digestion.
4 Control of Feeding (Appetite, Hunger) Feeding is controlled by the hypothalamus. (remember homeostasis = hypothalamus). How the hypothalamus determines we are hungry is not sure, but here are some hypotheses: 1. Gastric sensation hypothesis - filling of stomach or stretching of abdominal wall. Some diet aids attempt to work on this mannerlike a sponge that swells. 2. Glucostat hypothesis - body monitors glucose levels. Glucose uptake by liver cells influence vagus nerve and information is transmitted to lateral hypothalamus (Glucose Receptors). 3. Thermostat hypothesis - intake of food associated with rise in metabolic activity. Therefore, increase in heat. The increase in temperature reduces appetite. Closely tied to caloric need. In cooler temperatures- the more food we eat. 4. General nutritional state hypothesis - body can monitor usage of a particular nutrient (substance, vitamin, minerals).
5 Control of Feeding (Appetite, Hunger) 5. Intake of specific foods hypothesis - body may be able to monitor presence of certain foods or food groups. It is unlikely that a single hypothesis will explain appetite for food by itself. More than likely your interest in food is due to a number of factors. Interesting- tend to have appetite (craving) for different things a different times. Apparently to satisfy nutritional need at that time. 6. Psychological status hypothesis - sometimes we eat out of habit or boredom. Pleasure: food preferences, eat more in cafeteria, appetizers, dessert, Pleasure Centers in Hypothalamus. Social factors: cultural demands to be thin...anxiety. 7. Neurotransmitter and hormones Research has shown that neurotransmitters (serotonin) and hormones (leptin from fat cells and PYY from intestine) are involved in a feeling of fulfillment following eating. Carbohydrates increase serotonin levels in the brain, so one may eat carbohydrates when depressed. Use of drugs such as fenfluramine (FenPhen is a combo drug.) Biological Basis: fenfluramine increases serotoin levels, while phentermine is an amphetamine mimic that promotes a sympathetic response. Both curb appetite.) Taken off the market as heart failure occurred. Research in these areas may be very important in in reducing the alarming increase in childhood obesity in the U.S.
6 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) I. Mouth 1. Ingestion begins 2. Digestion a. Mechanical digestion - chewing = mastication. b. Chemical digestion Saliva- produced by the salivary glands, is important as it: 1. Begins the digestion of carbohydrates. Starches are broken down to disaccharides by amylase in the saliva. Only 3-5%, since food spends such short time in mouth. 2. Dissolves soluble foods. 3. Moistens food or lubricates food for swallowing. 4. Cleanses and moistens mouth- helps to prevent tooth decay. Saliva washes away acidic waste of bacteria that promotes tooth decay. 3. Swallowing Movement of bolus of food. A voluntary act using skeletal muscles. Tongue forces food against hard palate (roof of mouth).
7 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) II. Pharynx The food/drink moves into the oropharynx and stimulates receptors that go to the medulla oblongata. Involuntary impulses cause the soft palate and uvula to be forced up and close off opening from nose to pharynx. The larynx moves up under the tongue and the vocal cords come together which seals off the respiratory passage. The bolus passes through the laryngopharynx and enters the esophagus in 1-2 seconds.
8 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) III. Esophagus 1. Transportation of foods to stomach by peristalsis - wave like contraction of smooth muscle. Peristalsis is controlled by the medulla oblongata so is involuntary response. Takes about 4-8 seconds for bolus, 1 second for liquid to reach stomach. 2. Secretion of mucus by glandular cells acts as a lubricant of the bolus. No digestion or absorption occurs in the esophagus. 3. Vomiting - reverse peristalsis. Usually stimulated by irritation and distention of the stomach. Medulla oblongata vomit center causes abdominal wall muscles and diaphragm to squeeze the stomach and expel its contents through the open esophageal sphincters. Heart burn is due to HCl from the stomach contents entering the inferior part of the esophagus causing burning and irritation. Don t lie down after a meal. Prolonged exposure can lead to esophageal cancer.
9 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) IV. Stomach Major functions: 1. Storage (reservoir) 2. Chyme formation = combination of saliva, gastric juice, food, and drink. 3. Protein digestion by HCl and pepsin. (some lipase activity) 4. Little absorption of food. Water, ions, some drugs (alcohol, aspirin).
10 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) Digestion in the Stomach The stomach contains many gastric glands that produce gastric juice. Gastric juice = watery solution of HCl and pepsin, lipase, gastrin, and intrinsic factor for B12 absorption. 3 important types of cells in the stomach, each with different functions: 1. Parietal (oxyntic) cells- secrete HCl, hydrochloric acid which: a. Kills microbes in food. b. Denatures proteins. c. Converts pepsinogen to pepsin. 2. Chief (zymogenic) cells- secrete pepsinogen (inactive form) which is converted to pepsin (active form) in the presence of HCl. Breaks certain peptide bonds in proteins. Secrete gastric lipase (breaks down triglycerides). 3. (Mucous) Neck cells- secrete mucus that forms a protective layer barrier that prevents digestion of stomach wall (and absorption of materials).
11 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) The Small Intestine Structures 1. 3 sections of small intestine, in order: Duodenum, Jejunum & Ileum 2. Folds in small Intestine - All these folds dramatically increase surface area for absorption. a. Plicae of small intestine b. Villi- finger like projections Villi contain blood and lymph capillaries that will carry the nutrients away. c. Microvilli - absorptive simple columnar epithelium cell surface (w/ 1700 microvilli per cell, which makes for a massive area for absorption. 3. Structures (digestive glands) associated with the small intestine. Pancreas, liver, and gallbladder All produce digestive secretions
12 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) The Small Intestine-Function 1. Absorption of nutrients (microvilli is absorption unit). 90% of nutrients absorbed here 2. Digestion - Many digestive enzymes are present. 3. Secretion - of intestinal juice about 1-2 L/day. Slightly alkaline (7.6) mix of water and mucus. Provides a vehicle for chyme to move through the intestine to be absorbed. 4. Protection - lymphoid tissue (Peyer s patches) especially towards the end (ileum) of the small intestine. The colon contains huge numbers of bacteria that must be kept in check.
13 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) The Small Intestine Function Digestion in the Small Intestine We shall take a look at digestion of the basic food groups: Carbohydrates, Proteins, & Fats We will see that the pancreas is: 1. The primary source of digestive enzymes that act in the intestine. Pancreatic juice is ducted to duodenum also exocrine gland. 2. Provides the alkalinity (bicarbonate) necessary for creating optimum ph for enzyme activity in the small intestine. Pancreas
14 Digestion of Basic Food Groups End products Note: -ase on end indicates an enzyme that breaks down chemical. Note: significance of pancreas in all food groups.
15 Bile Bile (1 L/d) is produced in liver and stored in gallbladder. Greenish to brownish consisting of water, bile acids, phospholipids, bile pigments. Gives stool & urine its color. Bile serves to emulsify fats. It breaks down lipids so they can be absorbed. Emulsifies large lipid globules into 1mm droplets. If bile backs up due to liver injury or obstruction, bilirubin (from breakdown of heme group in rbc) will back up and deposit in body producing a yellow color = jaundice.
16 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) The Small Intestine Function Absorption in Small Intestine Absorption of the end products of digestion takes place through epithelial lining of small intestine. Microvilli offers increased surface area. Most end products of digestion, monosaccharides, amino acids, plus water, vitamins, and ions are absorbed into blood capillaries of the villi. Most dietary fatty acids (long chain) differ in that they are absorbed by the much leakier lacteals of the lymphatic system. Note - Any disruption of this lining may lead to discomfort, diarrhea, and malabsorption. The lining of the small intestine may be affected by chemotherapy, radiation therapy, toxins, or infection. Long chain fatty acid
17 Function and Control of Specific Digestive Organs (in order passed by bolus of food) Function of the Colon (large intestine) No more digestion by you, but some by bacteria of indigestible foods. Can be beneficial (vitamins) or embarrassing (gas). Important for: 1. Water absorption. 2. Electrolyte absorption. 3. Vitamin absorption- bacterial products Vit. K, B complex (B1, B2). Vitamin K is necessary for formation of clotting proteins in the liver. If given wide spectrum antibiotics that kills off bacteria, give Vit. K injections. 4. Formation of feces (stool, solid waste (hopefully)). As feces enter and fill the rectum, stretch receptors initiate a defecation reflex that empties the rectum to the anal canal. Once the reflex is triggered, only the voluntary external sphincter is holding the feces back so voiding can be postponed until an appropriate time.
18 Functions of the Liver 1. Detoxification: detoxifies alcohol, drugs, and other substances or modifies them so they are less toxic. 2. Bile formation 3. Metabolism and storage of many nutrients, vitamins, and minerals 4. Storage reservoir of blood in veins. 5. Cleanses blood from gut of bacteria. 6. Produces blood in fetus. 7. Destroys old RBC. The heme portion is absorbed as bilirubin that is secreted in the bile.
19 Hours a b c d e c a d b e
20 Intermediary Metabolism Intermediary metabolism is all the thousands of different chemical reactions in your cells. Intermediary metabolism mainly manages carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. To burn glucose, lipids, proteins, all use same reactions: 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs cycle- CO 2 and H 2 0 are wastes 3. Electron transport system (ETS)- needs O 2, = aerobic respiration makes most ATP If no O 2 = anaerobic respiration occurs = fermentation = lactic acid is produced
21 Intermediary Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Catabolism = oxidation = cellular respiration = chief source of ATP. CO 2, H 2 0 are wastes. Makes most of ATP, needs O 2 (aerobic respiration). If no O 2 = anaerobic reactions = fermentation = lactic acid. Anabolism Some glucose is converted to glycogen for storage. Can be reconverted to glucose for ATP. A.a., glycerol, lactic acid can be converted to glucose too. Triglycerides Catabolism Broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. Burned for energy in Krebs-ETS. Ketone bodies appear in large amounts during a diabetic crisis. Anabolism Synthesis of triglycerides from glucose and fatty acids = lipogenesis. Stored in adipose tissue.
22 Intermediary Metabolism Protein Catabolism Ammonia converted to urea in liver, excreted in urine. Can be converted to glucose, fatty acids, of ketone bodies. Anabolism Protein synthesis is directed by DNA and carried out by RNA and ribosomes.
23 Disorders of Digestive Tract Diarrhea - defecation of liquid stool. Caused by increased motility and decreased absorption of water by the intestines. Diarrhea can be caused by microbes (toxins or intestinal wall invasion), certain foods (some fruits increase motility) (lactose intolerance, enzyme deficiency with increased osmolarity in lumen), stress (anxiety increases parasympathetic activity to lower bowel with increased motility). Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance may occur if prolonged. Constipation - infrequent of difficult defecation due to lack of motility. Feces remain in colon too long with excessive water absorption so feces become dry and hard. Causes include lack of fiber in diet, improper bowel habits (failure to heed the call), lack of exercise, emotional upset, lack of adequate fluid intake.
24 Disorders of Digestive Tract Ulcers PUD = peptic ulcer disease = a crater like lesion in the gastro/intestinal membrane exposed to acidic gastric juice. Usually occurs in pyloric region (10%) or first part of duodenum (90%). Serious bleeding can occur (GI bleed) with anemia. 3 causes: a. Bacteria = Helicobacter pylori. b. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin. c. hypersecretion of HCl, e.g. a gastrin producing tumor. Food Poisoning Microbes can cause irritation of the intestines by direct invasion of the intestinal wall or by secreting toxins. Microbes find their way into foods where they multiply. Common causes are Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Staphylococcus toxin.
25 Disorders of Digestive Tract Botulism Ingested toxin poisoning that is produced by Clostridium botulinum. Found in improperly cooked non acidic foods. The toxin inhibits ACh release so skeletal muscle paralysis results: blurred vision, difficult breathing, swallowing, speech, general weakness.
26 Assignment 8 1. What part of the brain controls appetite? 2. Summarize each of the 6 hypotheses covered in lecture that serve to attempt to explain how appetite may be controlled. 3. Based on your own eating behavior, state which 2 hypotheses you can specifically relate to and why.
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Outline Digestive System
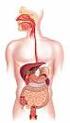 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
The Digestive System
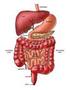 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
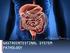 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
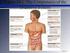 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Physiology of Digestive system II
 Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15
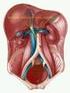 Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
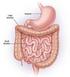 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
26. Digestive System
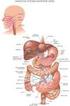 26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14
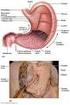 Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
The Digestive System
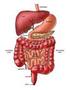 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm.
 Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Introduction. Digestive System. Physiology. Anatomy. Physiology. Alimentary Canal. Chapter 21
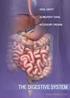 Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
The Digestive System
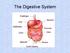 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Weds 5/20/15. Membranes - finish last lecture outline. Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system
 Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
Digestion. Processing of food Types. Mechanical (physical) Chemical. Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix. Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis
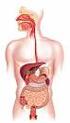 Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE
 CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
Session 20. The Digestive Organs. Session Outline. Introduction. Unit 6 Digestive System
 Unit 6 Digestive System Session 20 The Digestive Organs Session Outline Introduction 20.1Alimentary tract 20.2 Mouth 20.3Tongue 20.4Teeth 20.5Oesophagus 20.6 Stomach 20.7Small intestine 20.8 large intestine
Unit 6 Digestive System Session 20 The Digestive Organs Session Outline Introduction 20.1Alimentary tract 20.2 Mouth 20.3Tongue 20.4Teeth 20.5Oesophagus 20.6 Stomach 20.7Small intestine 20.8 large intestine
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made
GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is broken down by the teeth and the enzyme action of the saliva. The muscular
GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is broken down by the teeth and the enzyme action of the saliva. The muscular
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Chapter 25. The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function
 Chapter 25 The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function Gross Anatomy of Stomach Diaphragm Lesser omentum Lesser curvature Pyloric region: Antrum Pyloric canal Pylorus Pyloric sphincter Fundic
Chapter 25 The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function Gross Anatomy of Stomach Diaphragm Lesser omentum Lesser curvature Pyloric region: Antrum Pyloric canal Pylorus Pyloric sphincter Fundic
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry
 NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
BILIOPANCREATIC DIVERSION WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY
 WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made in conjunction
WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made in conjunction
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Classifications of animals: ruminant vs non-ruminant carnivore: meat-eating herbivore: plant-eating omnivore: both meat and plant-eating
 Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
