3 PART ONE: The Principles of Hematology PART TWO: Erythrocytes 89 5
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Francis
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTENTS Preface iv PART ONE: The Principles of Hematology 1 1 Safety and Quality in the Hematology Laboratory An Overview of the Hematology Laboratory 1 The Study of Hematology 1 Functions of the Hematology Laboratory 1 Safety in the Hematology Laboratory 2 The Safety Officer 2 Occupational Safety and Health Administration Acts and Standards 2 Avoiding Transmission of Infectious Diseases 3 Immune Status: Screening and Vaccination 5 Safe Work Practices and Protective Techniques for Infection Control 6 Safety Manual, Policies, and Practices 6 Standard Precautions 6 Handwashing 6 Personal Protective Equipment 7 Decontamination of Work Surfaces, Equipment, and Spills 8 General Infection Control Safety Practices 9 OSHA Medical Waste Standards 11 Quality Assessment in the Hematology Laboratory 12 Regulations and Organizations Impacting Quality 12 Components of Quality Assessment 12 Nonanalytical Factors in Quality Assessment 12 Quality Control in the Hematology Laboratory 16 Terms Used in Clinical Quality Control 16 Functions of a Quality Control Program 17 Using Statistical Analysis of Results in Quality Assessment 18 Other Statistical Applications in the Hematology Laboratory 20 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 20 REVIEW QUESTIONS 21 BIBLIOGRAPHY 23 2 Principles of Blood Collection Quality in Phlebotomy 25 Quality Assessment 25 Patient Care Partnership 25 The Phlebotomist as Laboratory Ambassador 26 Patients with Special Considerations 26 Pediatric Patients 26 Adolescent Patients 26 Geriatric Patients 26 Blood Collection Supplies and Equipment 26 Anticoagulants 26 Adverse Effects of Additives 27 Safe Blood Collection 27 Evacuated Blood Collection Tubes 29 Anticoagulants and Additives in Evacuated Blood Tubes 31 Capillary Blood 31 Specimen Handling Requirements 32 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 45 REVIEW QUESTIONS 47 REFERENCE 48 BIBLIOGRAPHY 48 3 Molecular Genetics and Cellular Morphology Cellular Ultrastructure and Organization 50 Cellular Membranes 50 Cell Volume Homeostasis 52 Reactive and Neoplastic Growth Processes 53 Cytoplasmic Organelles and Metabolites 53 Cellular Inclusions and Metabolites 54 Nuclear Characteristics 54 Chromosomes 56 Activities of the Nucleus 58 The Foundations of Genetic Interactions 60 Genetic Alterations 61 Molecular Techniques in Hematology 63 Minimal Residual Disease 63 Hematopathology 67 Gene Rearrangement Studies 69 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 69 REVIEW QUESTIONS 70 BIBLIOGRAPHY 72 4 Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis Defined 73 Origin of Blood Cells 73 Types of Human Stem Cells 73 Early Development of Blood Cells 73 Bone Marrow Sites and Function 75 Cellular Elements of Bone Marrow 76 Progenitor Blood Cells 76 Erythropoiesis 79 Granulopoiesis 79 Lymphopoiesis 79 Megakaryopoiesis 79 Other Cells Found in Bone Marrow 79 Interleukins 79 Hematopoietic Growth Factors 82 Examination of Maturing Blood Cells 83 General Cellular Characteristics 83 Nuclear Characteristics 83 Cytoplasmic Characteristics 85 Mature Blood Cells in Peripheral Blood 86 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 86 REVIEW QUESTIONS 87 BIBLIOGRAPHY 87 PART TWO: Erythrocytes 89 5 Erythrocyte Maturation, Physiology, and Lifecycle Erythropoiesis 90 Erythropoietin 90 General Characteristics of Maturation and Development 91 Developmental Stages 92 Reticulocytes 94 vi
2 Contents vii Disorders Related to Erythrocyte Maturation and Production 97 Disorders of Erythropoietin 97 Red Cell Increases 98 Defective Nuclear Maturation 98 Characteristics and Biosynthesis of Hemoglobin 98 Genetic Inheritance of Hemoglobin 98 Chemical Composition and Configuration of Hemoglobin 98 The Role of 2,3-Diphosphoglycerate 99 Oxygen Dissociation and Alterations 99 Carbon Dioxide Transport 100 Biosynthesis of Hemoglobin 101 Disorders Related to Hemoglobin Biosynthesis 104 Disorders of Heme (Porphyrin) Synthesis 104 Disorders of Iron Metabolism 105 Disorders of Globulin Synthesis 108 Ontogeny of Hemoglobin 108 Variant Forms of Normal Hemoglobin 109 Abnormal Hemoglobin Molecules 110 Analysis of Hemoglobin 110 Membrane Characteristics and Metabolic Activities of Erythrocytes 111 Membrane Characteristics 112 Cytoplasmic Characteristics 113 Metabolic Activities 113 Catabolism of Erythrocytes 114 Measurement of Erythrocytes 116 Mean Corpuscular Volume 116 Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin 117 Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration 117 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 118 CASE STUDIES 119 REVIEW QUESTIONS 121 BIBLIOGRAPHY Erythrocyte Morphology and Inclusions Erythrocytes: Normal and Abnormal 126 Types of Variations in Erythrocyte Size 126 Kinds of Variations in Erythrocyte Shape 127 Alterations in Erythrocyte Color 134 Varieties of Erythrocyte Inclusions 135 Alterations in Erythrocyte Distribution 137 Parasitic Inclusions in Erythrocytes 137 Malaria 137 Other Parasitic Inclusions 141 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 142 CASE STUDY 142 REVIEW QUESTIONS 143 BIBLIOGRAPHY Classification and Laboratory Assessment of Anemias Causes of Anemia 145 Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Anemia 145 Classification of Anemias 145 Laboratory Assessment of Anemias 146 Quantitative Measurements of Anemia 147 Semiquantitative Grading of Erythrocyte Morphology 147 Supplementary Assessment of Anemias 148 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 148 REVIEW QUESTIONS 148 BIBLIOGRAPHY Acute and Chronic Blood Loss Anemias Acute Blood Loss Anemia 150 Etiology 150 Physiology 150 Laboratory Findings 150 Chronic Blood Loss Anemia 150 Etiology 150 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 151 CASE STUDIES 151 REVIEW QUESTIONS 153 BIBLIOGRAPHY Aplastic and Related Anemias Aplastic Anemia 154 Etiology 154 Pathophysiology 155 Clinical Features 158 Laboratory Findings 158 Treatment 158 Congenital Red Blood Cell Related Disorders 159 Telomeres 159 Laboratory Findings in Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes 160 Pure Red Cell Aplasia 160 Diamond-Blackfan Anemia 160 Fanconi Anemia 161 Transient Erythroblastopenia of Childhood 162 Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anemia 163 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 163 CASE STUDIES 163 REVIEW QUESTIONS 165 BIBLIOGRAPHY Iron Deficiency Anemia and Anemia of Chronic Inflammation Scope of the Problem 166 Iron Deficiency Anemia 166 Early Diagnosis 166 Etiology 166 Epidemiology 167 Physiology 168 Pathophysiology 169 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 170 Laboratory Characteristics 170 Anemia of Inflammation or Anemia of chronic Disorders 173 Etiology 173 Pathophysiology 173 Laboratory Characteristics 174 Treatment 175 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 175 CASE STUDIES 176 REVIEW QUESTIONS 179 BIBLIOGRAPHY Megaloblastic Anemias Megaloblastic Anemias 181 Etiology 181 Epidemiology 182 Physiology 182 Vitamin B 12 (Cobalamin) Transport 182 Vitamin B 12 (Cobalamin) and Folic Acid Deficiencies 183 Pathophysiology 184 Gastric Pathological Findings 184 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 186 Laboratory Findings 186 Treatment and Monitoring Therapy 188 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 188 CASE STUDY 190 REVIEW QUESTIONS 191 BIBLIOGRAPHY 191
3 viii Contents 12 Hemolytic Anemias Hemolytic Anemias 192 Inherited Hemolytic Anemia 192 Acquired Hemolytic Anemia 197 Pathophysiology 200 Diagnostic Tests 201 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria 201 Etiology 201 Epidemiology 202 Pathophysiology 202 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 202 Laboratory Findings 203 Treatment 203 Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria 203 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 203 CASE STUDIES 204 REVIEW QUESTIONS 207 BIBLIOGRAPHY Hemoglobinopathies and Thalassemias Hemoglobin Defects 210 Demographics 210 Etiology 210 Sickle Cell Disease 211 Etiology 212 Epidemiology 212 Pathophysiology 212 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 213 General Signs and Symptoms 214 Laboratory Testing 214 Special Laboratory Testing 215 Management of Sickle Cell Disease 216 Sickle Cell Syndromes: Pathogenesis and New Approaches 218 Sickle b-thalassemia 218 Sickle-C Disease 219 Sickle Cell Trait 219 Thalassemia 220 Demographics 220 Etiology 220 Pathophysiology 220 b-thalassemia 220 α-thalassemia 223 Other Hemoglobinopathies 224 Hemoglobin C Disease 224 Hemoglobin SC Disease 224 Hemoglobin D Disease 224 Hemoglobin E Disease 224 Hemoglobin H Disease 225 Methemoglobinemia 225 Unstable Hemoglobins 225 Hereditary Persistance of Fetal Hemoglobin 225 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 226 CASE STUDIES 227 REVIEW QUESTIONS 232 BIBLIOGRAPHY 233 PART THREE: Leukocytes Leukocytes: The Granulocytic and Monocytic Series Introduction 235 The Granulocytic Series 235 Production of Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils 235 Sites of Development and Maturation 236 Development and Proliferation of Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils 236 Distribution of Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils 236 Normal Maturational Characteristics of Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils 237 Mature Forms 239 Granulation in Mature Forms 239 The Monocytic-Macrophage Series 240 Production and Development of Monocytes and Macrophages 240 Morphological Characteristics 241 Reference Ranges of Granulocytes and Monocytes 241 Functional Properties of Granulocytes and Monocytes 242 General Characteristics 243 The Role of Macrophages 243 Acute Inflammatory Response 243 Sepsis 245 Steps in Phagocytosis 245 Specialized Functions of Granulocytes 247 Assessment Methods 248 Total Leukocyte Count 248 Differential Blood Smear Evaluation 248 Absolute Cell Counts 248 Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate 248 Assessment of Eosinophils and Basophils 249 Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Test 249 Neutrophilic Function 249 Neutrophilic Hypersegmentation Index 249 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 249 CASE STUDY 250 REVIEW QUESTIONS 251 BIBLIOGRAPHY Nonmalignant Disorders of Granulocytes and Monocytes Quantitative Disorders 254 Leukocytosis 254 Leukocytopenia 255 Morphological Abnormalities of Mature Granulocytes 256 Toxic Granulation 256 Döhle Bodies 256 Hypersegmentation 256 Pelger-Huët Anomaly 256 May-Hegglin Anomaly 257 Chédiak-Higashi Syndrome 257 Alder-Reilly Inclusions 258 Ehrlichia 258 Abnormalities of Mature Granulocytes in Body Fluids 258 Qualitative Disorders 258 Defective Locomotion and Chemotaxis 258 Defects in Microbicidal Activity 259 Other Functional Anomalies of Neutrophils 259 Monocyte-Macrophage Disorders 259 Gaucher Disease 259 Niemann-Pick Disease 260 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 260 CASE STUDIES 260 REVIEW QUESTIONS 264 BIBLIOGRAPHY Leukocytes: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Anatomical Origin and Development of Lymphocytes 266 Sites of Lymphocytic Development 266 Lymphocyte Physiology 267 Normal Reference Values 267 Determining Absolute Lymphocyte Values 268 Morphological Characteristics of Normal Lymphocytes 268 Maturational Stages 269 Specific Lymphocyte Morphological Variations 272
4 Contents ix Characteristics of Lymphocytes 273 Major Lymphocyte Categories and Functions 273 Monoclonal Antibodies 274 Major Lymphocyte Membrane Characteristics and Development 274 Functional Testing of Lymphocytes 277 Plasma Cell Development and Maturation 277 Plasma Cell Development 277 Maturational Morphology 277 Plasmacytoid Lymphocytes 277 Plasma Cell Disorders 278 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 278 REVIEW QUESTIONS 279 BIBLIOGRAPHY Leukocytes: Nonmalignant Lymphocytic Disorders Characteristics of Lymphocytes 281 Lymphocytosis 281 Disorders Associated with Lymphocytosis 282 Infectious Mononucleosis 282 Cytomegalovirus Infection 286 Toxoplasmosis 287 Infectious Lymphocytosis 288 Bordetella pertussis (Haemophilus pertussis) Infection 289 Lymphocytopenia 289 Immune Disorders Associated with Lymphocytopenia 289 DiGeorge Syndrome 289 Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome(HIV/AIDS) 289 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 293 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 294 CASE STUDIES 294 REVIEW QUESTIONS 297 BIBLIOGRAPHY Characteristics of Leukemias, Lymphomas, and Myelomas Comparison of Leukemias, Lymphomas, and Myelomas 298 Forms of Leukemia 298 Classifications of Leukemias 299 French-American-British Classification 299 World Health Organization Classification 299 Prognosis and Treatment 300 Factors Related to the Occurrence of Leukemia 300 Genetic and Immunological Factors 300 Occupational Exposure 302 Environmental Exposure 302 Chemical and Drug Exposure 302 Genetic Abnormalities and Associations 302 Viral Agents 303 Secondary Causes of Leukemias 303 Demographic Distribution of Leukemia and Lymphomas 304 Ethnic Origin and Race 304 Gender 305 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 305 REVIEW QUESTIONS 306 BIBLIOGRAPHY Acute Leukemias Introduction 307 Epidemiology of Acute Leukemias 307 Prognosis of Acute Leukemias 308 French-American-British and World Health Organization Categories 308 French-American-British (FAB) Classification 308 World Health Organization (WHO) Organization Classfication 308 General Characteristics of Acute Myeloid Leukemias 309 Genetic Differences 309 Micro-RNAs 310 Acute Myeloid Leukemia 310 FAB M0 311 Acute Myeloid Leukemia (FAB M1) 311 Acute Myeloid Leukemia (FAB M2) 312 Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (FAB M3) 312 Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia (FAB M4) 313 Acute Monocytic Leukemia (FAB M5) 314 Erythroleukemia (FAB M6) 315 Selected Examples of Unusual Forms 316 Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia FAB M7 316 Epidemiology of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 316 Prognosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 317 Classifications of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 317 Characteristics of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 317 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 317 Laboratory Data 317 Special Identification Techniques 318 Treatment 319 Mixed Lineage Leukemia 319 Cytogenetic Analysis 319 Cytogenetic Analysis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia 319 Cytogenetics in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 320 Principles of Special Cytochemical Stains 320 Sudan Black B Stain 321 Myeloperoxidase Stain 326 Periodic Acid-Schiff Stain 322 Esterase Stains 323 Phosphatase Stains 324 Monoclonal Antibodies 325 Immunophenotyping 325 Lymphoid 325 Other Surface Membrane Markers 326 Life-Threatening Emergencies 326 Infection 326 Bleeding 326 Leukemic Infiltration of Organs 326 Metabolic Abnormalities 326 Hyperleukocytosis 327 Treatment Options 327 Relapse 328 Stem Cell Transplant 328 Future Trends Vaccines 328 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 328 CASE STUDIES 329 REVIEW QUESTIONS 333 BIBLIOGRAPHY Lymphoid and Plasma Cell Neoplasms Mature B-Cell Neoplasms Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma 337 Epidemiology 337 Etiology 337 Cytogenetics 338 Molecular Genetics 339 Staging and Prognosis 339 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 340 Laboratory Data 341 Treatment Options 341 Minimal Residual Disease 342 Hairy Cell Leukemia 342 Hairy Cell Leukemia Variant 343 Prolymphocytic Leukemia 344
5 x Contents Multiple Myeloma (Plasma Cell Myeloma) 344 Epidemiology 344 Etiology 344 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 344 Laboratory Data 344 Treatment 345 Waldenström Primary Macroglobulinemia (Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma) 346 Epidemiology 346 Etiology 346 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 346 Laboratory Data 346 Treatment 347 Lymphomas 347 Relationship Between Lymphomas and Leukemias 347 Characteristics 347 Categories 347 Pathophysiology 349 Precursors of Hodgkin Disease and B-Cell Lymphomas 350 Hodgkin Disease 350 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 351 Characteristics of Other Forms 352 Sézary Syndrome 353 Mature T-Cell and NK-Cell Neoplasms 353 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 353 CASE STUDIES 354 REVIEW QUESTIONS 358 BIBLIOGRAPHY 358 PART FOUR: Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Myeloproliferative Neoplasms General Characteristics of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms 362 Relationship of the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms 362 Common Disorders of Hemostasis and Coagulation 362 Prognosis and Treatment 363 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia 363 Epidemiology 363 Pathophysiology 363 Cytogenetics 364 Genetic Alterations 364 Laboratory Data 365 Cytogenetic Studies 367 Prognosis and Treatment 367 Minimal Residual Disease 368 Leukemia-Specific Targets 369 Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation 370 Polycythemia Vera, Essential Thrombocytosis (Essential Thrombocythemia), and Primary Myelofibrois 370 Polycythemia Vera 370 Epidemiology 370 Etiology 370 Pathophysiology 370 Karyotype 371 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 371 Laboratory Data 371 Abnormalities of Hemostasis and Coagulation 372 Other Laboratory Assays 372 Treatment 373 Prognosis and Complications 374 Primary Myelofibrosis 374 Epidemiology 374 Pathophysiology 374 Karyotype 375 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 375 Cellular Alterations 375 Prognosis 376 Treatment 376 Essential Thrombocytosis/Essential Thrombocythemia 376 Diagnostic Characteristics 376 Epidemiology 377 Pathophysiology 377 Karyotype 377 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 377 Laboratory Findings 377 Relationship of Thrombocythemia and PV 377 Treatment 378 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 378 CASE STUDIES 379 REVIEW QUESTIONS 382 BIBLIOGRAPHY Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myelodysplastic/ Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Classification 386 Myelodysplastic Syndromes 386 Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms 386 Pathophysiology 387 Myelodysplastic Syndrome 387 Etiology 388 Epidemiology 389 Chromosomal Abnormalities 389 Clinical Signs and Symptoms 390 Laboratory Manifestations 390 Features of Selected Types of Myelodysplastic Syndromes 391 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms 392 Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia 392 Other Classifications 393 Treatment Strategies 393 Relationship of Karyotype to Prognosis 394 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 395 CASE STUDIES 396 REVIEW QUESTIONS 397 BIBLIOGRAPHY 398 PART FIVE: Principles and Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis Principles of Hemostasis and Thrombosis Overview of Hemostasis and Thrombosis 400 Blood Vasculature: Structure and function 400 Arteries and Veins 400 Arterioles and Venules 400 Capillaries 400 Vasculature Physiology 401 The Role of Vasoconstriction in Hemostasis 401 The Role of the Endothelium 401 Maintenance of Vascular Integrity 402 The Megakaryocytic Cell Series 403 General Characteristics of Megakaryocytic Development 403 Cellular Ultrastructure of a Mature Platelet 405 Platelet Kinetics, Life Span, and Normal Values 406 Platelet Function in Hemostasis 406 Overall Functions of Platelets 406 Platelet Adhesion 406 Platelet Aggregation 407 Platelet Plug Consolidation and Stabilization 408 Laboratory Assessment of Platelets 408
6 Contents xi Blood Coagulation Factors 410 Basic Concepts of Blood Coagulation 410 Common Characteristics of Coagulation Factors 410 Characteristics of Individual Factors 410 The Mechanism of Coagulation 413 Coagulation Pathways 413 Thrombin-Mediated Reactions 414 Fibrinolysis 414 Other Systems and Inhibitors 415 Laboratory Assessment of Blood Coagulation Factors 416 International Normalized Ratio 416 Specialized Assays for Coagulation Factors 417 Anticoagulants 417 New Thromboplastins 418 Assays for Fibrin Formation 419 Normal Protective Mechanisms Against Thrombosis 420 Normal Blood Flow 420 Removal of Activated Clotting Factors and Particulate Material 420 The Natural Anticoagulant Systems 420 Cellular Regulators 424 Modern View of Hemostasis 424 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 424 REVIEW QUESTIONS 426 BIBLIOGRAPHY Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis Vascular Disorders 431 Abnormal Platelet Morphology 432 Quantitative Platelet Disorders 432 Thrombocytopenia 432 Thrombocytosis 436 Qualitative Characteristics of Platelets: Thrombocytopathy 436 Types of Platelet Dysfunctions 437 Bleeding Disorders Related to Blood Clotting 439 Defective Production 440 Disorders of Destruction and Consumption 445 Disorders Related to Elevated Fibrin Split Products 449 The Hypercoagulable State 450 Primary States of Hypercoagulability 450 Secondary States of Hypercoagulability 450 Pregnancy-Associated Thrombosis 450 General Features 451 Impaired Fibrinolysis 454 Antithrombin III Deficiency 456 Laboratory Assessment of Hypercoagulable States 457 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 458 CASE STUDIES 460 REVIEW QUESTIONS 462 BIBLIOGRAPHY 463 PART SIX: Fundamentals of Hematological Analysis Body Fluid Analysis Introduction 466 Cerebrospinal Fluid 466 Anatomy and Physiology 466 Production of Cerebrospinal Fluid 466 Specimen Collection: Lumbar Puncture 466 Laboratory Analysis 467 Pleural, Peritoneal, and Pericardial Fluids 473 Effusions: Transudates and Exudates 473 Pleural Fluid 473 Peritoneal Fluid 478 Pericardial Fluid 482 Seminal Fluid 484 Synovial Fluid 486 Anatomy and Physiology of Joints 486 Purpose of Arthrocentesis 486 Aspiration 487 Laboratory Assays 487 Body Fluid Slide Preparation 490 Staining of Body Fluid Sediment 490 Amniotic Fluid 490 CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS 490 REVIEW QUESTIONS 493 BIBLIOGRAPHY Manual Procedures in Hematology Procedural Format 498 Coagulation Procedures 516 Specimen Quality 516 Special Collection Techniques 516 Anticoagulants 517 Specimen Handling 517 Specimen Preparation 517 General Sources of Error 517 Quality Control 518 REVIEW QUESTIONS Instrumentation in Hematology Instrumental Principles 527 The Electrical Impedance Principle 527 The Optical Detection Principle 527 Characteristics of Light Scatter 527 Radio Frequency 528 Fundamentals of Laser Technology 528 Principles of Flow Cytometry 529 The Basis of Cellular Identification 529 Whole Blood Cell Analysis 531 Types of Automated Cell Counting Instruments 532 General Histogram Characteristics 543 Analysis of Instrumental Data Output 543 The Erythrocyte Histogram 543 Quantitative Descriptors of Erythrocytes 543 The Leukocyte Histogram 544 Platelet Histograms 545 Derived Platelet Parameters 546 Laser Technology 547 Red Blood Cells/Platelets 547 Peroxidase 548 Basophil/Lobularity (Nuclear) Channel 549 Lymphocyte Subtyping 549 Applications of Flow Cytometry 549 General Properties of Flow Cytometry 550 Hematological Applications 550 Clinical Applications of Flow Cytometry 550 Other Cellular Applications 551 Digital Microscopy 554 Artificial Neural Networks 554 Digital Cell Morphology 554 Instruments in Coagulation Studies 555 Electromechanical Methods 555 Photo-Optical Methods 555 Viscosity-based Detection System 558 Platelet Agglutination 559 Platelet Aggregation 559 New Automation 559 Summary 559 Instrumental Principles 559 Analysis of Electrical Impedance Instrumental Data Output 559
7 xii Contents Laser Technology 560 Applications of Flow Cytometry 560 Instruments in Coagulation Studies 560 CASE STUDIES 560 REVIEW QUESTIONS 569 BIBLIOGRAPHY 571 APPENDICES A Answers to Review Questions B The Basics of Medical Terminology C SI Units D English-Spanish Medical Phrases for the Phlebotomist E MSDS Sheet F Tube Guide G Frequently Used Abbreviations Glossary 591 Index 602
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e. Chapter 17: Blood
 Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
LYMPHOMA. BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons
 LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
Hematology Morphology Critique
 Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Cord blood Banking Transplant List for One USA Bank - StemCyte www.stemcyte.com/cordblood-banking-transplant-list
 Cells4Life is the oldest and largest cord blood storage company in the UK. We are governed by some of the world's most stringent medical laws, and are currently the only stem cell storage company in the
Cells4Life is the oldest and largest cord blood storage company in the UK. We are governed by some of the world's most stringent medical laws, and are currently the only stem cell storage company in the
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer
 Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology INTRODUCTION 2009 A university wishing to have an accredited program in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology must also
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology INTRODUCTION 2009 A university wishing to have an accredited program in Pediatric Hematology/Oncology must also
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Medical Laboratory Technology Program. Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives
 Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Estimated New Cases of Leukemia, Lymphoma, Myeloma 2014
 ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
Subtypes of AML follow branches of myeloid development, making the FAB classificaoon relaovely simple to understand.
 1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Introduction. About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each
 Introduction 1.1 Introduction: About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each year in the United States (Hope et al., 2003). Acute myelogenous leukemia has several names, including
Introduction 1.1 Introduction: About 10,500 new cases of acute myelogenous leukemia are diagnosed each year in the United States (Hope et al., 2003). Acute myelogenous leukemia has several names, including
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL VOLUME I RESPONSE ASSESSMENT LEUKEMIA CHAPTER 11A REVISED: OCTOBER 2015
 LEUKEMIA Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Response criteria in Acute Myeloid Leukemia for SWOG protocols is based on the review article Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults:
LEUKEMIA Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Response criteria in Acute Myeloid Leukemia for SWOG protocols is based on the review article Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood. Short Answer. Figure 10.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Young fetus: site of hematopoiesis together with the liver and bone marrow. Hgb WBC >----------< Plt Hct. Retic =
 Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Identify the components of the CBC and Differential and their clinical implications. 2. Identify normal pediatric
Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Identify the components of the CBC and Differential and their clinical implications. 2. Identify normal pediatric
information for payers and referrers
 a d u lt s t e m c e l l t r a n s p l a n tat i o n p r o g r a m information for payers and referrers Spring 2014 For more information, visit www.dfbwcc.org/bmt. o u r expertise Since its founding in
a d u lt s t e m c e l l t r a n s p l a n tat i o n p r o g r a m information for payers and referrers Spring 2014 For more information, visit www.dfbwcc.org/bmt. o u r expertise Since its founding in
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS
 Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS April - 2012 ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELL When a blood smear is inspected for abnormal
Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS April - 2012 ABNORMAL MORPHOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELL When a blood smear is inspected for abnormal
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Pre- Transformed Ig Surface Surface Secreted Myeloma Major malignant counterpart
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis
 Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis General Comments The laboratory studies listed below are helpful in the diagnosis and management
Laboratory Studies in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency, Latent Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficient Erythropoiesis General Comments The laboratory studies listed below are helpful in the diagnosis and management
immunologic-- immunophenotypes are found by monoclonal antibodies - B-progenitor cells T-progenitor cells, mature B cells
 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Childhood ALL was the first form of cancer shown to be curable with chemotherapy and irradiation. Lymphoid leukemias
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Childhood ALL was the first form of cancer shown to be curable with chemotherapy and irradiation. Lymphoid leukemias
Saving lives globally through mutual miracles. LifeCord is a public non-profit cord blood bank licensed by the FDA.
 Saving lives globally through mutual miracles LifeCord is a public non-profit cord blood bank licensed by the FDA. Donating your baby s cord to a public cord blood bank can save lives globally. You can
Saving lives globally through mutual miracles LifeCord is a public non-profit cord blood bank licensed by the FDA. Donating your baby s cord to a public cord blood bank can save lives globally. You can
Platelet Review July 2012. Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
 Platelet Review July 2012 Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Hemostasis Hemostasis is the process that leads to the stopping of bleeding Hemostasis involves blood vessels,
Platelet Review July 2012 Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Hemostasis Hemostasis is the process that leads to the stopping of bleeding Hemostasis involves blood vessels,
STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY
 9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions
 Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
What Leukemia Is. Understanding blood
 Leukemia is a malignant disease of the blood-forming cells. It involves white blood cells that do not mature and that reproduce too rapidly. Eventually, they replace the normal bone marrow, leaving insufficient
Leukemia is a malignant disease of the blood-forming cells. It involves white blood cells that do not mature and that reproduce too rapidly. Eventually, they replace the normal bone marrow, leaving insufficient
Diseases Treated by Blood Stem Cells
 Diseases Treated by Blood Stem Cells This is the only website to group hematopoietic (blood) stem cell treatments according to whether they are standard, in trial, or experimental. (Courtesy of Parents
Diseases Treated by Blood Stem Cells This is the only website to group hematopoietic (blood) stem cell treatments according to whether they are standard, in trial, or experimental. (Courtesy of Parents
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI
 Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - GRANULOCYTE FORMATION AND CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD
 ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
What Does My Bone Marrow Do?
 What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding.
 Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding. Bleeding may be spontaneous in the form of small haemorrhages into the
Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding. Bleeding may be spontaneous in the form of small haemorrhages into the
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010
 NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
Stem Cell Transplantation and the Canadian First Nations Community. Becky Luk (PTLS) Tanya Petraszko, MD
 Stem Cell Transplantation and the Canadian First Nations Community Becky Luk (PTLS) Tanya Petraszko, MD Why is there a need for stem cells? Our Story Why are we engaging the First Nations, Metis and Inuit
Stem Cell Transplantation and the Canadian First Nations Community Becky Luk (PTLS) Tanya Petraszko, MD Why is there a need for stem cells? Our Story Why are we engaging the First Nations, Metis and Inuit
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences
 Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S Mid AML 4321
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S Mid AML 4321
Myelodysplasia Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Plasma Cell (Multiple) Myeloma
 Myelodysplasia Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Plasma Cell (Multiple) Myeloma Hodgkin Lymphoma Overview Case Pathophysiology Diagnosis
Myelodysplasia Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Plasma Cell (Multiple) Myeloma Hodgkin Lymphoma Overview Case Pathophysiology Diagnosis
LAB: Blood Exploration
 Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
Interesting Case Review. Renuka Agrawal, MD Dept. of Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Duarte, CA
 Interesting Case Review Renuka Agrawal, MD Dept. of Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Duarte, CA History 63 y/o male with h/o CLL for 10 years Presents with worsening renal function and hypercalcemia
Interesting Case Review Renuka Agrawal, MD Dept. of Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Duarte, CA History 63 y/o male with h/o CLL for 10 years Presents with worsening renal function and hypercalcemia
MODERN HEMATOLOGY SECOND EDITION
 MODERN HEMATOLOGY SECOND EDITION CONTEMPORARY HEMATOLOGY Gary J. Schiller, MD, SERIES EDITOR Modern Hematology: Biology and Clinical Management, Second Edition, edited by REINHOLD MUNKER, ERHARD HILLER,
MODERN HEMATOLOGY SECOND EDITION CONTEMPORARY HEMATOLOGY Gary J. Schiller, MD, SERIES EDITOR Modern Hematology: Biology and Clinical Management, Second Edition, edited by REINHOLD MUNKER, ERHARD HILLER,
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2
 Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2 Leukaemia: Description A group of malignant disorders affecting: White blood cells (lymphocytes or leucocytes) Bone
Adult Medical-Surgical Nursing H A E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E : L E U K A E M I A 2 Leukaemia: Description A group of malignant disorders affecting: White blood cells (lymphocytes or leucocytes) Bone
CASE 2. Seven week old female infant presents with hepatosplenomegaly l and WBC 31.0k/mm 3, Hgb 9.2 g/dl, Plt 110k/mm 3 with 60% blasts
 CASE 2 Seven week old female infant presents with hepatosplenomegaly l and WBC 31.0k/mm 3, Hgb 9.2 g/dl, Plt 110k/mm 3 with 60% blasts A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate were performed (photos provided).
CASE 2 Seven week old female infant presents with hepatosplenomegaly l and WBC 31.0k/mm 3, Hgb 9.2 g/dl, Plt 110k/mm 3 with 60% blasts A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate were performed (photos provided).
www.lifesouthcord.org
 www.lifesouthcord.org www.lifesouth.org (888) 795-2707 LifeCord Gainesville, FL www.lifesouthcord.org John Wingard. M.D. LifeCord Medical Director Price Eminent Scholar and Professor of Medicine Deputy
www.lifesouthcord.org www.lifesouth.org (888) 795-2707 LifeCord Gainesville, FL www.lifesouthcord.org John Wingard. M.D. LifeCord Medical Director Price Eminent Scholar and Professor of Medicine Deputy
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma
 Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma
 Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma Luis Fayad, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medical Director Lymphoma/Myeloma Department Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non-Hodgkin s lymphomas (NHL) are a heterogeneous group of malignant
Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma Luis Fayad, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medical Director Lymphoma/Myeloma Department Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non-Hodgkin s lymphomas (NHL) are a heterogeneous group of malignant
CHAPTER 14: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: BLOOD. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. 2. Define the term hematology. 3. Name the average volume of blood in a human. 4. Name the two major components of blood
OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. 2. Define the term hematology. 3. Name the average volume of blood in a human. 4. Name the two major components of blood
PROGNOSIS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA PROGNOSIS IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA
 PROGNOSIS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA UNFAVORABLE Advanced age High leukocyte count at diagnosis Presence of myeloid antigens Late achievement of CR Chromosomal abnormalities: t(9:22)(q34:q11) t(4;11)(q21;q23)
PROGNOSIS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA UNFAVORABLE Advanced age High leukocyte count at diagnosis Presence of myeloid antigens Late achievement of CR Chromosomal abnormalities: t(9:22)(q34:q11) t(4;11)(q21;q23)
Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Acute leukemias and myeloproliferative neoplasms
 Acute leukemias and myeloproliferative neoplasms GERGELY SZOMBATH SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE IIIRD. DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Basics of acute leukemia Neoplastic disease Cell of origin is
Acute leukemias and myeloproliferative neoplasms GERGELY SZOMBATH SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE IIIRD. DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Basics of acute leukemia Neoplastic disease Cell of origin is
ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood
 70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
Dr. Vivian Pijuan-Thompson (Cytology) http://www.uab.edu/cds/academic/graduate/ct (Cytology)
 Clinical Laboratory Sciences (M.S.) Degree Offered: M.S. Directors: Dr. Janelle Chiasera, interim (CLS) Dr. Vivian Pijuan-Thompson (Cytology) Phone: (205) 975-3111 (Chiasera) (205) 934-3378 (Pijuan-Thompson)
Clinical Laboratory Sciences (M.S.) Degree Offered: M.S. Directors: Dr. Janelle Chiasera, interim (CLS) Dr. Vivian Pijuan-Thompson (Cytology) Phone: (205) 975-3111 (Chiasera) (205) 934-3378 (Pijuan-Thompson)
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) in children
 1 61.02 Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) in children AML can affect children of any age, and girls and boys are equally affected. Leukaemia Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) FAB classification of AML Causes of
1 61.02 Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) in children AML can affect children of any age, and girls and boys are equally affected. Leukaemia Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) FAB classification of AML Causes of
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY
 Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each
Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials
 LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT
 www.narayanahealth.org DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT About Narayana Health City Narayana Health, one of India's largest and the world's most economical healthcare service providers
www.narayanahealth.org DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT About Narayana Health City Narayana Health, one of India's largest and the world's most economical healthcare service providers
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Preparation of Blood Films
 Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Pathology No: SHS-CASE No. Date of Procedure: Client Name Address
 TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
TEL #: (650) 725-5604 FAX #: (650) 725-7409 Med. Rec. No.: Date of Procedure: Sex: A ge: Date Received: Date of Birth: Account No.: Physician(s): Client Name Address SPECIMEN SUBMITTED: LEFT PIC BONE MARROW,
STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA
 STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA OVO CLINIC I 8000 BLVD DECARIE, MONTREAL QC H4P 2S4 I 514.798.2000 I OVOCLINIC.COM 2 a therapeutic revolution As the
STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA OVO CLINIC I 8000 BLVD DECARIE, MONTREAL QC H4P 2S4 I 514.798.2000 I OVOCLINIC.COM 2 a therapeutic revolution As the
CAP Accreditation Checklists 2015 Edition
 CAP Accreditation Checklists 2015 Edition The College of American Pathologists (CAP) accreditation checklists contain the CAP accreditation program requirements, developed on more than 50 years of insight
CAP Accreditation Checklists 2015 Edition The College of American Pathologists (CAP) accreditation checklists contain the CAP accreditation program requirements, developed on more than 50 years of insight
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Haematopoietic Chimerism Analysis after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Haematopoietic Chimerism Analysis after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr Ros Ganderton, Ms Kate Parratt, Dr Debbie Richardson, Dr Kim Orchard and Dr Liz Hodges Departments of Molecular Pathology
Haematopoietic Chimerism Analysis after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr Ros Ganderton, Ms Kate Parratt, Dr Debbie Richardson, Dr Kim Orchard and Dr Liz Hodges Departments of Molecular Pathology
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
What we will discuss today
 Umbilical cord blood banking It s Utility? Dr. Nita Radhakrishnan Pediatric Hematology Oncology Unit, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi What we will discuss today What are stem cells? What are the sources
Umbilical cord blood banking It s Utility? Dr. Nita Radhakrishnan Pediatric Hematology Oncology Unit, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi What we will discuss today What are stem cells? What are the sources
Oncology Best Practice Documentation
 Oncology Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Solid Tumors Lymphomas Leukemias Myelodysplastic Syndrome Pathology Findings
Oncology Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Solid Tumors Lymphomas Leukemias Myelodysplastic Syndrome Pathology Findings
Immunophenotyping. Alberto Orfao, MD, PhD
 Immunophenotyping Alberto Orfao, MD, PhD Introduction Immunophenotyping of biological samples refers to the use of immunological tools (e.g. monoclonal and/or polyclonal antibodies) for the specific detection
Immunophenotyping Alberto Orfao, MD, PhD Introduction Immunophenotyping of biological samples refers to the use of immunological tools (e.g. monoclonal and/or polyclonal antibodies) for the specific detection
Childhood Leukemia. Normal bone marrow, blood, and lymphoid tissue
 Childhood Leukemia What is childhood leukemia? Cancer starts when cells start to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer. To learn more about how cancers start and spread,
Childhood Leukemia What is childhood leukemia? Cancer starts when cells start to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer. To learn more about how cancers start and spread,
Level Tow. Level Three
 Level One Code No Title Unit Eng 0012 English Language 2)2+1( Chm 0010 General Chemistry 2)2+1( Zoo 0010 General Biology 2)2+1( Com 0012 Introduction to Computer 2)2+1( Ter 0011 Medical Terminology 1)1+1(
Level One Code No Title Unit Eng 0012 English Language 2)2+1( Chm 0010 General Chemistry 2)2+1( Zoo 0010 General Biology 2)2+1( Com 0012 Introduction to Computer 2)2+1( Ter 0011 Medical Terminology 1)1+1(
Haematology what does your blood test mean?
 Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Platelet Transmission Electron Microscopy and Flow Cytometry 11/15/2015
 Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories Hot Topics. These presentations provide short discussion of current topics and may be helpful to you in your practice. Today our topic looks at hereditary platelet
Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories Hot Topics. These presentations provide short discussion of current topics and may be helpful to you in your practice. Today our topic looks at hereditary platelet
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Pre-HSCT Data
 Instructions for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Pre-HSCT Data (Form 2010) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the AML Pre-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Instructions for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Pre-HSCT Data (Form 2010) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the AML Pre-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears
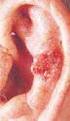 CHAPTER e17 Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears Dan L. Longo Some of the relevant findings in peripheral blood, enlarged lymph nodes, and bone marrow are illustrated in this chapter.
CHAPTER e17 Atlas of Hematology and Analysis of Peripheral Blood Smears Dan L. Longo Some of the relevant findings in peripheral blood, enlarged lymph nodes, and bone marrow are illustrated in this chapter.
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL BLOOD COMPONENT CRITERIA AND INDICATIONS SCREENING GUIDELINES
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL BLOOD COMPONENT CRITERIA AND INDICATIONS SCREENING GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS SUBJECT PAGE ADULT CRITERIA Red Blood Cells/Autologous 2 Washed Red Blood Cells 2 Cryoprecipitate
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL BLOOD COMPONENT CRITERIA AND INDICATIONS SCREENING GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS SUBJECT PAGE ADULT CRITERIA Red Blood Cells/Autologous 2 Washed Red Blood Cells 2 Cryoprecipitate
A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma
 A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma 1 A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma PREFACE Blood cancers and related disorders a serious health risk
A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma 1 A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma A Science Writer s Guide to Multiple Myeloma PREFACE Blood cancers and related disorders a serious health risk
BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation. Becky Luk, Patient & Transplant Liaison Specialist
 BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation Becky Luk, Patient & Transplant Liaison Specialist Our Story Why is there a need for stem cells? What is OneMatch Stem Cell & Marrow Newtork s role in Stem Cell
BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation Becky Luk, Patient & Transplant Liaison Specialist Our Story Why is there a need for stem cells? What is OneMatch Stem Cell & Marrow Newtork s role in Stem Cell
BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation. Our Story. Diseases treated with stem cell transplants. Why is there a need for stem cells?
 BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation Becky Luk, Patient & Transplant Liaison Specialist Our Story Why is there a need for stem cells? What is OneMatch Stem Cell & Marrow Newtork s role in Stem Cell
BCSLS Telehealth Stem Cell Transplantation Becky Luk, Patient & Transplant Liaison Specialist Our Story Why is there a need for stem cells? What is OneMatch Stem Cell & Marrow Newtork s role in Stem Cell
whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements
 bloodc components TERI JUNGE, CST/CFA whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements and the liquid element. The formed elements are cell fragments and cells, known as corpuscles, which
bloodc components TERI JUNGE, CST/CFA whole blood consists of two main elements: the formed elements and the liquid element. The formed elements are cell fragments and cells, known as corpuscles, which
FastTest. You ve read the book... ... now test yourself
 FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. Please refer back to relevant sections
FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. Please refer back to relevant sections
Hematopathology VII Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, And Hairy Cell Leukemia
 John L. Kennedy, M.D. UIC College of Medicine Associate Professor of Clinical Pathology M2 Pathology Course Lead Pathologist, VA Chicago Health Care System Lecture #43 Phone: (312) 569-6690 Thursday, November
John L. Kennedy, M.D. UIC College of Medicine Associate Professor of Clinical Pathology M2 Pathology Course Lead Pathologist, VA Chicago Health Care System Lecture #43 Phone: (312) 569-6690 Thursday, November
BLOOD Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 BLOOD Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of blood 1. Transport of substances: like Oxygen, CO2, nutrients, waste, heat, and hormones. 2. Protection: maintenance of normal Ph, normal body fluid volume, hemostasis,
BLOOD Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of blood 1. Transport of substances: like Oxygen, CO2, nutrients, waste, heat, and hormones. 2. Protection: maintenance of normal Ph, normal body fluid volume, hemostasis,
Anemia and Leukocytosis Answers
 Case #1 RBC abnormalities Anemia and Leukocytosis Answers History: A 19-year-old woman with anemia presents with a two day history of fever, joint pain, and left upper quadrant discomfort. She reports
Case #1 RBC abnormalities Anemia and Leukocytosis Answers History: A 19-year-old woman with anemia presents with a two day history of fever, joint pain, and left upper quadrant discomfort. She reports
INFORMATION KIT. americordblood.com 866.503.6005
 INFORMATION KIT americordblood.com 866.503.6005 QUALITY INNOVATION VALUE AMERICORD S FULL SUITE OF STEM CELL BANKING PRODUCTS CORD BLOOD 2.0 CORD TISSUE BANKING PLACENTA TISSUE BANKING Preserve up to two
INFORMATION KIT americordblood.com 866.503.6005 QUALITY INNOVATION VALUE AMERICORD S FULL SUITE OF STEM CELL BANKING PRODUCTS CORD BLOOD 2.0 CORD TISSUE BANKING PLACENTA TISSUE BANKING Preserve up to two
Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood
 Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
Application Note Primary Cell Analysis Enumeration and Viability of Nucleated Cells from Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, and Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cell Viability Introduction: Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Stem
Leukemia Acute Myeloid (Myelogenous)
 Leukemia Acute Myeloid (Myelogenous) What is acute myeloid leukemia? Cancer starts when cells in a part of the body begins to grow out of control and can spread to other areas of the body. There are many
Leukemia Acute Myeloid (Myelogenous) What is acute myeloid leukemia? Cancer starts when cells in a part of the body begins to grow out of control and can spread to other areas of the body. There are many
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Blood. Blood. Blood Composition. Blood Composition. Fractionation & Hemopoesis
 Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count
 RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count The most important components of a Full Blood Count report are, of course, the Haemoglobin, the White Cell Count and Differential and the Platelet Count. However,
RDW-- Interpreting the Full Blood Count The most important components of a Full Blood Count report are, of course, the Haemoglobin, the White Cell Count and Differential and the Platelet Count. However,
 About B Cell Lymphomas Groupmeeting Klipp/Spang, December 09 2002 Dennis Kostka Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Genetics Computational Molecular Biology Berlin 1 Overview Short History of Lymphoma Classification
About B Cell Lymphomas Groupmeeting Klipp/Spang, December 09 2002 Dennis Kostka Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Genetics Computational Molecular Biology Berlin 1 Overview Short History of Lymphoma Classification
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
