Anesthesia and Critical Care (updated 09/06)
|
|
|
- Prudence Pierce
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anesthesia and Critical Care (updated 09/06) 1. What is the mechanism of action of a local anesthetic? Discuss amides and esters. AL Local anesthetics produce anesthesia by inhibiting excitation of nerve endings or by blocking conduction in peripheral nerves. This is achieved by anesthetics reversibly binding to and inactivating sodium channels. Sodium influx through these channels is necessary for the depolarization of nerve cell membranes and subsequent propagation of impulses along the course of the nerve. When a nerve loses depolarization and capacity to propagate an impulse, the individual loses sensation in the area supplied by the nerve. The order of affinity of local anesthetics for different sodium channel states is open is better than inactivated, which is better than resting. Thus, the open state of the sodium channel is the primary target of local anesthetic molecules. The blocking of propagated action potentials is therefore a function of the frequency of depolarization. The mechanism for differential block, the block of pain perception without motor block, is still unclear. Amino esters and amino amides differ in several respects. Amino esters: are metabolized in the plasma via pseudocholinesterases, unstable in solution, much more likely than amino amides to cause allergic hypersensitivity reactions. Ex: lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, bupivacaine, etidocaine, and ropivacaine and levobupivacaine, shorter duration of action Amino amides: are metabolized in the liver with renal excretion, very stable in solution. Ex: cocaine, procaine, tetracaine, chloroprocaine, and benzocaine Physiologic activity of local anesthetics is a function of their lipid solubility, diffusibility, affinity for protein binding, percent ionization at physiologic ph, and vasodilating properties. Potency is directly related to lipid solubility, increased lipid solubility leads to faster nerve penetration and blockade of sodium channels.
2 Protein binding is related to the duration of action Ionized vs. Non ionized forms: non-ionized portion is the form that is capable of diffusing across nerve membranes and blocking sodium channels, causes a faster onset of action. Decreases in ph of tissues shifts equilibrium towards the ionized form causing delayed onset of action. All local anesthetics, with the exception of cocaine, are vasodilators. Vasodilation occurs via direct relaxation of peripheral arteriolar smooth muscle fibers. Greater vasodilator activity of a local anesthetic leads to faster absorption and, thus, shorter duration of action. To counteract this vasodilatation, epinephrine is often included in local anesthetic solutions 2. Are the effects of amides and esters additive? CB 3. You are operating on a 10-year-old who weighs 30 kg. How much Lidocaine can you give him? What are the symptoms of toxicity? How do you treat it? How does Lidocaine work? AL Lidocaine is an amide local anesthetic and a less commonly used antiarrhythmic that exerts its effects on nerve axon sodium channels, preventing depolarization. Lidocaine: 1% =10mg/ml Without Epi 5mg/kg = 150 mg or 15 ml with Epi or phenylephrine give 7 mg/kg = 210 mg or 21 ml Adverse reactions occur primarily in the CNS (neurotoxicity) and cardiovascular system (myotoxicity) because these tissues are also composed of excitable membranes, the target of local anesthetic action. In the CNS, a progression of signs and symptoms may be observed in the patient. The patient may report lightheadedness, tinnitus, circumoral numbness, a metallic taste, or double vision. Upon examination, the patient may become drowsy or slur speech and may develop nystagmus. At higher levels of anesthetics, the patient may become anxious and develop fine tremors of the muscles of the hands and/or face. These tremors may worsen and coalesce into a grand mal seizure. Ultimately, the patient may experience generalized CNS depression leading to hypoxia, acidosis, and respiratory arrest. Local anesthetics decrease the rate of depolarization of cardiac tissue, which is the rationale behind the use of lidocaine in treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. At higher concentrations, amplitude of the cardiac action potential is decreased, and the velocity of conduction is reduced. At toxic doses, the negative inotropic effects of local anesthetics may lead to bradycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or asystole. Other cardiovascular effects include hypotension, which occurs via the direct vasodilating effects of local anesthetics on peripheral arteriolar smooth muscle.
3 Adverse Reactions Significant Effects vary with route of administration. Many effects are dose related. Frequency not defined. Cardiovascular: Arrhythmia, bradycardia, arterial spasms, cardiovascular collapse, defibrillator threshold increased, edema, flushing, heart block, hypotension, sinus node supression, vascular insufficiency (periarticular injections) Central nervous system: Agitation, anxiety, apprehension, coma, confusion, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, euphoria, hallucinations, headache, hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, lethargy, lightheadedness, nervousness, psychosis, seizure, slurred speech, somnolence, unconsciousness Dermatologic: Angioedema, bruising (transdermal system), contact dermatitis, depigmentation (transdermal system), edema of the skin, itching, petechia (transdermal system), pruritus, rash, urticaria Gastrointestinal: Metallic taste, nausea, vomiting Local: Burning (ophthalmic), irritation (transdermal system), thrombophlebitis Neuromuscular & skeletal: Pain exacerbation (transdermal system), paresthesia, transient radicular pain (subarachnoid administration; up to 1.9%), tremor, twitching, weakness Ocular: Conjunctival hyperemia (ophthalmic), corneal epithelial changes (ophthalmic), diplopia, visual changes Otic: Tinnitus Respiratory: Bronchospasm, dyspnea, respiratory depression or arrest Miscellaneous: Allergic reactions, anaphylactoid reaction, sensitivity to temperature extremes Following spinal anesthesia: Positional headache (3%), shivering (2%) nausea, peripheral nerve symptoms, respiratory inadequacy and double vision (<1%), hypotension, cauda equina syndrome Postmarketing and/or case reports: ARDS (inhalation), asystole, chondrolysis (continuous intraarticular administration), disorientation, methemoglobinemia, skin reaction Treatment of Toxicity: -If lidocaine toxicity is suspected, stop the injection immediately and prepare to treat the reaction. -Ensure adequate oxygenation, whether by face mask or by intubation.
4 -Anticonvulsants such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates (diazepam 5-10 mg, thiopental mg) are the drugs of choice for seizure control. Phenytoin is not effective and should be avoided. Succinylcholine is sometimes also used to terminate the neuromuscular effects of seizures. Because succinylcholine paralyzes all muscles, the patient requires intubation. -In severe reactions, monitor the cardiovascular system (CVS) and support the patient with intravenous fluids and vasopressors as required. -Metabolic acidosis may develop, and the use of sodium bicarbonate can be considered, although, as in other instances of acute metabolic acidosis, this is controversial. 4. How much Epinephrine do you need to produce vasoconstriction? Plast Reconstr Surg 1973;51:129. CB 5. Your patient s temperature goes to 104 and his heart rate is up after induction of anesthesia. What do you do for malignant hyperthermia (MH)? What do you do if you patient has had a history of MH in the past? CB 6. Tell us about Cocaine. How does it work? What is a toxic dose? What are the symptoms of an overdose? How is it metabolized? AL Cocaine is an alkaloid derivative from the coca plant in honor of Pete- Erythroxylon coca. First introduced in the 1800 s, Freud is a famous for his human and self experiments with this drug was used in ophthalmology and dentistry. Coca Cola contained 4.5mg/180mL but was pulled off the Market in 1914 by the narcotics act which banned distribution except for medical use. MOA: anesthesia achieved by reversibly binding to and inactivating sodium channels, at the peripheral nerve terminals, inhibiting the sodium influx that is necessary for depolarization and propagation of impulses along the nerve terminal. CNS effects are achieved by inhibition of reuptake of Dopamine in the midbrain regions responsible for rewad mediation- hence the euphoria and arousal effect, decrease of coaine levels decreases the dopamine leading to a depression and craving.
5 PNS effects: blocks reuptake of NE in ANS and thought to stimulate relase of catecholamine from the adrenal gland- resulting in increased stimulation of SNS- resulting in tachycardia, hypertension, diaphoresis, mydriasis and tremors, and locally produces the desired vasocontrictive effect also through NE reuptake blockade. The safe maximum dosage is reported to be 200 mg or 2-3 mg/kg, but this is based on anecdotal observations rather than controlled studies. Even 200 mg can cause adverse reactions if rapidly absorbed It is rapidly absorbed in the mucus membranes with peak plasma levels at 15-60min, half life in serum in 30-90min. Hydrolysis by plasma protein psuedocholinesterases is responsible for most of the metabolism with its metabolites primarily benzoylecgonine & cocaethylene. In the Liver it is oxidatively metabolized to norcocaine- which can cause severe hepatic toxicity. That which is not metabolized is excreted in the urine unmetabolized- though to be upawards of 20%. Overdose:All due to cardiac, repiratory and CNS adrenergic effects.may result in hyptertension, tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, including direct cariotoxicity, angina, MI, CVI TIA, pulmonary edema, hepatotoxity (secondary to toxic metabolite) intestinal ischemia, seizures, CNS depression.tx: is supportive care- there is no antidote. Activate ACLS, propanolol, nitrates, CCB, alpha adrenergic blockers may be required to improve coronary Blood flow and restore normal rhythm. For seizures use diazepam, and aggressively treat hyperthermia with cooling blankets. 7. We often use Marcaine in tonsillectomies for longer acting analgesia. What is the dose? What are the particular side effects? AL Marcaine dosing per uptodate is Local anesthesia: Infiltration: 0.25% infiltrated locally. Maximun 175mg.
6 Bupivacaine (Marcaine) Bupivacaine with epinephrine Long ( min) Long ( min) Without epinephrine: 2.5 mg/kg; not to exceed 175 mg total dose With epinephrine: Not to exceed 225 mg total dose Side effects per emedicine confirmed with uptodate. All the side effects seemed to be similar to those of the other amide local anesthetics. Info is from the table of local anesthetic complications. Adverse reactions may occur following administration of local anesthetics and usually result from administration of too much drug. Adverse reactions may also occur following injection of very vascular sites or from accidental direct intravascular injection of the drug. Deaths following local anesthetic administration are always a result of overdosage. Tissue toxicity can be achieved by all local anesthetics if high concentrations are used. Adverse reactions occur primarily in the CNS (neurotoxicity) and cardiovascular system (myotoxicity) because these tissues are also composed of excitable membranes, the target of local anesthetic action. In the CNS, a progression of signs and symptoms may be observed in the patient. The patient may report lightheadedness, tinnitus, circumoral numbness, a metallic taste, or double vision. Upon examination, the patient may become drowsy or slur speech and may develop nystagmus. At higher levels of anesthetics, the patient may become anxious and develop fine tremors of the muscles of the hands and/or face. These tremors may worsen and coalesce into a grand mal seizure. Ultimately, the patient may experience generalized CNS depression leading to hypoxia, acidosis, and respiratory arrest. Local anesthetics decrease the rate of depolarization of cardiac tissue, which is the rationale behind the use of lidocaine in
7 treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. At higher concentrations, amplitude of the cardiac action potential is decreased, and the velocity of conduction is reduced. At toxic doses, the negative inotropic effects of local anesthetics may lead to bradycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or asystole. Other cardiovascular effects include hypotension, which occurs via the direct vasodilating effects of local anesthetics on peripheral arteriolar smooth muscle. Recognizing signs and symptoms of an adverse reaction to local anesthetics and administering emergency care in relation to the severity of the reaction are essential. With severe life-threatening reactions, immediately curtail the procedure. Activate advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols immediately, including intubation and defibrillation if indicated. Hypotension may require intravenous fluids and vasoconstrictor drugs for circulatory support. Control seizure activity with diazepam 5-10 mg IV. Succinylcholine may be required to stop ongoing tremors, but its use requires intubation and mechanical ventilation. Atropine and epinephrine may be indicated to treat bradycardia. 8. Discuss Toradol and its use in tonsillectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1996;122:937. CB 9. You need to sedate a child in the ER to repair a laceration. What is now recommended? HH 10. You are doing a bilobed flap on the nose for a BCCA. Should you inject the area w/lidocaine with Epinephrine or plain Lidcoaine? What will epinephrine do to the flap? TT 11. Discuss local anesthetics of facial surgery. Read and copy Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;101:840 for the group. TT 12. During a routine tonsillectomy in a 4-year-old (20kg), you find
8 that you are losing a lot of blood. The anesthesiologist is concerned. At what point should you consider transfusing the child. TT 13. You are planning a tonsillectomy in a pediatric patient with Down s Syndrome. Any special considerations? TT 14. Why has vasopressin been added to ACLS resuscitation protocols? Pharmacotherapy 2004;24: HH 15. Discuss the management of post-operative atrial fibrillation. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;79: HH
The Ideal Local Anesthetic. Pain and Anxiety. Percent Solution. Contents cont: Contents of a dental cartridge
 The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 PHARMACOLOGY FOR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 49 26 TH MARCH 2007 Dr J. Hyndman Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2)
PHARMACOLOGY FOR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 49 26 TH MARCH 2007 Dr J. Hyndman Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2)
Influence of ph Most local anesthetics are weak bases.
 Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
7. We often use Marcaine in tonsillectomies for longer acting analgesia. What is the dose? What are the particular side effects?
 7. We often use Marcaine in tonsillectomies for longer acting analgesia. What is the dose? What are the particular side effects? Marcaine dosing per uptodate is Local anesthesia: Infiltration: 0.25% infiltrated
7. We often use Marcaine in tonsillectomies for longer acting analgesia. What is the dose? What are the particular side effects? Marcaine dosing per uptodate is Local anesthesia: Infiltration: 0.25% infiltrated
PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman
 PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman Web Editor Jo Loader - jloader@doctors.org.uk Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2) How
PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman Web Editor Jo Loader - jloader@doctors.org.uk Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2) How
Local Anaesthetics. Local anesthetics (LA) Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects. 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves
 Local Anaesthetics Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects Local anesthetics (LA) 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves pain 2. Lowers myocardial excitability Treatment of arythmia
Local Anaesthetics Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects Local anesthetics (LA) 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves pain 2. Lowers myocardial excitability Treatment of arythmia
GUIDELINES FOR DRUG PRESCRIBING AND MONITORING
 GUIDELINES FOR DRUG PRESCRIBING AND MONITORING B. THERAPEUTIC GUIDELINES 1. LOCAL ANAESTHETIC (LA) AGENTS - STRUCTURAL CLASS & ALLERGY: Local anaesthetics are grouped into two categories depending on their
GUIDELINES FOR DRUG PRESCRIBING AND MONITORING B. THERAPEUTIC GUIDELINES 1. LOCAL ANAESTHETIC (LA) AGENTS - STRUCTURAL CLASS & ALLERGY: Local anaesthetics are grouped into two categories depending on their
developed in the 1930 s Amides had a faster onset and a longer half life so they lasted longer Amides quickly ikl replaced esters In dentistry today,
 Local Anesthetics History The first local anesthetics were cocaine and procaine (Novacain) developed in lt late 1800 s They were called esters because of their chemical composition Esters had a slow onset
Local Anesthetics History The first local anesthetics were cocaine and procaine (Novacain) developed in lt late 1800 s They were called esters because of their chemical composition Esters had a slow onset
Lidocaine 2% w/v solution for injection Summary of Product Characteristics
 Lidocaine 2% w/v solution for injection Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lidocaine 2% w/v solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 1 ml
Lidocaine 2% w/v solution for injection Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lidocaine 2% w/v solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 1 ml
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
 ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia)
 Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia) History August Bier introduced this block in 1908. Early methods included the use of two separate tourniquets and procaine was the local anesthetic of choice.
Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia) History August Bier introduced this block in 1908. Early methods included the use of two separate tourniquets and procaine was the local anesthetic of choice.
Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia
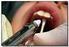 Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia On occasion, anesthesia providers will place field blocks either as supplementation for a marginal regional anesthetic block or as the sole form of anesthesia. In
Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia On occasion, anesthesia providers will place field blocks either as supplementation for a marginal regional anesthetic block or as the sole form of anesthesia. In
White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other.
 Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
Adrenergic agonists:-
 Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
table of contents drug reference
 table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
How To Treat Anesthetic With Local Anesthesia
 3. LOCAL ANESTHETICS INTRODUCTION Compared to general anesthesia with opioidbased perioperative pain management, regional anesthesia can provide benefits of superior pain control, improved patient satisfaction,
3. LOCAL ANESTHETICS INTRODUCTION Compared to general anesthesia with opioidbased perioperative pain management, regional anesthesia can provide benefits of superior pain control, improved patient satisfaction,
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers
 Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-a-[(methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula:
![Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-a-[(methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula: Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-a-[(methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula:](/thumbs/33/15931267.jpg) Lidocaine Hydrochloride 2% and Epinephrine Injection, USP Injections for Local Anesthesia in Dentistry R x only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine HCl and Epinephrine Injection, USP are sterile, nonpyrogenic, isotonic
Lidocaine Hydrochloride 2% and Epinephrine Injection, USP Injections for Local Anesthesia in Dentistry R x only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine HCl and Epinephrine Injection, USP are sterile, nonpyrogenic, isotonic
Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia
 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia Local anaesthetics are important tools used in the everyday practice of medicine. The first local anaesthetic was cocaine. In 1884, Koller used topical
Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia Local anaesthetics are important tools used in the everyday practice of medicine. The first local anaesthetic was cocaine. In 1884, Koller used topical
VISTARIL (hydroxyzine pamoate) Capsules and Oral Suspension
 VISTARIL (hydroxyzine pamoate) Capsules and Oral Suspension DESCRIPTION Hydroxyzine pamoate is designated chemically as 1-(p-chlorobenzhydryl) 4- [2-(2-hydroxyethoxy) ethyl] diethylenediamine salt of 1,1
VISTARIL (hydroxyzine pamoate) Capsules and Oral Suspension DESCRIPTION Hydroxyzine pamoate is designated chemically as 1-(p-chlorobenzhydryl) 4- [2-(2-hydroxyethoxy) ethyl] diethylenediamine salt of 1,1
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION
 Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use.
 EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. R x only DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. R x only DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
The Ideal Local Anesthetic. Iowa Dental Association 2009 Annual Session Local Anesthesia. Percent Solution. Contents cont:
 Iowa Dental Association 2009 Annual Session Local Anesthesia James Q. Swift DDS University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery The Ideal Local Anesthetic Water soluble/stable in solution
Iowa Dental Association 2009 Annual Session Local Anesthesia James Q. Swift DDS University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery The Ideal Local Anesthetic Water soluble/stable in solution
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia
 Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
3% Citanest Dental with Octapressin PRODUCT INFORMATION
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE 3% Citanest Dental with Octapressin PRODUCT INFORMATION 3% Citanest Dental with Octapressin contains prilocaine hydrochloride and felypressin as the active substances. The chemical
NAME OF THE MEDICINE 3% Citanest Dental with Octapressin PRODUCT INFORMATION 3% Citanest Dental with Octapressin contains prilocaine hydrochloride and felypressin as the active substances. The chemical
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION EPIPEN (epinephrine) Auto-Injector 0.3 mg EpiPen = one dose of 0.30 mg epinephrine (USP, 1:1000, 0.3 ml) EPIPEN JR (epinephrine) Auto-Injector 0.15 mg EpiPen Jr = one dose of 0.15
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION EPIPEN (epinephrine) Auto-Injector 0.3 mg EpiPen = one dose of 0.30 mg epinephrine (USP, 1:1000, 0.3 ml) EPIPEN JR (epinephrine) Auto-Injector 0.15 mg EpiPen Jr = one dose of 0.15
Epidural Anesthesia. Advantages of Epidural Anesthesia
 Epidural Anesthesia Epidural anesthesia involves the use of local anesthetics injected into the epidural space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. Epidural anesthesia requires
Epidural Anesthesia Epidural anesthesia involves the use of local anesthetics injected into the epidural space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. Epidural anesthesia requires
How To Understand The Effects Of Drugs On The Brain
 DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Most of the psychological and behavioural effects of psychoactive drugs is due the interaction they have with the nerve cells in the CNS (which includes the brain and peripheral nervous
DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Most of the psychological and behavioural effects of psychoactive drugs is due the interaction they have with the nerve cells in the CNS (which includes the brain and peripheral nervous
Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol. It has the following structural formula:
![Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol. It has the following structural formula: Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol. It has the following structural formula:](/thumbs/27/9698554.jpg) MARCAINE - bupivacaine hydrochloride injection, solution MARCAINE WITH EPINEPHRINE - bupivacaine hydrochloride and epinephrine bitartrate injection, solution Hospira, Inc. Marcaine Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
MARCAINE - bupivacaine hydrochloride injection, solution MARCAINE WITH EPINEPHRINE - bupivacaine hydrochloride and epinephrine bitartrate injection, solution Hospira, Inc. Marcaine Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR. Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University
 Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY
 ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
CLINICAL PROTOCOL FOR THE USE OF INJECTED LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN COMMUNITY TRUST SERVICES
 CLINICAL PROTOCOL FOR THE USE OF INJECTED LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN COMMUNITY TRUST SERVICES RATIONALE This clinical protocol outlines the injected local anaesthetics used by Trust services and the circumstances
CLINICAL PROTOCOL FOR THE USE OF INJECTED LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN COMMUNITY TRUST SERVICES RATIONALE This clinical protocol outlines the injected local anaesthetics used by Trust services and the circumstances
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
Data Sheet 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with Adrenaline 1:80,000
 Data Sheet 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with Adrenaline 1:80,000 (lignocaine 2% with adrenaline 1:80,000) Presentation 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with Adrenaline 1:80,000 solution for injection is a sterile, isotonic
Data Sheet 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with Adrenaline 1:80,000 (lignocaine 2% with adrenaline 1:80,000) Presentation 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with Adrenaline 1:80,000 solution for injection is a sterile, isotonic
Vasopressors. Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco
 Vasopressors Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco Overview Define shock states Review drugs commonly used to treat hypotension
Vasopressors Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco Overview Define shock states Review drugs commonly used to treat hypotension
F.E.E.A. FONDATION EUROPEENNE D'ENSEIGNEMENT EN ANESTHESIOLOGIE FOUNDATION FOR EUROPEAN EDUCATION IN ANAESTHESIOLOGY
 créée sous le Patronage de l'union Européenne Detailed plan of the program of six courses 1. RESPIRATORY 1. ESPIRATORY AND THORAX 1.1 Physics and principles of measurement 1.1.1 Physical laws 1.1.2 Vaporizers
créée sous le Patronage de l'union Européenne Detailed plan of the program of six courses 1. RESPIRATORY 1. ESPIRATORY AND THORAX 1.1 Physics and principles of measurement 1.1.1 Physical laws 1.1.2 Vaporizers
Local Anesthetics. Chemistry
 Local Anesthetics Local anesthetics produce a reversible loss of sensation in a portion of the body. Local anesthetics may be used as the sole form of anesthesia, in combination with general anesthesia,
Local Anesthetics Local anesthetics produce a reversible loss of sensation in a portion of the body. Local anesthetics may be used as the sole form of anesthesia, in combination with general anesthesia,
and Epinephrine Rx only
 Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP Rx only DESCRIPTION Bupivacaine Hydrochloride is 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-,
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP Rx only DESCRIPTION Bupivacaine Hydrochloride is 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-,
Conscious Sedation Policy
 PURPOSE Provide guidelines to ensure safe and consistent process for patient selection, administration, monitoring and discharge care of patients receiving conscious sedation. Conscious sedation refers
PURPOSE Provide guidelines to ensure safe and consistent process for patient selection, administration, monitoring and discharge care of patients receiving conscious sedation. Conscious sedation refers
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. 7-4. Given a group of statements, select the best definition of the term adrenergic (sympathomimetic) drug.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
Local anaesthetic and additive drugs
 Local anaesthetic and additive drugs Carol A Chong is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at St Bartholomew s and Homerton Hospitals, London. She qualified from the University of Queensland,
Local anaesthetic and additive drugs Carol A Chong is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at St Bartholomew s and Homerton Hospitals, London. She qualified from the University of Queensland,
!!! BOLUS DOSE IV. Use 5-10 mcg IV boluses STD ADRENALINE INFUSION. Use IM adrenaline in advance of IV dosing!
 ADRENALINE IVI BOLUS IV Open a vial of 1:1000 ADRENALINE 1 mg /ml Add 1 ml to 9 ml N/Saline = 1mg adrenaline in 10 ml (or 100 mcg/ml) Add 1 ml 1:10,000 to 9 ml N/Saline = 100 mcg adrenaline in 10 ml (or
ADRENALINE IVI BOLUS IV Open a vial of 1:1000 ADRENALINE 1 mg /ml Add 1 ml to 9 ml N/Saline = 1mg adrenaline in 10 ml (or 100 mcg/ml) Add 1 ml 1:10,000 to 9 ml N/Saline = 100 mcg adrenaline in 10 ml (or
Local Anesthetics and Adjuncts
 Local Anesthetics and Adjuncts Regional/VOS Rotation (Slides by Randall Malchow, MD) History Syringe, Needle 1850s Cocaine- 1884 Epi w/ LA- 1900 Procaine, Novacaine -1905 Tetracaine- 1929 Lidocaine- 1948
Local Anesthetics and Adjuncts Regional/VOS Rotation (Slides by Randall Malchow, MD) History Syringe, Needle 1850s Cocaine- 1884 Epi w/ LA- 1900 Procaine, Novacaine -1905 Tetracaine- 1929 Lidocaine- 1948
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection. Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (TARTRATE) STEROP 1 mg/1 ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this
Top-up for Cesarean section. Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern
 Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Pediatric Pharmacotherapy A Monthly Newsletter for Health Care Professionals Children s Medical Center at the University of Virginia
 Pediatric Pharmacotherapy A Monthly Newsletter for Health Care Professionals Children s Medical Center at the University of Virginia Volume 2 Number 12 December 1996 Medications for Neonatal and Pediatric
Pediatric Pharmacotherapy A Monthly Newsletter for Health Care Professionals Children s Medical Center at the University of Virginia Volume 2 Number 12 December 1996 Medications for Neonatal and Pediatric
Anaphylaxis: Treatment in the Community
 : Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
: Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection, USP Opioid Antagonist
 Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection, USP Opioid Antagonist Rx Only DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride, an opioid antagonist, is a synthetic congener of oxymorphone. In structure it differs from oxymorphone
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection, USP Opioid Antagonist Rx Only DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride, an opioid antagonist, is a synthetic congener of oxymorphone. In structure it differs from oxymorphone
M.W. 183.21; C 9 H 13 NO 3
 Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinepherine Injection, USP FOR LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN DENTISTRY CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW PROHIBITS DISPENSING WITHOUT PRESCRIPTION. DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine
Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinepherine Injection, USP FOR LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN DENTISTRY CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW PROHIBITS DISPENSING WITHOUT PRESCRIPTION. DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine
LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS FOR ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
 LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS FOR ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS Ansyr Plastic Syringe LifeShield Abboject Syringe R x only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection,
LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS FOR ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS Ansyr Plastic Syringe LifeShield Abboject Syringe R x only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection,
2% Xylocaine DENTAL with epinephrine 1:50,000
 2616-1 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with epinephrine 1:50,000 (Lidocaine HCl 2% and Epinephrine 1:50,000 Injection) 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with epinephrine 1:100,000 (Lidocaine HCl 2% and Epinephrine 1:100,000 Injection)
2616-1 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with epinephrine 1:50,000 (Lidocaine HCl 2% and Epinephrine 1:50,000 Injection) 2% Xylocaine DENTAL with epinephrine 1:100,000 (Lidocaine HCl 2% and Epinephrine 1:100,000 Injection)
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000
 UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 4 3 LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY Carl A. Kihm, DPM INTRODUCTION Local anesthetic (LA) infiltration, first introduced by Karl Schleich in 1892, has allowed surgeons
C H A P T E R 4 3 LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY Carl A. Kihm, DPM INTRODUCTION Local anesthetic (LA) infiltration, first introduced by Karl Schleich in 1892, has allowed surgeons
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new?
 Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new? DVM, DACVA Objective: Update on the new Small animal guidelines for CPR and a discussion of the 2012 Reassessment Campaign on
Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new? DVM, DACVA Objective: Update on the new Small animal guidelines for CPR and a discussion of the 2012 Reassessment Campaign on
SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions
 REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml)
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Adrenalin* Chloride Injection (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P.) 1:1000, 30
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Adrenalin* Chloride Injection (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P.) 1:1000, 30
Public Assessment Report. Table of Contents
 Public Assessment Report Lidocaine Injection BP with preservative 1% Lidocaine Injection BP with preservative 2% PL 01502/0070 PL 01502/0071 Hameln Pharmaceuticals Limited Table of Contents Page Lay Summary
Public Assessment Report Lidocaine Injection BP with preservative 1% Lidocaine Injection BP with preservative 2% PL 01502/0070 PL 01502/0071 Hameln Pharmaceuticals Limited Table of Contents Page Lay Summary
KAMACAINE 0.5% INJECTION
 KAMACAINE 0.5% Bupivacaine HCl Injection, USP KAMACAINE ADRENALINE 0.5% (5mg/ml + 5mcg/ml) Bupivacaine HCl and Epinephrine Injection, USP DESCRIPTION: Bupivacaine Hydrochloride USP, is 2-piperidinecarboxamide,
KAMACAINE 0.5% Bupivacaine HCl Injection, USP KAMACAINE ADRENALINE 0.5% (5mg/ml + 5mcg/ml) Bupivacaine HCl and Epinephrine Injection, USP DESCRIPTION: Bupivacaine Hydrochloride USP, is 2-piperidinecarboxamide,
Epinephrine is ( - )-3,4-Dihydroxy- -[(Methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula :
![Epinephrine is ( - )-3,4-Dihydroxy- -[(Methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula : Epinephrine is ( - )-3,4-Dihydroxy- -[(Methylamino) methyl] benzyl alcohol and has the following structural formula :](/thumbs/27/9698639.jpg) XYLOCAINE - lidocaine hydrochloride and epinephrine bitartrate injection, solution Dentsply Pharmaceutical Rx only Solutions for local anesthesia in Dentistry DESCRIPTION Sterile isotonic solutions containing
XYLOCAINE - lidocaine hydrochloride and epinephrine bitartrate injection, solution Dentsply Pharmaceutical Rx only Solutions for local anesthesia in Dentistry DESCRIPTION Sterile isotonic solutions containing
Arrest. What s a Nurse to do?
 Benzo s, Blockers, Coma & Cardiac Arrest What s a Nurse to do? Objectives Review of ACLS Algorithms for Cardiac Arrest Management Discuss the toxicology of Beta Blocker Poisoning Describe the clinical
Benzo s, Blockers, Coma & Cardiac Arrest What s a Nurse to do? Objectives Review of ACLS Algorithms for Cardiac Arrest Management Discuss the toxicology of Beta Blocker Poisoning Describe the clinical
PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key. For the following questions, circle the letter of the correct answer(s) or the word true or false.
 PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key 1 1. Define Procedural (Conscious) Sedation: A medically controlled state of depressed consciousness where the patient retains the ability to continuously
PHSW Procedural Sedation Post-Test Answer Key 1 1. Define Procedural (Conscious) Sedation: A medically controlled state of depressed consciousness where the patient retains the ability to continuously
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com
 Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Alabama Medications. Christopher J. Colvin January 2010
 Alabama Medications Christopher J. Colvin p January 2010 Activated Charcoal Used to absorb toxins ingested before they can be absorbed in the GI system. Contraindicated in AMS patients who cannot control
Alabama Medications Christopher J. Colvin p January 2010 Activated Charcoal Used to absorb toxins ingested before they can be absorbed in the GI system. Contraindicated in AMS patients who cannot control
2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Temporary Core Product Information Inde- (13May2013) Page 1 / 7 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT XYLONOR SPRAY, oromucosal spray, solution. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each gram contains:
Temporary Core Product Information Inde- (13May2013) Page 1 / 7 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT XYLONOR SPRAY, oromucosal spray, solution. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each gram contains:
Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP
 Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP R x only DESCRIPTION Norepinephrine (sometimes referred to as l-arterenol/levarterenol or l-norepinephrine) is a sympathomimetic amine which differs from
Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP R x only DESCRIPTION Norepinephrine (sometimes referred to as l-arterenol/levarterenol or l-norepinephrine) is a sympathomimetic amine which differs from
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 PART II SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lignospan Special (20 mg/12.5 microgram per ml) Solution for injection 2.2 ml 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Lidocaine
PART II SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lignospan Special (20 mg/12.5 microgram per ml) Solution for injection 2.2 ml 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Lidocaine
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
epinephrine (7) Table 1: Recommended Dosages for Both Strengths
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use. (articaine HCl and epinephrine) Injection; Intraoral Submucosal Injection Articaine hydrochloride
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use. (articaine HCl and epinephrine) Injection; Intraoral Submucosal Injection Articaine hydrochloride
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008
 Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
CNA HealthPro. Don t Be Numb to Local Anesthesia Risks
 CNA HealthPro Don t Be Numb to Local Anesthesia Risks It has been estimated that American dentists administer hundreds of millions of local anesthetic injections each year. 1 Because of their common occurrence
CNA HealthPro Don t Be Numb to Local Anesthesia Risks It has been estimated that American dentists administer hundreds of millions of local anesthetic injections each year. 1 Because of their common occurrence
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml. Solution for injection. Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,4mg/1ml ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,4mg/1ml ADRENALINE (HCl) STEROP 0,8mg/1ml Solution for injection Adrenaline (Levorenine, Epinephrine) Read all of this leaflet carefully
DNH 120 Management of Emergencies
 Revised: Fall 2015 DNH 120 Management of Emergencies COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: None Course Description: Studies the various medical emergencies and techniques for managing emergencies in the dental
Revised: Fall 2015 DNH 120 Management of Emergencies COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: None Course Description: Studies the various medical emergencies and techniques for managing emergencies in the dental
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET: ODONTOCAINE 2% WITH EPINEPHRINE FTAO32-002
 1 GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION ODONTOCAINE 2% WITH EPINEPHRINE 1: 100 000 Anesthetic Injectable Solutions for Dental Use: MEPIVACAINE Mepivacaine 2% with Epinephrine 1:100000 is a small-volume injectable
1 GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION ODONTOCAINE 2% WITH EPINEPHRINE 1: 100 000 Anesthetic Injectable Solutions for Dental Use: MEPIVACAINE Mepivacaine 2% with Epinephrine 1:100000 is a small-volume injectable
Community Ambulance Service of Minot ALS Standing Orders Legend
 Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
Lidocaine Infusion for Perioperative Pain Management. Marley Linder, PharmD Matt McEvoy, MD
 Lidocaine Infusion for Perioperative Pain Management Marley Linder, PharmD Matt McEvoy, MD Perioperative Surgical Home: PCS Shared Goals Improved Outcomes (pain, PONV, LOS, SSI) Improve Throughput (Clinic
Lidocaine Infusion for Perioperative Pain Management Marley Linder, PharmD Matt McEvoy, MD Perioperative Surgical Home: PCS Shared Goals Improved Outcomes (pain, PONV, LOS, SSI) Improve Throughput (Clinic
025-00076.003 06/29/2012 #136678
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXPAREL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXPAREL. EXPAREL (Bupivacaine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXPAREL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXPAREL. EXPAREL (Bupivacaine
Key Points. Autonomic Nervous System Drugs. Autonomic effects Sympathetic. Drugs can modify ANS activity by: Autonomic Nervous System
 Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE) ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 226 6 TH JUNE 2011 Prof. John Kinnear Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, UK Correspondence to John.Kinnear@southend.nhs.uk QUESTIONS
ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE) ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 226 6 TH JUNE 2011 Prof. John Kinnear Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, UK Correspondence to John.Kinnear@southend.nhs.uk QUESTIONS
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD. daniel.dunham@clemc.us
 Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD daniel.dunham@clemc.us Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD daniel.dunham@clemc.us Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
1. The potential sites of action for sympathomimetics and the difference between a direct and indirect acting agonist.
 1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin
 Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin Dwayne Cottel Regional Paramedic Educator Matthew Davis Medical Director of Education Learning Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin Dwayne Cottel Regional Paramedic Educator Matthew Davis Medical Director of Education Learning Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth
 Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth I. II. Background A. AWS can occur in anyone who consumes alcohol B. Risk correlates
Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth I. II. Background A. AWS can occur in anyone who consumes alcohol B. Risk correlates
Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity. Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland
 Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland Conflict of interest None Overview Local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST) Background
Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland Conflict of interest None Overview Local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST) Background
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. MARCAINE (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection USP) MARCAINE SPINAL (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in Dextrose Injection USP)
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION MARCAINE (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection USP) MARCAINE SPINAL (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in Dextrose Injection USP) MARCAINE E (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION MARCAINE (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection USP) MARCAINE SPINAL (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in Dextrose Injection USP) MARCAINE E (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection
Lidocaine HCl. Epinephrine (anhyd.) mg/ml
 Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP For Infiltration and Nerve Block. Ampul Fliptop Vial Multiple-dose Fliptop Vial Protect from light. Rx only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride and
Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP For Infiltration and Nerve Block. Ampul Fliptop Vial Multiple-dose Fliptop Vial Protect from light. Rx only DESCRIPTION Lidocaine Hydrochloride and
PREPARATIONS: Adrenaline 1mg in 1ml (1:1000) Adrenaline 100micrograms in 1ml (1:10,000)
 ADRENALINE Acute hypotension Via a CENTRAL venous line Initially 100-300 nanograms/kg/minute 0.1-0.3 microgram/kg/minute adjusted according to response up to a maximum of 1.5 micrograms/kg/minute. Increase
ADRENALINE Acute hypotension Via a CENTRAL venous line Initially 100-300 nanograms/kg/minute 0.1-0.3 microgram/kg/minute adjusted according to response up to a maximum of 1.5 micrograms/kg/minute. Increase
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
1 721566-04 451175A/Revised February 2010. 2 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl Injection, USP) 3 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl and epinephrine Injection, USP)
 1 7566-04 45A/Revised February 10 2 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl Injection, USP) 3 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl and epinephrine Injection, USP) 4 For Infiltration and Nerve Block 5 Rx only 6 DESCRIPTION : 7 Xylocaine
1 7566-04 45A/Revised February 10 2 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl Injection, USP) 3 Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl and epinephrine Injection, USP) 4 For Infiltration and Nerve Block 5 Rx only 6 DESCRIPTION : 7 Xylocaine
If you do not wish to print the entire pre-test you may print Page 2 only to write your answers, score your test, and turn in to your instructor.
 This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
Opioid Analgesics. Week 19
 Opioid Analgesics Week 19 Analgesic Vocabulary Analgesia Narcotic Opiate Opioid Agonist Antagonist Narcotic Analgesics Controlled substances Opioid analgesics derived from poppy Opiates include morphine,
Opioid Analgesics Week 19 Analgesic Vocabulary Analgesia Narcotic Opiate Opioid Agonist Antagonist Narcotic Analgesics Controlled substances Opioid analgesics derived from poppy Opiates include morphine,
