Total Knee Replacement
|
|
|
- Shavonne Flynn
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Total Knee Replacement Your guide to a successful outcome following surgery Name Date given Orthopaedic Department
2 Contents About the knee 3 Advice while you are waiting for your knee replacement 6 Enhanced recovery programme and Preload 7 8 What happens before your operation 9 Pre-operative knee group 9 Pre-assessment clinic 10 Admission day and the operation Physiotherapy 13 Bed exercises Discharge from hospital 19 Advice from six weeks 20 Maintenance exercises Possible complications 25 General advice 27 Appointments record 28 Helpful telephone numbers 29 2
3 You are booked for a knee replacement This booklet aims to provide you with information about the surgery and what will happen before and after the operation. Please bring this booklet with you to all your appointments regarding your knee replacement. Introduction This booklet has been written to help prepare you before you come into hospital for your Total Knee Replacement (TKR) operation. Other treatment options will have been discussed with you by your Consultant. Please read this booklet carefully and ask the ward physiotherapist if you are unsure about any information or instructions within the booklet, when you come into hospital or at your pre-operative knee group appointment. Remember, once the surgeon has replaced your knee, it is up to you, with guidance from the ward staff, to follow the advice and carry out the exercises in order to achieve the best results from your new knee. About the knee Your knee has three parts: your thigh bone (femur), shin bone (tibia) and knee cap (patella). Where the bones meet, they are covered with a smooth substance called articular cartilage which helps them slide over each other easily. The joint is held together with tough bands of tissue called ligaments and is lubricated with a special fluid. Arthritis is a process in which the articular cartilage is destroyed: once cartilage has been damaged or destroyed it is gone for good as it cannot repair or heal itself. Serious injury, wear and tear and a family history of arthritis all seem to play a part. Arthritis can develop over many years or fairly rapidly and can follow serious injury. 3
4 What is a total knee replacement? Total knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which the knee is resurfaced with artificial parts. Your knee replacement (prosthesis) will consist of a metal shell on the end of the femur and a metal and plastic trough on the tibia. A plastic button will be used to resurface the back of the kneecap if needed. An artificial knee is not a normal knee but aims to: Provide pain relief. Allow you to walk a good distance again. Correct deformity i.e. give you a straight leg. Remove symptoms such as giving way and locking. Improve your quality of life. The consultant will recommend this operation, however it is your choice to have this operation and the outcome is reliant on the amount of work you do. After the operation your deep osteoarthritic pain should resolve, however for a period of time this will be replaced with surgical pain from the trauma of the operation. It is important to take regular pain relief to allow you to perform your exercises. A total knee replacement is a large commitment and you must be motivated and prepared to spend time making the process a success. How long will I be in hospital? The average length of stay for a total knee replacement is 2-4 days, however this is dependant on your previous level of fitness, medical complications and home circumstances. If you are motivated you may be able to get home sooner. 4
5 How long will my knee replacement last? All knee replacements have a limited life expectancy dependant on an individual s age, weight and level of activity. Their longevity will vary but all knee replacements will eventually wear out. Currently years is the expected life span but up to 5% of knee replacements will not last 10 years. There is no guarantee that your particular implant will last a specific length of time. It is important to follow your Surgeon s, Therapist s and Nurse s advice after surgery. Why do implants fail? The most common reason for failure in a knee replacement is loosening or wear of the implant. This can usually be replaced with another one which is called a revision. Will I have restrictions after surgery? You will be advised against participating in high impact activities such as running, jumping, squash and contact sports. Will I notice anything different about my knee? You will notice some numbness on the outside of the scar. The area around your scar may feel warm for up to six months. In the initial postoperative period you will find your knee becomes stiff, this will improve with regular exercises. Initial swelling in your knee should settle in six weeks however your knee can continue to swell following activity for about a year. You may also notice some clicking as you move your knee due to the artificial surfaces coming together, this should improve in time. When will I be able to return to work? We recommend that most people will need at least six weeks off from work. Patients with more sedentary jobs may be able to return to work sooner. The timing of your return to work will depend on your progress. 5
6 When will I be able to drive? Most people would not be fit to drive in the first six weeks. If you have had your right knee replaced you must be able to perform an emergency stop effectively. Driving will depend on your progress and individual circumstances. Please seek advice from a health professional or at your six week follow up if you are unsure. Remember to let your insurance company know you have had an operation. Advice while you are waiting for your knee replacement General exercise General exercise is always of benefit and continues to be so whilst you are on the waiting list. It will also help your recovery following your operation. You may find that gentle exercise (within your limits of pain) such as cycling, swimming, or walking with periods of rest in between are of benefit. Specific exercise Exercising the muscles around the joint will help to maintain or possibly improve the strength of your muscles and also the range of movement of the joint. This will also benefit you after your operation. These exercises will be taught to you at the Pre-operative Knee Group. General health Keep yourself as fit and healthy as possible whilst you await your operation. This will greatly help with your recovery. If your general health deteriorates, it is important to contact your GP so that problems may be dealt with before your operation. In particular it is beneficial to stop or at least reduce, smoking. Pain relief If you are experiencing pain in your joint and you are not taking any pain medication, or the medication you are taking is not effective, your GP may be able to prescribe something to relieve your pain. 6
7 Load reduction Reducing the pressure taken through the knee may also help with the pain. You may find that using a walking stick, (held in the hand on the opposite side to the affected knee) will help reduce pressure whilst you are walking. Dieting to lose weight will reduce your anaesthetic risks and improve the life of the knee replacement. Adequate rest periods and avoidance of unnecessary strain also help to reduce the pressure on your knee joint. Skin and dental care If you have any cuts, abrasions, rashes or other skin conditions around your knee, leg or foot please see your GP as this may delay your surgery if left untreated. It is important to pay particular attention to foot hygiene. It is advisable to visit a dentist to ensure your teeth and gums are in good order prior to your operation. Infection in your teeth or gums may spread to your knee joint if left untreated. Enhanced recovery programme When you are admitted to hospital for your operation you will be taking part in an enhanced recovery programme. This programme of care aims to help you recover quickly and safely. The Enhanced Recovery Programme is about improving outcomes and speeding up the recovery period after your surgery, as well as reducing complications. For the programme to be successful, it is important that you actively participate in your own recovery programme and take responsibility for certain aspects of your recovery. This programme is different to traditional care and can improve your recovery considerably. The programme particularly focuses on: Reducing the physical stress of the operation. A structured approach to immediate post-operative management, including pain relief. Early mobilisation. Early return to normal diet. 7
8 Some patients will be able to benefit from all aspects of this programme, whilst others will be able to benefit from just some aspects of it. This will depend on several factors, particularly your state of health and fitness at the outset. However we will endeavour to use as much of the programme as is practicable in each individual patients case. Preload A key aspect of your enhanced recovery programme is that you will be given a carbohydrate (sugary) drink before your surgery. This drink is called preload. These drinks have several benefits to your recovery. They will: give you energy to help you recover reduce the risk of nausea (sickness) help your wounds heal reduce the risk of infection generally aid your recovery. You will receive the carbohydrate drinks at your pre-assessment clinic appointment. Preload: Preparation guidelines Step 1: Pour 400ml of water into a cup. Step 2: Add the contents of the sachet/s of preload into the cup, stir continuously until the powder has dissolved. Step 3: Drink as directed below. When to take preload Evening before surgery Eat your normal evening meal along with 2 sachets of preload. 2 sachets of preload in 400mls of water. 8
9 If your surgery is scheduled for the morning You should have nothing to eat or drink after 2am, but you may have a small amount of water and your carbohydrate drink, up to 2 hours before your operation. 1 sachet of preload in 400mls to be finished by 6am. If your surgery is scheduled for the afternoon You should have a light breakfast before 6.30am, and then have nothing except a small amount of water and your carbohydrate drink up to 2 hours before your operation. 1 sachet of preload in 400mls to be finished by 10.30am. These instructions will be clarified during a phone call that you will receive the evening prior to admission from the Elective Surgical Unit (ESU). It may be unknown whether you are on a morning or afternoon list at the preadmission clinic stage. On the day before your surgery you will be able to eat and drink as normal. In order to maximise your nutritional status we recommend you include a few extra snacks in your diet. You can eat a normal diet up to 6 hours before your surgery. What happens before the operation? Pre-operative Knee Group It is essential that you attend the group at any time before your operation as it will be beneficial in order to help you prepare for your operation. You may receive questionnaires in the post prior to attending the group. A member of the Physiotherapy Department is working alongside some of our Orthopaedic Consultants, to monitor the impact of total knee replacement surgery on patients. If you receive these questionnaires, please complete them and bring them with you to the Pre-operative Knee Group. The group is run by the Orthopaedic Physiotherapy team and it includes an informative talk on what to expect during your post-operative recovery, the importance of exercises for your knee replacement, and preparing for your discharge. It also includes a practical session involving 9
10 exercise and mobility aid (elbow crutches) demonstrations. You will have the opportunity to meet others who are going to have a total knee replacement and you can ask questions. Pre-assessment Clinic A few weeks before your operation you will be asked to attend the Pre-assessment Clinic. A thorough medical assessment will be carried out to make sure you are medically fit enough for surgery. At this clinic routine pre-operative tests including urine, blood, ECG (heart trace) and x-rays will be carried out. You will also be screened for MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus), a normally harmless bacterium that can on occasions cause wound infections. Part of the pre-admission process involves gathering accurate information regarding current medication, which is important for us to give you the best possible care. Please bring a list of your regular medication, including any inhalers, eye drops, patches or creams as you will be asked what medication you usually take, the dosage and how often. It may also be helpful for you to bring in the repeat prescription request forms from your GP surgery. Please also remember to mention any medicines you buy regularly (that are not prescribed by your doctor) and any herbal or vitamin supplements that you might be taking. In anticipation of the surgery you may be asked to stop taking some of your medications before coming in to hospital (e.g. if you take warfarin) and you may be prescribed alternative medications leading up to the operation. You will be advised by a Nurse or a Doctor if this is necessary. This appointment will also provide you with a further opportunity to speak to your Consultant, their Registrar or an Extended Scope Practitioner. You will also be asked to sign a consent form if you have not already done so. You can be in clinic for 3-4 hours 10
11 Before coming in to Hospital Ensure that you assess your home for ease of walking with crutches, sticks or a walking frame. Remove any loose rugs, which may cause you to trip. Put objects that you use regularly within easy reach so that you do not have to bend or stretch. Identify people who will help you do your shopping, washing and cleaning. Arrange transport in and out of hospital. Please make sure that you have at least 2-3 weeks supply of any regular medication which you are taking. If you live alone, try to arrange for someone to stay with you or visit you frequently for 1-2 weeks after your discharge. Admission day In addition to your personal belongings you will need to bring the following: Any regular medication you are taking (at least 2 weeks supply and in their original packaging) along with a copy of your repeat prescription request forms from your GP surgery if you have them. Please also bring any medications which you were asked to stop taking before the procedure, as you may need to restart these whilst in hospital. Please let us know if there have been any changes to your regular medications between your pre-assessment visit and the day of surgery. Appropriate foot wear e.g. trainers or well fitting shoes (NOT mules or flip flops ). Loose comfortable clothing (you will be encouraged to dress normally the day after your operation). Nightwear. Toiletry bag. Please leave any valuables at home 11
12 The operation The operation will usually take place under a general anaesthetic, but it is sometimes done with a spinal anaesthetic where your legs will be completely numb. The anaesthetist will discuss this with you before your operation takes place. The surgery takes approximately 1-2 hours. You will remain in the recovery area until your condition is stable and your pain is well controlled. Recovery Following surgery you will be returned to the ward lying on your back with a thick dressing over your knee. Nerve blocks inserted by the Anaesthetist in the operating theatre may leave your leg feeling weak and numb. You may have some of the following drains or tubes attached to you:- Wound drain(s): there may be a bottle attached via a tube to your knee wound. It prevents excess swelling and bruising and is usually removed after 24 hours. Fluids: you may have a tube in your arm connected to a drip to give you fluid until you are eating and drinking properly. Catheter: if you are unable to pass water following your operation, you may need a short term catheter. 12
13 Changes to medications It is normal to have some pain after the surgery and so you will be offered regular painkillers. It is very important that you take the painkillers regularly to keep your pain under control and speed up your rehabilitation. The painkillers can cause constipation but early walking and exercise can help this and if necessary you may be prescribed laxatives. If you wish to know more about the types of pain relief available, please discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you want any other information before you come into hospital, booklets about pain relief are available in the orthopaedic clinic. You may also be prescribed some medications to help the strength of your bones, such as calcium & vitamin D supplements and possibly a bisphosphonate to help bind the calcium into the bones. Please follow the instructions on how to take these carefully. You may also be prescribed medications to reduce the risk of a venous thromboembolism or VTE, which is a type of blood clot. The risk of developing a VTE may be increased by having surgery and being less mobile. During your hospital stay you may be prescribed medications to thin the blood. You may also need to complete a course when you go home. Please read the patient information leaflets supplied with new medications and discuss any concerns with your Doctor or Pharmacist. Physiotherapy You will begin physiotherapy as soon as possible after your operation. This can be the same day as your operation. The physiotherapist will teach you knee exercises, which you should continue independently. You will be shown how to safely get out of bed, stand and transfer into a chair. The physiotherapist will progress your mobility as able and prior to discharge you will be shown how to climb stairs safely with aids, if needed. 13
14 Bed exercises following knee surgery These exercises should be performed at least 4 times a day. 1. Deep Breathing Exercises (to prevent a chest infection) Sit upright in your bed or chair. Take 3 slow deep breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth. Keep your shoulders relaxed. Repeat every hour you are awake. 2. Ankle Pumping (to prevent blood clots) In the bed or chair, pump your feet up and down. If your heel becomes sore please elevate using pillows. Repeat as often as possible. 3. Bridging (to prevent bedsores) Lying on your back, bend your nonoperated leg and push through this and your arms to lift your bottom off the bed. Repeat as often as possible. Please only perform the exercises marked with a tick in the box. Repeat all exercises at least 4 times per day. 14
15 4. Static Quads Lying on your back. Pull your foot up and push your operated knee into the bed tightening your thigh muscles. Hold for 5 seconds Repeat 10 times 5. Hanging Out Place heel on roll (heel must be high enough so calf and knee are off the surface). Hold for up to 20 minutes This should be done when icing and resting your leg. You can also tighten and relax thigh muscle in this position. 6. Heel slides in bed Lying on the bed, place a plastic bag under the heel of your operated leg and slide your heel towards your bottom, you can use your hands to obtain as much bend in your knee as possible. You may use a plastic bag or doughnut under your heel to reduce friction. Hold for 5 seconds, then bend knee a little further before releasing, Repeat 10 times 15
16 7. Heel Digs Lying on your back, bend the operated knee slightly. Push your heel into the bed. Hold for 5 seconds Repeat 10 times 8. Buttock clenching Lying on your back. Squeeze your buttocks firmly together. Hold for 5 seconds Repeat 10 times 9. Knee extension over roll (Inner Range Quads) Place a rolled towel under your knee, pull your foot up and keep the knee in contact with the pillow whilst straightening the knee. Hold for 5 seconds Repeat 10 times DO NOT LEAVE YOUR OPERATED KNEE RESTING ON A PILLOW AS THIS WILL STOP YOU GETTING A STRAIGHT KNEE. 16
17 10. Straight leg raise Lying on a bed. Pull your foot up and brace your knee straight. Lift the leg 5 inches off the bed keeping your knee straight. You should have your non-operated leg bent up during this exercise. Then lower slowly back down to the bed. Hold for 5 seconds Repeat 10 times 11. Assisted knee flexion in sitting Sitting in a chair, slide your operated foot backwards along the floor to bend your knee as much as possible. Keeping your foot still, hold the arms of the chair and move your bottom forwards slowly. You should feel a stretch down the front of your knee as your knee bends. Hold for 5 seconds, then move your bottom back in the chair. Repeat 10 times. Steps and stairs the safest technique Use a banister if available and take one step at a time Going up Un-operated leg Operated leg Walking Aid(s) Coming down Walking Aid(s) Operated Leg Un-operated leg Remember Good leg up... Bad leg down 17
18 PRICE regime Protection Use walking aids to help you carry out your daily life until advised by your Physiotherapist. Rest You should increase the amount of walking you do slowly and take regular periods of rest. Ice Ice is used to reduce the amount of swelling, and can help to relieve pain. Do not use ice if you have cold allergies or circulatory problems. On the ward the physiotherapist will show you how to use a Cryocuff. Before using ice make sure you have normal sensation on the knee. Do not put ice directly on the skin. At home apply a bag of frozen peas or crushed ice wrapped in a damp towel onto the knee. Rest the ice on top of the knee, never rest the knee onto the ice. It is normal for the area to go red and slightly numb during icing. After the ice has been on for 5 minutes check the skin. If you notice that the area has gone white remove the ice immediately. If not, leave the ice in place for 20 minutes if you can tolerate it. Compression Your Physiotherapist may provide you with a tubigrip which you should wear throughout the day. Elevation Elevate the area as much as possible to help reduce swelling. The most effective way to do this is by spending one hour in the morning and afternoon lying flat on the bed with your operated leg resting on pillows so that your heel is higher than your heart. Ensure that your knee is straight whilst the leg is elevated. 18
19 Discharge from hospital Before you go home you must; Have an acceptable range of movement. Be able to get up from a low toilet (aids can be issued) Be able to walk independently and safely with the walking aid of choice. Be able to safely negotiate stairs with the same set up as yours at home. Be able to independently carry out your home exercise programme. On discharge the nursing staff will give you; Medication as appropriate. A letter for your GP. A sick certificate if required. Your physiotherapist will discuss follow-up physiotherapy arrangements. If you are coming back to the RSCH, an appointment will be made for you. If not, a referral will be sent to your local hospital and they will contact you with an appointment. If they have not contacted you within 2 weeks please let us know. Written instructions regarding follow up care for your wound and further appointments etc. You may be given stockings to wear at home. Practice nurse appointment. 19
20 Please do the following: Continue your exercises as instructed by your physiotherapist. You will need to continue to take your pain medication to allow you to do these. Apply your ice pack/frozen peas regularly. Try to take regular daily walks increasing the distance as you are able (however walking does not replace your exercise programme). Keep your wound clean and dry. Take a daily rest on your bed for at least an hour elevating your knee above heart level. Contact your GP if there is increased pain or swelling in your calf. Contact your GP if you are worried about signs of infection in your knee e.g. red, hot and swollen and/or oozing wound. Please avoid the following: Sitting for too long as you may become stiff and find it difficult to get up and going again. Resting with a pillow under your knee. Stepping your operated foot in front when sitting onto the chair. Walking with a stiff knee. It will take at least 12 weeks for your knee to feel like a knee and it will go on improving for 18 months. Advice after six weeks Housework Increase the amount of housework that you do over the next few months. Be careful when bending or twisting. You may kneel on your knee replacement if it is comfortable to do so but always kneel on something soft. It may take 1-2 years to be able to kneel on your knee. 20
21 Wound If your wound is tender to touch you may massage it firmly using moisturising cream to desensitise the skin and underlying tissues. You should only begin to massage once the stitches/staples have been removed and the wound is clean and dry (normally at around 2 weeks post operation). Sleeping You may adopt any sleeping position that is comfortable. You may wish to put a pillow between your knees. Avoid placing a pillow under your knee. If you are having problems sleeping because of pain please see your GP. Sport/Leisure Most sporting activities can be resumed after 3-6 months depending on comfort and level of competition. Low impact sports such as swimming, cycling, and golf are usually not a problem after your knee replacement. High impact sports, such as jogging, squash and football are not recommended. Gardening should be done with care. If possible use a kneeling stool and long handled tools. Travelling Ideally you should not travel within 3 months of your surgery. Sitting for prolonged periods increases the risk of developing Venous Thromboembolism (VTE). We do not recommended any form of prolonged travel within 6 weeks of surgery. Exercise Continue with the exercises as instructed by your physiotherapist. This will increase your strength and maintain a functional range of movement. You will need to continue some of your exercises to successfully regain your knee strength for the first year, and possibly the life of the knee replacement. Progress your walking distance, as you feel comfortable. 21
22 Maintenance exercises Please only perform the exercises marked with a tick in the box. Repeat the exercises once per day. 11. Wall Slides Place your back against the wall, step your feet away from the wall. Slide your back down the wall performing a small squat. Keep your knees over your toes. Repeat 10 times. 12. Balance Stand by a stable surface. Stand on your operated leg with your knee slightly bent. Try to take your hands off the supporting surface for 10 seconds. Progress by standing barefoot on different surfaces e.g. carpet / pillow. Progress again by moving your arms around. 22
23 13. Standing from a chair Sitting in a chair, place both feet level with one another. Stand up from the chair without using your hands, try to take the weight evenly through your legs. Repeat 10 times 14. Resisted Knee Flexion Sit in a chair, hook your non-operated leg behind the operated leg. Attempt to pull your operated leg under the chair and resist this movement with the other leg. Repeat 10 times 23
24 15. Resisted Knee Extension Sitting in a chair. Place your non-operated leg in front of the operated leg. Attempt to straighten your operated leg whilst resisting with your other leg. Repeat 10 times 16. Patellar Mobilisation Hold your kneecap as shown. Move your kneecap from side to side 5 times and up and down 5 times. 17. Hanging out Continue to hang out your knee to maintain extension. (see Post Op Exercise 5 on page 15) 24
25 Possible complications Your Consultant will discuss possible complications with you Anaesthetic and Medical We will make sure you are medically fit for your operation and measures will be used to reduce the risk of blood clots occurring. Any anaesthetic and major operation carries a very small increased risk of being complicated by the following medical conditions: Heart attack Stroke Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) (blood clot in the vein) Complications affecting the knee are less common. These can include; Stiffness Persistent knee pain Infection in the joint Loosening of the knee replacement Fractures around the knee replacement Blood Transfusion During and after the operation you will lose some blood. The blood you lose will usually be made up by your own body in the weeks after surgery. A blood transfusion is required in roughly less than 2% of patients. Blood needed for transfusion is always tested and matched to your own blood but still carries a very small risk associated with it such as:- 1. Rejection and reaction to the donor blood 2. Transmission of infection 25
26 Infection An infection can occur after any operation but it is particularly important that you understand its consequences when undergoing a knee replacement. You must look out for signs of an infection e.g. red, hot skin around the knee, feeling unwell or fever. Prophylactic antibiotics (to reduce the risk of infection at the time of the surgery) are routinely used. If you are concerned you may have an infection you should see the Orthopaedic team at the hospital via Accident and Emergency or Fracture Clinic. Venous thromboembolism This is possible following any surgery. You will be given daily medication to reduce this risk and will also be taught preventative circulatory exercises by your physiotherapist which you should begin immediately after your operation. Haematoma Bruising can develop around the wound and this can seep down towards your ankle and foot. This is not usually a problem and will resolve over a few weeks. Occasionally a more significant bruise (haematoma) occurs under the wound and this can delay healing. An operation may be required to release this collection of blood. This is more likely to happen if you are taking aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin or an anti-inflammatory medication (e.g. Ibuprofen, Voltarol). Please inform us at your pre-assessment appointment if you are taking this type of medication. The risk is reduced by stopping it for a week before your operation. Leg swelling Leg swelling is quite common after the operation. It tends to improve each night with rest and elevation. You are advised to use the PRICE regime to reduce swelling. If it is worsening or becomes painful then you need to seek advice as one of the causes of swelling in the first six weeks is venous thromboembolism. Swelling may remain around the knee for up to 12 months after the operation. 26
27 Vascular injury Where there is pre-existing vascular damage there may be damage to the arteries behind the knee. This will be identified and treated quickly should it arise. Nerve damage During the operation nerves in your leg can be damaged but this is rare. Nerve damage causes numbness and tingling in your leg. It can also weaken your ankle or foot. Instability If your knee gives way or buckles this can interfere with your daily life and can be painful. It also increases the wear and tear on your new knee. This will be improved by strengthening exercises, however, you should seek advice if this persists. You may need to wear a brace for a period of time. General advice If you develop pain in your calf or chest, or your wound becomes red, swollen, hot and /or oozing, please contact your GP urgently, or come to the Accident & Emergency department at the hospital. If you have any further questions that are not answered by this booklet, please ask the ward staff who are there to help you. You still have pain in your knee Your knee may carry on hurting despite the operation. Your surgeon will investigate to see if a cause can be found but sometimes they won t be able to find one. Usually the pain will improve but this can take several months and a background ache may persist. You have problems bending your knee If you had a stiff knee before your operation you may not gain a full range of movement afterwards. Less than 100 degrees of movement can lead to functional problems. If you have not achieved this by 3 months post surgery you may benefit from Manipulation Under Anaesthetic (MUA). 27
28 Please bring this booklet with you to all your appointments regarding your knee replacement. Appointments record Pre-assessment Clinic (in Fracture Clinic, RSCH) on: Pre-Operative Knee Group Date: Operation Date: Estimated Discharge Date: Post Operative Physiotherapy appointment: At: On: If you are not having physiotherapy at the RSCH a referral will be sent to your local hospital and they will contact you with an appointment. Follow up Orthopaedic Appointment (in fracture clinic) on: 28
29 Further information National Joint Registry (NJR) website: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) website: NHS website: British Orthopaedic Association website: ARC website: Helpful telephone numbers Fracture Clinic: Admissions Desk: ext 4355 RSCH Physiotherapy Department: RSCH Occupational Therapy Department: ext 4766 Bramshott Ward: ext 4065 / 4066 Ewhurst Ward: ext 4073 /
30 Notes and questions 30
31 31
32 Royal Surrey County Hospital (RSCH) NHS Foundation Trust fully subscribes to the National Patient Safety Agency (NPSA) Being Open best practice framework, November Contact details of independent advocacy services can be provided by our Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) who are located in far left corner as you enter the main reception area. PALS are also your first point of contact for health related issues, questions or concerns surrounding RSCH patient services. Contact details Telephone: Opening hours: Monday to Friday If you would like information documents in large print, on tape or in another language or form please contact us on: Review date: September 2014 Author: Susie Golding PIN The Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 2012
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet
 Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Programme
 Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip Replacement. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107
 Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions
 Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions PLEASE READ ALL OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. THEY WILL ANSWER MOST OF YOUR QUESTIONS. 1. You may walk
Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions PLEASE READ ALL OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. THEY WILL ANSWER MOST OF YOUR QUESTIONS. 1. You may walk
Ankle Arthroscopy and Follow-Up Physiotherapy
 Ankle Arthroscopy and Follow-Up Physiotherapy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have agreed that you might benefit from
Ankle Arthroscopy and Follow-Up Physiotherapy Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have agreed that you might benefit from
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway. Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS)
 Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion. What is a lumbar spinal fusion? Page 1 of 5
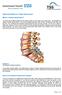 Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery (ERALS) programme: patient information and advice 2
 This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY. Dr C.S. Waller. Orthopaedic Surgeon
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
A Guide. To Revision Total Knee Replacement. Patient Information Leaflet
 A Guide This leaflet is available in large print, Braille and on tape. Please contact Geoff Pennock on 0151 604 7289. To Revision Total Knee Replacement Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
A Guide This leaflet is available in large print, Braille and on tape. Please contact Geoff Pennock on 0151 604 7289. To Revision Total Knee Replacement Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
total hip replacement
 total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
Rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. Walkers, Crutches, Canes
 Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement
 Your Knee Replacement at the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre A patient s guide to: Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement Welcome to Team Two at the NOC. Together you and your surgeon have
Your Knee Replacement at the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre A patient s guide to: Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement Welcome to Team Two at the NOC. Together you and your surgeon have
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers
 Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a knee replacement. What is a Knee
Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a knee replacement. What is a Knee
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
Rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. Walking after Total Knee Replacement. Continuous Passive Motion Device
 Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
Delivering Excellence. Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust. Information for Patients. Hip and Knee service. Total Knee Replacement NHS
 www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
A Guide Total Knee Replacement
 A Guide To Total Knee Replacement Surgical Services treating you well Introduction This booklet has been written to help you prepare for your operation. Specific practice may vary slightly from surgeon
A Guide To Total Knee Replacement Surgical Services treating you well Introduction This booklet has been written to help you prepare for your operation. Specific practice may vary slightly from surgeon
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM To get the best results from your surgery, it is important that you do your
PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM To get the best results from your surgery, it is important that you do your
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Ankle Stabilisation Procedure
 Ankle Stabilisation Procedure Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have been diagnosed with an unstable ankle. This leaflet
Ankle Stabilisation Procedure Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Following your consultation with a member of the Foot and Ankle team you have been diagnosed with an unstable ankle. This leaflet
Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
Recent Injuries. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The arthroscope is a fibre-optic telescope that can be inserted into a joint. A camera is attached to the arthroscope and the
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The arthroscope is a fibre-optic telescope that can be inserted into a joint. A camera is attached to the arthroscope and the
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients
 Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Self Management Program. Ankle Sprains. Improving Care. Improving Business.
 Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle
 Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a broström lateral ligament reconstruction of ankle under the care of Mr Sam Singh. It explains
Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a broström lateral ligament reconstruction of ankle under the care of Mr Sam Singh. It explains
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 012 Name of Leaflet: Total Knee Replacement Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date: April 2016 Total Knee Replacement Page 1
Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 012 Name of Leaflet: Total Knee Replacement Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date: April 2016 Total Knee Replacement Page 1
Total Knee Replacement
 Manchester Royal Infirmary Total Knee Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 2 What is a Total Knee Replacement? Total knee replacement is one of the most commonly performed orthopaedic operations
Manchester Royal Infirmary Total Knee Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 2 What is a Total Knee Replacement? Total knee replacement is one of the most commonly performed orthopaedic operations
Recovering from a broken hip
 Recovering from a broken hip Information for patients, relatives and carers Who will will look look after after me me during during my hospital my hospital stay? stay? A multidisciplinary team of healthcare
Recovering from a broken hip Information for patients, relatives and carers Who will will look look after after me me during during my hospital my hospital stay? stay? A multidisciplinary team of healthcare
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion.
 Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
Should I have a knee replacement?
 Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
A compressive dressing that you apply around your ankle, and
 Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients
 Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition
 Department of Neurosurgery Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition What happens when you are in hospital page 2 Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition This leaflet explains what to expect when you are
Department of Neurosurgery Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition What happens when you are in hospital page 2 Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition This leaflet explains what to expect when you are
Exercises and advice for patients recovering from thyroid surgery
 Exercises and advice for patients recovering from thyroid surgery Information for patients who have had surgery for conditions affecting their thyroid gland Following your thyroid surgery, the position
Exercises and advice for patients recovering from thyroid surgery Information for patients who have had surgery for conditions affecting their thyroid gland Following your thyroid surgery, the position
PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST
 PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST AIMS AND OBJECTIVES To demonstrate the use of physiotherapy assessment and treatment following: Hip Arthroplasty
PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST AIMS AND OBJECTIVES To demonstrate the use of physiotherapy assessment and treatment following: Hip Arthroplasty
Wrist Fracture. Please stick addressograph here
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
Pressure Ulcers. Occupational Therapy. This leaflet is for both yourself and Carers
 Pressure Ulcers Occupational Therapy This leaflet is for both yourself and Carers Contents What is a pressure ulcer? 3 Who is at risk of developing a pressure ulcer? 4 How can I avoid developing a pressure
Pressure Ulcers Occupational Therapy This leaflet is for both yourself and Carers Contents What is a pressure ulcer? 3 Who is at risk of developing a pressure ulcer? 4 How can I avoid developing a pressure
Ankle Sprain. Information and Rehabilitation. Grade II. Grade I. Grade III
 514-412-4400, ext. 23310 2300 Tupper street, C-831, Montreal (Quebec) H3H 1P3 Ankle Sprain Information and Rehabilitation An ankle sprain is a stretch or a tear of the ligaments (bands of tissue that hold
514-412-4400, ext. 23310 2300 Tupper street, C-831, Montreal (Quebec) H3H 1P3 Ankle Sprain Information and Rehabilitation An ankle sprain is a stretch or a tear of the ligaments (bands of tissue that hold
The advanced back rehabilitation programme
 Physiotherapy Department The advanced back rehabilitation programme This booklet explains what happens during the advanced back rehabilitation programme and how the exercises may help your condition. We
Physiotherapy Department The advanced back rehabilitation programme This booklet explains what happens during the advanced back rehabilitation programme and how the exercises may help your condition. We
Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy At the RNOH, our emphasis is patient specific, which encourages recognition of those who may progress slower then others. We also want
Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy At the RNOH, our emphasis is patient specific, which encourages recognition of those who may progress slower then others. We also want
GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE
 GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE GOING HOME After your TAVR procedure, you will need help when you go home. It is hard to predict how much help
GOING HOME AFTER YOUR TAVR PROCEDURE HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE GOING HOME After your TAVR procedure, you will need help when you go home. It is hard to predict how much help
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery
 Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
University College Hospital
 University College Hospital Total hip joint replacement and your recovery programme UCLH Trauma and Orthopaedic Team Please bring this booklet with you when attending your pre-assessment appointment and
University College Hospital Total hip joint replacement and your recovery programme UCLH Trauma and Orthopaedic Team Please bring this booklet with you when attending your pre-assessment appointment and
Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Welcome to Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Welcome to the Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital.
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Welcome to Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Welcome to the Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital.
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Surgery for hip fracture: Hemi-arthroplasty
 Surgery for hip fracture: Hemi-arthroplasty This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having surgery for a hip fracture. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can
Surgery for hip fracture: Hemi-arthroplasty This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having surgery for a hip fracture. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can
UK HealthCare Sports Medicine Patient Education December 09
 Meniscus tear Description The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the lower leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The meniscus
Meniscus tear Description The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the lower leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The meniscus
YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC
 YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 This leaflet aims to answer some of the questions you may have about your anaesthetic and contains fasting instructions.
YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 This leaflet aims to answer some of the questions you may have about your anaesthetic and contains fasting instructions.
Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program
 Patient Education: Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program Thank you for choosing Johns Hopkins for your hip replacement surgery. We use a team-based approach, and you are
Patient Education: Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program Thank you for choosing Johns Hopkins for your hip replacement surgery. We use a team-based approach, and you are
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy)
 Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program
 ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program 1. Introduction to Rehabilitation 2. The Keys to Successful Rehabilitation 3. Stage 1 (to the end of week 1) 4. Stage 2 (to the end of week 2) 5. Stage 3 (to the
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program 1. Introduction to Rehabilitation 2. The Keys to Successful Rehabilitation 3. Stage 1 (to the end of week 1) 4. Stage 2 (to the end of week 2) 5. Stage 3 (to the
Varicose Vein Surgery
 Information for patients Varicose Vein Surgery Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having varicose veins and your specialist has recommended varicose vein surgery. This leaflet explains
Information for patients Varicose Vein Surgery Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having varicose veins and your specialist has recommended varicose vein surgery. This leaflet explains
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A Guide for Patients Produced by the British Association for Surgery of the Knee and The British Orthopaedic Association (adapted) KNEE ARTHRITIS If your knee is affected by severe
Total Knee Replacement A Guide for Patients Produced by the British Association for Surgery of the Knee and The British Orthopaedic Association (adapted) KNEE ARTHRITIS If your knee is affected by severe
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY
 HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
it s time for rubber to meet the road
 your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
UK HealthCare Sports Medicine Patient Education December 09
 LCL injury Description Lateral collateral knee ligament sprain is a sprain (stretch or tear) of one of the four major ligaments of the knee. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a structure that helps
LCL injury Description Lateral collateral knee ligament sprain is a sprain (stretch or tear) of one of the four major ligaments of the knee. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a structure that helps
PHYSIOTHERAPY REHAB AFTER HIP ARTHROSCOPY
 PHYSIOTHERAPY REHAB AFTER HIP ARTHROSCOPY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 Introduction This leaflet has been compiled by the Physiotherapy Team to help you understand the hip
PHYSIOTHERAPY REHAB AFTER HIP ARTHROSCOPY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 Introduction This leaflet has been compiled by the Physiotherapy Team to help you understand the hip
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Patella Realignment Tibial Tuberosity Transfer with Lateral Release
 Patella Realignment Tibial Tuberosity Transfer with Lateral Release Alan M. Reznik, M.D. The Orthopaedic Group, LLC The knee is made of three bones, the kneecap (patella), the shin bone (tibia) and thigh
Patella Realignment Tibial Tuberosity Transfer with Lateral Release Alan M. Reznik, M.D. The Orthopaedic Group, LLC The knee is made of three bones, the kneecap (patella), the shin bone (tibia) and thigh
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
A Guide Total Hip Replacement
 A Guide To Total Hip Replacement Surgical Services treating you well Introduction This booklet has been written to help you prepare for your operation. Specific practice may vary slightly from surgeon
A Guide To Total Hip Replacement Surgical Services treating you well Introduction This booklet has been written to help you prepare for your operation. Specific practice may vary slightly from surgeon
We ve got your back. Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery
 We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
==Knee replacement surgery and your recovery programme
 40 Publication date: Apr 2006 Date last reviewed: May 2011 Date next review due: May 2013 Leaflet code: UCLH/S&C//SUR/ORTHO/TKR/3 University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Main switchboard:
40 Publication date: Apr 2006 Date last reviewed: May 2011 Date next review due: May 2013 Leaflet code: UCLH/S&C//SUR/ORTHO/TKR/3 University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Main switchboard:
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery
 Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery Steps you can take to get better sooner Patient s name:... Consultant s name:... Admission date:... Planned discharge date:... Type of operation:... Date of
Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery Steps you can take to get better sooner Patient s name:... Consultant s name:... Admission date:... Planned discharge date:... Type of operation:... Date of
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Living with Your New Knee
 AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION
 SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
Forefoot deformity correction
 Contact us Pharmacy Medicines Helpline If you have any questions or concerns about your medicines, please speak to the staff caring for you or call our helpline. t: 020 7188 8748 9am to 5pm, Monday to
Contact us Pharmacy Medicines Helpline If you have any questions or concerns about your medicines, please speak to the staff caring for you or call our helpline. t: 020 7188 8748 9am to 5pm, Monday to
