David J. Lederer, MD, MS
|
|
|
- Gervase Gordon
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COPD: Definition Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic airflow obstruction due to chronic bronchitis and/or pulmonary emphysema David J. Lederer, MD, MS Associate Medical Director, Lung Transplant Program Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons New York Presbyterian Lung Transplant and ILD Programs Chronic Bronchitis Pulmonary Emphysema Definition persistent cough and sputum production for at least three months in at least two consecutive years Submucosal gland hyperplasia Airway edema Mucus plugging and airways fibrosis Destruction of acinar walls Physiologic effects Loss of radial traction on airways Increased lung compliance Consequences Hyperinflation Airflow obstruction Risk Factors for COPD Centrilobular emphysema - Smoking-related - Upper lobe predominant Particulate exposure Tobacco smoke Occupational dusts Indoor air pollution (biomass fuel combustion) Genes Alpha-1 anti-trypsin (SERPINA1) Panlobular emphysema - alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency - Lower lobe (basilar) or diffuse Contributing factors Older age Male gender Low socioeconomic status Poor nutrition
2 Case: I m winded What is the next step? A 52 year old women with no medical history presents to your office with dyspnea with household chores for the past few months. She has a 60 cigarette packyear history and reports a smoker s cough for the past 5 years without change. She continues to smoke 10 cigarettes per day. No chest pain or edema. Breath sounds are quiet. No crackles, rhonchi, or wheezing. No edema or clubbing. 1. Alpha-1 anti-trypsin level 2. Chest CT scan (without contrast) 3. Spirometry with and without bronchodilator 4. Echocardiography Chest x-ray shows hyperinflation. You suspect COPD Spirometry results Diagnosis of COPD Causes of Airflow Obstruction Symptoms Airflow obstruction COPD Upper airway obstruction Lower airway obstruction COPD Asthma Bronchiectasis (e.g., cystic fibrosis) Large airway obstruction Tumor, stenosis, foreign body aspiration, et al. Bronchiolitis Pulmonary edema Carcinoid syndrome Airflow obstruction = FEV 1 /FVC ratio < 0.70
3 Clinical Presentation of COPD 10% of adults > 40 have COPD 24 million adults with COPD 50% undiagnosed Common symptoms Cough with sputum production (chronic bronchitis) Exertional dyspnea Muscular wasting During an exacerbation Change in sputum quantity, color, or consistency Wheezing Increased dyspnea Physical Exam in COPD Early disease = normal exam Common findings Increased anteroposterior chest diameter Barrel chest Bilaterally diminished breath sounds Skeletal muscle atrophy During an exacerbation Wheezing Rhonchi Cyanosis Spirometry is the BEST test for diagnosis and staging of COPD Stage FEV 1 /FVC FEV 1 ABG I: Mild >80% predicted Any II: Moderate 50 to 79% Any III: Severe 30 to 49% < 0.70 IV: Very Severe PaO 2 >60 mm Hg, and PaCO 2 <50 mm Hg PaO 2 < 60 mm Hg 30 to 49% or PaCO 2 > 50 mm Hg <30% Any What other diagnostic test should be performed? 1. Alpha-1-anti-trypsin level 2. Chest CT scan without contrast 3. Chest CT scan with contrast 4. Echocardiography α1-antitrypsin (AAT) Deficiency Autosomal co-dominant disorder caused by mutation in the SERPINA1 gene Phenotypes classified by migration in isoelectric ph gradient from A to Z (slowest migration) Case 1 Control Case 2 Paper electrophoresis of patient serum AAT alleles Allele Groups Examples Defect Normal Deficiency M X (Glu363Lys) S (Glu264Val) Z (Glu342Lys) M malton (Phe52del) None Intracellular degradation or accumulation Null Tyr160X No mrna or protein Laurell and Eriksson Dysfunctional M mineral springs Met358Arg Defective inhibition of elastase Stoller JK and Aboussouan LS. Lancet 2005.
4 AAT genotypes and emphysema risk α1-antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency Genotype Prevalence A1AT Serum Concentration Risk of Emphysema MM 91% mg/dl Background MS 6% mg/dl Background MZ 3% mg/dl Background SS 0.1% mg/dl Background SZ 0.1% mg/dl 20-50% ZZ 0.02% mg/dl % Stoller JK and Aboussouan LS. Lancet % of COPD pts have severe A1AD 59,000 Americans Only 10,000 are receiving replacement therapy All patients with COPD should be tested (serum level and/or phenotype) AAT is a serine protease inhibitor inhibits trypsin Inhibits neutrophil elastase Panlobular emphysema Younger pts with basilar emphysema Can also cause liver disease Treatment Intravenous pooled plasma α1-antitrypsin May slow the decline in lung function What is the next step? Management by COPD stage 1. Short-acting beta-agonist + tiotropium 2. Short-acting beta-agonist + inhaled corticosteroid 3. Short-acting beta-agonist + oral prednisone 4. Smoking cessation Stage FEV 1 Consider I: Mild >80% Risk factor reduction Influenza/pneumococcal vaccination Short acting inhaled β2 agonists II: Moderate 50 to 79% Long acting inhaled bronchodilators Pulmonary rehabilitation III: Severe 30 to 49% Inhaled corticosteroids (if wheezing or repeated exacerbations) IV: Very Severe <30%* Long term oxygen therapy Surgical therapy Non pharmacologic approaches to smoking cessation Behavioral counseling 5 A s & 5 R s Telephone based Computer program based Text messaging Group based therapy ASK ADVISE Brief Strategies to Help the Patient Willing to Quit Smoking Identify smokers at every visit Strongly urge all users to quit Alternative therapies Acupuncture less effective than nicotine replacement. Meta analyses suggest no effect Hypnosis meta analysis found insufficient data Financial incentives $750 works! ASSESS ASSIST ARRANGE Determine willingness to quit Aid the patient in quitting Schedule follow-up contact
5 Five R s for smokers who are unwilling to quit Intervention Encourage the patient to Examples Relevance Indicate why quitting is personally relevant Disease state or risk Family/kids Risks Identify negative health effects of tobacco use See next slide Rewards Roadblocks Repetition Identify benefits of tobacco cessation Identify barriers to quitting while you note elements of treatment to address those barriers Improved health Save money Smell better (!) Setting an example Reduced wrinkles Withdrawal symptoms Weight gain Depression Enjoyment of tobacco Risks of tobacco use Timing Risk Acute Dyspnea, cough, wheeze Asthma exacerbation Pregnancy harm Long term Atherosclerosis (acute MI, CVA, PAD) Cancer (lung, oral/pharyngeal/esophageal, pancreas bladder, cervix) COPD Environmental Spouses Lung cancer Heart disease Children More likely to smoke Low birth weight & SIDS Asthma/respiratory infections Smokers who are ready to quit Set a quit date (typically within 2 weeks) Build support by telling family/friends Remove all tobacco products TOTAL ABSTINENCE Be available to the patient Pharmacotherapy Pharmacologic therapies for tobacco cessation Agent Usage 6 month abstinenc e rate Nicotine replacement 25% Nicotine polacrilex (gum) 2 4mg piece every 1 2 hrs x 8 12 wks Nicotine lozenges 1 2mg every hour Nasal nicotine spray 0.5 mg each nare hourly x 3 6 months Nicotine inhaler 6 16 cartridges/day x 3 6 months Transdermal nicotine patch 16 24hrs/day x8 weeks Oral medication Buproprion 150mg x 3 days, then 300mg daily for 24% up to 6 months Varenicline See next slide 33% Varenicline Orally available partial agonist at the α4β2 subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Effects Stimulates nicotinic receptor (reduces withdrawal) Block nicotine from binding (reduces reward) Increases the odds of quitting three fold 33% 6 month quit rate Use: 0.5mg daily x 3 days, then 0.5 mg BID for 4 days, then 1mg BID for 11 more weeks. Quit smoking 1 weeks after initiating varenicline Successful quitters at 12 weeks should continue for 12 more weeks Nausea Headache Insomnia Abnormal dreams Varenicline Side Effects FDA Black box warning (2009) Depression Suicidal thoughts and actions FDA safety announcement (2011) Small increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events in patients with cardiovascular disease
6 Suggested approach to smoking cessation Use the 5 A s Dual approach Counseling Pharmacologic therapy Varenicline most effective May be combined with nicotine replacement Tailor therapy to the individual Comorbidities Preferences What treatment should be given? 1. Short-acting beta-agonist + tiotropium 2. Short-acting beta-agonist + inhaled corticosteroid 3. Short-acting beta-agonist + oral prednisone 4. Short-acting beta-agonist alone Selected Inhaled Medications for COPD Drug Class Drug Trade Names Use Short-acting β2- agonist (SABA) Long-acting β2- agonist (LABA) Short-acting anti-cholinergic Long-acting anti-cholinergic Albuterol Pirbuterol Levalbuterol Salmeterol Formoterol Arformoterol Ipratropium Ventolin Maxair Xopenex Serevent Foradil Brovana Atrovent Symptom relief Controller Symptom relief (slower than SABA) Tiotropium Spiriva Controller SABA/Anticholinergic Albuterol/Ipratropium Combivent Symptom relief Glucocorticoid LABA/Glucocorticoid Budesonide Fluticasone Mometasone Triamcinalone Becolmethasone Formoterol/Budesonide Salmeterol/Fluticasone Pulmicort Flovent Asmanex Azmacort Beclovent, Vanceril Symbicort Advair Controller Controller Management by COPD stage Stage FEV 1 Consider I: Mild >80% Risk factor reduction Influenza/pneumococcal vaccination Short acting inhaled β2 agonists II: Moderate 50 to 79% Long acting inhaled bronchodilators Pulmonary rehabilitation III: Severe 30 to 49% Inhaled corticosteroids (if wheezing or repeated exacerbations) IV: Very Severe <30%* Long term oxygen therapy Surgical therapy *You should be familiar with all of the Drug Classes and with the drugs in green font UPLIFT: Primary endpoint UPLIFT: COPD exacerbation Tashkin et al. NEJM 2008; 359: Tashkin et al. NEJM 2008; 359:
7 UPLIFT: Survival UPLIFT: Other benefits Decreased risk of respiratory failure RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.52 to 0.92) Decreased risk of serious cardiac events RR 0.84 (95% CI 0.93 to 0.98) Tashkin et al. NEJM 2008; 359: Tashkin et al. NEJM 2008; 359: Meta-analysis: CV events and anti-cholinergics Case - continued Over the next two years Three hospitalizations for acute exacerbations FEV 1 declines to 40% predicted Started on supplemental oxygen with exercise Initiates pulmonary rehabilitation Singh, S. et al. JAMA 2008;300: What additional treatment should be considered? 1. Lung transplantation 2. Theophylline 3. Long-term oral corticosteroids 4. Inhaled corticosteroids COPD Classification Stage FEV 1 % Add treatment Stage I: Mild > 80% Smoking cessation Vaccination Short-acting bronchodilators Long-acting bronchodilator Stage II: Moderate 50 to 79% Pulmonary rehabilitation Stage III: Severe 30 to 49% Inhaled glucocorticoids Stage IV: Very severe <30% Supplemental oxygen Surgical management GOLD guidelines:
8 TORCH: Primary endpoint TORCH: Acute Exacerbations p value Calverley et al. NEJM 2007;356: Calverley et al. NEJM 2007;356: TORCH: Adverse events Side effects of inhaled medications β2-agonists Tremor Tachycardia Hypokalemia LABA: Increased risk of severe exacerbation and asthma death? FDA recommends using LABAs only in combination with other controller therapy (such as inhaled corticosteroids Anti-cholinergics Dry mouth Cardiovascular events appear not be a concern with the formulation of tiotropium available in the US Inhaled glucocorticoids Oropharyngeal thrush (gargle & rinse to prevent) Cataracts Osteoporosis Increased risk of pneumonia in COPD pts? Calverley et al. NEJM 2007;356: Roflumilast: PDE-4 inhibitor Oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor FDA-approved to decrease exacerbation rate in patients with chronic bronchitis, severe airflow limitation, and a history of exacerbations Mechanisms Decreases airway inflammation Promotes airway smooth muscle relaxation Clinical Effects Improved FEV1 Decreases exacerbation rate Side effects Diarrhea Weight loss Hasn t been studied in combination with ICS Azithromycin for COPD Placebo-controlled RCT of 1,577 adults with COPD Azithromycin 250mg daily Benefits Decreased acute exacerbation rate Improved quality-of-life Concerns Hearing decrements more common (25% vs. 20%)?effect on microbial resistance Cardiovascular risk in a recent (non-copd) study Albert et al. NEJM 2011; 365:689-98
9 Long term oxygen therapy Surgery for COPD: LVRS Indicated for chronic hypoxemia PaO 2 < 55 mm Hg (SpO 2 < 88%) PaO mm Hg (SpO 2 < 89%) with one of the following: Hematocrit > 55% Cor pulmonale Dependent edema Improves Survival Pulmonary hemodynamics Exercise capacity Resect 25% of each lung Highly selected candidates Upper lobe predominant emphysema Low exercise capacity (by cardiopulmonary exercise testing) High risk candidates FEV1 < 20% predicted + DLCO < 20% predicted FEV1 < 20% predicted + homogeneous emphysema Improves symptoms, exercise capacity, QOL, survival Surgery for COPD: Lung Transplantation COPD: Acute exacerbation Replacement of one or both lungs with lungs from a deceased donor Highly selected candidates FEV1 < 20-25% Absence of extrapulmonary disease Benefits Improved survival only for some (not proven) Improved quality-of-life Improved exercise capacity 50% mortality at 5 years Increased sputum quantity, thickness, and/or change in color Often with systemic signs of infection, dyspnea Management Short-acting beta-agonists and anti-cholinergics Oxygen therapy, if indicated Systemic antibiotics Systemic corticosteroids (2 week taper) Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation For acute alveolar hypoventilation (hypercapnia) Improves dyspnea and decreases length-of-stay COPD: Summary of Therapies Summary Drug Symptoms FEV1 acute exacerbation rate mortality Short-acting beta-agonist X X Long-acting beta-agonist X X X Ipratropium X X Tiotropium X X X Inhaled corticosteroids X X X Azithromycin X Long-term oxygen therapy X X Alpha-1 replacement Lung volume reduction surgery X X X Lung transplantation X X X No therapy has been proven to change the rate of FEV1 decline over time Diagnosis Spirometry Management for all patients Smoking cessation influenza/pneumococcal vaccination! Test for alpha-1-anti-trypsin deficiency Pharmacotherapy based on FEV 1 Tiotropium for FEV1 < 80% Inhaled corticosteroids for FEV1<50% If recurrent exacerbations Inhaled long-acting beta-agonist if still symptomatic Consider Supplemental oxygen Referral for surgical therapies
Understanding COPD. Carolinas Healthcare System
 Understanding COPD Carolinas Healthcare System 2013 This self-directed learning module contains information about the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of COPD. Target Audience: All RNs and LPNs
Understanding COPD Carolinas Healthcare System 2013 This self-directed learning module contains information about the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of COPD. Target Audience: All RNs and LPNs
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations
 December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO. Leiden
 COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
medicineupdate to find out more about this medicine
 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
Pathway for Diagnosing COPD
 Pathway for Diagnosing Visit 1 Registry Clients at Risk Patient presents with symptoms suggestive of Exertional breathlessness Chronic cough Regular sputum production Frequent bronchitis ; wheeze Occupational
Pathway for Diagnosing Visit 1 Registry Clients at Risk Patient presents with symptoms suggestive of Exertional breathlessness Chronic cough Regular sputum production Frequent bronchitis ; wheeze Occupational
COPD. (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community
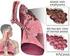 COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST...
 YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST... ...HERE S WHAT TO EXPECT You have been referred to an allergist because you have or may have asthma. The health professional who referred you wants you to
YOU VE BEEN REFERRED TO AN ASTHMA SPECIALIST... ...HERE S WHAT TO EXPECT You have been referred to an allergist because you have or may have asthma. The health professional who referred you wants you to
National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators
 National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators The COPD Educator will be able to achieve the following objectives. Performance objectives, denoted by the
National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators The COPD Educator will be able to achieve the following objectives. Performance objectives, denoted by the
GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY
 GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY Preferred Anticholinergics and Combinations Atrovent HFA (ipratropium) Combivent Respimat (ipratropium/albuterol) Ipratropium neb inhalation
GEORGIA MEDICAID FEE-FOR-SERVICE ASTHMA and COPD AGENTS PA SUMMARY Preferred Anticholinergics and Combinations Atrovent HFA (ipratropium) Combivent Respimat (ipratropium/albuterol) Ipratropium neb inhalation
AECOPD: Management and Prevention
 AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis
 COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Clinical Guideline. Recommendation 3: For stable COPD patients with respiratory symptoms
 Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Pulmonary Diseases. Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming. Overview of Pathophysiology
 Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Clinical Guideline. Recommendation 3: For stable COPD patients with respiratory symptoms
 Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
COPD MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL STANFORD COORDINATED CARE
 I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
Understanding COPD. An educational health series from
 Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM. Reproduced with permission of UofL Pulmonary s COPD Management Program
 Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section 5: Section 6: Section 7: Section 8: Section 9: What is COPD? How the Lungs work. Managing your COPD. Exercise Breathing
Welcome COPD MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section 5: Section 6: Section 7: Section 8: Section 9: What is COPD? How the Lungs work. Managing your COPD. Exercise Breathing
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
RES/006/APR16/AR. Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP
 RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
Drug therapy SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS SHORT-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS LONG-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS
 Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 CORAM S VOLUME 5 Coram LLC is a leading national provider of home infusion services, including alternate site of care and specialty pharmacy distribution. 12450 East Arapahoe Road, Suite A, Centennial,
CORAM S VOLUME 5 Coram LLC is a leading national provider of home infusion services, including alternate site of care and specialty pharmacy distribution. 12450 East Arapahoe Road, Suite A, Centennial,
Tests. Pulmonary Functions
 Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 COPD Guideline Team Team Leader Davoren A Chick, MD General Medicine Team Members Paul J Grant, MD General Medicine Meilan K Han, MD, MS Pulmonary Medicine R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Elisa B
COPD Guideline Team Team Leader Davoren A Chick, MD General Medicine Team Members Paul J Grant, MD General Medicine Meilan K Han, MD, MS Pulmonary Medicine R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Elisa B
MEDICATION GUIDE. SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol
 MEDICATION GUIDE SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol SYMBICORT 160/4.5 (budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation
MEDICATION GUIDE SYMBICORT 80/4.5 (budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol SYMBICORT 160/4.5 (budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg) Inhalation
CLINICAL PATHWAY. Acute Medicine. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease POCKET GUIDE TO COPD DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT, AND PREVENTION A Guide for Health Care Professionals REVISED 2011 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease POCKET GUIDE TO COPD DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT, AND PREVENTION A Guide for Health Care Professionals REVISED 2011 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive
COPD. What is COPD? How many people have COPD in Canada? Who gets COPD?
 What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011
 Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011 Deborah Richman MBChB FFA(SA) Director Pre-Operative Services Department of Anesthesia Stony Brook University Medical Center, NY drichman@notes.cc.sunysb.edu
Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011 Deborah Richman MBChB FFA(SA) Director Pre-Operative Services Department of Anesthesia Stony Brook University Medical Center, NY drichman@notes.cc.sunysb.edu
CCHCS Care Guide: Asthma
 GOALS SHORTNESS OF BREATH, WHEEZE, COUGH NIGHT TIME AWAKENINGS ACTIVITY INTERFERENCE SABA* USE FOR SYMPTOM CONTROL FEV1* OR PEAK FLOW EXACERBATIONS REQUIRING ORAL STEROIDS < 2 DAYS / WEEK 2 TIMES / MONTH
GOALS SHORTNESS OF BREATH, WHEEZE, COUGH NIGHT TIME AWAKENINGS ACTIVITY INTERFERENCE SABA* USE FOR SYMPTOM CONTROL FEV1* OR PEAK FLOW EXACERBATIONS REQUIRING ORAL STEROIDS < 2 DAYS / WEEK 2 TIMES / MONTH
COPD Intervention. Components:
 COPD Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, the causes, risks and complications. Explain COPD Explain how COPD is
COPD Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, the causes, risks and complications. Explain COPD Explain how COPD is
COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
1 ALPHA-1. What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? FOUNDATION
 What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit
 Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit July 26, 2014 Objectives Classify asthma by severity Prescribe
Stacie L. Penkova, PharmD, MHSA, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Critical Care Pharmacy Specialist Drug Information Coordinator Pharmacology Summit July 26, 2014 Objectives Classify asthma by severity Prescribe
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
 Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Your Patient workbook AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema your patient
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Your Patient workbook AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema your patient
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Prof. Florian Gantner. Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim
 Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P
 James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
Documenting & Coding. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC
 Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
The patient s response to therapy within the first hour in the Emergency Room is one of the most reliable ways to predict need for hospitalization.
 Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood
 Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood With exception of smoking cessation pulmonary rehabilitation is the single most effective intervention for any patient with COPD. A Cochrane review published
Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood With exception of smoking cessation pulmonary rehabilitation is the single most effective intervention for any patient with COPD. A Cochrane review published
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT. BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK
 IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
Medications. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Introduction
 Patient Education A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Do you know how each of your inhalers works to help your breathing? Do you know the correct order in which to use
Patient Education A guide to medications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Do you know how each of your inhalers works to help your breathing? Do you know the correct order in which to use
Pulmonary Disorders. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
How To Quit Smoking
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ065 WOMEN S HEALTH It s Time to Quit Smoking What are the dangers of smoking? How does smoking affect the body?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ065 WOMEN S HEALTH It s Time to Quit Smoking What are the dangers of smoking? How does smoking affect the body?
Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy
 Nebulizer Medications Origination: June 17, 2009 Review Date: October 21, 2015 Next Review: October, 2017 Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy DESCRIPTION Nebulizer medications are used to prevent and
Nebulizer Medications Origination: June 17, 2009 Review Date: October 21, 2015 Next Review: October, 2017 Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy DESCRIPTION Nebulizer medications are used to prevent and
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
A VNSNY SELF-CARE GUIDE
 A VNSNY SELF-CARE GUIDE For the Management of: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Visiting Nurse Service of New York A PATIENT SELF-CARE GUIDE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
A VNSNY SELF-CARE GUIDE For the Management of: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Visiting Nurse Service of New York A PATIENT SELF-CARE GUIDE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
Smoking Cessation in People with Severe Mental Illness. Lisa Dixon, M.D., MPH and Melanie Bennett, Ph.D. University of Maryland School of Medicine
 Smoking Cessation in People with Severe Mental Illness Lisa Dixon, M.D., MPH and Melanie Bennett, Ph.D. University of Maryland School of Medicine Smoking and Severe Mental Illness Smoking is a MAJOR problem
Smoking Cessation in People with Severe Mental Illness Lisa Dixon, M.D., MPH and Melanie Bennett, Ph.D. University of Maryland School of Medicine Smoking and Severe Mental Illness Smoking is a MAJOR problem
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests
 Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests Dr. Sally Osborne Cellular & Physiological Sciences University of British Columbia Room 3602, D.H Copp building 604 822-3421 sally.osborne@ubc.ca www.sallyosborne.com
Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests Dr. Sally Osborne Cellular & Physiological Sciences University of British Columbia Room 3602, D.H Copp building 604 822-3421 sally.osborne@ubc.ca www.sallyosborne.com
30 DAY COPD READMISSIONS AND PULMONARY REHAB
 30 DAY COPD READMISSIONS AND PULMONARY REHAB Trina M. Limberg, Bs, RRT, FAARC, MAACVPR Director, Preventative Pulmonary and Rehabilitation Services UC San Diego Health System OVERVIEW The Impact of COPD
30 DAY COPD READMISSIONS AND PULMONARY REHAB Trina M. Limberg, Bs, RRT, FAARC, MAACVPR Director, Preventative Pulmonary and Rehabilitation Services UC San Diego Health System OVERVIEW The Impact of COPD
1 ALPHA-1. Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? FOUNDATION FOUNDATION. Learn how being an Alpha-1 carrier can affect you and your family
 Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
COPD RESOURCE PACK SECTION 11. Fife Integrated COPD Care Pathways
 COPD RESOURCE PCK SECTION 11 Fife Integrated COPD Care Pathways In this section: 1. COPD Guidance treatment at each stage of the disease 2. Overview of Respiratory (COPD) Integrated Pathway 3. Chronic
COPD RESOURCE PCK SECTION 11 Fife Integrated COPD Care Pathways In this section: 1. COPD Guidance treatment at each stage of the disease 2. Overview of Respiratory (COPD) Integrated Pathway 3. Chronic
Insights for Improvement: Advancing COPD Care Through Quality Measurement. An NCQA Insights for Improvement Publication
 2009 Insights for Improvement: Advancing COPD Care Through Quality Measurement An NCQA Insights for Improvement Publication Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema,
2009 Insights for Improvement: Advancing COPD Care Through Quality Measurement An NCQA Insights for Improvement Publication Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema,
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Page 1 of 67 AJRCCM Articles in Press. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi:10.1164/rccm.201204-0596pp GOLD Executive Summary Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive
Page 1 of 67 AJRCCM Articles in Press. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi:10.1164/rccm.201204-0596pp GOLD Executive Summary Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment
 An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
An Overview of Asthma - Diagnosis and Treatment Asthma is a common chronic disorder of the airways that is complex and characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness,
Clinical Quality Measure Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW
 Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
Bronchodilators in COPD
 TSANZSRS Gold Coast 2015 Can average outcomes in COPD clinical trials guide treatment strategies? Long live the FEV1? Christine McDonald Dept of Respiratory and Sleep Medicine Austin Health Institute for
TSANZSRS Gold Coast 2015 Can average outcomes in COPD clinical trials guide treatment strategies? Long live the FEV1? Christine McDonald Dept of Respiratory and Sleep Medicine Austin Health Institute for
EMS Information Bulletin- #060
 BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES EMS Information Bulletin- #060 DATE: October 27, 2008 SUBJECT: TO: FROM: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Basic Life Support Pennsylvania EMS Organizations &
BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES EMS Information Bulletin- #060 DATE: October 27, 2008 SUBJECT: TO: FROM: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Basic Life Support Pennsylvania EMS Organizations &
RSPT 1410 Common Respiratory Drugs
 1 RSPT 1410 Wilkins: Chapter 32 2 Classifications Respiratory therapists administer several different class of drugs: (adrenergic) Parasympatholytics (anticholinergic) Mucoactives (mucolytic) Antiasthmatics
1 RSPT 1410 Wilkins: Chapter 32 2 Classifications Respiratory therapists administer several different class of drugs: (adrenergic) Parasympatholytics (anticholinergic) Mucoactives (mucolytic) Antiasthmatics
F r e q u e n t l y As k e d Qu e s t i o n s. Lung Disease
 Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway. Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD
 Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD Dr. Charlie Chan Health Quality Ontario Expert Panel Co-Chair May/June
Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD Dr. Charlie Chan Health Quality Ontario Expert Panel Co-Chair May/June
COPD Prescribing Guidelines
 South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
understanding the professional guidelines
 SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
Respiratory Care. A Life and Breath Career for You!
 Respiratory Care A Life and Breath Career for You! Respiratory Care Makes a Difference At 9:32 am, Lori Moreno brought a newborn baby struggling to breathe back to life What have you accomplished today?
Respiratory Care A Life and Breath Career for You! Respiratory Care Makes a Difference At 9:32 am, Lori Moreno brought a newborn baby struggling to breathe back to life What have you accomplished today?
Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy
 31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
Asthma Intervention. An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association.
 Asthma Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of asthma and the classification by severity, the risks and the complications. Define asthma Explain how lungs
Asthma Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of asthma and the classification by severity, the risks and the complications. Define asthma Explain how lungs
Smoking Cessation Program
 Smoking Cessation Program UHN Information for people who are ready to quit smoking Read this information to learn: why you should quit smoking how the Smoking Cessation Program works treatments to help
Smoking Cessation Program UHN Information for people who are ready to quit smoking Read this information to learn: why you should quit smoking how the Smoking Cessation Program works treatments to help
An Outcomes Strategy for COPD and Asthma: NHS Companion Document
 An Outcomes Strategy for COPD and Asthma: NHS Companion Document 1 DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy Clinical Estates HR / Workforce Commissioner Development IM & T Management Provider Development Finance
An Outcomes Strategy for COPD and Asthma: NHS Companion Document 1 DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy Clinical Estates HR / Workforce Commissioner Development IM & T Management Provider Development Finance
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Admission Order Set
 Patient Name: PHN: Page 1/1 Admit to Dr: Notified Consult: Dr: Family Dr: Precautions: Contact Droplet Enhanced Droplet Airborne - Reason: _ Code Status: Full Resuscitation or Consults: Reason: Dietician
Patient Name: PHN: Page 1/1 Admit to Dr: Notified Consult: Dr: Family Dr: Precautions: Contact Droplet Enhanced Droplet Airborne - Reason: _ Code Status: Full Resuscitation or Consults: Reason: Dietician
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Pulmonary Diseases and Exercise Testing. Pulmonary Diseases COPD. Two Main Types of COPD
 Pulmonary Diseases and Exercise Testing Types of Pulmonary Diseases Effect on Exercise Response Role of Exercise in Treatments Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Restrictive Pulmonary Vascular Diseases Hypo-ventilation
Pulmonary Diseases and Exercise Testing Types of Pulmonary Diseases Effect on Exercise Response Role of Exercise in Treatments Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Restrictive Pulmonary Vascular Diseases Hypo-ventilation
About one-half of all smokers die of a disease caused by smoking.the most common ones are lung cancer, heart disease, and strokes
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Stopping smoking Smoking harms your health, but it's difficult to stop. That s because most people who smoke have become addicted to nicotine, a chemical in tobacco.
Patient information from the BMJ Group Stopping smoking Smoking harms your health, but it's difficult to stop. That s because most people who smoke have become addicted to nicotine, a chemical in tobacco.
The asthmatic patient and sedation
 The asthmatic patient and sedation Introduction The sedation practitioner is often faced with difficult questions to answer before the administration of sedation. Our guidelines say clearly that we are
The asthmatic patient and sedation Introduction The sedation practitioner is often faced with difficult questions to answer before the administration of sedation. Our guidelines say clearly that we are
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids
 Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids Corticosteroids (steroids) are medicines that are used to treat many chronic diseases. Corticosteroids are very good at reducing inflammation (swelling) and mucus production
Inhaled and Oral Corticosteroids Corticosteroids (steroids) are medicines that are used to treat many chronic diseases. Corticosteroids are very good at reducing inflammation (swelling) and mucus production
NEWS NP S. Inside. Defining COPD. Is it COPD? National Prescribing Service Newsletter
 NP S NEWS National Prescribing Service Newsletter 5 1999 ISSN 1441-7421 Aug 99 Inside Bronchodilators and corticosteroids: Their use in COPD Give it up the best advice for COPD patients: NRT can help This
NP S NEWS National Prescribing Service Newsletter 5 1999 ISSN 1441-7421 Aug 99 Inside Bronchodilators and corticosteroids: Their use in COPD Give it up the best advice for COPD patients: NRT can help This
Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care. Asthma
 What is Asthma? Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care Asthma Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods
What is Asthma? Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care Asthma Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods
Stop Smoking. Key #2. It s Not Too Late to Benefit from Quitting! Health Benefits to Quitting. Other Reasons to Quit
 Key #2 Stop Smoking There are many different poisons that can be found in cigarettes, such as carbon monoxide, tar, rat poison, paint thinner, and lighter fluid, just to name a few. Any of these toxins,
Key #2 Stop Smoking There are many different poisons that can be found in cigarettes, such as carbon monoxide, tar, rat poison, paint thinner, and lighter fluid, just to name a few. Any of these toxins,
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 12 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Anna Murphy Case study and questions Day 1 Mr LT, a 68-year-old man, attended his general practitioner s (GP s) surgery for a routine check-up. He had been diagnosed
12 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Anna Murphy Case study and questions Day 1 Mr LT, a 68-year-old man, attended his general practitioner s (GP s) surgery for a routine check-up. He had been diagnosed
CMAG. CASE MANAGEMENT ADHERENCE GUIDELINES VERSION 1.0 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 CMAG CASE MANAGEMENT ADHERENCE GUIDELINES VERSION 1.0 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Guidelines from the Case Management Society of America for improving patient adherence to COPD therapies April
CMAG CASE MANAGEMENT ADHERENCE GUIDELINES VERSION 1.0 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Guidelines from the Case Management Society of America for improving patient adherence to COPD therapies April
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE PULMONARY CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE
 April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
COPD. Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
 COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome?
 Session on COPD: Novel Concepts and Promising New Drugs Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome? Through a CME Grant sponsored by New Treatment = Better Outcome? Tim S. Trinidad, MD Disclosure Present: COPD
Session on COPD: Novel Concepts and Promising New Drugs Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome? Through a CME Grant sponsored by New Treatment = Better Outcome? Tim S. Trinidad, MD Disclosure Present: COPD
 Never Quit Quitting Training Healthcare Providers to Integrate Cessation Counseling and Referral into Office Practice Lisa Krugman, MPH, MSW Washtenaw County Public Health Washtenaw County Smokers (HIP
Never Quit Quitting Training Healthcare Providers to Integrate Cessation Counseling and Referral into Office Practice Lisa Krugman, MPH, MSW Washtenaw County Public Health Washtenaw County Smokers (HIP
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
 Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT GUIDE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT
Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT GUIDE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CHEST PHYSICIANS AND THE CHEST FOUNDATION Living Well With COPD Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema YOUR PATIENT
RESPIRATORY VENTILATION Page 1
 Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
1 ALPHA-1. Healthcare Provider s Guide FOUNDATION. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Healthcare Provider s Guide Addressing the need for providing up-to-date information about screening, diagnosis, and treatment of this disorder 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION Healthcare
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Healthcare Provider s Guide Addressing the need for providing up-to-date information about screening, diagnosis, and treatment of this disorder 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION Healthcare
