Early Childhood and the Crisis in Oral Health. Dr. Stephen Abrams Dr. Ian McConnachie
|
|
|
- Lisa Weaver
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Early Childhood and the Crisis in Oral Health Dr. Stephen Abrams Dr. Ian McConnachie
2 Today as Part of a Continuum Current state of government action and ODA lobbying IADR 2008 ODA Special Report on Tooth Decay in Ontario`s Children Radio ads ODA web site Reprinted articles in Ontario Dentist from the California Dental Association ASM presentation: continue education of the oral health team Campaign on water fluoridation
3 Overview of Today s Presentation The Problem Current Concepts on Early Childhood Caries Assessment and Diagnostic Tools Dental Public Health
4 Overview of Today (cont d) Risk Management Strategies Community Mothers Infants Recommendations Provincial Public Health Local Public Health
5 The Problem
6 Dental Caries is one of the most common diseases among 5 17 year olds Percentage of children & adolescents ages 5 to 17 Caries Asthma Hay Fever Chronic Bronchitis Note: Data included decayed or filled primary and or decayed filled or missing permanent teeth. Asthma, chronic bronchitis and hay fever based upon household respondent about the sampled 5 17 year old Source NCHS 1996 Oral Health in America: A Report of the Surgeon General DHHS 2000
7 Public perception In other words no big deal
8 Our reality A very big deal
9 Early Childhood Caries - Prevalence < 4 yrs Data Collected using DMFT not ICDAS 4% Quebec convenience sample of month infants Veronneau et al 1% USA representative sample of mo infants Kasteet etal % USA sample of yr old children Kaste et al % Whole Cree population age months Quebec Veronneau et al % Whole Inuit population age months in NWT Albert et al % representative sample of mo old Ojibway Lawrence 2008 (N Ontario) infants 53% representative sample 408 children First Nations DEFT of % of caries in 31% of population in Manitoba Schroth et al 2005
10 Early Childhood Caries prevalence 0-5 years United States Decay rates dropped until 90 s Rates now documented as increasing 2-5 year olds 24% in % in Wide variability with population groups Dye et al, National Center for Health Statistics NHANES III 2007
11 Lida et al 2007
12 Ontario Prevalence 0-5 years 87% of First Nations sample Lawrence % in Health Units Survey* OAPHD % of Toronto 5-year olds * 25.1% in daycare community Leake 2001 Ottawa Public Health * * Survey under reports children sampled due to methods * Children sampled not representative of population in general
13 Defining the Problem - Prevalence Local Screening Program - London Ontario 46 % of children of entire elementary school district surveyed % (1 in 8) of all JK and K had untreated visible decay 4.5% required urgent care Of JK children who had experienced decay 49% did not have needs met Untreated or children needing treatment located in specific school districts Families least likely to afford treatment have highest levels of decay Current Data 5 yr olds from % needed dental work 67% observed decay free courtesy Dr. C. Friedman
14 Early Childhood Caries - risk factor for future caries - good indicator of future caries experience *Al Shalan TA, et al. Primary incisor decay before age 4 as a risk factor for future dental caries. Pediatr Dent. 19(1):37 41, 1997 *O'Sullivan DM, Tinanoff, N, The association of early dental caries patterns with caries incidence in preschool children., J Public Health Dent 56(2):81 3, 1996 *Kaste, LM, et al. The assessment of nursing caries and its relationship to high caries in the permanent dentition. J Public Health Dent. 52(2):64 8, 1992 *Almeida, Al et al. Future caries susceptibility in children with Early Childhood Caries following treatment under General Anesthesia. Pediatr Dent 22 (4) , 2000 BY THIS TIME IT IS TOO LATE
15 Terminology Early Childhood Caries Severe Early Childhood Caries Early Childhood Tooth Decay Baby Bottle Syndrome Nursing Bottle Syndrome Nursing Caries
16 Early Childhood Caries (ECC) The presence of 1 or more decayed (noncavitated or cavitated lesions), missing (due to caries), or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth in a child 71 months of age or younger. AAPD Definition from National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial research (NIDCR) workshop 1999
17 Severe Early Childhood Caries (S-ECC) Any sign of smooth-surface caries in a child younger than 3 years of age AAPD 1 or more cavitated, missing (due to caries), or filled smooth surfaces in primary maxillary anterior teeth, or decayed, missing or filled score of at least 4 (Age 3), 5 (age 4), or 6 (age 5) surfaces Drury et al 1999
18
19 Clinical presentation: early lesions Begins soon after dental eruption Typically develops on smooth surfaces Appear as chalky white decalcification Most often starts on lingual surfaces of maxillary incisors
20
21
22 Clinical Presentation (Early) Initial cavitation can appear on the lingual surface of the maxillary incisors
23 Later Tooth Decay
24 Baby Bottle Tooth Decay (Severe)
25 Facial cellulitis Infection spreading into surrounding tissues
26 Systemic Effects from Severe ECC Malnourishment in a population with severe early childhood caries, Clarke et al 2006 Among the findings: 66% have normal weight, 18 % underweight 28% have haemoglobin levels below acceptable and 46% in the low range of acceptable 51% have low albumin levels 77% have low ferritin Conclusion: children with severe tooth decay have borderline or low nourishment
27 Detrimental health effects of ECC pain, infection, loss of function affects learning, communication, nutrition, sleep lower body weight chronic inflammation psychological impact lasting detrimental impact on the dentition
28 Cariology What is Tooth Decay?
29 What do you need to create tooth decay? Teeth Food particularly carbohydrates Bacteria in Plaque or Biofilm
30 Elements involve in the Caries Process Plaque containing bacteria Caries Sugars & Carbohydrate Exposure Tooth When all three are present, and enough time passes, large carious lesions will occur
31 NIH Consensus Conference on Caries 2001 Dental caries is an infectious, communicable disease resulting in destruction of tooth structure by acidforming bacteria found in dental plaque, an intraoral biofilm, in the presence of sugar."
32 NIH Consensus Conference March 2001 Caries is a bacterial infection caused by specific bacteria. Caries is a reversible multi factorial process. In other words, caries is an infectious disease with cavitation being the last step of the process
33 The Paradigm Shift One can place a number of restorations in a mouth and yet not treat the underlying disease. The bacteria remain in the plaque biofilm on the remainder of the teeth capable of creating new areas of decalcification and cavitation. We need to shift from a surgical approach to a disease management & preventive approach.
34 The Shifting Focus of Dentistry Treatment of Prevention of Reduced Results of Dental Disease Risk Dental Disease Factors This should be particularly true in ECC
35 Caries Progression
36 Early Carious Lesion in Enamel
37 Pathogenesis of Dental Caries (biological balances) SALIVA PLAQUE PLAQUE Polysaccharides ENAMEL mouth Calcium Salts Plaque buffers SUGARS ACID inside of tooth Calcium Salts Salivary buffers Bacterial Enzymes Demineralization Re-mineralization
38 The Caries Balance Pathological Factors Acidogenic Bacteria (S. Mutans, S. Sobrinus & Lactobacilli) Reduced Salivary Flow Frequency of fermentable carbohydrate ingestion Protective Factors Saliva flow & components Proteins, calcium, phosphate, fluoride, immungloulins Antibacterials In saliva and extrinsic Fluoride, Chlorhexidine, iodine Caries No Caries Adapted from Featherstone, J. D. B., JADA 2000
39 Demineralization Dental Mineral Acid soluble Calcium phosphate + Organic Acids Demineralization Calcium & Phosphate into solution If fluoride is present in the water between the crystals it inhibits mineral loss
40 Remineralization Calcium in tooth Water (from saliva) + Phosphate In tooth Water (from Saliva) Remineralization Builds on existing crystal remnants New mineral less soluble Fluoride helps Fluoride speeds up remineralization creating a less soluble mineral
41 demineralization ph Critical ph FAP HAP deposit caries erosion ph remineralization Carious lesion forms at ph Erosion lesion forms when ph < 4.5
42 Healing a Small Cavity Initial Treatment (3 months) Lesion size is 2 mm x 4 mm along the gum line with difficult visual access Do not want to probe the lesion to check on integrity
43 What contributes to the extent of ph drop after glucose challenge? Type and amount of carbohydrate available Bacteria present Salivary composition and flow Other food ingested Thickness and age of dental plaque
44 Caries is a Bacterial Infection!
45
46 Mode of Transmission Both this spoon and pacifier have been in the mouth and then cultured in a selective broth. They show S. Mutans growing on them. Courtesy of Ivoclar Vivadent.
47 Caries Is An Infectious Disease: 1. Demonstration of Mother to Child Transmission of Streptococcus mutans using Multilocus Sequence Typing Lapirattanakul et al. Caries Research Genotypic Diversity of Mutans Streptococci in Brazilian Nursery Children Suggests Horizontal Transmission Mattos Graner et al. J Clin. Microbiology 2001
48 Bacteria Involved in Caries Streptococcus Mutans, Streptococcus Sobrinus Lactobaccillus
49 Plaque & Biofilms Some New Thoughts on Plaque
50 What is a Biofilm? A biofilm is a well organized, cooperating community of microorganisms. The slime layer that forms on rocks in streams is a classic example of a biofilm. Biofilms are everywhere in nature. It is estimated over 95% of bacteria existing in nature are in biofilms.
51 Plaque as a Biofilm Within the microcolonies are differing environments Microorganisms have primitive communication system Microorganisms in biofilm behave differently than bacteria in a culture medium Microorganisms in biofilm are resistant to antibiotics, antimicrobials, and host response
52 Plaque Biofilm Artist Depiction of Plaque Bioflim
53 CAMBRA Caries Management by Risk Assessment
54 A Caries Risk Assessment (CRA) is just weighing the factors of each patient.
55 And CAMBRA is just removing weight from one side and adding weight to the other.
56 The Shifting Focus of Dentistry Treatment of Prevention of Reduced Results of Dental Disease Risk Dental Disease Factors This should be particularly true in ECC
57 Risk Factors BioMedical Social Determinants
58 Risk Factors: History Child has special needs Socio economic status of the family Parents & siblings have decay
59 Risk Factors: Dental History Child has decay Time lapse since last cavity Child wears braces or oral appliance Reduced saliva flow
60 Risk Factors: Dental History Frequency of brushing Daily between meal exposure to sugars & carbohydrates On demand bottle Sippy cup Sports drinks & carbonated beverages
61 Risk Factors: Reduced Fluoride Exposure Fluoridated water Fluoride supplements Fluoridated toothpastes
62 Risk Factors: Clinical Evaluation Visible plaque Gingivitis Areas of enamel demineralization ICDAS 1 3 Enamel defects / deep fissures
63 Risk Factors: Clinical Evaluation Part 2 Radiographic evidence of caries Levels of Strep Mutans in saliva Use commercial tests Not critical for establishing risk
64 Caries Risk Indicators Clinical Conditions Environmental Characteristics General Health Conditions AAPD Caries Risk Assessment Tool (CAT) Low Risk Moderate Risk High Risk No carious teeth in past 24 months No enamel demineralization (enamel caries white spot lesions ) No visible plaque; no gingivitis Optimal systemic and topical fluoride exposure Consumption of simple sugar or foods strongly associated with caries initiation primarily at mealtimes Regular use of dental care in the established dental home Carious teeth in the past 24 months 1 area of enamel demineralization (enamel caries white spot lesions ) Gingivitis Suboptimal systemic fluoride exposure with optimal topical exposure Occasional between meal exposures to simple sugar or foods strongly associated with caries Mid level caregiver socioeconomic status Irregular use of dental services Carious teeth in the past 12 months More than 1 area of enamel demineralization (enamel caries whitespot lesions ) Visible plaque on anterior teeth Radiographic enamel caries High titers of mutans streptococci Wearing dental or orthodontic appliances Enamel hypoplasia Suboptimal topical fluoride exposure Frequent (ie, 3 or more) between meal exposures to simple sugars or foods associated strongly with caries Low level caregiver socioeconomic status (ie, eligible for Medicaid) No usual source of dental care Active caries present in the mother Children with special health care needs Conditions impairing saliva composition/flow Chart based on the AAPD Caries-Risk Assessment Tool. For more information on using the tool, refer to
65 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Pediatrics FIGURE 1 Child, family, and community influences on oral health outcomes of children Fisher-Owens, S. A. et al. Pediatrics 2007;120:e510-e520
66 Oral Health Individual Sex, Age, Genes, Biology Oral Health & Related Behaviours Diet, Hygiene, Smoking Alcohol, Injury Social & Community Context Social Norms, Peer Groups, Social Capital Cultural Identity, Social Network Economic, Political & Environmental Conditions Poverty, Housing, Sanitation, Leisure Facilities, Shopping Facilities Employment, Work / Educational Environment, Commercial Advertising, Social Policy)
67 Overview of the Morning The Problem ECC Current Concepts Assessment and Diagnostic Tools Dental Public Health
68 Dental Public Health Big picture reality getting to the populations Making connections Motivational interviewing Ottawa pilot project Role of medical community?
69 Big picture reality THE RESPONSIBILITY STARTS WITH GOVERNMENT
70 Ontario Statistics 55% with employer sponsored plans 4% with private dental plans 5% on government plans Balance self-paying 14.4% defined as low income (Statistics Canada) 70% of Ontarians visit a dentist annually Highest percentage in Canada
71 Ontario government perspective on government plan coverage Gap coverage High needs, not high risk Low socioeconomic levels Disabled and their families Emphasis on basic or urgent treatment with minimal emphasis on prevention or education Possible shift with new Phase II programme Other provincial governments have quite different strategies
72 36 Public Health Departments in the province All provide dental services required by mandatory provincial programs Some have dental clinics Services vary with local mandates and funding New proposals to Ministry January 2010 Over 4000 private dental practices
73 Mandatory government dental programs for public health Dental Indices Survey (DIS) Oral health screening Monitor fluoridation of water supply Provide Children In Need of Treatment Program (CINOT) Provide dental education to high risk schools,
74 Ontario Public Health Programs for At-Risk Children Healthy Babies, Healthy Children Best Starts Early Years Centers 18-month Well Baby Visit Nipissing District Developmental Screen Healthy Schools Initiative Oral Health involvement is not currently required as a part of these programs but may be done as local initiative
75 Dental Indices Survey (DIS) Value in giving very general overview of problem Non-calibrated Less than ideal examination No radiographs Inconsistent data collection methods Beynon et al 2004
76 Provincial government children s dental plans Children in Need of Treatment (CINOT) Ontario Works (OW) Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) Assistance for Children with Severe Disabilities (ACSD)
77 Number of Procedures CINOT Procendure Code Profile Restorative vs Preventive by Number of Procedures Paid for Preventive Restorative * Year
78 Prevention Strategies Communities Mothers Infants
79 Dental Public Health Big picture reality getting to the populations Making connections Individual oral health promotion Role of medical community
80 Dental Public Health Making connections Understanding the at-risk populations Variable with each health unit Mostly socio-economic criteria Sub-populations and understanding their needs is critical to success e.g. cultural, language
81 Dental Public Health Big picture reality getting to the populations Making connections Individual oral health promotion Role of medical community
82 Strategies for Primary Prevention of ECC
83 Motivational Interviewing Success in dentistry Early childhood caries Harrison RL, Wong T. An oral health promotion program for an urban minority population of preschool children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 2003 Oct;31(5):393 9
84 Dental Public Health Big picture reality getting to the populations Making connections Motivational interviewing Ottawa pilot project Role of medical community?
85 Ottawa Pilot Project Predates current new funding envelope Recognition of need to work outside of the box Funding by local budget with politician buy-in OPINION The current dental public health gold standard within the Ontario government constraints
86 Ottawa Pilot Project Selected Analysis of Statistics city-wide 11.3% need Group 1 city-wide in two groups 9.7% need Group 2 community age % need Group 3 sub-group across city age % need Group 4 daycare centers within group 2 community age % need
87 Dental Public Health Big picture reality getting to the populations Making connections Motivational interviewing Ottawa pilot project Role of medical community? Families First
88 Families First Model Youth at Risk Public Health Unit Dental Public Health Literacy CHC Dental Team Community Social Services Agencies Family Faculties of Dentistry Employment School Primary Health Team
89 Prevention Strategies Communities Mothers Infants
90 Evidence-based Dentistry Integration into clinical decision making Evolution of patient-centered care More rapid adjustment of clinical practice
91 The Infant Oral Health Exam Why The new standard of care Slight variations in recommendations Canadian Dental Association Ontario Dental Association Canadian Academy of Paediatric Dentistry American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry
92 The Infant Oral Health Exam How Dental Public Health Identify the populations Prioritize the education/prevention Unique skill sets Motivational interviewing Preventive therapies
93 The Infant Oral Health Exam How Private Dental Practice Optimal evidence-based preventive strategies Internal marketing and practice building
94 The 12 Month Oral Health Exam Objectives Recording medical history and dental history Complete oral exam Assess infant risk and determine prevention plan Provide anticipatory guidance Plan for comprehensive care Refer where appropriate if necessary
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108 Are Parents Interested? 1. How can my infant get cavities by 1 year? 2. I brush and floss. Isn t that enough? 3. I brush my child s teeth before bed like you showed us and in the morning now look at what happened? 4. My child eats no sweets yet we still have cavities? 5. What can I do as a parent to prevent cavities?
109 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Pediatrics FIGURE 1 Child, family, and community influences on oral health outcomes of children Fisher-Owens, S. A. et al. Pediatrics 2007;120:e510-e520
110 Elements: 1. Visual exam to assess risk 2. Parent / Guardian interview 3. Oral Hygiene Instruction 4. Set up frequency of visits 5. Develop a preventive protocol 6. Apply or dispense preventive therapies The key is to assess risk and have parent / caregiver provide proper care.
111
112
113
114 Risk Intervention Implementation into office Office prevention programme Patient tools Decision tree
115 Therapeutic and Preventive Interventions Parents and Caregivers Patients
116 Parents and Caregivers Knowledge transfer In-office education Individual oral health promotion models
117 Anticipatory Guidance for Mother Goal: anticipatory guidance for the mother both before the baby is born and following the infant s birth on several information items for her health and that of baby
118 Water Good for mom s health Does it have fluoride If bottled water, does it contain fluoride Benefit is to mothernot fetus
119 Oral Hygiene Care For mom s health as well as control of bacterial transfer Brush and floss daily to disturb cariogenic bacteria and reduce bacterial plaque levels Use toothpaste with fluoride
120 Diet Chose foods low in sugar. Eat healthy snacks like fruit, cheese and vegetables. Get enough calcium for mom and baby s healthy teeth and bones. Calcium is in milk, cheese, dried beans and leafy green vegetables. Avoid carbonated drinks
121 Canada s Food Guide Interactive guide for all family members sc.gc.ca/fn an/foodguide aliment/tour/indexing.php
122 Now is the time for mom to learn Get her mouth healthy Do a Smile Check on a baby How to clean a baby s teeth How to prevent early childhood caries Ask her doctor or dentist to check the baby s teeth by age one. Talk with her doctor or dentist about fluoride.
123 ODA s Ten Tips For Parents Downloadable from the website
124
125
126
127 Motivational Interviewing Success in dentistry Early childhood caries Harrison RL, Wong T. An oral health promotion program for an urban minority population of preschool children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 2003 Oct;31(5):393 9
128 Parents and Caregivers Caries infection transfer prevention Caries treatment Fluoride Xylitol Chlorhexidine other
129 Dental care for mother To maintain or to restore to health the oral tissues If dental caries are present, removal of decay and restoration of teeth
130 Dental Care for Mothers Univ of Wash Study 2009 Safe at any time during pregnancy (ACOG) High utilization if offered Significant increased utilization by children Mothers rated children s oral health higher Also Michigan PRAMS data
131 Mother chewing xylitol gum Recent evidence suggests that chewing xylitol gum kills cariogenic bacteria Chew 1 piece of gum for 5 minutes 3 5 times a day decreases the child s caries rate.
132 The Xylitol Story in Brief Natural long chain sugar Non-cariogenic Can reduce mutans strep in plaque and saliva Can reduce caries in young children, mothers and in children via their mothers
133 Key Xylitol Studies Soderling et al 2001 Maternal transmission of MS Xylitol gum Starts 3 months after delivery and for 21 months Fluoride varnish Applied at 6, 12, 18 months CHX varnish Applied at 6, 12, 18 months Measured MS levels in children at age 3 and 6
134 Key Xylitol Studies Soderling et al 2001 Children age 3 MS levels 2.3x higher with Fl Var and CHX Var in mother Children age 6 Protection maintained with same higher benefit of xylitol in mother Isokangas et al 2000 At 5 years, need for treatment 71-75% lower in Xylitol group
135 Why Xylitol and When Maternal 3 months post partum (Soderling 2001) Characteristic of infection at eruption determines life-long (Loesche 1985) Once colonized with benign, ms will not displace (Svanberg and Loesche 1977) May be due to less cariogenic xylitol-metabolizing ms strain (Trahan et al 1996)
136 Risk Intervention Implementation into office Office prevention programme Patient tools Decision tree
137 Apply or Dispense Therapies Xylitol Povidone Iodine Remineralization Agents Fluoride Other
138 Additional In-Office Strategies Knowledge transfer Pit and Fissure sealants A.R.T.
139 Knowledge transfer Awareness of the problem Diet Oral hygiene
140 Sugar + Acid = Double Trouble (a partial list) Acid (ph) Sugar (12 oz) Water tsp Propel fitness water tsp Minute Maid OJ tsp Red Bull tsp Sprite tsp Diet Coke tsp Gatorade tsp Coke Classic tsp Battery Acid tsp Lab tests: Dr. J Ruby, Univ. of Alabama Birmingham School of Dentistry Minnesota Dental Association, Sip All Day, Get Decay c2002
141
142
143 Remineralization Fluoride Effect on teeth more topical Other remineralization agents Effects topical and subsurface
144 Remineralization Topical Fluoride Toothpaste Fluoride Rinse Fluoride Varnish Bottled Water Water Fluoridation
145 A brief review Fluoride action Effect largely topical At low levels Inhibits demineralization at crystal surfaces Enhances remineralization at crystal surfaces At high levels Inhibits bacterial enzymes
146 Fluoride-Some Interesting Pieces Low levels after several hours in plaque and saliva can have a profound effect on demin/remin i.e. TOOTHPASTE MOUTHRINSE? Lynch RJ, Navada R, Walia R, Low levels of fluoride in plaque and saliva and their effects on the demineralization and remineralization of enamel: role of fluoride toothpastes. Int Dent J 2004:54(5 Suppl 1):304-9
147 TOPICAL FLUORIDE Toothpaste Position Statements Canadian Dental Association American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry
148 CDA Position on Use of Fluorides in Caries Prevention Fluoride toothpaste twice daily Parents brush under 3 years and assist 3 6 years Smear of toothpaste All children supervised or assisted til appropriate dexterity
149
150 Topical Fluoride-The Gold Standard J Dent Educ. 71(3): American Dental Education Association Professionally Applied Topical Fluoride: Evidence- Based Clinical Recommendations American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs Key words: fluoride, caries, caries prevention, evidencebased dentistry, clinical recommendations
151 ADA Evidence-Based Recommendations Assess Decide Caries Risk Low Medium High Whether to apply fluoride Type of fluoride Frequency of application How often to re-evaluate
152 Advice ADA Evidence-based Recommendations Professionally Applied Topical Fluoride Risk group /Age Low Medium Less than 6 years Patient may not receive any additional benefit Varnish every 6 months High Varnish every 6 months (or 3 months)
153 ADA Evidence-based recommendations Professionally Applied Topical Fluoride Low risk under 6 years -fluoridated water and toothpaste may provide adequate caries prevention in low risk category -fluoride foam and gel not recommended in this age group
154 5% NaF = approx 22,500 ppm Fluoride Varnish No special equipment No prophylaxis prior to application Easy to apply Dries on contact with saliva Safe and well tolerated Inexpensive Less fluoride than with gel or foam
155 Fluoride and Safety Concerns Two real issues Fluoride toxicity Fluorosis Age of greatest risk for fluorosis 0 3 years Especially months Findings and recommendations of the Fluoride Expert Panel Health Canada Jan 2007
156 Fluorosis Total daily fluoride intake from all sources should not exceed mg F/kg of body weight in order to minimize the risk of dental fluorosis Canadian Dental Association Nov. 2008
157 0.243% NaF 5.0% NaF Current Toothpastes NOTE: Federal advisory panel recommends low-dose fluoride toothpaste be available for children in Canada
158 Other Remineralization Agents A rapidly changing environment Role in dental public health likely limited Role in private practice promising
159 Recommendations Provincial Public Health Local Public Health
160 If I Had 45 Million Dollars Provincial Public Health -province-wide survey of ECC status using CHMS protocol mandatory dental programmes changes collaboration with organized dentistry expert panel composition oral health rep on provincial programs for at risk infants
161 If I Had 45 Million Dollars Local Public Health identify high risk populations for ECC develop local consultative panel with patient groups and local dental society establish valid baseline data collaborative evidence-based oral health literacy strategy collaborative preventive interventions
162 o f Healthy Early enamel decay Advanced enamel decay T Demineralization Remineralization Remineralization therapies Detection Systems X-Ray Drill, Bill, and Fill
163 Some worthwhile web sites to investigate Dental (ODA) Can download this presentation, background papers and charting tools (Minnesota Dental Assoc.) (California Dental Association Foundation)
164 Some worthwhile web sites to investigate: Canada Food Guide (interactive) sc.gc.ca/fn an/food guide aliment/tour/indexing.php Private practice implementation (Dr. R. Ehrlich) Patient info brochure
165 Tooth Decay Infectious Disease Controlling Risk Factors helps in prevention Early Detection = Minimal Intervention First Teeth First Visit
166
Fluoride Products for Oral Health: Professional Information
 Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
First Dental Visit by Age One
 CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
CONTINUING EDUCATION August 2004 First Dental Visit by Age One A guide to the new recommendations Recommended by American Dental Association American Academy of Pediatrics American Academy of Pediatric
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH
 FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
FIRST SMILES: DENTAL HEALTH BEGINS AT BIRTH The purpose of this monograph is to improve the oral health and overall pediatric health of children, birth to 5 years old, including those with disabilities
Oral Health Risk Assessment
 Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
THE TRUTH. What it is like to provide baby dental care. Beth Noel RDH, BS
 THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
Oral Health QUESTIONS
 Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry
 CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians
 Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH
 INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
INFANT ORAL HEALTH and how to use FLUORIDE VARNISH Infant Oral Health Material Developed by: J. Douglass BDS, DDS H. Silk MD A. Douglass MD of the University of Connecticut in cooperation with Connecticut
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE
 WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
WELL CHILD, WELL SMILE What Primary Care Providers Can Do To Improve Children s Oral Health Heidi Baines, MD Anchorage Neighborhood Health Center Alaska Academy of Family Physicians 27 th Annual Scientific
Your child s heart problem and dental care
 Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Oral health care is vital for seniors
 Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Evidence Review: Dental Health Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health
 Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
Evidence Review: Population and Public Health BC Ministry of Health March 2014 (update from September 2006) This is a review of evidence and best practice that should be seen as a guide to understanding
A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs
 A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs The Future: Quality Outcome Measures Using CAMBRA Bob Russell, DDS, MPH The Future Increase Federal Funding to Expand FQHCs
A 3-Step Approach to Improving Quality Outcomes in Safety Net Dental Programs The Future: Quality Outcome Measures Using CAMBRA Bob Russell, DDS, MPH The Future Increase Federal Funding to Expand FQHCs
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children. we design therapies to treat or remineralize early carious lesions?
 Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Impact of Removing Clinical Preventive Oral Health Services from Ontario Public Health Standards
 STAFF REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Impact of Removing Clinical Preventive Oral Health Services from Ontario Public Health Standards Date: August 1, 2014 To: From: Wards: Board of Health Medical Officer of Health
STAFF REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Impact of Removing Clinical Preventive Oral Health Services from Ontario Public Health Standards Date: August 1, 2014 To: From: Wards: Board of Health Medical Officer of Health
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices
 Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
The Chococeutical way of Life. He lthy Teeth. Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates
 The Chococeutical way of Life He lthy Teeth Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates Xyl ceuticals approach to Preventive Dentistry The Problem The new Approach For many years, Preventive Dentistry has
The Chococeutical way of Life He lthy Teeth Xylitol tooth re-mineralization chocolates Xyl ceuticals approach to Preventive Dentistry The Problem The new Approach For many years, Preventive Dentistry has
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs
 Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of
 The Consequences of Untreated Dental Disease in Children Poor oral health in infants and children destroys more than just a smile. Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of individual
The Consequences of Untreated Dental Disease in Children Poor oral health in infants and children destroys more than just a smile. Although largely preventable by early examination, identification of individual
oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y
 oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y 2 0 1 0 Acknowledgments: The CDA Foundation would like to thank the project s co-chairs,
oral health During Pregnancy & Early Childhood: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Health Professionals F e b r u a r y 2 0 1 0 Acknowledgments: The CDA Foundation would like to thank the project s co-chairs,
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme
 The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
School-Based Oral Health Care. A Choice for Michigan Children.indd 1
 School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
School-Based Oral Health Care A Choice for Michigan Children School Based Oral Health Care: A Choice for Michigan Children is part of an information set meant to serve as a guideline for school personnel
The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries
 The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries George Acs, Richard Shulman, Man Wai Ng, Steven Chussid Purpose: Methods: Results: The purpose of this study
The Effect of Dental Rehabilitation on the Body Weight of Children with Early Childhood Caries George Acs, Richard Shulman, Man Wai Ng, Steven Chussid Purpose: Methods: Results: The purpose of this study
Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014
 Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO VERMONT ORAL HEALTH PLAN 2013... 3 THE BURDEN OF ORAL DISEASE IN VERMONT... 6 Children... 6 Adults... 8 Older Adults... 10 Disparities...
Vermont Oral Health Plan 2014 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION TO VERMONT ORAL HEALTH PLAN 2013... 3 THE BURDEN OF ORAL DISEASE IN VERMONT... 6 Children... 6 Adults... 8 Older Adults... 10 Disparities...
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS. brought to you by:
 CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows
 Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
3. Preventing bacteria from producing sufficient organic acid to demineralize tooth surface.
 FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
FACT SHEET - Dental Health : Vol. 1 No. 4 January 1998 Fluoride Used for Dental Caries Prevention Piyada Prasertsom. DDS. MSc. Dental Health Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Tel:
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY
 DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
DENTAL FLUOROSIS A FAST GROWING PROBLEM OF THE MODERN AESTHETIC DENTISTRY S. К. Matelo, Т. V. Kupets Dental fluorosis is attributed to the group of non-carious diseases of type one, in other words to a
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children.
 An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
An assessment of Connecticut pediatricians' recommendations regarding oral health care in young children. Principal Investigator: Kristin Gebhard, MSIV Selective Advisor: Bruce Bernstein, Ph.D. Abstract:
The state of children s oral health in England
 The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
Dental Care for Infants
 Dental Care for Infants Ivonne Ganem, DMD, MPH Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce387/ce387.aspx Disclaimer: Participants
Dental Care for Infants Ivonne Ganem, DMD, MPH Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce387/ce387.aspx Disclaimer: Participants
Karen L Carson MD, FAAP
 Karen L Carson MD, FAAP Dental varnish application as a covered benefit first presented by Dr. Ben Hoffman and Albert Bourbon, PA November, 2007 at the NM Pediatric Society Council Meeting Who is the Pediatric
Karen L Carson MD, FAAP Dental varnish application as a covered benefit first presented by Dr. Ben Hoffman and Albert Bourbon, PA November, 2007 at the NM Pediatric Society Council Meeting Who is the Pediatric
FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS
 1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
1 FLUORIDE VARNISH MANUAL FOR MEDICAL CLINICIANS Smiles for Life A National Oral Health Curriculum Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Group on Oral Health SMILES FOR LIFE is a comprehensive oral health
Ann A. Stueck, MSN,RN
 Integrating Bright Futures into Public Health at the State and Local Levels Oral Health Theme Murray L. Katcher, MD, PhD, FAAP Moderator Chief Medical Officer for Community Health Promotion State MCH Medical
Integrating Bright Futures into Public Health at the State and Local Levels Oral Health Theme Murray L. Katcher, MD, PhD, FAAP Moderator Chief Medical Officer for Community Health Promotion State MCH Medical
Evaluation of a Caries Risk Assessment Model in an Adult Population
 Evaluation of a Caries Risk Assessment Model in an Adult Population by Ferne Kraglund A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Graduate Department of Dentistry
Evaluation of a Caries Risk Assessment Model in an Adult Population by Ferne Kraglund A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Graduate Department of Dentistry
Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services
 Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services Long Term (2010) Subcommittee Outcome Objective: By 2010, increase by 10 percentage points
Health Priority: Access to Primary and Preventive Health Services Objective 4: Access to Oral Health Services Long Term (2010) Subcommittee Outcome Objective: By 2010, increase by 10 percentage points
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology
 Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Oral health in Iran. Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran
 International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Medical/Dental Integration or Integrated Patient Centered Healthcare. October 18, 2013
 Medical/Dental Integration or Integrated Patient Centered Healthcare October 18, 2013 Forces Driving Integrate The Affordable Care Act The Nature of Oral Disease Financing Technology Practice Models/ Integrated
Medical/Dental Integration or Integrated Patient Centered Healthcare October 18, 2013 Forces Driving Integrate The Affordable Care Act The Nature of Oral Disease Financing Technology Practice Models/ Integrated
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
CAMBRA: Best Practices in Dental Caries Management
 Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. CAMBRA: Best Practices in Dental Caries Management A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Michelle Hurlbutt, RDH,
Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. CAMBRA: Best Practices in Dental Caries Management A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Michelle Hurlbutt, RDH,
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION.
 CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
Oral Health in Medicine Competencies for the Undergraduate Medical Education Curriculum
 Oral Health in Medicine Competencies for the Undergraduate Medical Education Curriculum Domains (8) General Oral Health Screening; Dental Caries; Periodontal Disease; Oral Cancer and Prevention; Oral-Systemic
Oral Health in Medicine Competencies for the Undergraduate Medical Education Curriculum Domains (8) General Oral Health Screening; Dental Caries; Periodontal Disease; Oral Cancer and Prevention; Oral-Systemic
Region of Waterloo Public Health Dental Health Program Report 2011-2014. April 2015
 Region of Waterloo Public Health Dental Health Program Report 2011-2014 April 2015 Authors: Grace Bermingham, Chris Harold, Jan Herbison, Dr. Robert Hawkins and Meghan Randall Contributors: Kerri Hutchinson
Region of Waterloo Public Health Dental Health Program Report 2011-2014 April 2015 Authors: Grace Bermingham, Chris Harold, Jan Herbison, Dr. Robert Hawkins and Meghan Randall Contributors: Kerri Hutchinson
Semester I Dental Anatomy (Basic Orofacial Anatomy)
 Dental Assisting Curriculum Example The dentalcare.com CE library offers over 150 courses that can be used in conjunction with your dental assisting curriculum. The guide below recommends courses to assign,
Dental Assisting Curriculum Example The dentalcare.com CE library offers over 150 courses that can be used in conjunction with your dental assisting curriculum. The guide below recommends courses to assign,
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care. Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203
 Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
Improving the Oral Health of Pregnant Women and Young Children: Opportunities for Policymakers
 National Mater nal and Child Oral Issue Health Brief Policy December Center 2011 ISSUE BRIEF August 2012 Improving the Oral Health of Pregnant Women and Young Children: Opportunities for Policymakers Introduction
National Mater nal and Child Oral Issue Health Brief Policy December Center 2011 ISSUE BRIEF August 2012 Improving the Oral Health of Pregnant Women and Young Children: Opportunities for Policymakers Introduction
Non-carious dental conditions
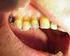 Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
 DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
Issue Brief: Expanding Access to Oral Health Care in Idaho
 Issue Brief: Expanding Access to Oral Health Care in Idaho Oral diseases can be attributed to bacterial infections that, if left untreated, can affect other systems of the body. A growing number of studies
Issue Brief: Expanding Access to Oral Health Care in Idaho Oral diseases can be attributed to bacterial infections that, if left untreated, can affect other systems of the body. A growing number of studies
State of North Carolina. Medicaid Dental Review
 State of North Carolina Medicaid Dental Review October 2010 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is committed to improving pediatric dental care in the Medicaid program
State of North Carolina Medicaid Dental Review October 2010 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is committed to improving pediatric dental care in the Medicaid program
Ohio Public Health Association
 Ohio Public Health Association Dental Care Access: A Public Health Issue April 17 th, 2014 Presented by: Audia Ellis, MSN, RN, FNP BC audiaellis@yahoo.com Objectives Evaluate the current state of dental
Ohio Public Health Association Dental Care Access: A Public Health Issue April 17 th, 2014 Presented by: Audia Ellis, MSN, RN, FNP BC audiaellis@yahoo.com Objectives Evaluate the current state of dental
MI Paste. GC America Inc. Advancing the Art and Science of Dentistry
 MI Paste PROfessionally SPECified Tooth Treatment Delivering Bio-Available Calcium and Phosphate TM Contains 002265 PROSPEC MI Paste 10-Pack Contains: 10 Tubes of MI Paste (40g each), two tubes of each
MI Paste PROfessionally SPECified Tooth Treatment Delivering Bio-Available Calcium and Phosphate TM Contains 002265 PROSPEC MI Paste 10-Pack Contains: 10 Tubes of MI Paste (40g each), two tubes of each
EARLY CHILDHOOD & SCHOOL ORAL HEALTH CURRICULA AND RESOURCES
 EARLY CHILDHOOD & SCHOOL ORAL HEALTH CURRICULA AND RESOURCES Promoting Children s Oral Health: A Curriculum for Health Professionals and Child Care Providers. California Childcare Health Program, Oakland,
EARLY CHILDHOOD & SCHOOL ORAL HEALTH CURRICULA AND RESOURCES Promoting Children s Oral Health: A Curriculum for Health Professionals and Child Care Providers. California Childcare Health Program, Oakland,
get more customers who need more, Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program
 Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program customers who need more, get more For eligible Cigna Dental customers. The Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program was first to enhance dental coverage
Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program customers who need more, get more For eligible Cigna Dental customers. The Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program was first to enhance dental coverage
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO!
 VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Alberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health
 lberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Notice to the reader on Review of Water Fluoridation October 1, 2010 November 7, 2014 November 7, 2014 Notice to the reader Re: Review of Water
lberta Health, Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Notice to the reader on Review of Water Fluoridation October 1, 2010 November 7, 2014 November 7, 2014 Notice to the reader Re: Review of Water
Asuccessful infant oral care program is based on early intervention.1,2 It
 Clinical Considerations for an Infant Oral Health Care Program Abstract: The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry and the American Association of Pediatrics recommend dental assessments and evaluations
Clinical Considerations for an Infant Oral Health Care Program Abstract: The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry and the American Association of Pediatrics recommend dental assessments and evaluations
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions. Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes
 Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
State of Mississippi. Oral Health Plan
 State of Mississippi Oral Health Plan 2006 2010 Vision Statement: We envision a Mississippi where every child enjoys optimal oral health; where prevention and health education are emphasized and treatment
State of Mississippi Oral Health Plan 2006 2010 Vision Statement: We envision a Mississippi where every child enjoys optimal oral health; where prevention and health education are emphasized and treatment
Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services:
 Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services: SUMMARY OF EIGHT STATE REPORTS: (Alabama, Arizona, Maryland, Nebraska, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Texas and Virginia)
Innovative State Practices for Improving The Provision of Medicaid Dental Services: SUMMARY OF EIGHT STATE REPORTS: (Alabama, Arizona, Maryland, Nebraska, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Texas and Virginia)
America s Oral Health
 a me r i c a s Most Trusted D e n t a l l P a n America s Oral Health The Role of Dental Benefits Compiled and published by Delta Dental Plans Association, this report cites data from a number of industry
a me r i c a s Most Trusted D e n t a l l P a n America s Oral Health The Role of Dental Benefits Compiled and published by Delta Dental Plans Association, this report cites data from a number of industry
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Children s Outcomes Research Program The Children s Hospital Aurora, CO Colorado Health Outcomes Program Univ. of Colorado Denver Aurora, CO
 Co-located Dental Hygienist Project: Baseline Early Childhood Caries Prevalence Rates and Parent Oral Health Knowledge, Attitudes, Beliefs and Behaviors Children s Outcomes Research Program The Children
Co-located Dental Hygienist Project: Baseline Early Childhood Caries Prevalence Rates and Parent Oral Health Knowledge, Attitudes, Beliefs and Behaviors Children s Outcomes Research Program The Children
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth.
 Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth. The spacing between children s baby teeth is important because it allows enough room for the bigger, permanent
Primary teeth are also called baby teeth. By age 3 years, there are usually 20 primary teeth. The spacing between children s baby teeth is important because it allows enough room for the bigger, permanent
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003
 Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
SUMMARY REPORT on THE FINDINGS of the ORAL HEALTH COMPONENT of the
 SUMMARY REPORT on THE FINDINGS of the ORAL HEALTH COMPONENT of the CANADIAN HEALTH MEASURES SURVEY 2007 2009 Health Canada is the federal department responsible for helping the people of Canada maintain
SUMMARY REPORT on THE FINDINGS of the ORAL HEALTH COMPONENT of the CANADIAN HEALTH MEASURES SURVEY 2007 2009 Health Canada is the federal department responsible for helping the people of Canada maintain
How To Prevent Dental Caries
 This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
This report may be used, in whole or in part, as the basis for development of clinical practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, or a basis for reimbursement and coverage policies. AHRQ
How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums
 Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Reaching New Heights in Health with School-Based Oral Health Programs White Paper
 Reaching New Heights in Health with School-Based Oral Health Programs White Paper Massachusetts Coalition for Oral Health 2011 The Massachusetts Coalition for Oral Health (MCOH) is comprised of public
Reaching New Heights in Health with School-Based Oral Health Programs White Paper Massachusetts Coalition for Oral Health 2011 The Massachusetts Coalition for Oral Health (MCOH) is comprised of public
Diagnosis of caries and caries test. Dr.V.P.Hariharavel
 Diagnosis of caries and caries test Dr.V.P.Hariharavel CARIES ROT / DECAY Ernest Newbrun 1989 Dental caries is defined as a pathological process of localized destruction of tooth tissues by microorganisms.
Diagnosis of caries and caries test Dr.V.P.Hariharavel CARIES ROT / DECAY Ernest Newbrun 1989 Dental caries is defined as a pathological process of localized destruction of tooth tissues by microorganisms.
KEYWORDS: EARLY CHILDHOOD CARIES, POST-DOCTORAL TEACHING
 Scientific Article Management of caries in the child three years of age and younger: a survey of post-doctoral pediatric dentistry program directors N. Sue Seale, DDS, MSD Alice Kendrick, PhD Dr. Seale
Scientific Article Management of caries in the child three years of age and younger: a survey of post-doctoral pediatric dentistry program directors N. Sue Seale, DDS, MSD Alice Kendrick, PhD Dr. Seale
Promoting Oral Health
 Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
Promoting Oral Health Oral diseases are among the most prevalent health problems in the United States. The 198 Surgeon General's Report to the Nation listed dental disease as a critical health problem
[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location
![[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location](/thumbs/31/14971568.jpg) Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Dental Hygienist. Dental hygienists help maintain the dental health of their patients and educate them about proper oral hygiene.
 Dental Hygienist At a Glance Dental hygienists help maintain the dental health of their patients and educate them about proper oral hygiene. Search by Cluster Medical & Health Typical Range: 55K - 73K
Dental Hygienist At a Glance Dental hygienists help maintain the dental health of their patients and educate them about proper oral hygiene. Search by Cluster Medical & Health Typical Range: 55K - 73K
Electronic Oral Health Risk Assessment Tools
 SCDI White Paper No. 1074 Approved by ADA Council on Dental Practice May 2013 ADA SCDI White Paper No. 1074 Electronic Oral Health Risk Assessment Tools 2013 Copyright 2013 American Dental Association.
SCDI White Paper No. 1074 Approved by ADA Council on Dental Practice May 2013 ADA SCDI White Paper No. 1074 Electronic Oral Health Risk Assessment Tools 2013 Copyright 2013 American Dental Association.
Career paths and opportunities for the Dental Assistant
 Career paths and opportunities for the Dental Assistant Ms Eleanor Schroeder Program Coordinator Dental Assistant Programs Session overview Career pathways for the qualified Dental Assistant (Certificate
Career paths and opportunities for the Dental Assistant Ms Eleanor Schroeder Program Coordinator Dental Assistant Programs Session overview Career pathways for the qualified Dental Assistant (Certificate
Promoting and Enhancing the Oral Health of the Public HHS ORAL HEALTH INITIATIVE 2010
 Promoting and Enhancing the Oral Health of the Public HHS ORAL HEALTH INITIATIVE 2010 Table of Contents ADMINISTRATION FOR CHILDREN AND FAMILIES... 4 Head Start Dental Home Initiative... 4 CENTERS FOR
Promoting and Enhancing the Oral Health of the Public HHS ORAL HEALTH INITIATIVE 2010 Table of Contents ADMINISTRATION FOR CHILDREN AND FAMILIES... 4 Head Start Dental Home Initiative... 4 CENTERS FOR
Ohio s. School Nurse TOOLKIT BROUGHT TO YOU BY: July 2014 A GUIDE TO HELP MAKE GOOD DECISIONS FOR YOUR SCHOOL S ORAL HEALTH PROGRAM
 Ohio s School Nurse TOOLKIT BROUGHT TO YOU BY: July 2014 A GUIDE TO HELP MAKE GOOD DECISIONS FOR YOUR SCHOOL S ORAL HEALTH PROGRAM ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health
Ohio s School Nurse TOOLKIT BROUGHT TO YOU BY: July 2014 A GUIDE TO HELP MAKE GOOD DECISIONS FOR YOUR SCHOOL S ORAL HEALTH PROGRAM ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health
the 2010 Indian Health Service Oral Health Survey of American Indian and Alaska Native Preschool Children
 the 2010 Indian Health Service Oral Health Survey of American Indian and Alaska Native Preschool Children i the 2010 Indian Health Service Oral Health Survey of American Indian and Alaska Native Preschool
the 2010 Indian Health Service Oral Health Survey of American Indian and Alaska Native Preschool Children i the 2010 Indian Health Service Oral Health Survey of American Indian and Alaska Native Preschool
3. Entry Requirements
 1. Introduction The EFP has previously published its recommendations concerning undergraduate and specialist education in periodontology. The aim of this document is to give guidance to those authorities
1. Introduction The EFP has previously published its recommendations concerning undergraduate and specialist education in periodontology. The aim of this document is to give guidance to those authorities
Oral Health Program. Strategic Plan. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Oral Health Program Strategic Plan 2011 2014 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic
Oral Health Program Strategic Plan 2011 2014 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic
Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians
 2015 Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians CPT Codes: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are developed and maintained by the American Medical Association. The codes consist
2015 Oral Health Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Physicians CPT Codes: Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are developed and maintained by the American Medical Association. The codes consist
Table of Contents. PREFACE... i ACKNOWLEDGMENTS... ii
 U GUIDE TO CHILDREN'S DENTAL CARE IN Medicaid October 2004 Table of Contents PREFACE... i ACKNOWLEDGMENTS... ii DENTAL CARIES IN U.S. CHILDREN... 1 Prevalence and Risk... 1 Severity... 2 Unmet Treatment
U GUIDE TO CHILDREN'S DENTAL CARE IN Medicaid October 2004 Table of Contents PREFACE... i ACKNOWLEDGMENTS... ii DENTAL CARIES IN U.S. CHILDREN... 1 Prevalence and Risk... 1 Severity... 2 Unmet Treatment
Dental Health Services in Canada
 Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
Dental Health and Epilepsy
 Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health
 In This Monitor: Preventive Oral Health, Primary Care, Children s Coverage December 2008 The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health Chris Cantrell Introduction Twenty-five state Medicaid programs
In This Monitor: Preventive Oral Health, Primary Care, Children s Coverage December 2008 The Role of Physicians in Children s Oral Health Chris Cantrell Introduction Twenty-five state Medicaid programs
Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care
 Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care Can old dogs learn new tricks? Suzanne Boulter, MD, FAAP Adjunct Professor of Pediatrics Dartmouth Medical School Learning Points Opportunities and challenges
Use of a Risk Assessment Tool in Primary Care Can old dogs learn new tricks? Suzanne Boulter, MD, FAAP Adjunct Professor of Pediatrics Dartmouth Medical School Learning Points Opportunities and challenges
help overcome neglect of Dental health
 COMMUNITY BENEFIT System s mobile clinics help overcome neglect of Dental health BY STEPHEN HOLLISTER, M.A. In the poorest neighborhoods of Orange County, Calif., 1 in 3 schoolchildren screened during
COMMUNITY BENEFIT System s mobile clinics help overcome neglect of Dental health BY STEPHEN HOLLISTER, M.A. In the poorest neighborhoods of Orange County, Calif., 1 in 3 schoolchildren screened during
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
Final Report Format. Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum
 Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
Final Report Format Follow-Up Activities to EHS/HS State/Territorial Oral Health Forum State /Territory: Maryland Person submitting report: Linda Zang Activities originally proposed and how they relate
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS
 FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
FLUORIDE VARNISH TRAINING MANUAL FOR MASSACHUSETTS HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS THIS INFORMATION IS SUPPORTED BY MASSHEALTH AND IS CREATED IN CONJUNCTION WITH MATERIALS FROM: Society of Teachers in Family
