My Guide to Sugar Diabetes
|
|
|
- Rafe Hicks
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 My Guide to Sugar Diabetes 3
2 CONTRIBUTORS WE DEDICATE THIS GUIDE TO ALL SOUTH CAROLINIANS AND THEIR FAMILIES WHO STRUGGLE WITH DIABETES. The development of this guide was a collaborative effort of the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control, the Medical University of South Carolina Colleges of Nursing and Medicine and REACH The first and second editions were developed by: Ida Spruill, RN, MSC, MSN Cheryl Stepka-Tracy, RN, MA, CDE Yaw Boateng, MS, MPH, RD Project SUGAR Director REACH 2010, Community Educator Health Systems Coordinator Medical University of South Carolina Diabetes Initiative of South Carolina SC Diabetes Prevention and Medical University of South Carolina Control Program, DHEC This edition was developed by: Carolyn M. Jenkins, DrPH, FAAN Yaw Boateng, MS, MPH, RD Barbara A. Carlson, MLIS Assoc. Professor,College of Nursing Health Systems Coordinator Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Library Medical University of South Carolina SC Diabetes Prevention and Science and Informatics Control Program, DHEC Medical University of South Carolina Other Contributors Dr. John Colewell Denise Wood Dr. Deborah Carson William S. Robinson Ellen Babb Pamela Arnold Dr. Deyi Zheng Tammy McCottry Dr. Rhonda Hill Tammy Butler Gayenell Magwood Barbara Wright-Mallory Isabel Caldera Ragan DuBose Dr. James Coleman Carolyn Cavannaugh Diane Kennedy Jane Parker Elizabeth Todd-Heckel Dr. Elizabeth Mayer Davis Sharon Cash Beverly Highland Anna Johnson Florene Linnen Virginia Thomas Dr. Lisa Waddell Charles Hossler Wendy Taylor Betty Rouse South Carolina Diabetes Prevention and Control Program Diabetes Initiative of South Carolina Enterprise/MUSC Neighborhood Health Program (HAD-ME) Project SUGAR Nurses REACH 2010 Partners REACH 2010 Community Health Advisors Georgetown County Diabetes CORE Group Permission to Reproduce/Public Domain This guide is public domain. Anyone may reproduce any or all of the contents. It is also available on the South Carolina Diabetes Prevention and Control Program web site the Diabetes Initiative of South Carolina web site at and the REACH 2010 web site at This guide is supported by Grants/Cooperative Agreements U50/CCU and U32/CCU from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 3rd Edition,
3 TABLE OF CONTENTS Contributors... Inside Cover Introduction... 4 Taking Care of My Diabetes... 8 Diabetes Medication The Highs and Lows of Sugar Diabetes and My Body Special Days My Rights and Responsibilities Resources My Gold Card Mini Record My Notes on Diabetes
4 INTRODUCTION Sugar Diabetes Diabetes is a serious disease that affects how my body uses food. My body changes the food I eat into sugar. My blood carries sugar to the cells of my body. Insulin made by my pancreas helps move sugar from my blood into my cells where it can be used for energy. If sugar builds up in the blood instead of going into my body s cells, then I get high blood sugar or sugar diabetes. Over time, high levels of sugar or sugar diabetes can hurt my body and cause problems to my eyes, heart, kidneys, feet, blood vessels, and nerves. If I have diabetes, it is important to know how to take care of myself to protect my body. Diabetes can hurt my body. I will protect my body and help my diabetes by eating healthy, losing weight (if overweight) and by daily physical activity. When I have diabetes, I don t have enough insulin or my body can t use the insulin I have. So my body can t move sugar into my body s cells and muscles for energy. The sugar stays in my blood. When this happens I have high blood sugar or sugar diabetes. The amount of sugar in my blood is called my blood sugar number or blood sugar level. I must have the right blood sugar levels (90-130) to stay healthy. 4
5 How Will I Feel If I Have Sugar Diabetes? If I have sugar diabetes and my blood sugar numbers are high, I might: Go to the bathroom often Get very thirsty Get very hungry Have blurry vision Lose a lot of weight Have sores that heal slowly Have more infections than usual Feel very tired Have dry skin A few people who have high blood sugar or diabetes may not notice any of the above signs. If a member of my family has one or some of these signs, I will have them see a health care provider. A simple blood test can tell if someone has sugar diabetes. 5
6 What Should My Blood Sugar Numbers Be? If I have high blood sugar, I have sugar diabetes. I will ask my health care provider how I can control my blood sugar and other problems caused by diabetes. Blood Sugar Numbers 70 to 100 is normal Blood Sugar 101 to 125 means I have Prediabetes ( borderline ) 126 or higher after eating no food for 8 hours or more means I have Diabetes 200 or higher after eating, also means I have Diabetes If I have been told I have prediabetes, I will work with my health care provider to prevent diabetes. If I have diabetes, I will work to keep my blood sugar at 90 to 130 before meals and less than 180 about 2 hours after starting a meal. 6
7 Why Do So Many People Have Sugar Diabetes? Years ago, people were more active. In many cases we grew our own food and ate healthier. Today, many people eat too much food that has too many calories, and our serving sizes are too big. Many people don t get enough physical activity. Many more people are overweight or obese. I am more likely to get diabetes if: Someone in my family has diabetes I am African American, American Indian, Hispanic/Latino or Asian Pacific Islander I am overweight I do not exercise I gave birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds I have high blood pressure I have high blood fats (triglycerides) and/or low good cholesterol (HDL) I have polycystic ovary disease (PCOS) Choosing healthy foods, being active and keeping my weight down lowers my chances of having sugar diabetes. 7
8 TAKING CARE OF MY DIABETES Are There Different Types of Diabetes? YES! Type 1 diabetes is when my body can t make any insulin at all. Type 2 diabetes is when my body makes SOME insulin but not enough, or the insulin my body makes doesn t work well. Insulin cannot work well if I am overweight and do not exercise. Most people have Type 2 diabetes. What Do Blood Sugar Numbers Mean? We all have sugar in our blood. The amount of sugar in my blood is called my blood sugar number or blood sugar level. For most people with diabetes, healthy blood sugar levels are: 90 to 130 Before Meals Less than Hours After Starting a Meal 110 to 140 At Bedtime I will ask my health care provider what blood sugar numbers or blood sugar levels are right for me. 8
9 If I Have Diabetes, What Can I Eat? To help control my blood sugar and help me feel better, I need to watch what I eat or drink, how much I eat or drink, and when I eat or drink. Here are some tips for making healthy eating choices: Eat breakfast, lunch, and dinner each day with 4 5 hours between each meal and don t skip meals Eat a variety of foods at each meal. Avoid fried, salty, and junk food Choose small serving sizes for starchy vegetables, cereal, bread, rice, grits, pasta, fruit or dairy products at each meal Eat foods without adding extra salt. Most processed foods are high in salt. Read food labels. Choosing foods lower in sodium or with no salt added will help control my blood pressure.. Eat less fried and fatty meat; instead, eat fish, chicken or turkey with skin removed Limit fats by using no more than 2-3 teaspoons of margarine, sour cream, gravy, salad dressing, and mayonnaise each day Choose low fat or fat free milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products Eat small portions of food and avoid second helpings Drink water, sugar free drinks, and use sugar substitutes, Equal, Sweet & Low, and Splenda to sweeten drinks Eat less sugar and avoid regular soda, drinks with sugar, candies, cakes, pies, cookies, and other such foods 9
10 How Much Should I Eat? Choose this many servings from these food groups to have 1,200 to 1,600 calories a day: Serving Sizes: 4-5 starches or starchy vegetables 4 vegetables 2 low fat or fat free milk or yogurt 2-3 meat servings or meat substitutes 2 fruits 3 fat servings or less Starches or Starchy Vegetables: 1/2 bagel, English muffin, pita, hamburger or hot dog bun, 1 slice of bread, roll, tortilla; 1/2 cup grits, oatmeal or pasta; 1/2 cup rice; 1/2 cup bran cereal; 1/2 cup corn, lima beans, or peas Vegetables: 1 cup raw, or 1/2 cup cooked Fruits: 1 medium fruit, such as an apple, orange, or pear; 1/2 cup canned fruit in its own juice; 1 small banana, 1 and 1/2 cup watermelon or berries, 1/2 cup fruit juice Milk: 1 cup low fat, 1% or fat free milk, or sugar free, fat free, or low fat ice cream or yogurt Meats: 1/2 breast, or leg and thigh of chicken; 2 slices roast beef or pot roast; 1 medium pork chop; 1 small hamburger patty; 2-3 oz fish (like a deck of cards); 6 medium sardines; 6 shrimp Fats: 1 teaspoon oil, 2 teaspoons diet margarine; 1 tablespoon nuts or seeds without shells; 1 tablespoon salad dressing; 2 teaspoons peanut butter 10
11 How Should My Plate Look? A snack may be used between meals if needed. I will make healthy choices and control serving sizes. Foods that help me control my diabetes are also healthy for my entire family. 11
12 Physical Activity or Exercise Exercising my body every day will make a difference. Physical activity helps me lower my blood sugar levels. Exercise can also: Lower my blood pressure Help me control or lose weight Give me more energy Help my heart and lungs work better Help my blood circulation Help reduce stress What Kind of Physical Activity is Good for People with Diabetes? Many of my daily physical activities are forms of exercise. I can make exercise a part of my life every day by: Moving my body or body parts Walking Doing chair exercises Dancing Gardening Cleaning the house or car I will check with my health care provider before I start an exercise program. I will drink at least 6-8 cups of water each day. I will walk early in the morning or after sundown on very hot days. 12
13 DIABETES MEDICATION Taking my diabetes medication is important. I will not change, skip, or stop my medication without checking with my health care provider first. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin (the needle). People with type 2 diabetes may need to: Take pills Take insulin (the needle) Sometimes take both pills and the needle If I need medication to control my diabetes, I will ask my health care provider when and how to take it. I can also ask my pharmacist any questions about my diabetes medicines, and any medicines, vitamins, and herbs I take on my own. 13
14 How Do I Take My Diabetes Pills Safely? Diabetes pills can help people with diabetes lower their blood sugar. Diabetes pills are not insulin. My health care provider may prescribe one or more pills to lower my blood sugar levels. To safely take my diabetes pills I will: Ask my health care provider when is the best time to take my diabetes pills Ask how often I should take my pills, or how many times a day I should take my pills Ask if my pills have any side effects and what to do if I have any side effects Ask my health care provider what to do if I forget to take my pills or have no way to buy my pills Keep pills and all medicine OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN Not take extra diabetes pills if I forgot to take it earlier Not take fewer pills than my health care provider prescribed Not skip or miss taking pills Not skip meals because skipping meals can make my blood sugar fall too low 14
15 Type 2 Diabetes Pills All of these pills are called Sulfonylureas. These medicines can help my body make more insulin to help lower my blood sugar and control my diabetes. My health care provider can decide if I need to take any of these pills to help me control my blood sugar. Amaryl (Glimepiride) Diabeta (Glyburide) Diabinese (Chlorpropamide) Dymelor (Acetohexamide) Glucotrol (Glipizide) Glucotrol XL (Glipizide) Glynase (Glyburide) Glynase Prestab (Micronized Glyburide) Micronase (Glyburide) Orinase (Tolbutamide) Prandin (Repaglinide) Starlix (Nateglinide) Different people need different medicines to control sugar diabetes. I will not share my diabetes medicines with anyone. I will not take anyone else s diabetes medicines. 15
16 More Type 2 Diabetes Pills The following pills are called Biguanides. These medications decrease the amount of glucose or sugar my liver makes and puts in my blood. Yes, my liver makes sugar and can sometimes make too much. These pills help lower my blood sugar level and control my diabetes. Glucophage (Metformin) Glucophage XR (Metformin) Extended release tablets The pills below are called Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors. These medications slow my digestion of carbohydrates such as starches, so that my blood sugar will not rise too high after I eat. Precose Glyset (Acarbose) (Miglitol) The medications below are called Thiazolidinediones and help my muscle cells respond to insulin and use glucose better. Avandia Actos (Rosiglitazine) (Pioglitazone) 16
17 Combination (2 in 1) Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes The following medications contain two medicines that have been combined to make one medicine. This helps to reduce the number of pills I take each day. Glucovance Metaglip Avandamet Contains glyburide and metformin Contains glipizide and metformin Contains rosiglitazone and metformin My health care provider will decide the best medicine to help me control my diabetes. I will tell my health care provider about any other medicines, vitamins, and herbs I am taking. If I have any problems getting or taking my diabetes medicines, I will ask my health care provider or pharmacist to help me. 17
18 Insulin Why are Insulin Shots Needed? Our bodies need insulin to live. When our bodies do not make insulin or make enough of it, we need to take insulin (the needle) every day. Sometimes we need both diabetes pills and insulin. How Do I Care for Insulin? I will keep extra unopened insulin in the refrigerator. Cold insulin stings! I will take my bottle of insulin out of the refrigerator at least 15 minutes before my shot. I will never put my insulin in the freezer. I will not leave insulin in a hot place (sunny window, in the car on hot days). When Should I Take My Insulin Shot? I will check with my health care provider to decide when is the best time to take my insulin (the needle). I will ask my health care provider how to balance my insulin with the foods I eat. 18
19 Where Should I Give My Insulin Shot? The best place to give an insulin shot is in my stomach area. These are also good places for insulin shots. I will NOT: Skip my insulin shots Use insulin if it is clumpy or has crystals in it 19
20 THE HIGHS AND LOWS OF SUGAR High Blood Sugar When my blood sugar stays too high I have high blood sugar. This can happen when: I am sick I eat too much food I take too little insulin or diabetes pills I feel stressed I am less active than usual 20
21 How Do I Feel When I Have High Blood Sugar? Sometimes I may feel good when my blood sugar is too high or I may: Be thirsty Need to use the bathroom a lot to pass water or urinate Feel very sleepy Be hungry Have blurry or fuzzy vision Over time high blood sugar levels will damage my body even though I feel good. 21
22 What Should I Do if I Think I Have High Blood Sugar? Check my blood sugar with a blood glucose meter Check my temperature for a fever Check to make sure I have taken my diabetes medicine Call my health care provider if I have questions about what to do If my blood sugar number is over 180 for 3 days in a row: I will drink lots of water I should call my health care provider I will check to see if I am following my meal plan I can also take a walk or do some other exercise I might be told to take extra medicine by my health care provider If my blood sugar number is over 250 for 2 days and I take insulin: I must call my health care provider I will drink lots of water I will ask my health care provider about what physical activity I can do as exercise I will check my urine for ketones 22
23 Low Blood Sugar When my blood sugar is under 70, I have low blood sugar. This happens if: I take too much insulin I take too many diabetes pills I exercise more than usual but don t eat enough food I don t eat enough food or if I eat my meals too late I drink too much alcohol I skip meals 23
24 How Do I Feel When I Have Low Blood Sugar? Sweaty Shaky or nervous Crabby Hungry Sleepy or confused Tired If I am not sure my sugar is low but I have some of these signs, I will check my blood sugar with a blood glucose meter and then treat it. If I donʼt take pills or the needle, I wonʼt usually have low blood sugar. I will teach someone in the house how to check and treat low blood sugar. I will learn my signs of low blood sugar. 24
25 What Should I Do When I Feel I Have Low Blood Sugar? I should immediately check my blood sugar number with a blood sugar meter. If my blood sugar is below 70, I will eat or drink about 15 grams of carbohydrate (such as a half cup of fruit juice or 3 to 5 pieces of hard candy or 3 graham crackers). I should wait 15 minutes after I have eaten and check my blood sugar level again. If my blood sugar is still below 70, I should eat or drink another half cup of fruit juice or 3 to 5 pieces of hard candy or 3 graham crackers. If after another 15 minutes my blood sugar level is still below 70, I will call my health care provider. I should eat a small snack like crackers and fruit if my next meal is more than 30 minutes away. I will not drive if my blood sugar is below 70. If I am taking Precose (acarbose) or Glyset (miglitol) with any other diabetes medicines and have low blood sugar, I MUST treat it by: Taking 2 to 3 glucose tablets or Drinking a cup of skim milk NOTE: Treating it any other way may not help me. 25
26 DIABETES AND MY BODY If my blood sugar stays high for a long period of time, it can cause damage to my body. Parts of my body that can be damaged by diabetes are: Blood Vessels Heart Nerves Kidneys Feet Eyes Teeth and Gums Sexual Ability Although I may not feel bad, high blood sugar can damage my body. 26
27 Blood Vessels Keeping my blood sugar and blood fats at healthy levels will help protect my blood vessels and prevent serious health problems. It is also very important to keep my blood pressure at a healthy level to protect my blood vessels and prevent a stroke, kidney disease, or other problems. A healthy blood pressure level for people with diabetes should be at least below 130/80. It is best for blood pressure to be below 120/80. To keep my blood pressure and blood fats under control I will: Get my blood pressure checked often Always take my blood pressure medication Stop smoking Avoid salty foods and eat less than 1 teaspoon of salt a day Eat healthy foods including fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grain breads and cereals, and lean meats Avoid fat meats and foods fried in fat, lard or butter Exercise for at least minutes a day on most days Find ways to lower stress in my life Not drink more than 1-2 drinks of alcoholic beverage a day 27
28 Heart I will protect my heart by keeping my blood sugar, blood fats, and blood pressure under control. I will call my health care provider if I have: Shortness of breath Swollen ankles I will have a lab test to measure fats in my blood every year: Total Cholesterol (all the fats in my blood) Less than 200 HDL (good cholesterol) More than 45 for men and more than 55 for women LDL (bad cholesterol) Less than 100 Triglycerides (fats) Less than
29 Warning Signs Stroke Sudden numbness or weakness of face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body Sudden trouble seeing or loss of vision in one or both eyes Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination Sudden severe headaches with no known cause Heart Attack Chest discomfort such as fullness, squeezing or pain in the center of the chest lasting more than a few minutes Pain spreading to the shoulders, neck, arms, back, jaw, or stomach Chest discomfort with shortness of breath, lightheadedness, fainting, sweating, or nausea If I or someone I know has signs of a Stroke or Heart Attack CALL Don t wait to see if signs will go away! 29
30 Nerves The nerves in my body can be damaged by diabetes. I will tell my health care provider if my hands or feet have any of the following: Pain Burning Tingling Numbness Cold Feet I will tell my health care provider if I have any problems with: Sex Diarrhea Constipation Nausea Stomach Pains 30
31 What Will I Do to Help Protect the Nerves in My Body? Keep blood sugar levels close to normal or to levels decided with my health care provider Keep blood pressure close to normal (120/80 or less) or within the range decided with my health care provider Stop smoking Stop chewing tobacco Drink less alcohol (never more than one or two drinks a day) See my health care provider at least every six months 31
32 Kidneys Sugar diabetes can damage my kidneys, and I can get diabetic kidney disease. High blood pressure can also damage my kidneys, and I can get kidney disease. I need to keep my kidneys healthy! To keep my kidneys healthy, I will: Keep my blood pressure and blood sugar under control Have my urine checked at least once a year to test for small amounts of protein Follow a healthy meal plan Eat no more than 1 teaspoon of salt a day Lose weight if I am overweight Exercise for at least minutes a day on most days Drink at least 6-8 cups of water each day Stop smoking I will not feel symptoms of diabetic kidney disease. I must ask my doctor to check my urine for early signs of kidney disease at least each year. If I have early signs of kidney disease, I will ask what can be done to protect my kidneys. 32
33 Feet Diabetes can cause damage to my feet. To keep my feet in good shape I must: Keep my blood sugar under control Not smoke Check my feet each day for cuts, blisters, and bruises and call my health care provider if I notice any problems Wash my feet every day in warm water and pat dry. I will check the water temperature with my wrist or elbow to make sure the water is not too hot. Never put oil or lotion between my toes Wear socks and comfortable shoes that protect my feet NEVER go barefoot, not even in the house Shake out and feel inside my shoes before putting them on Keep physically active I will call my health care provider right away if a cut, sore, blister or bruise on my foot does not begin to heal after one day. I will take off my shoes and socks and ask my health care provider to check my feet each visit. 33
34 Eyes Diabetes can cause blindness. This blindness can be prevented. Finding eye disease and treating it early can save my sight. Symptoms usually do not come until after the disease has advanced. I will keep my eyes healthy by having a dilated eye exam at least once a year I may have no symptoms at first I may see fine I may have no pain I know the keys to keeping my eyes healthy are: Having a dilated eye exam at least once a year Keeping my blood sugar and blood pressure under control Not smoking I will also call my eye doctor if my vision is blurry and my blood sugar has been normal. If I have ANY changes in my vision, I will call my doctor. I still need to have the dilated eye exam at least once a year! 34
35 Teeth and Gums People with sugar diabetes are more likely to have problems with their teeth and gums. Controlling my blood sugar will help me avoid gum problems. To help my teeth and gums stay healthy, I will: Brush my teeth at least twice a day Floss my teeth at least once a day Visit my dentist at least every six months Get my teeth cleaned every six months at my dentist s office Tell my dentist I have sugar diabetes Tell my dentist about any problems I have with my teeth and gums Keep my blood sugar level under control 35
36 Immunizations Diabetes makes it harder for my body to fight some illnesses. I can help protect my body from some illness by getting two important immunizations (shots). Flu Flu is a serious illness that can be prevented by getting a flu shot every year. I will get a flu shot every year between October and November. Pneumonia A serious disease that causes severe infections of the lungs is called pneumonia. Getting the pneumonia vaccine can prevent pneumonia. I will ask my health care provider about getting a pneumonia vaccine or shot and how long it will protect me from pneumonia. 36
37 SPECIAL DAYS When I feel sick or have the flu, my blood sugar may be higher. When I am sick I will: Continue to take my insulin or my diabetes pills Check my blood sugar at least every 4 hours Try toast, a little juice, or soup if I cannot eat regular meals or keep food in my stomach Drink lots of liquids if I cannot eat regular meals Test my urine for ketones with a keto-stick I will call my health care provider right away if: I can t keep food or liquids down more than 2 times (I throw up) I have diarrhea or runny stools more than 2 times I have a fever or my breath smells fruity My blood sugar is 250 or higher I have trouble breathing I have ketones in my urine 37
38 Traveling Traveling can be fun and exciting, but may change my regular eating and activity patterns. While I am traveling I will: Wear an ID bracelet that says I have diabetes Carry hard candy, such as 5-6 Lifesaver candies, for low sugar spells Take extra diabetes supplies, insulin, medication, and diabetes pills with me Take the name and phone number of my health care provider with me Be sure to eat regular meals and get my exercise Be sure to check my blood sugar more often Take my diabetes medicine as prescribed by my health care provider Ask my health care provider when and how to take my diabetes medicines if I am changing time zones as I travel 38
39 MY RIGHTS AND RESPONSIBILITIES I have the right at my first diabetes visit to: A medical history A physical examination Laboratory tests for diabetes A diabetes management plan Have my questions answered in a way that I can understand I have a right to the following exams: Blood pressure and pulse Heart Skin Teeth/gums Eyes Thyroid Feet Nerves I have a right to the following tests: A1C (Blood Test) Kidney function (urine or blood test) EKG (heart) Blood tests for cholesterol and other fats I have a right to know my test results, what they mean and what to do to improve my health and treat my diabetes. 39
40 If I Have Sugar Diabetes, What Do I Need to Do to Take Care of My Diabetes? Eat healthy foods in the right serving sizes at regular times Get exercise or physical activity on most days Check my feet each day Check my blood sugar levels each day Check my blood pressure See a health care provider on a regular basis Ask my health care provider about pneumonia and flu vaccines See a dentist at least twice a year Keep a report card record of how well I control my diabetes Check my goals for diabetes each month I must love myself because my body is a temple. 40
41 RESOURCES If I need help getting my diabetes medicine or finding a health care provider, I can contact: REACH 2010: Charleston & Georgetown Diabetes Coalition (Charleston or Georgetown County only) (843) A diabetes coalition working to eliminate the health disparities for African Americans with diabetes by supporting diabetes education, nutrition, and exercise programs, sharing reliable and current information, advocating for positive change in health care systems, and linking people with financial assistance programs for health services. American Diabetes Association (ADA) (Nationwide) (800) The leading national nonprofit organization providing diabetes information, research, and advocacy to prevent and cure diabetes. The ADA will put you in contact with your local chapter, and link you with excellent diabetes education programs. The ADA also has a list of diabetes specialists for each state. Commun-I-Care (South Carolina only) (800) Provides primary health care services and medication to working adults who do not have Medicare or Medicaid, do not qualify for Veterans Health Benefits, cannot afford any health insurance, and meet income guidelines. Tri-County Project Care (Berkeley, Charleston or Dorchester County only) (843) Provides comprehensive, affordable health care services for the working uninsured. To enroll, patients must be employed, have no other health insurance, be between years old, meet minimum and maximum income guidelines based on family size, and provide proof of income. 41
42 South Carolina Primary Health Care Association (SCPHCA) (South Carolina only) (803) Provides a listing of all community health care centers that provide health care to all based on a sliding fee scale. Most also provide medications on a sliding fee scale. To find the health center nearest you, call the SCPHCA. East Cooper Community Outreach (ECCO) (843) A charitable organization dedicated to helping needy neighbors mainly living in the East Cooper area (but clients can come from any surrounding area counties). Med-I-Assist program, free dental clinic, clothing and household furnishings, advisory service. Provides Food Pantry and financial assistance to East Cooper area only. If I need information on diabetes or a speaker on diabetes for my group, I can contact: REACH 2010: Charleston & Georgetown Diabetes Coalition (Charleston or Georgetown County only) (843) A diabetes coalition working to eliminate the health disparities for African Americans with diabetes by supporting diabetes education, nutrition, and exercise programs, sharing reliable and current information, advocating for positive change in health care systems, and linking people with financial assistance programs for health services. SC DHEC Diabetes Prevention and Control Program (803) Supports community diabetes education, health systems interventions, and coalition development to help reduce the incidence and severity of diabetes in SC. Diabetes Today, an interactive program, introduces community leaders to a program process for addressing community issues related to diabetes. 42
43 Diabetes Initiative of South Carolina (843) A comprehensive statewide initiative of community outreach programs, health professional education, and diabetes surveillance to improve diabetes in SC. Project SUGAR - MUSC (843) Sea Island Genetic African American Family Registry is a community-based research study focusing on families with or affected by SUGAR diabetes (Type 2 Diabetes). American Diabetes Association (ADA) (Nationwide) (800) The leading national nonprofit organization providing diabetes information, research, and advocacy to prevent and cure diabetes. The ADA will put you in contact with your local chapter, and link you with excellent diabetes education programs. The ADA offers high quality diabetes cookbooks, menus, and educational materials. MedlinePlus (Internet) A web site of reliable health information from the world s largest medical library, the National Library of Medicine. Look under Health Topics, then D for Diabetes. Hands on Health-SC (843) A consumer health web site for South Carolinians. Links to web sites with good, plain language health and wellness information. Includes Spanish language sites. If I need help with getting a dentist, I can contact: South Carolina Dental Association (800) Provides a list of state-wide public assistance dental clinics. East Cooper Community Outreach (ECCO) (843) A nonprofit ecumenical charitable organization dedicated to helping needy neighbors mainly living in the East Cooper area (but clients can come from any surrounding area Counties). Free dental clinic. 43
44 44
45 45
46 MY NOTES ON DIABETES 46
47 MY NOTES ON DIABETES 47
48 This publication was supported by Grant/Cooperative Agreement Number U50/CCU from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. REACH 2010: Charleston and Georgetown Diabetes Coalition If I need further information or have questions about diabetes, I can call
Take Charge of Your Diabetes
 Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes. A Guide for Adults
 Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
High blood sugars caused by steroids
 High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
Type 2 Diabetes. Increase of diabetic complications as HAIC increases
 Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know
 High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
There are three major forms of this disease.
 For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
High Blood Sugar. Printable Materials
 Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Goodman Diabetes Service Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes People who have type 2 diabetes may need to take medicine to help lower their blood glucose, in addition to being active & choosing healthy
Goodman Diabetes Service Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes People who have type 2 diabetes may need to take medicine to help lower their blood glucose, in addition to being active & choosing healthy
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes?
 Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
4 Steps. For Life. to Control Your Diabetes. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
Diabetes WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW. What is Diabetes? Inside:
 Diabetes WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW What is Diabetes? Diabetes means that there is too much sugar in your blood. Too much sugar causes damage to the body. Diabetes happens when there is a problem with a hormone
Diabetes WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW What is Diabetes? Diabetes means that there is too much sugar in your blood. Too much sugar causes damage to the body. Diabetes happens when there is a problem with a hormone
Carbohydrate Counting for Patients with Diabetes. Lauren Dorman, MS RD CDE Registered Dietitian & Certified Diabetes Educator
 Carbohydrate Counting for Patients with Diabetes Lauren Dorman, MS RD CDE Registered Dietitian & Certified Diabetes Educator Program Purpose To increase knowledge of carbohydrate counting skills for nurses
Carbohydrate Counting for Patients with Diabetes Lauren Dorman, MS RD CDE Registered Dietitian & Certified Diabetes Educator Program Purpose To increase knowledge of carbohydrate counting skills for nurses
Medications for Diabetes
 AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43 PM Page 1 Medications for Diabetes An Older Adult s Guide to Safe Use of Diabetes Medications THE AGS FOUNDATION FOR HEALTH IN AGING AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43
AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43 PM Page 1 Medications for Diabetes An Older Adult s Guide to Safe Use of Diabetes Medications THE AGS FOUNDATION FOR HEALTH IN AGING AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43
Eating Well with Diabetes. Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator
 Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes
 type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
Diabetes. Patient Education. What you need to know. Diabetes Facts. Improving Health Through Education. What is Diabetes?
 Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me
 gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes occurs when your body cannot make adequate use of sugar in the blood. It is first found during pregnancy.
gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes occurs when your body cannot make adequate use of sugar in the blood. It is first found during pregnancy.
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy
 My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and snacks throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and snacks throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
Diabetes 101. Lifestyle Recommendations to Manage Diabetes. Cassie Vanderwall. Licensed, Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer
 Diabetes 101 Lifestyle Recommendations to Manage Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall Licensed, Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Diabetes 101- Outline What is Diabetes? What can I do to control Diabetes?
Diabetes 101 Lifestyle Recommendations to Manage Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall Licensed, Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Diabetes 101- Outline What is Diabetes? What can I do to control Diabetes?
Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
Myth vs. Reality: Diabetes Related
 Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
My Diabetes Care Plan
 My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
High Blood Sugar, Low Blood Sugar. Let s Check our Blood Sugar
 High Blood Sugar, Low Blood Sugar Testing your blood sugar Check with your provider to see if and when he/she wants you to check your blood sugar. Keep a record of your blood sugar numbers, the date and
High Blood Sugar, Low Blood Sugar Testing your blood sugar Check with your provider to see if and when he/she wants you to check your blood sugar. Keep a record of your blood sugar numbers, the date and
Maintaining Nutrition as We Age
 SS-207-06 For more information, visit the Ohio Department of Aging web site at: http://www.goldenbuckeye.com and Ohio State University Extension s Aging in Ohio web site at: http://www.hec.ohio-state.edu/famlife/aging
SS-207-06 For more information, visit the Ohio Department of Aging web site at: http://www.goldenbuckeye.com and Ohio State University Extension s Aging in Ohio web site at: http://www.hec.ohio-state.edu/famlife/aging
Understanding Diabetes
 Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Ready, Set, Start Counting!
 Ready, Set, Start Counting! Carbohydrate Counting a Tool to Help Manage Your Blood Glucose When you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose in a healthy range will help you feel your best today and in
Ready, Set, Start Counting! Carbohydrate Counting a Tool to Help Manage Your Blood Glucose When you have diabetes, keeping your blood glucose in a healthy range will help you feel your best today and in
You may continue to use your old manuals by writing in the detailed changes below:
 STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
Steroid Induced Diabetes
 What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)? Hyperglycemia is a high level of sugar in the blood. Blood sugar is also called glucose. Some people are unable to process the sugar that is found in food and
What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)? Hyperglycemia is a high level of sugar in the blood. Blood sugar is also called glucose. Some people are unable to process the sugar that is found in food and
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey
 Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
What is Diabetes?... 1. What is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?... 4. Driving... 6. What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)?...
 Table of contents Page What is Diabetes?... 1 What is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?... 4 Driving... 6 What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)?... 10 What are ketones?... 12 What do I do when I am sick?...
Table of contents Page What is Diabetes?... 1 What is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?... 4 Driving... 6 What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)?... 10 What are ketones?... 12 What do I do when I am sick?...
Background (cont) World Health Organisation (WHO) and IDF predict that this number will increase to more than 1,3 million in the next 25 years.
 Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
How To Eat When You Have Type 2 Diabetes
 Dear Patient: Welcome to NorthShore University HealthSystem (NorthShore). We are committed to supporting you in your educational process. This packet has been designed to provide you with important basic
Dear Patient: Welcome to NorthShore University HealthSystem (NorthShore). We are committed to supporting you in your educational process. This packet has been designed to provide you with important basic
Diabetes. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010
 Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Carbohydrate Counting for Pediatric Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. Review Date 4/08 K-0591
 Carbohydrate Counting for Pediatric Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Review Date 4/08 K-0591 Program Purpose To increase knowledge of carbohydrate counting and insulin management skills for those caring for
Carbohydrate Counting for Pediatric Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Review Date 4/08 K-0591 Program Purpose To increase knowledge of carbohydrate counting and insulin management skills for those caring for
Diabetes. 2. Types. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know. One test used to diagnose diabetes is a fasting blood glucose test.
 1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
Eat Well, Live Well Lesson 9: The Lowdown on Cholesterol
 Getting Started 1. Review lesson plan before each session 2. Copy handouts. 3. Gather supplies Eat Well, Live Well Lesson 9: The Lowdown on Cholesterol Supplies Needed 1. Handouts 2. Supplies for activity:
Getting Started 1. Review lesson plan before each session 2. Copy handouts. 3. Gather supplies Eat Well, Live Well Lesson 9: The Lowdown on Cholesterol Supplies Needed 1. Handouts 2. Supplies for activity:
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
 Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Diabetes Fundamentals
 Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Learn about Diabetes. Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. You can learn how to take care of your diabetes.
 Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes
 HealthSelectSM Lose and Win Session 13 of Texas Pre-diabetes & type II diabetes Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes Chances are that you know someone that
HealthSelectSM Lose and Win Session 13 of Texas Pre-diabetes & type II diabetes Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes Chances are that you know someone that
Starting insulin treatment for people with type 2 diabetes. What you need to know
 Starting insulin treatment for people with type 2 diabetes What you need to know Contents Information 3 Any questions? 3 Glossary of terms 3 Why do I need insulin? 4 What does insulin do? 5 Why are there
Starting insulin treatment for people with type 2 diabetes What you need to know Contents Information 3 Any questions? 3 Glossary of terms 3 Why do I need insulin? 4 What does insulin do? 5 Why are there
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Healthy Meals for Diabetes
 managingdiabetes TM SELECTHEALTH WINTER 2015 Healthy Meals for Diabetes Your doctor can help you make a meal plan that fits your needs. Your meal plan tells you when to eat meals and snacks, how much to
managingdiabetes TM SELECTHEALTH WINTER 2015 Healthy Meals for Diabetes Your doctor can help you make a meal plan that fits your needs. Your meal plan tells you when to eat meals and snacks, how much to
DIABETES & HEALTHY EATING
 DIABETES & HEALTHY EATING Food gives you the energy you need for healthy living. Your body changes most of the food you eat into a sugar called glucose. (glucose) Insulin helps your cells get the sugar
DIABETES & HEALTHY EATING Food gives you the energy you need for healthy living. Your body changes most of the food you eat into a sugar called glucose. (glucose) Insulin helps your cells get the sugar
Low Fat Diet after Cardiac Surgery With or Without Chyle Leak
 Low Fat Diet after Cardiac Surgery With or Without Chyle Leak What is chyle? Chyle (sounds like kyle) is a milky white fluid that contains protein, fat, cholesterol, lymphocytes, and electrolytes. It is
Low Fat Diet after Cardiac Surgery With or Without Chyle Leak What is chyle? Chyle (sounds like kyle) is a milky white fluid that contains protein, fat, cholesterol, lymphocytes, and electrolytes. It is
My Diabetes Care Plan
 My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
Nutrition Information from My Plate Guidelines
 Nutrition Information from My Plate Guidelines Note: This information was compiled from the website: http://www.choosemyplate.gov/ for participants in the 4-H Food Prep Contest 1/12/16. The information
Nutrition Information from My Plate Guidelines Note: This information was compiled from the website: http://www.choosemyplate.gov/ for participants in the 4-H Food Prep Contest 1/12/16. The information
Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk
 Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative Take Control of
Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative Take Control of
TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention
 TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Researchers in this study are part of a larger group called Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet.
TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Researchers in this study are part of a larger group called Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet.
Carbohydrate Counting (Quiz Number: Manatee3032009)
 Page 1 The goal of Carbohydrate Counting is to make clear to you which foods affect your blood glucose and then to spread these foods evenly throughout the day (or to match insulin peaks and durations).
Page 1 The goal of Carbohydrate Counting is to make clear to you which foods affect your blood glucose and then to spread these foods evenly throughout the day (or to match insulin peaks and durations).
Carbohydrate Counting for Patients With Diabetes. Review Date 4/08 D-0503
 Carbohydrate Counting for Patients With Diabetes Review Date 4/08 D-0503 Program Objectives At the end of the session you will know how to: Define carbohydrate counting Identify the relationship between
Carbohydrate Counting for Patients With Diabetes Review Date 4/08 D-0503 Program Objectives At the end of the session you will know how to: Define carbohydrate counting Identify the relationship between
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
Bariatric Surgery: Step III Diet
 Bariatric Surgery: Step III Diet This diet is blended foods with one new solid food added daily. The portions are very small to help prevent vomiting. Warning: This diet does not have enough calories,
Bariatric Surgery: Step III Diet This diet is blended foods with one new solid food added daily. The portions are very small to help prevent vomiting. Warning: This diet does not have enough calories,
Starting insulin for people with type 2 diabetes
 Starting insulin for people with type 2 diabetes What you need to know Contents Page Why do I need insulin? 3 What does insulin do? 4 Why are there different types of insulin? 4 How do I take insulin?
Starting insulin for people with type 2 diabetes What you need to know Contents Page Why do I need insulin? 3 What does insulin do? 4 Why are there different types of insulin? 4 How do I take insulin?
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
 Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Pregnancy is a time of great change. Your body is changing to allow your baby to grow and develop. Good nutrition will help you meet the extra demands of pregnancy while
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Pregnancy is a time of great change. Your body is changing to allow your baby to grow and develop. Good nutrition will help you meet the extra demands of pregnancy while
Take Control of Your Diabetes
 Take Control of Your Diabetes It is the best thing you can do for yourself. It might be hard sometimes, but it is worth it! In no time at all, you will feel better and have more energy. Get Started Test
Take Control of Your Diabetes It is the best thing you can do for yourself. It might be hard sometimes, but it is worth it! In no time at all, you will feel better and have more energy. Get Started Test
What is Gestational Diabetes?
 What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational (jes-tay-shun-ul) diabetes is a type of diabetes that can happen during pregnancy. It means you have never had diabetes before. Having gestational diabetes means
What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational (jes-tay-shun-ul) diabetes is a type of diabetes that can happen during pregnancy. It means you have never had diabetes before. Having gestational diabetes means
Insulin Dependent Diabetes Trust
 Insulin Dependent Diabetes Trust Type 2 and You April 2010 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Welcome to the third issue of Type 2 and You. In this issue we look at healthy
Insulin Dependent Diabetes Trust Type 2 and You April 2010 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Welcome to the third issue of Type 2 and You. In this issue we look at healthy
Resources for Carbohydrate Counting
 Resources for Carbohydrate Counting The Diabetes Carbohydrate and Fat Gram Guide By LeaAnn Holzmeister, RD, CDE American Diabetes Association See contact information below The Doctor s Pocket Calorie,
Resources for Carbohydrate Counting The Diabetes Carbohydrate and Fat Gram Guide By LeaAnn Holzmeister, RD, CDE American Diabetes Association See contact information below The Doctor s Pocket Calorie,
how to control blood glucose during PREGNANCY?
 how to control blood glucose during PREGNANCY? one HOW THE BODY WORKS DURING PREGNANCY During all pregnancies, the placenta makes a called human placental lactogen which allows the baby to grow and develop.
how to control blood glucose during PREGNANCY? one HOW THE BODY WORKS DURING PREGNANCY During all pregnancies, the placenta makes a called human placental lactogen which allows the baby to grow and develop.
Diabetes. Living with. Better Health Guide. Anywhere, TN 11111. 1008 Main Street. Janet James. BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1
 BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
But what does my body need? (No...it is not just candy and soda!)
 Chapter 35: Page 349 In the last chapter, you learned how important your immune system is to your survival. This week, you are going to learn how to keep your immune system strong and ready to protect
Chapter 35: Page 349 In the last chapter, you learned how important your immune system is to your survival. This week, you are going to learn how to keep your immune system strong and ready to protect
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Do children with diabetes need a special diet?
 Do children with diabetes need a special diet? No! The basic nutritional needs of a child or adolescent with diabetes is the same as their peers Healthy eating is important for all children Children with
Do children with diabetes need a special diet? No! The basic nutritional needs of a child or adolescent with diabetes is the same as their peers Healthy eating is important for all children Children with
Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
 Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes pills can help to manage your blood sugar. These pills are not insulin. They work to manage your blood sugar in several ways. You may be given a combination of
Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes pills can help to manage your blood sugar. These pills are not insulin. They work to manage your blood sugar in several ways. You may be given a combination of
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Nutrition Guidelines for Diabetes
 Nutrition Guidelines for Diabetes Eating healthy foods and keeping a healthy body weight are very important parts of a diabetes treatment plan. A healthy diet and weight helps to keep your blood sugar
Nutrition Guidelines for Diabetes Eating healthy foods and keeping a healthy body weight are very important parts of a diabetes treatment plan. A healthy diet and weight helps to keep your blood sugar
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know
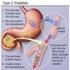 Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Self-care guide for people with diabetes
 Self-care guide for people with diabetes English Version Supported by an unrestricted grant from 1 When the diagnosis is diabetes..................03 What is diabetes?............................04 What
Self-care guide for people with diabetes English Version Supported by an unrestricted grant from 1 When the diagnosis is diabetes..................03 What is diabetes?............................04 What
is for A1c (blood sugar level) What causes unhealthy levels of blood sugar?
 diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
A Beginner s Guide to Carbohydrate Counting
 A Beginner s Guide to Carbohydrate Counting This slide show explains: What foods contain carbohydrates How much of these foods you can eat Where to look up the carb content of foods Pia has a Bachelors
A Beginner s Guide to Carbohydrate Counting This slide show explains: What foods contain carbohydrates How much of these foods you can eat Where to look up the carb content of foods Pia has a Bachelors
Hypoglycemia and Diabetes
 My Doctor Says I Should Avoid Low Blood Glucose Reactions... How Can I Prevent Them? BD Getting Started Hypoglycemia and Diabetes What You Should Know About Low Blood Glucose Reactions If you are taking
My Doctor Says I Should Avoid Low Blood Glucose Reactions... How Can I Prevent Them? BD Getting Started Hypoglycemia and Diabetes What You Should Know About Low Blood Glucose Reactions If you are taking
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dietary and Lifestyle Guidelines
 Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Dietary and Lifestyle Guidelines Risk factors for NAFLD Typically, but not always seen in patients who are overweight. May have Diabetes and or insulin resistance high
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Dietary and Lifestyle Guidelines Risk factors for NAFLD Typically, but not always seen in patients who are overweight. May have Diabetes and or insulin resistance high
Diabetes: Medications
 Diabetes: Medications Presented by: APS Healthcare Southwestern PA Health Care Quality Unit (APS HCQU) May 2008 sh Disclaimer Information or education provided by the HCQU is not intended to replace medical
Diabetes: Medications Presented by: APS Healthcare Southwestern PA Health Care Quality Unit (APS HCQU) May 2008 sh Disclaimer Information or education provided by the HCQU is not intended to replace medical
Benefits of exercise:
 Exercise makes your blood sugar go down! Your body needs to be active! Exercise is a part of good diabetes care Benefits of exercise: Exercise makes your blood sugar go down Helps to keep your blood pressure
Exercise makes your blood sugar go down! Your body needs to be active! Exercise is a part of good diabetes care Benefits of exercise: Exercise makes your blood sugar go down Helps to keep your blood pressure
Carbohydrate Counting
 Carbohydrate Counting What is Carbohydrate Counting? Carbohydrate counting is a meal-planning tool that many people use to manage their blood sugar. Carbohydrate counting, or carb counting, is done by
Carbohydrate Counting What is Carbohydrate Counting? Carbohydrate counting is a meal-planning tool that many people use to manage their blood sugar. Carbohydrate counting, or carb counting, is done by
Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y, Sleeve Gastrectomy and Duodenal Switch. Gastric Restrictive Procedures. Phase III Regular Consistency
 Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y, Sleeve Gastrectomy and Duodenal Switch Gastric Restrictive Procedures Phase III Regular Consistency The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment
Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y, Sleeve Gastrectomy and Duodenal Switch Gastric Restrictive Procedures Phase III Regular Consistency The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment
No More Carb Confusion
 No More Carb Confusion Choosing carbs ( carbohydrates ) wisely helps you control your blood sugar and weight. What is low-carb dieting? What can it do for you when you're trying to control your blood sugar
No More Carb Confusion Choosing carbs ( carbohydrates ) wisely helps you control your blood sugar and weight. What is low-carb dieting? What can it do for you when you're trying to control your blood sugar
Homework Help Heart Disease & Stroke
 Preventing Heart Disease & Stroke What causes heart disease and stroke? high blood pressure high cholesterol diabetes smoking stress drinking too much alcohol not being physically active being overweight
Preventing Heart Disease & Stroke What causes heart disease and stroke? high blood pressure high cholesterol diabetes smoking stress drinking too much alcohol not being physically active being overweight
Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS
 Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS Please complete the following form by filling in the blanks or by circling the answer provided. Last Name: First Name M.I. Address: City, State,
Borgess Diabetes Center PATIENT REGISTRATION/DEMOGRAPHICS Please complete the following form by filling in the blanks or by circling the answer provided. Last Name: First Name M.I. Address: City, State,
Diabetes means you have too much sugar in
 WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies
 Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #5 High Blood Cholesterol (date) Course
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #5 High Blood Cholesterol (date) Course
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Healthy Eating for Diabetes
 Healthy Eating for Diabetes What is diabetes and why is it important to manage it? Diabetes occurs when there is too much glucose in the blood. Learning how to manage your diabetes will help you feel better
Healthy Eating for Diabetes What is diabetes and why is it important to manage it? Diabetes occurs when there is too much glucose in the blood. Learning how to manage your diabetes will help you feel better
Beating insulin resistance through lifestyle changes
 Beating insulin resistance through lifestyle changes This information is relevant to people at risk for type 2 diabetes, those who already have type 2 diabetes, pre- diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome
Beating insulin resistance through lifestyle changes This information is relevant to people at risk for type 2 diabetes, those who already have type 2 diabetes, pre- diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Blood Sugar Log. Breakfast (daily) Before Lunch Before Dinner Bedtime
 Blood Sugar Log Date Before Breakfast (daily) Before Lunch Before Dinner Bedtime DIABETES MANAGEMENT (HEMOGLOBIN A1c) Your Hemoglobin A1c is the blood test that tells your doctor how well you are managing
Blood Sugar Log Date Before Breakfast (daily) Before Lunch Before Dinner Bedtime DIABETES MANAGEMENT (HEMOGLOBIN A1c) Your Hemoglobin A1c is the blood test that tells your doctor how well you are managing
Duke Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Pre-op Nutrition Questionnaire
 Duke Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Pre-op Nutrition Questionnaire Name Date How long have you been considering weight loss surgery? Which procedure are you interested in having? Gastric
Duke Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Pre-op Nutrition Questionnaire Name Date How long have you been considering weight loss surgery? Which procedure are you interested in having? Gastric
Diabetes: Carbohydrate Counting
 COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE AND LIFE SCIENCES COOPERATIVE EXTENSION AZ1617 February 2014 Diabetes: Carbohydrate Counting Nicole A. Greene, Natalia N. Billias, Nobuko Hongu Figure: Diabetes, hyperglycemia What
COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE AND LIFE SCIENCES COOPERATIVE EXTENSION AZ1617 February 2014 Diabetes: Carbohydrate Counting Nicole A. Greene, Natalia N. Billias, Nobuko Hongu Figure: Diabetes, hyperglycemia What
Take Control Nutrition Tools for Diabetes. 50/50 plate Portions Servings
 Take Control Nutrition Tools for Diabetes 50/50 plate Portions Servings Eat more Vegetables Especially non starchy vegetables Choosing Foods to manage blood glucose Select a variety of colors and types
Take Control Nutrition Tools for Diabetes 50/50 plate Portions Servings Eat more Vegetables Especially non starchy vegetables Choosing Foods to manage blood glucose Select a variety of colors and types
High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes:
 Prepared in collaboration with High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes: Are you at risk? Updated 2012 People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure. What is blood pressure? The force
Prepared in collaboration with High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes: Are you at risk? Updated 2012 People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure. What is blood pressure? The force
Gestational diabetes. Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy. What is gestational diabetes?
 Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
Healthy at Heart FEELING GOOD. Reduce Your CV Risk. It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Issue 3
 Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
