Measuring support for tobacco control policy in selected areas of six countries
|
|
|
- Meghan Sabrina Day
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tobacco Control 1998;7: Measuring support for tobacco control policy in selected areas of six countries Robert G Laforge, Wayne F Velicer, Deborah A Levesque, Joseph L Fava, David J Hill, Penelope E Schofield, Dennis Fan, Hein De Vries, William O Shisana, Mark Conner Cancer Prevention Research Center, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, Rhode Island, USA R G Laforge W F Velicer D A Levesque JLFava Centre for Behavioural Research in Cancer, Anti-Cancer Council of Victoria, Victoria, D J Hill P E Schofield Faculty of Business Administration, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China DFan Department of Health Education, University of Limburg, Limberg, HDeVries University of the Western Cape, Cape Town, South Africa W O Shisana Department of Psychology, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK M Conner Correspondence to: Dr RG Laforge, Cancer Prevention Research Center, 2 Chafee Road, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, Rhode Island , USA. waa101@uriacc.uri.edu Abstract Objective To explore the validity, reliability, and applicability of using a short, psychometrically sound survey instrument to measure population attitudes toward tobacco control policies. Design Surveys. Subjects and setting Student respondents attending university in (n = 403), Hong Kong (n = 336), the (n = 351), South Africa (n = 291), the United Kingdom (n = 164) and the United States (n = 241); total n = Main outcome measure The Smoking Policy Inventory (SPI), a 35-item scale. SPI scores were adjusted for age, income, gender, and smoking status. Estimates of internal consistency and tests of factorial invariance were conducted in each sample. Results Across all six countries, the SPI was found to be highly reliable and to have a consistent factor structure, indicating that the SPI scale represents a higher order construct that assesses general attitudes about tobacco control policy with five dimensions. In general, the degree of endorsement of anti-tobacco policies as measured by the SPI reflected the extent and strength of tobacco control legislation in those countries. Dutch students were the least likely, and n and Hong Kong students the most likely, to support tobacco control policies. Conclusions It is possible to develop appropriate and meaningful measurement tools for assessing support of tobacco control policies. Strong evidence was found for internal reliability and structural invariance of the SPI. The SPI may be a useful mechanism for monitoring ongoing policy initiatives, making cross-cultural comparisons, and evaluating population receptiveness to proposed policy approaches. (Tobacco Control 1998;7: ) Keywords: policies, tobacco control, Smoking Policy Inventory Introduction Although smoking rates are stable or declining in industrialised countries, they are on the increase in many developing countries. This has led health researchers to predict a worldwide pandemic of tobacco-related illness and death beginning early in the next century. 1 4 An estimated 500 million people alive today will die from tobacco-related disease and death. 2 These concerns have given rise to global strategies to implement comprehensive tobacco control policies. 5 8 There is growing evidence from around the world that anti-smoking policies can result in decreases in tobacco consumption Since 1970, the World Health Organisation has endorsed successively stronger resolutions appealing to governments to adopt comprehensive tobacco control legislation, arguing by implication that it is their ethical duty to protect the health of their people Countries are urged to adopt polices that protect non-smokers rights to breathe clean air; ensure that all health personnel set a non-smoking example; restrict production, promotion, and use of tobacco; eliminate sales and marketing to minors; require prominent health warnings; establish programmes to assist smokers to stop smoking; provide resources for promoting anti-smoking messages; and monitor trends in tobacco consumption As new policies are adopted it becomes increasingly important to evaluate the impact of these policies on smoking behaviours and on the public acceptance of tobacco control policies. This paper addresses one aspect of this problem: the need for sound measurement instruments that can reliably assess the support for tobacco control policies in diverent countries. The purpose of this paper is to explore whether the Smoking Policy Inventory (SPI), a short instrument that measures degree of support for tobacco control policies, is internally consistent and a valid instrument across diverent populations. Details about the SPI instrument development and its initial validation have been published previously. 18 Administration of the SPI in six diverent countries provides the opportunity to explore whether the measurement properties of the instrument can be replicated in diverent settings with varying traditions and degrees of historical support for tobacco control policies. Methods PROCEDURES Public health researchers from six countries (, Hong Kong, the, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the United States) were invited to participate in an international collaborative study of smoking policies. To facilitate comparability of the policy instrument and survey questionnaire, eligibility was restricted to researchers from
2 242 Laforge, Velicer, Levesque, et al countries whose primary language was English. The was also included because, although English is a secondary language, the university student population is proficient in the language. Each research group was asked to administer the survey questionnaire to approximately university students during the 1993 academic year. The sample size requirement was established as suycient to enable assessment of the factor structure of the instrument in each setting. A standardised survey questionnaire was developed at the University of Rhode Island (URI) and was printed on optical scan forms and mailed to the participating sites. All surveys were anonymous, and contained a code for identification of country of origin. Completed questionnaires were mailed back to URI for data processing and statistical analysis. MEASURES The questionnaire contained 28 items relating to demographics, smoking history, and knowledge about the risks associated with smoking. The 35-item Smoking Policy Inventory (SPI), a five-dimensional scale measuring attitudes and opinions about tobacco control and smoking policies was included. 18 The five dimensions are: (a) advertising and promotion, (b) public education, (c) laws and penalties, (d) taxes and fees, and (e) environmental restrictions on smoking. Each of the five SPI scales have seven items which are scored from 1 to 5. The SPI has a hierarchical structure, producing scores for each of the five separate dimensions, and a total score indicating overall support of tobacco control policy. 18 TOBACCO CONTROL POLICY ENVIRONMENT All participating co-authors contributed a review of the tobacco control policy environment in their respective countries covering each of the five domains of the SPI at the time of the survey. With the exception of the United States, the reviews of the policy environment from each country were written before results of the surveys were available to the collaborators from that country. Because the American research team led this project, a sample review of the American policy environment derived from published sources was written and distributed to collaborators in the other countries as a model to be used for their review. These qualitative reviews are summarised and presented as background material for comparison with the results of SPI data from the corresponding student surveys. This qualitative summary was validated against published references relating to international tobacco control legislation. 15 SAMPLE Data were collected from a total of 1786 students from six countries: (n = 403), Hong Kong (n = 336), the (n = 351), South Africa (n = 291), the United Kingdom (n = 164), and the United States (n = 241). Researchers in each country chose the method for data collection, as explained below. In four countries the survey was administered in the classroom, in two (the and the United Kingdom) the survey was delivered by mail or after class and returned later. Participation rates were not typically measured, although participation from countries that administered the survey in classrooms experienced few, if any, refusals. All data were collected during the 1993 academic year. In, the questionnaire was administered to 412 first-year university students from four universities in or near Melbourne,. All students answered the questionnaire in classrooms or tutorial settings under the supervision of a tutor or research assistant. In Hong Kong, questionnaires were handed out and completed in classrooms. A total of 336 students from six diverent courses participated. All students were ethnic Chinese and it is estimated that more than 95% of them had been living in Hong Kong for at least 10 years. In the, 900 questionnaires were distributed to the mail boxes of health science students of the University of Limburg. The purpose of the study was explained in an introductory letter, and those who returned the questionnaires (351 students, or 39%) were eligible for one of seven prizes of 75 guilders (approximately US$42). In South Africa, the sample consisted of 291 undergraduate students enrolled in an industrial psychology course at the University of the Western Cape. The questionnaires were administered during class time and no special credit was given for participation. All students were black that is, African, coloureds (approximately 60%), or Indians. There were no refusals. In the United Kingdom, the survey was administered to first-year psychology students at the University of Leeds, England. Questionnaires were handed out in a lecture class with the request that they be completed during the students own time and returned to a collection point in the Department of Psychology. A total of 300 questionnaires were distributed and 170 questionnaires were returned, of which 163 responses were usable (54% response rate). In the United States, 241 undergraduate students enrolled in an introductory psychology course at the University of Rhode Island completed the survey in the classroom under supervision of the instructor. Students were given course credit for their participation, and there were no refusals. Results SAMPLE CHARACTERISTICS Selected characteristics of the student samples by country are presented in table 1. The distribution of smoking status by country was about 20%, except for Hong Kong, where only 3.0% reported smoking. The distribution of former smokers was about 12%, again with the exception of Hong Kong. The country samples divered by age, although the range of ages did not vary greatly. Students from South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the tended to be older. The students were
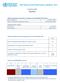
3 Measuring support for tobacco control policy 243 Table 1 Selected characteristics (%) of the study samples across six countries (n = 403) Hong Kong (n = 336) (n=351) South Africa (n=291) United Kingdom (n = 164) Current smoker Former smoker Age (years) < > Men* Family income* Lower Lower-middle Middle Upper-middle Upper Parent(s) smoked* % Yes No of friends who smoke* > *p< United States (n = 241) predominantly women, ranging from slightly more than 50% to almost 80%. Family income varied considerably across countries as well, with South African students reporting lower family income rankings than the other countries. Students from the and the United States were more likely to report that one or both of their parents were smokers. The number of friends who smoked varied across countries, and is generally consistent with other measures of smoking status. PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPI An analysis using LISREL 19 examined the factorial invariance of the SPI across the six international samples. The hierarchical model previously fit to this measure, consisting of a single second-order factor (general attitude about smoking policy) and five first-order factors (the five domains measured by the SPI scales), was fit in each of the six samples. The Tucker-Lewis Index 20 indicated a high degree of factorial invariance across the six samples. The obtained values of the Tucker-Lewis Index for goodness of fit were: (a), 0.949; (b) Hong Kong, 0.909; (c) the, 0.975; (d) South Africa, 0.918; (e) United Kingdom, 0.926; and (f) United States, Inter-item reliability of the SPI subscales was compared across countries using Cronbach s coeycient α and is presented in table 2. The SPI scales were internally consistent across samples from diverent countries. The item-scale reliability coeycient α for four of the five scales was 0.80 or greater typically over 0.90 across samples from all six countries. The public education scale α ranged from 0.68 to 0.75 across countries. SMOKING POLICY INVENTORY The unadjusted mean SPI scale scores and standard deviations for each of the five SPI scales are also presented in table 2. The SPI scale scores represent the degree of support for tobacco control policy, with higher scores Table 2 Means, standard deviations (SD), and coeycient α for the five Smoking Policy Inventory (SPI) scales for six countries SPI scale (n = 403) Hong Kong (n = 336) (n = 351) South Africa (n = 291) United Kingdom (n = 164) United States (n = 241) Advertising and promotion X c SD α Public education X c SD α Laws and penalties X c SD α Taxes and fees X c SD α Restrictions on smoking X c SD α Total SPI score X c SD X c = unadjusted mean score.
4 244 Laforge, Velicer, Levesque, et al Table 3 Selected tobacco control policies by country sample in 1993, according to investigators qualitative reports SPI scale Hong Kong South Africa United Kingdom United States Advertising and promotion Ban tobacco ads in electronic broadcast media Yes Yes Yes Partial Yes Yes Ban tobacco ads in print media Yes No Partial No No Partial Ban billboard ads Yes Partial No No No No Ban free samples and promotional items Yes Yes No No No Partial Ban tobacco sponsorship of sports events Yes Partial No No No No Ban smokeless tobacco Yes No No No No Partial Ban tobacco promotion in public cinema Yes Yes No No No Partial Public education Health warnings on cigarettes packs Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Health warnings on advertising Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Strong anti-tobacco health promotion Yes Yes Partial No Partial Yes Laws and penalties Minimum age-of-purchase laws Yes Yes No No Partial Yes Strong enforcement of penalties for sales to minors Yes Yes No No No Partial Limits on pack size, including number of cigarettes per pack Yes No Yes No No Yes Taxes and fees Federal excise tax on tobacco Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Tax increases intended to decrease smoking Yes Yes Partial No Yes Partial Environmental restrictions Restaurants Partial Yes Partial No Partial Partial Hospitals and medical care facilities Yes Yes Partial Partial Partial Partial Public transportation Yes Yes Partial Partial Partial Yes Workplaces Yes Partial Partial No Partial Partial Schools Yes Yes Partial No Yes Yes Yes = legislation or regulation is fully in evect. No = legislation or regulation is not in evect. Partial = policy only partially implemented throughout country. SPI = Smoking Policy Inventory. indicating greater support. In general within each country, students were more likely to endorse policies to enhance public education on the health and social consequences of smoking, and increased environmental restrictions. Support tended to be lowest for advertising and promotional controls, as well as for laws and penalties. Smokers in each of the six samples reported significantly lower scores on the SPI (p<0.01), suggesting less favourable attitudes toward tobacco control polices than among nonsmokers. The correlation between total SPI score and current smoking status ranged from r = 0.36 to r = 0.48 across the six samples. Similarly, total SPI score was negatively associated with number of friends who smoke in each of the six samples (range: r = 0.16 to r = 0.37, p<0.01). Men scored significantly lower than women on total SPI score in three samples: South Africa (r = 0.19), Hong Kong (r = 0.21), and the United Kingdom (r = 0.28). There was a weak but statistically significant association with family income in the (r = 0.18) and Hong Kong (r = 0.16) samples. TOBACCO CONTROL POLICY A comprehensive review of the details of tobacco control policy in each of the six countries is beyond the scope of this paper. Characterising the policy environment requires an evaluation of the mix of local, regional, or national governmental legislation, as well as public agency activities and private industry initiatives. 17 A qualitative overview of the policy environment can provide insight into the historical background, useful for evaluating the external validity of the results obtained from the student surveys. Table 3 summarises the investigators qualitative reports of each country s policy environment using several tobacco control initiatives that were assessed during the study year. The policies were ranked by degree of adoption or implementation (full, partial, or none). Table 3 suggests that during the study year tobacco control policies were more likely to have been adopted or more fully implemented in and Hong Kong, and were least likely to have been adopted in the and South Africa. The United States and United Kingdom were between these extremes. RELATIONSHIP OF SPI SCORES TO THE TOBACCO CONTROL POLICY ENVIRONMENT Because the six student samples in this study were drawn for convenience, and are not representative of the general population nor of the general population of students within each country, observed diverences among countries may misrepresent true diverences among them. However, comparisons can be made within country, and with the general pattern of relationships between SPI scores and the policy environment. It is important to remember that assessment of the policy environment provides a snapshot of a dynamic process, which in this case reflects what was occurring in Significant changes have taken place in some countries, such as South Africa, since 1993, but it is beyond the scope of this article to discuss these changes. In general, the SPI score appears to be related to the tobacco control policy environment in each country. For example, students from the two countries that have the most aggressive programmes of tobacco control, and Hong Kong, were also very likely to endorse anti-smoking policies generally. Students from exhibited strong support for advertising and promotion regulations, which is consistent with more than two decades of anti-smoking activism in that country, which has led to enactment of some of the most stringent advertising and promotional
5 Measuring support for tobacco control policy 245 regulations in the world. Students from the, which has fewer tobacco control policies, tended to score low on the SPI. Students from the United Kingdom and exhibited relatively greater support, and Dutch students relatively less support, for strict laws and penalties for tobacco sales to minors than all countries. Discussion A major finding of this study is that meaningful and standardised assessment of tobacco control policy can be made using the Smoking Policy Inventory. The 35-item SPI provides a consistent measure of support for tobacco control policy, which was found to be robust across a variety of samples that were heterogeneous with respect to gender, type of student, income, smoking status, and parental and social smoking environment. Across all six countries, the psychometric analyses revealed excellent internal consistency and a highly comparable factor structure for the SPI. These findings provide strong evidence of the internal reliability and the structural invariance of the SPI, implying that the five underlying constructs of tobacco control policy are common across countries, and can be accurately measured and compared using the SPI scores. Although this study relied on nonrepresentative convenience samples, and is thereby limited in its utility for making comparative statements, the measurement properties of the SPI suggest that further research is indicated to evaluate its applicability as a practical instrument for cross-cultural research and policy evaluation. The SPI should be applied cross-culturally, using more comparable samples, to explore this possibility. The observed correspondence between the tobacco control policy environment and SPI score is further evidence of the validity of the SPI. Public support for tobacco control policy as measured by the SPI reflects in some measure the historical and policy environment in each country. Countries with recent history of strong advocacy for tobacco control, such as and Hong Kong, tended to score high. On the other hand, the, which is third in Europe with respect to tobacco distribution, production and has a strong liberal tradition with regard to tobacco control issues, scored low. Dutch students were the most likely to endorse taxes and fees, which may relate to the generally favourable attitude by the Dutch toward using taxes as an acceptable policy mechanism for addressing many social problems. Students from the three countries with more moderate tobacco control policy environments the United States, the United Kingdom, and South Africa expressed moderate levels of support for anti-smoking policies. At the time of the survey, South Africa was undergoing a major social transition away from the apartheid system toward a more egalitarian future. Although the tobacco control environment in South Africa might be characterised as relatively weak in 1993, the modest support for tobacco control exhibited by the mostly black and coloured students may represent growing aspirations for new policies in a government in the midst of major social change. The modest support for tobacco control policy in the United States and United Kingdom may reflect the mixed success that tobacco control advocates have had in achieving widespread adoption of evective tobacco control regulatory policies in those countries. Strong support for regulations against tobacco sales to minors was found in the United Kingdom, which at the time had relatively weak tobacco control policies in this area. If this finding is representative of the population at large, it would suggest that the political environment may be ripe for strategic advocacy of laws and penalties for sales to minors in the United Kingdom. Similar to findings from other studies of support for smoking policy, smoking status, gender, and income were found to be related to support for tobacco control policies. Separate analyses of data from the six countries have found that previous smoking experience is the most important predictor of SPI score. Indeed, it is a consistent finding that smokers report less support for tobacco control policies than non-smokers This relationship held for current and former smoking status, parental smoking history, number of friends who smoke, and being bothered by smoke. Additional research is needed to further develop the SPI. One limitation of the SPI relates to the observed ceiling evects in the SPI education subscale. Public education received strong endorsement in all countries, suggesting that the educational policies as measured by this subscale are widely accepted and not controversial. The high scores (average score 30.7 out of a possible 35) also imply that the education scale may be too restrictive due to ceiling evects, which place an upper limit on the variance that can be assessed by this scale. This finding indicates that the education subscale is of limited usefulness in assessing variation in support for tobacco control education. Another potential area for further research includes assessing support for litigation as a mechanism for tobacco control policy. This was not assessed in the initial development of the SPI, but has recently become an important focal point in discussions of tobacco policy in the United States. The validity and applicability of the SPI have only been partially demonstrated in this study. Additional research with adult samples will be needed to demonstrate its validity in general population settings. Such studies should also assess populations longitudinally to evaluate the stability and variability of the SPI over time. The use of convenience samples, which may be prone to selection bias, is an important limitation of this study. There are important diverences in sample selection across the six countries in this study, and comparison of differences from these data cannot be considered valid. The particular convenience samples described here are not representative samples of the general population, nor of the student
6 246 Laforge, Velicer, Levesque, et al population in these countries. For example, the smoking rate of 15% in this Dutch student sample was considerably lower than the national average of 35% for young people aged years in 1993 (personal communication with Dr DeVries, 12 December 1994). Similarly, the smoking rate among n college students in this study (20%) is lower than that reported for all n adults aged years (36%). 27 In the other four countries, however, the smoking rates in our samples are similar to those in age-comparable general population studies Conclusion This study addresses an important gap in the policy development literature, and demonstrates that it is possible to develop appropriate measurement tools for assessing support for tobacco control policies that can be broadly applicable. There are many potential applications of the SPI for tobacco control research, evaluation, and policy development. The short 35-item portable nature of the SPI makes it especially appropriate for large population survey research, and for monitoring within-population trends. The findings of this study imply that cross-cultural comparisons of tobacco control policy using the SPI may also be appropriate, given comparably representative samples. The SPI has been replicated across several diverse samples and has been shown to be highly reliable, structurally invariant, and with good external validity. The relatively short length of the instrument, capturing five broad dimensions of tobacco control policy, makes it a convenient substitute for the unstandardised approach to survey assessment of tobacco control policies. This work was supported by Grants CA27821, CA63045, and CA50087 from the National Cancer Institute. The authors would like to thank Ruth Roemer for her thoughtful review of an earlier draft of this paper. 1 Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, et al. Mortality from smoking in developed countries : indirect estimates from national vital statistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Peto R, Lopez AD. Worldwide mortality from current smoking patterns: WHO consultative group on statistical aspects of tobacco-related mortality. In: Durston B, Jamrozik K, eds. Tobacco and health 1990 the global war. Proceedings of the seventh world conference on tobacco and health, 1 5 April Perth: Health Department of Western, 1990: Peto R. Keynote address. 27th Annual meeting of the Society for Epidemiologic Research, Miami Florida, 16 June Marshal M. The second fatal impact: cigarette smoking, chronic disease and the epidemiological transition in Oceania. Soc Sci Med 1991;33: World Health Organisation. Controlling the smoking epidemic: report of the WHO Expert Committee on Smoking Control. WHO technical report series no 636. Geneva: WHO, World Health Organisation Smoking control strategies in developing countries: report of a WHO Expert Committee. WHO technical report series no 695. Geneva: WHO, World Health Organisation. Legislative strategies for a smokefree Europe. Copenhagen: WHO European OYce, World Health Organisation. Action plan on tobacco or health for Manila, Philippines: WHO Regional OYce for the Western Pacific, New Zealand Toxic Substances Board. Tobacco or health: an end tobacco advertising and promotion. Wellington, New Zealand, Pierce JP, Macaskill P, Hill D. Long-term evectiveness of mass media led anti-smoking campaigns in. Am J Public Health, 1990;80: US Department of Health and Human Services. Smoking and health in the Americas: a 1992 report of the surgeon general in collabration with the Pan American Health Organization. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Centre, OYce on Smoking and Health, 1992 (DHHS Publication No (CDC) ) 12 American Medical Association Council on Scientific AVairs. The worldwide smoking epidemic: tobacco trade, use and control. JAMA 1990;263: Pierce JP, Evans N, Farkas AJ, et al. Tobacco use in California. An evaluation of the tobacco control program, San Diego, California: University of California, 1994: World Health Organisation. Legislative responses to tobacco use. Foreword by Ruth Roemer. Dordrecht, : Martinus NijhoV, Roemer R. Legislative action to combat the world tobacco epidemic, 2nd ed. Geneva: World Health Organisation, Chapman S, Yach D, Salogee Y, et al. All Africa Conference on Tobacco Control. BMJ 1994;308: Roemer R. Fighting threats to legislative advances in tobacco control. Presented at the 122nd annual meeting of the American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, 31 October Velicer WF, Laforge RG, Levesque DA, et al. The development and initial validation of the Smoking Policy Inventory. Tobacco Control 1994;3: Joreskog KG, Sorbom D. LISREL 7: A guide to the program and applications, 2nd ed. Chicago, Illinois: SPSS, Tucker LR, Lewis C. A reliability coeycient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika 1973;38: Pederson LL, Shelley BB, Ashley MJ, et al. A population survey on legislative measures to restrict smoking in Ontario: 2. Knowledge, attitudes and predicted behavior. Am J Prev Med 1986;2: JeVery RW, Forster JL, Schmid TL, et al. Community attitudes toward public policies to control alcohol, tobacco, and high fat food consumption. Am J Prev Med 1990;6: Laforge RG, Velicer WF, Levesque DA, et al. Predictors of support for anti-smoking policies among students in six countries. Presented at the 16th annual meeting of the Society of Behavioral Medicine, March Schofield PE, Hill DJ, Velicer WF. Smoking policy interventions: is n youth in favor of them? Health Promotion J Aust 1996;7: Pederson L, Bull SB, Ashley MJ, et al. A population survey on legislative measures to restrict smoking in Ontario: 3. Variables related to attitudes of smokers and nonsmokers. Am J Prev Med 1989;5: Martin G, Steyn K, Yach D. Belief about smoking and health and attitudes toward tobacco control measures. South Afr Med J 1992;82: Hill DJ, White VM. n adult smoking prevalence in Aust J Public Health 1995:19:3. 28 Hong Kong Council on Smoking and Health. Health or smoking: the facts Hong Kong, China: Council on Smoking and Health, Slayen PW. What do young adults really know, think and do about their health? South Afr Med J 1980;57: Borkon L, Baird DM, SiV M. Tobacco smoking among students at the University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. South Afr Med J 1983,64: Johnston LD, O Malley PM, Bachman JG. National survey results on drug use from the Monitoring the Future Study, , Vol. II. College students and young adults. Rockville, Maryland: National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, (NIH Publication No )
 SLIDE 1: Good morning; I would like to thank the organizers for the opportunity to speak today on a significant issue the relationship between tobacco taxation and public health. Much of the background
SLIDE 1: Good morning; I would like to thank the organizers for the opportunity to speak today on a significant issue the relationship between tobacco taxation and public health. Much of the background
The Role of Nurses in Tobacco Control
 The Role of Nurses in Tobacco Control Stella Bialous, RN, MScN, DrPH Tobacco Policy International The Role of Nurses in Tobacco Control There are over 11 million nurses in the world, and they have the
The Role of Nurses in Tobacco Control Stella Bialous, RN, MScN, DrPH Tobacco Policy International The Role of Nurses in Tobacco Control There are over 11 million nurses in the world, and they have the
Tanzania. Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. 29 July 2007. Contents. Introduction
 Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control Tanzania Introduction Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death in the world today, and is estimated to kill more than five
Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control Tanzania Introduction Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death in the world today, and is estimated to kill more than five
Position Statement: Nicotine Dependence
 Position Statement: Nicotine Dependence I. Treatment and Prevention In accordance with the avowed purposes of NAADAC, The Association for Addiction Professionals prompting and supporting the most appropriate
Position Statement: Nicotine Dependence I. Treatment and Prevention In accordance with the avowed purposes of NAADAC, The Association for Addiction Professionals prompting and supporting the most appropriate
PUBLIC EDUCATION CAMPAIGNS REDUCE TOBACCO USE
 PUBLIC EDUCATION CAMPAIGNS REDUCE TOBACCO USE The scientific evidence is substantial and clear: public education campaigns reduce the number of youth who start smoking, increase the number of smokers who
PUBLIC EDUCATION CAMPAIGNS REDUCE TOBACCO USE The scientific evidence is substantial and clear: public education campaigns reduce the number of youth who start smoking, increase the number of smokers who
Country profile. Austria
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Austria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Austria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Saving Lives, Saving Money. A state-by-state report on the health and economic impact of comprehensive smoke-free laws
 Saving Lives, Saving Money A state-by-state report on the health and economic impact of comprehensive smoke-free laws 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary...............................................................................2
Saving Lives, Saving Money A state-by-state report on the health and economic impact of comprehensive smoke-free laws 2011 Table of Contents Executive Summary...............................................................................2
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Democratic People's Republic of Korea WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 17 June 2003 Date of
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Democratic People's Republic of Korea WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 17 June 2003 Date of
Patterns of smoking in the Baltic Republics
 J Epidemiol Community Health 1999;53:277 282 277 Patterns of smoking in the Baltic Republics Iveta Pudule, Daiga Grinberga, Kamelija Kadziauskiene, Algis Abaravicius, Sirje Vaask, Aileen Robertson, Martin
J Epidemiol Community Health 1999;53:277 282 277 Patterns of smoking in the Baltic Republics Iveta Pudule, Daiga Grinberga, Kamelija Kadziauskiene, Algis Abaravicius, Sirje Vaask, Aileen Robertson, Martin
Stop-smoking battle still raging 50 years after surgeon general published health risks
 Stop-smoking battle still raging 50 years after surgeon general published health risks By Lois M. Collins, Deseret News National Edition Published: Saturday, Jan. 11 2014 8:20 p.m. MST A half-century ago,
Stop-smoking battle still raging 50 years after surgeon general published health risks By Lois M. Collins, Deseret News National Edition Published: Saturday, Jan. 11 2014 8:20 p.m. MST A half-century ago,
COMPREHENSIVE TOBACCO PREVENTION AND CESSATION PROGRAMS EFFECTIVELY REDUCE TOBACCO USE
 COMPREHENSIVE TOBACCO PREVENTION AND CESSATION PROGRAMS EFFECTIVELY REDUCE TOBACCO USE Tobacco control programs play a crucial role in the prevention of many chronic conditions such as cancer, heart disease,
COMPREHENSIVE TOBACCO PREVENTION AND CESSATION PROGRAMS EFFECTIVELY REDUCE TOBACCO USE Tobacco control programs play a crucial role in the prevention of many chronic conditions such as cancer, heart disease,
Some possible survey questions
 Some possible survey questions This appendix provides examples of the types of questions you could ask in your surveys depending on your research objectives. These questions come from the National ASH
Some possible survey questions This appendix provides examples of the types of questions you could ask in your surveys depending on your research objectives. These questions come from the National ASH
Country profile. Bhutan
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Bhutan WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 09 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Bhutan WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 09 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Quitline Tax Increase. Survey NEW ZEALAND POLICE CITIZENS SATISFACTION RESEARCH (TN/10/19) Six Month Follow Up. Contents
 Market Research Proposal Proposal Prepared For New Zealand Police Quitline Tax Increase Research Report Prepared for The Quit Group January 2011 Survey Six Month Follow Up NEW ZEALAND POLICE CITIZENS SATISFACTION
Market Research Proposal Proposal Prepared For New Zealand Police Quitline Tax Increase Research Report Prepared for The Quit Group January 2011 Survey Six Month Follow Up NEW ZEALAND POLICE CITIZENS SATISFACTION
SMOKING TOBACCO: SMOKING
 TOBACCO: SMOKING One in 4 adults in Guam is a smoker. Among youth, 1 in 5 smokes. Guam s smoking rate is higher than most US States and Territories; this has remained unchanged since 2001. T O B A C C
TOBACCO: SMOKING One in 4 adults in Guam is a smoker. Among youth, 1 in 5 smokes. Guam s smoking rate is higher than most US States and Territories; this has remained unchanged since 2001. T O B A C C
Smoking in Casinos Survey
 Smoking in Casinos Survey Are London casino workers concerned about exposure to other people s tobacco smoke at work? August 2005 Prepared by: Paul Pilkington, Lecturer in Public Health, University of
Smoking in Casinos Survey Are London casino workers concerned about exposure to other people s tobacco smoke at work? August 2005 Prepared by: Paul Pilkington, Lecturer in Public Health, University of
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Country profile. Saudi Arabia
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Saudi Arabia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 24 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Saudi Arabia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 24 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal
WHY THE FDA SHOULD REGULATE TOBACCO PRODUCTS
 WHY THE FDA SHOULD REGULATE TOBACCO PRODUCTS WHAT IF a product consumed by nearly 50 million Americans every day killed one-third of those who became regular users and one-half of those who use it for
WHY THE FDA SHOULD REGULATE TOBACCO PRODUCTS WHAT IF a product consumed by nearly 50 million Americans every day killed one-third of those who became regular users and one-half of those who use it for
Colorado s 2005 Tobacco Tax Increase, Cigarette Consumption, and Tax Revenues
 Colorado s 2005 Tobacco Tax Increase, Cigarette Consumption, and Tax Revenues Tobacco Program and Evaluation Group University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center Theresa Mickiewicz, MSPH Arnold
Colorado s 2005 Tobacco Tax Increase, Cigarette Consumption, and Tax Revenues Tobacco Program and Evaluation Group University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center Theresa Mickiewicz, MSPH Arnold
BrokenPromises. AState-by-StateLookatthe 1998StateTobaccoSettlement 16YearsLater
 BrokenPromises toourchildren AState-by-StateLookatthe 1998StateTobaccoSettlement 16YearsLater Broken Promises to Our Children: A State-by-State Look at the 1998 State Tobacco Settlement 16 Years Later
BrokenPromises toourchildren AState-by-StateLookatthe 1998StateTobaccoSettlement 16YearsLater Broken Promises to Our Children: A State-by-State Look at the 1998 State Tobacco Settlement 16 Years Later
2009 Mississippi Youth Tobacco Survey. Office of Health Data and Research Office of Tobacco Control Mississippi State Department of Health
 9 Mississippi Youth Tobacco Survey Office of Health Data and Research Office of Tobacco Control Mississippi State Department of Health Acknowledgements... 1 Glossary... 2 Introduction... 3 Sample Design
9 Mississippi Youth Tobacco Survey Office of Health Data and Research Office of Tobacco Control Mississippi State Department of Health Acknowledgements... 1 Glossary... 2 Introduction... 3 Sample Design
3 Focus the Evaluation Design
 3 Focus the Evaluation Design Now that you and your stakeholders have a clear understanding of your program, your evaluation team will need to focus the evaluation. The evaluation team must decide the
3 Focus the Evaluation Design Now that you and your stakeholders have a clear understanding of your program, your evaluation team will need to focus the evaluation. The evaluation team must decide the
INFORMATION. Tobacco Control Policy. Information from the
 Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Tobacco Control Policy INFORMATION Background Cigarette smoking is a major cause of heart attack,
Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Tobacco Control Policy INFORMATION Background Cigarette smoking is a major cause of heart attack,
The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup
 Chapter 3 The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup of 1 Million Men and Women David M. Burns, Thomas G. Shanks, Won Choi, Michael J. Thun, Clark W. Heath, Jr., and Lawrence
Chapter 3 The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup of 1 Million Men and Women David M. Burns, Thomas G. Shanks, Won Choi, Michael J. Thun, Clark W. Heath, Jr., and Lawrence
Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends. 2012 Edition
 Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition This report was prepared by Jessica Reid, MSc, and David Hammond, PhD. Data analysis was completed
Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition This report was prepared by Jessica Reid, MSc, and David Hammond, PhD. Data analysis was completed
Health Professionals Survey on Tobacco Use and Cessation Counseling -- Lebanon 2005
 Health Professionals Survey on Tobacco Use and Cessation Counseling -- Lebanon 2005 Georges Saade (1) Charles W Warren (2) Nathan R Jones (2) Ali Mokdad (3) Samira Asma (2) (1) Non Communicable Disease
Health Professionals Survey on Tobacco Use and Cessation Counseling -- Lebanon 2005 Georges Saade (1) Charles W Warren (2) Nathan R Jones (2) Ali Mokdad (3) Samira Asma (2) (1) Non Communicable Disease
Role Model Behaviors of Nursing Faculty in Japan and the United States
 原 著 Role Model Behaviors of Nursing Faculty in Japan and the United States Tomomi Kameoka Naomi Funashima Patricia Ann. Gorzka Kumiko Hongo Nobuko Yamashita Toshiko Nakayama Mika Hattori National College
原 著 Role Model Behaviors of Nursing Faculty in Japan and the United States Tomomi Kameoka Naomi Funashima Patricia Ann. Gorzka Kumiko Hongo Nobuko Yamashita Toshiko Nakayama Mika Hattori National College
VISION MISSION GOAL AND OBJECTIVES
 VISION MISSION GOAL AND OBJECTIVES 3. Vision, Mission, Goal and Objectives 3.1. Vision To create a tobacco-free society 3.2. Mission 3.3. Goal To promote individual, community and government responsibility
VISION MISSION GOAL AND OBJECTIVES 3. Vision, Mission, Goal and Objectives 3.1. Vision To create a tobacco-free society 3.2. Mission 3.3. Goal To promote individual, community and government responsibility
Country profile. Sri Lanka
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Sri Lanka WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 23 September 2003 Date of ratification (or legal
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Sri Lanka WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 23 September 2003 Date of ratification (or legal
YOUTH DRUG SURVEY CHARLOTTE-MECKLENBURG PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 YOUTH DRUG SURVEY CHARLOTTE-MECKLENBURG PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2010 Paul C. Friday, Ph.D. Research & Training Specialists, Inc. Concord, NC June, 2011 Special appreciation is extended to Helen Harrill, John Basilice,
YOUTH DRUG SURVEY CHARLOTTE-MECKLENBURG PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2010 Paul C. Friday, Ph.D. Research & Training Specialists, Inc. Concord, NC June, 2011 Special appreciation is extended to Helen Harrill, John Basilice,
Country profile. Nigeria
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Nigeria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Nigeria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Drugged Driving. What is Drugged Driving? How Many People Take Drugs and Drive?
 Drugged Driving What is Drugged Driving? "Have one [drink] for the road" was, until recently, a commonly used phrase in American culture. It has only been within the past 20 years that as a Nation, we
Drugged Driving What is Drugged Driving? "Have one [drink] for the road" was, until recently, a commonly used phrase in American culture. It has only been within the past 20 years that as a Nation, we
Tobacco Use Among Students Attending Historically Black Colleges and Universities: Prevalence, Patterns and Norms
 12th Annual Summer Public Health Research Videoconference on Minority Health Tobacco Use Among Students Attending Historically Black Colleges and Universities: Prevalence, Patterns and Norms Michelle Laws,
12th Annual Summer Public Health Research Videoconference on Minority Health Tobacco Use Among Students Attending Historically Black Colleges and Universities: Prevalence, Patterns and Norms Michelle Laws,
Campaign against alcohol, drugs and substance abuse. ANC YL Policy Position
 Campaign against alcohol, drugs and substance abuse. ANC YL Policy Position Introduction The National Executive Committee of the African National Congress Youth League and subsequently the 23 rd National
Campaign against alcohol, drugs and substance abuse. ANC YL Policy Position Introduction The National Executive Committee of the African National Congress Youth League and subsequently the 23 rd National
Country profile. Slovakia
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Slovakia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 19 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Slovakia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 19 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal
SMOKE-FREE GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHWAY SPONSORED GROUPS
 SMOKE-FREE GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHWAY SPONSORED GROUPS 1. HEALTHWAY S SMOKE FREE REQUIREMENTS 1.1 Introduction From 1 July 2010 Healthway introduced a new condition of funding that all organisations entering
SMOKE-FREE GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHWAY SPONSORED GROUPS 1. HEALTHWAY S SMOKE FREE REQUIREMENTS 1.1 Introduction From 1 July 2010 Healthway introduced a new condition of funding that all organisations entering
WHO Europe Ministry of Health European Union
 RFP: SPECIALISED AGENCY TO PRODUCE COMMUNICATION MATERIALS FOR THE NATION-WIDE COMMUNICATION CAMPAIGN TARGETING CURRENT AND POTENTIAL TOBACCO USERS REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL 1. Background Tobacco use is the
RFP: SPECIALISED AGENCY TO PRODUCE COMMUNICATION MATERIALS FOR THE NATION-WIDE COMMUNICATION CAMPAIGN TARGETING CURRENT AND POTENTIAL TOBACCO USERS REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL 1. Background Tobacco use is the
Factorial Invariance in Student Ratings of Instruction
 Factorial Invariance in Student Ratings of Instruction Isaac I. Bejar Educational Testing Service Kenneth O. Doyle University of Minnesota The factorial invariance of student ratings of instruction across
Factorial Invariance in Student Ratings of Instruction Isaac I. Bejar Educational Testing Service Kenneth O. Doyle University of Minnesota The factorial invariance of student ratings of instruction across
Alcoholic Beverages Drinking among Female Students in a Tourist Province, Thailand
 Alcoholic Beverages Drinking among Female Students in a Tourist Province, Thailand Wirin Kittipichai Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand E-mail: phwkt@mahidol.ac.th Hatairat
Alcoholic Beverages Drinking among Female Students in a Tourist Province, Thailand Wirin Kittipichai Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand E-mail: phwkt@mahidol.ac.th Hatairat
Country profile. Cuba
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Cuba WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Cuba WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
[This page intentionally left blank.]
![[This page intentionally left blank.] [This page intentionally left blank.]](/thumbs/27/9688430.jpg) [This page intentionally left blank.] Raising Smart, Healthy Kids in Every State Expanding Early Education Initiatives with Funding from the Federal Tobacco Tax Table of Contents Introduction... 1 The
[This page intentionally left blank.] Raising Smart, Healthy Kids in Every State Expanding Early Education Initiatives with Funding from the Federal Tobacco Tax Table of Contents Introduction... 1 The
Now we ve weighed up your application for our protection products, it s only fair we talk you through our assessment process. More than anything, we
 how we assess your application UNDERWRITING EXPLAINED. Now we ve weighed up your application for our protection products, it s only fair we talk you through our assessment process. More than anything,
how we assess your application UNDERWRITING EXPLAINED. Now we ve weighed up your application for our protection products, it s only fair we talk you through our assessment process. More than anything,
Assessing the Perceptions and Usage of Substance Abuse among Teenagers in a Rural Setting
 Journal of Rural Community Psychology Vol E12 No 2 Assessing the Perceptions and Usage of Substance Abuse among Teenagers in a Rural Setting Regina Fults McMurtery Jackson State University Department of
Journal of Rural Community Psychology Vol E12 No 2 Assessing the Perceptions and Usage of Substance Abuse among Teenagers in a Rural Setting Regina Fults McMurtery Jackson State University Department of
Country profile. Canada
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Canada WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 15 July 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile Canada WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 15 July 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Tobacco use is one of the chief preventable causes of
 Special Report Differences in Worldwide Tobacco Use by Gender: Findings from the Global Youth Tobacco Survey Global Youth Tobacco Survey Collaborating Group ABSTRACT: The World Health Organization (WHO)
Special Report Differences in Worldwide Tobacco Use by Gender: Findings from the Global Youth Tobacco Survey Global Youth Tobacco Survey Collaborating Group ABSTRACT: The World Health Organization (WHO)
Tobacco dependence is a serious and deadly problem
 Integrating Tobacco Dependence Treatment and Tobacco-Free Standards Into Addiction Treatment: New Jersey s Experience Jonathan Foulds, Ph.D.; Jill Williams, M.D.; Bernice Order-Connors, L.C.S.W.; Nancy
Integrating Tobacco Dependence Treatment and Tobacco-Free Standards Into Addiction Treatment: New Jersey s Experience Jonathan Foulds, Ph.D.; Jill Williams, M.D.; Bernice Order-Connors, L.C.S.W.; Nancy
Americans Current Views on Smoking 2013: An AARP Bulletin Survey
 Americans Current Views on Smoking 2013: An AARP Bulletin Survey November 2013 Americans Current Views on Smoking 2013: An AARP Bulletin Survey Report Prepared by Al Hollenbeck, Ph.D. Copyright 2013 AARP
Americans Current Views on Smoking 2013: An AARP Bulletin Survey November 2013 Americans Current Views on Smoking 2013: An AARP Bulletin Survey Report Prepared by Al Hollenbeck, Ph.D. Copyright 2013 AARP
CITY OF EAST PALO ALTO A COMMUNITY HEALTH PROFILE
 CITY OF EAST PALO ALTO A COMMUNITY HEALTH PROFILE www.gethealthysmc.org Contact us: 650-573-2398 hpp@smcgov.org HEALTH BEGINS WHERE PEOPLE LIVE Over the last century, there have been dramatic increases
CITY OF EAST PALO ALTO A COMMUNITY HEALTH PROFILE www.gethealthysmc.org Contact us: 650-573-2398 hpp@smcgov.org HEALTH BEGINS WHERE PEOPLE LIVE Over the last century, there have been dramatic increases
Waterpipe tobacco smoking among college students in South Carolina. 13 August 2014 SC TRIG Medical University of South Carolina
 Waterpipe tobacco smoking among college students in South Carolina 13 August 2014 SC TRIG Medical University of South Carolina Acknowledgments Frederick Kates, MBA PhD Candidate Dept. of Health Services
Waterpipe tobacco smoking among college students in South Carolina 13 August 2014 SC TRIG Medical University of South Carolina Acknowledgments Frederick Kates, MBA PhD Candidate Dept. of Health Services
Education Campaign Plan Worksheet
 Education Campaign Plan Worksheet GEORGIA TOBACCO-FREE COLLEGES & UNIVERSITIES TOOL KIT This worksheet should be used as a guide. Don t worry about filling in each item in this exact order. Developing
Education Campaign Plan Worksheet GEORGIA TOBACCO-FREE COLLEGES & UNIVERSITIES TOOL KIT This worksheet should be used as a guide. Don t worry about filling in each item in this exact order. Developing
Alcohol Marketing, the Alcohol Industry and Their Impact on Binge Drinking by Adolescents
 Alcohol Marketing, the Alcohol Industry and Their Impact on Binge Drinking by Adolescents Thomas F. Babor, PhD, MPH The University of Connecticut School of Medicine Department of Community Medicine and
Alcohol Marketing, the Alcohol Industry and Their Impact on Binge Drinking by Adolescents Thomas F. Babor, PhD, MPH The University of Connecticut School of Medicine Department of Community Medicine and
Healthy ageing and disease prevention: The case in South Africa and The Netherlands
 Healthy ageing and disease prevention: The case in South Africa and The Netherlands Sebastiana Kalula, 1 Ger Tielen 2 and Monica Ferreira 1 Medical advances, improved health care and prudent health behaviour
Healthy ageing and disease prevention: The case in South Africa and The Netherlands Sebastiana Kalula, 1 Ger Tielen 2 and Monica Ferreira 1 Medical advances, improved health care and prudent health behaviour
Position Paper. Tobacco Prevention and Control in the California Community Colleges
 Position Paper Tobacco Prevention and Control in the California Community Colleges Written by: Beth Hoffman, RN, MSN Naomi Kitajima NP, MSN Kimberlee Homer Vagadori, MPH Adopted by HSACCC Executive Board
Position Paper Tobacco Prevention and Control in the California Community Colleges Written by: Beth Hoffman, RN, MSN Naomi Kitajima NP, MSN Kimberlee Homer Vagadori, MPH Adopted by HSACCC Executive Board
Alcohol and Other Drugs
 Alcohol and Other Drugs Policy and Procedure No. 126 Definitions Drugs - refer to alcohol and illegal drugs and tobacco. Reasonable is defined as moderate, not excessive or not exceeding the limit. Social
Alcohol and Other Drugs Policy and Procedure No. 126 Definitions Drugs - refer to alcohol and illegal drugs and tobacco. Reasonable is defined as moderate, not excessive or not exceeding the limit. Social
The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample
 Addictive Behaviors 29 (2004) 843 848 The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample Irene Markman Geisner*, Mary
Addictive Behaviors 29 (2004) 843 848 The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample Irene Markman Geisner*, Mary
Smoking in Hong Kong. Smoking in Hong Kong. Female Smoking. Policies and Strategies to tackle Smoking and Drug Abuse in Hong Kong
 Conference on Lifestyle and Health, Geneva, Switzerland July 6-8, 2009 Policies and Strategies to tackle Smoking and Drug Abuse in Hong Kong Professor S.H.Lee Emeritus Professor of Community Medicine,
Conference on Lifestyle and Health, Geneva, Switzerland July 6-8, 2009 Policies and Strategies to tackle Smoking and Drug Abuse in Hong Kong Professor S.H.Lee Emeritus Professor of Community Medicine,
Country profile. India
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile India WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 10 September 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2015 Country profile India WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 10 September 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Access to meaningful, rewarding and safe employment is available to all.
 Home Previous Reports Links Downloads Contacts The Social Report 2002 te purongo oranga tangata 2002 Introduction Health Knowledge and Skills Safety and Security Paid Work Human Rights Culture and Identity
Home Previous Reports Links Downloads Contacts The Social Report 2002 te purongo oranga tangata 2002 Introduction Health Knowledge and Skills Safety and Security Paid Work Human Rights Culture and Identity
Journal of. Employee Assistance. The magazine of the Employee Assistance Professionals Association VOL. 36 NO. 2 2 ND QUARTER 2006
 Employer Initiatives to Stop Smoking by Mary Hill, LCSW, CEAP As more employers take aggressive steps to reduce health care costs arising from employees tobacco use, EAPs can and must help ensure the process
Employer Initiatives to Stop Smoking by Mary Hill, LCSW, CEAP As more employers take aggressive steps to reduce health care costs arising from employees tobacco use, EAPs can and must help ensure the process
San Diego County 2010
 Indicators of Alcohol and Other Drug Risk and Consequences for California Counties San Diego County 21 Indicators of Alcohol and Other Drug Risk and Consequences for California Counties San Diego County
Indicators of Alcohol and Other Drug Risk and Consequences for California Counties San Diego County 21 Indicators of Alcohol and Other Drug Risk and Consequences for California Counties San Diego County
Cultural Competency -Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs on HBCU College Campuses
 Cultural Competency -Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs on HBCU College Campuses Presented by Alyssa C. Ryan, 2011 graduate of the University of the Virgin Islands Former Student Peer Educator and 2011-2013
Cultural Competency -Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs on HBCU College Campuses Presented by Alyssa C. Ryan, 2011 graduate of the University of the Virgin Islands Former Student Peer Educator and 2011-2013
Underage Drinking. Underage Drinking Statistics
 Underage Drinking Underage drinking is a serious public health problem in the United States. Alcohol is the most widely used substance of abuse among America s youth, and drinking by young people poses
Underage Drinking Underage drinking is a serious public health problem in the United States. Alcohol is the most widely used substance of abuse among America s youth, and drinking by young people poses
Oklahoma county. Community Health Status Assessment
 Oklahoma county Wellness Score 2014 Community Health Status Assessment Mental and Social Health Overall Mental Health score The World Health Organization defines mental health as a state of well-being
Oklahoma county Wellness Score 2014 Community Health Status Assessment Mental and Social Health Overall Mental Health score The World Health Organization defines mental health as a state of well-being
Chapter 13 Patterns of Tobacco Use Among U.S. Youth, Young Adults, and Adults
 Chapter 13 Patterns of Tobacco Use Among U.S. Youth, Young Adults, and Adults Introduction 703 Data Sources 703 Key Epidemiologic Measures 704 Historical Trends in Tobacco Use 705 Trends in Tobacco Use
Chapter 13 Patterns of Tobacco Use Among U.S. Youth, Young Adults, and Adults Introduction 703 Data Sources 703 Key Epidemiologic Measures 704 Historical Trends in Tobacco Use 705 Trends in Tobacco Use
Adolescents responses to cigarette advertisements: links between exposure, liking, and the appeal of smoking
 Tobacco Control 1998;7:129 133 129 Adolescents responses to cigarette advertisements: links between exposure, liking, and the appeal of smoking JeVrey Jensen Arnett, George Terhanian Department of Human
Tobacco Control 1998;7:129 133 129 Adolescents responses to cigarette advertisements: links between exposure, liking, and the appeal of smoking JeVrey Jensen Arnett, George Terhanian Department of Human
2014 Assessment of Smoking Policies and Practices in Residential and Outpatient Treatment Facilities in Sonoma County
 2014 Assessment of Smoking Policies and Practices in and Treatment Facilities in Sonoma County Terese Voge, Project Director Sonoma County Department of Health Services Health Policy Planning and Evaluation
2014 Assessment of Smoking Policies and Practices in and Treatment Facilities in Sonoma County Terese Voge, Project Director Sonoma County Department of Health Services Health Policy Planning and Evaluation
E-cigarette Briefing for Health & Social Care Professionals
 E-cigarette Briefing for Health & Social Care Professionals 1. The Context 1.1 Smoking is the largest single cause of premature deaths and preventable ill-health in England. In 2011 among adults aged 35
E-cigarette Briefing for Health & Social Care Professionals 1. The Context 1.1 Smoking is the largest single cause of premature deaths and preventable ill-health in England. In 2011 among adults aged 35
NEW JERSEY COLLEGES EXPEL TOBACCO
 NEW JERSEY COLLEGES EXPEL TOBACCO January 2013 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Tobacco-Free U: New Jersey Colleges Expel Tobacco was written by Michael Seserman, MPH, RD, and Jennifer L. Sullivan, MS Ed, Directors of
NEW JERSEY COLLEGES EXPEL TOBACCO January 2013 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Tobacco-Free U: New Jersey Colleges Expel Tobacco was written by Michael Seserman, MPH, RD, and Jennifer L. Sullivan, MS Ed, Directors of
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD FOR THE MARKETING OF TOBACCO PRODUCTS
 MARKETING OF TOBACCO PRODUCTS STATEMENT OF PURPOSE Imperial Tobacco Group PLC believes that tobacco products are for adults. The Group is committed to promoting and selling its products responsibly, within
MARKETING OF TOBACCO PRODUCTS STATEMENT OF PURPOSE Imperial Tobacco Group PLC believes that tobacco products are for adults. The Group is committed to promoting and selling its products responsibly, within
University of Bath Students Union
 University of Bath Students Union Paper UC 2004/5-7 General Principles CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY BUSU is committed to developing a comprehensive strategy on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
University of Bath Students Union Paper UC 2004/5-7 General Principles CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY BUSU is committed to developing a comprehensive strategy on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
EVALUATION OF FACTORS PREDICTING ACADEMIC STAFF ACCEPTANCE OF E-LEARNING AT THE CENTRE FOR DISTANCE LEARNING, UNIVERSITY OF MAIDUGURI, NIGERIA
 EVALUATION OF FACTORS PREDICTING ACADEMIC STAFF ACCEPTANCE OF E-LEARNING AT THE CENTRE FOR DISTANCE LEARNING, UNIVERSITY OF MAIDUGURI, NIGERIA Abstract Yusuf Ismail Centre for Distance Learning University
EVALUATION OF FACTORS PREDICTING ACADEMIC STAFF ACCEPTANCE OF E-LEARNING AT THE CENTRE FOR DISTANCE LEARNING, UNIVERSITY OF MAIDUGURI, NIGERIA Abstract Yusuf Ismail Centre for Distance Learning University
College Smoking Policies and Smoking Cessation Programs: Results of a Survey of College Health Center Directors
 College Smoking Policies and Smoking Cessation Programs: Results of a Survey of College Health Center Directors Henry Wechsler, PhD; Kathleen Kelley, MBA; Mark Seibring, BA/BS; Meichun Kuo, ScD; Nancy
College Smoking Policies and Smoking Cessation Programs: Results of a Survey of College Health Center Directors Henry Wechsler, PhD; Kathleen Kelley, MBA; Mark Seibring, BA/BS; Meichun Kuo, ScD; Nancy
Participation and pass rates for college preparatory transition courses in Kentucky
 U.S. Department of Education March 2014 Participation and pass rates for college preparatory transition courses in Kentucky Christine Mokher CNA Key findings This study of Kentucky students who take college
U.S. Department of Education March 2014 Participation and pass rates for college preparatory transition courses in Kentucky Christine Mokher CNA Key findings This study of Kentucky students who take college
Part I. Changing Risk Behaviors and Addressing Environmental Challenges
 Part I Changing Risk Behaviors and Addressing Environmental Challenges Chapter 1 Tobacco Reducing Tobacco Use Initiation RECOMMENDED INTERVENTIONS Increasing the Unit Price for Tobacco Products 10 Mass
Part I Changing Risk Behaviors and Addressing Environmental Challenges Chapter 1 Tobacco Reducing Tobacco Use Initiation RECOMMENDED INTERVENTIONS Increasing the Unit Price for Tobacco Products 10 Mass
Optional Life Insurance Benefits
 Optional Life Insurance Benefits For Eligible Employees of Augsburg College Policy # 201359 A Worldwide Presence Our parent company s operations currently service millions of people in the United States,
Optional Life Insurance Benefits For Eligible Employees of Augsburg College Policy # 201359 A Worldwide Presence Our parent company s operations currently service millions of people in the United States,
The Benefits of a Creating a Healthy Work Environment
 Eaton County Substance Abuse Advisory Group (ECSAAG) Barry-Eaton District Health Department The Benefits of a Creating a Healthy Work Environment This presentation includes: Harmful affects of alcohol,
Eaton County Substance Abuse Advisory Group (ECSAAG) Barry-Eaton District Health Department The Benefits of a Creating a Healthy Work Environment This presentation includes: Harmful affects of alcohol,
Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students
 Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students ABSTRACT Joseph Adwere-Boamah Alliant International University A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to predict
Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students ABSTRACT Joseph Adwere-Boamah Alliant International University A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to predict
Written Example for Research Question: How is caffeine consumption associated with memory?
 Guide to Writing Your Primary Research Paper Your Research Report should be divided into sections with these headings: Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References. Introduction:
Guide to Writing Your Primary Research Paper Your Research Report should be divided into sections with these headings: Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References. Introduction:
TOBACCO CESSATION WORKS: AN OVERVIEW OF BEST PRACTICES AND STATE EXPERIENCES
 TOBACCO CESSATION WORKS: AN OVERVIEW OF BEST PRACTICES AND STATE EXPERIENCES Despite reductions in smoking prevalence since the first Surgeon General s report on smoking in 1964, approximately 46 million
TOBACCO CESSATION WORKS: AN OVERVIEW OF BEST PRACTICES AND STATE EXPERIENCES Despite reductions in smoking prevalence since the first Surgeon General s report on smoking in 1964, approximately 46 million
NHS Swindon and Swindon Borough Council. Executive Summary: Adult Alcohol Needs Assessment
 NHS Swindon and Swindon Borough Council Executive Summary: Adult Alcohol Needs Assessment Aim and scope The aim of this needs assessment is to identify, through analysis and the involvement of key stakeholders,
NHS Swindon and Swindon Borough Council Executive Summary: Adult Alcohol Needs Assessment Aim and scope The aim of this needs assessment is to identify, through analysis and the involvement of key stakeholders,
The Importance and Impact of Nursing Informatics Competencies for Baccalaureate Nursing Students and Registered Nurses
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
Center for Health Statistics
 Center for Health Statistics May 2004 COUNTY HEALTH FACTS No. 04-03 County Health Facts is a series of reports using California Health Interview Survey data to describe the health status of California
Center for Health Statistics May 2004 COUNTY HEALTH FACTS No. 04-03 County Health Facts is a series of reports using California Health Interview Survey data to describe the health status of California
Summary. Introduction
 General discussion, Summary, Samenvatting Summary Introduction Nursing students are taught to provide client-centred, so-called holistic nursing care to patients. Taking a holistic approach means that
General discussion, Summary, Samenvatting Summary Introduction Nursing students are taught to provide client-centred, so-called holistic nursing care to patients. Taking a holistic approach means that
Adam C. Zaleski. College of Natural Sciences Travel Award (2008). Received $300 in travel expenses to attend annual conference and present research.
 Zaleski 1 Work Address: Adam C. Zaleski Florida Gulf Coast University Department of Behavioral and Social Sciences Modular 1, Office #27 10501 FGCU Blvd. South Fort Myers, FL 33965-6565 Office Phone: (239)
Zaleski 1 Work Address: Adam C. Zaleski Florida Gulf Coast University Department of Behavioral and Social Sciences Modular 1, Office #27 10501 FGCU Blvd. South Fort Myers, FL 33965-6565 Office Phone: (239)
CASE STUDY Master Tobacco Settlement Agreement A Three State Comparison of the Allocation of Funds
 1 CASE STUDY Master Tobacco Settlement Agreement A Three State Comparison of the Allocation of Funds Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death and disease in our society. Cigarette smoking
1 CASE STUDY Master Tobacco Settlement Agreement A Three State Comparison of the Allocation of Funds Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death and disease in our society. Cigarette smoking
An Example of SAS Application in Public Health Research --- Predicting Smoking Behavior in Changqiao District, Shanghai, China
 An Example of SAS Application in Public Health Research --- Predicting Smoking Behavior in Changqiao District, Shanghai, China Ding Ding, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA ABSTRACT Finding predictors
An Example of SAS Application in Public Health Research --- Predicting Smoking Behavior in Changqiao District, Shanghai, China Ding Ding, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA ABSTRACT Finding predictors
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues
 echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
should know souri s tobacco sion www.dhss.mo.gov/smokingandtobacco (7/05) 1
 Wha hat t you should know about Missouri souri s tobacco youth access s and posse session sion laws www.dhss.mo.gov/smokingandtobacco (7/05) 1 Introduction Tobacco use, particularly smoking, has been cited
Wha hat t you should know about Missouri souri s tobacco youth access s and posse session sion laws www.dhss.mo.gov/smokingandtobacco (7/05) 1 Introduction Tobacco use, particularly smoking, has been cited
Fire Death Rate Trends: An International Perspective
 Topical Fire report SerieS Fire Death Rate Trends: An International Perspective Volume 12, Issue 8 / July 2011 These topical reports are designed to explore facets of the U.S. fire problem as depicted
Topical Fire report SerieS Fire Death Rate Trends: An International Perspective Volume 12, Issue 8 / July 2011 These topical reports are designed to explore facets of the U.S. fire problem as depicted
Determinants, Key Players and Possible Interventions
 Major in Human Health, Nutrition and Environment, FS 2010 Public Health Concepts Determinants, Key Players and Possible Interventions David Fäh Aims Have an idea about which parameters can influence health
Major in Human Health, Nutrition and Environment, FS 2010 Public Health Concepts Determinants, Key Players and Possible Interventions David Fäh Aims Have an idea about which parameters can influence health
Substance Abuse Prevention Dollars and Cents in Arkansas: A Cost-Benefit Analysis
 Substance Abuse Prevention Dollars and Cents in Arkansas: A Cost-Benefit Analysis February 2010 Office of Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention Division of Behavioral Health Services, Arkansas Department of
Substance Abuse Prevention Dollars and Cents in Arkansas: A Cost-Benefit Analysis February 2010 Office of Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention Division of Behavioral Health Services, Arkansas Department of
JSNA Factsheet Template Tower Hamlets Joint Strategic Needs Assessment 2010 2011
 JSNA Factsheet Template Tower Hamlets Joint Strategic Needs Assessment 2010 2011. Executive Summary This fact sheet considers breast cancer, with a particular emphasis on breast screening and raising awareness
JSNA Factsheet Template Tower Hamlets Joint Strategic Needs Assessment 2010 2011. Executive Summary This fact sheet considers breast cancer, with a particular emphasis on breast screening and raising awareness
Academic Performance of IB Students Entering the University of California System from 2000 2002
 RESEARCH SUMMARY Academic Performance of IB Students Entering the University of California System from 2000 2002 IB Global Policy & Research Department August 2010 Abstract This report documents the college
RESEARCH SUMMARY Academic Performance of IB Students Entering the University of California System from 2000 2002 IB Global Policy & Research Department August 2010 Abstract This report documents the college
Tobacco Questions for Surveys A Subset of Key Questions from the Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) 2 nd Edition GTSS
 GTSS GLOBAL TOBACCO SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Tobacco Questions for Surveys A Subset of Key Questions from the Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) 2 nd Edition GTSS GLOBAL TOBACCO SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Tobacco
GTSS GLOBAL TOBACCO SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Tobacco Questions for Surveys A Subset of Key Questions from the Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) 2 nd Edition GTSS GLOBAL TOBACCO SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Tobacco
Broken Promises to Our Children: The 1998 State Tobacco Settlement Fifteen Years Later
 Broken Promises to Our Children: The 1998 State Tobacco Settlement Fifteen Years Later A Report on the States Allocation of the Tobacco Settlement Dollars Table of Contents Overview Executive Summary...
Broken Promises to Our Children: The 1998 State Tobacco Settlement Fifteen Years Later A Report on the States Allocation of the Tobacco Settlement Dollars Table of Contents Overview Executive Summary...
Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc.
 Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc. Introduction Alcohol and drug abuse and dependence are worldwide concerns. In China,
Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc. Introduction Alcohol and drug abuse and dependence are worldwide concerns. In China,
Substance abuse in Iranian high school students
 Addictive Behaviors 32 (2007) 622 627 Short Communication Substance abuse in Iranian high school students Asghar Mohammad Poorasl, Rezagholi Vahidi, Ali Fakhari, Fatemeh Rostami, Saeed Dastghiri Tabriz
Addictive Behaviors 32 (2007) 622 627 Short Communication Substance abuse in Iranian high school students Asghar Mohammad Poorasl, Rezagholi Vahidi, Ali Fakhari, Fatemeh Rostami, Saeed Dastghiri Tabriz
WORLD. Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees
 2011 WORLD Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees WORLD Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees The World Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees identifies mobility trends among GMAT examinees
2011 WORLD Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees WORLD Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees The World Geographic Trend Report for GMAT Examinees identifies mobility trends among GMAT examinees
Statistical Snapshot of Underage Drinking
 Statistical Snapshot of Underage Drinking Alcohol consumption and dangerous patterns of drinking are widespread among adolescents and lead to many adverse consequences for underage drinkers and others.
Statistical Snapshot of Underage Drinking Alcohol consumption and dangerous patterns of drinking are widespread among adolescents and lead to many adverse consequences for underage drinkers and others.
