Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in Central Africans
|
|
|
- Hester Ferguson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2008) 16: Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in Central Africans Longo- Mbenza B 1, Nkondi Mbadi A Nsungu J 2, Mbungu Fuele S 3 University of Kinshasa, Division of Cardiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Epidemiology, 1 General Hospital of Kinshasa 2, Lomo Medical Center 3, Unity of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Congo Abstract Objective: to assess the prevalence and the risk factors of diabetic (DR) in urban diabetics from Kinshasa, DRC. Methods: this is a community-based cross-sectional survey and a case-control study on diabetic in Kinshasa, the capital of DRC. The medical charts of all diabetics (n=3010) 20 years were studied to estimate the prevalence of DR during November % (n=301) of these were randomly selected to reveal 95 diabetics with DR and 206 diabetics without DR (control). Both groups were matched for primary care centre, sex, age, body mass index, and waist circumference, attending the primary care centres between December 2004 and December 2005, and were screened for DR using stereo color photography and ophthalmoscopy. Results: the overall prevalence rate of DR in the population was 31.6% (n=950 95% confidence interval [CI]: ). Delayed diagnosis of diabetes ( 55 years) in the study sample in women, men with high socioeconomic status, and pregnancy onset after the diagnosis of DR among women, were identified as variables for Univariate analysis and for significant risk factors of DR. Logistic regression analysis showed that longer duration of diabetes ( 4years) (LDD), systolic arterial hypertension (SAH), higher pulse pressure ( 60 mmhg, clinical pre-atherosclerosis/arterial stiffness), and family history of diabetes (FHD), were the significant and independent determinants of DR in the sample study. The multivariate risk of DR conferred by these determinants is enhanced among female diabetics (y= SHT LDD + FHD; p<0.01) and patients with type 2 diabetes (y= SHT + LDD FHD; p<0.05). The adjusted odds-ratio for DR conferred by higher pulse pressure was 5 (95% CI ; p<0.05. Conclusion: Longer duration of diabetes, arterial systolic hypertension, and higher pulse pressure (arterial stiffness) were the most significant independent risk factors of diabetic. However, a population-based study is warranted to identify the risk factors, as well as the prevalence of diabetic. Keywords: Africans, diabetic, prevalence, pulse pressure, risk factors, type-2 diabetes mellitus. Introduction Diabetes mellitus () is a massive problem worldwide with 171 million with the condition today and projected to increase to 360 millions in In Sub-Saharan Africa in general 2 and in Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) in particular 3 the prevalence of varies from 1-2% in rural areas to 16% in urban areas. One of the diabetic microvascular complications is diabetic (DR) which is defined as damage to microvascular system in the retina due to prolonged hyperglycaemia and is an important cause of blindness in the world. 4 However, hospital-based data on DR in African settings are fragmented. 5 Because of the large number of diabetic subjects, DR is likely to pose a heavy public health burden in Sub-Saharan Africa. Community-based data on the prevalence and risk factors of DR in Kinshasa, DRC (Central Africa), are lacking. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and the Received on: 13/06/07 Accepted on: 04/03/08 Correspondence to: Prof. Longo - Mbenza Benjamin, MD, PhD University of kinshasa, BP 783,Kinshasa xi campus, dr congo longombenza@yahoo.fr, Phone: risk factors of diabetic in urban diabetics from Kinshasa, DRC. Material and methods Study of DR prevalence The findings of two color fundus photographs and ophthalmoscopy performed on both eyes of all diabetic patients (n=3010) aged 20 years and belonging to all (n= 24) primary care centres for in Kinshasa, the largest city (7 millions inhabitants) and capital of DRC were retrospectively analysed in November Univariate and multivariate risk factors of diabetic Ten percent (n=301 cases), inclusive of known diabetics with DR, were randomly selected using random digits. Those diabetics with DR (n=95) and 206 controls (diabetics without DR) matched for primary care centres, sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and waist circumference were requested to participate in the cross-sectional and analytic study carried out in the interval between December 2004 and December Verbal informed consent was obtained from all eligible patients at the examination site. After the study approval by the University of Kinshasa committee of 17
2 Long-Mbenza et al Table 1: Univariate risk of diabetic conferred by longer duration of diabetics mellitus ( 4 years) Variables or (ci 95%) P In study population 4 (2.7 to 7.1) < Among men 3.7 (1.5 to 2.7) <0.01 Among women 4.4 (2.5 to 7.7) < In patients with type (2.2 to 8.4) < Table 2: Insulin treatment related univariate risk of diabetic Variables or (ci 95%) P In study population 2 (1.2 to 3.5) <0.01 In men 1.3 (0.5 to 3.1) Ns In women 2.7 (1.4 to 5.4) <0.001 In patients with type (1.4 to 4.1) <0.001 Ns: p>0.05, not significant. ethics, all participants were referred to the ophthalmologist (NK J) for diabetic screening. The presence and absence of DR were confirmed in case and controls, respectively Questionnaire The questionnaire used to obtain information in this crosssectional study was adapted from the study by Blessey. 6 The questionnaire sought relevant information on age, sex, delayed diagnosis (age at diagnosis), duration, treatment compliance, family history of, ethnicity, treatment, socioeconomic status, weight, height, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), pulse pressure, type of, pills use and pregnancy after onset. The questionnaire was tested in a pilot study with 20 patients prior to the main study. Based on their responses and the level of understanding of the questions in the standardized questionnaire administered during 30 minutes, some ambiguous or unclear questions were restructured or modified. Procedure Data were collected during working hours (10:00 am 15:00 pm). The researchers interacted with each respondent and their physical (anthropometry), clinical (blood pressure components and ophthalmologic characteristics) were noted. Participants had two colour retinal photography ff 450 plus camera (Carl Zeiss Meditec, Jenna, Germany), of one randomly selected eye and ophthalmoscopy performed on both eyes at the examination. A detailed fundus examination was done at the best possible mydriasis, after dilating the pupils with tropicamide (1%) and phenylephrine (10%), using 90 d lens and slit lamp biomicroscope. Definitions The diagnosis of at age 55 years was considered delayed. The duration was defined by the time interval in years between the diagnosis date and the date of the present study. Ethnicity was defined by the cultural background according to the language (Kongo, Ngala, Luba, Swahili). Longer duration of was set at a level of 4 years (median). The intake of 4 drinks/day was considered excessive alcohol intake. was defined by a fasting glycaemia 126 mg/dl (7 mmol/l) (7). Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 140 mmhg or greater or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 90 mmhg or greater or under antihypertensive drug treatment as recommended by the 1999 WHO guideline committee. 8 Higher pulse pressure (SBP-DBP 60 mmhg) defined pre-clinical atherosclerosis or arterial stiffness. 9 The minimum criterion for diagnosis of DR was the presence of at least one definite microaneurysm in any field photographed. Photographs were assessed and assigned a level, and the final diagnosis for each patient was determined from the grading of the worse eye according to the ETDRS criteria for severity of disease in the individual eye, 10 and from photographs against a light board using Donaldson s stereo viewer. Statistical analysis SPSS for windows version 10.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois, USA) was used for statistical analysis. Data are reported as proportions (%) sometimes with 95% confidence interval (95%CI) and mean ± SD values. The chi-square test was used to compare proportions. Comparisons between groups for continuous variables were made using the student t-test. The univariate risk of DR was assessed in calculating odds ratios (OR) and its 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) with Mantel Haenszel chi-squared test for comparisons. For multivariate analysis, logistic regression models were used to identify independent predictors (determinants) of DR. Two logistic regression models were used because of the colinearity between pulse pressure 60 mmhg and arterial systolic hypertension. Statistical significance was set at a level of < Results Study of DR prevalence The prevalence of overt diabetic (DR) was 31.6% (n=950/3010 diabetics) (95% CI; ). Risk factors of DR In pooled data of cases and controls, 7(2.3%) were suffering from type 1 and 294 (97.7%) from type 2. Univariate analysis There was no significant association (p>0.05) between age (56.9±12.1 years vs 58.1±11.8 years), sex, ethnicity, profession, smoking, excessive alcohol intake, education attainment, residence, and the presence of diabetic (results not presented). Compared to men with low socioeconomic status (12.8% n=6), men with high socioeconomic status presented higher univariate risk of diabetic (40.9% n=27, or=5 ci95% 1.7 to 14.3; p<0.001). 18
3 Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in central Africans Table 3: Anthropometry, components of blood pressure, and hypertension duration according to the presence of diabetic in the population Variables Presence of diabetic Absence of Diabetic Weight (kg) 58.1 ± ± 12.9 ns Height (m) ± ± 0.1 ns BMI(kg/m 2 ) 23.1 ± ± 5 ns Waist girth 86.1 ± ± 12.7 ns (cm) SBP(mmHg) ± ± 22.4 <0.05 DBP(mmHg) 74.4 ± ± 13.6 ns Pulse pressure 56.9 ± ± 15.2 <0.001 (mmhg) Hypertension 4.4 ± 5 4 ± 6 ns duration (years) Ns: p>0.05, not significant Table 4: Pulse pressure ( 60 mmhg) associated risk of diabetic Variables OR (CI 95%) P In study population 2.3 (1.4 to 3.9) <0.001 In men 3.4 (1.4 to 8.1) <0.01 In women 1.9 (1.01 to 3.5) <0.05 In patients with type (1.4 to 3.8) <0.001 Table 5: Predictors of diabetic in the study population with logistic regression not including pulse pressure 60 mmhg Independent variables Systolic hypertension (SBP 140 mmhg) duration ( 4 years) Family Beta ES Wald Adjusted OR (CI 95%) (1.7 to 10.4) P p < (1.5 to 9.1) < ( history of to 8.7) Constant < Adjusted or for sex, age, socioeconomic status, smoking, alcohol intake, profession, education attainment, type of, and treatment. There was a significant association between the presence of diabetic and the diagnosis of at the age 55 years in the study population (36.6% n=56 vs 25.5% n=37, or=1.7 CI 95%=1.02 to 2.8; p<0.05), in women (38.5% n=40 vs 24.7% n=20, OR=2 CI95%=1.01 to 3.7; p<0.05), but not in men (37.7% n=16 vs 26.6% n=17; p>0.05). There was a very significant association between the presence of diabetic and longer duration of ( 4 years) in general, and in both women and type 2- diabetes in particular (Table 1). Table 6: Higher pulse pressure, family history of and longer duration identified significant predictors of diabetic in the study population Independent variables Beta ES Wald Adjusted OR (CI 95%) (1.2 to 8.8) Family <0.05 history of ( 1.4 <0.01 duration to 8.5) ( 4 years) Pulse ( 2 to <0.00 pressure 12.8) 1 ( 60 ) Constant <0.05 Adjusted or for sex, age, socioeconomic status, smoking, alcohol intake, profession, education attainment, type of, and treatment The association between diabetic and insulin treatment was significant in the study population, women and type-2 diabetes, but not in men (Table 2). The anthropometric parameters, DBP, and hypertension duration were not related to the diabetic while higher levels of SBP and pulse pressure were significantly associated with the presence of diabetic in the study population (Table 3). In the study population, arterial hypertension (p>0.05) and diastolic arterial hypertension (p>0.05) were not associated with diabetic, whereas systolic arterial hypertension was significantly associated with diabetic (OR=2.3 CI 95% 1.4 to 3.8; p<0.01). The significant association between pulse pressure 60 mmhg (pre-clinical atherosclerosis/ arterial stiffness) and diabetic was shown in the study population, men, women, and type-2 (Table 4). Family history of was significantly associated with diabetic among women (55.6% vs 25.9%, OR=2.9 CI 95%= 1.0 to 3.7; p>0.05), but not in the study population (41.6% vs 26.3%; p>0.05) or in men (30 % vs 27.3%; p>0.05), in type-1 (50% vs 33.3%), and in type- 2 (41.3% vs 25.7%). The use of contraceptive pills was not associated with diabetic (31.6% vs 33.5%; p>0.05), whereas the onset of pregnancy after the diagnosis of diabetic was significantly associated with diabetic (65% vs 28%, or=3.2 CI95%= 1.2 to 13.2; p<0.05) among women. In the type-1, diabetic was not associated with SBP and pulse pressure, respectively (results not shown). Multivariate analysis In the first multivariate analysis (without higher pulse pressure), systolic arterial hypertension, longer duration of p 19
4 Long-Mbenza et al, and family history of were identified as significant and independent determinants (predictors) of diabetic in the study population (Table 5). However systolic arterial hypertension was not a significant predictor of diabetic in men (y= duration; p<0.05) while diabetic was predicted by systolic arterial hypertension, longer duration, and family history of in women (y= systolic hypertension longer duration ± family history of ; adjusted or conferred by systolic hypertension = 4.3 CI95%= 1.5 to 14.2; p<0.01); adjusted or conferred by duration 4 years = 2.9 CI95% 1.5 to 8.4; p<0.05); and adjusted or conferred by family history of =4.8 CI95%= 1.4 to 16.9; p<0.01) and in type -2 (y= systolic hypertension duration 4 years family history of ; adjusted or conferred by systolic hypertension = 3.7 CI95% =1.5 to 9.5; p<0.01; adjusted or conferred by duration 4 years =4.1 CI95%= 1.7 to 10.4; p<0.01); and adjusted or conferred by family history of =3.5 CI95%= 1.2 to 10; p<0.05). When the last logistic regression analysis had not included systolic arterial hypertension, pulse pressure 60 mmhg (pre-clinical atherosclerosis) conferred higher adjusted or and statistical power for diabetic in the study population (Table 6). Discussion Prevalence of diabetic (DR) This study reports the prevalence of DR (31.6%) in diabetic urban Africans with exclusive type-2 (97.7%). The current increase of in general and that of DR in particular may be attributed to the past rapid economic, demographic, epidemiologic and nutritional changes experienced in Sub-Saharan Africa. 2,3 These changes life style has resulted in an increased prevalence of obesity and. This study suggests that the prevalence of DR in Congolese diabetics is lower than 75% reported among Caucasians from USA. 12,13 However, this confirms the findings shown in developing countries of Sub-Saharan Africa (prevalence of DR between 15 and 52%) 14,15, India 16 and Pakistan. 17 Genetic and environmental factors, geographic sites, methodology, and hospital-related biases might explain the different prevalence rates of DR from the literature. 16 In Indian sub-continent, the onset of type-2 is at a younger age, 18 obesity is less common, 19 and genetic factors appear to be stronger. 20 To exclude the limitations that underscore DR prevalence data, the present community-based study involved selecting a representative sample of diabetics by the analysis of medical charts and inclusion of newly diagnosed DR by using international standard/etdrs. 10 In Sub-Saharan Africa with the epidemic size increase in in general and in type-2 in particular, 1-3 diabetic is fast becoming an important cause of visual disability. As visual disability in is largely preventable and treatable, this study aimed also at identifying modifiable (environment) and non modifiable (genetics) risk factors of DR. Indeed, many epidemiologic surveys have reported valuable information on the prevalence of DR in western societies that is useful for identifying individuals at high risk and for the planning of public health policies. 13 Risk factors and determinants of diabetic The present univariate and multivariate analyses suggest that the onset and progression of DR result from the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. This is logical as is a multifactorial disease. Multivariate analysis has identified the determinants of DR excluding confounding factors. In univariate analysis, age, gender, ethnicity, profession, smoking, excessive alcohol intake, education attainment, residence, and contraceptive pill use for women were not identified as significant risk factors for DR. However, several studies 21 have reported age 50 years, cigarette smoking, alcohol and contraceptive pills use as risk factors for DR. The significant univariate risk factors for DR in these African diabetics were delayed diagnosis of in the study population, men with high socioeconomic status, women with delayed diagnosis of, and pregnancy after DR onset among women. Gender as a systemic risk factor of DR Studies from literature 22 has shown varying results when predicting sex as a risk factor for developing DR. Male preponderance in DR has been shown in India, 16 the UKPDS, 23 the Hyderabad Study, 24 and a study of Pima Indians. 25 Farhan et al. 26 reported similar prevalence of DR in male and female type-2 diabetics from Kuwait. Pregnancy It is well established that DR can progress rapidly during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and poor glycaemic control in the 1 st trimester. 22 Smoking and alcohol intake There are studies which did not show a significant impact of smoking and alcohol 28 on the genesis of DR as reported in the present study. However, increased monoxide (CO) and platelet anomalies explain the deleterious role of tobacco in the pathogenesis of DR. 29 Insulin treatment The present higher prevalence of DR among these diabetic Africans, women, and patients with type-2 on insulin treatment, may be explained by the fact that patients with DR may have been preferentially treated with insulin. Insulin therapy related immune vascularitis is perhaps responsible for the presence of DR. 25 Delayed diagnosis of Delayed diagnosis of is characteristic for Africans with DR. 14 This factor of DR justifies improvement of diabetes care in Africans using a multidisciplinary approach. Systemic arterial hypertension and diastolic arterial hypertension Contrary to this study, African studies have shown a significant association between DR and arterial 20
5 Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in central Africans hypertension. 14,30,31 Control of arterial hypertension in these diabetics may justify the absence of a significant correlation, as the impact of hypertension duration was also not different. However, the entry of the anomalies of the BP components (SBP, DBP, and pulse pressure) within separate multivariate analyses confirmed the effects of increased shear stress of blood flow to damage the retinal capillary endothelial cells in the eyes of diabetics during aging. 22 Multivariate analysis The major and independent risk factors (determinants) for DR in this study population were duration 4 years, family history of, systolic arterial hypertension (sbp 140 mmhg), and higher pulse pressure 60 mmhg (pre-clinical atherosclerosis or arterial stiffness), consistent with findings of the world literature. 16,22,30-35 Logistic regression analyses revealed that the effect of these major risk factors for DR was stronger in diabetic women and type-2 diabetics than in diabetic men. This raises the possibility that there are differences in susceptibility to DR in certain ethnic groups. Family history of DR Several studies have outlined the role of genetic factors in susceptibility to DR as some patients develop DR in spite of good control and others escape DR despite poor control. 36,37 Duration of diabetic disease Longer duration of diabetes mellitus is probably the strongest predictor for development of DR. Ignorance, poverty, and delayed diagnosis of may explain the shorter mean duration of in this study (6 years) in comparison with good control of and longer duration of (20 years) in western countries before the onset of DR. 4 Atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness This study confirms the deleterious action of higher pulse pressure 60 mmhg (pre-clinical atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness) which predicts diabetic cardiomyopathy, 9 overt atherosclerosis and congestive heart failure 38 among central African diabetics from Kinshasa, DRC. It is also consistent with Indian studies which showed a significant association between pre-clinical atherosclerosis / arterial stiffness (Intima-Media thickness) with DR, even after adjusting for age, duration of, HBA1C, serum cholesterol, serum triglycerides, and microalbuminuria. 39 In addition to BP components, recent studies in western subjects have reported that DR is associated with atherosclerotic end points Our recent study has also concluded that diabetic predicts incident ischemic stroke in Africans with diabetes, independent of other risk factors. Those associations suggest that common pathogenic mechanisms (impaired auto-regulation, hyperperfusion, vascular endothelial growth factor, oxidant stress) might predispose to diabetic micro and macroangiopathy. 22 Limitations and strengths Because of low resources, other risk factors of DR such as HBA1C, renal disease, elevated serum lipids, and hypoglutathionaemia 22 were not assessed by this study. Furthermore, a limitation of the study is that, because it was a cross-sectional study, no information on causality was obtained. However, the strengths of this study are that it was based on retinal photography, ophthalmoscopy, and international standards of DR definition, and it was also the first study from Central Africa to report on prevalence and risk factors of DR using stereo retinal color photography. Moreover, the study included a representative population with, and results could be extrapolated to the all diabetics from Kinshasa city. Conclusion The present study suggests that among urban diabetics from Kinshasa with epidemic rate of type 2 diabetes, the prevalence of diabetic is high and similar to that reported in other African cities. Diabetic will pose a double burden for DRC. This emphasizes the need for routine retinal screening of diabetic individuals to detect diabetic in the early stages. A strong positive association was observed between longer duration of diabetes, systolic arterial hypertension, higher pulse pressure, family history of diabetes, and the presence of diabetic. The risk of diabetic conferred by these determinants is enhanced among female diabetics and type 2 diabetics. References 1. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes. Estimates for years 2000 and projection for 2030.Diabetes Care 2004; 27: Sobngwi G, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Vexan P, et al. Diabetes in Africans. Diabetes Metab 2001; 27: Longo Mbenza B, Vangu Ngoma D, Nahimana D, et al. The WHO stepwise approach to assess prevalence and risk factors of non-communicable diseases in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo. CVJA 2007;11: Murray Mcgavin DD. Diabetes and diabetic. Community Eye Health 1996; 9: Gill G, Mbany JC, Alberti G. Diabetes in Africa. Reach, Cambridge, UK 1995 : Blessey R. Epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology of ischemic heart. Physical Ther 1985; 65: Mayfield J. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus: New criteria. American Family Physician 1998; 58: Guidelines subcommittee world health organization. International society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension. J Hypertens 1999; 17: Longo- Mbenza B. The role of early hemodynamic impairment and disease duration on diabetic cardiomyopathy and hypertension in central Africans with atherosclerosis. J Diabetes Complications 2001; 15:
6 Long-Mbenza et al 10. Early treatment of diabetic study research group. Grading diabetic from stereoscopic colour fundus photographs: an extension of the modified airlie house classification. Etdrs report number 10. Ophthalmology 1991; 98: Omran AR. The epidemiologic transition: a theory of the epidemiology of population change. The Milbank memorial fund quarterly. Bull World Health Org 2001; 79: Dwyer MS, Melton J, Ballard DJ, et al. Incidence of diabetic and blindness: a population-based study in Rochester, Minnesota. Diabetes Care 1985; 8: The eye diseases prevalence research group. The prevalence of diabetic among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol 2004; 122: Sidibe EH. Diabetic in Dakar and review of African literature: epidemiologic elements. Diabetes Metab 2000; 26: Rotchford AP, Rotchford KM. Diabetes in rural South Africa an assessment of care and complications. S Afr Med J 2002; 7: Rema M, Premkumar S, Anitha B, et al. Prevalence of diabetic in urban India: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (URES) eye study, I Invest. Ophtalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: Jamal-U-Din, Qureshi MB, Khan AJ, et al. Prevalence of diabetic among individuals screened positive for diabetes in five community based eye camps in northern karachi, pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2006; 18: Mohan V, Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, et al. High prevalence of maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) among Indians. Diabetes Care 1985; 8: Joshi SR. Metabolic syndrome: emerging clusters of the Indian phenotype. J Assoc Physicians India 2003; 51: Viswanathan M, Mohan V, Snehalatha C, Ramachandran A. High prevalence of type 2 (noninsulin dependent) diabetes among the offspring of conjugal type 2 diabetic parents in India. Diabetologia 1985; 28 : Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, Demets DLI. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. II. Prevalence and risk of diabetic when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102: Rema M, Pradeepa R. Diabetic : An Indian perspective. Indian J Med Res 2007; 125: Kohner EM, Aldington SJ, Stratton IM et al..diabetic at diagnosis of non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, 30. Arch Ophthalmol 1998; 116: Dandona L, Dandona R, Naduvilath TJ et al. Population based assessment of diabetic in an urban population in southern India. Br J Ophthalmol 1999; 83: Nagi DK, Pettitt DJ, Bennett PH, et al. Diabetic assessment by Fundus photograph in Pima Indians with impaired glucose tolerance and NID. Diabet Med 1997; 14: Farhan H, Osama AM, Nasif A, Al-Otaibi S. The prevalence of diabetic and associated risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Al-Naeem (Kuwait). Middle East Journal of Family Medicine 2005; 3: El-Hifnawy MAM, Faadel AM, Ateia JA. Risk factors for diabetic univariate and multivariate analyses. Saudi J Ophthalmol 1992; 6: Moss SE, Klein R, Klein BK. Alcohol consumption and the prevalence of diabetic. Ophthalmology 1998 ; 105(5): Nielsen MM, Hjollund E. Smoking and diabetic microangiopathy. Lancet 1978; 2: Erasmus RTI, Alananu RA, Bojuwoye B, et al. Diabetic in Nigerians: relation to duration of diabetes, type of treatment control. East Afr Med J 1989; 66: Singer ED,Nathan, Fogie HA, Schachat AP. Screening for diabetic. Am Intern Med 1992; 116: Agardh E, Agardh CD, Koul S, Torffvit O. A four year follow up study on the incidence of diabetic in older onset diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1994; 11: Cohen O, Norumberg K, Neumann E, Dekel H. Complication free duration and the risk of development of in elderly diabetic patients. Arch intern Med 1998; 158: Yoshida Y, Hagura R, Hara Y, et al. Risk factors for the development of diabetic in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2001; 51: Klein BK, Klein R, Moss SE. A cohort study of the relationship of diabetic to blood pressure. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113: Rema M, Saravanan G, Deepa R. Familial clustering of diabetic in South Indian type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med 2002; 19: Hallman, Huber JC Jr, Gonzalez VH, et al. Familial aggregation of severity of diabetic in Mexican Americans from Starr County Texas. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: Longo-Mbenza B. Higher pulse pressure, congestive heart failure, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis in Congolese diabetics. First All Africa Congress on Cardiopathies, Diabetes and Strokes. Pan-African Society of Cardiology, Nairobi, Kenya, 2007; Rema M, Mohan V, Deepa R, Ravikumar R. Association and arterial stiffness with diabetic. The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 2). Diabetes Care 2004; 27: Kim YH, Hong MK, Song JM, et al. Diabetic as a predictor of late clinical events following percutaneous coronary intervention. J Invasive Cardiol 2002; 14:
7 Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in central Africans 41. Klein BE, Klein R, Mcbride PE, et al. Cardiovascular disease, mortality, and retinal microvascular characteristics in type 1 diabetes: Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. Arch Intern Med 2004; 164: Cheung N, Rogers S, Couper DJ, et al..is diabetic an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke? Stroke 2007; 38:
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
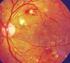 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital
 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613
 Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
 Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition:
 Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
PREVALENCE OF VISUAL IMPAIRMENT AMONG DIABETIC PATIENTS IN THE KUMBA URBAN AREA, CAMEROON
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 4 May 2016, pp. 872-876 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ PREVALENCE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 4 May 2016, pp. 872-876 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ PREVALENCE
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Hypertension and Diabetes Status. 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey
 Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change?
 C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment
 Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA
 EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
 44 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 62 published on 1st of every month 1st june, 2014 review article Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2
44 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 62 published on 1st of every month 1st june, 2014 review article Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2
Scottish Diabetes Survey
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Foreword The Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 data reflects many aspects of the quality of diabetes care across the whole of Scotland.
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Foreword The Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 data reflects many aspects of the quality of diabetes care across the whole of Scotland.
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Diabetes Complications
 Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost
 Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
Role of Body Weight Reduction in Obesity-Associated Co-Morbidities
 Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]
![Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]](/thumbs/28/12601472.jpg) Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world. Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ)
 Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease A global epidemic Diabetes in Africa
 DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
Original Research Paper
 1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence
 Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence Real-World Evidence for Successful Market Access WHITEPAPER REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE Generating real-world evidence requires the right
Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence Real-World Evidence for Successful Market Access WHITEPAPER REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE Generating real-world evidence requires the right
The Cross-Sectional Study:
 The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Support Supplement
 CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs
 T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Type 1 Diabetes ( Juvenile Diabetes)
 Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Follow-up Study Emily Y. Chew, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris III, MD,
The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Follow-up Study Emily Y. Chew, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris III, MD,
DISCLOSURES RISK ASSESSMENT. Stroke and Heart Disease -Is there a Link Beyond Risk Factors? Daniel Lackland, MD
 STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study
 Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study Titus F. Msoka Supervisors Marceline van Furth Yvo Smulders
Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study Titus F. Msoka Supervisors Marceline van Furth Yvo Smulders
Jill Malcolm, Karen Moir
 Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Majeda Fikree* Baderuldeen Hanafi** Zahra Ali Hussain** Emad M Masuadi*** Objective: To determine the
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Majeda Fikree* Baderuldeen Hanafi** Zahra Ali Hussain** Emad M Masuadi*** Objective: To determine the
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
 Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT
 Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes
 Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
REPORT ON DIABETES i
 AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA AU CONFERENCE OF MINISTERS OF HEALTH (CAMH6) Sixth Ordinary Session, 22-26 April 2013, Addis Ababa, ETHIOPIA CAMH/Exp/6(VI) iv THEME: The Impact of Non-Communicable
AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA AU CONFERENCE OF MINISTERS OF HEALTH (CAMH6) Sixth Ordinary Session, 22-26 April 2013, Addis Ababa, ETHIOPIA CAMH/Exp/6(VI) iv THEME: The Impact of Non-Communicable
Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients.
 Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients. Prevalence of OSA and diabetes Prevalence of OSA Five
Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients. Prevalence of OSA and diabetes Prevalence of OSA Five
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders. Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness
 Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk
 Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk Vascular Risk Reduction (VRR) Welcome! Presentation & Activities Focus: Managing known risk factors for vascular disease. Engage, collaborate and have
Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk Vascular Risk Reduction (VRR) Welcome! Presentation & Activities Focus: Managing known risk factors for vascular disease. Engage, collaborate and have
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward
 Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward Presentation at HA Convention 2008 6 May, 2008 Dr. M K Cheung Associate Consultant Department of Family Medicine Community Care Division New Territories
Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward Presentation at HA Convention 2008 6 May, 2008 Dr. M K Cheung Associate Consultant Department of Family Medicine Community Care Division New Territories
3.5% 3.0% 3.0% 2.4% Prevalence 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0%
 S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
Atherosclerosis of the aorta. Artur Evangelista
 Atherosclerosis of the aorta Artur Evangelista Atherosclerosis of the aorta Diagnosis Classification Prevalence Risk factors Marker of generalized atherosclerosis Risk of embolism Therapy Diagnosis Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis of the aorta Artur Evangelista Atherosclerosis of the aorta Diagnosis Classification Prevalence Risk factors Marker of generalized atherosclerosis Risk of embolism Therapy Diagnosis Atherosclerosis
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease
 Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
HDL Cholesterol Subfractions and the Effect of Testosterone Replacement in Hypogonadism
 HDL Cholesterol Subfractions and the Effect of Testosterone Replacement in Hypogonadism E. Bolu 1, A. Sonmez 1, S. Tapan 2, A. Taslipinar 1, A. Aydogdu 1, C. Meric 1, Y. Basaran 1, G. Uckaya 1, M. Serdar
HDL Cholesterol Subfractions and the Effect of Testosterone Replacement in Hypogonadism E. Bolu 1, A. Sonmez 1, S. Tapan 2, A. Taslipinar 1, A. Aydogdu 1, C. Meric 1, Y. Basaran 1, G. Uckaya 1, M. Serdar
METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS
 METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS Andrew M. Cislo, PhD Megan J. Ehret, PharmD, MS, BCPP Robert L. Trestman, MD, PhD Kirsten Shea, MBA www.uchc.edu Background Metabolic
METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS Andrew M. Cislo, PhD Megan J. Ehret, PharmD, MS, BCPP Robert L. Trestman, MD, PhD Kirsten Shea, MBA www.uchc.edu Background Metabolic
EUROPEAN JOURNAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
 Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Deakin Research Online
 Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Institute of Applied Health Sciences. University of Aberdeen DATABASE REVIEW. Grampian University. Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES
 DATABASE REVIEW Grampian University Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES SERVICES DATABASE Page 1 Contents Contents 2 Introduction 3 History 3 Overview of Database 3 Database Structure 4 Main Table Summary
DATABASE REVIEW Grampian University Hospitals NHS Trust GRAMPIAN DIABETES SERVICES DATABASE Page 1 Contents Contents 2 Introduction 3 History 3 Overview of Database 3 Database Structure 4 Main Table Summary
Cohort Studies. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs
 St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs Michael Graven, MD, MSc,, MPH, FAAP Health Informatics and Neonatal Pediatrics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia CANADA
St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs Michael Graven, MD, MSc,, MPH, FAAP Health Informatics and Neonatal Pediatrics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia CANADA
Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University
 Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University Presentation for Asia Health Policy Program at Stanford University November 7th, 2014 Outline Introduction Background
Hai Fang, PhD Professor China Center for Health Development Studies Peking University Presentation for Asia Health Policy Program at Stanford University November 7th, 2014 Outline Introduction Background
Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project
 410 Br J Ophthalmol 1998;82:410 414 Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project Catherine A McCarty, Conrad W Lloyd-Smith, Sharon E Lee, Patricia M Livingston,
410 Br J Ophthalmol 1998;82:410 414 Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project Catherine A McCarty, Conrad W Lloyd-Smith, Sharon E Lee, Patricia M Livingston,
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population. Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology
 Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Shutterstock TACstock
 Shutterstock TACstock 10 Introduction Since 2000, the IDF Diabetes Atlas has detailed the extent of diabetes and this seventh edition shows how it is impacting every country, every age group and every
Shutterstock TACstock 10 Introduction Since 2000, the IDF Diabetes Atlas has detailed the extent of diabetes and this seventh edition shows how it is impacting every country, every age group and every
Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group.
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Sponsor. Novartis Generic Drug Name. Vildagliptin. Therapeutic Area of Trial. Type 2 diabetes. Approved Indication. Investigational.
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention
 Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Quantifying Life expectancy in people with Type 2 diabetes
 School of Public Health University of Sydney Quantifying Life expectancy in people with Type 2 diabetes Alison Hayes School of Public Health University of Sydney The evidence Life expectancy reduced by
School of Public Health University of Sydney Quantifying Life expectancy in people with Type 2 diabetes Alison Hayes School of Public Health University of Sydney The evidence Life expectancy reduced by
Clinical Study The Sweet Spot: Continued Search for the Glycemic Threshold for Macrovascular Disease A Retrospective Single Center Experience
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 874706, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/874706 Clinical Study The Sweet Spot: Continued Search for the Glycemic Threshold for Macrovascular
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 874706, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/874706 Clinical Study The Sweet Spot: Continued Search for the Glycemic Threshold for Macrovascular
6.4 Diabetes. 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion. Background. Developments since 2004. See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.
 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS
 THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005. Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007
 Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2
 IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
ASSOCIATED FACTORS OF EJECTION FRACTION IN INSULIN-TREATED PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 204 vol. 8, no. 4 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS ASSOCIATED FACTORS OF EJECTION FRACTION IN INSULIN-TREATED PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES Gina Botnariu
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 204 vol. 8, no. 4 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS ASSOCIATED FACTORS OF EJECTION FRACTION IN INSULIN-TREATED PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES Gina Botnariu
The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes
 DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
