The Prospects for the Development of the Key Sectors in the Warmińsko- -Mazurskie Voivodeship Research Report
|
|
|
- Christiana Lynch
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The project co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund within the Regional Operational Programme of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship for years fot. Tomasz Raczyński economy The Prospects for the Development of the Key Sectors in the Warmińsko- -Mazurskie Voivodeship Research Report 1
2
3 Editorial staff: Urszula Tomczyk Małgorzata Juchniewicz, Ph.D., Professor of UWM Dariusz Śledź Tadeusz Toczyński Justyna Byczkowska-Ślęzak Project Manager: Dariusz Śledź, Ph.D. A Project co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund as a part of the Regional Operational Programme Warmia-Masuria for the years
4 Table of contents: INTRODUCTION RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Concept of research Purpose and scope of research Data acquisition techniques PEST analysis Expert survey Emi-structured interview (ssi) Synthetic index of key sectors (siks). Synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (siho) Focused group interviews (fgi) Individually deepened interviews (idi) Computer-assisted telephone interviews (cati) / online interviews Swot analysis Expert panels PEST analysis Introduction Natural conditions and evaluation of natural resources Demographic preconditions Social aspects of growth and development Economic conditions of commercial conditions Technological and infrastructural preconditions of growth Summary IDENTIFICATION OF KEY SECTORS AND HIGH OPPORTUNITY SECTORS KEY SECTORS AND HIGH OPPORTUNITY SECTORS Agricultural sector: cultivation of crops and animal breeding Foodstuffs manufacture sector Woodworking and furniture manufacture sector Rubber manufacture sector Machinery and equipment manufacture sector Building sector Motor vehicles repair and trade sector Tourism sector Perspectives and forecasts of growth of key sectors HIGH OPPORTUNITY SECTORS Fishery sector Power and heating sector Ict services sector Business consultancy sector Medical services and dependent persons social support sector Perspectives and forecasts of growth of high opportunity sectors
5 6. THE LARGEST ENTERPRISES OF WARMIŃSKO-MAZURSKIE VOIVODESHIP IN KEY AND HIGH OPPORTUNITY SECTORS SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS GLOSSARY OF TERMS REFERENCES LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURES RESEARCH TOOLS Industry evaluation sheet expert survey Semi-structured interview (ssi) questionnaire Scenario of focused group interviews (fgi) Scenario for individual deepened interviews (idi) Questionnaire for computer-assisted telephone interviews (cati) Expert panel scenario
6
7 Introduction T he economic growth of a Voivodeship, including the sectors most favourable to business, not only depends on internal factors, but also on the global conditions in which markets function. The process of European integration, the extensive opening of economic markets and progression of globalisation has made Poland increasingly dependent on the foreign (outside) economic situation. The world s financial market crisis is significant to the economy of the state, and hence it should also be considered from the perspective of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The perspectives for development of key sectors in Warmia-Masuria can only be tackled by conducting an analysis of the outside situation. Only then is it possible to identify and take action to maximise the use of existing resources, and as a result, improve competitiveness and growth of the Voivodeship. The positive effects of actions connected with the growth of the Voivodeship should not only be reflected by its commercial sphere, but also in its social aspects. Otherwise, there is no real growth, only an increase in the value of specific economic markers. Therefore, it is important to invest in key sectors in a manner which will provide tangible effects for the Voivodeship s inhabitants, i.e. by providing jobs and proper quality of infrastructure both social (including health care, social services, education, leisure and culture) and technical. It must be noted on the other hand, that the existing economic and social resources, as well as the quality and commitment of human resources determine the scope and pace of investment performance, which translates into growth of the region. This Report is the result of investigative and research tasks carried out by the Institute of Research and Studies of the OSB Group commissioned by the Office of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship Marshal. The research in the development perspectives of key and high opportunity sectors is carried out as part of a Project co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund and titled A coherent system of of investor services in the Warmia and Mazury - professional impact of economic promotion. The purpose of the research presented in this Report is to identify key and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship s economy. The identification is accompanied by a detailed analysis of conditions pertinent to its functioning in specific sectors and of factors which contribute to the attractiveness of the sectors. Primary determinants and barriers of growth have also been identified for these sectors. The research has been conducted in accordance with the requirements of the Contract Subject Specification, the Terms of Reference and the procedures proposed in the Bid for sector analysis. This work shall aid in strategic and operating decisions made by businesses, prospective investors, institutes for development of Warmia- Masuria and regional authorities. 5
8 1. Research methodology The accomplishment of the research project was based on basic principles of sociological and economic research. The basic assumption was to conduct research in order to achieve the goals desired by the Employer Concept of research The basic assumptions for the sector analysis research model were derived from the basics of socio-economic research methodology, econometrics and classical sector and competitor analysis formed by Michael E. Porter. The developed model serves as a measurement tool in this research project, required for identification of key sectors and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship s economy. An assessment of investment attractiveness in key sectors and a forecast of their directions of growth have also been completed. Key sectors The main areas in the key sector analysis are the characteristics of their various operating aspects and the analysis of their investment attractiveness. Based on the data gathered, a strategic analysis of sectors has also been made, including the perspectives and forecasts of growth. The specific analyses included: a structural analysis of sectors, competitor analysis factors and basics of competitiveness strategy. The main assumption of these analyses is to reference to Porter s five force analysis: 1. entry 2. threat of substitute products/services 3. bargaining power of customers 4. bargaining power of suppliers 5. rivalry of present competitors The defined forces establish the level of intensity of competitive rivalry in the sector. The forces with the greatest impact on the sector s economic position determine the vectors of strategic action. It must be stressed here that sector competition is not only formed by businesses which deliver the same type of products or services, but also by consumers and customers. It is especially critical when considering the criterion of sector classification adopted in the research. According to Porter and other economic scientists, the area of business activity of a domain does not define a sector. When defining the boundaries of a sector, it can be considered that competition in related sectors is natural and desirable. The structural analysis of the sectors which are construed in the first stage of the research as business domains (according to PKD of 2007, i.e. the Polish Business Classification) has created an operational definition of key industries in the region. The structural analysis covered the aforementioned five force analysis: Key sec- tors have been identified with the procedures based on econometric analysis of public statistical data, desk research of statistical data, program documentation and other sources, including business and economy experts. Next, based on the data collected by field research, strategic groups were determined, and followed by the development of boundaries of their definitions and conditions of their operation in the region. The next goal of the structural analysis was to characterise specific sectors, analyse their investment attractiveness and determine perspectives and growth forecasts for key sectors. High opportunity sectors Identification of high opportunity sectors involved a similar procedure as the one planned for identification of key sectors. The high opportunity sectors have been selected by a synthetic measure made of diagnostic attributes which constitute sector capitals. The calculations are also based on a set of public statistical data and expert evaluation. The scheme of classification of sectors in the high opportunity group was different. Important elements concerning this typology, are perspectives of growth. The growth s function regarding selected attributes has a linear increase (from 2005) and small variations in time. It is also important to note that the research conducted by using expert surveys exhibits an increase in the rank of evaluation of foreseeable chances for implementation in relation to the evaluation of the present condition. This research employed verification of results by a panel of experts invited to cooperate. The purpose of the high change sectors analysis was to present the conditions of these sectors operation in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship and to identify its perspectives and forecast of growth. In order to obtain the most reliable results, a methodological triangulation was planned in order to involve various techniques and sources of data acquisition. Due to the fact that economic processes and their interrelations are very complex, various research methods and techniques were employed. Individual research procedures cover selected aspects of the problem along with irrelevant phenomena; hence reactive field research was used in combination with non-reactive methods, covering investigation of legacy data sources: public statistics, development strategies, publications and scientific papers Purpose and scope of research Primary goal of research The purpose of the research was to prepare Perspectives of growth in key sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. This work is an analysis encompassing identification of the present level of development/growth and the perspectives of key developmental sectors and high opportunity sectors which exhibit a strong potential of growth in the Warmian-Masurian Region. The analysisidentified key economic sectors and sectors with the highest growth opportunities in the Warmian-Masurian Voivode- 6
9 Table 1. Relation between research methods, techniques and tools and problems present within the domain of research and analyses. Item Scope of research Detailed scope Identification and characteristics of key sectors. Identification of high opportunity sectors Research methods and techniques applied to enable answering a given question 1. Basis for selection of diagnostic attributes: public statistical data, scientific papers and research results, data from registers of the Voivodeship Employment Office in Olsztyn, program and strategic documents for the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The attributes being sector variables according to the PKD section, concerning: financial performance results, investment, innovation and human resources. PEST analysis Economic significance, social significance, natural environment significance. 2. Evaluation of the regional sectors according to the PKD 2007 section Potential opportunities for R&D and technological development Expert survey SIGF and SIHO synthetic index Perspectives of implementation of advanced solutions, processes and products. Variation coefficient reduction of attributes with high discrimination potentials. 3. Development of the classification model for key sectors and high opportunity sectors Standardisation conversion of variables which classify the studied population into a comparable form. Person s test for independence of diagnostic attributes. Calculation of the synthetic index for partial capitals of items in economic sectors and high opportunity sectors using Perkal s method. Economic profile. Characteristics of products of specific sectors. Key sectors largest companies. 4. Characteristics of key sectors Directions and intensity of export and import. Workforce availability including specific qualifications. Other specific resources. Analysis of investment attractiveness per sectors and sector attractiveness factors key sectors 5. Structural determinants of sector competition intensity 6. Bargaining power of customers 7. Bargaining power of suppliers 8. Strategic groups in key sectors Barriers of entry: economy of scale, Diversification of products, capital requirements, access to distribution channels, worse cost situation, operating experience and scale, state policy. Rivalry of competitors in terms of: price, advertisement war, launching of new products, expansion of customer service scope and guarantees. Barriers of exit: economic (highly specialised resources), fixed costs (transfer of employees, production maintenance), strategic interdependencies (capacity of operation on the market, access to capital markets, common facilities), emotional (identification with business domain, loyalty to employees, fear for professional career, pride), state-imposed and social restrictions (discouraging from resignation due to care for preservation of present job). Preconditions: relation of concentration or level of purchase to level of sales, share of products sold in buyer s costs, diversification of products on the market, profit volume (company as a buyer), integration of buyers, quality of products, access to complete product information. Preconditions: relation of concentration of the sector and suppliers, competition with other substitute products, significance of the sector as customer to suppliers, capacity to retain disbursement or generation of reserves, diversification of products or costs, and integration of supplier s group. Discriminants in strategic groups: - products of approximate quality, advancement and technology - use of similar distribution channels - comparable price levels - similar groups of customers as consumers - services, after-sales services are similar - similar methods and techniques of advertisement campaigns Expert survey SIGF and SIHO synthetic index FGI interviews PEST analysis SSI interviews FGI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews Expert survey IDI interviews CATI interviews 7
10 Cost strategy: - effectiveness of scale based on investment in facilities - lowering of costs based on experience, control of direct and general costs, omission of negligible customers, minimising the costs of R&D expenditures, after-sales service or advertisement, or no participation in these costs. 9. Competitor s strategies 10. Risk according to the strategy of competition 11. Innovation of business entities 12. Threat of substitute products 13. Threat of competition which potentially can enter the market 14. Sector instability 15. Analysis of investment attractiveness of key sectors 16. Strategic analysis of key sectors Diversification: - accentuation of products (not cost-wise) - customer loyalty - frequent resignation from mass sales - increase in expenditures for R&D, advertisement and promotion - high significance of quality of materials used in production Concentration occupation of a market niche: - customer groups - geographical niche (territory) - product niche Concentration occupation of a market niche: - customer groups - geographical niche (territory) - product niche Cost strategy: - technological delay - obsolete intangible resources - high risk of competitive entry into the area - low prestige of company trademarks - low level of product changes, inability to meet the changing needs of buyers - cost inflation - limited capacity of maintaining a price distance from competitor products - low differentiation of products in the market Diversification: - loss of buyers to less expensive substitute products - decreased demand from buyers concerning product diversification - simulation of competitors. Concentration: - increasing the diversification of costs between the competition which operates on a large scale and concentrated entities - decrease in product differences as related to competition - entry of competition to subsegments of a given market Innovation per areas: - products - processes - marketing solutions - organisational solutions Threat of substitute products related to: - concentration on different types of products - consumer groups (diversified, homogeneous) - product quality Analysis of potential competitor: - potential of mergers and strengthening of present competitors - acquisition of present companies - market limitation (product, price, quality, territory) - synergism of companies participating in the given sector - customers or suppliers can integrate Preconditions of probability of competitive war: - significance of information flow in the market - use of larger resources and capacity to enforce results which are favourable to the company - barriers of entry/exit - change in volume of demand Sector attractiveness criteria: - size - market growth - market diversity - structure of competition - technological significance - social considerations - environmental considerations - legal aspects - human factors Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities for growth Growth threats Perspectives and forecasts of growth of regional key sectors Expert survey IDI interviews CATI interviews IDI Interviews CATI Interviews PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey IDI interviews CATI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews Expert survey IDI interviews CATI interviews Expert survey IDI interviews CATI interviews PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey FGI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey FGI interviews IDI interviews SWOT analysis Expert panel 8
11 17. Perspectives and forecasts of growth Design of scenarios per basic evolutionary processes: - long-term changes in the rate of growth - changes in supported buyer segments - decrease of uncertainty - spreading of protected knowledge - change of scale (spreading, shrinking) - changes in expenditure costs and currency exchange rates - process innovations - product innovations - organisational innovations - marketing innovations - changes in policy of the state - barriers of entry and exit PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey FGI interviews Expert panel Definition of high opportunity sectors Identification of sectors with high opportunity of growth: Characteristics of high opportunity sectors Determinants of competitive advantages in high opportunity sectors Sectors with high opportunity of growth: - economic significance, social significance, natural environment significance - potential opportunities for use of R&D and technologies - perspectives of implementation of advanced solutions, processes and products Items: 1, 2, 3, and 4 of the table Economic profile Characteristics of local market structure: - products characteristics - largest companies on the local market - directions and intensity of export and import - workforce availability including specific qualifications - availability of other specific resources Preconditions of competitive advantages: - outcome capital - structural capital - human resources Strengths Weaknesses 22. Strategic analysis of key sectors Opportunities for growth Growth threats Perspectives and forecasts of growth of high opportunity sectors 23. Perspectives and forecasts of growth Source: Proprietary work based on reference sources: Design of scenarios per basic evolutionary processes: - long-term changes in the rate of growth - changes in supported buyer segments - decrease of uncertainty - spreading of protected knowledge - change of scale (spreading, shrinking) - changes in expenditure costs and currency exchange rates - process innovations - product innovations - organisational innovations - marketing innovations - changes in policy of the state - barriers of entry and exit PEST analysis SSI interviews PEST analysis Expert survey SIGF and SIHO synthetic index PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey FGI interviews IDI interviews CATI interviews PEST analysis IDI interviews CATI interviews PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey IDI interviews SWOT analysis PEST analysis SSI interviews Expert survey FGI interviews Expert panel ship. Moreover, it also presented a detailed analysis of their attractiveness. Primary determinants and barriers of growth have also been identified and analysed for these sectors. Specific goals of research: 1. Evaluation of preconditions valid for the economic growth of Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (PEST). 2. Determination of key sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (identification of dominating sectors, characteristics of specific sectors, economic profile, characteristics of products from specific sectors, largest businesses operating in specific sectors, directions and intensity of export and import, availability of workforce including specific qualifications, availability of other specific resources). 3. Evaluation of key sector investment attractiveness (broken down into specific sectors and sector attractiveness factors), including but not limited to the following factors: competition within the sector, barriers of entry/exit, bargaining power of customers, bargaining power of suppliers, strategic groups and their strategies of competition, innovativeness of entities operating in key sectors, threat of substitutes, threat of competition which potentially can enter the market. The analysis of investment attractiveness of key sectors includes a synthesis (for individual sectors) in the form of identification of the factors which determine the dynamics of the sector, major drivers of change in the sector and the evaluation of their impact on the situation in the sector. 4. Determination of strength and weaknesses of key sectors and the opportunities of and threats to their growth (SWOT).Determination of perspectives and forecasts of key sectors growth 5. Determination of high opportunity sectors in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (definition of high opportunity sectors, i.e. the sectors with a high potential for growth, identification of sectors with high potentials of growth, characteristics of specific sectors considering e.g. economic profiles, characteristics of local markets (inducing the characteristics of products of specific sectors and the largest businesses operating in individual sectors), directions 9
12 and intensity of export and import, availability of workforce including specific qualifications, availability of other specific resources and competitive advantages significant to high opportunity sectors located in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship). 6. Determination of strength and weaknesses of high opportunity sectors and the opportunities of and threats to their growth (SWOT). 7. Determination of perspectives and forecasts of high opportunity sectors growth. The accomplished analysis of investment attractiveness of key sectors and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship is a synthetic analysis (for individual sectors) in the form of identification of factors which determine the dynamics of the sector, major drivers of change in the sector and the evaluation of their impact on the situation in the sector Data acquisition techniques PEST analysis PEST analysis is a method of studying secondary material; however, due to the identity of its procedures it has been adopted as a separate method of research. The first stage of the PEST analysis was to emphasize the key factors of specific economic segments in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. Outside factors, which constitute the environments potential, have been grouped into the following subjects: 1. Natural conditions and evaluation of natural resources. 2. Demographic and social preconditions. 3. Economic conditions of commercial conditions. 4. Technological and infrastructural preconditions of growth. The data analysis timeline starts in This specific period is adopted due to the changes in the commercial operation classification described in the PKD. The current PKD 2007 classification has significantly changed the structure of national business units, which makes it problematic to compare the data with the previous classification of PKD Even now the Central Statistical Office continues to tally its records; yet not all attributes which characterise the national business units have been adapted to the current criteria of the division. The goal of the successive stage of PEST was to determine the impact of specific outside environment factors on key sectors and high opportunity sectors in the regional economy. A set of factors has been developed and broken into the types of impact. The outcome of the stage in question resulted in a selection of factors which significantly affect specific sectors and factors which will have significance in the future. The third and last stage focused on indicating what kind of effects identified factors had on the growth of the economy in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship Expert survey The technique of the expert survey was accomplished as approximate to the general assumptions of the Delphi method. Due to the extremely short project lead time, the technique consisted of providing the experts with a one-time survey to review the sectors of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The next stage, which was aimed at developing a consensus of opinion of the experts on key sectors and high opportunity sectors, were focused group interviews (FGI). Sixty-four of the experts were invited to take part in this stage. The research was performed during a period when a lot of participants were out on leave. Thus, a numerous part of the invited refused to participate, due to planned travels or excess of duties in substitution for absent cooperatives. The expert survey was carried out among seventeen individuals who represented the following: The Warmian-Masurian Centre of Regional Studies of the Statistical Office The University of Warmia and Mazury, Faculty of Economics The University of Warmia and Mazury, Faculty of Economic, Department of Agricultural Business and Environmental Economy The Warmia and Mazury Agency of Regional Development in Olsztyn The Warmian-Masurian Council of Federation of Scientific and Technical Associations NOT in Olsztyn The Foundation for Regional Business Support Suwalska Specjalna Podstrefa Ekonomiczna S.A. (The Suwałki Special Economic Subzone S.A.) The Office of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship Marshal, Department of Rural Areas and Agricultural Development The Masurian Conference and Recreation Centre Zamek - Ryn Sp. z o.o. The expert survey constituted a research method by which, and thanks to the knowledge and experience of the experts, key sectors and high opportunity sectors were identified in the Warmian- Masurian Voivodeship economy. The selection of the sample was intentional. The experts invited to participate in the research have factual knowledge and professional experience. The participants are industry specialists in the following sectors: agriculture industry and building services Once filled out by the experts, the survey forms were analysed and the preliminary results were then discussed in focused group interviews. Moreover, a matrix of results was developed from the acquired data and included investigated attributes of the synthetic index of key sectors (SIKS) and the synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (SIHO). The research tool was an evaluation sheet for industries in each sector listed according to the PKD 2007 section (in the form of a survey questionnaire). Each sheet was enclosed with a PKD 2007 business classification scheme. The industry evaluation sheet consisted of three sections: 1. Imprint respondent s data 2. An evaluation in the following areas: Its significance in the forming of social, economic and natural environment situations R&D and technological development opportunities of implementation 3. Evaluation rationale for specific areas. 10
13 fot. Tomasz Raczyński The questionnaire structure was planned in a manner which enabled identification of two sector groups, i.e. key and high opportunity sectors Semi-structured interview (SSI) Semi-structured interviews gathered more detailed and quantitative data which enabled a qualitative analysis to be performed to determine the scale of operational preconditioning of the sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The use of a quantitative interview, including elements of a quantitative approach to the problems, provided high-quality data regarding the investment attractiveness of the region s sectors. Semi-structured interviews were carried out with representatives of local territorial government units. The selection of the sample was intentional. The representatives of all county (powiat) units in local territorial governments were invited to participate. All starosts agreed to participate and gave interviews either in person or through authorised persons (N=21) Synthetic index of key sectors (SIKS). Synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (SIHO) 1 The synthetic index of key sectors (SIKS) and the synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (SIHO) in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship relies on a group of 3 primary determinates in the sector s market position: outcome capital, human resources and structural capital. Implementing a classification model based on this synthetic index in the research optimised the evaluation objectiveness of the factors which build the position of the sectors in the regional market. Simultaneously, introduction of the researched legacy and expert data allowed the model to merge systematically gathered statistical measures with the knowledge and experience of individuals engaged in the process of economic growth. Selecion model of diagnostic attributes. The factors which form structural preconditions of sectors in the regional economy have been identified by the verification procedures applied to the data from primary and secondary sources. The primary sources included the results gathered from the expert survey. The secondary sources were derived from the records of the Central Statistical Office. The sources characterise the business activity according to the PKD 2007 sections: A - agriculture, hunting, forestry B - mining and recovery C - industrial processing D - generation and supply of electrical power, gas, steam, hot water and air conditioning E - water supply; waste and sewage management, business related to recultivation/restoration F - building G - wholesale and retail sales; repair of motor vehicles including motorcycles H - transport, logistics and warehouse management I - business related lodging and catering J - information and communication K - financial and insurance businesses L - business related to real estate market maintenance M - professional, scientific and technical business N - administration and supporting businesses P - education Q - health care and social support R - culture, entertainment and recreation S - other businesses of service The building procedures regarding the synthetic index of key sectors (SIKS) and the synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (SIHO) were split into two stages: 1 The model of the synthetic index of key sectors and high opportunity sectors located in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship was prepared using the following literature (Z. Brodziński, 2011; M.J. Stankiewicz (ed.), 2006; M.W. Staniewski, 2008; S. Galata 2004; K. Wierzbicki, 1999; A. Sopińska, 2010; T. Dudycz, 2005; G. Kobyłko, 2006). 11
14 Table 2. The list of attributes according to the partial capital of the synthetic measure. human resources structural capital Attributes Businesses registered solely to natural persons Mean gross remuneration Mean employment according to economic sectors and PKD 2007 (per person) The employed with defined working time full time The employed with defined working time part time No. of enterprises % employment rate % discharge rate Gross value of fixed assets in enterprises (current fixed prices) in millions of PLN Value of investment expenditures in national commerce according to the PKD 2007 section private sector Value of investment expenditures in national commerce according to the PKD 2007 section public sector In-house expenditures actually incurred on innovation according to the PKD 2007 sections Entities with foreign capital (commercial companies and partnerships) Employment costs Gross added value (GDP current prices) Overall business revenues Revenue earning costs for overall business Gross profit outcome capital Gross loss Obligatory liabilities of gross financial results Obligatory liabilities of gross financial results income tax Profit + net positive financial result Loss + net negative or zero financial result Gross return on turnover Net return on turnover Financial fluidity stage I Financial fluidity stage II Financial fluidity stage III Long-term liabilities Short-term liabilities Revenue earning costs for overall business Own cost of products sold Value of sold goods and materials Own cost of products sold Overall business revenues Total revenue from sales of goods and materials Total revenue from export sales of goods and materials Source: Proprietary work based on CSO data. Stage I The first stage of building the synthetic measure involved selecting attributes from the data sets recorded in public statistical sources. The attributes were then grouped into 3 categories of sector capitals (see table 2): outcome capital structural capital human resources Stage I resulted in the matrix of preliminary diagnostic attributes. Stage II The data matrix derived from the results of stage I was a preliminary list of diagnostic attributes. It was then verified with the use of econometric tests: selection model of diagnostic attributes standardisation of diagnostic attributes values 12
15 Selection model of diagnostic attributes The first assumption was to adopt a rule that only the attributes; the value of which differentiates specific PKD section sectors in a statistically significant way, enable determination of their position and growth opportunities on the regional market. Pursuant to this, the attributes with high discrimination potentials were then reduced. The degree of diversification was determined with the variation coefficient (Vi) test. Based on the adopted variation coefficient critical value (Vi 0.15), the attributes which did not differentiate the investigated population were rejected. In other words, the value in all sectors was calculated in approximation and according to the PKD sections. Standardisation of diagnostic attributes values The next step involved standardisation of the values according to the following formula due to the fact that the selected diagnostic attributes expressed in different calculation units prevent comparison: xij - xj tij = Sj where: tij standardised value of attribute j for industry i xij value of attribute j for industry i xj arithmetic mean of attribute j Sj standard deviation of attribute j m number of variables n number of objects The standardisation of the attribute values involved conversion of differing studied population variables into a comparable form. Standardisation is a requirement in the preparation of data for comparative analysis and interpretation of the impact of the attributes on the classification of sectors as key and high opportunity sectors. Moreover, the standardised attributes allow homogenisation of the nature of the variables into two categories: stimulants and destimulants. The standardised values of destimulants were derived from the following formula: tij = - ) xij - xj ) Sj where: tij standardised value of attribute j for industry i xij value of attribute j for industry i xj arithmetic mean of attribute j Sj standard deviation of attribute j m number of variables n number of objects Correlation coefficients matrix The next stage in succession was to build a matrix of correlation of standardised attribute values where the variability coefficient was Vi>0.15 in the sectors. The final set of attributes included those poorly correlated among them, and yet highly correlated with other attributes. The idea of Person s test was to find statistically significant relations between the investigated variables. Inference was possible, including the determination of the factors which determined the situation and the position in the regional economic structure. Calculation of the synthetic index and evaluation of the sector position in the economy The method of calculation of the synthetic index for the partial capitals of key and high opportunity sectors was based on Perkal s method with the following formula:. m 1 Pi = tij = m where: Pi index of sector position in the regional economic structure tij standardised value of attribute for the PKD section m number of attributes included in the synthetic index j attribute number in the i- field. The evaluation of the values of the synthetic indexes for the market position of key sectors in the economy and the high growth opportunity sectors in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship was conducted applying the method of standardised sums (Pi), separately for specific partial capitals: outcome, structural and human resources. Then the arithmetic mean was calculated, where its value determines the value of the synthetic index. The classification of key sectors was accomplished with the use of SYNTHETIC INDEX OF KEY SECTORS (SWSK): KW + KL + KS = SWSK SYNTHETIC INDEX OF HIGH OPPORTUNITY SECTORS (SWWS): KW + KL + KS = SWWS dichotomous typology, producing two groups: key sectors in the regional economy [Wi Wp+Sw] other sectors [Wi <Wp+Sw] 1 j=1 m where: Wp mean value, Sw standard deviation. The classification of high opportunity sectors was accomplished with the use of dichotomous typology, producing two groups: high opportunity sectors in the regional economy [(Wi є key sectors) showing a growth tendency of the outcome capital m xij - xj j=1 Sj 13
16 and a chance for implementation during the period after 2005] other sectors Focused group interviews (FGI) The key intent of FGI was to discuss and review the results of the expert survey, the data obtained from the local territorial government representative survey, the results of the synthetic indexes of key and high opportunity sectors and the material obtained in the PEST analysis. The investigation was based on a panel review. The respondents of the expert survey were presented with preliminary results of the survey, which were then discussed, reviewed and verified. The selection of the sample was intentional. The invited participants included respondents who took part in the expert survey and representatives of entrepreneurs who were connected with tourism services, consulting, trade and building. Three group meetings were held with twenty participants. The result produced key and high opportunity sectors in the economy of Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship Individually deepened interviews (IDI) The purpose of the IDI was to gather qualitative and deepened data on the factors and preconditions which shape the economic structural position and the growth opportunities of key and high opportunity sectors in the regional economy. The selection of the sample was intentional. The following were invited to participate: key sector representatives (N=8) high opportunity sector representatives (N=6) The selected sample allowed interviewing people whose knowledge and professional experience enriched the information in the research, and broadened our present knowledge about the preconditions of business in key and high opportunity sectors Computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATI) / online interviews The purpose of this investigation was to obtain qualitative data which provided detailed characteristics of the preconditions, the determinants and the position of significant key and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The investigation employed computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATI) and, depending on the interview method preferred by individual respondents, an online survey. The investigated population included: national business entities which were included in key sectors after passing an identification process for key sectors (SIKS) national business entities operating in high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship as identified by the use of the identification process The selection of the sample for the quantitative investigation of key and high opportunity sectors was representative; and was accomplished by calculating the exact size of the representative random sample by the sector fraction. The calculation of the minimum sample size employed a confidence coefficient of 0.9 and a maximum fraction estimate error of 5%. The number of interviews was increased in the sector groups where the sample size was below N=30. Due to low population sizes, a high rate of obsolete REGON records and the inability to update contact data for the sectors of fishery, plastics manufacture and power and heating, the number of interviews concluded was insufficient for a statistical analysis. The minimum sample size which can be adopted in the analysis of small populations at an acceptable level is N=30. The results presented for the indicated sectors constitute a case study. Due to the fact that each of the sectors was identified as a high opportunity sector, the sampling in specific fractions was accomplished with the values established for the entire population. Table 3. The CATI sample size among the representatives of the enterprises from key and high opportunity sectors. Sector Agricultural sector: plant cultivation and animal breeding Po p u l a - tion Fishery sector Foodstuff manufacture sector Wood and furniture manufacture sector Rubber and plastic products manufacture sector Machinery and equipment manufacture sector Power and heating sector Building sector Motor vehicles repair and trade sector ICT services sector Business consultancy sector Medical services and dependent persons social support sector Tourism sector Source: Proprietary work based on CSO data Sample The basis for the calculation of the sample size was derived from national business entity data registered in REGON SWOT analysis The purpose of the SWOT analysis was an extended SWOT for the growth of sectors. The analysis was accomplished using primary and secondary data analysis results obtained by quantitative and qualitative field research. The SWOT results made it possible to determine options of strategic operation concerning support of sectors which are critical to the growth of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship and the identified high opportunity sectors. The results also included actions intended to improve strengths by employing opportunities and abolishing or minimising weaknesses. 14
17 On one hand, the resources and the tools of operation in key and high opportunity sectors were investigated; on the other hand, the impact of the environment was also studied. This allowed the analysis to identify the opportunities of growth for key and high opportunity sectors based on key resources, and to determine the threats to the process. The results served to evaluate the main preconditions which affect the economic growth in the region and to develop final recommendations for the actions aimed at removing diagnosed weaknesses and minimising threats Expert panels The panel meetings were held in the final stage of the research project, i.e. during the development of the preliminary final research report. The main goal of the discussion panels was to present the results and the preliminary conclusions to a group of experts. Sixteen experts participated in three subject panels. Based on the collected materials, the perspectives of growth were defined and a discussion was held concerning the basic problems which serve to build growth scenarios for key and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The selection of the sample was intentional. The experts invited to participate in the three panel meetings have factual knowledge and professional experience in the economic growth of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The meeting members represented the following: local territorial governments non-governmental organisations R&D units large enterprise entrepreneurs in key and high opportunity sectors science and arts The main purpose here was to have a group of specialists develop the basic preconditions of growth in key and high opportunity sectors to form the foundation for the growth scenarios of key and high opportunity sectors in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. The materials collected in qualitative and quantitative research was evaluated and critically reviewed. 15
18 2. PEST analysis 2.1. Introduction T he analysis of the Voivodeship s socio-economic status allowed to identify the factors which create the conditions and directions of change in specific sectors in the region. Outside and internal factors were also identified as affecting the business entity structure of key and high opportunity sectors in the economy of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship. These are grouped by the following topics: 1. natural conditions and evaluation of natural resources 2. demographic preconditions 3. social aspects of growth and development 4. economic conditions of commercial conditions 5. technological and infrastructural preconditions of growth The materials collected during the research also constituted an input for building the synthetic index of key sectors (SIKS) and the synthetic index of high opportunity sectors (SIHO), which were the subject of study in the successive parts of the project Natural conditions and evaluation of natural resources Territorial division Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship is located in the north-eastern quarter of Poland. The area of the Voivodeship includes the historical lands of Warmia, Masuria and Powiśle. The southern border is adjacent to Masovian Voivodeship, the west part borders with Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Pomeranian Voivodeship, the east borders with Podlaskie Voivodeship and the northern border is adjacent to Kaliningrad Oblast of the Russian Federation, hence being the external border of Poland and the European Union. Its position in the Central Europe, and more specifically on the East- West axis, near the Baltic region (as the Voivodeship is connected with the sea by the Vistula Lagoon) and in the neighbourhood of Kaliningrad Oblast, makes the Voivodeship an important link within the trans-european communication system. 2 However, the communication infrastructure does not allow to fully employ this advantage as a factor of growth; it negatively affects the access to communication and the investment attractiveness of the region. The most urging problem in this respect is to improve the communication and international access of the region, with the extension of the road infrastructure having top priority. The total length of the Voivodeship s borders was 980 km in The distribution of the borderline with specific neighbours was as follows: 208 km (21.2%) the border with Kaliningrad Oblast of the Russian Federation 196 km (20.0%) the border with Pomeranian Voivodeship 133 km (13.6%) the border with Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship 218 km (22.2%) the border with Masovian Voivodeship 225 km (23.0%) the border with Podlaskie Voivodeship There are 8 state border crossings in the Voivodeship, including 4 roadway crossings (Bezledy, Gołdap, Gronowo, Grzechotki), 2 railroad crossings (Braniewo, Skandawa) and 2 sea harbour border terminals (Elbląg, Frombork). FIGURE 1. ADMINISTRATIVE DIVISION OF THE WARMIŃSKO-MAZURSKIE VOIVODESHIP Braniewo Bartoszyce Gołdap Elbląg Lidzbark Warmiński Kętrzyn Węgorzewo Giżycko Olecko Ostróda OLSZTYN Mrągowo Ełk Iława Pisz Nowe Miasto Lubawskie Działdowo Nidzica Szczytno Source: Authors own work 16 2 Polska rozwój regionów prezentacja regionów województwo warmińsko-mazurskie (Poland. Development of Regions. Presentation of Regions. Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship). The Marshal s Office of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship. Olsztyn 2008, p. 200.
19 The overall surface area of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship in 2010 was km2, which was 7.7% of Poland s surface, making the Voivodeship the fourth largest in Poland. Concerning the administrative division into territorial units, the following is identified in the Voivodeship as required by the UE regional statistics: 3 subregions: Elbląg, Ełk and Olsztyn; 19 counties (powiats): Bartoszyce, Braniewo, Działdowo, Elbląg, Ełk, Giżycko, Gołdap, Iława, Kętrzyn, Lidzbark, Mrągowo, Nidzica, Nowe Miasto, Olecko, Olsztyn, Ostróda, Pisz, Szczytno and Węgorzewo; 2 county cities: Elbląg and Olsztyn; 116 municipalities (gminas), including: 16 city gminas, 33 cityrural gminas and 67 rural gminas. The Elbląg subregion is located in the western part of the Voivodeship and occupies 31.0% of the Voivodeship s surface. The subregion includes Braniewo powiat, Działdowo powiat, Elbląg powiat, Iława powiat, Nowe Miasto powiat, Ostróda powiat and Elbląg city powiat. The Ełk subregion covers 6347 km2, 3 which is 26.3% of the Voivodeship. The subregion lies in the eastern part of Warmińsko- Mazurskie Voivodeship and includes Ełk powiat, Giżycko powiat, Gołdap powiat, Olecko powiat, Pisz powiat and Węgorzewo powiat. The last subregion here is located in the centre of the studied area. It is the Olsztyn subregion, which covers the largest section of the Voivodeship (42.7%). The subregion includes Bartoszyce powiat, Kętrzyn powiat, Lidzbark powiat, Mrągowo powiat, Nidzica powiat, Szczytno powiat and Olsztyn city powiat. The powiats, or counties in the Voivodeship are very diversified in the terms of surface area. Among the total of powiats, the powiat cities have the smallest surface areas their total area constitutes 0.7% of the entire Voivodeship. Olsztyn powiat is the largest one, since it covers 11.7% of the Voivodeship. The sustainable growth of the region depends critically on the grid and distribution of cities. The settlement network of Warmińsko- Mazurskie Voivodeship with Olsztyn being its central regional place and two other large centres, i.e. Elbląg in the west and Ełk in the east, as well as the evenly distributed powiat cities complemented by a grid of small centres enables proper area management and efficient services for the population. The network exhibits certain persistence, and the emerging socio-economic tendencies and the demographic forecasts do not assume any significant changes in the area. 4 The Voivodeship cities are significant to the local systems which surround the former, and most of them have highly valuable tourism features. However, the cities require support for the municipal infrastructure, enterprise and revitalisation, where the latter applies especially to decommissioned military and industrial areas. 5 There were 49 cities and 3903 rural places in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship accounting to the 2010 reports. Each localisation occupied an average of 493 km2 of the overall Voivodeship surface area (with the Polish average of 346 km2). The Voivodeship s urban population is concentrated the three largest urban centres: Olsztyn, Elbląg and Ełk, where the population exceeds 100 thousand in just two of them, namely Olsztyn and Elbląg. Olsztyn is the Voivodeship capital city and the largest urban centre in the northeastern parts of Poland between Gdańsk and Białystok. The size span of the cities in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship is quite large; small and the smallest cities tend to dominate in the region. Concerning the structure of cities, 78% consist of cities with up to 20 thousand inhabitants. There are no cities with more than 200 thousand inhabitants in the Voivodeship, whereas the cities of this population account for 1.9% of the national total. The land usage structure in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship was distributed as follows in 2010: arable lands 54.7% of the Voivodeship s surface area (at the Polish average of 60.3%) forests, tree and brush lands 32.4% (at the Polish average of 30.6%) flooded terrains 5.7% (at the Polish average of 2.1%) developed and urbanised terrain 3.6% (at the Polish average of 5.0%) other types of land (ecological purposes land, wasteland, assorted) 3.5% (at the Polish average of 2.0%). Climate and soil conditions Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship is one of the most attractive areas of Poland, both in terms of landscape and tourism values. The local natural values are: diversified terrain configuration, highly varied geological structure, abundance of surface waters, large forest complexes, rich flora and fauna with species unique in the entire Europe and numerous areas of natural protection. These territories are among Europe s last lands dominated by natural environment, landscape and cultural features. The exceptional values of nature in Warmia-Masuria have had them included within the functional area called Poland s Green Lungs. Moreover, a significant part of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship has been included in the NATURA 2000 network. Pursuant to the Regulation of the Ministry of Environment dated July concerning the Natura 2000 Special Avian Protection Areas (Polish Journal of Laws, issue 229 item 2313 as amended), the NATURA 2000 network within the limits of the Voivodeship includes 16 Special Avian Protection Areas at the total surface area of thousand ha and 44 Special Habitat Protection Areas, amounting to thousand ha, which accounts for 34.4% of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship (at the Polish average of 29.8%). The land configuration of the Voivodeship has typical late glacial features, with a varied sculpture and highly diverse morphological forms (including a large number of lakes). There are tree primary physiogeographic lands (provinces) in the Voivodeship, spread along the parallels: the Baltic Littoral in the north-western part, dominated by plains with rich cohesive soils and low forestation ratio, varied by lands of a dynamic sculpture; The Baltic Lakeland, which is located in the middle belt and occupies most of the Voivodeship s surface area; this territory is elevated above the northern and southern provinces and characterised by a large number of lakes, a rolling sculpture and mosaicking landscapes; The Old-Glacial Lowlands and Plateaus on the fragments of the 3 Regionalny Program Operacyjny Warmia i Mazury na lata (The Regional Operational Programme of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship for years ). Passed by the Management of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship on November Olsztyn 2007, p Ibidem, p Ibidem, p
20 Voivodeship. The high soil variation and the diversified land sculpture, especially in the middle belt of the Voivodeship, significantly decrease the farming value of soils. 8 This also faces the agricultural business in the Voivodeship with a demand for extensive technical solutions, which raises unit production costs and makes profitableness lower than elsewhere in Poland. Analysing the individual environmental factors in separation disallows comparison of production capacities between specific regions or administrative units. Hence there is a need to synthetically express the evaluation of agricultural production natural conditions by using an arbitrarily adopted score classification. The establishment of the classification index considers the farming quality and usefulness of soils, the agricultural climate, the land sculpture and water conditions. The general index of agricultural production space in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship is 66.0 points (the 10th in Poland), where the national average is 66.6 points. The index varies significantly between powiats, with the lower than average Voivodeship values in 12 counties, i.e. Działdowo, Ełk, Giżycko, Gołdam, Olsztyn city powiat, Mrągowo, Nidzica, Nowe Miasto, Olecko, Olsztyn, Pisz and Szczytno. fot. Wojciech Wójcik/fotowojcik.pl southern part, which feature poorly varied sculpture, no lakes and generally low and moderately rich soils. 6 There are specific climate conditions prevailing in Warmińsko- Mazurskie Voivodeship, as determined by the presence of numerous water reservoirs. The Voivodeship is among the coldest areas in Poland, where the Atlantic air masses constantly clash with the continental front. The climate in the western part of the Voivodeship depends on the Baltic Sea, while the eastern part is clearly under the influence of the continental climate. This varies the average temperatures and the vegetation period, which is approximately 10 days shorter in the east than in the western part of the Voivodeship. These shorter than average vegetation and grazing periods largely affects the economic effects of farming. The mean annual temperature of the Voivodeship is one of the lowest recorded in Poland and varies throughout the territory. The mean annual precipitation vary from 540 mm near Ryn and Sępopole to almost 700 mm in the areas of Elbląg and Górowo Iławeckie. In the recent years a specific increase has been observed in the number of days when subtropical air flows into the area, resulting in both frosty, sunny and warm, rainy winters, with hot, dry summers occurring alternately with cold and damp ones. 7 The soil structure of Warmia-Masuria is highly diversified. They include varying grades, from cohesive and drainage basin soils around Kętrzyn through brown soils on Sępopole Plain and fen soils near Elbląg to light, sandy soils in the southern part of the The natural resources of the region are very modest. Economically viable minerals occur generally in the subsurface layer of Quaternary deposits. The surveyed mineral deposits of the Voivodeship occur irregularly; the middle and southern parts of the region has higher amounts of construction minerals, while the northern part is abundant with minerals of medical use. The mineral deposits in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship includes: peat, clay, meadow lime, lake chalk and natural aggregate, quartz sands and silt minerals. The wealth of these materials is insufficient for a feasible exploitation on a large industrial scale. 9 Flooded land The terrain of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship are among those with the highest rate of surface waters in Poland. The surface water network consists of numeral lakes, water holes, rivers, canals and a part of the Vistula Lagoon. The share of flooded lands in the Voivodeship surface area was more than double the Polish average in The total flooded area of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship amounted to thousand ha, with 17.5 thousand ha being the terrain flooded by inland sea waters (22.0% of the national surface area under inland sea waters), thousand ha were under flowing surface waters (23.3% of the national surface area under flowing surface waters) and 3.6 ha were under standing surface waters (5.8% of the national surface area under standing surface waters). The Voivodeship s surface waters belong to four drainage basins: the Vistula Basin, the Pregoła Basin, the Niemen Basin and the basin of the Przymorze rivers. The river network in the Voivodeship is extensively developed, yet divided. It mainly features short river runs with small river basins. The highest resources of flowing waters are in the following rivers: Łyna, Drwęca, Pisa and Pasłęka. 10 There are approximately 2600 lakes in the Voivodeship, including Śniardwy, the largest Polish lake (113.4 km2) and Mamry 11 (102.8 km2). The sheer number of relatively large water reservoirs can be employed as one of the development forces in the region of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship. This can favour new jobs in 18 6 Program ochrony środowiska województwa warmińsko-mazurskiego na lata z uwzględnieniem perspektywy na lata (The Environmental Protection Program of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship for the years with the perspectives for the years ). The Marshal s Office of Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship. Olsztyn 2007, p Strategia Zintegrowanego Rozwoju Gmin Północnego Obszaru Wielkich Jezior Mazurskich (The Strategy for Integrated Growth of Gminas in the Northern Area of Great Masurian Lakes), p Strategia Rozwoju Społeczno-Gospodarczego Województwa Warmińsko-Mazurskiego do roku 2020 (The Strategy of Socio-Economic Growth in Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodeship before the Year 2020). Olsztyn 2005, p. 20., 9 Strategia Zintegrowanego Rozwoju Gmin, op. cit., p Program ochrony środowiska, op. cit., p The water system of Mamry Lake: Mamry, Święcajty, Kirsajty, Dargin, Dobskie, Kisajno.
Guide book. 5 th Business Forum of Baltic and Eastern Markets. Lidzbark Warmiński. 4 October 2013
 5 th Business Forum of Baltic and Eastern Markets Guide book Lidzbark Warmiński 4 October 2013 Table of contents 1. About the event... 3 2. Schedule... 4 3. About the Organizer... 5 4. Economic potential
5 th Business Forum of Baltic and Eastern Markets Guide book Lidzbark Warmiński 4 October 2013 Table of contents 1. About the event... 3 2. Schedule... 4 3. About the Organizer... 5 4. Economic potential
RECOMMENDATIONS ON BUSINESS PLAN PREPARATION
 RECOMMENDATIONS ON BUSINESS PLAN PREPARATION 1. General provisions Business plan must contain: name of the investment project, as well description of its essence and feasibility; substantiation of the
RECOMMENDATIONS ON BUSINESS PLAN PREPARATION 1. General provisions Business plan must contain: name of the investment project, as well description of its essence and feasibility; substantiation of the
SUWAŁKI REGION SUWAŁKI OLECKO EŁK GRAJEWO AUGUSTÓW SEJNY SUWAŁKI 69 316 OLECKO 22 091 EŁK 60 103 GRAJEWO 22 243 AUGUSTÓW 30 482 SEJNY 5 640
 SUWAŁKI REGION MAIN CITIES: SUWAŁKI OLECKO EŁK GRAJEWO AUGUSTÓW SEJNY POPULATION: SUWAŁKI 69 316 OLECKO 22 091 EŁK 60 103 GRAJEWO 22 243 AUGUSTÓW 30 482 SEJNY 5 640 Data for 31 XII 2014. SUWAŁKI REGION
SUWAŁKI REGION MAIN CITIES: SUWAŁKI OLECKO EŁK GRAJEWO AUGUSTÓW SEJNY POPULATION: SUWAŁKI 69 316 OLECKO 22 091 EŁK 60 103 GRAJEWO 22 243 AUGUSTÓW 30 482 SEJNY 5 640 Data for 31 XII 2014. SUWAŁKI REGION
Competitive Advantage of Libyan Business Environment
 Economics World, ISSN 23287144 May 2014, Vol. 2, No. 5, 325332 D DAVID PUBLISHING Competitive Advantage of Libyan Business Environment Salem Abdulla Azzaytuna University, Tripoli, Libya The economic development
Economics World, ISSN 23287144 May 2014, Vol. 2, No. 5, 325332 D DAVID PUBLISHING Competitive Advantage of Libyan Business Environment Salem Abdulla Azzaytuna University, Tripoli, Libya The economic development
REPORT ON DEMAND FOR INNOVATIONS IN THE FRAMEWORK OF INNOREGIO MAŁOPOLSKA PROJECT
 InnoRegioMałopolska Project Financed from the 6th Framework Program REPORT ON DEMAND FOR INNOVATIONS IN THE FRAMEWORK OF INNOREGIO MAŁOPOLSKA PROJECT Written by: Łukasz Frydrych 1 Contents 1. Introduction...
InnoRegioMałopolska Project Financed from the 6th Framework Program REPORT ON DEMAND FOR INNOVATIONS IN THE FRAMEWORK OF INNOREGIO MAŁOPOLSKA PROJECT Written by: Łukasz Frydrych 1 Contents 1. Introduction...
Scope of Capital Measurement and Classifications
 From: Measuring Capital - OECD Manual 2009 Second edition Access the complete publication at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264068476-en Scope of Capital Measurement and Classifications Please cite this
From: Measuring Capital - OECD Manual 2009 Second edition Access the complete publication at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264068476-en Scope of Capital Measurement and Classifications Please cite this
Small Business Data Assess Your Competition Define Your Customers
 Small Business Data Assess Your Competition Define Your Customers Census Bureau Data Can Answer Many Questions What Is Census Bureau Data? Economic / business data Economic Census County Business Patterns
Small Business Data Assess Your Competition Define Your Customers Census Bureau Data Can Answer Many Questions What Is Census Bureau Data? Economic / business data Economic Census County Business Patterns
Personal Accident and Health Insurance in Malaysia, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016
 Personal Accident and Health Insurance in Malaysia, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016 Market Intelligence Report Reference code: IS0055MR Published: September 2012 www.timetric.com Timetric John Carpenter
Personal Accident and Health Insurance in Malaysia, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016 Market Intelligence Report Reference code: IS0055MR Published: September 2012 www.timetric.com Timetric John Carpenter
A programme of the National Centre for Research and Development
 A programme of the National Centre for Research and Development GO_GLOBAL.PL Increasing the scale of commercialisation of research results or development works of Polish companies on global markets 1.
A programme of the National Centre for Research and Development GO_GLOBAL.PL Increasing the scale of commercialisation of research results or development works of Polish companies on global markets 1.
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3186483/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3186483/ Business Intelligence and Analytics Software Market by Segment, by Services, by Deployment Mode, by Org. Size, by Verticals,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3186483/ Business Intelligence and Analytics Software Market by Segment, by Services, by Deployment Mode, by Org. Size, by Verticals,
Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions
 Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions November, 2003 This list of market assessment tools was prepared by Development Alternatives Inc. (DAI) as an internal working document to support
Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions November, 2003 This list of market assessment tools was prepared by Development Alternatives Inc. (DAI) as an internal working document to support
Access to Financing Survey (AFS)
 Access to Financing Survey (AFS) Methodology Index Access to Financing Survey: Methodology 1 Objectives and need for the operation...3 2 Research scopes...4 3 Statistical units...5 4 Classification variables...6
Access to Financing Survey (AFS) Methodology Index Access to Financing Survey: Methodology 1 Objectives and need for the operation...3 2 Research scopes...4 3 Statistical units...5 4 Classification variables...6
Life Insurance in Pakistan, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225320/ Life Insurance in Pakistan, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016 Description: Synopsis The report provides in depth market
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225320/ Life Insurance in Pakistan, Key Trends and Opportunities to 2016 Description: Synopsis The report provides in depth market
Green Alternative for the Northern Poland macroregion Baltic Eco-Energy Cluster
 Green Alternative for the Northern Poland macroregion Baltic Eco-Energy Cluster The Baltic Eco-Energy Cluster (BKEE) is a common initiative of the Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery PAS, University of Warmia
Green Alternative for the Northern Poland macroregion Baltic Eco-Energy Cluster The Baltic Eco-Energy Cluster (BKEE) is a common initiative of the Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery PAS, University of Warmia
The Role of Market Analysis in Developing Efficient Marketing Audit
 Abstract The Role of Market Analysis in Developing Efficient Marketing Audit Violeta Radulescu Lecture, PhD, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest E-mail: vio.radulescu@yahoo.com Marketing Audit is an
Abstract The Role of Market Analysis in Developing Efficient Marketing Audit Violeta Radulescu Lecture, PhD, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest E-mail: vio.radulescu@yahoo.com Marketing Audit is an
Innovation Survey Into the Cornish Marine Sector 2006 to 2008 www.nea2.eu
 Innovation Survey Into the Cornish Marine Sector 2006 to 2008 www.nea2.eu Contents 1. Executive Summary 2. Introduction and Background 3. Results: About Activities that Support Innovation 4. Results: About
Innovation Survey Into the Cornish Marine Sector 2006 to 2008 www.nea2.eu Contents 1. Executive Summary 2. Introduction and Background 3. Results: About Activities that Support Innovation 4. Results: About
Financial results of 2013 Outlook 2014+ 12 March 2014
 Financial results of 2013 Outlook 2014+ 12 March 2014 DUON benefits from liberalisation of electric energy and gas markets: summary of 2013 +56% increase of revenues to almost PLN 400 m +54% increase of
Financial results of 2013 Outlook 2014+ 12 March 2014 DUON benefits from liberalisation of electric energy and gas markets: summary of 2013 +56% increase of revenues to almost PLN 400 m +54% increase of
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3493957/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3493957/ Warranty Management System Market by Types (Claim & Transaction Management, Warranty Analytics, Billing & Administration
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3493957/ Warranty Management System Market by Types (Claim & Transaction Management, Warranty Analytics, Billing & Administration
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3291653/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3291653/ Video Analytics Market by Type (Hardware, Video Analytics Software, and Services), Applications (Intrusion Management,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3291653/ Video Analytics Market by Type (Hardware, Video Analytics Software, and Services), Applications (Intrusion Management,
Feasibility Study Requirements. Qatar Development Bank
 Feasibility Study Requirements Qatar Development Bank i. Feasibility Study Requirements The Feasibility study should ideally encompass the following areas / sections A. Executive Summary. B. Project details
Feasibility Study Requirements Qatar Development Bank i. Feasibility Study Requirements The Feasibility study should ideally encompass the following areas / sections A. Executive Summary. B. Project details
ARIMNet 2 Call 2014-15
 Coordination of the Agricultural Research In the Mediterranean Area Call i text ARIMNet 2 Call 2014-15 SUBMISSION Pre-proposal by December 1 st, 2014 Full Proposal by May 11 th 2015 on http://arimnet-call.eu/
Coordination of the Agricultural Research In the Mediterranean Area Call i text ARIMNet 2 Call 2014-15 SUBMISSION Pre-proposal by December 1 st, 2014 Full Proposal by May 11 th 2015 on http://arimnet-call.eu/
MarketsandMarkets. http://www.marketresearch.com/marketsandmarkets-v3719/ Publisher Sample
 MarketsandMarkets http://www.marketresearch.com/marketsandmarkets-v3719/ Publisher Sample Phone: 800.298.5699 (US) or +1.240.747.3093 or +1.240.747.3093 (Int'l) Hours: Monday - Thursday: 5:30am - 6:30pm
MarketsandMarkets http://www.marketresearch.com/marketsandmarkets-v3719/ Publisher Sample Phone: 800.298.5699 (US) or +1.240.747.3093 or +1.240.747.3093 (Int'l) Hours: Monday - Thursday: 5:30am - 6:30pm
Procurement Outsourcing Services¹
 Procurement Outsourcing Services¹ The following overview of the procurement outsourcing services in Australia is mainly based on the information provided by IBISWorld and consists of additional information
Procurement Outsourcing Services¹ The following overview of the procurement outsourcing services in Australia is mainly based on the information provided by IBISWorld and consists of additional information
Export Business Plan Guide
 Export Business Plan Guide Table of Contents Introduction... 4 SECTION 01: CURRENT SITUATION ANALYSIS... 5 Company Overview... 5 Availability of Resources... 6 SWOT Analysis... 9 SECTION 02: MARKET ANALYSIS...
Export Business Plan Guide Table of Contents Introduction... 4 SECTION 01: CURRENT SITUATION ANALYSIS... 5 Company Overview... 5 Availability of Resources... 6 SWOT Analysis... 9 SECTION 02: MARKET ANALYSIS...
www.ssse.com.pl The Science and Technology Park Poland East, Suwałki 17.06.2015 r
 www.ssse.com.pl The Science and Technology Park Poland East, Suwałki 17.06.2015 r SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONE Special Economic Zone is separated, uninhabited area of Polish territory, where business activities
www.ssse.com.pl The Science and Technology Park Poland East, Suwałki 17.06.2015 r SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONE Special Economic Zone is separated, uninhabited area of Polish territory, where business activities
1. Introduction LAND VALUE MAP AS A SOURCE OF INFORMATION ABOUT LOCAL REAL ESTATE MARKET. GEODEZJA TOM 11 Zeszyt 1/1 2005
 GEODEZJA TOM 11 Zeszyt 1/1 2005 Sabina róbek*, Rados³aw Cellmer*, Jan Kuryj* LAND VALUE MAP AS A SOURCE OF INFORMATION ABOUT LOCAL REAL ESTATE MARKET 1. Introduction A land value map can be a highly important
GEODEZJA TOM 11 Zeszyt 1/1 2005 Sabina róbek*, Rados³aw Cellmer*, Jan Kuryj* LAND VALUE MAP AS A SOURCE OF INFORMATION ABOUT LOCAL REAL ESTATE MARKET 1. Introduction A land value map can be a highly important
Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION. on Poland s 2014 national reform programme
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2.6.2014 COM(2014) 422 final Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION on Poland s 2014 national reform programme and delivering a Council opinion on Poland s 2014 convergence
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2.6.2014 COM(2014) 422 final Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION on Poland s 2014 national reform programme and delivering a Council opinion on Poland s 2014 convergence
The Economic Impacts of Reducing. Natural Gas and Electricity Use in Ontario
 The Economic Impacts of Reducing Natural Gas and Electricity Use in Ontario Prepared for Blue Green Canada July 2013 Table of Contents Executive Summary... i Key Findings... i Introduction...1 Secondary
The Economic Impacts of Reducing Natural Gas and Electricity Use in Ontario Prepared for Blue Green Canada July 2013 Table of Contents Executive Summary... i Key Findings... i Introduction...1 Secondary
 Notes to the Quarterly Report for Q4 FY03 1. Accounting principles adopted in the preparation of the quarterly report; information on changes in adopted accounting principles The report has been drawn
Notes to the Quarterly Report for Q4 FY03 1. Accounting principles adopted in the preparation of the quarterly report; information on changes in adopted accounting principles The report has been drawn
Tom Serwatka, Business Advisor MV Small Business Development Center SUNY Institute of Technology serwatt@sunyit.edu 315-792-7557
 Tom Serwatka, Business Advisor MV Small Business Development Center SUNY Institute of Technology serwatt@sunyit.edu 315-792-7557 1 Objectives of Presentation To walk you through the steps needed to create
Tom Serwatka, Business Advisor MV Small Business Development Center SUNY Institute of Technology serwatt@sunyit.edu 315-792-7557 1 Objectives of Presentation To walk you through the steps needed to create
BUSINESS VALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE
 BUSINESS VALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE The responses to the questions contained in this questionnaire will be used in our valuation analysis. As such, please provide as much detail in your responses as possible.
BUSINESS VALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE The responses to the questions contained in this questionnaire will be used in our valuation analysis. As such, please provide as much detail in your responses as possible.
Community Futures Management Consultant in a Box
 Community Futures Management Consultant in a Box Strategic Business Planning Purpose of this Document The purpose of this document is to provide you with the process that a management consultant would
Community Futures Management Consultant in a Box Strategic Business Planning Purpose of this Document The purpose of this document is to provide you with the process that a management consultant would
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3340542/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3340542/ Location Analytics Market by Tools (Geocoding and Reverse Geocoding, Data Integration and ETL, Reporting and Visualization,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3340542/ Location Analytics Market by Tools (Geocoding and Reverse Geocoding, Data Integration and ETL, Reporting and Visualization,
Business Plan for XXX
 Business Plan for XXX Version: 1.0 Date: [Elements in italics are indications to explain the business plan concepts: they should be deleted and not appear in the completed version of the business plan.
Business Plan for XXX Version: 1.0 Date: [Elements in italics are indications to explain the business plan concepts: they should be deleted and not appear in the completed version of the business plan.
Biomass Supply Chains in South Hampshire
 Biomass Supply Chains in South Hampshire 1 Executive Summary This report provides an analysis of how biomass supply chains could be developed within the area covered by the Partnership for Urban South
Biomass Supply Chains in South Hampshire 1 Executive Summary This report provides an analysis of how biomass supply chains could be developed within the area covered by the Partnership for Urban South
The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1
 The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1 Ing. Mikulá Cár, PhD. National Bank of Slovakia The energy industry and energy prices are becoming a subject of political decisions
The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1 Ing. Mikulá Cár, PhD. National Bank of Slovakia The energy industry and energy prices are becoming a subject of political decisions
UK Government Information Economy Strategy
 Industrial Strategy: government and industry in partnership UK Government Information Economy Strategy A Call for Views and Evidence February 2013 Contents Overview of Industrial Strategy... 3 How to respond...
Industrial Strategy: government and industry in partnership UK Government Information Economy Strategy A Call for Views and Evidence February 2013 Contents Overview of Industrial Strategy... 3 How to respond...
CRM Analytics Market by Type - Global Forecast to 2019
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3160606/ CRM Analytics Market by Type - Global Forecast to 2019 Description: CRM Analytics Market by Type (Sales Analytics, Customer
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3160606/ CRM Analytics Market by Type - Global Forecast to 2019 Description: CRM Analytics Market by Type (Sales Analytics, Customer
Case Interview - Frameworks
 WWW.MCONSULTINGPREP.COM Case Interview - Frameworks For more free and detailed materials on Management Consulting Preparation, visit www.mconsultingprep.com 2014 MConsultingPrep, Inc. COMPLETE FRAMEWORKS
WWW.MCONSULTINGPREP.COM Case Interview - Frameworks For more free and detailed materials on Management Consulting Preparation, visit www.mconsultingprep.com 2014 MConsultingPrep, Inc. COMPLETE FRAMEWORKS
Municipality of Koszalin
 Municipality of Koszalin Second biggest municipal centre in the West Pomeranian Province Population approx. 107 993 Area 98.33 km2 Geographical location 2 km in straight line to the Baltic Sea, forest
Municipality of Koszalin Second biggest municipal centre in the West Pomeranian Province Population approx. 107 993 Area 98.33 km2 Geographical location 2 km in straight line to the Baltic Sea, forest
Business Plan Helpsheet
 NORTHERN IRELAND Business Plan Helpsheet Published by Chartered Accountants Ulster Society with content from CCAB-I and the Irish Banking Federation Business Plan Helpsheet 01 Contents This helpsheet has
NORTHERN IRELAND Business Plan Helpsheet Published by Chartered Accountants Ulster Society with content from CCAB-I and the Irish Banking Federation Business Plan Helpsheet 01 Contents This helpsheet has
Social Media Analytics Market by Type, Applications, Vertical, Region - Global Forecast to 2020
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3617252/ Social Media Analytics Market by Type, Applications, Vertical, Region - Global Forecast to 2020 Description: "Social Media
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3617252/ Social Media Analytics Market by Type, Applications, Vertical, Region - Global Forecast to 2020 Description: "Social Media
Employment Outlook to November 2018
 Based on the Department of Employment s 2014 employment projections Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Projected employment growth by industry... 3 Projected employment growth by skill level... 5 Projected
Based on the Department of Employment s 2014 employment projections Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Projected employment growth by industry... 3 Projected employment growth by skill level... 5 Projected
Internet of Things (IoT) Analytics Market by Application Platform, Solutions, Deployment, Process, Regions - Global Forecast to 2020
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3300451/ Internet of Things (IoT) Analytics Market by Application Platform, Solutions, Deployment, Process, Regions - Global Forecast
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3300451/ Internet of Things (IoT) Analytics Market by Application Platform, Solutions, Deployment, Process, Regions - Global Forecast
Trading Policy and Georgian Export
 Trading Policy and Georgian Export Gelashvili Madona Associate Professor, Faculty of Business and Economics, Sokhumi State University, Tbilisi, Georgia Abstract Introduction and aim: Georgian foreign trade
Trading Policy and Georgian Export Gelashvili Madona Associate Professor, Faculty of Business and Economics, Sokhumi State University, Tbilisi, Georgia Abstract Introduction and aim: Georgian foreign trade
Business Plan Guidelines
 Business Plan Guidelines The following Business Plan Format checklist is meant as a guideline only listing the most important sections of the business plan in the order in which they will likely appear
Business Plan Guidelines The following Business Plan Format checklist is meant as a guideline only listing the most important sections of the business plan in the order in which they will likely appear
POLISH INFORMATION AND FOREIGN INVESTMENT AGENCY R&D SECTOR IN POLAND
 POLISH INFORMATION AND FOREIGN INVESTMENT AGENCY Foto: AA+W Fotolia.com R&D SECTOR IN POLAND The R&D sector in Poland characteristics and possibilities of support Characteristics of the Polish economy
POLISH INFORMATION AND FOREIGN INVESTMENT AGENCY Foto: AA+W Fotolia.com R&D SECTOR IN POLAND The R&D sector in Poland characteristics and possibilities of support Characteristics of the Polish economy
Quarterly Credit Conditions Survey Report Contents
 Quarterly Credit Conditions Report Contents List of Figures & Tables... 2 Background... 3 Overview... 4 Personal Lending... 7 Micro Business Lending... 9 Small Business Lending... 12 Medium-Sized Business
Quarterly Credit Conditions Report Contents List of Figures & Tables... 2 Background... 3 Overview... 4 Personal Lending... 7 Micro Business Lending... 9 Small Business Lending... 12 Medium-Sized Business
Industrial Park in Zambrów Białystok
 Podlaskie Total area of the 20 187 km 2 voivodeship Number of citizens: 1 188 800 - in urban areas 60.6 % Population per 1 km 2 59 persons/km 2 Principal city Bialystok Bigger cities in the Suwałki, Łomża,
Podlaskie Total area of the 20 187 km 2 voivodeship Number of citizens: 1 188 800 - in urban areas 60.6 % Population per 1 km 2 59 persons/km 2 Principal city Bialystok Bigger cities in the Suwałki, Łomża,
Regions of Portugal - Madeira
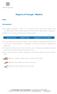 Regions of - Area Why? The archipelago is made up of the following islands, Porto Santo, Desertas (three uninhabited Islands: Deserta Grande, Bugio and Ilhéu Chão) and the Nature Reserve of Selvagens has
Regions of - Area Why? The archipelago is made up of the following islands, Porto Santo, Desertas (three uninhabited Islands: Deserta Grande, Bugio and Ilhéu Chão) and the Nature Reserve of Selvagens has
Strategic Marketing Planning Audit
 Strategic Marketing Planning Audit Violeta Radulescu Lecturer, PhD., Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest Email: vio.radulescu@yahoo.com Abstract Market-oriented strategic planning is the process of
Strategic Marketing Planning Audit Violeta Radulescu Lecturer, PhD., Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest Email: vio.radulescu@yahoo.com Abstract Market-oriented strategic planning is the process of
Financial Projections
 Financial Projections Introduction Any business plan must include a section detailing the financial projections, because these projections are a forecast of the future economic-financial results of the
Financial Projections Introduction Any business plan must include a section detailing the financial projections, because these projections are a forecast of the future economic-financial results of the
THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY
 THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY Management Marketing - Tourism Ec. Ecaterina Nicoleta Ciurez Ph.D University of Craiova, Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Craiova,
THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY Management Marketing - Tourism Ec. Ecaterina Nicoleta Ciurez Ph.D University of Craiova, Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Craiova,
Growing Forward 2 In Newfoundland and Labrador
 Growing Forward 2 In Newfoundland and Labrador Business Plan Minimum Requirements Version1.0 Growing Forward 2 in Newfoundland and Labrador - 1 - Business Plan Minimum Requirements Minimum Requirements
Growing Forward 2 In Newfoundland and Labrador Business Plan Minimum Requirements Version1.0 Growing Forward 2 in Newfoundland and Labrador - 1 - Business Plan Minimum Requirements Minimum Requirements
Professor: Dr. Mary Flannery Teaching Assistant: Jia-Yuh Chen ECON 136 Business Strategy February 27, 2006
 CASE STUDY Professor: Dr. Mary Flannery Teaching Assistant: Jia-Yuh Chen ECON 136 Business Strategy February 27, 2006 INDUSTRY ANALYSIS The retail industry is dominated by few retail giants, with Wal-Mart
CASE STUDY Professor: Dr. Mary Flannery Teaching Assistant: Jia-Yuh Chen ECON 136 Business Strategy February 27, 2006 INDUSTRY ANALYSIS The retail industry is dominated by few retail giants, with Wal-Mart
Sustainable Industries: creating opportunities through service innovation
 Sustainable Industries: creating opportunities through service innovation Dr Jari Kuusisto Smart Innovation Festival 2008 Brisbane May 2008 Dr Jari Kuusisto Outline of the presentation Introduction Economic
Sustainable Industries: creating opportunities through service innovation Dr Jari Kuusisto Smart Innovation Festival 2008 Brisbane May 2008 Dr Jari Kuusisto Outline of the presentation Introduction Economic
Quarterly Credit Conditions Survey Report
 Quarterly Credit Conditions Report Contents List of Figures & Tables... 2 Background... 3 Overview... 4 Personal Lending... 7 Micro Business Lending... 10 Small Business Lending... 12 Medium-Sized Business
Quarterly Credit Conditions Report Contents List of Figures & Tables... 2 Background... 3 Overview... 4 Personal Lending... 7 Micro Business Lending... 10 Small Business Lending... 12 Medium-Sized Business
Project Portfolio Management Software Market by Platform, by Business Solutions, by Deployment Mode & by Regions - Global Forecast to 2019
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3066444/ Project Portfolio Management Software Market by Platform, by Business Solutions, by Deployment Mode & by Regions - Global
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3066444/ Project Portfolio Management Software Market by Platform, by Business Solutions, by Deployment Mode & by Regions - Global
Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225374/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225374/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Business Analytics Market by Software, by Deployment Type, by End User, by Vertical, and by Geography - Global Forecast to 2019
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3150133/ Business Analytics Market by Software, by Deployment Type, by End User, by Vertical, and by Geography - Global Forecast
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3150133/ Business Analytics Market by Software, by Deployment Type, by End User, by Vertical, and by Geography - Global Forecast
The impact of external environment on organizational development strategy
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The impact of external environment on organizational development strategy Alina Voiculet and Nicoleta Belu and Denisa Elena Parpandel and Ionela Carmen Rizea Constantin
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The impact of external environment on organizational development strategy Alina Voiculet and Nicoleta Belu and Denisa Elena Parpandel and Ionela Carmen Rizea Constantin
Northern Dimension Policy Framework Document (effective as 1 January 2007)
 Northern Dimension Policy Framework Document (effective as 1 January 2007) 1. Introduction 1. The Northern Dimension covers a broad geographic area from the European Arctic and Sub- Arctic areas to the
Northern Dimension Policy Framework Document (effective as 1 January 2007) 1. Introduction 1. The Northern Dimension covers a broad geographic area from the European Arctic and Sub- Arctic areas to the
Fair Competition Commission. THE FAIR COMPETITION COMMISSION PROCEDURE RULES, 2013 Rule 33(2) MERGER NOTIFICATION (Application for Merger Clearance)
 FCC.8 Fair Competition Commission THE FAIR COMPETITION COMMISSION PROCEDURE RULES, 2013 Rule 33(2) To: The Fair Competition Commission MERGER NOTIFICATION (Application for Merger Clearance) Application
FCC.8 Fair Competition Commission THE FAIR COMPETITION COMMISSION PROCEDURE RULES, 2013 Rule 33(2) To: The Fair Competition Commission MERGER NOTIFICATION (Application for Merger Clearance) Application
What this topic is about. The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing
 Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
SUMMARY. Capitalised terms are defined in the section headed Definitions.
 This summary aims to give you an overview of the information contained in this prospectus. As this is a summary, it does not contain all the information that may be important to you. You should read the
This summary aims to give you an overview of the information contained in this prospectus. As this is a summary, it does not contain all the information that may be important to you. You should read the
REPORT ON THE CONDITION OF SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISE SECTOR IN POLAND IN 2011-2012
 REPORT ON THE CONDITION OF SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISE SECTOR IN POLAND IN 2011-2012 selected chapters from the complete version of the Report available in Polish PARP, 2013 Report on the condition
REPORT ON THE CONDITION OF SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISE SECTOR IN POLAND IN 2011-2012 selected chapters from the complete version of the Report available in Polish PARP, 2013 Report on the condition
REQUEST FOR QUOTATION No. 34/2013 Date of issuance: 13.12.2013. Training courses may be conducted in English or Polish.
 REQUEST FOR QUOTATION No. 34/2013 Date of issuance: 13.12.2013 The Foundation for Polish Science runs the SKILLS project, cofounded by the European Union within the European Social Fund (The Operational
REQUEST FOR QUOTATION No. 34/2013 Date of issuance: 13.12.2013 The Foundation for Polish Science runs the SKILLS project, cofounded by the European Union within the European Social Fund (The Operational
Coca-Cola Case Analyses. <Student Name> <Name and Section # of course> <Instructor Name> <Date>
 Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3384906/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3384906/ Cloud Storage Market by Solutions (Primary Storage Solution, Backup Storage Solution, Cloud Storage Gateway Solution, and
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3384906/ Cloud Storage Market by Solutions (Primary Storage Solution, Backup Storage Solution, Cloud Storage Gateway Solution, and
Automotive Suppliers Survey
 The outlook for 2014 remains optimistic. The key to success will be innovation and R&D, the key to survive will be skilled labour. Automotive Suppliers Survey Slovakia, 2014 Consultancy firm PwC in cooperation
The outlook for 2014 remains optimistic. The key to success will be innovation and R&D, the key to survive will be skilled labour. Automotive Suppliers Survey Slovakia, 2014 Consultancy firm PwC in cooperation
Event Management Software Market by Component, Software, Service, Deployment Mode, Organization size, Verticals, and Region - Global Forecast to 2020
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3498979/ Event Management Software Market by Component, Software, Service, Deployment Mode, Organization size, Verticals, and Region
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3498979/ Event Management Software Market by Component, Software, Service, Deployment Mode, Organization size, Verticals, and Region
Managing trade credit risk in the recovering economy. July 2015
 Managing trade credit risk in the recovering economy July 201 1 QBE - Managing trade credit risk in the recovering economy Introduction In our latest survey of UK businesses, 22% of respondents reported
Managing trade credit risk in the recovering economy July 201 1 QBE - Managing trade credit risk in the recovering economy Introduction In our latest survey of UK businesses, 22% of respondents reported
Enterprise Mobility Management Market by Solution, by Services - Global Forecast to 2019
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3160843/ Enterprise Mobility Management Market by Solution, by Services - Global Forecast to 2019 Description: Enterprise Mobility
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3160843/ Enterprise Mobility Management Market by Solution, by Services - Global Forecast to 2019 Description: Enterprise Mobility
'LJL7D/ 0(',$ 0JPW Digital Strategies tisdag den 29 september 2009
 Digital Strategies The beginning of the end Today - Internet & Strategy Tuesday 29th - Management and ethics Wednesday (30th) - Seminar presentations Next Wednesday (7th)- Seminar presentations Thursday
Digital Strategies The beginning of the end Today - Internet & Strategy Tuesday 29th - Management and ethics Wednesday (30th) - Seminar presentations Next Wednesday (7th)- Seminar presentations Thursday
3.1 CONDUCTING MARKET RESEARCH; DRAWING THE RIGHT CONCLUSIONS. Doing Market Research. Market Research; Examples Of Information Needed
 31 MARKET RESEARCH 3 CONDUCTING MARKET RESEARCH; DRAWING THE RIGHT CONCLUSIONS Doing Market Research Market Research; Examples Of Information Needed Market Research 1 Market Research 2 Some Market Research
31 MARKET RESEARCH 3 CONDUCTING MARKET RESEARCH; DRAWING THE RIGHT CONCLUSIONS Doing Market Research Market Research; Examples Of Information Needed Market Research 1 Market Research 2 Some Market Research
The regional variation of foreign direct investment in Poland
 Scientific Journal Warsaw University of Life Sciences SGGW Problems of World Agriculture volume 14 (XXIX), number 4, 2014: 83 91 Elżbieta Kacperska 1 Department of Agricultural Economics and International
Scientific Journal Warsaw University of Life Sciences SGGW Problems of World Agriculture volume 14 (XXIX), number 4, 2014: 83 91 Elżbieta Kacperska 1 Department of Agricultural Economics and International
Services and Distribution
 13 Services and Distribution Retail sales decreased by 1.1% in volume and 0.7% in value in 2012. The volume of retail sales of automotive fuel decreased by 7.6% in 2012. The value of the Non-Financial
13 Services and Distribution Retail sales decreased by 1.1% in volume and 0.7% in value in 2012. The volume of retail sales of automotive fuel decreased by 7.6% in 2012. The value of the Non-Financial
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3288503/
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3288503/ Disaster Recovery as a Service Market by Solution (Disaster Planning & Testing, Real-Time Replication, Backup Solution,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3288503/ Disaster Recovery as a Service Market by Solution (Disaster Planning & Testing, Real-Time Replication, Backup Solution,
 UPC International Relations Plan 2003-2006 Servei de Comunicació Institucional de la UPC, 2003 (7077) Contents Introduction Teaching Subsection 1: The European Higher Education Area Subsection 2: The internationalisation
UPC International Relations Plan 2003-2006 Servei de Comunicació Institucional de la UPC, 2003 (7077) Contents Introduction Teaching Subsection 1: The European Higher Education Area Subsection 2: The internationalisation
Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225332/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2225332/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Chilean Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Identity and Access Management Market by Deployments, by Components, by Organization Size - Global Forecast to 2019
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3104619/ Identity and Access Management Market by Deployments, by Components, by Organization Size - Global Forecast to 2019 Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3104619/ Identity and Access Management Market by Deployments, by Components, by Organization Size - Global Forecast to 2019 Description:
Business Plan Template
 Business Plan Template 1. Executive Summary... 3 1.1. Description of Business... 3 1.2. Finance Required... 3 1.3. Financial Projections... 3 1.4. Business Differentiators... 3 1.5. Business Credibility...
Business Plan Template 1. Executive Summary... 3 1.1. Description of Business... 3 1.2. Finance Required... 3 1.3. Financial Projections... 3 1.4. Business Differentiators... 3 1.5. Business Credibility...
How To Help The World Coffee Sector
 ICC 105 19 Rev. 1 16 October 2012 Original: English E International Coffee Council 109 th Session 24 28 September 2012 London, United Kingdom Strategic action plan for the International Coffee Organization
ICC 105 19 Rev. 1 16 October 2012 Original: English E International Coffee Council 109 th Session 24 28 September 2012 London, United Kingdom Strategic action plan for the International Coffee Organization
APPENDIX 3 TO ANNEX VIII LIECHTENSTEIN SCHEDULE OF SPECIFIC COMMITMENTS
 APPENDIX 3 TO ANNEX VIII LIECHTENSTEIN SCHEDULE OF SPECIFIC COMMITMENTS I. HORIZONTAL COMMITMENTS 1 ALL SECTORS INCLUDED IN THIS SCHEDULE The level of commitments in a particular sector shall not be construed
APPENDIX 3 TO ANNEX VIII LIECHTENSTEIN SCHEDULE OF SPECIFIC COMMITMENTS I. HORIZONTAL COMMITMENTS 1 ALL SECTORS INCLUDED IN THIS SCHEDULE The level of commitments in a particular sector shall not be construed
General Corporate Social Responsibility Policy 20/10/15
 General Corporate Social Responsibility Policy 20/10/15 CONTENT GENERAL CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY POLICY 3 OBJECTIVES 3 1. Objectives of the General Corporate Social Responsibility Policy 3 PRINCIPLES
General Corporate Social Responsibility Policy 20/10/15 CONTENT GENERAL CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY POLICY 3 OBJECTIVES 3 1. Objectives of the General Corporate Social Responsibility Policy 3 PRINCIPLES
In order to maintain its position as a global economic leader and
 A Report from the California Business Roundtable and the Campaign for College Opportunity E X E C U T I V E S U M M A RY Embargoed until 10am PST April 26th 2006 Keeping California s Edge The Growing Demand
A Report from the California Business Roundtable and the Campaign for College Opportunity E X E C U T I V E S U M M A RY Embargoed until 10am PST April 26th 2006 Keeping California s Edge The Growing Demand
Law on Fire Safety of the Republic of Azerbaijan
 Chapter I. General provisions Law on Fire Safety of the Republic of Azerbaijan Article 1. Key definitions used in this Law Following definitions are applied for the purposes of this Law: 1) Fire- uncontrolled
Chapter I. General provisions Law on Fire Safety of the Republic of Azerbaijan Article 1. Key definitions used in this Law Following definitions are applied for the purposes of this Law: 1) Fire- uncontrolled
Appendix A. The Business Plan
 Appendix A The Business Plan A key element of business success is a business plan, a written statement of the rationale for the enterprise and a step-by-step explanation of how it will achieve its goals.
Appendix A The Business Plan A key element of business success is a business plan, a written statement of the rationale for the enterprise and a step-by-step explanation of how it will achieve its goals.
Effectiveness of Customer Relationship Management Programs
 Evgeni Stanimirov * Summary: Customer relationship management (CRM) has been among the most widely debated topics in the field of marketing during the last decade. Regardless of the significant interest
Evgeni Stanimirov * Summary: Customer relationship management (CRM) has been among the most widely debated topics in the field of marketing during the last decade. Regardless of the significant interest
An Export Marketing Research Project. Guidance Notes
 An Export Marketing Research Project Guidance Notes 2 An Export Marketing Research Project Introduction UKTI encourages British business to use marketing research as an integral part of their export strategy.
An Export Marketing Research Project Guidance Notes 2 An Export Marketing Research Project Introduction UKTI encourages British business to use marketing research as an integral part of their export strategy.
Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2104740/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2104740/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Strategy for 2012 to 2015. An active player from rural areas to the metropolis
 Strategy for 2012 to 2015 ELY Centre for An active player from rural areas to the metropolis Well-being and impact through cooperation network The operating environment of the Centre for Economic Development,
Strategy for 2012 to 2015 ELY Centre for An active player from rural areas to the metropolis Well-being and impact through cooperation network The operating environment of the Centre for Economic Development,
Approved by Management Committee 24/03/11 Strategy Document
 ELHA POLICY Date Issued May 2007 Last Revised March 2011 Department Asset Management Title Asset Management Strategy Objective To outline the Association s strategy for managing its assets Responsible
ELHA POLICY Date Issued May 2007 Last Revised March 2011 Department Asset Management Title Asset Management Strategy Objective To outline the Association s strategy for managing its assets Responsible
Helpsheet Business Plan Guidance
 Helpsheet Business Plan Guidance Published jointly by CCAB-I and the Irish Banking Federation This helpsheet has been prepared by the Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies - Ireland (CCAB-I) and
Helpsheet Business Plan Guidance Published jointly by CCAB-I and the Irish Banking Federation This helpsheet has been prepared by the Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies - Ireland (CCAB-I) and
Organic farming. A guide on support opportunities for organic producers in Europe. Agriculture and Rural Development
 Organic farming A guide on support opportunities for organic producers in Europe Agriculture and Rural Development This publication is an informative document intended for organic farmers, processors and
Organic farming A guide on support opportunities for organic producers in Europe Agriculture and Rural Development This publication is an informative document intended for organic farmers, processors and
North Bay Industry Sector Rankings (By County) October 2015 Jim Cassio
 North Bay Rankings (By County) October 2015 Jim Cassio North Bay Rankings (By County) Source: EMSI (Economic Modeling Specialists, Intl.) Contents Lake County... 3 Jobs... 3 Job Growth (Projected)...
North Bay Rankings (By County) October 2015 Jim Cassio North Bay Rankings (By County) Source: EMSI (Economic Modeling Specialists, Intl.) Contents Lake County... 3 Jobs... 3 Job Growth (Projected)...
Annual Report 2007 COMMERCIAL FINANCE WWW.INGCOMFIN.PL
 2007 Annual Report 2007 COMMERCIAL FINANCE WWW.INGCOMFIN.PL It is with pleasure that I present to you the Annual Report of 2007 which describes the activity of ING Commercial Finance Polska S.A. Last year
2007 Annual Report 2007 COMMERCIAL FINANCE WWW.INGCOMFIN.PL It is with pleasure that I present to you the Annual Report of 2007 which describes the activity of ING Commercial Finance Polska S.A. Last year
Introduction to. Aalborg s Sustainability Strategy 2013-2016
 Introduction to Aalborg s Sustainability Strategy 2013-2016 2 Foreword Aalborg should be a sustainable municipality, which will be to the benefit of local citizens, businesses and the environment. With
Introduction to Aalborg s Sustainability Strategy 2013-2016 2 Foreword Aalborg should be a sustainable municipality, which will be to the benefit of local citizens, businesses and the environment. With
Modeling Transaction Prices of Properties Based on Qualitative and Quantitative Features**
 GEOMATICS AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Volume 4 Number 3 2010 El bieta Jasiñska*, Edward Preweda*, Jan Ruchel* Modeling Transaction Prices of Properties Based on Qualitative and Quantitative Features**
GEOMATICS AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Volume 4 Number 3 2010 El bieta Jasiñska*, Edward Preweda*, Jan Ruchel* Modeling Transaction Prices of Properties Based on Qualitative and Quantitative Features**
