Normal Aging versus Alzheimer Disease Drugs to treat the symptoms that are not due to old age. Leah Wright, HBSc. BSP student June 2006
|
|
|
- Debra Sutton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Normal Aging versus Alzheimer Disease Drugs to treat the symptoms that are not due to old age. Leah Wright, HBSc. BSP student June 2006
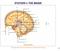
2 Alzheimer Disease is a form of dementia that affects 5% of men and women over age 65 and 50% of people over age 85. 1,2 Dementia is a neurological disorder that severely obstructs a person s ability to perform normal activities of daily living such as feeding, dressing, and bathing oneself. 1,2,3,4,13 Alzheimer Disease gradually, but progressively, impairs memory, learning, reason, judgment, and communication skills. Alzheimer Disease most commonly occurs sporadically but in some cases it is hereditary. 2,3,4 The cause of Alzheimer Disease is unknown, however, it is known that damage to the brain occurs several years or even decades before symptoms appear. Once Alzheimer Disease becomes symptomatic irreversible damage has already occurred. 2,3 Symptoms such as changes in behavior occur because of damage to certain areas of the brain. 4 The brain is composed of five general regions: the limbic system, the temporal lobes, the parietal lobes, the frontal lobe, and the occipital lobe. 4 The limbic system, where memory and emotion originate, is affected early on. This often results in difficulty finding objects and/or forgetting where objects were placed. 4 The temporal lobes are the area where learning and short term memory are processed. Damage to this region can result in lapses in a person's recent memory and the inability to recognize familiar faces and places. 4 The parietal lobes control spatial information and make a person able to put activities into sequence. Damage to these lobes by Alzheimer Disease leaves a person unable to clearly express his or her thoughts, get dressed or find his or her way. 4 The frontal lobe is needed to plan and organize activities, it also regulates behavior; once damaged a person may lose interest in favorite activities and may behave in inappropriate ways. 4 The occipital lobe is generally not affected by Alzheimer Disease, however, the surrounding visual areas may be affected which can lead to loss of depth vision and/or the inability to see movement. 4 Physical changes occur in the brain either as a result of damage or they may actually cause the damage. Under the microscope there are four different findings that are indicative of Alzheimer Disease: plaques, tangles, beta amyloid, and degenerated nerve cells. 1,2,3,4 Plaques are clumps of abnormal protein that accumulate outside nerve cells, whereas tangles are composed of a different protein that twists together and deposits inside nerve cells. 2,3 Betaamyloid is an atypical protein that is formed when something triggers a normal protein to be cut incorrectly. Beta amyloid tends to accumulate within plaques. 5 Patients with Alzheimer Disease have irregular concentrations of several neurotransmitters that are important for proper brain function. 3 Acetylcholine is important for stimulating muscle contraction and the release of hormones involved in wakefulness, attentiveness, anger, aggression, sexuality, and thirst. 6 Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that is important for attentiveness, emotions, sleeping, dreaming, and learning. 6 Serotonin
3 contributes to the regulation of body temperature, sleep, mood, appetite, and pain. 6 Glutamate is associated with learning and memory. 6 Early warning signs of Alzheimer Disease include: memory loss that affects daily functioning, difficulty performing familiar or routine tasks, language problems, disorientation with regards to time and place, poor judgment, problems with abstract thinking, misplacing things, changes in mood and/or behavior, changes in personality, and/or loss of interest in favorite pasttimes. 4 It is important to remember that these are not normal signs of aging and Alzheimer Disease can only be diagnosed by a qualified health care professional. 1 Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease is made following a systematic assessment that rules out other possibilities by looking at medical history, mental status, physical examination, laboratory tests, and psychiatric 4, 7,17 and/or psychological evaluations. Once diagnosed, Alzheimer Disease is categorized into 7 different stages: 2,3,4 STAGE 1 None No problems with activities of daily living STAGE 2 Very mild Forgetting names, trouble finding words STAGE 3 Mild Difficulty traveling to new location or dealing with problems STAGE 4 Moderate Difficulty with complex tasks i.e. shopping STAGE 5 Moderately severe Needs help choosing clothing and prompting to bathe STAGE 6 Severe Requires assistance dressing, bathing & toileting STAGE 7 Very severe Limited vocabulary, loss of ability to walk and sit, unable to smile The goal of therapy for patients with Alzheimer Disease is first and foremost to slow progression of the disease, it is also important to lighten the burden placed on caregivers by treating cognitive, behavioral and psychological symptoms. 7,17 Currently there are two types of drugs that are approved for use in Alzheimer Disease. Three of the drugs are used to treat patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain, the fourth drug is used to treat patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer Disease by decreasing glutamate levels (glutamate is an excitatory amino acid found in the brain, over stimulation of glutamate receptors leads to toxicity and nerve cell death). 16,17 None of the four Alzheimer Disease drugs is a cure; they are used to decrease symptoms and slow progression of the disease. 1,2,3,8,10,13,15,17 In Alzheimer Disease acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is important for memory, undergoes substantial degradation by an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase. Cholinesterase inhibitors are a class of drugs that inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine by blocking acetylcholinesterase. 8 Compared to placebo cholinesterase inhibitors have been shown to be effective at improving cognitive function, activities of daily living capability, and behavior. 8 All three are fairly well tolerated. Donepezil and rivastigmine have been directly compared to one
4 another and there is no significant difference in efficacy although donepezil has fewer incidences of adverse effects. 8 Unfortunately there is no evidence that any of the cholinesterase inhibitors can alter the course of the underlying dementia, thus they are not a cure for Alzheimer Disease. 10,13,15 The efficacy of various treatments is measured using two different scales: Alzheimer Disease Assessment Scale Cognitive (ADAS Cog) which assesses memory, orientation, attention, reasoning, and language, and Clinician s Interview Based Impression of Change (CIBIC plus) which evaluates the following four areas: general, cognitive, behavioral and activities of daily living. 10,13,15,17 Clinical studies have shown that all four drugs approved for use in Alzheimer Disease have statistically significantly improved the above two measures of efficacy as compared to placebo. 10,13,15,17 Aricept or donepezil is a cholinesterase inhibitor that is indicated for mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease. 9,10 Donepezil reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase which results in an increased concentration of acetylcholine that is available for nerve impulses in the brain. 1,9,10 Orally donepezil is 100% bioavailable. Drug concentrations peak in 3 to 4 hours and it takes 15 days to reach steady state because the half life is 70 hours. Donepezil is 96% bound to plasma proteins. Four metabolites are formed via CYP2D6/3A4 metabolism and 57% of the drug is renally excreted. No dosage adjustments are required for either renal or hepatic impairment. 9,10 Donepezil is dosed once daily starting with 5mg at bedtime and increasing to 10 mg at bedtime after four weeks. 1,7,9,10 Common side effects of donepezil (greater than 5%) include: insomnia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, anorexia, fatigue, headache, and muscle cramps. 7,8,9,10 A one month supply of donepezil costs approximately $ Donepezil is not on the Saskatchewan Drug Formulary but coverage may be obtained pending approval via Exceptional Drug Status (EDS). 11 Exelon or rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor that is indicated for treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease. 12,13 Rivastigmine reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. 1,7,12,13 Rivastigmine is only 40% orally bioavailable. Rivastigmine concentrations peak one hour after administration and the half life is 1.5 hours thus the drug needs to be dosed twice daily. Rivastigmine is 40% bound to plasma proteins. Rivastigmine undergoes minimal metabolism in the liver, it is 97% renally excreted. The initial dose of rivastigmine is 1.5 mg twice daily which should be increased to 3 mg twice daily after one month (the maximum dose is 6 mg twice daily). 12,13 The most common side effects of rivastigmine (greater than 5%) are more extensive in both number and magnitude than the other two cholinesterase inhibitors: dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal pain, fatigue, insomnia, confusion, depression, anxiety, malaise, somnolence, dyspepsia, constipation, urinary tract infection and falls. 1,7,9,12,13 Rivastigmine has significant gastrointestinal adverse effects, for example 47% of patients develop nausea and 31% of patient experience vomiting. 13 No dosage adjustment is required in renal or hepatic impairment. 13 A one month supply of rivastigmine costs about $ Rivastigmine is not on the Saskatchewan Drug Formulary but coverage may be obtained pending approval via EDS. 11 Reminyl*ER or galantamine is a long acting cholinesterase inhibitor that is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease. 14,15 Galantamine prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, it also stimulates nicotinic receptors to release more acetylcholine. Thus the drug has dual mechanisms that work to increase acetylcholine levels in the brain. 1,7,14,15 Galantamine has an oral bioavailability of %. Drug concentrations peak one hour after administration, it takes less than 6 days to reach steady state. The half life is 7 hours and the drug is 18% plasma protein bound. Galantamine should be taken in the morning with food. Galantamine is dosed once daily due to the extended release nature of the product formulation. This drug is extensively metabolized in the liver by CYP2D6/3A4 and 25% is excreted in the urine. Dose adjustments are indicated in both hepatic
5 and renal disease. 14,15 The initial dose of galantamine is 8 mg daily, the dose can be increased by 8 mg daily every 4 weeks to a maximum daily dose of 24 mg. The most common side effects of galantamine (greater than 5%) are nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, anxiety and depression. 14,15 A one month supply of galantamine costs $ $ Galantamine is not on the Saskatchewan Drug Formulary but coverage may be obtained pending approval via EDS. 11 Ebixa or memantine is used to treat moderate to severe dementia by inhibiting the stimulation of receptors in the brain by glutamate thus resulting in decreased nerve cell toxicity and nerve cell death. 16,17 Memantine does not disrupt normal nerve cell function as it only exerts its inhibitory effect under conditions of excessive glutamate stimulation. Memantine is 100% bioavailable. Peak concentrations are reached after 3 to 7 hours. The half life is 60 to 80 hours, thus steady state concentrations are not reached until day eleven. The drug has been found to be 45 % bound to plasma proteins. Memantine is 57 82% excreted in the urine and dose adjustments are required if the patient has reduced renal function. The initial dose of memantine is 5 mg daily, the dose can be increased by 5 mg each week to a maximum dose of 20 mg daily. 16,17 The most common side effects of memantine (greater than 5%) are dizziness, confusion, headache, and constipation. 16,17 A one month supply of memantine 10 mg per day costs $ Memantine is not on the Saskatchewan Drug Formulary, nor is there EDS criteria. 11 The EDS criteria required by Saskatchewan Health is as follows for all cholinesterase inhibitors indicated for treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer type. 11 A physician must diagnose Alzheimer Disease using criteria set by the American Psychiatric Association which includes development of memory impairment as well as the loss of word comprehension, muscle coordination and/or the ability to interpret sensory stimuli. Diagnosis also requires a gradual and continual decline in function that results in significant impairment and is not due to any other disease, condition or medication. 19 Furthermore, the patient must not be concurrently taking any other anticholinergic medication. 11 Lastly in order for Saskatchewan Health to provide EDS coverage for donepezil, galantamine, or rivastigmine a Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of 10 to (Appendix 1), and the completion of a Functional Activities Questionnaire are required. Part one of the MMSE tests vocal responses involving orientation, memory, and attention, while part two of the MMSE tests the patient s ability to name, follow verbal and written commands and to write spontaneous sentences as well as copy a complex polygon. The maximum total score possible is Alzheimer Disease is a devastating condition in which a person progressively loses the ability to function independently and self sufficiently. The cause of Alzheimer Disease is currently unknown thus it is virtually impossible to prevent or cure the disease. There are currently four pharmaceutical agents on the market which target two distinct mechanisms in order to alleviate some of the symptoms of Alzheimer Disease and potentially slow disease progression. A search of the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews found one article in which the author has compared the three cholinesterase inhibitors. 8 The article reviewed numerous studies in the literature that focused on donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine versus placebo. One study compared donepezil and rivastigmine. The author concluded that all three acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are effective in reducing the symptoms of Alzheimer Disease. It is difficult to say which agent is the best because there was only one head to head trial. However, donepezil and galantamine are both once daily dosing which makes administration simpler and easier. In the trial that compared donepezil and rivastigmine, the two drugs were found to be comparable in efficacy but donepezil had significantly less frequent and less severe side effects. 8 Patients should not take more than one of donepezil, rivastigmine or galantamine at the same time due to the similarities in mechanism of action. If a patient does not
6 respond to or cannot tolerate one of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors then they may be switched to another. Memantine has a completely different mechanism of action so it may be used in combination with any of the other three drugs, however it is not eligible for EDS coverage. Alzheimer Disease is a progressively debilitating disease with no cure. Four drugs (Table 1) are available to assist in reducing progression of the disease and to alleviate symptoms thus improving the quality of life of both the patient and the caregiver.
7 Table 1 Comparison of available medications for Alzheimer Disease Mechanism of Action Efficacy Side effects (>5%) Aricept 9,10 (Donepezil) Inhibits acetylcholinesterase Effective in reducing progression and symptoms in mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease Insomnia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, anorexia, fatigue, headache, and muscle cramps Exelon 12,13 (Rivastigmine) Inhibits acetylcholinesterase Effective in reducing progression and symptoms in mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease Dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal pain, fatigue, insomnia, confusion, depression, anxiety malaise, somnolence, dyspepsia, constipation, Reminyl 14,15 (Galantamine) Inhibits acetylcholinesterase Effective in reducing progression and symptoms in mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, depression, fatigue, insomnia, anorexia, weight loss, abdominal pain, flatulence urinary tract infection Cost $180 per month $207 $750 per month $210 $220 per month Ebixa 16,17 (Memantine) Inhibits N methyl Daspartate type glutamate receptors Effective in reducing progression and symptoms in moderate to severe Alzheimer Disease Dizziness, confusion, headache, constipation $195 per month
8 Appendix 1 Mini Mental Status Examination 20
9 References 1. National Institute for Health. 1 June 2006 < 2. Alzheimer's Association. 1 June 2006 < 3. Young, Koda Kimble. Applied Therapeutics: The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6 th ed. 4. Alzheimer Society of Canada. 1 June 2006 < 5. "Experimental Alzheimer Drugs Targeting Beta Amyloid and the "Amyloid Hypothesis"" Alzheimer's Association. 1 June 2006 < 6. McGill University. 9 June 2006 < 7. Canadian Pharmacists Association. Therapeutic Choices." Dementias Birks J. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer s disease. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD Lexi Comp (Lexi Drugs Donepezil) [computer program]. Lexi Comp; April 18, Aricept, donepezil hydrochloride. [product monograph]. Kirkland (QC): Pfizer Canada, 2005 July Saskatchewan Health. Formulary. July June 2006 < 12. Lexi Comp (Lexi Drugs Rivastigmine) [computer program]. Lexi Comp; April 18, Exelon, rivastigmine tartarate. [product monograph]. East Hanover (NJ): Novartis, 2005 October. 14. Lexi Comp (Lexi Drugs Galantamine) [computer program]. Lexi Comp; April 18, Reminyl*, galantamine hydrobromide extended release capsule. [product monograph]. Toronto (ON): Janssen Ortho Inc, 2001 July Lexi Comp (Lexi Drugs Memantine) [computer program]. Lexi Comp; April 18, Ebixa, memantine. [product monograph]. Denmark: Lundbeck, Stueck Pharmacy, Leader, SK. Retail Drug Prices. 19. American Psychiatric Association, "The diagnostic and Statistical Manual." Criteria for Diagnosis of Dementia of the Alzheimer s Type. 20. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini Mental State A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:
Objectives. Aging and Forgetfulness Define Dementia Types of Dementia Treatment
 Dementia David Lam, MD, FRCPC, Psychiatry Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Neurosciences McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Objectives Aging and Forgetfulness Define
Dementia David Lam, MD, FRCPC, Psychiatry Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Neurosciences McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Objectives Aging and Forgetfulness Define
Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW
 Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW Diagnosis of Dementia : DSM-IV criteria Loss of memory and one or more other cognitive abilities Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia
Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW Diagnosis of Dementia : DSM-IV criteria Loss of memory and one or more other cognitive abilities Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia
Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease
 IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
Alzheimer Disease (AD)
 1 Alzheimer Disease (AD) 2 Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease that attacks the brain and results in impaired memory, thinking and behavior. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer
1 Alzheimer Disease (AD) 2 Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease that attacks the brain and results in impaired memory, thinking and behavior. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer
Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease
 IS 11 October 2011 Information sheet Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Aricept work?... 1 Who might benefit from Aricept?... 2 What effect
IS 11 October 2011 Information sheet Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Aricept work?... 1 Who might benefit from Aricept?... 2 What effect
DRUG APPROVAL PROCESS FOR THE TREATMENT OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE
 Research DRUG APPROVAL PROCESS FOR THE TREATMENT OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE There are certain principles that should be followed when involving people with Alzheimer s disease in research. For more information,
Research DRUG APPROVAL PROCESS FOR THE TREATMENT OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE There are certain principles that should be followed when involving people with Alzheimer s disease in research. For more information,
**Form 1: - Consultant Copy** Telephone Number: Fax Number: Email: Author: Dr Bernard Udeze Pharmacist: Claire Ault Date of issue July 2011
 Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Primary Care Update January 28 & 29, 2016 Alzheimer s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment
 Primary Care Update January 28 & 29, 2016 Alzheimer s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Kinga Szigeti, MD Associate Professor UBMD Neurology UB Department of Neurology Questions How do we differentiate
Primary Care Update January 28 & 29, 2016 Alzheimer s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Kinga Szigeti, MD Associate Professor UBMD Neurology UB Department of Neurology Questions How do we differentiate
Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease
 IS 17 October 2011 Information sheet Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Reminyl work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Reminyl
IS 17 October 2011 Information sheet Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Reminyl work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Reminyl
U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets. Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc.
 U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc. Unmet Need in Moderate to Severe Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Ongoing clinical deterioration
U.S. Scientific Update Aricept 23 mg Tablets Dr. Lynn Kramer President NeuroScience Product Creation Unit Eisai Inc. Unmet Need in Moderate to Severe Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Ongoing clinical deterioration
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa )
 Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia
 Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine (review) and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease (amended)
 Issue date: November 2006 (amended September 2007, August 2009) Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine (review) and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease (amended) Includes a review of NICE
Issue date: November 2006 (amended September 2007, August 2009) Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine (review) and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease (amended) Includes a review of NICE
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD)
 SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Version: 3 Date Approved: June 2011 Review
SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine Clinical Indication: Treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Version: 3 Date Approved: June 2011 Review
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonist Memantine (CWM TAF ONLY)
 Bro Taf Localities Drugs & Therapeutics Committee SHARED CARE Drugs: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Donepezil, Rivastigmine and Galantamine (Cardiff and Vale and Cwm Taf) Protocol No. CV 52 N-methyl-D-aspartate
Bro Taf Localities Drugs & Therapeutics Committee SHARED CARE Drugs: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Donepezil, Rivastigmine and Galantamine (Cardiff and Vale and Cwm Taf) Protocol No. CV 52 N-methyl-D-aspartate
Emergency Room Treatment of Psychosis
 OVERVIEW The term Lewy body dementias (LBD) represents two clinical entities dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson s disease dementia (PDD). While the temporal sequence of symptoms is different
OVERVIEW The term Lewy body dementias (LBD) represents two clinical entities dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson s disease dementia (PDD). While the temporal sequence of symptoms is different
Long Term Care Formulary HCD - 09. Anti-Dementia Drugs (e.g. donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, memantine)
 1 of 8 USE OF CHOLINESTERASE (AChE) INHIBITORS The cholinesterase inhibitor anti-dementia drugs are indicated for the symptomatic treatment of patients with mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer s
1 of 8 USE OF CHOLINESTERASE (AChE) INHIBITORS The cholinesterase inhibitor anti-dementia drugs are indicated for the symptomatic treatment of patients with mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer s
Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia
 Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
2012 Medical School for Actuaries Nov. 6-7, 2012 Session #1: Alzheimer s Disease
 2012 Medical School for Actuaries Nov. 6-7, 2012 Session #1: Alzheimer s Disease Dylan Wint, M.D. ALZHEIMER DISEASE Dylan Wint, M.D. Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health DEFINITIONS Cognitive related to thinking,
2012 Medical School for Actuaries Nov. 6-7, 2012 Session #1: Alzheimer s Disease Dylan Wint, M.D. ALZHEIMER DISEASE Dylan Wint, M.D. Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health DEFINITIONS Cognitive related to thinking,
Being an advocate for good care. Useful medications What to expect When to be concerned
 Being an advocate for good care Useful medications What to expect When to be concerned Common Medical Questions 1. What medications are available to help with memory loss? Cholinesterase Inhibitors The
Being an advocate for good care Useful medications What to expect When to be concerned Common Medical Questions 1. What medications are available to help with memory loss? Cholinesterase Inhibitors The
Alzheimer s disease. What is Alzheimer s disease?
 Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 38 Alzheimer s Disease
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 38 Alzheimer s Disease Outline of Today s Lecture Why is Alzheimer s disease a problem? What is Alzheimer s Disease? What causes Alzheimer s disease? How can
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 38 Alzheimer s Disease Outline of Today s Lecture Why is Alzheimer s disease a problem? What is Alzheimer s Disease? What causes Alzheimer s disease? How can
Staging and Treatment of Dementia
 Staging and Treatment of Dementia Ami Hall DO 10/25/14 1 Objectives What are the two most common types of dementias seen in a primary care office How are they staged What treatments are available Definition
Staging and Treatment of Dementia Ami Hall DO 10/25/14 1 Objectives What are the two most common types of dementias seen in a primary care office How are they staged What treatments are available Definition
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD. Pharmacological interventions. Anti-dementia drugs. Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence
 Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Pharmacotherapy of BPSD Abhilash K. Desai MD Medical Director Alzheimer s Center of Excellence Pharmacological interventions Reducing medication errors. Reducing potentially inappropriate medication prescription.
Update on Treatment of the Dementias
 Update on Treatment of the Dementias Mark Pippenger, MD Behavioral Neurology Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures I will be discussing off-label
Update on Treatment of the Dementias Mark Pippenger, MD Behavioral Neurology Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures I will be discussing off-label
Everyone has mild memory lapses from time to time. You go
 Coping With Memory Loss Everyone has mild memory lapses from time to time. You go from the kitchen to the bedroom to get something, only to find yourself wondering what you needed. You can t find your
Coping With Memory Loss Everyone has mild memory lapses from time to time. You go from the kitchen to the bedroom to get something, only to find yourself wondering what you needed. You can t find your
Dementia. Your medicine. Information for you. Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa
 Dementia Your medicine Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats
Dementia Your medicine Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats
Medication for Dementia (Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors)
 Older People s Mental Health Service Medication for Dementia (Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors) August 2011 ^ ãéãäéê çñ `~ãäêáçöé råáîéêëáíó eé~äíü m~êíåéêë What are they? A group of medications used to
Older People s Mental Health Service Medication for Dementia (Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors) August 2011 ^ ãéãäéê çñ `~ãäêáçöé råáîéêëáíó eé~äíü m~êíåéêë What are they? A group of medications used to
Shared Care Protocol for the Prescription of Memantine for Alzheimer s disease
 Shared Care Protocol for the Prescription of Memantine for Alzheimer s disease 1. REFERRAL CRITERIA Patients of any age that are suspected to be suffering from moderate to severe Alzheimer s disease will
Shared Care Protocol for the Prescription of Memantine for Alzheimer s disease 1. REFERRAL CRITERIA Patients of any age that are suspected to be suffering from moderate to severe Alzheimer s disease will
NHS ONEL and NELFT Shared Care Guidelines. Management of medications for Alzheimer s disease. Patient Name : Date of Birth: NHS No:
 NHS ONEL and NELFT Shared Care Guidelines Management of medications for Alzheimer s disease DOCUMENT TO BE SCANNED INTO ELECTRONIC RECORDS AND FILED IN NOTES Patient Name : Date of Birth: NHS No: Name
NHS ONEL and NELFT Shared Care Guidelines Management of medications for Alzheimer s disease DOCUMENT TO BE SCANNED INTO ELECTRONIC RECORDS AND FILED IN NOTES Patient Name : Date of Birth: NHS No: Name
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 23 March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta217
 Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease Technology appraisal guidance Published: 23 March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta217 NICE 2011. All rights reserved.
Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease Technology appraisal guidance Published: 23 March 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta217 NICE 2011. All rights reserved.
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: donepezil The pharmacological management of Alzheimer s disease: The place of donepezil 28 BPJ Issue 30
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: donepezil The pharmacological management of Alzheimer s disease: The place of donepezil 28 BPJ Issue 30 Donepezil to be funded for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease As the world
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: donepezil The pharmacological management of Alzheimer s disease: The place of donepezil 28 BPJ Issue 30 Donepezil to be funded for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease As the world
Information for Prescribing Anti-dementia Drugs. November 2012
 Information for Prescribing Anti-dementia Drugs The aim of this document is to provide information about the prescribing of anti-dementia medication for adult patients with dementia following an assessment
Information for Prescribing Anti-dementia Drugs The aim of this document is to provide information about the prescribing of anti-dementia medication for adult patients with dementia following an assessment
Disclosures. Case: Ms. K. Case: Ms. K. Dementia: Considering When to Start, Stop, and Continue Medications 4/23/15. * Nothing to disclose
 Dementia: Considering When to Start, Stop, and Continue Medications * Nothing to disclose Disclosures Lianne Hirano, MD UW Division of Gerontology & Geriatric Medicine 4/23/15 Current Concepts in Drug
Dementia: Considering When to Start, Stop, and Continue Medications * Nothing to disclose Disclosures Lianne Hirano, MD UW Division of Gerontology & Geriatric Medicine 4/23/15 Current Concepts in Drug
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE Title: The prescribing and monitoring of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer s Disease. Scope: Pennine Care NHS Foundation Trust NHS
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE Title: The prescribing and monitoring of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer s Disease. Scope: Pennine Care NHS Foundation Trust NHS
The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s
 10:15am - 11:15am: Breakout 2 - Mental Health Option B: The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s ACPE UAN 0107-0000-10-013-L01-P 0.1 CEU/1.0 Hr. Activity Type: Application-Based
10:15am - 11:15am: Breakout 2 - Mental Health Option B: The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s ACPE UAN 0107-0000-10-013-L01-P 0.1 CEU/1.0 Hr. Activity Type: Application-Based
Dementa Formulary Guidance [v1.0]
![Dementa Formulary Guidance [v1.0] Dementa Formulary Guidance [v1.0]](/thumbs/29/13622067.jpg) Dementa Formulary Guidance [v1.0] 1. Introduction These Guidelines are intended for routine use. However there will be instances where they are not suitable for the patient you are managing, where more
Dementa Formulary Guidance [v1.0] 1. Introduction These Guidelines are intended for routine use. However there will be instances where they are not suitable for the patient you are managing, where more
Prescribing Framework for Donepezil in the Treatment and Management of Dementia
 Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Prescribing Framework for Donepezil in the Treatment and Management of Dementia Patients Name:.. NHS Number: Patients Address:... (Use addressograph sticker) GP
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Prescribing Framework for Donepezil in the Treatment and Management of Dementia Patients Name:.. NHS Number: Patients Address:... (Use addressograph sticker) GP
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Alzheimer s disease. Information sheet
 IS27 September 2003 Information sheet Alzheimer s disease Introduction This information sheet is for people with early Alzheimer s disease who want to know more about their illness, and for carers of people
IS27 September 2003 Information sheet Alzheimer s disease Introduction This information sheet is for people with early Alzheimer s disease who want to know more about their illness, and for carers of people
basics of alzheimer s disease What it is and what you can do
 basics of alzheimer s disease What it is and what you can do What is Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s (AHLZ-high-merz) is a disease of the brain that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior.
basics of alzheimer s disease What it is and what you can do What is Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s (AHLZ-high-merz) is a disease of the brain that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior.
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function
 Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
Alzheimer Disease Pharmacologic Treatment and Treatment Research Lon S. Schneider, MD, MS
 Review Article Alzheimer Disease Pharmacologic Treatment and Treatment Research Lon S. Schneider, MD, MS ABSTRACT Purpose of Review: This article reviews marketed pharmacologic treatments for Alzheimer
Review Article Alzheimer Disease Pharmacologic Treatment and Treatment Research Lon S. Schneider, MD, MS ABSTRACT Purpose of Review: This article reviews marketed pharmacologic treatments for Alzheimer
CEN Outreach Neurological Disorders
 CEN Outreach Neurological Disorders Migraine, Mul,ple Sclerosis, Alzheimer s Disease Migraine Migraine is the most common neurological disorder in the developed world Almost 1 in 5 Americans will have
CEN Outreach Neurological Disorders Migraine, Mul,ple Sclerosis, Alzheimer s Disease Migraine Migraine is the most common neurological disorder in the developed world Almost 1 in 5 Americans will have
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia
 Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
Clinical Audit: Prescribing antipsychotic medication for people with dementia Trust, team and patient information Q1. Patient's DIS number... Q2. Patient s residence: Home Residential Home Nursing Home
Treatments for Major Depression. Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are:
 Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Dementias have become a major public health concern. Clinical Guidelines
 Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Effectiveness of Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine for Treating Dementia: Evidence Review for a Clinical Practice Guideline Parminder Raina, PhD; Pasqualina
Annals of Internal Medicine Clinical Guidelines Effectiveness of Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine for Treating Dementia: Evidence Review for a Clinical Practice Guideline Parminder Raina, PhD; Pasqualina
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Health Information Sheet
 Health Information Sheet What is depression? Depression -- How Medicine Can Help Depression is a medical illness like diabetes or high blood pressure. It affects about 17% of people at some time in their
Health Information Sheet What is depression? Depression -- How Medicine Can Help Depression is a medical illness like diabetes or high blood pressure. It affects about 17% of people at some time in their
Adjunctive psychosocial intervention. Conditions requiring dose reduction. Immediate, peak plasma concentration is reached within 1 hour.
 Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for Alzheimer s disease
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for Alzheimer s disease NICE technology appraisal guidance advises on when and
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for Alzheimer s disease NICE technology appraisal guidance advises on when and
SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION Office of Disability Adjudication and Review DECISION JURISDICTION AND PROCEDURAL HISTORY
 P-6 SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION Office of Disability Adjudication and Review DECISION IN THE CASE OP Kristina Marie Townsend (Claimant) (Wage Earner) CLAIM FOR Period of Disability and Disability Insurance
P-6 SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION Office of Disability Adjudication and Review DECISION IN THE CASE OP Kristina Marie Townsend (Claimant) (Wage Earner) CLAIM FOR Period of Disability and Disability Insurance
How To Write Long Term Care Insurance
 By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression
 Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire. Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor?
 St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor? Who referred you to the MS Center? List any other doctors you see: Reason you have
St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor? Who referred you to the MS Center? List any other doctors you see: Reason you have
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over
 Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Financial Advisors and Alzheimer s Disease: What You Need to Know
 Financial Advisors and Alzheimer s Disease: What You Need to Know In today s aging society, with people living longer lives, chances are good that you ll be called upon to assist clients who have Alzheimer
Financial Advisors and Alzheimer s Disease: What You Need to Know In today s aging society, with people living longer lives, chances are good that you ll be called upon to assist clients who have Alzheimer
Alzheimer's: The Latest Assessment and Treatment Strategies
 Questions from chapter 1 Alzheimer's: The Latest Assessment and Treatment Strategies 1) What is a loss of cognitive and intellectual powers without changes in consciousness. a) dementia b) delusions c)
Questions from chapter 1 Alzheimer's: The Latest Assessment and Treatment Strategies 1) What is a loss of cognitive and intellectual powers without changes in consciousness. a) dementia b) delusions c)
Alzheimer s Disease 2009. Alzheimer s Disease. Markets, Pipeline and Opportunities. April 2009. By John Bates Ph.D. 1 Copyright 2009 Biopharm Reports
 Alzheimer s Disease Markets, Pipeline and Opportunities April 2009 By John Bates Ph.D 1 About the Author John Bates is a consultant and author in the drug markets and R&D fields. After a first degree in
Alzheimer s Disease Markets, Pipeline and Opportunities April 2009 By John Bates Ph.D 1 About the Author John Bates is a consultant and author in the drug markets and R&D fields. After a first degree in
Depression Flow Chart
 Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Travel to Africa 2005. David V. Diamond, MD MIT Medical Department
 Travel to Africa 2005 David V. Diamond, MD MIT Medical Department 1 General Advice: Overall risks are low for diseases other than Traveler's diarrhea Preventative measures to avoid exposure to mosquito
Travel to Africa 2005 David V. Diamond, MD MIT Medical Department 1 General Advice: Overall risks are low for diseases other than Traveler's diarrhea Preventative measures to avoid exposure to mosquito
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance
 Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Karen Drexler, M.D. ALCOHOLISM AND DEPRESSION
 Karen Drexler, M.D. for the DUMC Alcohol Awareness Task Force ALCOHOLISM AND DEPRESSION Overview What is major depression? What is alcohol dependence? Does depression lead to alcohol dependence? Does alcohol
Karen Drexler, M.D. for the DUMC Alcohol Awareness Task Force ALCOHOLISM AND DEPRESSION Overview What is major depression? What is alcohol dependence? Does depression lead to alcohol dependence? Does alcohol
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis. Managing Specific Issues
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing Specific Issues Feeling blue The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky. True depression
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing Specific Issues Feeling blue The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky. True depression
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Cerdelga (eliglustat)
 EMA/743948/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Cerdelga (eliglustat) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Cerdelga, which details the measures to be taken in order to
EMA/743948/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Cerdelga (eliglustat) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Cerdelga, which details the measures to be taken in order to
Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury
 Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury The consequences of a brain injury on any individual, family or relationship are far reaching. A brain injury not only impacts
Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury The consequences of a brain injury on any individual, family or relationship are far reaching. A brain injury not only impacts
INTRODUCTION TO TRAINING
 DEMENTIA TRAINING FOR CAREGIVERS BY LINDA THOMSON LPN/ ADMINISTRATOR ALF INTRODUCTION TO TRAINING IDENTIFY WHAT NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDERS ARE STAGES HOW DO WE COMMUNICATE TO PERSON WITH DEMENTIA BEHAVIORS
DEMENTIA TRAINING FOR CAREGIVERS BY LINDA THOMSON LPN/ ADMINISTRATOR ALF INTRODUCTION TO TRAINING IDENTIFY WHAT NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDERS ARE STAGES HOW DO WE COMMUNICATE TO PERSON WITH DEMENTIA BEHAVIORS
Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research
 Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research Bryce B. Reeve, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Health Policy and Management Member, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center bbreeve@email.unc.edu Standardized,
Enhancing the Child s Voice in Clinical Care and Research Bryce B. Reeve, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Health Policy and Management Member, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center bbreeve@email.unc.edu Standardized,
Major Depression. What is major depression?
 Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Testosterone Therapy for Women
 Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR TREATMENT OF DEMENTIA 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR TREATMENT OF DEMENTIA 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR TREATMENT OF DEMENTIA 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration
Progression MIDDLE STAGE. What is Alzheimer s disease?
 Progression MIDDLE STAGE This document is one in a five-part series on the stages of Alzheimer s disease and is written for the person with the disease, their family and caregivers. The middle stage of
Progression MIDDLE STAGE This document is one in a five-part series on the stages of Alzheimer s disease and is written for the person with the disease, their family and caregivers. The middle stage of
How To Treat An Elderly Patient
 1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
Dementia with Lewy bodies
 IS 18 April 2011 Information sheet Dementia with Lewy bodies Introduction... 1 Key points... 1 What is dementia with Lewy bodies?... 1 How many people are affected by DLB?.. 2 What is the cause?... 2 Symptoms...
IS 18 April 2011 Information sheet Dementia with Lewy bodies Introduction... 1 Key points... 1 What is dementia with Lewy bodies?... 1 How many people are affected by DLB?.. 2 What is the cause?... 2 Symptoms...
Barbara Cadario, B.Sc.(Hon), B.Sc.Phm., M.Sc. Junior Editor: Karen L.A. Wlock, B.Sc.(Pharm.) - Memantine This edition edited by: B.
 Volume 28 (1) 2008 Senior Editor: Contents Barbara Cadario, B.Sc.(Hon), B.Sc.Phm., M.Sc. - Dementia Therapy Junior Editor: Karen L.A. Wlock, B.Sc.(Pharm.) - Memantine This edition edited by: B. Cadario
Volume 28 (1) 2008 Senior Editor: Contents Barbara Cadario, B.Sc.(Hon), B.Sc.Phm., M.Sc. - Dementia Therapy Junior Editor: Karen L.A. Wlock, B.Sc.(Pharm.) - Memantine This edition edited by: B. Cadario
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole)
 EMA/303592/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen, which details the measures
EMA/303592/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen (aripiprazole) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Aripiprazole Pharmathen, which details the measures
IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology
 Print ISSN 2319-2003 Online ISSN 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology doi: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20150415 Research Article A prospective open-label randomized comparative
Print ISSN 2319-2003 Online ISSN 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology doi: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20150415 Research Article A prospective open-label randomized comparative
Ultram (tramadol), Ultram ER (tramadol extended-release tablets); Conzip (tramadol extended-release capsules), Ultracet (tramadol / acetaminophen)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.02.35 Subject: Tramadol Acetaminophen Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Tramadol Acetaminophen
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.02.35 Subject: Tramadol Acetaminophen Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Tramadol Acetaminophen
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies
 Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
Local Clinical Trials
 Local Clinical Trials The Alzheimer s Association, Connecticut Chapter does not officially endorse any specific research study. The following information regarding clinical trials is provided as a service
Local Clinical Trials The Alzheimer s Association, Connecticut Chapter does not officially endorse any specific research study. The following information regarding clinical trials is provided as a service
Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments
 Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments for Opiate and Alcohol Use Disorders Richard N. Whitney, MD Medical Director Addiction Services Shepherd Hill Newark, Ohio Medication Assisted Treatment
Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments for Opiate and Alcohol Use Disorders Richard N. Whitney, MD Medical Director Addiction Services Shepherd Hill Newark, Ohio Medication Assisted Treatment
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
How to identify, approach and assist employees with young onset dementia: A guide for employers
 How to identify, approach and assist employees with young onset dementia: A guide for employers What is dementia? Dementia involves the decline of cognitive functions. Young Onset Dementia, also known
How to identify, approach and assist employees with young onset dementia: A guide for employers What is dementia? Dementia involves the decline of cognitive functions. Young Onset Dementia, also known
NEW PATIENT CLINICAL INFORMATION FORM. Booth Gardner Parkinson s Care & Movement Disorders Center Evergreen Neuroscience Institute
 NEW PATIENT CLINICAL INFORMATION FORM Booth Gardner Parkinson s Care & Movement Disorders Center Evergreen Neuroscience Institute Date: Name: Referring Doctor: How did you hear about us? NWPF Your Physician:
NEW PATIENT CLINICAL INFORMATION FORM Booth Gardner Parkinson s Care & Movement Disorders Center Evergreen Neuroscience Institute Date: Name: Referring Doctor: How did you hear about us? NWPF Your Physician:
10 warning signs of alzheimer s disease
 10 warning signs of alzheimer s disease the compassion to care, the leadership to conquer Your memory often changes as you grow older. But memory loss that disrupts daily life is not a typical part of
10 warning signs of alzheimer s disease the compassion to care, the leadership to conquer Your memory often changes as you grow older. But memory loss that disrupts daily life is not a typical part of
Mental health issues in the elderly. January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca
 Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR:
 PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
A G U I D E F O R U S E R S N a l t r e x o n e U
 A GUIDE FOR USERS UNaltrexone abstinence not using a particular drug; being drug-free. opioid antagonist a drug which blocks the effects of opioid drugs. dependence the drug has become central to a person
A GUIDE FOR USERS UNaltrexone abstinence not using a particular drug; being drug-free. opioid antagonist a drug which blocks the effects of opioid drugs. dependence the drug has become central to a person
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Financial advisors and Alzheimer s disease: What you need to know
 Financial advisors and Alzheimer s disease: What you need to know In today s aging society, with people living longer lives, chances are high that you ll be called upon to assist clients who are caring
Financial advisors and Alzheimer s disease: What you need to know In today s aging society, with people living longer lives, chances are high that you ll be called upon to assist clients who are caring
DEMENTIA EDUCATION & TRAINING PROGRAM
 The pharmacological management of aggression in the nursing home requires careful assessment and methodical treatment to assure maximum safety for patients, nursing home residents and staff. Aggressive
The pharmacological management of aggression in the nursing home requires careful assessment and methodical treatment to assure maximum safety for patients, nursing home residents and staff. Aggressive
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease
 Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Intellectual Symptoms Amnesia: Loss of memory function
 Definition of Dementia (de mens) Latin for out of mind Permanent loss of multiple intellectual functions Alois Alzheimer first described this disease in 1906 in a brain specimen from an autopsy. Alzheimer
Definition of Dementia (de mens) Latin for out of mind Permanent loss of multiple intellectual functions Alois Alzheimer first described this disease in 1906 in a brain specimen from an autopsy. Alzheimer
Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Stephen L. Benson, Psy.D. November 17, 2015
 Stephen L. Benson, Psy.D. November 17, 2015 Biomedical view of dementia Lyman (1989) suggested that the biomedical view of dementia includes three features: First, dementia is pathological and individual,
Stephen L. Benson, Psy.D. November 17, 2015 Biomedical view of dementia Lyman (1989) suggested that the biomedical view of dementia includes three features: First, dementia is pathological and individual,
Dementia: Delivering the Diagnosis
 Dementia: Delivering the Diagnosis Daniel D. Christensen, M.D. Clinical Professor of Psychiatry Clinical Professor of Neurology Adjunct Professor of Pharmacology University of Utah Diagnosing Dementia
Dementia: Delivering the Diagnosis Daniel D. Christensen, M.D. Clinical Professor of Psychiatry Clinical Professor of Neurology Adjunct Professor of Pharmacology University of Utah Diagnosing Dementia
