ARC Epidemiology Unit, The University of Manchester, Manchester 2. Norfolk Arthritis Register, Norfolk 3. Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK
|
|
|
- Randell Simmons
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LUCRĂRI ORIGINALE THE ROLE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS GENETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY MARKERS IN THE PREDICTION OF EROSIVE DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH EARLY INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS REGISTER Darren Plant 1, Wendy Thomson 1, Mark Lunt 1, Edward Flynn 1, Paul Martin 1, Steven Eyre 1, Tracey Farragher 1, Diane Bunn 2,3, Jane Worthington 1, Deborah Symmons 1, Anne Barton 1 1 ARC Epidemiology Unit, The University of Manchester, Manchester 2 Norfolk Arthritis Register, Norfolk 3 Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK Summary Objectives. Recent whole-genome and candidate gene association studies in RA have identifi ed a number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that predispose to disease with moderate risk. It remains poorly understood how recently identifi ed genetic factors may contribute to RA severity. We therefore sought to investigate the role of recently identifi ed RA susceptibility SNP markers in predicting erosive outcome in patients with recent-onset infl ammatory polyarthritis (IP). Methods. DNA and X-ray data were available for 1049 patients who were registered between 1990 and 2003 with the Norfolk Arthritis Register (NOAR); a primary care-based inception cohort of patients with recent-onset IP. Demographic and clinical data were recorded at inclusion, and at yearly assessments thereafter. Patients were genotyped for 18 SNP markers. The presence of serum anti citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPAs) was assessed in samples collected at inclusion to the NOAR. The association of serological and genetic markers with poor radiological (Larsen) score at Years 1 and 5, and erosions at Years 1 and 5 was investigated. Results. Baseline ACPA positivity was associated with erosive disease and higher radiological damage. SNP markers within the TRAF1/C5 locus were associated with erosive disease at Year 1 (rs : odds ratio (OR) 1.53 (95% CI 1.14, 2.05)) and Year 5 (rs : OR 1.47 (95% CI 1.07, 2.02)). None of the SNP markers tested was associated with Larsen score. Conclusion. Our results are in keeping with a previous report and suggest that the TRAF1/C5 region is associated with risk of development of radiological erosions in IP/RA patients. The fi nding requires replication in other large data sets. Key words: genetic association, erosions, infl ammatory polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis INTRODUCTION Increasingly, physicians would like to identify which patients presenting with inflammatory joint disease are likely to develop severe disease before they satisfy ACR classification criteria for RA, so that appropriate treatment can be introduced before irreversible damage occurs. The importance of antibodies directed against citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPAs) in this regard has been increasingly appreciated in recent years (1-5). For example, we have reported previously that, in the Norfolk Arthritis Register (NOAR), an inception cohort of patients with inflammatory polyarthritis (IP), only 45% of whom satisfied ACR classification criteria for RA at baseline, the presence of ACPA was strongly associated with the development of erosions by 5 years (1). However, ACPA do not Sursa: Oxford Journals Medicine, Rheumatology. Volume 50, Issue1, Pp REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, An
2 228 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN 2010 perfectly correlate with severe outcome. For example, in the same study, there were a significant minority of patients who did not have these antibodies at baseline but developed severe disease, as assessed by radiological erosions (1). Hence, the identification of markers that would refine the accuracy of ACPA in predicting disease severity would be an important clinical advance. Genetic factors play an important role in determining development of persistent and destructive IP, and are estimated to account for 50 60% of disease susceptibility. In patients of European ancestry, the strongest genetic susceptibility effects are conferred by the HLA-DRB1 locus on chromosome 6 (6) (the shared epitope (SE)) and the protein tyrosine phosphatase 22 (PTPN22) gene on chromosome 1p13 (7). In terms of disease outcome, the HLA-DRB1 locus is associated with the development of radiological erosions (8). The functional susceptibility single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within PTPN22 does not appear to associate with disease out come in persistent IP or RA (9). Recent whole-genome and candidate gene disease association studies have identified further non-hla RA susceptibility loci (i.e. 6q23, TRAF1/C5, STAT4, IL2RB, KIF5A, PRKCQ, IL2_IL21, CD226, CCL21, CD40, CTLA4, IL2RA, AFF3 and IL7R), defined by SNP markers that associate with susceptibility with low-to-moderate risk (10-19). What is less clearly understood, however, is the role of these SNP susceptibility markers in determining disease outcome as measured by the presence of radiographic erosions in patients with persistent IP. Using a large primary care-based inception cohort of patients with recent-onset IP, we examined the relationship of baseline prognostic factors, including ACPA positivity, carriage of HLA-SE risk alleles and the newly confirmed RA SNP susceptibility markers, with radiological erosion at 1 and 5 years of follow-up. METHODS Subjects The NOAR is a primary care-based inception cohort of patients with recent-onset IP. Further details of this register are described elsewhere (20). In brief, patients aged >16 years at symptom onset, who had synovitis of two or more joints, lasting >4 weeks, and whose symptom onset was after 1 January 1990, are recruited from general practitioners and rheumatologists in the catchment area, formerly covered by the Norwich Health Authority (UK). Ethical approval was obtained from the Norwich District Health Authority Research Ethics Committee, and all participants gave informed consent. Clinical and demographic data were collected by a research nurse via a structured interview and clinical exa mi nation shortly after registration (baseline). In addition, DNA and serum samples were collected to permit genetic and serological studies. Excluded from the study were patients who received a clinical diagnosis other than RA, IP, PsA or post-viral arthritis at baseline assessment or subsequent follow-up. Data collection Demographic data included age, date of symptom onset and gender. Clinical data included information on DMARD and steroid therapy. X-rays of the hands and feet were taken at 1 and/or 2 years in patients who satisfied ACR criteria for RA (or would satisfy ACR criteria for RA should evidence of erosions be detected), and at 5 years unselectively. They were read independently by two observers using the Larsen method (21) with a third observer arbitrating in case of disagreement. ACPAs were measured using the CCP2 detection kit (positivity >5 U/ml; Axis-Shield, Cambridgeshire, UK) using baseline serum samples. The presence of HLA-SE copy number (0, 1 or 2 copies) was detected using a semi-automated reverse hybridization method (Dynal Biotech, Wirral, UK). Genotyping Eighteen SNPs were selected for genotyping using Sequenom MassArray technology according to the manufacturer s instructions, using iplex chemistry (Sequenom, Hamburg, Germany). The SNPs were markers associated with RA susceptibility in cohorts tested by our group and others and consisted of: rs (AFF3), rs (CCL21), rs (CD226), rs (CD40), rs and rs (CTLA4), rs (IL2/IL21), rs (IL2RA), rs (IL2RB), rs (IL7R), rs (KIF5A), rs (PRKCQ), rs (STAT4), rs , rs and rs (6q23), rs and rs (TRAF1/C5). Only those SNPs with a genotype success rate of >90% were included in the analysis. Statistical analysis Univariate analysis The IP patients with X-ray data at 5 years (5-year IP cohort) were unselected and are most representative
3 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN of those in whom the identification of risk factors to inform decisions regarding treatment would be most helpful. First, therefore, logistic regression was used to investigate the association of potential prognostic markers with erosive disease, as a binary outcome, by the 5-year follow-up. Patients were defined as having erosive disease if they had a Larsen score >2 in at least one joint of the hands or feet. Secondly, in order to determine whether markers were associated with the severity or extent of erosive disease in those with erosions, negative binomial regression models were used to investigate the association between potential prognostic markers and Larsen scores by Year 5 in patients with confirmed erosive disease. Negative binomial regression models were employed to model count data, in preference to Poisson regression, to account for any over-dispersion of variance. The subgroup of patients who satisfied the ACR criteria for RA by the fifth anniversary follow-up (5-year RA subgroup) was analysed separately (22). The subgroup of patients w ith X-ray data at 1 year (1-year IP cohort) are not an unselected group. X-rays were only undertaken at Year 1 if the subjects had met or could meet ACR classification criteria for RA. Hence, they represent a more severe subset of all patients presenting with IP and it was hypothesized that markers with evidence of association with erosions in the IP group as a whole may show stronger evidence for association in this more severe subgroup. Therefore, the same analysis was undertaken investigating markers for association with erosions and Larsen score by Year 1 in the 1-year IP cohort as detailed above for the 5-year IP cohort. All the analyses were repeated after adjustment for treatment (i.e. ever treated with DMARDs/steroids following symptom onset) to determine whether this materially altered the findings. Multivariate analysis ACPA positivity is strongly predictive of radiographic erosions in RA (1-5); therefore, SNP markers were investigated in the context of ACPA status. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to investigate the role of SNP markers in predicting erosions at Years 5 and 1 following adjustment for ACPA status, and to investigate SNP markers in the stratum of patients who were either positive or negative for these antibodies. In addition, SNP markers were investigated in the context of HLA-SE allele carriage (i.e. carriage of at least one SE allele). All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 9 (2005. Stata Statistical Software: Release 9; Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). RESULTS Study population characteristics Genotyping data were available from 2611 IP patients, of which 2538 passed genotyping quality control (97% success). Radiological data were available for 1378 patients. One thousand and fortynine patients had both genotype and X-ray data and remained available to study. Six hundred and sixtythree IP patients had X-ray data available for Year 5 (5-year IP cohort) of whom 489 patients satisfied ACR criteria for RA (5-year RA subgroup), while 761 IP patients had X-ray data available for Year 1 (1-year IP cohort). Three hundred and seventy-five patients were X-rayed at both time points of 234 patients who were initially non-erosive (by Year 1), 80 (34%) developed erosive disease by Year 5 (all 375 patients satisfied ACR criteria for RA by 5-year follow-up and were included in the 5-year analysis). The characteristics of these patients are summarized in Table 1. TABLE 1. Summary of cohort characteristics
4 230 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN 2010 Radiological erosions by Year 5 We have previously reported that the presence of ACPA is associated with the development of erosions (1). In this extended data set, we again found that ACPA positivity was strongly associated with erosive disease in the 5-year IP cohort as a whole and in the 5-year RA subgroup (Table 2; for complete table of results, see supplementary table 1, available as supplementary data at Rheumatology Online). As expected, due to the strong correlation between ACPA and HLA-SE, carriage of HLA-SE alleles also strongly associated with erosive disease at 5 years (Table 2). Only 2 of the 18 SNPs tested showed a trend towards association with the presence of erosions by Year 5. Both SNPs map to the TRAF1/C5 locus and the minor allele of both markers is associated with susceptibility to RA in multiple populations (23). The SNP marker rs (TRAF1/C5) was asso ciated, by carriage of the minor allele, with erosive disease by the 5-year follow-up in both the 5-year IP cohort as a whole and the RA subset (Table 2). The other SNP, rs , showed a trend towards association but this did not achieve statistical signi ficance (Table 2). Moderate linkage disequilibrium exists between rs and rs , R 2 = 0.67 (24). Adjustments for DMARD/steroid treatment did not materially alter these findings (analysis not shown). Although ACPA status, carriage of HLA-SE alleles and carriage of the minor allele of the SNP markers were associated with the presence of erosions by 5 years, only ACPA positivity and HLA- SE carriage were associated with higher Larsen score by Year 5 in both the 5-year IP cohort as a whole and in the 5-year RA subgroup (Table 3). There was no association of the SNP markers rs and rs with Larsen score by Year 5 (Table 3). Radiological erosions by year 1 As expected, ACPA and HLA-SE status also strongly associated with the development of erosions in the 1-year IP cohort (Table 2; for complete table of results, see supplementary table 1, available as supplementary data at Rheumat ology Online). Both the rs and rs TRAF1/C5 SNPs were associated, by carriage of the minor allele, with erosive disease at Year 1 (Table 2). The odds ratios (ORs) conferred by carriage of the minor allele were higher in the 1-year RA group compared with the 5-year IP cohort as a whole in keeping with our hypothesis that the 1-year IP cohort represents a more severe group (Table 2). However, this is unlikely to be an important effect, illustrated by extensive overlap in CIs between Years 1 and 5, and, in addition, the contrary was observed for ACPA positivity (Table 2). For both SNPs, carriage of one copy of the risk allele appeared to confer a higher risk of erosions than carriage of two copies when compared with carriage of no copies. However, there were low numbers of patients with two copies of TABLE 2. Association between prognostic markers and erosive disease
5 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN TABLE 3. Association between prognostic factors and Larsen score in patients with erosive disease either risk allele and a substantial overlap in CIs was observed. None of the other SNP markers tested showed association with erosions in this 1-year RA cohort. Multivariate analysis of genetic markers: ACPA status Multivariate logistic regression models were used to assess the improvement in predicting erosions in IP patients who carried the risk allele of either rs or rs , over and above that estimated from ACPA positivity alone. In the 5-year IP cohort, carriage of the risk allele for either rs (n = 572; OR 1.65 (95% CI 1.13, 2.42); P = 0.01) or rs (n = 571; OR 1.52 (95% CI 1.00, 2.29); P = 0.05) conferred risk of erosions in IP patients following adjustment for ACPA positivity, and effect sizes were similar in the ACPA-negative patients (n = 404; OR 1.52 (95% CI 0.98, 2.38); P = 0.06) and (n = 403; OR 1.42 (95% CI 0.88, 2.29); P = 0.15) were compared with the ACPA-positive subgroup (n = 168; OR 2.07 (95% CI 0.97, 4.40); P = 0.06) and (n = 168; OR 1.80 (95% CI 0.82, 3.90); P = 0.14) for rs and rs , respectively (difference in effect between patient stratum P = 0.50 for rs and P = 0.62 for rs ). Following adjustment for ACPA positivity, carriage of the risk allele of rs also predicted erosive disease in the 1-year IP cohort (n = 672; OR 1.62 (95% CI 1.13, 2.33); P = 0.009). Importantly, carriage of the minor allele conferred risk of erosions in ACPAnegative patients (n = 407; OR 2.30 (95% CI 1.39, 3.80); P = 0.001), but not in ACPA-positive patients (n = 265; OR 1.00 (95% CI 0.56, 1.79); P = 0.99) and this difference was significant (P = 0.03). The result was corroborated by receiver operating characteristic analysis in which inclusion of rs did not improve the diagnostic utility of ACPA positivity (analysis not shown). Similarly, carriage of the risk allele for rs was predictive of erosions at Year 1 following adjustment for ACPA positivity (n = 675; OR 1.48 (95% CI 1.06, 2.08); P = 0.02) and conferred risk of erosions in ACPA-negative patients (n = 408; OR 1.71 (95% CI 1.11, 2.65); P = 0.02), but not ACPA-positive patients (n = 267; OR 1.18 (95%CI 0.68, 2.04); P = 0.6). The difference was not significant (P = 0.3). Both rs and rs were investigated in the context of HLA-SE carriage to see if a statistical interaction between the genetic loci existed; however, none was detected (data not shown). DISCUSSION Recent large-scale whole-genome and candidate gene association studies have identified a number of SNP markers that reproducibly associate with RA susceptibility, substantially improving our understanding of the genetic component of disease susceptibility. While this is important, it is unlikely to have an immediate clinical impact unless these markers also associate with prognosis or treatment response. We hypothesized that genetic susceptibility markers may also be important predictors of outcome. In the current study, the SNP markers rs
6 232 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN 2010 and rs (TRAF1/C5) were associated with erosive disease (Table 2), but not with higher Larsen scores at either Year 1 or Year 5 in patients with erosive disease (i.e. Larsen score of >2 in at least one joint; Table 3). In contrast, ACPA positivity and carriage of HLA-SE were associated with the pre sence of erosions, Larsen score and with the number of eroded joints (data not shown). This suggests that, unlike ACPA status and carriage of HLA-SE, the TRAF1/C5 locus may predict those patients who are more likely to develop erosive disease, but not the severity or extent of erosions. It should be noted that in this investigation, 18 SNPs mapping to 14 loci were assessed for association with disease outcome resulting in multiple testing and the consequent potential of generating false positive results. No correction has been applied, so as not to preclude the identification of small putative effects, but, if it had, neither of the SNP markers would have achieved statistical significance at the corrected threshold (P < 0.003). However, the association of the TRAF1/C5 locus with erosive disease has previously been reported (with the SNP rs ; in R 2 = 1 with rs ) (25). Hence, the current findings provide further support that this locus is associated with disease outcome. In the current study, the effect seen at the rs SNP locus in patients homozygous for the risk allele was observed to be lower than that observed for heterozygotes, albeit with considerable overlap in the CIs. Although the effect at this locus is consistent with a dominant model, this pattern perhaps reflects the small number of observations in the homozygous patient group (Table 2). However, validation of association of the locus with disease severity is required in larger, independent data sets. Logistic regression analyses found that the TRAF1/ C5 genetic markers (rs and rs ) predict erosive disease independent of ACPA status; indeed, the effect appears stronger in ACPA-negative patients at Year 1. This could be more helpful clinically as this subgroup is often not treated as intensively as ACPA-positive patients. The presence of genetic risk alleles may highlight the potential for erosive damage and prompt clinicians to consider earlier, more aggressive treatment regimes. The sensitivity (80% for rs and 66% for rs ) and specificity (36% for rs and 46% for rs ) of genotyping at either locus, in ACPA-negative patients, to predict the development of erosions by Year 1 is too low to be clinically useful at the current time but, as more markers of severity are identified, this may become viable in the future. Failure to detect associations with the other susceptibility loci tested may reflect inadequate power. Assuming a 50% increase in risk of developing erosions, the study had 14 95% power to detect the effect of carriage of a susceptibility allele at eight of the loci tested (rs (14%), rs (64%), rs (80%), rs (88%), rs (90%), rs (91%), rs (94%) and rs (95%)) at Year 5 in IP patients, at the 5% significance level. There was >95% power for the remaining loci. The study therefore had limited power to detect modest effects due to the limited sample size, particularly for some of the subgroups analysed and may, therefore, represent false negative findings. For many of these regions, either multiple polymorphisms have been associated with suscep tibility and/or the true causal variants have not yet been identified resulting in a further loss in power to identify potential modest severity effects. National and international collaboration is likely to be required to establish large enough cohorts to fully explore genetic predictors of outcome. Alternatively, genetic susceptibility markers may differ from those contributing to disease severity. If this is true, there is a need for a separate wellpowered within-cohort genome-wide association study to identify genetic markers of outcome and to improve the predictive models over and above the presence of ACPA positivity alone. These data add more weight to the case for routine screening for ACPA in clinical practice in order to identify those patients who are likely to have a poor prognosis in terms of radiographic erosions. These data also add to the evidence that SNP markers within the TRAF1/C5 locus are associated with the risk of erosive disease and suggest that this effect is independent of ACPA. Acknowledgements Genotyping was performed by E.F., P.M. and S.E. D.P. and E.F. are supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme AutoCure funding. Funding: We thank the Arthritis Research Campaign for their support (ARC grant reference no ). This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust. Funding to pay the Open Access publication charges for this article was provided by the arthritis research campaign (grant no ). Disclosure statement: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
7 REVISTA ROMÂNĂ DE REUMATOLOGIE VOL. XIX NR. 4, AN REFERENCES 1. Bukhari M, Thomson W, Naseem H, et al The performance of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in predicting the severity of radiologic damage in inflammatory polyarthritis: results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56: De RL, Peene I, Hoffman IE, et al Rheumatoid factor and anticitrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic value, associations with radiological progression rate, and extra-articular manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63: Forslind K, Ahlmen M, Eberhardt K, Hafstrom I, Svensson B Prediction of radiological outcome in early rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: role of antibodies to citrullinated peptides (anti-ccp). Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63: Inanc N, Dalkilic E, Kamali S, et al Anti-CCP antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 2007;26: Quinn MA, Gough AK, Green MJ, et al Anti-CCP antibodies measured at disease onset help identify seronegative rheumatoid arthritis and predict radiological and functional outcome. Rheumatology 2006;45: Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1987;30: Begovich AB, Carlton VE, Honigberg LA, et al A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet 2004;75: Harrison B, Thomson W, Symmons D, et al The influence of HLA- DRB1 alleles and rheumatoid factor on disease outcome in an inception cohort of patients with early inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42: Naseem H, Thomson W, Silman A, Worthington J, Symmons D, Barton A The PTPN22*C1858T functional polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to inflammatory polyarthritis but neither this nor other variants spanning the gene is associated with disease outcome. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67: Barton A, Thomson W, Ke X, et al Rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility loci at chromosomes 10p15, 12q13 and 22q13. Nat Genet 2008;40: Barton A, Thomson W, Ke X, et al. Re-evaluation of putative rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility genes in the post-genome wide association study era and hypothesis of a key pathway underlying susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 2008;17: Barton A, Eyre S, Ke X, et al Identification of AF4/FMR2 family, member 3 (AFF3) as a novel rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility locus and confirmation of two further pan-autoimmune susceptibility genes. Hum Mol Genet 2009;18: Bowes J, Barton A Recent advances in the genetics of RA susceptibility. Rheumatology 2008;47: Hafler JP, Maier LM, Cooper JD, et al CD226 Gly307Ser association with multiple autoimmune diseases. Genes Immun 2008;10: Plenge RM, Seielstad M, Padyukov L, et al TRAF1-C5 as a risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 2007;357: Plenge RM, Cotsapas C, Davies L, et al Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2007;39: Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Lee AT, et al Common variants at CD40 and other loci confer risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2008;40: Thomson W, Barton A, Ke X, et al Rheumatoid arthritis association at 6q23. Nat Genet 2007;39: Zhernakova A, Alizadeh BZ, Bevova M, et al Novel association in chromosome 4q27 region with rheumatoid arthritis and confirmation of type 1 diabetes point to a general risk locus for autoimmune diseases. Am J Hum Genet 2007;81: Symmons DP, Silman AJ The Norfolk Arthritis Register (NOAR). Clin Exp Rheumatol 2003;21:S Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn 1977;18: Lunt M, Symmons DP, Silman AJ An evaluation of the decision tree format of the American College of Rheumatology 1987 classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: performance over five years in a primary care-based prospective study. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52: Patsopoulos NA, Ioannidis JP Susceptibility variants for rheumatoid arthritis in the TRAF1-C5 and 6q23 loci: a meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. Advance Access published May 15, 2009, doi: /ard International HapMap Project HapMap Genome Browser. ((9 March 2009, date last accessed)) Kurreeman FA, Padyukov L, Marques RB, et al A candidate gene approach identifies the TRAF1/C5 region as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Med 2007;4:e278. Vizitaţi site-ul SOCIETĂŢII ROMÂNE DE REUMATOLOGIE
Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean Populations
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 2, February 2009, pp 364 371 DOI 10.1002/art.24245 2009, American College of Rheumatology Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 2, February 2009, pp 364 371 DOI 10.1002/art.24245 2009, American College of Rheumatology Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean
Women s Hospital and The Broad Institute, Boston, Massachusetts; 3 Doyt L. Conn, MD: Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia; 4 Beth L.
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3547 3553 DOI 10.1002/art.27732 2010, American College of Rheumatology Most Common Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3547 3553 DOI 10.1002/art.27732 2010, American College of Rheumatology Most Common Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series
 Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri
 Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Correspondence to
Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Correspondence to
The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Yan Du Peking University People s Hospital 100044 Beijing CHINA
The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Yan Du Peking University People s Hospital 100044 Beijing CHINA
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE
 ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
Novel Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Locus at 22q12 Identified in an Extended UK Genome-Wide Association Study
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 24 30 DOI 10.1002/art.38196 2014 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 24 30 DOI 10.1002/art.38196 2014 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton
 Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton Biobanks why should we collect samples? Anti-TNF treatment in RA Cost approx. 8,000/person/year 30-40% RA patients do not respond Rare, serious
Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton Biobanks why should we collect samples? Anti-TNF treatment in RA Cost approx. 8,000/person/year 30-40% RA patients do not respond Rare, serious
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Medical Policy Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response
 Research Original Investigation Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response SebastienViatte, MD, PhD; Darren Plant, PhD; Buhm Han, PhD; Bo Fu,
Research Original Investigation Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response SebastienViatte, MD, PhD; Darren Plant, PhD; Buhm Han, PhD; Bo Fu,
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Outline. Personal profile & research interests. Rheumatology research in Ireland. Current standing. Future plans
 Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Viatte S, Plant D, Han B, et al. Association of HLA-DRB1 haplotypes with rheumatoid arthritis severity, mortality, and treatment response. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.3435.
Supplementary Online Content Viatte S, Plant D, Han B, et al. Association of HLA-DRB1 haplotypes with rheumatoid arthritis severity, mortality, and treatment response. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.3435.
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective. Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway
 Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Early identification and treatment - the Norwegian perspective Till Uhlig Dept of Rheumatology Diakonhjemmet Hospital Oslo, Norway Oslo Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry (ORAR) Very early Arthritis Clinic
Identification of BACH2 and RAD51B as Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Loci in a Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Data
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 65, No. 12, December 2013, pp 3058 3062 DOI 10.1002/art.38183 2013 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatism is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 65, No. 12, December 2013, pp 3058 3062 DOI 10.1002/art.38183 2013 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatism is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset
 Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset Lori B. Chibnik 1 *, Brendan T. Keenan 1, Jing Cui 2, Katherine P. Liao 2, Karen H. Costenbader 2, Robert
Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset Lori B. Chibnik 1 *, Brendan T. Keenan 1, Jing Cui 2, Katherine P. Liao 2, Karen H. Costenbader 2, Robert
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Modelling Genetic And Environmental Risk Factors Ian Scott Arthritis Research UK Clinical Research Fellow Declaration Of Interests: No Competing Interests Describe
Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Modelling Genetic And Environmental Risk Factors Ian Scott Arthritis Research UK Clinical Research Fellow Declaration Of Interests: No Competing Interests Describe
GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES. Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital
 GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital Autoimmune diseases Affects approximately 5 % of the population Results from an
GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital Autoimmune diseases Affects approximately 5 % of the population Results from an
Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments
 Rheumatology 5;(Suppl. ):iv9 iv Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments L. A. Criswell and P. K. Gregersen doi:.9/rheumatology/kei5 Most of
Rheumatology 5;(Suppl. ):iv9 iv Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments L. A. Criswell and P. K. Gregersen doi:.9/rheumatology/kei5 Most of
ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference. Conference Report
 ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference 1. Summary: Conference Report As Myositis is so rare, undertaking Myositis genetic research had proved extremely difficult prior to 2000, because
ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference 1. Summary: Conference Report As Myositis is so rare, undertaking Myositis genetic research had proved extremely difficult prior to 2000, because
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective
 Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective Noam Jacob, MD, Chaim O. Jacob, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies HLA Risk allele Key Points More
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective Noam Jacob, MD, Chaim O. Jacob, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies HLA Risk allele Key Points More
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mauro D Amato 1, Marco Zucchelli 1, Maria Seddighzadeh 2, Francesca Anedda 1,3, Staffan Lindblad 2, Juha Kere 1, Lars
Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mauro D Amato 1, Marco Zucchelli 1, Maria Seddighzadeh 2, Francesca Anedda 1,3, Staffan Lindblad 2, Juha Kere 1, Lars
Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the
 Chapter 5 Analysis of Prostate Cancer Association Study Data 5.1 Risk factors for Prostate Cancer Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the disease has
Chapter 5 Analysis of Prostate Cancer Association Study Data 5.1 Risk factors for Prostate Cancer Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the disease has
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis
 Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis & Axial Spondyloarthritis 奇 美 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 陳 宏 安 Rheumatoid arthritis Most common chronic inflammatory joint disease Multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis Published in the September 2010 Issues of A&Rand ARD Phases of the Project Phase 1 Data analysis Phase 2 Consensus process Predictors of
Mechanisms of Disease: genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers in the development of rheumatoid arthritis
 Mechanisms of Disease: genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers in the development of rheumatoid arthritis Lars Klareskog*, Leonid Padyukov, Johnny Lorentzen and Lars Alfredsson SUMMARY Rheumatoid
Mechanisms of Disease: genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers in the development of rheumatoid arthritis Lars Klareskog*, Leonid Padyukov, Johnny Lorentzen and Lars Alfredsson SUMMARY Rheumatoid
IL1A and IL1B: A Search For Network Marketing Agreements
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 7, July 2008, pp 1947 1957 DOI 10.1002/art.23592 2008, American College of Rheumatology A Broad Analysis of IL1 Polymorphism and Rheumatoid Arthritis Alyssa K. Johnsen,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 7, July 2008, pp 1947 1957 DOI 10.1002/art.23592 2008, American College of Rheumatology A Broad Analysis of IL1 Polymorphism and Rheumatoid Arthritis Alyssa K. Johnsen,
A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in Koreans
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 1, January 2006, pp 90 96 DOI 10.1002/art.21536 2006, American College of Rheumatology A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 1, January 2006, pp 90 96 DOI 10.1002/art.21536 2006, American College of Rheumatology A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit
 Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
Lack of association between TRAF1/C5 rs10818488 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis in Iranian population
 The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2013) 14, 63 67 Ain Shams University The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics www.ejmhg.eg.net www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lack of association
The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2013) 14, 63 67 Ain Shams University The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics www.ejmhg.eg.net www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lack of association
Rheumatoid Arthritis Laboratory Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis
 Clinical Focus C L N C A L F O C U S R H E U M AT O D A R T H R T S Rheumatoid Arthritis Laboratory Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis CLNCAL BACKGROUND Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease
Clinical Focus C L N C A L F O C U S R H E U M AT O D A R T H R T S Rheumatoid Arthritis Laboratory Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis CLNCAL BACKGROUND Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers. Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine
 Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis and the use of linkage and association studies to identify disease genes
 The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis and the use of linkage and association studies to identify disease genes Jane Worthington, Anne Barton and Sally L. John Arthritis Research Campaign Epidemiology
The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis and the use of linkage and association studies to identify disease genes Jane Worthington, Anne Barton and Sally L. John Arthritis Research Campaign Epidemiology
GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION
 From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION Chun Lai Too 杜 翠 麗 Stockholm 2012 On
From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION Chun Lai Too 杜 翠 麗 Stockholm 2012 On
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS VERSION 1 - REVIEW. Jeffrey Sparks Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School USA 25-Nov-2015
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
Name of Policy: Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Name of Policy: Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Policy #: 353 Latest Review Date: August 2011 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews
Name of Policy: Anti-CCP Testing for Rheumatoid Arthritis Policy #: 353 Latest Review Date: August 2011 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews
Media Release. Basel, 11 June 2009. RA patients with enhanced response identified
 Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence. of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of
 1 HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of psoriasis: a case control study Lotus Mallbris, MD, PhD, Katarina Wolk, MD, Fabio Sánchez
1 HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of psoriasis: a case control study Lotus Mallbris, MD, PhD, Katarina Wolk, MD, Fabio Sánchez
Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Original Policy Date January /2014
 MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 5, October, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.5.274 Review Article Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges Changsoo Kang Department
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 5, October, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.5.274 Review Article Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges Changsoo Kang Department
GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters
 GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters Michael B Miller , Michael Li , Gregg Lind , Soon-Young
GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters Michael B Miller , Michael Li , Gregg Lind , Soon-Young
How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado
 How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado Outline 1) Brief overview of natural history of RA and how current understanding of disease
How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado Outline 1) Brief overview of natural history of RA and how current understanding of disease
Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis
 Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis Y.H. Lee 1, S.-C. Bae 2 and G.G. Song 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of
Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis Y.H. Lee 1, S.-C. Bae 2 and G.G. Song 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of
IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production
 IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production Lisa M. Maier 1,2., Christopher E. Lowe 3., Jason Cooper 3, Kate Downes
IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production Lisa M. Maier 1,2., Christopher E. Lowe 3., Jason Cooper 3, Kate Downes
Heritability: Twin Studies. Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait
 TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records
 Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records ARTICLE Fina Kurreeman, 1,2,3 Katherine Liao, 1 Lori Chibnik,
Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records ARTICLE Fina Kurreeman, 1,2,3 Katherine Liao, 1 Lori Chibnik,
Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis. Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger
 Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger Psoriasis Chronic, inflammatory skin condition Characteristic lesions, can affect substantial proportion
Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger Psoriasis Chronic, inflammatory skin condition Characteristic lesions, can affect substantial proportion
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist
 Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis
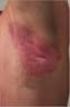 Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
1. Title 2. Background
 1. Title EARLY PsA Effectiveness of early Adalimumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis patients from Reuma.pt, the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register, Portuguese RheumatoLogy SocietY (SPR) 2. Background
1. Title EARLY PsA Effectiveness of early Adalimumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis patients from Reuma.pt, the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register, Portuguese RheumatoLogy SocietY (SPR) 2. Background
Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis
 Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis Thesis Éva Palkonyai M.D. Semmelweis University, Budapest School of Ph.D. Studies Supervisor: Péter Gergely MD, D.Sci Budapest 2006. 1 Contents 1. Introduction
Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis Thesis Éva Palkonyai M.D. Semmelweis University, Budapest School of Ph.D. Studies Supervisor: Péter Gergely MD, D.Sci Budapest 2006. 1 Contents 1. Introduction
Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
 Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:201 205 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1620-4 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Rh. Ll. Smith
Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:201 205 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1620-4 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Rh. Ll. Smith
SNPbrowser Software v3.5
 Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
Refining the Complex Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotype Based on Specificity of the HLA DRB1 Shared Epitope for Antibodies to Citrullinated Proteins
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 11, November 2005, pp 3433 3438 DOI 10.1002/art.21385 2005, American College of Rheumatology Refining the Complex Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotype Based on Specificity
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 11, November 2005, pp 3433 3438 DOI 10.1002/art.21385 2005, American College of Rheumatology Refining the Complex Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotype Based on Specificity
Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007
 Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007 1. Summary This paper covers the procedures that should be followed
Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007 1. Summary This paper covers the procedures that should be followed
Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages
 Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages Zheng-Ming CHEN Professor of Epidemiology Nuffield Dept. of Population Health, University of Oxford Big Data for Health Policy
Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages Zheng-Ming CHEN Professor of Epidemiology Nuffield Dept. of Population Health, University of Oxford Big Data for Health Policy
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals. RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014
 Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects
 Report on the Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects Background and Goals of the Workshop June 5 6, 2012 The use of genome sequencing in human research is growing
Report on the Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects Background and Goals of the Workshop June 5 6, 2012 The use of genome sequencing in human research is growing
Quality Standards Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Quality Standards Rheumatoid Arthritis Minutes of the TEG 2 meeting held on 5 th November at the NICE offices in Manchester Attendees Topic Expert Group Members Robert Moots (RM), Patrick Kiely (PK), Diana
Quality Standards Rheumatoid Arthritis Minutes of the TEG 2 meeting held on 5 th November at the NICE offices in Manchester Attendees Topic Expert Group Members Robert Moots (RM), Patrick Kiely (PK), Diana
Measuring and Improving the Quality of Care for Patients With. Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Measuring and Improving the Quality of Care for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis section 1 reporting Measuring and Improving the Quality of Care for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis An estimated 1.3
Measuring and Improving the Quality of Care for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis section 1 reporting Measuring and Improving the Quality of Care for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis An estimated 1.3
Contribution of Fcγ. polymorphism and copy number variation to the risk of ACPA positive rheumatoid arthritis CHAPTER 5
 CHAPTER 5 Contribution of Fcγ receptor IIIA gene 158V/F polymorphism and copy number variation to the risk of ACPA positive rheumatoid arthritis M.M. Thabet T.W.J. Huizinga R.B. Marques G. Stoeken Rijsbergen
CHAPTER 5 Contribution of Fcγ receptor IIIA gene 158V/F polymorphism and copy number variation to the risk of ACPA positive rheumatoid arthritis M.M. Thabet T.W.J. Huizinga R.B. Marques G. Stoeken Rijsbergen
Symptoms ongoing for 6/12, initially intermittent in nature.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
Rheumatoid Arthritis Case Study INTRODUCTION Each student will have watched the relevant MDT member carrying out their initial assessment on the same newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patient. Videos
THE RISK DISTRIBUTION CURVE AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Ralph Stern Cardiovascular Medicine University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan. stern@umich.
 THE RISK DISTRIBUTION CURVE AND ITS DERIVATIVES Ralph Stern Cardiovascular Medicine University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan stern@umich.edu ABSTRACT Risk stratification is most directly and informatively
THE RISK DISTRIBUTION CURVE AND ITS DERIVATIVES Ralph Stern Cardiovascular Medicine University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan stern@umich.edu ABSTRACT Risk stratification is most directly and informatively
Linköping University Post Print. CARD8 p.c10x polymorphism is associated with inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis
 Linköping University Post Print CARD8 p.c10x polymorphism is associated with inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis Alf Kastbom, Martin Johansson, Deepti Verma, Peter Söderkvist and Solbritt
Linköping University Post Print CARD8 p.c10x polymorphism is associated with inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis Alf Kastbom, Martin Johansson, Deepti Verma, Peter Söderkvist and Solbritt
EVIDENCE OF SNP EFFECT ON THE RISK OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: EFFECTS OF COVARIATE ADJUSTMENT UPON ASSOCIATION RESULTS
 EVIDENCE OF SNP EFFECT ON THE RISK OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: EFFECTS OF COVARIATE ADJUSTMENT UPON ASSOCIATION RESULTS Suely Ruiz GIOLO 1 Júlia Maria Pavan SOLER 2 Maria Jacqueline BATISTA 3 Márcio Augusto
EVIDENCE OF SNP EFFECT ON THE RISK OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: EFFECTS OF COVARIATE ADJUSTMENT UPON ASSOCIATION RESULTS Suely Ruiz GIOLO 1 Júlia Maria Pavan SOLER 2 Maria Jacqueline BATISTA 3 Márcio Augusto
Undifferentiated arthritis Disease course assessed in several inception cohorts
 Undifferentiated arthritis Disease course assessed in several inception cohorts K.N. Verpoort, H. van Dongen, C.F. Allaart, R.E.M. Toes, F.C. Breedveld, T.W.J. Huizinga Leiden University Medical Center,
Undifferentiated arthritis Disease course assessed in several inception cohorts K.N. Verpoort, H. van Dongen, C.F. Allaart, R.E.M. Toes, F.C. Breedveld, T.W.J. Huizinga Leiden University Medical Center,
Anti Carbamylated Protein Antibodies (Anti- CarP) are Present in Arthralgia Patients and Predict the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Anti Carbamylated Protein Antibodies (Anti- CarP) are Present in Arthralgia Patients and Predict the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis Jing Shi 1 * Lotte A. van de Stadt 2 * E.W. Nivine Levarht 1 Tom
Anti Carbamylated Protein Antibodies (Anti- CarP) are Present in Arthralgia Patients and Predict the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis Jing Shi 1 * Lotte A. van de Stadt 2 * E.W. Nivine Levarht 1 Tom
A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Country Annex Report: UK
 A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis Country Annex Report: UK October 2009 1 Interviews In the UK, five rheumatologists and one patient representative were interviewed. The
A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis Country Annex Report: UK October 2009 1 Interviews In the UK, five rheumatologists and one patient representative were interviewed. The
Psoriasis, Incidence, Quality of Life, Psoriatic Arthritis, Prevalence
 1.0 Abstract Title Prevalence and Incidence of Articular Symptoms and Signs Related to Psoriatic Arthritis in Patients with Psoriasis Severe or Moderate with Adalimumab Treatment (TOGETHER). Keywords Psoriasis,
1.0 Abstract Title Prevalence and Incidence of Articular Symptoms and Signs Related to Psoriatic Arthritis in Patients with Psoriasis Severe or Moderate with Adalimumab Treatment (TOGETHER). Keywords Psoriasis,
EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research
 EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research September 16, 2014 Dana C. Crawford, PhD Associate Professor Epidemiology and Biostatistics Institute for Computational Biology Single Nucleotide
EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research September 16, 2014 Dana C. Crawford, PhD Associate Professor Epidemiology and Biostatistics Institute for Computational Biology Single Nucleotide
The EliA System Time for the essentials Cost efficient and flexible A boost in service for your laboratory and your clinicians
 CCP The EliA System Time for the essentials completely automated (true walk-away, overnight runs) easy instrument management by Phadia Data Manager (IDM) software barcode-reader protocols, QC and raw data
CCP The EliA System Time for the essentials completely automated (true walk-away, overnight runs) easy instrument management by Phadia Data Manager (IDM) software barcode-reader protocols, QC and raw data
Dissecting the Heterogeneity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Through Linkage Analysis of Quantitative Traits
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 1, January 2007, pp 58 68 DOI 10.1002/art.22325 2007, American College of Rheumatology Dissecting the Heterogeneity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Through Linkage Analysis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 1, January 2007, pp 58 68 DOI 10.1002/art.22325 2007, American College of Rheumatology Dissecting the Heterogeneity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Through Linkage Analysis
Environmental, genetic and immunological determinants of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 University of Zurich University Hospital of Zurich Environmental, genetic and immunological determinants of Rheumatoid Arthritis FORALLVENT Symposium Basel, 2007 Diego Kyburz, M.D. Division of Rheumatology
University of Zurich University Hospital of Zurich Environmental, genetic and immunological determinants of Rheumatoid Arthritis FORALLVENT Symposium Basel, 2007 Diego Kyburz, M.D. Division of Rheumatology
How does Vectra DA measure my RA disease activity? What is Vectra DA? The more you and your doctor know about your RA, the better you can manage it
 KNOW YOUR RA SCORE 65 58 50 42 40 35 29 21 15 The advanced blood test that helps you and your doctor better understand your rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity with a single score 1 What is Vectra
KNOW YOUR RA SCORE 65 58 50 42 40 35 29 21 15 The advanced blood test that helps you and your doctor better understand your rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity with a single score 1 What is Vectra
Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations
 Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations Data presented from the publication: M. de Wit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:891-5. Epub Apr 7, 2011.
Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target : the patient version of the international recommendations Data presented from the publication: M. de Wit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:891-5. Epub Apr 7, 2011.
SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis
 SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis Joanna L. Kelley, PhD Postdoctoral Scholar, Stanford University Enakshi Singh, MSc HANA Product Management, SAP Labs LLC Outline Use cases Genomics review Challenges in
SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis Joanna L. Kelley, PhD Postdoctoral Scholar, Stanford University Enakshi Singh, MSc HANA Product Management, SAP Labs LLC Outline Use cases Genomics review Challenges in
Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
 A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
 American Medical Journal 3 (1): 56-66, 2012 ISSN 1949-0070 2012 Science Publications High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
American Medical Journal 3 (1): 56-66, 2012 ISSN 1949-0070 2012 Science Publications High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
Immune modulation in rheumatology. Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association
 Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
NGS and complex genetics
 NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view. Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London
 DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
ITT Advanced Medical Technologies - A Programmer's Overview
 ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) is a biotechnology company (SME) established in Turkey. Its activity area is research,
ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) is a biotechnology company (SME) established in Turkey. Its activity area is research,
Development and Validation of a Screening Questionnaire for Psoriatic Arthritis
 Development and Validation of a Screening Questionnaire for Psoriatic Arthritis Dafna D. Gladman 1, Catherine T. Schentag 1, Brian D. Tom 2, Vinod Chandran 1, Cheryl F. Rosen 1 Vernon T. Farewell 2 1 University
Development and Validation of a Screening Questionnaire for Psoriatic Arthritis Dafna D. Gladman 1, Catherine T. Schentag 1, Brian D. Tom 2, Vinod Chandran 1, Cheryl F. Rosen 1 Vernon T. Farewell 2 1 University
Varianti genetiche e interazione gene-asbesto nel mesotelioma pleurico
 Varianti genetiche e interazione gene-asbesto nel mesotelioma pleurico Tunesi Sara, Ferrante Daniela, Mirabelli Dario, Andorno Silvano, Betti Marta, Fiorito Giovanni, Guarrera Simonetta, Casalone Elisabetta,
Varianti genetiche e interazione gene-asbesto nel mesotelioma pleurico Tunesi Sara, Ferrante Daniela, Mirabelli Dario, Andorno Silvano, Betti Marta, Fiorito Giovanni, Guarrera Simonetta, Casalone Elisabetta,
Developing a National Audit for Rheumatoid and Early Inflammatory Arthritis Ian Rowe
 Developing a National Audit for Rheumatoid and Early Inflammatory Arthritis Ian Rowe Chair Clinical Affairs Committee, BSR Outline The British Society for Rheumatology Challenges in improving patient outcomes
Developing a National Audit for Rheumatoid and Early Inflammatory Arthritis Ian Rowe Chair Clinical Affairs Committee, BSR Outline The British Society for Rheumatology Challenges in improving patient outcomes
Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data
 Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data Jim Stankovich Menzies Research Institute University of Tasmania J.Stankovich@utas.edu.au Outline Introduction Confounding variables and linkage
Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data Jim Stankovich Menzies Research Institute University of Tasmania J.Stankovich@utas.edu.au Outline Introduction Confounding variables and linkage
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Long-Term Impact of Delay in Assessment of Patients With Early Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3537 3546 DOI 10.1002/art.27692 2010, American College of Rheumatology Long-Term Impact of Delay in Assessment of Patients With Early Arthritis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3537 3546 DOI 10.1002/art.27692 2010, American College of Rheumatology Long-Term Impact of Delay in Assessment of Patients With Early Arthritis
Improved Survival in Psoriatic Arthritis With Calendar Time
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 8, August 2007, pp 2708 2714 DOI 10.1002/art.22800 2007, American College of Rheumatology Improved Survival in Psoriatic Arthritis With Calendar Time Yaser Ali, 1 Brian
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 56, No. 8, August 2007, pp 2708 2714 DOI 10.1002/art.22800 2007, American College of Rheumatology Improved Survival in Psoriatic Arthritis With Calendar Time Yaser Ali, 1 Brian
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection
 Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Bone Erosions in Patients with RA: Exploring the Impact of the Anatomy of Interest on the Relationship Between MRI and X-ray Erosion Detection Michael Tomizza, BSc, MSc Candidate October 15, 2014: Hamilton
Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC
 Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC Coordinatore Pietro Invernizzi A.I.S.F., Rome, 25 February 2011 STUDY 1 Primary biliary cirrhosis Identification of common and uncommon
Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC Coordinatore Pietro Invernizzi A.I.S.F., Rome, 25 February 2011 STUDY 1 Primary biliary cirrhosis Identification of common and uncommon
