Conservative Management of Urinary Incontinence
|
|
|
- Hilary Bradford
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE No. 186, December 2006 Conservative Management of Urinary Incontinence This guideline has been reviewed and approved by the Executive and Council of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. PRINCIPAL AUTHORS Magali Robert, MD, FRCSC, Calgary AB Sue Ross, PhD, Calgary AB UROGYNAECOLOGY COMMITTEE Scott A. Farrell (Chair), MD, FRCSC, Halifax NS William Andrew Easton, MD, FRCSC, Scarborough ON Annette Epp, MD, FRCSC, Saskatoon SK Lise Girouard, RN, Winnipeg MB Chandra Gupta, MD, FRCSC, Winnipeg MB Francois Lajoie, MD, FRCSC, Sherbrooke QC Danny Lovatsis, MD, FRCSC, Toronto ON Barry MacMillan, MD, FRCSC, London ON Magali Robert, MD, FRCSC, Calgary AB Sue Ross, PhD, Calgary AB Joyce Schachter, MD, FRCSC, Ottawa ON Jane Schulz, MD, FRCSC, Edmonton AB David H. L. Wilkie, MD, FRCSC, Vancouver BC Abstract Objective: To outline the evidence for conservative management options for treating urinary incontinence. Options: Conservative management options for treating urinary incontinence include behavioural changes, lifestyle modification, pelvic floor retraining, and use of mechanical devices. Outcomes: To provide understanding of current available evidence concerning efficacy of conservative alternatives for managing urinary incontinence; to empower women to choose continence therapies that have benefit and that have minimal or no harm. Evidence: The Cochrane Library and Medline (1966 to 2005) were searched to find articles related to conservative management of incontinence. Review articles were appraised. Values: The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Benefits, Harms, Costs: Evidence for the efficacy of conservative management options for urinary incontinence is strong. These options can be advocated as primary interventions with minimal or no harm to women. : 1. Pelvic floor retraining (Kegel) exercises should be recommended for women presenting with stress incontinence. (I-A) 2. Proper performance of Kegel exercises should be confirmed by digital vaginal examination or biofeedback. (I-A) 3. Follow-up should be arranged for women using pelvic floor retraining, since cure rates are low and other treatments may be indicated. (III-C) 4. Kegel exercises may be offered as an adjunct to other treatments for overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome, but they should not be the only treatment offered for these symptoms. (I-B) 5. Although functional electrical stimulation (FES) has not been studied as an independent modality, it may be used as an adjunct to pelvic floor retraining, especially in patients who have difficulty identifying and contracting the pelvic muscles. (III-C) 6. FES should be offered as an effective option for the management of OAB. (I-A) 7. Vaginal cones may be recommended as a form of pelvic floor retraining for women with stress incontinence. (I-A) 8. Continence pessaries should be offered to women as an effective, low-risk treatment for both stress and mixed incontinence. (II-B) 9. Bladder training (bladder drill) should be recommended for symptoms of OAB, since it has no adverse effects (III-C), and it is as effective as pharmacotherapy. (I-B) 10. Behavioural management protocols using lifestyle changes in combination with bladder training and pelvic muscle exercises are highly effective and should be used to treat urinary incontinence. (I-A) J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2006;28(12): Key Words: Urinary incontinence, stress incontinence, overactive bladder, urge incontinence, conservative management This guideline reflects emerging clinical and scientific advances as of the date issued and is subject to change. The information should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed. Local institutions can dictate amendments to these opinions. They should be well documented if modified at the local level. None of these contents may be reproduced in any form without prior written permission of the SOGC. DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE
2 Key to evidence statements and grading of recommendations, using the ranking of the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care Quality of Evidence Assessment* I: Evidence obtained from at least one properly randomized controlled trial. II-1: Evidence from well-designed controlled trials without randomization. II-2: Evidence from well-designed cohort (prospective or retrospective) or case-control studies, preferably from more than one centre or research group II-3: Evidence obtained from comparisons between times or places with or without the intervention. Dramatic results in uncontrolled experiments (such as the results of treatment with penicillin in the 1940s) could also be included in this category. III: Opinions of respected authorities, based on clinical experience, descriptive studies, or reports of expert committees Classification of A. There is good evidence to recommend the clinical preventive action B. There is fair evidence to recommend the clinical preventive action C. The existing evidence is conflicting and does not allow to make a recommendation for or against use of the clinical preventive action; however, other factors may influence decision-making D. There is fair evidence to recommend against the clinical preventive action E. There is good evidence to recommend against the clinical preventive action I. There is insufficient evidence (in quantity or quality) to make a recommendation; however, other factors may influence decision-making The quality of evidence reported in these guidelines has been adapted from the Evaluation of Evidence criteria described in the Canadian Task Force on the Periodic Preventive Health Exam Care. 13 included in these guidelines have been adapted from the Classification of criteria described in the Canadian Task Force on the Periodic Preventive Health Exam Care. 13 INTRODUCTION The most common types of urinary incontinence (the involuntary loss of urine) are stress incontinence and urge incontinence. Stress incontinence is the involuntary leaking of urine during effort or exertion, or while sneezing or coughing. Urge incontinence, or overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome, involves a constellation of symptoms including frequency, urgency, and leakage immediately preceded by urgency. 1 The rate of urinary incontinence in adult women is 20% to 50%. 2 This has a significant impact on their quality of life. 3 5 Surgical and pharmacotherapeutic treatment is available, but the risks and benefits are not always acceptable to women. 6,7 Conservative management is usually advocated as an initial intervention since it carries minimal risks This consensus guideline will review the interventions presently available. The quality of evidence reported in these guidelines has been described using evaluation of evidence criteria outlined in the report of the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care (Table). 13 PELVIC FLOOR RETRAINING Pelvic floor rehabilitation programs are aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor musculature. This musculature includes the levator ani group, the external anal sphincter, and the striated urethral sphincter. The rehabilitation programs may include simple oral or written information, exercises performed with biofeedback, pelvic muscle contractions stimulated by functional electrical stimulation (FES), motor relearning exercises, or any combination of the above. Success is dependent on a continuous, regular home exercise program to avoid deconditioning. 14 Because many different teaching modalities, lengths of treatment, and outcome measures have been used, comparison of trial outcomes is difficult. 15 However, the same principles used for training any striated muscle should be respected in pelvic floor retraining. Written and oral instructions are not adequate, as approximately 30% of women are unable to contract their pelvic floor on demand and 25% actually promote incontinence by straining. 16 Examples of Training Programs 1. Written instructions. These instructions will usually include an explanation of the pathophysiology of urinary incontinence, a description of the relevant pelvic floor anatomy, and an exercise program. 2. Exercises with biofeedback. Biofeedback devices such as vaginal cones and vaginal balloon devices provide tactile or visual digital display feedback to facilitate identification and recruitment of the correct muscles. 3. Functional electrical stimulation. These devices produce low level electric current, which causes pelvic muscles to contract, simulating a voluntary pelvic contraction DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE 2006
3 Conservative Management of Urinary Incontinence Effect on Stress Incontinence Pelvic floor retraining has been recommended for the conservative treatment of stress incontinence, OAB, and mixed incontinence. Contracting the muscles of the pelvic floor is thought to press the urethra against the symphysis to augment pressure transmission to the urethra during a cough and also directly to increase intraurethral pressure. 17 Although these effects will happen reflexively when the pelvic floor muscles are strengthened by regular exercise, timing the contraction to coincide with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure (coughing, jumping, etc.) can further enhance the effect. Both strength and coordination are important for this knack manoeuvre. Pelvic floor muscle retraining appears to be more effective than no therapy for stress and mixed incontinence, but there are only a few randomized studies comparing muscle retraining with other treatment modalities. Long-term studies are also lacking. It is therefore not possible to ascertain whether muscle retraining is more effective than other treatments. 15 In a review, short-term subjective cure rates for stress incontinence were approximately 21% (9 36%), and short-term subjective significant improvement rates were 69% (55 85%). 18 After two years, less than 50% of women continued to exercise regularly. 16 This led to a two-year cure rate of 8% (0 9%) and a significant improvement rate of 40% (20 42%). After 15 years, 28% were exercising weekly and 36% periodically, yet only 46% had gone on to surgery. Those women who had been satisfied following the therapy 15 years earlier were less likely to seek further interventions. 14 Pelvic floor muscle retraining is often combined with biofeedback and behavioural modification. Although randomized trials have not shown an advantage with the addition of biofeedback, it is often recommended. It is felt that direct auditory or visual feedback improves both pelvic floor awareness and patient motivation. 15 Motor relearning exercises ( knack ) involve contracting the pelvic floor during problematic situations (e.g., coughing, sneezing, jumping, and lifting). Knack can reduce leakage episodes during coughing by 73% to 98%, 15,19 and should therefore be added to a rehabilitation program. 15 Effect on Overactive Bladder Syndrome How contracting the pelvic musculature can inhibit detrusor contractions is unclear. It may be that the pelvic muscle contraction causes a reflex inhibition of the detrusor muscle. 20 A benefit may be realized even if the bladder contraction is not completely inhibited, as the urethral pressure will be increased thereby increasing resistance to urine flow. There is insufficient evidence to advocate the use of pelvic floor retraining for OAB. 15 There are few randomized controlled trials, and all use different treatment modalities. There is weak evidence that pelvic floor retraining may be beneficial and equivalent to medical management Pelvic floor retraining (Kegel) exercises should be recommended for women presenting with stress incontinence. (I-A) 2. Proper performance of Kegel exercises should be confirmed by digital vaginal examination or biofeedback. (I-A) 3. Follow-up should be arranged for women using pelvic floor retraining, since cure rates are low and other treatments may be indicated. (III-C) 4. Kegel exercises may be offered as an adjunct to other treatments for OAB syndrome, but they should not be the only treatment offered for these symptoms. (I-B) FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is the application of electrical stimulation to the pudendal nerve. The two effects seen with this therapy depend upon the frequencies used; they are a passive contraction of the pelvic floor muscles or a reflex inhibition of bladder contractions. 18 The advantage of this therapy is that it does not require voluntary patient effort, but its disadvantage is that the passive muscle contractions are weaker than voluntary ones. Effect on Stress Incontinence Because of the diversity of protocols studied, findings concerning the role of FES are inconclusive. 15 It is recommended as an effective teaching modality for very weak pelvic musculature as it can jump-start the muscles. 21 In a randomized prospective study comparing FES with pelvic exercises for treatment of stress incontinence, both modalities significantly reduced symptoms. 22 Effect on Overactive Bladder Syndrome FES has been utilized mostly to treat OAB syndrome. One-year follow-up after treatment shows cure rates of 30% (22 33%) and improvement rates of 72% (70 73%) Although FES has not been studied as an independent modality, it may be used as an adjunct to pelvic floor retraining, especially in patients who have difficulty identifying and contracting the pelvic muscles. (III-C) 6. FES should be offered as an effective option for the management of OAB. (I-A) DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE
4 VAGINAL CONES Since pelvic floor retraining has high discontinuation rates, vaginal cones were developed to make it easier to perform pelvic floor contractions. The cones are placed in the vagina above the level of the pelvic floor musculature. Contraction of these muscles is required to prevent the cone from slipping out of the vagina. A 15-minute session, twice daily, is usually recommended. The vaginal cones are of varying weights, and a woman inserts a cone of increasingly heavier weight as she is able to retain it. The advantages of using cones as a method of exercising the pelvic muscles include ease of use, shallow learning curve, and short daily time commitment, all of which may lead to increased compliance. Effect on Stress Incontinence Cones appear to be effective. The risk of having stress incontinence after using vaginal cones is less than with no treatment (relative risk [RR] 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI] ), but there is no difference when cones are compared with pelvic floor muscle retraining or electrostimulation. 22 Using cones with pelvic floor retraining or electrostimulation appears to be no more beneficial than using cones alone. 23 This evidence is limited by the heterogeneity of the trials. Early discontinuation of cones is seen in approximately 25% of users (0 63%). This is comparable to the drop-out rates for electrostimulation and pelvic floor retraining. Recommendation 7. Vaginal cones may be recommended as a form of pelvic floor retraining for women with stress incontinence. (I-A) MECHANICAL DEVICES FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE Pessaries have been used since ancient times for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse. 24 More recently, pessaries designed for the specific treatment of urinary stress incontinence have been developed. These pessaries work by providing mechanical support to the urethra. Urethral plugs are devices placed inside the urethra. All mechanical devices are traditionally used for stress incontinence and not for OAB symptoms. Effect on Stress Incontinence: Pessaries There are no randomized trials looking at pessaries. Three studies examining the effect of continence pessaries have been published Retrospective studies by Donnelly and Farrell found that over 50% of women with either pure stress incontinence or mixed incontinence treated with pessaries were satisfied with the results and continued pessary use for up to 11 months. 25,27 These authors relied for the most part on the incontinence ring and the ring with support and knob. Robert, who used the incontinence dish and incontinence ring, had a 24% cure rate in a prospective intent-to-treat cohort study lasting one year. 26 In patients with a history of pelvic surgery, pessary success rates were reduced. Complications with pessaries were minimal. Effect on Stress Incontinence: Urethral Plugs The few studies looking at urethral plugs report a 43% median success rate, 28 but enthusiasm must be tempered by the fact that users experience a 30% urinary tract infection rate. No recent studies have been published, which may indicate a waning enthusiasm for urethral plugs. 8. Continence pessaries should be offered to women as an effective, low-risk treatment for both stress and mixed incontinence. (II-B) BLADDER TRAINING Bladder training is also called bladder drill. It works by activating cortical inhibition over the sacral micturition reflex centre. 29 Bladder training is aimed at increasing the voiding interval and decreasing urgency and associated urge incontinence. It is used in patients with OAB symptoms including urgency, frequency, urgency incontinence, and nocturia. There are usually three components to the training: patient education, scheduled voiding, and positive reinforcement. 29 Fluid management, bladder diaries, and urge suppression are often added. The specific behavioural techniques may not be as important in the treatment effect as providing all the components together. 29 Effect on Overactive Bladder Syndrome A Cochrane review of bladder training for urinary incontinence in adults 30 found five trials, involving 457 participants, that assessed the effect of bladder training on female urinary incontinence Two studies comparing bladder training with no treatment found no statistically significant treatment effects. 31,32 Two studies comparing bladder training with drugs found that bladder training resulted in higher rates of perceived cure among participants. 33,34 There is a 50% rate of side effects with the use of anticholinergics. 30 One trial found no difference between bladder training and pelvic muscle training plus biofeedback. 35 Two recently published randomized trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of bladder training in women. 10,11 Dougherty et al. compared behavioural management for continence 1116 DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE 2006
5 Conservative Management of Urinary Incontinence (BMC), a three-step sequenced protocol including self-monitoring, bladder training, and pelvic muscle exercises, with no treatment. 10 Self-monitoring included reduction in caffeine consumption, adjustment of the amounts and timing of fluid intake, decreasing excessively long voiding intervals, and making dietary changes to promote bowel regularity. After self-monitoring, participants went on to do bladder training and, if necessary, pelvic muscle exercises with biofeedback. At two years, the BMC group had decreased its urinary incontinence severity by 61%, and the control group s severity increased by 184%. Subak et al. randomized women to six weeks of bladder training or no treatment, and found that the treatment group had a 40% decrease in mean weekly incontinence episodes. 11 Despite such improvements, it is likely that only a small number of patients will be completely cured of their bladder symptoms Bladder training (bladder drill) should be recommended for symptoms of OAB, since it has no adverse effects (III-C), and it is as effective as pharmacotherapy. (I-B) 10. Behavioural management protocols using lifestyle changes in combination with bladder training and pelvic muscle exercises are highly effective and should be used to treat urinary incontinence. (I-A) Summary of Conservative Incontinence Treatment Options Stress Incontinence Pelvic floor retraining stressing the knack by using verbal or written instruction for patients able to voluntarily contract the pelvic floor manual, auditory, or visual biofeedback functional electrical stimulation for those unable to voluntarily contract pelvic muscles vaginal cones pessaries Overactive Bladder Pelvic floor retraining, with pelvic floor contraction with symptoms of urgency FES Bladder retraining (bladder drill) Combinations of lifestyle modification, bladder drill, and pelvic muscle retraining CONCLUSION The practice of the conservative management of urinary incontinence is widespread and should be encouraged. All modalities appear to be more effective than no therapy. Unlike surgical treatment of urinary incontinence, which carries a significant risk of complications and poor long-term outcomes, conservative management is associated with minimal adverse outcomes. For a significant number of patients, the results of conservative management are satisfactory and may obviate the need for medical or surgical interventions. REFERENCES 1. Abrams P, Cordozol L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rossier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardization Subcommittee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn 2002;21: Bump RC, Norton PA. Epidemiology and natural history of pelvic floor dysfunction. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 1998; 25: Wyman J F. The costs of urinary incontinence. Eur Urol 1997;32(s2): Grimby A, Milsom I, Molander U, Wiklund I, Ekelund P. The influence of urinary incontinence on the quality of life of elderly women. Age Ageing 1993;22: Temml C, Haidinger G, Schmidbauer J, Schatzl G, Madersbacher S. Urinary incontinence in both sexes: prevalence rates and impact on quality of life and sexual life. Neurourol Urodyn 2000;19: Black N, Griffiths J, Pope C, Bowling A, Abel P. Impact of surgery for stress incontinence on morbidity: cohort study. BMJ 1997;315: Diokno A, Yuhico M Jr. Preference, compliance and initial outcome of therapeutic options chosen by female patients with urinary incontinence. J Urol 1995;154: Burgio KL. Behavioral treatment options for urinary incontinence. Gastroenterology 2004;126 (Suppl 1): S Karram MM, Partoll L, Rahe J. Efficacy of nonsurgical therapy for urinary incontinence. J Reprod Med 1996;41: Dougherty MC, Dwyer JW, Pendergast JF, Boyington AR, Tomlinson BU, Coward RT, et al.. A randomized trial of behavioral management for continence with older rural women. Res Nurs Health 2002;25: Subak LL, Quesenberry CP Jr, Posner SF, Cattolica E, Soghikian K. The effect of behavioral therapy on urinary incontinence: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2002;100: Diokno AC, Sampselle CM, Herzog AR, Raghunathan TE, Hines S, Messer KL, et al. Prevention of urinary incontinence by behavioral modification program: a randomized, controlled trial among older women in the community. J Urol 2004;171: Woolf SH, Battista RN, Angerson GM, Logan AG, Eel W. Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. New grades for recommendations from the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Can Med Assoc J 2003;169(3): B K, Kvarstein B, Nygaard I. Lower urinary tract symptoms and pelvic floor muscle exercise adherence after 15 years. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105 (Pt 1): Hay-Smith EJC, Bo K, Berghmans LCM, Hendricks HJM, de Bie RA, vanwaalwijk Doorn ESC. Pelvic muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;(1). 16. Bump RC, Hurt WG, Fantl JA, Wyman JF. Assessment of Kegel pelvic muscle exercise performance after brief verbal instruction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165: Delancey J. Structural support of the urethra as it relates to stress incontinence: the hammock hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170: Robert M, Mainprize TC. Biofeedback and functional electrical stimulation. In: Drutz H, Herschorn S, Diamant N, eds. Urogynecology and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery. London, UK: Springer-Verlag; DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE
6 19. Miller JM, Ashton-Miller JA, Delancey JO. A pelvic muscle precontraction can reduce cough related urine loss in selected women with mild SUI. J Am Geriatr Soc 1998;46: Berghmans LC, Hendriks HJ, de Bie RA, van Wallwijk van Doorn ES, Bo K, van Kerebroeck PE. Conservative treatment of urge urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. BJU Int 2000;85: Reckemeyer I, Jundt K, Drinovac V, Dimpfl T, Peschers UM. Pelvic floor re-education with electrical stimulation: how many women learn how to contract? Neurourol Urodyn 2002;21: Seo JT, Yoon H, Kim YH. A randomized prospective study comparing new vaginal cone and FES-Biofeedback. Yonsei Med J 2004;45: Herbison P, Plevnik S, Mantle J. Weighted vaginal cones for urinary incontinence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD Miller DS. Contemporary use of the pessary. In: Drogemueller W, Sciarra JJ, eds. Gynecology and Obstetrics. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;1992: Farrell SA, Singh B, Aldakhil L. Continence pessaries in the management of urinary incontinence in women. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2004;26: Robert M, Mainprize T. Long-term assessment of the incontinence ring pessary for the treatment of stress incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 2002;13: Donnelly MJ, Powell-Morgan S, Olsen AL, Nygaard IE. Vaginal pessaries for the management of stress and mixed urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2004;15: Vierhout ME, Lose G. Preventive vaginal and intra-urethral devices in the treatment of female urinary stress incontinence. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 1999;106: Fantl JA, Newman DK, Colling J, et al. Urinary incontinence in adults: Acute and chronic management. Clinical practice guideline, No 2, 1996 Update. Rockville, MD:US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; March AHCPR Publication No Wallace SA, Roe B, Williams K, Palmer, M. Bladder training for urinary incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD Fantl A, Wyman JF, McClish DK, Harkins SW, Elswick RK, Taylor JR, et al. Efficacy of bladder training in older women with urinary incontinence. JAMA 1991;265: Lagro Janssen AL, Debruyne FM, Smits AJ, Van Weel C. The effects of treatment of urinary incontinence in general practice. Fam Pract 1992;9: Colombo M, Zanetta G, Scalambrino S, Milani R. Oxybutynin and bladder training in the management of female urinary urge incontinence: a randomized study. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 1995;6: Jarvis GJ. A controlled trial of bladder drill and drug therapy in the management of detrusor instability. Br J Urol 1981;53: Wyman JF, Fantl AJ, McClish DK, Bump RC. The Continence Program for Women Research Group. Comparative efficacy of behavioral interventions in the management of female urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179: Burgio KL. Influence of behavior modification on overactive bladder. Urology 2002;60(Suppl 1): DECEMBER JOGC DÉCEMBRE 2006
SOGC Recommendations for Urinary Incontinence
 The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
PROCEEDINGS INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT
 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL
 GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Stress incontinence. Supported by an unrestricted grant from
 Stress incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing conservative therapies
Stress incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing conservative therapies
THE EVALUATION OF STRESS INCONTINENCE PRIOR TO PRIMARY SURGERY
 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES No. 127, April 2003 THE EVALUATION OF STRESS INCONTINENCE PRIOR TO PRIMARY SURGERY These guidelines have been prepared by the Urogynaecology Committee and were approved
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES No. 127, April 2003 THE EVALUATION OF STRESS INCONTINENCE PRIOR TO PRIMARY SURGERY These guidelines have been prepared by the Urogynaecology Committee and were approved
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMB
 The patient doesn't want anything "invasive": What can we offer? Case driven workshop on intractable overactive bladder Workshop 11 Dr Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMD International Continence Society
The patient doesn't want anything "invasive": What can we offer? Case driven workshop on intractable overactive bladder Workshop 11 Dr Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMD International Continence Society
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE. Stress Urinary Incontinence
 PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
Urinary Incontinence. Types
 Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Urinary Incontinence Definitions
 (AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
(AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery?
 Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
Pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women
 Pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women Hay-Smith EJC, Bø K, Berghmans LCM, Hendriks HJM, de Bie RA, van Waalwijk van Doorn ESC This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
Pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women Hay-Smith EJC, Bø K, Berghmans LCM, Hendriks HJM, de Bie RA, van Waalwijk van Doorn ESC This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Question ID: 6 Question type: Intervention Question: Does treatment of overactive bladder symptoms prevent falls in the elderly?
 PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY SERVICE: Urinary Incontinence Treatments
 Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP. Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX.
 Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX Surgery Presenter Disclosure No Conflict of Interest to disclose No Financial
Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX Surgery Presenter Disclosure No Conflict of Interest to disclose No Financial
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds
 Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
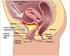
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Korean Women - Study Proves That Syndrome Does Not Effect on Sexual Life
 (25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
(25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY SERVICE: Urinary Incontinence Treatments
 Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following Pelvic Floor Surgery
 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE SOGC Clinical Practice Guideline No. 248, September 2010 (Replaces No. 74, July 1998) Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE SOGC Clinical Practice Guideline No. 248, September 2010 (Replaces No. 74, July 1998) Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following
Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis Updated January 2011 by Diane Lee Introduction The research in the last decade has led to a clearer understanding of how load is transferred through the low back
Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis Updated January 2011 by Diane Lee Introduction The research in the last decade has led to a clearer understanding of how load is transferred through the low back
Urinary Incontinence. Evaluation and Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overview. Stress vs.
 Urinary Incontinence Evaluation and Treatment of Overactive Bladder Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Common - 25%
Urinary Incontinence Evaluation and Treatment of Overactive Bladder Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Common - 25%
ARTICLE IN PRESS Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx
 Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Maturitas journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/maturitas Review Pelvic floor exercise for urinary incontinence: A systematic
Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Maturitas journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/maturitas Review Pelvic floor exercise for urinary incontinence: A systematic
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care
 A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation?
 Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Patient. Frequently Asked Questions. Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
The effect of home biofeedback training on stress incontinence
 Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004: 83: 973 977 Copyright # Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect
Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004: 83: 973 977 Copyright # Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients Dissatisfied With Overactive Bladder Medication
 Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006
 Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Stress Urinary Incontinence Information for patients What is Stress Incontinence? Stress incontinence is a leakage of urine occurring on physical
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Stress Urinary Incontinence Information for patients What is Stress Incontinence? Stress incontinence is a leakage of urine occurring on physical
Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence
 Original Article SOLIFENACIN AND MIXED URINARY INCONTINENCE STASKIN and TE Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence DAVID R. STASKIN
Original Article SOLIFENACIN AND MIXED URINARY INCONTINENCE STASKIN and TE Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence DAVID R. STASKIN
Efficacy of behavioural training in treating symptoms of urinary urgency and urge urinary incontinence
 Journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Women s Health, Autumn 2011, 109, 14 19 CASE REPORT Efficacy of behavioural training in treating symptoms of urinary urgency and urge urinary
Journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Women s Health, Autumn 2011, 109, 14 19 CASE REPORT Efficacy of behavioural training in treating symptoms of urinary urgency and urge urinary
GLOSSARY of research terms
 GLOSSARY of research terms JLA Urinary Incontinence Working Partnership Workshop to set research priorities in Urinary Incontinence November 2008 Terms in bold are commonly used clinical/research terms.
GLOSSARY of research terms JLA Urinary Incontinence Working Partnership Workshop to set research priorities in Urinary Incontinence November 2008 Terms in bold are commonly used clinical/research terms.
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women(review)
 Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women (Review) Dumoulin C, Hay-Smith J This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women (Review) Dumoulin C, Hay-Smith J This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a
 Menopause Matters from Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women www.menopause.org Tyler M. Muffly, MD; Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD Overactive bladder is a debilitating health condition
Menopause Matters from Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women www.menopause.org Tyler M. Muffly, MD; Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD Overactive bladder is a debilitating health condition
Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
Urinary Incontinence in the Elderly
 Urogenital Urinary Incontinence in the Elderly Dr. Lynn Stothers, MD, MHSc, FRCSC, Assistant Professor of Surgery/Urology, Associate Member, Department of Health Care and Epidemiology, University of British
Urogenital Urinary Incontinence in the Elderly Dr. Lynn Stothers, MD, MHSc, FRCSC, Assistant Professor of Surgery/Urology, Associate Member, Department of Health Care and Epidemiology, University of British
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women
 Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB)
 OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder in menopausal women
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder in menopausal women Tyler M. MUFFLY, MD a, Fellow Marie Fidela R. PARAISO, MD a, Professor From the a Center of Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Disorders, Obstetrics,
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder in menopausal women Tyler M. MUFFLY, MD a, Fellow Marie Fidela R. PARAISO, MD a, Professor From the a Center of Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Disorders, Obstetrics,
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse. Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION
 PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
The Well Woman Centre. Adult Urinary Incontinence
 The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
BIOFEEDBACK IN THE TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULTS
 BIOFEEDBACK IN THE TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULTS March 2000 Frank V. Lefevre, M.D. Assistant Professor General Internal Medicine Northwestern Medical School and Director of Special Assessments
BIOFEEDBACK IN THE TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULTS March 2000 Frank V. Lefevre, M.D. Assistant Professor General Internal Medicine Northwestern Medical School and Director of Special Assessments
Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder
 Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder Learn more about OAB in the Powder Room www.powderroom.ca Table of Contents Learning about overactive bladder (OAB) 1 What is overactive bladder (OAB)? 2
Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder Learn more about OAB in the Powder Room www.powderroom.ca Table of Contents Learning about overactive bladder (OAB) 1 What is overactive bladder (OAB)? 2
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women (Review)
 Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women (Review) Dumoulin C, Hay-Smith EJC, Mac Habée-Séguin G This is a reprint of a Cochrane
Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women (Review) Dumoulin C, Hay-Smith EJC, Mac Habée-Séguin G This is a reprint of a Cochrane
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care
 Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care Background Incontinence (i.e., loss of bladder and/or bowel control) is a significant health care problem, which affects
Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care Background Incontinence (i.e., loss of bladder and/or bowel control) is a significant health care problem, which affects
Mesh Erosion and What to do
 Disclosures Mesh Erosion and What to do None Michelle Y. Morrill, MD Chief of Urogynecology, TPMG Director of Urogynecology, Kaiser San Francisco Assistant Professor, Volunteer Faculty Dept of Ob/Gyn,
Disclosures Mesh Erosion and What to do None Michelle Y. Morrill, MD Chief of Urogynecology, TPMG Director of Urogynecology, Kaiser San Francisco Assistant Professor, Volunteer Faculty Dept of Ob/Gyn,
Las Vegas Urogynecology
 Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Complications of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for stress urinary incontinence
 Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:1353 1357 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1210-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for stress urinary incontinence Ingrid Kristensen & Maysoon
Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:1353 1357 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1210-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure for stress urinary incontinence Ingrid Kristensen & Maysoon
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler
 Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
NKR 33 Urininkontinens, PICO 3: Bør kvinder med urininkontinens tilbydes behandling
 NKR 33 Urininkontinens, PICO 3: Bør kvinder med urininkontinens tilbydes behandling med et vaginalt hjælpemiddel? Review information Authors Sundhedsstyrelsen 1 1 The Danish Health and Medicines Authority
NKR 33 Urininkontinens, PICO 3: Bør kvinder med urininkontinens tilbydes behandling med et vaginalt hjælpemiddel? Review information Authors Sundhedsstyrelsen 1 1 The Danish Health and Medicines Authority
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources
 Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
Saint Mary s Hospital. Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit. Overactive Bladder. Information for Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence
 Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence Manage your Fluid Intake: There is no scientific evidence that states we need eight 8 oz. glasses (64 oz.) of
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence Manage your Fluid Intake: There is no scientific evidence that states we need eight 8 oz. glasses (64 oz.) of
