INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY OF LIFE ASSESSMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH URINARY INCONTINENCE
|
|
|
- Isaac Stokes
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nagoya J. Med. Sci ~ 131, 2007 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY OF LIFE ASSESSMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH URINARY INCONTINENCE MOMOKAZU GOTOH Department of Urology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine ABSTRACT In order to improve the quality of medical care, an assessment of patients quality of life (QOL) has been recognized to be important as well as an assessment of physical impairment. Since diseases affect a wide range of QOL facets, including physical, emotional, and social conditions, disease severity and treatment efficacy should not be assessed only by clinical parameters. Urinary incontinence has a strong influence on patients QOL. Health-related QOL is a multidisciplinary and subjective construct that refers to an individual s perception of his/her state of health or disease. The treatment of urinary incontinence should be selected based on questionnaires. Since 1987, various questionnaires for QOL assessment in patients with urinary incontinence have been developed. During the meeting of the International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI), held in 1998, 2001, and 2004, various QOL questionnaires for urinary incontinence were assessed and ranked based on scientific verifications. This paper describes the influence of urinary incontinence on QOL and the measurement of QOL in patients with several urinary problems. Key Words: Quality of life, Urinary incontinence, Questionnaire INTRODUCTION We acquire a urinary habit as an essential behavior in social life through toilet training, which starts in early childhood. In the process of acquiring the urinary habit, we form a mental and social concept that urination is a very personal matter that should be kept private. Therefore, leakage of urine in public is one of the most miserable incidents in social life both for infants and adults. The mental trauma associated with leakage is severe and it may induce a feeling of embarrassment, alienation, isolation, or depression. Urinary frequency or urinary incontinence affects a person s relationships both with the surrounding people and society as a whole. In the case of the elderly, urinary frequency or urinary incontinence variously affects even their caretakers lifestyles. The assessments of disease severity and treatment efficacy, and the treatment selection for urinary incontinence, have traditionally been performed based on objective findings obtained by urodynamic examination and the pad test. However, since 1987, various QOL assessment questionnaires have been developed for patients with urinary incontinence, and in recent years, subjective symptoms and QOL have become more important than objective findings. The first International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI), supported by the World Health Organization (WHO), was held in Monaco (1998), and the second and third were held in Paris (2001) and Corresponding author: Momokazu Gotoh, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Urology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, 65 Tsurumai-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya , Japan 123
2 124 Momokazu Gotoh Monaco (2004), respectively. The Subcommittee of Symptom and QOL Assessment of the ICI has confirmed the importance of symptom and QOL assessment for patients with urinary incontinence. Moreover, the subcommittee has assessed the validity of questionnaires for QOL assessment, the findings of which have been previously reported. Furthermore, the subcommittee has been developing a simple questionnaire for symptom and QOL assessment that can be used internationally. 1) Although a QOL assessment for urinary frequency has not been developed, a QOL assessment for overactive bladder a condition in which patients feel urgency accompanied by urinary frequency or urge incontinence has been developed in recent years. I. The questionnaire for subjective symptom and QOL assessment There are various methods used to assess the symptoms and QOL of patients with urinary incontinence. Although medical history taking has traditionally been employed, a questionnaire to be filled in by patients has been adopted in recent years. Medical history taking is not a standardized method and its contents differ according to doctors and patients. Generally, doctors QOL assessments tend to be lower than patients QOL assessments. Regarding urinary incontinence, it is difficult for patients to express their symptoms and impediments to doctors because of shame. Therefore, a questionnaire for symptom and QOL assessment filled in by patients is recommended. The questionnaire can measure the existence and degree of urinary symptoms, including urinary incontinence, and the influence of urinary symptoms on patients daily life and QOL. II. Conditions of the questionnaire The questionnaire is an objective method designed to measure subjective phenomena such as symptoms and QOL. The process of developing the questionnaire is not simple and many trials may be required in order to confirm that a certain questionnaire can measure the desired parameters, and that it addresses the relevant objectives. Since the questionnaire is a tool for assessing QOL scientifically, the arbitrary development of questionnaires should be avoided, and the reliability and validity of the questionnaire as a measurement tool should be scientifically verified. Reliability includes factors such as internal consistency and the test-retest method whereas validity includes criterion and construct validity. Moreover, the responsiveness to a change before and after medical treatment should be verified. Furthermore, if the questionnaire is to be used in clinics, simplicity is an additional important criterion. III. Relationship between the questionnaire and other clinical assessments The relationship among subjective symptoms, QOL assessment, and urodynamic findings is complicated. Generally, with urinary symptoms, the relationship among subjective symptoms, QOL assessment, and objective urodynamic assessment is not clear: however, each of these facets is considered important for assessing patients with urinary incontinence. Recently, QOL assessment using a questionnaire has been recognized as a method of assessing the influence of urinary symptoms on patients lives. IV. The recommendation ranking of questionnaires for symptoms and QOL During the second ICI, studies on symptoms and QOL were investigated based on reports
3 QOL ASSESSMENT IN INCONTINENT PATIENTS 125 Table 1 Criteria for recommendation of questionnaires for urinary incontinence at the third consultation Grade of recommendation Grade A (highly recommended) Grade A new (highly recommended) Grade B (recommended) Evidence required (published) Validity, reliability and responsiveness established with rigour in several data sets. Validity, reliability and responsiveness indicated with rigour in one data set. Validity, reliability and responsiveness indicated but not with rigour. Validity and reliability established with rigour in several data sets. Table 2 Criteria for recommendation of questionnaires for pelvic organ prolapse and fecal incontinence at the third consultation Grade of recommendation Grade A (highly recommended) Grade B (recommended) Grade C (with potential) Evidence required (published) Validity, reliability and responsiveness established with rigour. Validity and reliability established with rigour, or validity, reliability and responsiveness indicated. Early development-further work required and encouraged. obtained from databases such as Cochran, Medline, and Pub-Med, and a recommendation ranking of various questionnaires, mainly for urinary incontinence, was decided based on the degree of the verification. In this study, databases such as Pub-Med, Medline, PsychInfo, and LOCATORolus were searched between January 2001 and June Questionnaires on the symptoms of and the QOL of patients with, extensive abnormalities additional to urinary incontinence, such as lower urinary tract symptoms, fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic organ prolapse were assessed. Based on this assessment, a recommendation ranking of these questionnaires was decided. Tables 1 and 2 show the criteria of the recommendation ranking of questionnaires adopted by the subcommittee. 2-31) V. The recommended questionnaires for symptoms and QOL The questionnaires for symptoms and QOL include generic questionnaires and disease-specific questionnaires. The generic questionnaires have been developed to generally measure the QOL of patients with extensive diseases and conditions. In contrast, the disease-specific questionnaires have been developed to assess the influence of specific disease on QOL and changes in QOL due to treatment. Although the generic questionnaires are a generally useful means of assessing differences in QOL according to diseases and conditions, they are unable to assess the specificity of specific diseases. Therefore, the disease-specific questionnaires are used clinically. Since QOL questionnaires are required to include multidisciplinary assessments, factors such as physical function, social activity, personal relations, work, mentality, health satisfaction, life satisfaction, sexual life, sleep, pain, fatigue, and vitality should all be assessed. The questionnaires for the symptoms and QOL of urinary incontinence, lower urinary tract symptoms, fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic organ prolapse, which have been
4 126 Momokazu Gotoh recommended by the ICI Subcommittee of Symptom and QOL Assessment are shown in Tables 3 7. Table 3 Recommended questionnaires for the evaluation of urinary incontinence and urinary incontinence/lower urinary tract symptoms/overactive bladder-grade A Combined symptoms and quality of life impact of urinary incontinence Men and women ICIQ (grade A new ) 2) Women Bristol Female LUTS-SF (grade A) 3) SUIQQ (grade A new ) 4) Men ICSmaleSF (grade A) 5) Combined symptoms and quality of life impact of overactive bladder Men and women OAB-q (grade A new ) 6) Symptoms of urinary incontinence Women Urogenital Distress Inventory (grade A) 7) UDI-6 (grade A) 8) Incontinence Severity Index (grade A) 9) BFLUTS (grade A) 10) Men ICSmale-LUTS primarily (grade A) 11) DAN-PSS-LUTS primarily (grade A) 12) Quality of life impact of urinary incontinence Men and women Quality of life in persons with UI(I-QOL) (grade A) 13) SEAPI-QMM 14) Women King s Health Questionnaire (KHQ) (grade A) 15) Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ) (grade A) 16) IIQ-7 16) Urinary Incontinence Severity Score (UISS) (grade A new ) 17) CONTILIFE (grade A new ) 18) Men None Table 4 Recommended questionnaires for the evaluation of symptoms and quality of life impact of pelvic organ prolapse Grade A None Grade B Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory (PFDI) 19) Pelvic Floor Impact Questionnaire (PFIQ) 19) Grade C P-QOL/St. Mary s Questionnaire Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Questionnaire e-paq Pelvic Floor Symptoms Questionnaire Danish Prolapse Questionnaire ICIQ-Vaginal Symptoms Questionnaire (not published)
5 QOL ASSESSMENT IN INCONTINENT PATIENTS 127 Table 5 Recommended questionnaires for the evaluation of symptoms and quality of life impact of fecal incontinence Grade A None Grade B Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scale 20) Manchester Health Questionnaire 21) Birmingham Bowel and Urinary Symptom Questionnaire (BBUS-Q) 22) Grade C Wexner score Faecal Incontinence Survey Elderly Bowel Symptoms Questionnaire Postpartum Flatal and Faecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scale Bowel Disease Questionnaire Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index Table 6 Recommended generic questionnaires for the evaluation of symptom and QOL impact of urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse Grade A SF-36 / SF-12 23) Rand-36 24) EuroQoL EQ-5D 25) Nottingham Health Profile 26) Sickness Impact Profile 27) Table 7 Recommended questionnaires for the evaluation of sexual function impact of urinary incontinence Grade A Men and women Golombok-Rust Inventory of Sexual Satisfaction 28) Men International Index of Erectile Function 29) ICS sex 30) BPHQOL9 31) Grade B Men and women Psychosocial Adjustment to Illness Scale Women Pelvic Organ Prolapse/Urinary Incontinence Sexual Questionnaire Brief Index of Sexual Function for Women Men Brief Sexual Function Inventory
6 128 Momokazu Gotoh VI. Development of an ICIQ-SF for urinary incontinence In order to clinically utilize the questionnaires and to internationally compare the studies on urinary incontinence, a simple questionnaire for symptoms and QOL, which can be used as an international criterion for assessment, is required. The Subcommittee of Symptom and QOL Assessment has been developing its original questionnaire for the symptoms of and QOL of patients with, urinary incontinence since the first ICI, and has developed an ICI Questionnaire-Short Form (ICIQ-SF) for urinary incontinence. The ICIQ-SF includes 10 questions on the frequency of urinary incontinence, degree of hindrance, frequency in use of a napkin, type of napkin, subjective assessment of the amount of urinary incontinence (the ordinary amount of urinary incontinence and the largest amount of urinary incontinence), influence on daily life, influence on social life, influence on sexual life, and quality of general life. Moreover, age, gender, and a subjective assessment of the cause of urinary incontinence are also included in the ICIQ-SF. The ICIQ-SF was verified and recommended as grade A new by the ICI. During the verification of the ICIQ-SF, considerable duplications were observed among the questions. Therefore, the ICIQ-SF was amended such that the final edition had only 3 questions related to the frequency of urinary incontinence, the ordinary amount of urinary incontinence, and the influence on daily life. These 3 questions were assessed on the basis of the data from 469 cases. Moreover, since the assessment of the cause of urinary incontinence is important for clinicians, a question related to the subjective assessment of the cause of urinary incontinence was included in the final edition. However, this question was not scored. The scores of the 3 questions were summed and the resulting totals ranged between 0 and 21 points. The ICIQ-SF was developed for all patients with urinary incontinence regardless of gender and age. The validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the ICIQ-SF for urinary incontinence were verified in Britain, and by 2004 the verified ICIQ-SF had been translated into 27 languages including Japanese, Dutch, Spanish, and Swedish. The translation into Japanese was performed using a standard method based on linguistic validation. 32) The validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the Japanese edition of the ICIQ-SF for urinary incontinence were also verified, and the results were comprehensively discussed in the report. 33) VII. Creation of an ICIQ unit In order to create an international standard assessment tool for pelvic problems related to functional disorders of the lower urinary tract, vagina, and lower alimentary canal, the ICI is creating an ICIQ unit. The situation of creating the ICIQ unit is shown in Tables 8 and 9, and this will be gradually published on the ICIQ website ( VIII. Items recommended by the Subcommittee of Symptom and QOL Assessment During the third ICI, the following items for symptom and QOL assessment were recommended for use in clinics and studies. 1. Regarding the diagnosis and treatment of urinary incontinence, clinicians should select an appropriate questionnaire from the list indicated by the ICI in order to assess the situation of urinary incontinence and its influence on patients life. 2. Clinicians are recommended to discuss the objective of using questionnaires in their medical examinations. 3. The grade A questionnaire is recommended for use in a randomized controlled trial related to the treatment of urinary incontinence.
7 QOL ASSESSMENT IN INCONTINENT PATIENTS 129 Table 8 ICIQ Units for symptom assessment Condition Core Modules Optional Modules Symptoms Lower urinary tract symptoms Male ICIQ-MLUTS Female ICIQ-FLUTS Male ICIQ-MLUTS Female ICIQ-FLUTS LF Vaginal symptoms ICIQ-VS Anal symptoms ICIQ-BS Patients Urinary incontinence ICIQ-UI SF ICIQ-UI LF Nocturia ICIQ-N Overactive bladder ICIQ-OAB Neurogenic ICIQ-Neuro Children ICIQ-LUTSC Table 9 ICIQ units for QOL assessment Condition Recommended add-on modules QOL Generic QOL Lower urinary tract symptoms ICIQ-LUTS qol SF-12 Vaginal symptoms ICIQ-VS qol SF-12 Fecal symptoms ICIQ-BS qol SF-12 Urinary incontinence ICIQ-LUTS qol SF-12 Nocturia ICIQ-N qol SF-12 Overactive bladder ICIQ-OAB qol SF-12 Neurogenic SF-12 Children ICIQ-LUTSC qol 4. Researchers are recommended to undertake further studies on the following items: Application of the grade A questionnaire to the wide range of examinations. Further examination of the sensitivity to a clinical change in grade A new, grade B, and insufficiently verified questionnaires. Development of a new questionnaire for special groups such as the elderly and infant. Description of the validity of the questionnaire as well as the method, objective, and statistical analysis used in the study. Examination of the influence of the questionnaire used in clinical treatment as well as an examination of the cost, participants burden, and ease of performance in the randomized controlled trial. CONCLUSION REMARKS In the third ICI, various questionnaires, which have been developed for the symptom and QOL assessment of fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic organ prolapse, in addition to
8 130 Momokazu Gotoh urinary incontinence, were ranked based on appropriate verifications of validity, reliability, and responsiveness, and were recommended according to the subject (male or female). Moreover, in order to create an international standard assessment tool for pelvic problems related to functional disorders of the lower urinary tract, vagina, and lower alimentary canal, an ICIQ unit is currently being created by the ICI. In the future, the questionnaire recommended by the Subcommittee of Symptom and QOL Assessment is expected to be used as the international standard. REFERENCES 1) Donovan J, Bosch R, Gotoh M, Jackson S, Naughton M, Radley S, Valiquette L. Symptom and Quality of Life Assessment, Chapter 10. In INCONTINENCE, edited by Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A. pp , 2005, Health Publication Ltd, UK. 2) Avery K, Donovan J, Peters DJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. A brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn, 2004; 23: ) Brookes ST, Donovan JL, Wright M, Jackson S, Abrams P. A scored form of the Bristol Female Lower Urinary tract Symptoms questionnaire: data from a randomized controlled trial of surgery for women with stress incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2004; 191: ) Kulseng-Hanssen S, Borstad E. The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and after surgery for stress incontinence. BJOG, 2003; 110: ) Donovan JL, Peters TJ, Abrams P, Brookes ST. Scoring the ICSmaleSF questionnaire. J Urol, 2000; 164: ) Coyne K, Revicki D, Hunt R. Psychometric validation of an overactive bladder symptom and health-related quality of life questionnaire: the OAB-q. Qual Life Res, 2003; 11: ) Shumaker SA, Wyman JF, Uebersax JS, McClish D, Fantl JA. Health-related quality of life measures for women with urinary incontinence: the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Distress Inventory. Qual Life Res, 1994; 3: ) Uebersax JS, Wyman JF, Shumaker SA, McClish DK, Fantl AJ. Short forms to assess life quality and symptom distress for urinary incontinence in women: the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Distress Inventory. Neurourol Urodyn, 1995; 14: ) Sandvik H, Hunskaar S, Seim A, Hermstad R, Vanvik A, Bratt H. Validation of a severity index in female urinary incontinence and its implementation in an epidemiological survey. J Epidemiol Com Health Med, 1993; 47: ) Jackson S, Donovan J, Brookes S, Eckford S, Swithinbank L, Abrams P. The Bristol Female Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms questionnaire: development and psychometric testing. Br J Urol, 1996; 77: ) Donovan JL, Abrams P, Peters TJ. The ICS- BPH Study: the psychometric validity and reliability of the ICSmale questionnaire. Br J Urol, 1996; 77: ) Hald T, Nordling J, Andersen JT, Bilde T, Meyhoff HH, Ealter S. A patient weighted symptom score system in the evaluation of uncomplicated benign prostatic hyperplasia. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl, 1991; 138: ) Dugan E, Cohen SJ, Robinson D. The quality of life of older adults with urinary incontinence: determining generic and condition specific predictors. Qual Life Res, 1998; 7: ) Stothers L. Reliability, validity, and gender differences in the quality of life index of the SEAPI-QMM incontinence classification system. Neurourol Urodyn, 2004; 23: ) Kelleher CJ, Cardozo LD, Khullar V, Salvatore S. A new questionnaire to assess the quality of life of urinary incontinent women. Br J Obstet Gynecol, 1997; 104: ) Uebersax JS, Wyman JF, Shumaker SA. Short forms to assess life quality and symptom distress for urinary incontinence in women: the incontinence impact questionnaire and the urogenital distress inventory. Neurourol Urodyn, 1995; 14: ) Stach-Lempinen B, Kirkinen P, Laippala P, Metsanoja R, Kujansuu E. Do objective urodynamic or clinical findings determine impact of urinary incontinence or its treatment on quality of life? Urology, 2004; 63: ) Amarenco G, Arnould B, Carita P, Haab F, Labat JJ, Richard F. European psychometric validation of the CONTILIFE: a Quality of Life questionnaire for urinary incontinence. Eur Urol, 2003; 43: ) Barber MD, Kuchibhatla MN, Pieper CF, Bump RC. Psychometric evaluation of 2 comprehensive condition-specific quality of life instruments for women with pelvic floor disorders. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2001;
9 QOL ASSESSMENT IN INCONTINENT PATIENTS : ) Rockwood TH, Church JM, Fleshman JW. Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scale: quality of life instrument for patients with fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum, 2000; 43: ) Bug GJ, Kiff ES, Hosker G. A new condition-specific health-related quality of life questionnaire for the assessment of women with anal incontinence. Br J Obstet Gynecol, 2001; 108: ) Hiller L, Radley S, Mann CH. Development and validation of a questionnaire for the assessment of bowel and lower urinary tract symptoms in women. Br J Obstet Gynecol, 2002; 109: ) Ware JE. Sf-36: Health Status Questionniare. Quality Quest Inc ) Hays RD, Sherbourne CD, Mazel RM. The RAND 36-Item Health Survey 1.0. Health Econ, 1993; 2: ) Donovan JL, Peters TJ, Abrams P. Scoring the ICSmaleSF questionnaire. J Urol, 2000; 164: ) Grimby A, Milsom I, Molander U, Wiklund I, Ekelund P. The influence of urinary incontinence on the quality of life of elderly women. Age Ageing, 1993; 22: ) Gaudenz R. Der inkontinenz-fragebogen, mit dem neuen urge-score and stress-score. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd, 1979; 39: ) Rust J, Golombok S. The Golombok-Rust Inventory of Sexual Satisfaction (GRISS). Br J Clin Psych, 1985; 1985: ) Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for the assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology, 1997; 49: ) Frankel SJ, Donovan JL, Peters TJ. Sexual dysfunction in men with lower urinary tract symptoms. J Clin Epidemiol, 1998; 51: ) Lukacs B, Comet D, Grange JC, Thibault P. Construction and validation of a short-form benign prostatic hypertrophy health-related quality of life questionnaire. Br J Urol, 1997; 80: ) Gotoh M, Donovan J, Corcos J, Naughton M, Homma Y. Symptom and QOL questionnaire for urinary incontinence, scored ICIQ-SF (International Consultation on Incontinence-Questionnaire: Short From), JNBS. 2001; 12: ) Donovan J, Naughton M, Gotoh M, Kelleher CJ. Committee 6, Symptom and Quality of Life Assessment. In INCONTINENCE (2nd ed.), edited by Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A. pp , 2002, Plymbridge Distributers Ltd, UK.
Monitoring patient status over time using common pain and musculoskeletal outcome measures
 icahe Outcomes Calculator Incontinence Version User Manual Monitoring patient status over time using common pain and musculoskeletal outcome measures Prepared by Research Team The International Centre
icahe Outcomes Calculator Incontinence Version User Manual Monitoring patient status over time using common pain and musculoskeletal outcome measures Prepared by Research Team The International Centre
Available from Deakin Research Online: http://hdl.handle.net/10536/dro/du:30019160. Reproduced with the kind permission of the copyright owner.
 Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the published version of the presentation: O'Connell, Beverly 2008, Developing
Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the published version of the presentation: O'Connell, Beverly 2008, Developing
Chapter 3. Urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in community-dwelling women aged 20-45 years: Risk factors and quality of life.
 Chapter 3 Urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in community-dwelling women aged 20-45 years: Risk factors and quality of life. CH van der Vaart, MD, JRJ de Leeuw, PhD, JPWR Roovers, MD, APM Heintz,
Chapter 3 Urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in community-dwelling women aged 20-45 years: Risk factors and quality of life. CH van der Vaart, MD, JRJ de Leeuw, PhD, JPWR Roovers, MD, APM Heintz,
Evaluation of urgency in women, with a validated Urgency, Severity and Impact Questionnaire (USIQ)
 DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0770-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of urgency in women, with a validated Urgency, Severity and Impact Questionnaire (USIQ) Lior Lowenstein & Mary P. FitzGerald & Kimberly Kenton
DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0770-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of urgency in women, with a validated Urgency, Severity and Impact Questionnaire (USIQ) Lior Lowenstein & Mary P. FitzGerald & Kimberly Kenton
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
CHSD. Refining Continence Measurement Tools. Centre for Health Service Development
 CHSD Centre for Health Service Development Refining Continence Measurement Tools RefiningContinenceMeasurementToolsRefiningContinenceMeasurementT oolsrefiningcontinencemeasurementtoolsrefiningcontinencemeasurem
CHSD Centre for Health Service Development Refining Continence Measurement Tools RefiningContinenceMeasurementToolsRefiningContinenceMeasurementT oolsrefiningcontinencemeasurementtoolsrefiningcontinencemeasurem
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men
 Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
Korean Women - Study Proves That Syndrome Does Not Effect on Sexual Life
 (25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
(25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION
 PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation?
 Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Th e effects of stress urinary incontinence on the quality of life of Turkish women in the reproductive age group
 Original Article Turk J Med Sci 2012; 42 (5): 845-851 TÜBİTAK E-mail: medsci@tubitak.gov.tr doi:10.3906/sag-1104-17 Th e effects of stress urinary incontinence on the quality of life of Turkish women in
Original Article Turk J Med Sci 2012; 42 (5): 845-851 TÜBİTAK E-mail: medsci@tubitak.gov.tr doi:10.3906/sag-1104-17 Th e effects of stress urinary incontinence on the quality of life of Turkish women in
Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life?
 42) Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life? Drahorádová P. 1, Mašata J. 1, Martan A. 1, Švabík K. 1, Pavlíková M. 2 1 Charles University in Prague, 1st Medical
42) Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life? Drahorádová P. 1, Mašata J. 1, Martan A. 1, Švabík K. 1, Pavlíková M. 2 1 Charles University in Prague, 1st Medical
Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence
 Original Article SOLIFENACIN AND MIXED URINARY INCONTINENCE STASKIN and TE Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence DAVID R. STASKIN
Original Article SOLIFENACIN AND MIXED URINARY INCONTINENCE STASKIN and TE Short- and long-term efficacy of solifenacin treatment in patients with symptoms of mixed urinary incontinence DAVID R. STASKIN
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Comparative analysis of summary scoring systems in measuring fecal incontinence
 J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:326-331 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.326 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903ㆍeISSN 2093-0488 Comparative analysis of summary
J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:326-331 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.326 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903ㆍeISSN 2093-0488 Comparative analysis of summary
Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Fecal incontinence (Encopresis) It is the fecal incontinence condition observed in children with chronic constipation over 1-2 years.
 WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
PROCEEDINGS INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT
 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE. Stress Urinary Incontinence
 PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
Correlation Between Psychological Stress Levels and the Severity of Overactive Bladder
 1 Correlation Between Psychological Stress Levels and the Severity of Overactive Bladder Symptoms H. Henry Lai, Vivien Gardner, Joel Vetter From the Division of Urologic Surgery, Department of Surgery,
1 Correlation Between Psychological Stress Levels and the Severity of Overactive Bladder Symptoms H. Henry Lai, Vivien Gardner, Joel Vetter From the Division of Urologic Surgery, Department of Surgery,
A community-based epidemiological survey of female urinary incontinence: The Norwegian EPINCONT Study
 Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 53 (2000) 1150 1157 A community-based epidemiological survey of female urinary incontinence: The Norwegian EPINCONT Study Yngvild S. Hannestad*, Guri Rortveit, Hogne Sandvik,
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 53 (2000) 1150 1157 A community-based epidemiological survey of female urinary incontinence: The Norwegian EPINCONT Study Yngvild S. Hannestad*, Guri Rortveit, Hogne Sandvik,
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds
 Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Urinary Incontinence: an overview!! Neil Harris Consultant Urological Surgeon, Leeds Content 1. Epidemiology of pelvic floor dysfunction Urinary incontinence Bowel dysfunction Sexual dysfunction 2. Treatment
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Urinary incontinence poses major medical
 ONE SIZE DOES NOT FIT ALL: MANAGEMENT OF THE DIFFICULT PATIENT * Karl J. Kreder, Jr, MD ABSTRACT Although the prevalence of urinary incontinence varies greatly depending on the criteria used to define
ONE SIZE DOES NOT FIT ALL: MANAGEMENT OF THE DIFFICULT PATIENT * Karl J. Kreder, Jr, MD ABSTRACT Although the prevalence of urinary incontinence varies greatly depending on the criteria used to define
Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMB
 The patient doesn't want anything "invasive": What can we offer? Case driven workshop on intractable overactive bladder Workshop 11 Dr Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMD International Continence Society
The patient doesn't want anything "invasive": What can we offer? Case driven workshop on intractable overactive bladder Workshop 11 Dr Beth Shelly PT, DPT, WCS, BCB PMD International Continence Society
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients Dissatisfied With Overactive Bladder Medication
 Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Combined Effects of Behavioral Intervention and Tolterodine in Patients With Overactive Bladder Medication Carl G. Klutke,, Kathryn L. Burgio, Jean F. Wyman, Zhonghong Guan, Franklin Sun, Sandra Berriman
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources
 Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
Case Study Activity: Managing Overactive Bladder in the Community Pharmacy Answers to Interactive Questions and Resources Case 1: Identifying Overactive Bladder Activity Preview Overactive bladder (OAB)
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP
 CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 Original Article UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Humera Ansar, Fauzia Adil and Aftab A. Munir ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To know the occurrence of unreported urinary and anal incontinence in
Original Article UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Humera Ansar, Fauzia Adil and Aftab A. Munir ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To know the occurrence of unreported urinary and anal incontinence in
5-Year Continence Rates, Satisfaction and Adverse Events of Burch Urethropexy and Fascial Sling Surgery for Urinary Incontinence
 5-Year Continence Rates, Satisfaction and Adverse Events of Burch Urethropexy and Fascial Sling Surgery for Urinary Incontinence L. Brubaker,*, H. E. Richter, P. A. Norton, M. Albo, H. M. Zyczynski, T.
5-Year Continence Rates, Satisfaction and Adverse Events of Burch Urethropexy and Fascial Sling Surgery for Urinary Incontinence L. Brubaker,*, H. E. Richter, P. A. Norton, M. Albo, H. M. Zyczynski, T.
Patient. Frequently Asked Questions. Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery?
 Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
Should SUI Surgery be Combined with Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery? Geoffrey W. Cundiff, M.D. 36 th National Congress of the South African Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists SASOG 2014 Learning
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines
 GYNAECOLOGY Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines NATALIA PRICE and SIMON R JACKSON The John Radcliffe
GYNAECOLOGY Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines NATALIA PRICE and SIMON R JACKSON The John Radcliffe
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women
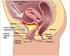 Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms
 THE OVERACTIVE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE BLADDER MEDICAL JOURNAL The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms Jassim Mohammad Alkhazraji*, Ban
THE OVERACTIVE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE BLADDER MEDICAL JOURNAL The Efficacy of the Antimuscarinic Drug Oxybutynin in the Treatment Women with Overactive Bladder (OAB) Symptoms Jassim Mohammad Alkhazraji*, Ban
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Brian Louis Cohen, M.D., M.P.H.
 Brian Louis Cohen, M.D., M.P.H. MEDICAL TRAINING Fellowship in Female Urology, Voiding Dysfunction, and Reconstructive Urology Anticipated, July 2007 June 2008 Residency in Urology, July 2003 June 2007
Brian Louis Cohen, M.D., M.P.H. MEDICAL TRAINING Fellowship in Female Urology, Voiding Dysfunction, and Reconstructive Urology Anticipated, July 2007 June 2008 Residency in Urology, July 2003 June 2007
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse. Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Urinary incontinence and Prolapse Dr Zeelha Abdool Consultant OBGYN Steve Biko Academic Hospital Definitions: IUGA/ICS standardized terminology Urinary incontinence (symptom): complaint of involuntary
Question ID: 6 Question type: Intervention Question: Does treatment of overactive bladder symptoms prevent falls in the elderly?
 PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
Pelvic Symptoms in Women With Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Symptoms in Women With Pelvic Organ Prolapse Lara J. Burrows, MD, Leslie A. Meyn, MS, Mark D. Walters, MD, and Anne M. Weber, MD, MS From the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive
Pelvic Symptoms in Women With Pelvic Organ Prolapse Lara J. Burrows, MD, Leslie A. Meyn, MS, Mark D. Walters, MD, and Anne M. Weber, MD, MS From the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive
Six Month Pilot Analysis: Improving Rehabilitation for Men with Prostate Cancer in North East London
 Six Month Pilot Analysis: Improving Rehabilitation for Men with Prostate Cancer in North East London June 2015 Helen Whitney (Physiotherapist and Prostate Cancer Project Lead) Thufayel Islam (Prostate
Six Month Pilot Analysis: Improving Rehabilitation for Men with Prostate Cancer in North East London June 2015 Helen Whitney (Physiotherapist and Prostate Cancer Project Lead) Thufayel Islam (Prostate
OAB (Overactive Bladder)
 OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care
 A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
A review of antimuscarinic prescribing for urinary incontinence in primary care Seema Gadhia On behalf of NHS Buckinghamshire Medicines Management Team In Collaboration with Introduction Urinary incontinence
SOGC Recommendations for Urinary Incontinence
 The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
Review The psychosocial impact of urinary incontinence in women
 The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist 10.1576/toag.13.3.143.27665 http://onlinetog.org 2011;13:143 148 Review Review The psychosocial impact of urinary incontinence in women Authors Amy J Sinclair / Ian N Ramsay
The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist 10.1576/toag.13.3.143.27665 http://onlinetog.org 2011;13:143 148 Review Review The psychosocial impact of urinary incontinence in women Authors Amy J Sinclair / Ian N Ramsay
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Bothersome urinary symptoms and disease-specific quality of life in patients with benign prostatic obstruction
 Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology, 2007; 41: 3241 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bothersome urinary symptoms and disease-specific quality of life in patients with benign prostatic obstruction High prevalence
Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology, 2007; 41: 3241 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bothersome urinary symptoms and disease-specific quality of life in patients with benign prostatic obstruction High prevalence
GLOSSARY of research terms
 GLOSSARY of research terms JLA Urinary Incontinence Working Partnership Workshop to set research priorities in Urinary Incontinence November 2008 Terms in bold are commonly used clinical/research terms.
GLOSSARY of research terms JLA Urinary Incontinence Working Partnership Workshop to set research priorities in Urinary Incontinence November 2008 Terms in bold are commonly used clinical/research terms.
INCONTINENCE OUTCOME MEASURES FOR URINARY JERRY G. BLAIVAS
 ELSEVIER OUTCOME MEASURES FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Objectives. To discuss the rudiments of data that need to be collected in order to develop validated, reproducible, well-accepted
ELSEVIER OUTCOME MEASURES FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Objectives. To discuss the rudiments of data that need to be collected in order to develop validated, reproducible, well-accepted
A Swedish version of a quality of life questionnaire for partners of men with symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction
 Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology, 2008; 42: 126131 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Swedish version of a quality of life questionnaire for partners of men with symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction
Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology, 2008; 42: 126131 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Swedish version of a quality of life questionnaire for partners of men with symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction
Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial Chantale Dumoulin, PhD, PT, Marie-Claude Lemieux, MD, FRCSC, Daniel Bourbonnais, PhD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial Chantale Dumoulin, PhD, PT, Marie-Claude Lemieux, MD, FRCSC, Daniel Bourbonnais, PhD,
Urinary incontinence during pregnancy
 Urinary incontinence during pregnancy Stian Langeland Wesnes 1,2 MD, Guri Rortveit 2,3 MD PhD, Kari Bø 4 PT PhD, Steinar Hunskaar 2 MD PhD Bergen, Norway From 1 Department of medicine, Haugesund Hospital,
Urinary incontinence during pregnancy Stian Langeland Wesnes 1,2 MD, Guri Rortveit 2,3 MD PhD, Kari Bø 4 PT PhD, Steinar Hunskaar 2 MD PhD Bergen, Norway From 1 Department of medicine, Haugesund Hospital,
Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review
 Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
Comparison of Fesoterodine, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin and Solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder A systematic review Hamed Kakarª, Bastiaantje M. Kok b, Sahar Mokhles c, Malalay Sarwar d * Supervisors:
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
Information for patients. Sex and Incontinence. Royal Hallamshire Hospital
 Information for patients Sex and Incontinence Royal Hallamshire Hospital Why is sex important? We may choose to be sexual, regardless of our age, physical status or stage of life. Those with health problems
Information for patients Sex and Incontinence Royal Hallamshire Hospital Why is sex important? We may choose to be sexual, regardless of our age, physical status or stage of life. Those with health problems
Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care
 Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care Background Incontinence (i.e., loss of bladder and/or bowel control) is a significant health care problem, which affects
Role of the Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse or Continence Care Nurse in Continence Care Background Incontinence (i.e., loss of bladder and/or bowel control) is a significant health care problem, which affects
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Instruments Available for Use in Assessment Center
 Instruments Available for Use in Assessment Center The Assessment Center Instrument Library includes instruments from PROMIS, Neuro QoL, NIH Toolbox and Health LiTT. All instruments are available for use
Instruments Available for Use in Assessment Center The Assessment Center Instrument Library includes instruments from PROMIS, Neuro QoL, NIH Toolbox and Health LiTT. All instruments are available for use
Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
 Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy Dobson DaVanzo & Associates, LLC Vienna, VA 703.260.1760 www.dobsondavanzo.com Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy Dobson DaVanzo & Associates, LLC Vienna, VA 703.260.1760 www.dobsondavanzo.com Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section
 The new england journal of medicine original article Urinary after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section Guri Rortveit, M.D., Anne Kjersti Daltveit, Ph.D., Yngvild S. Hannestad, M.D., and Steinar Hunskaar,
The new england journal of medicine original article Urinary after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section Guri Rortveit, M.D., Anne Kjersti Daltveit, Ph.D., Yngvild S. Hannestad, M.D., and Steinar Hunskaar,
es of Urinary Incontinence:
 Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder. Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital
 Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Overactive bladder Approximately 34 million adults in the United States The International
Case Study on the use of Electro acupuncture for Overactive Bladder Siu Cheetham Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Overactive bladder Approximately 34 million adults in the United States The International
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a
 Menopause Matters from Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women www.menopause.org Tyler M. Muffly, MD; Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD Overactive bladder is a debilitating health condition
Menopause Matters from Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Midlife Women www.menopause.org Tyler M. Muffly, MD; Marie Fidela R. Paraiso, MD Overactive bladder is a debilitating health condition
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
Position Statement on Mesh Midurethral Slings for Stress Urinary Incontinence The polypropylene mesh midurethral sling is the recognized worldwide standard of care for the surgical treatment of stress
ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE
 ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE About urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence affects around 3.5 million people of all ages in the UK (DoH 2000; the Continence Foundation 2000). For many, urinary
ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE About urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence affects around 3.5 million people of all ages in the UK (DoH 2000; the Continence Foundation 2000). For many, urinary
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures
 Systematic review Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures 37 37 44 Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures Authors Jefferson
Systematic review Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures 37 37 44 Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures Authors Jefferson
Depressive Symptoms and Treatment of Women with Urgency Urinary Incontinence
 Depressive symptoms and treatment of women with urgency urinary incontinence Rachel Kafri, Arad Kodesh, Jeffrey Shames, Jacob Golomb & Itshak Melzer International Urogynecology Journal Including Pelvic
Depressive symptoms and treatment of women with urgency urinary incontinence Rachel Kafri, Arad Kodesh, Jeffrey Shames, Jacob Golomb & Itshak Melzer International Urogynecology Journal Including Pelvic
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
INCONTINENCE. 5 th EDITION 2013 ICUD EDITORS PAUL ABRAMS - LINDA CARDOZO - SAAD KHOURY - ALAN WEIN BLADDER CANCER
 er Cancer has been prepared by an international ion and recommendations of a group of well known o review the literature and present a clear collegial r Cancer. This book is a valuable working tool for
er Cancer has been prepared by an international ion and recommendations of a group of well known o review the literature and present a clear collegial r Cancer. This book is a valuable working tool for
Quality of Life of Children
 Quality of Life of Children with Mental Illness Martha J. Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Children s Psychiatric Center Outpatient Services Objectives History
Quality of Life of Children with Mental Illness Martha J. Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Children s Psychiatric Center Outpatient Services Objectives History
Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:53 59 (2001) Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Daniele Porru, 1 * Giuliana Campus, 2 Alessandro Caria, 2 Giuliana
Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:53 59 (2001) Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Daniele Porru, 1 * Giuliana Campus, 2 Alessandro Caria, 2 Giuliana
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Prepared by
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Prepared by
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
