Reporter s Guide to. Prostate Cancer
|
|
|
- Colleen Short
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reporter s Guide to Prostate Cancer
2 Table of Contents What is Prostate Cancer? 3 Who is at Risk for Prostate Cancer? 3 How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed? 3 How is Prostate Cancer Treatment Determined? 4 Current Prostate Cancer Treatments 5 Prostate Cancer Treatments by Recurrence Risk 6 Challenges in Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments 6 Can Prostate Cancer be Prevented? 7 Glossary of Terms 7 Additional Resources 9 2
3 What is Prostate Cancer? Cancer occurs when the process of normal cell division is disrupted; new cells form when the body doesn t need them or when old and damaged cells don t die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth, or tumor, and can either be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). 1 Called prostate cancer or cancer of the prostate, this disease occurs when cancer cells form in the tissues of the prostate, a gland located around the urethra (under the bladder) in men that produces part of the seminal fluid. It tends to grow slowly compared with most other cancers. However, depending on factors including characteristics specific to the patient and the tumor, prostate cancer can manifest as a slow-growing tumor to a very aggressive, metastatic and potentially fatal disease. 2 This shows the prostate and nearby organs National Cancer Institute Who is at Risk for Prostate Cancer? Although any man can develop prostate cancer, there are certain factors that increase the risk. These include: 1 Age Those older than age 65 are at higher risk. Family history Risk increases if a father, brother or son developed prostate cancer. Race African Americans are at higher risk than Caucasians and Hispanics. It is less common in Asians, Pacific Islanders, American Indians and Alaskan Natives. Pre-cancerous prostate changes Changes such as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, a prostate lesion, can be a precursor to cancer. Genetic (chromosomal) abnormalities Abnormalities such as an altered or missing gene may contribute to risk. This shows the inside of the prostate, urethra, rectum, and bladder Excluding skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men in the United States. 1 In 2010, more than 217,000 new cases of prostate cancer were estimated, and more than 32,000 men died from the disease, making it the second leading cause of cancer death behind lung cancer. 3,4 How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed? There are certain symptoms that may be associated with prostate cancer and should be checked with a health care provider, including: 5 Trouble passing urine or a frequent urge to urinate, especially at night Weak or interrupted urine stream Pain, burning or blood when urinating Painful ejaculation or blood in the semen Nagging pain in the back, hips or pelvis 3
4 There are prostate cancer screening tests that are used to help detect the disease at an early stage 5 before symptoms are present, confirm diagnosis or monitor progression of the disease. These include: Digital rectal examination (DRE): Insertion of a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum by a physician to check for hard or lumpy areas in the prostate through the rectal wall. 1 Prostate-specific antigen (PSA): PSA, a protein produced by the prostate that is released in very small amounts into the bloodstream, can often signify when the prostate doesn t function properly. Typical range references are laboratory, age and race dependent. However, levels over 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) may require additional monitoring and follow-up. 6 Transrectal ultrasound: Insertion of a probe that acts as an ultrasound into the rectum to check the prostate for abnormal areas. 1 A biopsy is a definitive way to confirm or rule out prostate cancer: Transrectal biopsy: Insertion of needles through the rectum into the prostate to remove small tissue samples that are evaluated by a pathologist for cancer. 1 How is Prostate Cancer Treatment Determined? Many factors are taken into consideration to determine a treatment plan for prostate cancer. These can include a man s life expectancy, age, co-morbidities (additional health risks), his preference regarding treatment and the potential side effects of treatments. 7 Clinically, among the most important factors in considering a treatment plan are the combination of PSA level, Gleason score and staging of prostate cancer. 5 Gleason score is an assessment of the aggressiveness of the tumor under the microscope. Gleason score is rated on a scale from 2 to 10. A lower Gleason score (2 to 4) may mean the cancer is less aggressive. A higher Gleason score (7 to 10) suggests a more aggressive cancer. 6 Staging determines the extent, or spread, of prostate cancer. There are four stages: 1 { Stage I: The tumor is confined to the prostate. { Stage II: The tumor is more advanced or a higher grade than Stage I, but doesn t extend beyond the prostate. { Stage III: The tumor extends beyond the prostate and may have invaded the seminal vesicles (tubular glands above the prostate), but cancer cells haven t spread to the lymph nodes. { Stage IV: The tumor may have invaded the bladder, rectum or nearby structures (beyond the seminal vesicles), and may have spread to the lymph nodes, bones or other parts of the body. This is known as advanced, or metastatic, prostate cancer. Taken together, PSA levels and rate of change, Gleason score and staging can help determine the prognosis and risk of progression or recurrence of disease. This relative recurrence risk is an important factor when fashioning a treatment plan. 7 4
5 Current Prostate Cancer Treatments Prostate cancer treatment options, depending on recurrence risk and other factors, include: Active Surveillance The cancer is carefully monitored for signs of progression through regular PSA blood tests and DREs at least every six months and a biopsy at least yearly. Treatment may be started if symptoms develop or additional tests are abnormal. Active surveillance may avoid or delay side effects related to treatment, but may reduce the chance to control the cancer before it spreads. 7 Surgery Surgery is an option for early prostate cancer. A radical prostatectomy removes the entire prostate gland and some surrounding tissue. 6 If there is concern the cancer has spread beyond the prostate, a doctor may perform a pelvic lymph node dissection to remove lymph nodes near the prostate for signs of cancer. 1 Since the testicles are a primary source of testosterone, they may be surgically removed a procedure called an orchiectomy for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. 6 There can be significant side effects from surgical procedures, including erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence. However, the latest surgical techniques for early stage disease have shown improvement in cure rates and tolerability. 6 Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy uses directed radioactive exposure to kill the cancer cells and surrounding tissues. Radiation can be administered from outside the body (external beam) or inside the body via pellets placed in the prostate (brachytherapy). In the later stages of prostate cancer, radiation may be used to reduce pain. High doses of radiation can increase the rate of side effects, such as urinary problems, erectile dysfunction and rectal bleeding. However, technology improvements have allowed for precise targeting of radiation, which can minimize side effects. 6 Hormone (Androgen Deprivation) Therapy Androgens are masculinizing sex hormones, which play a critical role in the development and progression of prostate cancer. 8 A prime target for therapeutic intervention in men with prostate cancer is halting or slowing the body s testosterone production, which can slow the growth of cancer, or even shrink it. Hormone therapy is used alone for prostate cancer that has returned after previous treatment; before, during or after radiation therapy; or for prostate cancer that has metastasized. 9 Therapy that blocks natural hormones includes orchiectomy, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists and antiandrogens. Typically, once the disease has become resistant to initial hormone therapy, manipulation with antiandrogenic agents is employed. 9 Side effects of hormone therapy include decreased libido, breast tenderness and enlargement, loss of bone density and muscle mass, weight gain and hot flashes. 6 Androgen deprivation therapy has also been shown to increase elevated fasting plasma glucose and to increase risk of cardiovascular events. 10 Side effects may be managed by making changes in the treatment regimen or using additional therapies that may address these side effects. 6 Immunotherapy Novel treatment approaches are emerging to stimulate a patient s own immune system to help manage prostate cancer progression. 11 5
6 Chemotherapy When the cancer has metastasized, or advanced, beyond the prostate area and no longer responds to hormone therapy, chemotherapy may be used to kill the circulating cancer cells. Side effects of chemotherapy, which kills fast-growing cancer cells but can also harm rapidly dividing normal cells, may include hair loss, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue and an increased risk of infection, bruising and bleeding. Most side effects generally stop when chemotherapy is stopped. 1 Supportive Care Also known as palliative care, this involves providing care, both physical and psychosocial, for a person with prostate cancer who is no longer eligible for, or desires, aggressive medical treatment. The intention is not a cure but to provide comfort and pain relief. 1 Prostate Cancer Treatments by Recurrence Risk Recurrence risk looks at factors such as the likelihood that prostate cancer is confined to the prostate or has spread to lymph nodes, or will advance or metastasize after treatment. 7 Low Prostate cancer remains in the prostate area. Treatment may include active surveillance or radiation therapy, or a radical prostatectomy possibly accompanied by a pelvic lymph node dissection for staging the cancer. 7 Intermediate Treatment options are similar to low recurrence risk, but androgen deprivation therapy with or without brachytherapy may be used. Treatment path will depend in part on whether the cancer has spread into the lymph nodes. 7 High, Very High or Metastatic (Advanced) Treatment may include a combination of hormone therapy, radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection. Ongoing follow-up or treatment is then determined by laboratory parameters, x-ray and/or presence of clinical signs and symptoms. 7 Challenges in Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments One of the greatest challenges facing health care providers is how to treat a person whose prostate cancer has spread following treatment with hormone therapy. Metastatic advanced prostate cancer, also referred to as castration-resistant prostate cancer or CRPC, occurs when cancer has metastasized beyond the prostate and disease progresses despite conventional hormone therapies. 12 This occurs because testosterone continues to be produced by the adrenal glands and tumor tissue and thus can help fuel the 13, 14 tumor s growth. Men with asymptomatic metastatic CRPC may be treated with a secondary hormone therapy or immunotherapy. Men with symptomatic metastatic CRPC may receive chemotherapy or palliative radiation therapy. If the tumor continues to progress after chemotherapy, additional chemotherapy or a secondary hormone therapy may be used. 7 6
7 Can Prostate Cancer be Prevented? Currently, there is no way to prevent prostate cancer. Eating a wide variety of vegetables and fruits each day, limiting intake of red meats and dairy products, maintaining an active lifestyle and healthy weight, refraining from smoking and consuming only moderate amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 prostate cancer. Glossary of Terms Active surveillance A treatment option for prostate cancer that involves careful monitoring for signs that the disease has advanced and includes: regular PSA tests, DREs and other tests such as routine biopsies, but not medical treatment. 6 Adrenal glands Glands located near the kidneys that produce male hormones, including 5 to 10 percent of a man s testosterone. In prostate cancer treatment, antiandrogens are used to block testosterone produced by the adrenal glands. 20 Advanced prostate cancer Cancer has moved beyond the prostate region to the lymph nodes, bones or other parts of the body. 21 Androgen Category of sex hormones which stimulate activity of secondary male sex organs and encourage development of male sex characteristics. 1 Androgen receptors A protein molecule that carries androgen s messages or instructions to prostate cells. Androgen receptors are over-expressed in advanced prostate cancer contributing to prostate cancer growth even if androgen has been blocked. 22 Antiandrogens Compounds that block the biologic effects of androgens, such as testosterone, produced by the adrenal glands. 1 Brachytherapy (internal radiation) Placement of tiny radioactive seeds inside the prostate to attack the cancer; used for early stage prostate cancer that is relatively slow-growing. 6 Castrate level Occurs when the level of a man s testosterone drops by 90 to 95 percent due to surgical or chemical (drug) therapy. 9 Chemotherapy Treatment with drugs that kill cancer cells. Side effects of chemotherapy, which kills fast-growing cancer cells but can also harm rapidly dividing normal cells, may include but are not limited to: hair loss, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue and an increased risk of infection, bruising and bleeding. Most side effects generally stop when chemotherapy is stopped. 1 7
8 Digital rectal examination (DRE) Insertion of a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum by a physician to check for hard or lumpy areas in the prostate through the rectal wall. 1 External beam radiation Prostate cancer treatment in which radiation is focused on the prostate gland from a source outside the body. 6 Gleason score An assessment of the aggressiveness of the tumor under the microscope. Gleason score is rated on a scale from 2 to 10. A lower Gleason score (2 to 4) may mean the cancer is less aggressive. A higher Gleason score (7 to 10) suggests a more aggressive cancer. A Gleason score report may consist of two numbers (e.g., 3, 4). The first number is the grade assigned to the cancer type that is most numerous in the tissue sample. The second number is the grade assigned to the cancer type that is the second-most numerous. To determine the total Gleason score, these two numbers are added 6, 20 together. Hormone therapy Therapy used to reduce levels of male hormones, or androgens (including testosterone), that feed prostate cancer growth. Hormone therapy can include surgery (orchiectomy) to remove the testicles or drugs such as antiandrogens, which are given in conjunction with other medicines. 1 Androgen deprivation therapy This is another term for a class of medications that compete with androgens to stimulate the androgen receptor, which drives prostate cancer growth. 20 Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists/antagonists A type of hormone therapy that prevents the pituitary gland from releasing LHRH, which regulates the production of testosterone by the testicles. 20 Orchiectomy Surgical removal of the testicles to stop the body s production of testosterone, a hormone that can feed prostate cancer growth. Orchiectomy is not frequently used compared to treatment with drugs, but its effect on testosterone levels is used as a benchmark for the drop that should be achieved with the use of LHRH agonists. 20 Immunotherapy Treatment to boost or restore the ability of the immune system to fight cancer, infections and other diseases. 11 Pelvic lymph node dissection Removal and evaluation of lymph nodes near the prostate gland to determine if the prostate cancer has spread. Lymph nodes are small glands that fight infections but can also serve as vehicles for transporting cancer cells throughout the body. 1 8
9 Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test Measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by prostate gland cells, in the blood. Used as a screening tool, as prostate cancer or benign (not cancerous) conditions can also increase a PSA level. 6 Radiation therapy Use of high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. The two main types of radiation therapy are external beam radiation and brachytherapy (internal radiation). 6 Radical prostatectomy Surgery to remove the entire prostate gland plus some surrounding tissue to remove the cancer. 6 Recurrence Risk An assessment of how likely it is that prostate cancer will come back, depending on a combination of factors that include changes in the blood PSA level, Gleason score and staging of the tumor. Recurrence risk is an important consideration when determining treatment options. 7 Transrectal biopsy Insertion of needles through the rectum into the prostate to remove small tissue samples that are evaluated by a pathologist for cancer. 1 Transrectal ultrasound Insertion of a probe that acts as an ultrasound into the rectum to check the prostate for abnormal areas. 1 Additional Resources Non-Profit Support and Advocacy Organizations American Cancer Society CancerCare Cancer Support Community Men s Health Network Prostate Cancer Foundation Prostate Conditions Education Council Prostate Health Education Network 9
10 Prostate Net The Prostate Cancer Research Institute Us TOO International Prostate Cancer Education and Support Network Women Against Prostate Cancer ZERO - The Project to End Prostate Cancer Government and Professional Societies American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) American Urological Association (AUA) American Urological Foundation National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) National Cancer Institute 10
11 References 1. National Cancer Institute. What you need to know about prostate cancer. Published September Accessed September 29, Joniau S, Van Poppel H. Localized prostate cancer: can we better define who is at risk of unfavourable outcome? Br J Urol Int Mar;101(suppl 2): Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, CA Cancer J Clin. 2010; 60; American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; National Cancer Institute. Understanding prostate changes: a health guide for men. booklet.pdf. Published September Accessed September 29, Prostate Cancer Foundation. An introduction to prostate cancer. E15C5D8BB6B1%7D/IntroProstateCancer.pdf. Accessed September 29, National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines for patients, prostate cancer. V Accessed February 3, Chen Y, Clegg NJ, Scher HI. Anti-androgens and androgen-depleting therapies in prostate cancer: new agents for an established target. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10: Perlmutter MA, Lepor H. Androgen deprivation therapy in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Rev Urol. 2007;9(suppl 1):S3-S Levine GN, D Amico AV, Berger P, et al, on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, the American Cancer Society, and the American Urological Association. Androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer and cardiovascular risk. A science advisory from the American Heart Association, American Cancer Society, and American Urological Association. Circulation. 2010;121: Immunotherapy. Dictionary of Cancer Terms. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Cancer Institute. cancer.gov/dictionary/?cdrid= Accessed September 15, Hotte SJ, Saad F. Current management of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Oncol. 2010;17(suppl 2):S72-S Brawer M. New treatments for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Rev Urol. 2008;10(4): Hofland J, van Weerden WM, Dits NF, et al. Evidence of limited contributions for intratumoral steroidogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70(3): Chan R, Lok K, Woo J. Prostate cancer and vegetable consumption. Mol Nutr Food Res Feb;53(2): Venkateswaran V, Haddad AQ, Fleshner NE, et al. Association of diet-induced hyperinsulinemia with accelerated growth of prostate cancer (LNCaP) xenografts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(23): Antonelli JA, Jones LW, Bañez LL, et al. Exercise and prostate cancer risk in a cohort of veterans undergoing prostate needle biopsy. J Urol. Epub 2009 Sep Huncharek M, Haddock KS, Reid R, Kupelnick B. Smoking as a risk factor for prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of 24 prospective cohort studies. Am J Public Health. 2010;100(4): Gong Z et al. Alcohol consumption, finasteride, and prostate cancer risk: results from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. Cancer, 2009 Aug 15;115(16): Carroll PR, Carducci MA, Zietman AL, Rothaermel JM. Report to the nation on prostate cancer: a guide for men and their families. Santa Monica, CA: Prostate Cancer Foundation; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Prostate cancer--advanced. Accessed May 16, Heinlein CA, Chang C. Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer. Endocrine Reviews April;25(2):
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer HORMONE THERAPY FOR ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer HORMONE THERAPY FOR ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma
 A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
Prostate Cancer Screening
 Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Prostate Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team June Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Roswell Park scientists and clinicians:
 The Prostate Cancer Center at Roswell Park Connects You to Nationally Recognized Experts for State-of-the-Art Treatment Options and Compassionate, Evidence-based Care Founded in 1898, Roswell Park Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Center at Roswell Park Connects You to Nationally Recognized Experts for State-of-the-Art Treatment Options and Compassionate, Evidence-based Care Founded in 1898, Roswell Park Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT
 MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
SIGNPOSTS. Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer. Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer
 SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
Testing for Prostate Cancer. Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me?
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report
 Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer. Understanding Your Treatment Options
 After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
After Diagnosis: Prostate Cancer Understanding Your Treatment Options What s inside How will this booklet help me?... 3 What is the prostate?... 4 What is prostate cancer?... 4 Who gets prostate cancer?...
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts
 Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
Prostate Cancer Information and Facts Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnutsized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system.
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer
 Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
CONTENTS. What is Cancer?... 2. What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?... 3. Who's at Risk?... 3 Diagnosis & Staging Tests... 3
 CONTENTS Introduction................................. 1 What is Cancer?.............................. 2 What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?....... 3 Who's at Risk?................................
CONTENTS Introduction................................. 1 What is Cancer?.............................. 2 What Should I Know About Prostate Cancer?....... 3 Who's at Risk?................................
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
 Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate cancer: English Prostate cancer This fact sheet is about how prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated. We also have fact sheets in your language about chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, side
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
PROSTATE CANCER. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk
 Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer: Understanding Your Risk When the urologist calls with the life-changing news that your prostate biopsy is positive for prostate cancer, an office appointment is made to
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
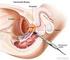 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Treatment Choices for Men
 National Cancer Institute Treatment Choices for Men With Early-Stage Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Things to Remember Many men with prostate
National Cancer Institute Treatment Choices for Men With Early-Stage Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Things to Remember Many men with prostate
National Cancer Institute
 National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This booklet is only
National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This booklet is only
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You?
 Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 2005 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology
 Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions
 Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men
 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Prostate Cancer In-Depth
 Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Prostate Cancer In-Depth Introduction Prostate cancer is the most common visceral malignancy among American men. In the year 2003, there are expected to be 220,000 new cases and nearly 29,000 deaths in
Getting checked for Prostate Cancer
 Getting checked for Prostate Cancer Quick guide for men and their families and whanau Stay well for your family and whanau. doctor, nurse or health professional about prostate cancer. You should do this
Getting checked for Prostate Cancer Quick guide for men and their families and whanau Stay well for your family and whanau. doctor, nurse or health professional about prostate cancer. You should do this
Asymptomatic or smoldering myeloma with no symptoms and slow growing cancer cells
 ESSENTIALS Multiple Myeloma Diagnosed with Multiple Myeloma? It s important to understand everything you can about your diagnosis, possible treatments, and places to go for support and care. Cancer is
ESSENTIALS Multiple Myeloma Diagnosed with Multiple Myeloma? It s important to understand everything you can about your diagnosis, possible treatments, and places to go for support and care. Cancer is
Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
PROSTATE CANCER. Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American
 PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
A start to help you understand prostate cancer
 A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
Understanding Prostate Cancer. The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients. Advanced Care. Improving Lives.
 Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Prevention Series. Prostate Cancer. How to reduce your risk. Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca
 Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prevention Series Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 www.cancer.ca Prostate Cancer How to reduce your risk Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
M6-1 NOTE. Each major learning point is clearly identified by boldface type throughout the guide and emphasized in the PowerPoint presentation.
 Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Prostate Cancer. Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology
 Prostate Cancer Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology ABOUT ASCO The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is the world s leading professional
Prostate Cancer Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology ABOUT ASCO The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is the world s leading professional
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer
 Know Your Options A Prostate Cancer Education Program Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer US TOO International, Inc. National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Know Your Options A Prostate Cancer Education Program Understanding Treatment Choices for Prostate Cancer US TOO International, Inc. National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
cure A Patient s Guide Prevention Strategies Screening & Diagnosis Treatment Options Side Effects Resources Tips for Dealing with Sexual Dysfunction
 A Patient s Guide toprostate Cancer Prevention Strategies Screening & Diagnosis Treatment Options Side Effects Resources Tips for Dealing with Sexual Dysfunction cure C ancer U pdates, R esearch & E ducation
A Patient s Guide toprostate Cancer Prevention Strategies Screening & Diagnosis Treatment Options Side Effects Resources Tips for Dealing with Sexual Dysfunction cure C ancer U pdates, R esearch & E ducation
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa
 PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments
 Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments Guest Expert: Kevin, DO Associate Professor of Medical Oncology, Yale Cancer Center www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with
Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatments Guest Expert: Kevin, DO Associate Professor of Medical Oncology, Yale Cancer Center www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with
