Eradication of established murine mesothelioma tumours by combined immunotherapy
|
|
|
- Pamela Heath
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eradication of established murine mesothelioma tumours by combined immunotherapy Shruti Krishnan, B.Sc (Micro), Grad Dip (ForenSc), M.Sc (Micro), M (ForSci) This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy The University of Western Australia School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences 2015
2
3 ABSTRACT Despite the recent progress made in applying immunotherapy for the treatment of various cancers, such a therapy has not been developed for treating mesothelioma. Mesothelioma has a latency period of years with a median survival being 9-10 months from diagnosis. Due to the lack of early diagnostic capabilities, patients in general, present with well-advanced disease that renders many therapeutic options ineffective. Standard treatments for the management of mesothelioma are limited due to late diagnoses, significant toxicities and the occurrences of relapses. Targeted therapies such as immunotherapy are selective and are aimed at stimulating the host s immune system to produce complete tumour destruction. The work described in this thesis, and the work of others in both mouse tumour models and clinical settings has shown that simultaneous targeting of multiple immune mechanisms results in better outcomes. A major deterrent to boosting anti-tumour immune activity was the immunosuppressive environment within the growing tumours themselves. Work carried out by our laboratory, and others, defined the role of T regs and TGF-β in suppressing immune responses to growing tumours. This led to the hypothesis that overcoming immune suppression alone was not sufficient, and perhaps an additional boost to effector T cell activity would improve the outcome. Chapter 3 investigated the improved efficacy of the timed combination of three immune modulators (anti-cd25mab, anti-tgf-βmab and anti-ctla-4mab) in the AE17 model (timed triple immunotherapy, TTI). Treatment with the TTI completely eradicated tumours in 50% of the C57BL/6J mice, with maintenance of low T reg numbers nine days after treatment initiation. The cured mice also showed complete resistance to re-challenge with the same tumour cells and had an increased percentage iii
4 of CD4 + CD44 + T cells, indicative of immune memory creation. Increased effector T cell function was also observed during the rechallenge (Kissick et al., 2012). Chapter 4 shows that the 50% cure rate of AE17 tumours could be raised to 100% by doubling the dosage of anti-tgf-βmab in the TTI protocol. It was also found that the standard TTI treatment produced complete clearance in the non-tgf-β AB1 murine mesothelioma tumours in all BALB/c mice. Additionally, combining all three agonist antibodies into a single intra-tumoural triple immunotherapy cocktail (TIC) for injection into the established tumours was found to be as effective as the TTI in the AB1 model. Chapter 5 investigated the role of B cells in TIC and TTI mediated tumour eradication. Mice cured by the treatment showed elevated levels of tumour specific IgG antibodies. These antibodies were higher against whole live tumour cells than cell lysates. Time-course studies of tumour clearance showed; (a) that IgG levels were not elevated during tumour clearance and (b) that B cell numbers were increased in the tumour draining lymph nodes and spleens during tumour clearance. Finally, employment of B-cell knock-out mice indicated a significant role for B cells in the successful eradication of the established tumours by the TIC. Chapter 6 detailed preliminary studies examining the efficacy of the triple immunotherapy on eradicating non-mesothelioma tumours. TIC treatment tested on the murine tumours (B16 melanoma, EO771 and 4T1 breast carcinoma tumours) showed that it was ineffective in eradicating tumours. However, a transient delay in tumour growth and improvement in survival times were observed in the EO771 and 4T1 breast carcinoma models. Further optimisations of the concentration of the triple immunotherapy components, and/or the addition of a fourth component are discussed. Additional work in this chapter showed that the 100% cure rate observed against AB1 iv
5 tumours at 9mm 2 dropped to 20% when the tumours were bigger (25mm 2 ). When two 9mm 2 tumours were grown on each mouse and only one tumour was treated, the results showed reduced efficacy in eradication of the treated tumour and delayed growth of the untreated tumour. Overall, the findings of this thesis indicate that: a) targeting multiple immune mechanisms simultaneously can completely eradicate established tumours, b) immunity to the eradicated tumour is achieved and c) that clinical translation to mesothelioma patients (phase I) is warranted. v
6 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... iii TABLE OF CONTENTS... vi ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS... xii STATEMENT OF CANDIDATE CONTRIBUTION... xvi ABBREVIATIONS... xvii LIST OF FIGURES... xxi LIST OF TABLES... xxiv PUBLICATIONS AND PROCEEDINGS... xxv Chapter 1 Literature Review Introduction Etiology of mesothelioma Importance of early diagnosis of mesothelioma Standard treatments for mesothelioma Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation therapy Murine models of mesothelioma Immunosurveillance and cancer control Immunotherapy Enhancing anti-tumour effector activity by immunotherapy Importance of immune checkpoint blockade Overcoming immune suppressive mechanisms employed by growing tumours Regulatory T cells TGF-β, a key immunosuppressive cytokine Strategies targeting tumour-intrinsic evasion mechanisms Role of T regs in mesothelioma Impact of T reg cell depletion on survival Combination therapies are necessary for overcoming immune suppressive mechanisms vi
7 1.8.1 Simultaneous targeting of T regs and TGF-β is more beneficial Boosting effector cell function Role of B cells in immunotherapy for mesothelioma Extending combination therapy to other tumours Aims of the thesis Chapter 2 Materials and methods Murine tumour cell lines Tissue culture Storage of tumour cell lines Resuscitation of frozen stocks Passage of tumour cell lines Harvesting cells for in vivo use Cell counting In vivo use of tumour cell lines Inoculation of tumour cells Measurement of subcutaneous tumours Euthanasia of tumour bearing mice Treatment regimens Preparation of anti-cd25mab treatments Preparation of anti-ctla-4mab treatments Preparation of anti-tgf-βmab treatments Preparation of triple immunotherapy cocktail (TIC) Treatment administration Timed triple immunotherapy (TTI) treatment administration at 9mm Intra-tumoural (i.t) administration of a single dose of triple immunotherapy cocktail (TIC) Sample preparation and analysis by flow cytometry Preparation of lymph nodes and tumours Preparation of spleen cells Live/dead viability dye (eflour 780) staining Cell surface staining for flow cytometry Intracellular Fox P3 and Ki-67 staining Preparation of compensation controls for flow cytometry Flow cytometric analysis of samples vii
8 Analysis of T cells Analysis of Regulatory T cells Analysis of DC cells Determination of relative expression of CD Determination of cell numbers Isolation of immune cells by Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) Adoptive transfer of immune cells into mice Tumour specific Immunoglobulin detection analysis Preparation of serum Preparation of cell lysate coated ELISA immunosorbent plates Detection of tumour cell lysate specific IgG in serum Detection of IgG in serum specific to live tumour cells Measurement of optical density of serum IgG specificity Statistical analysis Materials and Reagents Mice Reagents ELISA reagents Equipment Buffers, media and solutions CHAPTER 3 Development and characterisation of an effective triple immunotherapy in a TGF-β secreting murine mesothelioma model (AE17 model) Introduction Results Intra-tumoural administration of anti-cd25mab together with intraperitoneal anti-ctla-4mab and sequential anti-tgf-βmab, completely eradicates established AE17 murine mesothelioma tumours Administration of timed triple immunotherapy into established AE17 tumours inhibits re-accumulation of T regs in tumour draining lymph nodes TTI treatment results in greater maturation of DCs and subsequent activation of effector T cells in the TDLNs A specific anti-tumour memory response results from TTI treatment viii
9 Sustained depletion of T regs in the TDLNs of re-challenged AE17 cured mice Induction of memory T cells by the TTI treatment Discussion CHAPTER 4 Improved efficacy of the triple immunotherapy in the non-tgf-β secreting murine mesothelioma model (AB1 model) Introduction Results Timed administration of antibodies targeting CD25, TGF-β and CTLA-4 completely cleared established AB1 sub-cutaneous tumours in 100% of BALB/c mice A combined, single administration of the triple treatment as a cocktail (TIC) is sufficient to induce complete clearance of AB1 tumours in close to 90% of animals Induction of systemic immune response in cured mice Susceptibility of cured mice to re-challenge with syngeneic alternate tumour type-4t1 breast carcinoma Incomplete neutralisation of TGF-β within the AE17 tumour microenvironment is integral to the suboptimal response generated in AE17 tumour bearing mice treated with TTI Sub-optimal response observed in partial responders despite attempts at recovering them with additional top-up of immunotherapy treatment Increased anti-tgf-βmab dosage in the original TTI results in complete tumour eradication in AE17 tumour bearing mice Induction of systemic immune response in the mice cured using mtti Discussion Chapter 5 Evidence of B cell involvement in triple immunotherapy Introduction Result Detection of tumour specific IgG antibodies in the serum of AE17 tumourbearing mice by ELISA Elevated levels of tumour specific IgG antibodies in the sera of AE17 tumour-bearing mice cured by TTI ix
10 Partial cross-reactivity of IgG antibodies in TTI cured mice to B16 melanoma cell lysates and spleen cell lysates Development of a living whole cell ELISA for detecting serum IgG levels against AE17 tumour cells Increased reactivity of serum IgG to whole AE17 live cells in TTI long-term cured mice Increased levels of AB1 tumour specific IgG in sera of mice 95 days post treatment with the TTI or TIC Partial cross-reactivity of IgG antibodies in TTI and TIC cured mice to syngeneic 4T1breast carcinoma cells IgG antibodies present in the TTI and TIC cured BALB/c mice are tumour specific and not auto-reactive Tumour specific antibodies are not elevated during tumour eradication Elevated B cell numbers during TIC induced tumour eradication B cells are vital to the efficacy of the combined triple immunotherapy B cells are required for successful treatment of AB1 tumours by TIC Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment is critical to tumour clearance Discussion Chapter 6 Preliminary investigations of the intra-tumoural triple immunotherapy in other tumour models and its effects on distal tumours Introduction Results Detection of high levels of T regs within the tumour microenvironment of non-mesothelioma tumours by flow cytometry TIC treatment is not effective in eradicating B16 melanoma tumours in C57BL/6J mice Increased dosage of all three components of TIC has no effect on tumour retardation Transient period of EO771 breast carcinoma tumour growth retardation in C57BL/6J mice treated with TIC x
11 6.2.4 Increased survival time in 4T1 tumour-bearing BALB/c mice treated with either TIC or dtic Efficacy of the triple immunotherapy is diminished with an increase in tumour burden TIC treatment was effective in generating partial concomitant immunity a preliminary study on the effect of TIC on distal tumours Discussion Conclusion and future perspectives Future of the triple immunotherapy Addition of more agonist antibodies to the TIC treatment to improve tumour regression Chapter 7 Bibliography xi
12 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to express my gratitude to my supervisors Assoc. Prof. Manfred Beilharz, Asst. Prof. Demelza Ireland and Dr. Haydn Kissick. Manfred, I would like to thank you for accepting me into your lab and for teaching me everything I know now. I would especially like to thank you for your patience and constant diligence when I needed help with my research. I am very grateful that I could approach you to ask questions irrespective of whether they were related to lab work, designing experiments, candidature or scholarship. Your encouragement and advice in regard to research and a future scientific career have been invaluable. I have learnt a great deal on how to further my career as a research scientist, and it is all thanks to you. Thank you for having faith in me. Dem, I am very grateful for your patient guidance and for always being there for me. You have always been very helpful with everything regarding the experimental designs, the data interpretation, critical reading of manuscripts and of course, my thesis chapters. Your insights have been invaluable, and I will always be very grateful. Haydn, you were there in the beginning when I was barely equipped with the task at hand. Thank you for patiently helping me with so many things initially when I had just started my Ph.D. All the animal work, flow cytometry, tissue culturing and data interpretation, I learnt from you. Thank you. Parts of the experimental work described in this thesis were performed by other members of the Beilharz laboratory. Specifically, Dr. Haydn Kissick assisted me with the performance and interpretation of experiments described in chapter 3 at the beginning of my Ph.D. work in March The following experimental work was conducted with the 2012 Honours student Emily Bakker: The initial TTI (see section 4.2.1) and TIC (see section 4.2.2) treatment experiments in the AB1 murine xii
13 mesothelioma model; initial experiments on IgG detection following the cure of AB1 tumours (see section 5.2.4) and the single tumour burden experiment described in section The following year, a new Honours student, Cassandra Lee assisted in the following experiments: the IgG detection experiments in sections and and the time-course experiments described in and I would also like to thank Dr. Sara Greay, Dr. Cornelia Hooper and Dr. Erika Bosio for their support and assistance throughout the difficult times faced during my candidature. I would not be the person or a scientist that I am today if it had not been for you. Not only have you guys been there for support during this whole experience but you have also shared your knowledge as young successful scientists and have given me the confidence that I could make a good researcher as well. Chandelle, you have been a great office buddy- thanks for cheering me up in the laboratory when it seemed impossible to smile. Thank you for sharing my enthusiasm for the goodies available at conferences and for distracting me from my nervousness for public speaking. Cassandra and Milly, thank you for being such exceptionally good students! Your input into the project has been invaluable. I will miss all of you, and I wish, wherever life takes us, we will always find a way to stay in touch (Thank god for social networking sites!!). I would like to thanks the Dust Disease Board of NSW for funding part of the research presented in my thesis. I am very grateful to the University of Western Australia for awarding me with a Scholarship for International Research Fees (SIRF), University Postgraduate Award for International Students (UPAIS) and the UWA Travel Award. Without the financial support provided, none of this would have been possible. I would also like to acknowledge the School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine (UWA) for allowing me to undertake my research within the school. xiii
14 Furthermore, I would like to acknowledge some of our collaborators. I would like to thank Tracy Lee-Pullen, Irma Larma and Matthew Linden from CMCA for their excellent assistance with operating the flow cytometer, designing my antibody panels and data analyses on FlowJo. A special thanks to Kathy Heel for patiently teaching me the importance of maintaining gating strategies for all samples being analysed. I appreciate the assistance provided by Sandy Goodin, Kelly Hunt, Neill Wilson and the rest of the staff at M block, Animal Care Unit of the University of Western Australia for assisting with animal monitoring. Thank you! I feel incredibly blessed to have so many amazing people in my life. I would like to take this opportunity to thank my friends and family for their love and support; when I needed them the most. Dibakar, Paritosh and Prashant: you guys are the best! You had been there to lend an ear when I needed someone to talk to and your humour, it astonishes me but yet, I do not think I have ever laughed so much. Thanks, also for having me over at your houses and for taking time to teach me how to cook. I would also like to thank all the new friends I made since I first arrived in Australia and for all the good times we have had together. Thanks for being such great friends. Chloe and Jerome, you guys have been the best housemates, and I am extremely blessed to have you guys in my life. You welcomed me into your home and made me feel like I was part of your family. Thank you for all the fun moments we have had together: the yummy salads, pasta, interesting conversations, Zombie marathon, a shared passion for star wars, dancing, the dinner parties, the list is endless.. xiv
15 To my most treasured family: Amma, Appa, Vasanth, Santosh and Chitra. All of you have been integral to making me a strong and independent person. If it were not for your love and support, none of this would have been possible. To my dear husband Vasanth, you have made me a better person from the moment you came into my life. You are definitely, the person who has motivated and inspired me the most; and made me try harder to achieve my goals and to never give up hope. You are unquestionably my better half, and I love you for that. Thanks for being there for me. Amma and Appa, what can I say: you have inspired and encouraged me every step of the way! I am forever grateful to you for always believing in me and for the unconditional love you have been giving me. I honestly believe that I could not have finished my candidature without my parents and my husband. Love you guys. My thoughts also go to my beloved great-uncle Seetharaman, who believed in me long before I believed in myself. xv
16 STATEMENT OF CANDIDATE CONTRIBUTION I hereby declare that all of the work described within this thesis was performed by myself. Exceptions are the few experimental contributions from other members of the Beilharz laboratory detailed in the acknowledgements. Shruti Krishnan A/Prof Manfred Beilharz Candidate Co-ordinating supervisor April 2015 xvi
17 ABBREVIATIONS + Immunopositive - Immunonegative # Number o C Degrees (Celsius) µg Microgram µl Microlitre 2-ME AON APC APCs ARC ATP BCG BD BKO CD Cm 2 CTL CTLA-4 DAPI DC DD ddh 2 O DMSO DNA EDTA 2-Mercaptoethanol Antisense Oligonucleotides Allophycocyanin Antigen Presenting Cells Animal Resource Centre Adenosine Tri-phosphate Bacillus of Calmette and Guerin Becton Dickinson B-cell Knockout Cluster of differentiation Centimetres squared Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Cytotoxic T lymphocyte Antigen-4 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole Dendritic Cell Denileukin Diftitox Distilled deionised water Dimethyl Sulphoxide Deoxyribonucleic acid Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid xvii
18 ELISA ELISPOT EPP FACS FCS FDA FITC FoxP3 FSC GCV GITR GM-CSF Gy hr HRP HSV i.p i.t IDO IFN IGF IgG IL IMRT LCMV mab MDSC MFI Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Enzyme-linked Immunospot Extrapleural Pneumonectomy Fluorescence-activated cell sorting Foetal Calf Serum Food and Drug Administration Fluorescein isothiocyanate Forkhead box P3 Forward Scatter Ganciclovir Glucocorticoid Induced TNF Factor Granulocyte/Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Gray (unit) Hour Horseradish Peroxidase Herpes Simplex Virus Intra-peritoneal Intra-tumoural Indoleamine -2,-3 -dioxygenase Interferon Insulin-like Growth Factor Immunoglobulin G Interleukin Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Lymphocytic Chorio-Meningitis Virus Monoclonal antibody Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Mean Fluorescence Intensity xviii
19 MHC min ml MM NK cells NKT OD PBS PD-1 PDGF PD-L1 PE Major histocompatibility complex Minute Millilitre Murine Mesothelioma Null Killer cells Natural Killer T cells Optical Density Phosphate Buffered Saline Programmed Death-1 Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Programmed Death Ligand-1 R-Phycoerythrin PE-Cy 7 Phycoerythrin-Cyanine 7 PerCP-Cy5.5 pfu RCC RPMI RT s.c SCC SD SMART SMRP SSC Peridinin-chlorophyll proteins-cyanine5.5 Plaque-forming units Renal Cell Carcinoma Roswell Park Memorial Institute Radiation Therapy Subcutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Standard Deviation Surgery for mesothelioma after radiation therapy Soluble Mesothelin-Related Protein Side Scatter SV40 Simian Virus 40 TAA TCR TDLN Tumour Associated Antigen T Cell Receptor Tumour Draining Lymph Node xix
20 T eff TGF-β TIC tk TNF TPA T regs TTI UT UWA VEGF WT Effector T cells Transforming Growth Factor-β Triple Immunotherapy Cocktail Thymidine kinase Tumour Necrosis Factor Tissue Polypeptide Antigen Regulatory T cells Timed Triple Immunotherapy Untreated University of Western Australia Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Wild-type xx
21 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1. 1 Major mechanisms by which potent anti-tumour immune responses can be generated Figure 2. 1 Timed Triple Immunotherapy (TTI) experiment protocol Figure 2. 2 Gating strategy for analysing CD4 + and CD8 + T cells Figure 2. 3 Gating strategy for T reg estimation in TDLNs and tumours Figure 2. 4 Gating strategy for analysing dendritic cells Figure Improved survival with complete tumour eradication in 46% of mice treated with timed triple immunotherapy (TTI) a significant improvement over double immunotherapy (DI) Figure Sustained depletion of T reg cells in TDLNs by TTI treatment even 3 days post treatment completion Figure 3. 3 Enhanced CD80 expression by dendritic cells and increased effector T cell levels in mice treated with TTI Figure 3. 4 Sustained depletion of T regs in the TDLNs of re-challenged cured mice Figure 3. 5 Induction of memory T cells in mice cured of AE17 murine mesothelioma by TTI treatment Figure 4.1 Complete tumour eradication in 100% of AB1 tumour bearing BALB/c mice treated with TTI Figure 4. 2 Tumour growth kinetics and survival of AB1 tumour bearing BALB/c mice following treatment with the timed triple immunotherapy (TTI) or the triple immunotherapy cocktail (TIC) xxi
22 Figure 4. 3 Tumour growth of partial responders to the TTI treatment is not significantly different from the DI treated mice Figure 4. 4 Failed recovery of partial responders despite attempts with secondary round of immunotherapy Figure 4. 5 Complete tumour eradication in 100% of AE17 tumour bearing C57BL/6J mice treated with mtti Figure 5. 1 Elevated AE17 cell lysate specific IgG antibodies detected in the sera of AE17 end-point tumour bearing untreated mice Figure 5. 2 Elevated levels of tumour specific IgG observed in sera of TTI cured mice compared to untreated controls Figure 5. 3 Partial cross-reactivity of IgG antibodies in the serum of TTI long-term cured mice to syngeneic B16 melanoma tumour cell lysates Figure 5. 4 Detection of increased reactivity of serum IgG in TTI cured mice to whole live AE17 cells Figure 5. 5 Increased reactivity of serum IgG to whole AE17 live cells in TTI cured mice compared to AE17 cell lysates Figure 5. 6 Elevated levels of tumour specific IgG antibodies detected in combined immunotherapy (TTI and TIC) treated mice Figure 5. 7 Partial cross-reactivity high against live syngeneic 4T1 tumour cells in TTI and TIC cured mice Figure 5. 8 Low levels of auto-reactive antibodies in TTI and TIC cured mice Figure 5. 9 No significant change in serum IgG levels in TIC treated mice up to 20 days post treatment Figure Changes in B cell percentage post TIC treatment Figure Successful tumour eradication with TIC requires B cells xxii
23 Figure Anti-tumour efficacy of TIC treatment is augmented by B cells Figure Manipulation of tumour microenvironment is important for successful clearance of established tumours Figure 6. 1 Detection of T regs within non-mesothelioma tumours grown in both C57BL/6J and BALB/c mice Figure 6. 2 Growth of melanoma tumours in C57BL/6J mice is unhindered by TIC treatment Figure 6. 3 Double the dosage of all three components in the TIC has no effect on melanoma growth in C57BL/6J mice Figure 6. 4 Treatment with TIC or dtic did not significantly improve survival of mice bearing EO771 tumours Figure 6. 5 Improved survival with TIC or dtic in BALB/c mice bearing 4T1 tumours, compared to mice left untreated Figure 6. 6 Central zone of tumour clearance observed in mice post treatment with dtic Figure 6. 7 Tumour eradication efficacy of TTI treatment lowered with increase in tumour burden in AB1 tumour bearing BALB/c mice Figure 6. 8 TIC treatment of single primary tumour in mice co-challenged simultaneously with AB1 tumours was effective in generating partial concomitant immunity to secondary tumours xxiii
24 LIST OF TABLES Table 1. 1 Monotherapies used for the depletion of T regs in murine mesothelioma models Table 2. 1 Mono-clonal antibodies Table 2. 2 Antibodies used for flow cytometry Table 3. 1 TTI cured mice are resistant to re-challenge with original inoculum (AE17) and partially resistant to syngeneic B16 melanoma re-challenge Table 4. 1 BALB/c mice cured of established AB1 tumours with TTI or TIC are resistant to re-challenge Table 4. 2 Immunological memory generated in BALB/c mice cured of established AB1 tumours with TIC are tumour specific Table 4. 3 No significant improvement in immune cell numbers in partial responders Table 4. 4 Mice cured of established AE17 tumours with mtti are resistant to rechallenge xxiv
25 PUBLICATIONS AND PROCEEDINGS Publication arising from Ph.D. candidature 1. Kissick, H. T., Ireland, D. J., Krishnan, S., Madondo, M. & Beilharz, M. W Tumour eradication and induction of memory against murine mesothelioma by combined immunotherapy. Immunology and Cell Biology, 90, (This paper covers the data described in chapter 3 and represents the early stages of the development of the successful timed triple immunotherapy (TTI) for the treatment of subcutaneous murine mesothelioma) 2. Krishnan, S., Bakker, E., Lee, C., Kissick, H. T., Ireland, D. J. & Beilharz, M. W Successful combined intra-tumoural immunotherapy of established murine mesotheliomas requires B cell involvement. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, (In press). (This paper covers the data described in chapters 4 and 5 of this thesis which concerns the development and characterisation of the triple therapy cocktail (TIC) and also includes the role of B cells in TIC mediated tumour eradication) Conference proceedings 1. Krishnan, S., Ireland, D. J., Kissick, H. T. & Beilharz, M. W. (2011) Improved success rate with a triple immunotherapy for the treatment of mesothelioma. The Australian Society for Medical Research, Western Australian scientific symposium, Australia. Oral 2. Krishnan, S., Ireland, D. J., Kissick, H. T. & Beilharz, M. W. (2011) Characterisation of a successful triple immunotherapy for the treatment of mesothelioma. Combined Biological Science Meeting, Australia. Poster xxv
26 3. Krishnan, S., Ireland, D. J., Kissick, H. T. & Beilharz, M. W. (2012) Tumour eradication and induction of memory against murine mesothelioma by combined immunotherapy. Australian Society for Medical Research, Western Australian scientific symposium, Australia. Oral 4. Krishnan, S., Bakker, E., Ireland, D. J., Kissick, H. T. & Beilharz, M. W. (2012) Tumour eradication and induction of memory against murine mesothelioma by combined immunotherapy. Combined Biological Science Meeting, Australia. Oral 5. Krishnan, S., Bakker, E., Lee, C., Kissick, H. T., Ireland, D. J. & Beilharz, M. W. (2014). Successful combined intra-tumoural immunotherapy of established murine mesotheliomas requires B cell involvement. International Cytokine and Interferon Society, Cytokines Down Under in 2014: From Bench to Beyond. Australia. Poster xxvi
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY. Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds
 NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
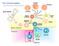 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
1 page Overview. CONCURRENT 1D, 1E, 1F Biology & Pathogenesis Multi-Modality Immunology 1
 1 page Overview 21 Oct Tuesday 1500 on REGISTRATION 1800 Welcome Reception & Cocktails at the Cape Town International Conference Centre (CTICC) 22 Oct Wednesday 0730 REGISTRATION 0830 OPENING 0900 PLENARY
1 page Overview 21 Oct Tuesday 1500 on REGISTRATION 1800 Welcome Reception & Cocktails at the Cape Town International Conference Centre (CTICC) 22 Oct Wednesday 0730 REGISTRATION 0830 OPENING 0900 PLENARY
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality
 Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality Introduction While using the body s own immune system as a
Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality Introduction While using the body s own immune system as a
Oncos Therapeutics: ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. March 2015. Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder
 Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art
 Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art Paul Baas The Netherlands Cancer Institute August 12, 2011, Carlsbad, CA Summary Diagnosis; epithelial type subdivided Pleiomorphic vs other Staging: IASLC-IMIG
Malignant Mesothelioma State of the Art Paul Baas The Netherlands Cancer Institute August 12, 2011, Carlsbad, CA Summary Diagnosis; epithelial type subdivided Pleiomorphic vs other Staging: IASLC-IMIG
CLINICAL POLICY Department: Medical Management Document Name: Opdivo Reference Number: CP.PHAR.121 Effective Date: 07/15
 Page: 1 of 6 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Page: 1 of 6 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Osteosarcoma: treatment beyond surgery
 Osteosarcoma: treatment beyond surgery Eric Chow, DVM DACVS Sue Downing, DVM DACVIM-Oncology Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma: treatment beyond surgery Eric Chow, DVM DACVS Sue Downing, DVM DACVIM-Oncology Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. Osteosarcoma
Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update
 Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases Research Institute Bernie Banton Centre University of Sydney Australia Physicians Week RACP 19-5-2009 Health Risks of Asbestos Fibers
Malignant Mesothelioma: an Update Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases Research Institute Bernie Banton Centre University of Sydney Australia Physicians Week RACP 19-5-2009 Health Risks of Asbestos Fibers
Mesothelioma. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
MesoPDT. Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI. Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology
 MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma
 The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
Griffith University - Case for Support. Mesothelioma Research Program
 Griffith University - Case for Support Mesothelioma Research Program Professor Lyn Griffiths Director, Dean, Research and Director, Genomics Research Centre (GHI) Established in 2007. Integrated health
Griffith University - Case for Support Mesothelioma Research Program Professor Lyn Griffiths Director, Dean, Research and Director, Genomics Research Centre (GHI) Established in 2007. Integrated health
BNC105 CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS REACH KEY MILESTONES CLINICAL PROGRAM TO BE EXPANDED
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 3 August 2011 ABN 53 075 582 740 BNC105 CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS REACH KEY MILESTONES CLINICAL PROGRAM TO BE EXPANDED Data from renal cancer trial supports progression of the trial: o Combination
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 3 August 2011 ABN 53 075 582 740 BNC105 CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS REACH KEY MILESTONES CLINICAL PROGRAM TO BE EXPANDED Data from renal cancer trial supports progression of the trial: o Combination
Lessons learned from the Western Australian experience with mesothelioma
 Lessons learned from the Western Australian experience with mesothelioma Alison Reid, Western Australian Institute for Medical Research In partnership with Nick de Klerk, Nola Olsen, Jan Sleith, Geoffrey
Lessons learned from the Western Australian experience with mesothelioma Alison Reid, Western Australian Institute for Medical Research In partnership with Nick de Klerk, Nola Olsen, Jan Sleith, Geoffrey
An Introduction To Immunotherapy And The Promise Of Tissue Phenomics
 An Introduction To Immunotherapy And The Promise Of Tissue Phenomics INSIDE: n The Potential of Immunotherapy n Towards an Understanding of Immunotherapy n Current Approaches to Immunotherapy n The Immunotherapy
An Introduction To Immunotherapy And The Promise Of Tissue Phenomics INSIDE: n The Potential of Immunotherapy n Towards an Understanding of Immunotherapy n Current Approaches to Immunotherapy n The Immunotherapy
Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer
 Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Mesothelioma Research Program University of Toronto Asbestos related diseases Mesothelioma Lung
Screening, early referral and treatment for asbestos related cancer Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Mesothelioma Research Program University of Toronto Asbestos related diseases Mesothelioma Lung
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Advances in Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Reason for Hope
 Advances in Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Reason for Hope Daniel H. Sterman, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine and Surgery Co-Director, PENN Mesothelioma and Pleural Program University
Advances in Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Reason for Hope Daniel H. Sterman, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine and Surgery Co-Director, PENN Mesothelioma and Pleural Program University
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment
 Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment Immunotherapy and Lung Cancer Immunotherapy is quickly developing as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapy
Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment Immunotherapy and Lung Cancer Immunotherapy is quickly developing as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapy
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Summary of treatment benefits
 Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
PRODYNOV. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI. Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology
 PRODYNOV Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI
PRODYNOV Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Update on Clinical Trials and Foundation Funded Grants
 Update on Clinical Trials and Foundation Funded Grants Mary Hesdorffer, MS, APRN-BC Medical Liaison Meso Foundation www.curemeso.org Delivering the Diagnosis Delivering the Diagnosis Day 1 Taking control
Update on Clinical Trials and Foundation Funded Grants Mary Hesdorffer, MS, APRN-BC Medical Liaison Meso Foundation www.curemeso.org Delivering the Diagnosis Delivering the Diagnosis Day 1 Taking control
Malignant Mesothelioma Recent Advances
 Malignant Mesothelioma Recent Advances Dr AS Paul 04 Aug 06 DM Seminar Malignant mesothelioma A tumour of serosal surfaces Pleura, peritoneum Increasing incidence worldwide Association with asbestos exposure
Malignant Mesothelioma Recent Advances Dr AS Paul 04 Aug 06 DM Seminar Malignant mesothelioma A tumour of serosal surfaces Pleura, peritoneum Increasing incidence worldwide Association with asbestos exposure
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Principal Investigator: Valerie W. Rusch, MD, FACS, Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Protocol 1101-1088 Phase I study of intra-pleural administration of GL-ONC1 in patients with malignant pleural effusion: primary, metastases and mesothelioma Principal Investigator: Valerie W. Rusch, MD,
Protocol 1101-1088 Phase I study of intra-pleural administration of GL-ONC1 in patients with malignant pleural effusion: primary, metastases and mesothelioma Principal Investigator: Valerie W. Rusch, MD,
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2
 Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Cancer Therapies 3. Adjunctive Therapies On completion of this module the RN will State the difference between a normal
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 2 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Cancer Therapies 3. Adjunctive Therapies On completion of this module the RN will State the difference between a normal
Mesothelioma 2014. Paul Baas Department of Thoracic Oncology The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam
 Mesothelioma 2014 Paul Baas Department of Thoracic Oncology The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam Disclosures Grants from Pfizer and Roche Advisor for MSD and Verastem Once upon a time. http://amlbenzene.net/diseases-asbestos.htm
Mesothelioma 2014 Paul Baas Department of Thoracic Oncology The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam Disclosures Grants from Pfizer and Roche Advisor for MSD and Verastem Once upon a time. http://amlbenzene.net/diseases-asbestos.htm
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know
 Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Overview of Phase 1 Oncology Trials of Biologic Therapeutics
 Overview of Phase 1 Oncology Trials of Biologic Therapeutics Susan Jerian, MD ONCORD, Inc. February 28, 2008 February 28, 2008 Phase 1 1 Assumptions and Ground Rules The goal is regulatory approval of
Overview of Phase 1 Oncology Trials of Biologic Therapeutics Susan Jerian, MD ONCORD, Inc. February 28, 2008 February 28, 2008 Phase 1 1 Assumptions and Ground Rules The goal is regulatory approval of
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Cancer Immunotherapy: immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and adoptive T-cell therapies - Overview
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3066973/ Cancer Immunotherapy: immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and adoptive T-cell therapies - Overview Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3066973/ Cancer Immunotherapy: immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and adoptive T-cell therapies - Overview Description:
Therapeutic Goods Administration Orphan Drugs Program: Discussion paper
 Therapeutic Goods Administration Orphan Drugs Program: Discussion paper Submission from the Clinical Oncology Society of Australia and Cancer Council Australia March 2015 The Clinical Oncology Society
Therapeutic Goods Administration Orphan Drugs Program: Discussion paper Submission from the Clinical Oncology Society of Australia and Cancer Council Australia March 2015 The Clinical Oncology Society
Latest advances in the treatment of mesothelioma
 Latest advances in the treatment of mesothelioma Assoc Prof Thomas John Medical Oncologist, NHMRC Fellow Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute 28 th March 2015 Disclosures Nil relevant Honoraria:
Latest advances in the treatment of mesothelioma Assoc Prof Thomas John Medical Oncologist, NHMRC Fellow Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute 28 th March 2015 Disclosures Nil relevant Honoraria:
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy
 CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication. Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic
 Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
Pulling the Plug on Cancer Cell Communication Stephen M. Ansell, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Why do Waldenstrom s cells need to communicate? Waldenstrom s cells need activating signals to stay alive. WM cells
Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development
 Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development Sanjeeve Bala, MD, MPH Ovarian Cancer Endpoints Workshop FDA White Oak September 3, 2015 Overview Immune agents from
Ovarian Cancer and Modern Immunotherapy: Regulatory Strategies for Drug Development Sanjeeve Bala, MD, MPH Ovarian Cancer Endpoints Workshop FDA White Oak September 3, 2015 Overview Immune agents from
Predictive Biomarkers for PD1 Pathway Inhibitor Immunotherapy
 Predictive Biomarkers for PD1 Pathway Inhibitor Immunotherapy Michael B. Atkins, M.D. Deputy Director Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Michael Atkins, MD Consulting Fees (e.g., advisory
Predictive Biomarkers for PD1 Pathway Inhibitor Immunotherapy Michael B. Atkins, M.D. Deputy Director Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Michael Atkins, MD Consulting Fees (e.g., advisory
Anti-PD1 Agents: Immunotherapy agents in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Claire Vines, 2016 Pharm.D. Candidate
 + Anti-PD1 Agents: Immunotherapy agents in the treatment of metastatic melanoma Claire Vines, 2016 Pharm.D. Candidate + Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. + Objectives Summarize NCCN
+ Anti-PD1 Agents: Immunotherapy agents in the treatment of metastatic melanoma Claire Vines, 2016 Pharm.D. Candidate + Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. + Objectives Summarize NCCN
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point during their lifetime. 3
 1. What is cancer? 2. What causes cancer?. What causes cancer? 3. Can cancer be prevented? The Facts One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point
1. What is cancer? 2. What causes cancer?. What causes cancer? 3. Can cancer be prevented? The Facts One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point
MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION
 MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION HUI MIN CHEAH PhD Candidate School of Medicine and Pharmacology University of Western Australia Lung Institute of Western Australia
MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION HUI MIN CHEAH PhD Candidate School of Medicine and Pharmacology University of Western Australia Lung Institute of Western Australia
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Understanding series. new. directions. 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org. A guide for the patient
 Understanding series LUNG CANCER: new treatment directions 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS What s New in lung cancer? Advancements...4 Changes in genes that
Understanding series LUNG CANCER: new treatment directions 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS What s New in lung cancer? Advancements...4 Changes in genes that
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen
 Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen Documentation Phase II clinical trial of preparation Panagen was performed in compliance with the following documentation: Approval of
Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen Documentation Phase II clinical trial of preparation Panagen was performed in compliance with the following documentation: Approval of
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES
 ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
Immune Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
 Immune Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer December 16, 2014 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-229-3239 Toll Only:
Immune Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer December 16, 2014 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-229-3239 Toll Only:
Medical Therapies Limited EGM Presentation
 Medical Therapies Limited EGM Presentation Maria Halasz Chief Executive Officer 5 May 2009 1 Agenda 1. Company information 2. Recent developments 3. Business strategy 4. Key value inflection points for
Medical Therapies Limited EGM Presentation Maria Halasz Chief Executive Officer 5 May 2009 1 Agenda 1. Company information 2. Recent developments 3. Business strategy 4. Key value inflection points for
Cancer and the immune system: can we beat cancer at its own game?
 Cancer and the immune system: can we beat cancer at its own game? Andrew R. Haas, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Philadelphia, Pa Why can t immune
Cancer and the immune system: can we beat cancer at its own game? Andrew R. Haas, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Philadelphia, Pa Why can t immune
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT
 1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition
 Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Laboratory of Tumor
Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Laboratory of Tumor
Cancer Clinical trials:
 Cancer Clinical trials: All you need to know A booklet for patients with cancer The future of cancer therapy F O R E W O R D If you have cancer, clinical trials may offer you additional treatment options.
Cancer Clinical trials: All you need to know A booklet for patients with cancer The future of cancer therapy F O R E W O R D If you have cancer, clinical trials may offer you additional treatment options.
Immuno-Oncology, The New Era of Cancer Treatment. Ted Lee, MD, MPH Disease Area Head, IO, Pac Rim, Bristol Myers Squibb
 Immuno-Oncology, The New Era of Cancer Treatment Ted Lee, MD, MPH Disease Area Head, IO, Pac Rim, Bristol Myers Squibb 1 Disclosures Dr. Ted Lee is an employee of Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. New Therapies
Immuno-Oncology, The New Era of Cancer Treatment Ted Lee, MD, MPH Disease Area Head, IO, Pac Rim, Bristol Myers Squibb 1 Disclosures Dr. Ted Lee is an employee of Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. New Therapies
Mesothelioma. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
INSERM/ A. Bernheim. Overcoming clinical relapse in multiple myeloma by understanding and targeting the molecular causes of drug resistance
 A. Bernheim Overcoming clinical relapse in multiple myeloma by understanding and targeting the molecular causes of drug resistance OVER-MyR is funded by the European Commission within its FP7 specific
A. Bernheim Overcoming clinical relapse in multiple myeloma by understanding and targeting the molecular causes of drug resistance OVER-MyR is funded by the European Commission within its FP7 specific
New Advances in Cancer Treatments. March 2015
 New Advances in Cancer Treatments March 2015 Safe Harbour Statement This presentation document contains certain forward-looking statements and information (collectively, forward-looking statements ) within
New Advances in Cancer Treatments March 2015 Safe Harbour Statement This presentation document contains certain forward-looking statements and information (collectively, forward-looking statements ) within
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine
 Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine and Translational Research College of Medicine 1. Introduction: The College of Medicine, while consolidating on its undergraduate innovative educational programs, decided to
Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine and Translational Research College of Medicine 1. Introduction: The College of Medicine, while consolidating on its undergraduate innovative educational programs, decided to
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM
 REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
REPORT PERSPECTIVES IN LUNG CANCER 2010 AMSTERDAM Valerie Van Damme, Isabelle Wauters, Johan Vansteenkiste Univ. Hospital Leuven and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Introduction Perspectives in Lung Cancer (PILC)
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Kinsey McCormick Hematology Fellow s Conference January 10, 2014
 Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Kinsey McCormick Hematology Fellow s Conference January 10, 2014 Overview Overview of immune checkpoints Immune checkpoints as mechanism of immune evasion
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Kinsey McCormick Hematology Fellow s Conference January 10, 2014 Overview Overview of immune checkpoints Immune checkpoints as mechanism of immune evasion
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll
An overview of CLL care and treatment. Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham
 An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
Overview of Mesothelioma. Raffit Hassan, M.D.
 Overview of Mesothelioma Raffit Hassan, M.D. Mesothelioma Is an aggressive tumor that arises from the serosal surfaces of body cavities In 1960, Wagner reported increased incidence of mesothelioma in asbestos
Overview of Mesothelioma Raffit Hassan, M.D. Mesothelioma Is an aggressive tumor that arises from the serosal surfaces of body cavities In 1960, Wagner reported increased incidence of mesothelioma in asbestos
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Post-operative intrapleural chemotherapy for mesothelioma
 Post-operative intrapleural chemotherapy for mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, MD John Skoglund Chair for Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme-Onc-Transplant University of Minnesota Medical School Efficacy
Post-operative intrapleural chemotherapy for mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, MD John Skoglund Chair for Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme-Onc-Transplant University of Minnesota Medical School Efficacy
Your Immune System & Melanoma Treatment
 Your Immune System & Melanoma Treatment Immunotherapy and Melanoma Immunotherapy is rapidly emerging as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer. For people with melanoma, the news is particularly
Your Immune System & Melanoma Treatment Immunotherapy and Melanoma Immunotherapy is rapidly emerging as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer. For people with melanoma, the news is particularly
Update on Mesothelioma
 November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
November 8, 2012 Update on Mesothelioma Intro incidence and nomenclature Update on Classification Diagnostic specimens Morphologic features Epithelioid Histology Biphasic Histology Immunohistochemical
International Symposium on Malignant Mesothelioma 2011 -- curemeso.org
 Measles virotherapy for malignant mesothelioma Manish R. Patel, D.O. Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota June 25, 2011 Medical Treatment of Mesothelioma Majority of patients are not
Measles virotherapy for malignant mesothelioma Manish R. Patel, D.O. Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota June 25, 2011 Medical Treatment of Mesothelioma Majority of patients are not
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma in Singapore
 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION C SP Yip 1, HN Koong 2, CM Loo 3, KW Fong 1* Abstract Aim: To examine the clinical characteristics and outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in Singapore. Methods and
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION C SP Yip 1, HN Koong 2, CM Loo 3, KW Fong 1* Abstract Aim: To examine the clinical characteristics and outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in Singapore. Methods and
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work
 Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy
 Regulatory T, tumour immunity and immunotherapy Weiping Zou Abstract Tumours express a range of antigens, including self-antigens. Regulatory T are crucial for maintaining T-cell tolerance to self-antigens.
Regulatory T, tumour immunity and immunotherapy Weiping Zou Abstract Tumours express a range of antigens, including self-antigens. Regulatory T are crucial for maintaining T-cell tolerance to self-antigens.
Cancer patients waiting for potentially live-saving treatments in UK
 Cancer patients waiting for potentially live-saving treatments in UK 29 May 2005 UK patients are waiting too long for new treatments, according to a 'Dossier of Delay' compiled by information charity CancerBACUP.
Cancer patients waiting for potentially live-saving treatments in UK 29 May 2005 UK patients are waiting too long for new treatments, according to a 'Dossier of Delay' compiled by information charity CancerBACUP.
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005
 Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
A Local Stability of Mathematical Models for Cancer Treatment by Using Gene Therapy
 International Journal of Modeling Optimization, Vol 5, No 3, June 2015 A Local Stability of Mathematical Models for Cancer Treatment by Using Gene Therapy Dwi Lestari Ratnasari Dwi Ambarwati Abstract This
International Journal of Modeling Optimization, Vol 5, No 3, June 2015 A Local Stability of Mathematical Models for Cancer Treatment by Using Gene Therapy Dwi Lestari Ratnasari Dwi Ambarwati Abstract This
OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone.
 Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
