Atrial Fibrillation. By Danielle Flint
|
|
|
- Corey Garrison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atrial Fibrillation By Danielle Flint
2 Outline Definition Epidemiology Clinical Aspects Treatment Effects of Exercise Exercise Testing Exercise Prescription Summary References
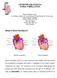
3 Definition: What is Atrial Fibrillation? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a cardiac arrhythmia, or abnormal heart rhythm. During an arrhythmia, the heart can beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular rhythm. Fibrillating means quivering and is named in relation to the atria, the upper two chambers of the heart. So in other words, AF is an irregular heart rhythm due to a disruption with the atrium. The atria quiver instead of beat effectively.
4 Definition: What is Atrial Fibrillation? Cont The internal electrical system controls the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat. To understand AF, it helps to understand the internal electrical system of the heart.
5 Definition: What is Atrial Fibrillation? Cont -internal electrical system In a healthy individual without AF, an electrical signal spreads from the top of the heart to the bottom with each heartbeat. As it travels, it causes the heart to contract and pump blood. Each electrical signal begins in the SA node in the right atrium and then travels through the right and left atria which causes the atria to contract and pump blood into the ventricles. The electrical signal then moves down to the AV node where it slows to allow the ventricles to finish filling with blood. Electrical signal then leaves the AV node and travels to the ventricles. This causes the ventricles to contract and pump blood out to the lungs and rest of the body. Ventricles relax, process starts all over again.
6 Definition: -internal electrical system In an individual with AF, the heart s electrical signals don t begin in the SA node. Instead they begin in another part of the atria or in the nearby pulmonary veins. The signals don t travel normally and may spread throughout the atria in a rapid, disorganized way. Abnormal signals flood AV node with electrical impulses and as a result, the ventricles also begin to beat very fast, however, the AV node can t conduct the signals to the ventricles as fast as they arrive. This imbalance creates a fast and irregular rhythm.
7 Definition -internal electrical system Healthy Individual Electrical signal begins in SA node, travels to right and left atria and then down to AV node. Signal slows, allowing time for ventricles to fill with blood, then moves down to ventricles. SA node fires off an electrical signal to begin a new heartbeat times a minute. Individual with AF Electrical signal begins in a part of the atria or nearby pulmonary veins. Signals spread throughout aria in a rapid, disorganized way and flood AV node with impulses. AV node can t conduct them to ventricles as fast as they arrive. In AF, the ventricles may beat times a minute.
8 Video
9 So, what s the problem in AF? The concern in individuals with atrial fibrillation is that the uncoordinated act of the two upper and two lower chambers doesn t allow the heart to pump blood effectively out of them. The amount of blood pumped out of the ventricles to the body is based on the randomness of the atrial beats so the body may get rapid small amounts of blood at some times or occasional larger amounts of blood at others.
10 So what s the problem in AF? While often not life-threatening on it s own, this inadequate supply of blood increases the risk of experiencing major complications such as stroke and heart attack. The leading type of atrial fibrillation occurs when the heart s two upper chambers contract improperly and can cause blood to back up into the heart, possibly leading to clot formation. Clot formation is one of the biggest scares of atrial fibrillation because it can travel to the brain and cause a stroke to occur.
11 Epidemiology Most common arrhythmia found in clinical practice. Accounts for 1/3 of hospital admissions for cardiac rhythm disturbances. Strokes from AF account for 6-24% of all ischemic strokes. Approximately 2.2 million individuals in U.S have AF. Incidence of AF increases with age. Prevalence over age 80 is about 8%. Number of patients with AF is likely to increase during next 50 years due to the growing proportion of elderly individuals. Men are more likely to have AF, although women have a higher, longterm risk of complications causing premature death.
12 Causes Hypertension Primary heart diseases (CAD, mitral stenosis, congenital heart disease, etc.) Previous heart surgery Lung diseases Excessive alcohol consumption Hyperthyroidism Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Dual-chamber pacemakers Family history of AF can increase likeliness Sometimes the cause is unknown
13 Risk Factors Risk increases as you age MAJOR- CAD, heart failure, rheumatic heart disease, structural heart defects, pericarditis (membrane sac around heart is inflamed) Other risk factors- obesity, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, metabolic syndrome, high dose steroid therapy treatments (asthma), hyperthyroidism, diabetes, lung disease, alcohol, and even caffeine in some people can trigger AF.
14 Types of Atrial Fibrillation 3 types of atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal AF- the abnormal electrical signals and rapid heart rate begin suddenly and then stop on their own. Symptoms can be mild or severe and last for seconds, minutes, hours, or days Persistent AF- when the abnormal heart rhythm continues until it's stopped with treatment. Permanent AF- normal heart rhythm can't be restored with the usual treatments. Both paroxysmal and persistent AF may become more frequent and, over time, result in permanent AF.
15 Clinical Aspects Signs and Symptoms Palpitations- feel like your heart is fluttering, skipping a beat, etc. Shortness of breath Weakness or difficulty exercising Chest pain Dizziness or fainting Fatigue Confusion
16 Clinical Aspects Diagnosis For those without symptoms it is generally discovered in a physical exam. Once it has been discovered, there are many diagnostic tests and procedures: EKG Holter and Event Monitor Stress Test Echocardiography Transeophageal Echocardiography Chest X Ray Blood tests
17 EKG Most useful test for diagnosing AF. Measures hearts electrical activity. Remember: P waves represent depolarization of atria which causes atrial contraction QRS complex reflects depolarization of ventricles T wave reflects repolarization of muscle fibers in ventricles. In AF there are no P waves; instead there are bizarre and irregular deflections referred to as fibrillation or f waves. They have no rhythmic patterns.
18 Atrial Fibrillation Healthy Individual w/o AF
19 Holter and Event Monitors Two most common types of portable EKGs Carry heart s electrical activity for a full 24 or 48 hour period. You may wear an event monitor for 1 to 2 months, or as long as it takes to get a recording of your heart during symptoms.
20 Stress Test AF may be easier to diagnose when the heart is forced to work harder during exercise. During stress tests you exercise to increase your heart rate while heart tests are done. Ex. while wearing an EKG.
21 Echocardiography Uses sound waves to create a moving picture of your heart. Test provides information about the size and shape of your heart and how well your heart chambers and valves are working. The sound waves bounce off the structures of your heart, and a computer converts them into pictures on a screen.
22 Transesophageal Echocardiography TEE takes pictures of your heart through the esophagus. This can be more effective than a thoracic echocardiography. During this test the transducer is attached to the end of a flexible tube that s guided down your throat and into your esophagus. Medicine is usually given to relax before procedure. TEE can also detect blood clots that may be developing in the atria because of AF.
23 Chest X Ray & Blood Tests Chest X Rays can show fluid buildup in the lungs and other complications of AF. Blood Tests check the level of thyroid hormone and the balance of your body s electrolytes.
24 Treatment Goals of treatment: Prevention of blood clots from forming, thereby reducing risk of stroke. Controlling how many times a minute the ventricles contract (rate control). With this the irregular heart rhythm continues, but the person feels better & has fewer symptoms. Restoring normal heart rhythm (rhythm control). Treating underlying disorder that s causing or raising the risk of AF, ex. Hyperthyroidism.
25 Treatment Who needs treatment? People who have AF but don t have symptoms may not need treatment. AF may even go back to a normal heart rhythm on its own. Some doctors may choose to use an electrical procedure or medicine to restore the heart rhythm to normal in those who have AF for the first time. Those who have persistent or permanent AF need treatment to control their heart rates and prevent complications.
26 Treatment Blood Clot Prevention- arguably the most important part of treating AF. Blood-thinning medicinces including: Warfarin- most effective and must have regular blood tests to check how well medicine is working. Heparin Aspirin
27 Treatment Rate Control- medicines can be prescribed to help bring the heat rate to a normal level. Rate control is the recommended treatment for most patients who have AF, even though abnormal heart rhythm continues. Most people feel better and can function when their heart rates are well-controlled. Medicines include: Beta blockers (metoprolol and atenolol) Calcium channel blockers (diltiazem and verapamil) Digitalis (digoxin).
28 Treatment Rhythm Control- this treatment approach is recommended for people who aren t functioning well with rate control treatment or who have just started having AF. The longer you have AF, the less likely that an abnormal heart rhythm can be restored to normal. Especially if > 6mos. Medicines Amiodarone, sotalol, flecainide, propafenone, dofetilide, and ibutilide.
29 Treatment Procedures Electrical cardioversion- procedure to restore a fast or irregular heartbeat to a normal rhythm. Low-energy shocks are given to your heart to trigger a normal rhythm. Temporarily put to sleep before the shocks are given.
30 Treatment Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)- may be performed before electrical cardiography to rule out blood clots in the atria. If blood clots are discovered then a bloodthinning medication may be taken for a time to get rid of the clots before electrical cardiography can take place.
31 Treatment Catheter ablation- during this procedure a wire is inserted through a vein in the leg or arm and threaded to the heart. Radio wave energy is sent through the wire to destroy abnormal tissues that may be disrupting the normal flow of electrical signals. Sometimes used to destroy AV node where a pacemaker must then surgically be implanted to maintain a normal heart rhythm.
32 Treatment Maze surgery- surgeon makes small cuts or burns in the atria that prevent the spread of disorganized electrical signals. Requires open-heart surgery so is usually only performed when a person requires heart surgery for another reason.
33 Effects of Exercise People who have AF can live normal, active lives. Exercise is one of the best ways to prevent AF. However, because AF causes reduced cardiac output, exercise capacity, and fatigue, it may be difficult for an individual with AF to exercise.
34 Effects of Exercise Most notable feature in clients with AF is a rapid, irregular ventricular response. HR in individuals with AF is comparatively high at any level of exercise. It is important to take into consideration any medications they may be taking, such as beta blockers, etc. and the effect that these have on exercise. Exercise tolerance is typically 20% lower than age-matched normal subjects. However, AF alone (no underlying CAD) achieve peak oxygen consumption values typical of age-matched subject in normal sinus rhythm. Determination of systolic blood pressure can be difficult.
35 Effects of Exercise Training Insufficient scientific literature is available concerning the effects of exercise training specifically in patients with AF. Major concern in terms of exercise training in clients with AF is the underlying heart disease, particularly valvular disease, chronic heart failure, and CAD. The presence of these underlying diseases should be the foremost consideration in exercise programming for individuals with AF.
36 Exercise Testing Maximal exercise testing can be safely performed to objectively characterize the functional capabilities of individuals with AF. Exercise testing can be helpful in determining the effectiveness of rate control therapy. Reduction in exercise capacity associated with AF is a direct function of the underlying heart disease. Therefore, moderately incremented protocols such as the Naughton or ramp are recommended. Contraindications to exercise testing related to comorbidities and other underlying conditions, such as stability of chronic heart failure, etc. should take precedence over AF itself. In absence of other clinical indications for stopping, clients with AF may be safely taken to fatigue or shortness of breath endpoints.
37 Exercise Testing Age- predicted maximal heart rate targets are particularly USELESS in AF because of the rapid and highly variable ventricular response. HR most accurately measured using calipers over at least a 6 s rhythm strip during exercise. BP may also be difficult to receive.
38 Exercise Testing Methods Measures Endpoints Aerobic- cycle (ramp protocol W/min; staged protocol W/min stage) 12-lead ECG, HR Serious dysrhythmias >2 mm ST-segment depression or elevation Ischemic threshold T-wave inversion with significant ST change SBP 250 mmhg or DBP >115 mmhg +3 or greater on +1 to +4 angina scale Endurance- 6 min walk Distance walked Rest stops allowed; note stops in record Flexibility- goniometry Angle of flexion/extension
39 Exercise Prescription As population ages, # of individuals with AF will increase. 2 major factors to consider in exercise programming are: 1. Concomitant or underlying heart disease 2. Inherent unreliability of the pulse rate for prescribing exercise intensity. Goals can also change if patient has experienced a stroke. Exercise intensity should be prescribed based on work rate and perceived exertion levels (RPE). Frequency, duration, intensity, and progression of exercise are similar to those for clients in normal sinus rhythm referred to a rehabilitation program.
40 Exercise Prescription AF can be intermittent and therefore the rhythm should be determined on a daily basis. Many patients with AF will be elderly and comorbid conditions such as osteoporosis, diabetes, obesity, etc. must be considered. Longer sampling of the pulse may be needed for reliable HR.
41 Exercise Prescription Modes Goals Int/Freq/Dur Time to goal Aerobic- large muscle activities Arm/leg ergometry Increase VO2 peak Increase ADLs RPE 11-16/ % VO2 peak or HR reserve 3-7 days/week min/session 3 months Resistance- Weight machines Increase strength High reps, low resistance (12-15 reps) 2-3 nonconsecutive days/week 2-3 months Flexibility- upper & lower body ROM activities Increase flexibility Reduce risk of injury 3-5 days/week 2-4 months
42 Summary Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia that has to do with a disruption in the internal electrical system of the heart. The two upper chambers and lower chambers no longer work in a coordinated fashion. Concern in AF individuals is blood is not able to adequately be pumped out of the heart. Complications can be heart damage resulting in a heart attack as well as clots that can travel as an embolus to the brain and cause a stroke. 2.2 million individuals in U.S. Incidence increases with age and precedence is 8% over 80 yrs. Males more likely. Causes can include hypertension, primary heart disease, previous heart surgery, hyperthyroidism, and family history. Risk factors include obesity, high BP, sleep apnea, metabolic syndrome, high steroid therapy treatment, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, alcohol, caffeine. 3 types of atrial fibrillation. Paroxysmal, Persistent, Permanent Signs/symptoms- palpitations, shortness of breath, weakness, difficulty exercising, chest pain, dizziness or fainting, fatigue, confusion
43 Summary Diagnosis can be by an EKG, stress test, echocardiography, TEE, chest x ray, blood tests. Treatments can include blood clot prevention with blood thinners, rate control, rhythm control Procedures include electrical cardioversion, TEE, catheter ablation, maze surgery. Effects of exercise reduced cardiac output & ex. Capacity. Fatigue. Rapid & irregular ventricular response. Increased heart rate. Need to remember to take into consideration any medications. 20% lower exercise tolerance Major concern in ex. Training is underlying HD. In exercise testing you cannot rely on age related HR values. BP can be unreliable as well. RPE. Foremost concern is underlying heart disease and if ruled out, safe to test AF clients to shortness of breath or fatigue. Naugton or ramp tests. Exercise prescription should take into consideration the individual and any underlying issues that may come with them.
44 References Durstine, Larry J., Moore, Geoffrey E., Painter, Patricia L. (2009). ACSM S Eercise Management for Persons With Chronic Diseases and Disabilities. United States of America: Kerry O Rourke. Snow, Vincenza, Weiss, Kevin B., LeFebre, Michale, McNarmara, Robert, Bass, Eric, Green, Lee A., Michl, Keith, Owens, Douglas K., Susman, Jeffrey, Allen, Deborah I., Mottur-Pilson, Christel. (2003). Management of Newly Detected Atrial Fibrillation: Clinical Practice Guideline from the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine, 139, Fluster, Valentin, Ryden, Lars E., Crikns, Harry J., Ellenbogen, Kenneth A., Kay, Neal G., Prystowsky, Eric N. (2006). ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. ACC/AHA/ESC Practice Guidelines, 114, Atrial Fibrillation. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Retrieved February 3, 2011 from: How Exercise Helps Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Health Center. (2008). Retrieved Februray 3, 2011 from: Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation. American Heart Association. (2011). Retrieved Februray 3, 2011 from: Atrifal Fibrillation. Wikipedia. (2011). Retrieved February 1, 2011 from: Ehrat, Karen S. (1978). THE ART OF ADULT AND PEDIATRIC EKG INTERPRETATION A Self-Instructional Text for Health Care Professionals and Related Genera. Tucson, Arizona: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company.
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Atrial Fibrillation. Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
Atrial Fibrillation Centre
 About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
5 MILLION AMERICANS 1. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) AFib affects an estimated
 A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
Visited 9/14/2011. What is Atrial Fibrillation? What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation. The Normal Heart Rhythm. 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM
 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. A Guide for Adults
 Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Living with. Atrial Fibrillation
 Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. What you need to know
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION What you need to know Table of contents Atrial fibrillation overview... 1 What is a-fib?.... 2 Risk factors for a-fib... 3 Symptoms of a-fib.... 4 Complications from a-fib... 4 How
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION What you need to know Table of contents Atrial fibrillation overview... 1 What is a-fib?.... 2 Risk factors for a-fib... 3 Symptoms of a-fib.... 4 Complications from a-fib... 4 How
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
written by Harvard Medical School Atrial Fibrillation Coping With a Chaotic Heartbeat www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School Atrial Fibrillation Coping With a Chaotic Heartbeat www.patientedu.org What Is Atrial Fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a fast and irregular heartbeat. It occurs in
written by Harvard Medical School Atrial Fibrillation Coping With a Chaotic Heartbeat www.patientedu.org What Is Atrial Fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a fast and irregular heartbeat. It occurs in
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm
 Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information
 Patient Information Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Page 1 of 8 Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information Emory University Hospital Midtown Cardiac Electrophysiology Service
Patient Information Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Page 1 of 8 Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information Emory University Hospital Midtown Cardiac Electrophysiology Service
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter
 Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information
 AF A Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation
 A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society SM This information is not intended
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society SM This information is not intended
Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide
 Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide ATRIAL FIBRILLATION CENTER AT UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER www.heart.urmc.edu 585-275-4775 INTRODUCTION Our goal at the Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide ATRIAL FIBRILLATION CENTER AT UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER www.heart.urmc.edu 585-275-4775 INTRODUCTION Our goal at the Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation. Treatment Guide
 Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Advances in the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation At VCU Medical Center
 Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
 Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Atrial Fibrillation. The Beat Goes On. Living with AFib. Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices.
 Atrial Fibrillation The Beat Goes On Living with AFib Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices. What is AFib? This booklet is for you if you have AFib, or if you are at risk for AFib. This booklet
Atrial Fibrillation The Beat Goes On Living with AFib Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices. What is AFib? This booklet is for you if you have AFib, or if you are at risk for AFib. This booklet
Listen to Your Heart. What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke. The S-ICD System. The protection you need
 Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat. Initiated by the World Hypertension League
 Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood Pressure. It is a chronic medical
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood Pressure. It is a chronic medical
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation. Patient Information. 828361 Dec 19-12
 Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information 828361 Dec 19-12 Contents Introduction 1 Treatment & decrease stroke options 2 Information for people who are taking warfarin (Coumadin ) 5 Information for people
Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information 828361 Dec 19-12 Contents Introduction 1 Treatment & decrease stroke options 2 Information for people who are taking warfarin (Coumadin ) 5 Information for people
About the British Heart Foundation
 Atrial fibrillation About the British Heart Foundation The British Heart Foundation (BHF) is the nation s heart charity, saving lives through pioneering research, patient care and vital information. What
Atrial fibrillation About the British Heart Foundation The British Heart Foundation (BHF) is the nation s heart charity, saving lives through pioneering research, patient care and vital information. What
www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat).
 www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat). Contents Introduction 5 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation
www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat). Contents Introduction 5 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers
 1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Prepared by Karen Jones MBA and Nancy Marco NP for the Complex Arrhythmia Clinic Toronto General Hospital Peter Munk Cardiac Centre University Health
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Prepared by Karen Jones MBA and Nancy Marco NP for the Complex Arrhythmia Clinic Toronto General Hospital Peter Munk Cardiac Centre University Health
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Summa cardiovascular institute. A Patient s Guide to AFib Treatment
 Summa cardiovascular institute A Patient s Guide to AFib Treatment Healthy Heart Atrial Fibrillation Risk Factors Normal impulse Sinoatrial (SA) node Left Atrium According to the Heart Rhythm Society,
Summa cardiovascular institute A Patient s Guide to AFib Treatment Healthy Heart Atrial Fibrillation Risk Factors Normal impulse Sinoatrial (SA) node Left Atrium According to the Heart Rhythm Society,
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A CAREGIVER s Guide to. Complicated Atrial Fibrillation
 A CAREGIVER s Guide to Complicated Atrial Fibrillation Introduction Atrial fibrillation (also known as AFib or AF) is a common heart condition, particularly among older people. It s estimated that AF affects
A CAREGIVER s Guide to Complicated Atrial Fibrillation Introduction Atrial fibrillation (also known as AFib or AF) is a common heart condition, particularly among older people. It s estimated that AF affects
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Living with. A Guide for Patients and Families 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T 613.761.5000 WWW.OTTAWAHEART.CA UOHI 77
 Living with Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Patients and Families UOHI 77 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T 613.761.5000 WWW.OTTAWAHEART.CA PLEASE BRING THIS BOOK WITH YOU TO THE HEART INSTITUTE Patient
Living with Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Patients and Families UOHI 77 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T 613.761.5000 WWW.OTTAWAHEART.CA PLEASE BRING THIS BOOK WITH YOU TO THE HEART INSTITUTE Patient
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Introduction. What is syncope?
 Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient
 Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women
 What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
Let s talk about: Stroke
 Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Your information prescription
 Prepared on 12 May 2015 Serial number: MRP158FU View this prescription online http://www.nhs.uk/ipg/pages/ippreviewcover.aspx?ref=mrp158fu More health information at http://www.nhs.uk Your information
Prepared on 12 May 2015 Serial number: MRP158FU View this prescription online http://www.nhs.uk/ipg/pages/ippreviewcover.aspx?ref=mrp158fu More health information at http://www.nhs.uk Your information
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Atrial Fibrillation Know your risk of stroke Know your treatment options
 Atrial Fibrillation Know your risk of stroke Know your treatment options Lorrie Langdon MS, RN, CHFN, Heart Failure Program Emily O Hern, RN, Electrophysiology Lab Deanna Walborn, RN, Electrophysiology
Atrial Fibrillation Know your risk of stroke Know your treatment options Lorrie Langdon MS, RN, CHFN, Heart Failure Program Emily O Hern, RN, Electrophysiology Lab Deanna Walborn, RN, Electrophysiology
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
 Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device
 WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
Atrial fibrillation. Quick reference guide. Issue date: June 2006. The management of atrial fibrillation
 Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation
 The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Living with Your Pacemaker
 Brief Statement Additional Device Information An implantable pacemaker system relieves symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances. They do this by restoring normal heart rates. A normal heart rate provides
Brief Statement Additional Device Information An implantable pacemaker system relieves symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances. They do this by restoring normal heart rates. A normal heart rate provides
Atrial fibrillation/flutter: When to refer, What tests, What meds
 Atrial fibrillation/flutter: When to refer, What tests, What meds Warren Smith Green Lane Cardiovascular Service Auckland City Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand Why might it not be a good idea to cardiovert
Atrial fibrillation/flutter: When to refer, What tests, What meds Warren Smith Green Lane Cardiovascular Service Auckland City Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand Why might it not be a good idea to cardiovert
Atrial Fibrillation Cardiac rate control or rhythm control could be the key to AF therapy
 Cardiac rate control or rhythm control could be the key to AF therapy Recent studies have proven that an option of pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic therapy is available to patients who suffer from AF.
Cardiac rate control or rhythm control could be the key to AF therapy Recent studies have proven that an option of pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic therapy is available to patients who suffer from AF.
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
