Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism. 1,500,000 new cases per year
|
|
|
- Alexina Cooper
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pulmonary Thromboembolism Jim Allen, MD Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year Oft t ti Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU patients Untreated mortality is 30% 1
2 Clinical Case Clinical Case CT Angiogram 28 year old woman Three days previously: charley horse in the left calf Sudden onset right pleuritic chest pain and dyspnea Past medical history: negative Medications: birth control pills Clinical Case Clinical Case CT Angiogram Vital signs: - Temperature BP 166/90 - HR 92 - RR 18 - O2% = 94% Lungs clear to auscultation Leg exam normal CBC: normal Electrolytes: normal Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP): normal Troponin I: normal 2
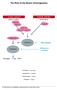
3 Venous Stasis Why Did She Clot? Immobility Bed rest Surgery Cor pulmonale Obesity Virchow s Triad Endothelial Injury Stasis Hypercoagulability Thrombosis Endothelial Injury Previous DVT Trauma Surgery Femoral venous catheters 3
4 Heritable Hypercoaguability Factor V Leiden mutation Prothrombin G-A20210 mutation Hyperhomocysteinemia Protein C deficiency Protein S deficiency Anti-thrombin III deficiency Elevated factors VIII, IX, & XI A B C Factor V Protein C X Factor V Leiden Factor II Factor II Factor II Clot No Clot Clot Protein C Factor V Leiden The Genetic Epicenter of Factor V Leiden Causes resistance to activated protein C 4% of Americans are heterozygotes Contributes to about 10-26% of DVT/PE Heterozygotes = 7 fold increased risk plus OCPs = 35 fold increased risk Homozygotes = 80 fold increased risk 4
5 United States Racial Distribution of Factor V Leiden 5.3% Caucasian Americans 2.2% Hispanic Americans 1.2% African Americans 1.2% Native Americans 0.4% Asian Americans Hyperhomocysteinemia* Causes Drug causes Genetic Methotrexate Poor nutrition Phenytoin Renal Carbamazepine insufficiency Malignancy Theophylline Hypothyroidism High animal fat diet *3-fold increased risk Prothrombin G-A20210 Mutation Causes increased prothrombin levels Contributes to about 6-8% of all DVT/PE Heterozygotes = 3 fold increased risk heterozygote + factor V Leiden = 10 fold risk Homozygotes = very high risk Acquired Hypercoaguability Pregnancy Hyperhomocysteinemia Anti-phospholipid antibodies Malignancies Drugs: Estrogens Tamoxifen Bevacizumab Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia 5
6 Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies IgG Antibodies Systemic lupus erythematosus Sjogren s Rheumatoid arthritis Scleroderma IgM Antibodies Infections: - HIV - Hepatitis i - Sepsis Medications: - Phenytoin - Hydralazine Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia When suspected, discontinue all heparin pending HIT study Initial treatment = argatroban, lepirudin, or danaparoid Long-term (3-6 month) Coumadin Thrombocytopenia and Heparin Non-Immune Platelets > 100,000 Days 1-5 of heparin Not thrombogenic Immune Platelets fall by > 50% (usually < 100,000) Between day 5-14 of heparin Highly thrombogenic 2.6% of patients treated > 4 days Beware of COPD exacerbations One out of four patients hospitalized with COPD exacerbations have PE Signs and symptoms are often similar to usual COPD exacerbations The risk is higher for inpatients Be suspicious in patients lacking typical bronchitis symptoms Chest 2009; 135:
7 Deep Venous Thrombosis Diagnosis D-dimer greatest value when negative in low/moderate risk patients Duplex ultrasound - Sensitivity & specificity = 99% - Accuracy best for femoral DVT Venography CT scanning MRI Image courtesy of GE Healthcare; used with permission Image courtesy of GE Healthcare; used with permission Image courtesy of GE Healthcare; used with permission 7
8 Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms Dyspnea 80% Pleurisy 70% Cough 50% Hemoptysis 30% Signs Increased A-a gradient 95% Tachypnea 92% Tachycardia 44% Fever 43% Image courtesy of GE Healthcare; used with permission Calf Vein Thrombosis 20% propagate into proximal veins Anticoagulation necessary if propagate Safest approach is to treat all cases for 3 months Serial duplex ultrasounds if anticoagulation is risky Well s Criteria for PE 3.0 Signs of DVT 1.5 HR > Immobilization for > 3 days or surgery in past 4 months 1.5 Previous PE 1.0 Hemoptysis 1.0 Malignancy 3.0 PE as or more likely than other diagnoses 4 points PE unlikely 5 points PE likely 8
9 PERC (PE Rule out Criteria) Age < 50 Heart rate < 100 SaO2 > 95% No hemoptysis No estrogen use No prior DVT or PE No unilateral leg swelling No surgery/trauma in past 4 weeks Cardiomegaly 29 cm 18 cm Chest X-Ray Findings Cardiomegaly Enlarged pulmonary artery Atelectasis Elevated hemidiaphragm Regional oligemia Pleural effusion Hampton s hump Hampton s Hump 9
10 Atelectasis Cardiac Enzymes Troponin I - Elevated in 30-50% of moderate to large PE - Correlates with embolism size and worse outcome BNP - Level > 90 predicts worse outcome, especially if the troponin I is elevated D-Dimer In Pulmonary Embolism Sensitivity = 95% Specificity < 50% False positives are frequent after surgery and in hospitalized patients Negative test is strong evidence against DVT/PE in patients with low clinical suspicion Only validated for outpatients Ventilation Perfusion Scan Still the best initial test for some patients Most valuable if normal Clinical decision making requires: - V/Q scan probability - Clinical probability 10
11 Ventilation/Perfusion Scan Normal ventilation scan Perfusion scan showing pulmonary embolus Perfusion scan showing resolved pulmonary embolus Pulmonary Angiogram Gold standard Negative study excludes PE Relatively low complication rate False positives rare Probability of Pulmonary Embolus CT Pulmonary Angiogram V/Q Probabil lity Clinical Suspicion High Intermediate Low High 96% 88% 56% Intermediate 66% 28% 16% Low 40% 16% 4% JAMA 1990; 263: Specificity about 95% Sensitivity about 85% O Optimal study requires: - Recent generation CT scanner - Technician experience - Radiologist experience 11
12 One channel CT: Fewer image slices per scan Less sensitive for PE Reconstructed high speed multi-channel CT angiogram Multi channel CT: More image slices per scan More sensitive for PE Image courtesy of GE Healthcare; used with permission CT Pulmonary Angiogram Normal Pulmonary emboli Inadequate technique 12
13 Probability Of True PE High Clinical Suspicion Medium Clinical Suspicion Low Clinical Suspicion CTPA/CTV 96% 90% 57% Positive CTPA/CTV Negative 18% 8% 3% N Engl J Med 2006; 354: PIOPED II Conclusions CTPA should not be used alone CTPA positive in main or lobar arteries more accurate than CTPA positive in segmental arteries 13
14 What Rules Out PE? Normal V/Q scan Low clinical suspicion and D-dimer less than 500 ng/ml Normal angiogram Low probability V/Q and normal D-dimer Negative CT-PA plus normal D-dimer In other situations, clinical judgment is required Practical Use of CT-PA What does NOT rule out PE? If the clinical suspicion is high: In the ED: If clearly positive = PE present If negative: - Negative D- dimer = no PE - Positive D- dimer = clinical judgment In the ICU: If clearly positive = PE present If negative: - Low clinical suspicion = no PE - Intermediate or high clinical suspicion = additional testing Low probability V/Q scan alone Negative CT-PA alone Normal D-dimer test alone Negative MRI 14
15 So, what is the best initial test? CT scan: Previous PE Significant underlying lung disease V/Q scan: Dye allergy Renal insufficiency?patients with normal CXR Duplex ultrasound: Pregnancy ICU patients with transportation risks D-dimer Low risk outpatients Initial Resuscitation Oxygen Maintain blood pressure: IV fluids Vasopressors Telemetry monitoring ICU care for patients with severe hypoxemia or with hypotension Predictors of worse outcome Shoot first, ask questions later Shock Severe hypoxemia Elevated troponin I BNP > 90 RV dysfunction by echo 15
16 Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Heparin Low molecular weight heparin Fondaparinux Coumadin Thrombolytics IVC filters Catheter extracation/fragmentation Surgical embolectomy Heparin Dosing Bolus with 80 u/kg IV infusion of u/kg Check PTT Q6 hrs until stable, then QD Keep PTT seconds* Check platelets every other day Minimum 5 day infusion * Appropriate therapeutic range may vary by hospital lab Initial Treatment DVT: Outpatients: LMW heparin Inpatients: LMW heparin* Unfractionated heparin PE: Outpatients: no FDA-approved treatments! Inpatients: LMW heparin* Unfractionated heparin *Avoid LMW heparin in 1. obese (weight > 150 kg) 2. renal failure (creatinine clearance <25) Low Molecular Weight Heparins Equally or more effective than heparin Equal or less bleeding than heparin Lower incidence of thrombocytopenia Lower incidence of thrombocytopenia Longer half life Monitoring PTT unnecessary Dose once or twice daily Problems: renal insufficiency & obesity 16
17 Coumadin Start on day #1 of heparin Initial dose = 5 mg Keep K INR Genetic testing may help guide dosing in the future Thromboembolism in patients with cancer Patients can clot through Coumadin Use minimum of 6 months heparin or low molecular weight heparin Patients remain hypercoaguable as long as they still have cancer Duration of treatment Reversible factor: minimum of 3 months First idiopathic: minimum of 3 months and consider extended therapy Second DVT/PE: extended anticoagulation if bleeding risk is low D-dimer predicts recurrence 608 patients with venous thromboembolism treated > 3 months 233 had elevated D- dimer after treatment Patients randomly assigned to anticoagulation or no treatment N Engl J Med 2006; 355:
18 Anticoagulants on the horizon: Idrabiotaparinux SQ anticoagulant not requiring INR monitoring Rivaroxaban oral anticoagulant not requiring INR monitoring only FDA approved for atrial fibrillation and DVT prophylaxis Apixaban oral anticoagulant not requiring INR monitoring Dabigatran oral anticoagulant not requiring INR monitoring only FDA approved for atrial fibrillation Upper extremity DVT Initial therapy: heparin (low molecular weight or unfractionated) Long term treatment with Coumadin as per DVT *None are currently approved for PE by the FDA Inferior Vena Cava Filters Indications: Contraindication to anticoagulation Failure of anticoagulation Complications of anticoagulation Varieties: Permanent Retrievable Mortality of Pulmonary Embolus Untreated: 30% Heparin Treated: 2% 18
19 Complications of Thrombolytics in Pulmonary Embolus Cerebral hemorrhage 3% Major bleeding 9% Other Treatments Surgical embolectomy Mainly if thrombolysis is contraindicated or fails Best outcomes at experienced centers Catheter techniques Mainly if thrombolysis is contraindicated or fails Best outcomes at experienced centers Bottom Line: Pulmonary embolism is a medical disease in most patients Heparin vs. Thrombolytics in PE Uncomplicated Heparin Alone X Thrombolytics Shock X Resp. Failure X RV Dysfunction?? High Troponin?? The Key to Improving Mortality from PE is to Prevent PE 19
20 DVT/PE Prevention Strategies Medical/Surgical Patients SQ heparin Low molecular weight heparin Adjusted dose Coumadin Pneumatic compression devices Fondaparinux Orthopedic patients Low molecular weight heparin Fondaparinux Dabigatran Rivaroxaban SQ heparin Coumadin Aspirin Pneumatic compression devices Watch for new anticoagulants! Clinical Case Outcome Factor V Leiden heterozygous Treatment Low molecular weight heparin Coumadin x 6 months stop oral contraceptives Now pregnant and on prophylactic low molecular weight heparin The new world of pay for performance 1. Your prophylaxis record will be publicly reported 2. Failure to prevent = failure to get paid Key Points: No imaging test is perfect Your clinical assessment is critical Treatment decisions need to be individualized for individual patients 20
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 3 CLOTTING DISORDERS Original authors: Edith A. Nutescu, Jessica B. Michaud, Joseph A. Caprini, Louis W. Biegler, and Robert R. McCormick Abstracted by Kellie R. Brown Introduction The normal balance
CHAPTER 3 CLOTTING DISORDERS Original authors: Edith A. Nutescu, Jessica B. Michaud, Joseph A. Caprini, Louis W. Biegler, and Robert R. McCormick Abstracted by Kellie R. Brown Introduction The normal balance
Paul G. Lee. 2 ND YEAR RESEARCH ELECTIVE RESIDENT S JOURNAL Volume III, 1998-1999. A. Objective
 A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
Thrombophilia. Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003
 Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update
 UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary embolism.
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary
PULMONARY EMBOLISM: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders
 Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER
 UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism
 Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014
 ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
Chronic Thromboembolic Disease. Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition. Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical
 Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition Pulmonary Hypertension due to chronic thromboembolism 6 months post acute PE:
Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition Pulmonary Hypertension due to chronic thromboembolism 6 months post acute PE:
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Anticoagulation at the end of life. Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk
 Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013
 Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES
 APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation. Dan Johnson, Pharm.D.
 Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS
 NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
Hypercoagulable States
 Hypercoagulable States Daniel A. Forman, DO daniel.forman@readinghealth.org 610 509 5067 April 26, 2014 Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Hereditary thrombophilias How long to treat Newer agents
Hypercoagulable States Daniel A. Forman, DO daniel.forman@readinghealth.org 610 509 5067 April 26, 2014 Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Hereditary thrombophilias How long to treat Newer agents
Disclosure. New Agents for Treatment of DVT. Prevalence of DVT VTE. Normal Hemostasis 7/17/2015. Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU
 New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
Thrombosis and Hemostasis
 Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
NHS FIFE WIDE POLICY - HAEMATOLOGY MANAGEMENT OF ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY DURING MAJOR AND MINOR ELECTIVE SURGERY
 MANAGEMENT OF ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY DURING MAJOR AND MINOR ELECTIVE SURGERY The scope of this guideline is to simplify the management of patients on oral anticoagulation undergoing major and minor surgery.
MANAGEMENT OF ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY DURING MAJOR AND MINOR ELECTIVE SURGERY The scope of this guideline is to simplify the management of patients on oral anticoagulation undergoing major and minor surgery.
Traditional anticoagulants
 TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient
 Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia
 Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia Ann-Marie Liberman B.Sc.Phm., ACPR Clinical Pharmacist, Cardiac Surgery Clinical Trials Pharmacist Royal Columbian Hospital Fraser Health Disclosure Participated in research
Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia Ann-Marie Liberman B.Sc.Phm., ACPR Clinical Pharmacist, Cardiac Surgery Clinical Trials Pharmacist Royal Columbian Hospital Fraser Health Disclosure Participated in research
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: MOBILITY WITH A DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Page 1 of 10
 Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
3/3/2015. Patrick Cobb, MD, FACP March 2015
 Patrick Cobb, MD, FACP March 2015 I, Patrick Cobb, MD, DO NOT have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict
Patrick Cobb, MD, FACP March 2015 I, Patrick Cobb, MD, DO NOT have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict
Time of Offset of Action The Trial
 New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
Hypercoagulability How to Expect the Unexpected. Beth Saft, DO VOMA Conference 2012
 Hypercoagulability How to Expect the Unexpected Beth Saft, DO VOMA Conference 2012 Who is at Risk Most Common Hypercoagulability Objectives + When to Test What to do with the Test Results Who gets a DVT
Hypercoagulability How to Expect the Unexpected Beth Saft, DO VOMA Conference 2012 Who is at Risk Most Common Hypercoagulability Objectives + When to Test What to do with the Test Results Who gets a DVT
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins to patients.
 UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE TEMPLE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO TREATMENT OF DVT JOSE MISSRI, M.D. PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CHIEF OF CARDIOLOGY TEMPLE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DVT/PE: Magnitude of the Problem Death 60,000 300,00 Pulmonary Hypertension
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO TREATMENT OF DVT JOSE MISSRI, M.D. PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CHIEF OF CARDIOLOGY TEMPLE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DVT/PE: Magnitude of the Problem Death 60,000 300,00 Pulmonary Hypertension
6/19/2012. Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. No conflicts of interest to declare
 Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of unusual bleeding Maintain effective tissue perfusion Implementation
 Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Anticoagulation Dosing at UCDMC Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h
 Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid
 New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid Bruce Davidson, MD, MPH Clinical Professor of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Division University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle USA
New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid Bruce Davidson, MD, MPH Clinical Professor of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Division University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle USA
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
How To Increase Warfarin
 Anticoagulants for venous thromboembolic disease- Optimizing the old, ushering in the new. Daniel A. Forman, DO RPS Hematology Oncology daniel.forman@readinghealth.org 610 509 5067 cell RHS Anticoagulation
Anticoagulants for venous thromboembolic disease- Optimizing the old, ushering in the new. Daniel A. Forman, DO RPS Hematology Oncology daniel.forman@readinghealth.org 610 509 5067 cell RHS Anticoagulation
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Children and Young Adults
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in MSRHTC P.O. Box 6507 Aurora, CO 80045-0507 (303) 724-0724 An Overview for Patients and Health Care Providers 2 15 GLOSSARY: venous thrombosis = a condition of
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in MSRHTC P.O. Box 6507 Aurora, CO 80045-0507 (303) 724-0724 An Overview for Patients and Health Care Providers 2 15 GLOSSARY: venous thrombosis = a condition of
Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9 th Edition : ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease: Are we practicing evidence-based medicine? The 2012 ACCP Guidelines and Beyond (Buzz Lightyear) Jeffrey L. Garland, MD, FCCP Associate Chair
Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease: Are we practicing evidence-based medicine? The 2012 ACCP Guidelines and Beyond (Buzz Lightyear) Jeffrey L. Garland, MD, FCCP Associate Chair
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery
 Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Standard Operating Procedure. Author s job title. Pharmacist.
 Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Disclosures
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Venous Thromboembolism Guideline Team Team Leader Grant M Greenberg, MD, MA, MHSA Family Medicine Team Members Brian J Brophy, MD General Medicine Kirk A Frey, MD,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Venous Thromboembolism Guideline Team Team Leader Grant M Greenberg, MD, MA, MHSA Family Medicine Team Members Brian J Brophy, MD General Medicine Kirk A Frey, MD,
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants
 FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
Session 3 Topics. Argatroban. Argatroban. Drug Use and Adverse Effects. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
Failure or significant adverse effects to all of the alternatives: Eliquis and Xarelto
 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
Prescriber Guide. 20mg. 15mg. Simply Protecting More Patients. Simply Protecting More Patients
 Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
Pulmonary Embolism. Manny Mathew, M.D, FCCP Pulmonary/Critical Care
 Pulmonary Embolism Manny Mathew, M.D, FCCP Pulmonary/Critical Care. Objectives 1. Pretest Probability for DVT/PE (Wells Criteria, Geneva Score) 2. D-Dimer, when is it appropriate and how to Interpret
Pulmonary Embolism Manny Mathew, M.D, FCCP Pulmonary/Critical Care. Objectives 1. Pretest Probability for DVT/PE (Wells Criteria, Geneva Score) 2. D-Dimer, when is it appropriate and how to Interpret
10/10/13. Anil Chopra University Health Network University of Toronto
 Anil Chopra University Health Network University of Toronto Participant in several advisory boards and have received unrestricted education and research grants at UHN: Leo, BI, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Bayer,
Anil Chopra University Health Network University of Toronto Participant in several advisory boards and have received unrestricted education and research grants at UHN: Leo, BI, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Bayer,
Anticoagulation Essentials! Parenteral and Oral!
 Anticoagulation Essentials! Parenteral and Oral! Anti-Xa and Anti-IIa! Parenteral Anticoagulants! Heparin family (indirect anti-xa and anti-iia):! UFH! LMWH (enoxaparin, fondaparinux)! Direct thrombin
Anticoagulation Essentials! Parenteral and Oral! Anti-Xa and Anti-IIa! Parenteral Anticoagulants! Heparin family (indirect anti-xa and anti-iia):! UFH! LMWH (enoxaparin, fondaparinux)! Direct thrombin
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
TSOAC Initiation Checklist
 Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM
 Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
2.5mg SC daily. INR target 2-3 30 mg SC q 12 hr or 40mg daily. 10 mg PO q day (CrCl 30 ml/min). Avoid if < 30 ml/min. 2.
 Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Traveller s Thrombosis. Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven
 Traveller s Thrombosis Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven Case 1: To thromboprophylaxe or not Women, aged 49, BMI 29, Combined Oral Contraceptives. Family history of provoked
Traveller s Thrombosis Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven Case 1: To thromboprophylaxe or not Women, aged 49, BMI 29, Combined Oral Contraceptives. Family history of provoked
1/7/2012. Objectives. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation(AF) Stroke in AF. Stroke Risk Stratification in AF
 Objectives Atrial Fibrillation and Prevention of Thrombotic Complications: Therapeutic Update Andrea C. Flores Pharm.D Pharmacy Resident at the Miami VA Healthcare System Review the epidemiology, pathophysiology
Objectives Atrial Fibrillation and Prevention of Thrombotic Complications: Therapeutic Update Andrea C. Flores Pharm.D Pharmacy Resident at the Miami VA Healthcare System Review the epidemiology, pathophysiology
ANTICOAGULATION USE FOR THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE
 ANTICOAGULATION USE FOR THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE Jamie N. Nadler, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo Department of medicine Division
ANTICOAGULATION USE FOR THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE Jamie N. Nadler, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo Department of medicine Division
SIGN. Prevention and management of venous thromboembolism. Quick Reference Guide. December 2010. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
 SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network Part of NHS Quality Improvement Scotland 122 Prevention and management of venous thromboembolism Quick Reference Guide ecember 2010 This Quick Reference
SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network Part of NHS Quality Improvement Scotland 122 Prevention and management of venous thromboembolism Quick Reference Guide ecember 2010 This Quick Reference
PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients. Information For Patients
 Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
East Kent Prescribing Group
 East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013
 New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
4/9/2015. Risk Stratify Our Patients. Stroke Risk in AF: CHADS2 Scoring system JAMA 2001; 285: 2864-71
 Anticoagulation in the 21 st Century Adam Karpman, D.O. Saint Francis Medical Center/Oklahoma State University Medical Center Disclosures: None Atrial Fibrillation Most common arrhythmia in clinical practice.
Anticoagulation in the 21 st Century Adam Karpman, D.O. Saint Francis Medical Center/Oklahoma State University Medical Center Disclosures: None Atrial Fibrillation Most common arrhythmia in clinical practice.
What is the appropriate duration of treatment for VTE? Any advances in predicting recurrence?
 What is the appropriate duration of treatment for VTE? Any advances in predicting recurrence? Beverley Hunt Thrombosis & Haemostasis, King s College Guy s & St Thomas Trust Medical Director of Lifeblood:
What is the appropriate duration of treatment for VTE? Any advances in predicting recurrence? Beverley Hunt Thrombosis & Haemostasis, King s College Guy s & St Thomas Trust Medical Director of Lifeblood:
CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION
 CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION Michael S. McHale, M.D., F.A.C.P. Avera Medical Group Hematology & Oncology Medications Coumadin / Warfarin Unfractionated Heparin Low Molecular Weight Heparin
CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION Michael S. McHale, M.D., F.A.C.P. Avera Medical Group Hematology & Oncology Medications Coumadin / Warfarin Unfractionated Heparin Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)
 Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Dr. Art Szkotak artur.szkotak@albertahealthservices.ca University of Alberta Hospital Edmonton, AB NOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTI):
Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Dr. Art Szkotak artur.szkotak@albertahealthservices.ca University of Alberta Hospital Edmonton, AB NOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTI):
NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl
 NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl Mikele Wissing, RN June 2014 Introduction until recently, was the unrivaled medication for treatment
NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl Mikele Wissing, RN June 2014 Introduction until recently, was the unrivaled medication for treatment
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations
 Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
Post-ISTH review: Thrombosis-I New Oral Anticoagulants 臺 大 醫 院 內 科 部 血 液 科 周 聖 傑 醫 師
 Post-ISTH review: Thrombosis-I New Oral Anticoagulants 臺 大 醫 院 內 科 部 血 液 科 周 聖 傑 醫 師 The antithrombotic efficacy is limited but the risk of bleeding is indefinite Fuster V et al. Circulation 2011;123:e269-e367
Post-ISTH review: Thrombosis-I New Oral Anticoagulants 臺 大 醫 院 內 科 部 血 液 科 周 聖 傑 醫 師 The antithrombotic efficacy is limited but the risk of bleeding is indefinite Fuster V et al. Circulation 2011;123:e269-e367
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis. Mark Crowther
 New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT
 THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU
 Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS kelly.sawyer@beaumont.edu Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS kelly.sawyer@beaumont.edu Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis*
 Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Review of Non-VKA Oral AntiCoagulants (NOACs) and their use in Great Britain
 Review of Non-VKA Oral AntiCoagulants (NOACs) and their use in Great Britain Dr Alexander (Ander) Cohen Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals, King s College London, UK Pavia Spring Meeting 13 June 2014 Overview
Review of Non-VKA Oral AntiCoagulants (NOACs) and their use in Great Britain Dr Alexander (Ander) Cohen Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals, King s College London, UK Pavia Spring Meeting 13 June 2014 Overview
