Reflective experiences of Post Graduate Certificate in Education students during teaching practice
|
|
|
- Zoe Cunningham
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reflective experiences of Post Graduate Certificate in Education students during teaching practice Abstract Taole MJ University of South Africa Reflective teaching has become a focus of interest and a powerful movement in teacher education. The complexity of teaching requires teachers to question their practices for their own professional development in order to improve and to increase learner performance. This article aims at investigating student teachers reflective experiences during teaching practice period. A qualitative inquiry was used in the study. Eight student teachers enrolled for a language teaching module in a one year Post Graduate Certificate in Education (PGCE) initial teacher education programme for intermediate phase was randomly selected to participate in the study. Data were obtained through interviews. It became clear from the data that reflective teaching is a challenge to student teachers, as a results they could not acknowledge their shortcomings in their classroom performance. In addition, participants reflected on teaching methods and teaching media and believe that these could enhance learning and teaching. It is also the view of participants that collaboration among colleagues and a positive attitude could enhance teachers reflective practices. Keywords: pre-service, teacher-emotions, pedagogic strategies, qualitative research, attitudes, collaboration. Reflective experiences, Page 1
2 Introduction and background Reflective teaching is a significant element in student teachers initial training programme. It has also been widely acknowledged by many researchers as an approach that could promote teachers professional development and improves the quality of teaching and learning. Jacobs, Vakalisa and Gawe (2011:60) contend that reflective teaching offers teachers the opportunity to renew their practice and to understand the effects of their teaching. They further state that reflective teaching provides information on how teachers connect with learners meaningfully thus promoting sound teaching and learning practice. Killen (2007:100) states that: Reflection helps teachers to appreciate that they too can be producers of educational knowledge because through their careful consideration of their learning and teaching experiences they can develop insight that will help them and their colleagues to better understand teaching and learning. The above quote suggests that through reflective practice teachers can contribute to the body of knowledge regarding teaching and learning. It also stresses collaboration among colleagues so that they can assist one another to improve their practice. In addition, reflective teaching enables teachers to take charge of their own development. Akbari (2007:192) suggests that reflective teaching will make teachers question clichés that they have learned during their formative years and will also enable them to develop more informed practice. Teachers will integrate the knowledge they have gained during pre-service training with their practical experiences and make informed choices based on the situations they find themselves in. As Braun and Crumpler (2004:61) suggest, those who do not reflect upon their practices will be likely to teach as they were taught and thus ineffective teaching strategies will be replicated. Therefore, reflective teaching assist teachers in refining their beliefs and theories about teaching as they will relate what they knew and learned to their practical experiences. Killen (2007:98) maintains that unless teachers understand what they are doing and why they are doing it, there is little chance that their efforts will result in student learning or that their actions will be morally and ethically appropriate. This suggests that reflection will improve practice if teachers learn from it. Reflective teaching has been defined and interpreted in numerous ways, from a variety of point of view, by various researchers and groups. This paper will adopt the following definition of reflective teaching as Jacobs et al (2011:56) advocate: reflective teaching is a continuous cycle of systematic self- evaluation by a teacher of his/her own teaching through open discussion with colleagues or written analysis. This suggests that reflective teaching is a deliberate, planned and a collaborative effort. Teachers are expected to work together and not in silos for effective teaching and learning. The South African Department of Education (DoE) has embarked on the intensive training of teachers since the dawn of democracy in According to the DoE (2011:20) quality education is still an elusive concept in the country as teachers still lack the professional qualities that would enable them to function effectively in the classroom. This article argues that teachers as agents of change need to reflect on their teaching practices so as to learn from their previous experiences. Teachers need to question their practices and be open to different possibilities in their teaching experiences. It should be noted that teachers can question their practices if they know how. Yang (2009:11) indicates that critical reflection does not come naturally to most teachers, therefore appropriate opportunities for reflection should be provided Reflective experiences, Page 2
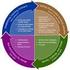
3 to student-teachers. This suggests that reflectivity is a skill that needs to be acquired by learning and not by automatic occurrence. Research has been conducted on reflective teaching as an essential part in teachers professional development, (Griffiths 2000; Killen 2007; Akbari 2007; Conley, De Beer, Dunbar- Kriege, Du Plessis, Gravett, Lomofsky, Merckel, November, Peterson, Robinson & Van der Merwe 2010; Jacobs 2011). Little has been done to investigate student teachers reflective experiences during teaching practice. Griffiths (2000:545) argues that reflection is taken for granted rather than being made explicit. There is an assumption that student teachers will automatically reflect on their practices. This article is a contribution on the discourse on reflective practice in an initial teacher education programme. It also aims at suggesting strategies that could assist student teachers to become reflective teachers. A qualitative enquiry was used for the research and data were collected through interviews. The participants were students from the University of South Africa (Unisa). These participants enrolled for a language teaching module in a one-year Post Graduate Certificate in Education (PGCE), which is an initial teacher education programme for intermediate phase. This study is structured as follows: the first part gives the introduction and conceptualisation of reflective teaching. This is followed by the theoretical framework, research question, research design and methods, findings and discussions. Lastly, the conclusions and recommendations will be presented at the end of the study. Theoretical frameworks The changing demand and responsibilities placed on teachers requires them to be reflective in order to respond appropriately to their changing circumstances (Killen 2007:98). The importance of reflective teaching in South African context is encompassed by the Norms and Standards for Educators (Department of Education 2000). The Norms and Standards for Educators policy acknowledge that teachers need to take charge of their personal and professional development. In addition, the Norms and Standards for Educators require teachers to have reflective competence. Killen (2007:99) defines reflective competence as the ability to integrate performance with decision-making and understanding, and adapting to change unforeseen circumstances. Furthermore, Killen (2007) adds that this would not be possible if teachers have not mastered the ability to reflect on their practices. Teachers need to constantly make decisions and adapt their teaching to suite the diverse needs of learners in their classrooms. Reflective thinking involves the notion that learning and teaching requires use of multiple strategies to accomplish a particular goal. Therefore, there is need for teachers to acknowledge that the method or strategy that they use in the classroom represents one of the different strategies available to assist them to accomplish their teaching-learning goals. Killen (2007:94) contend that any approach to teaching or reflection that does not acknowledge that other approaches have some merit is dangerous. It should be mentioned that no approach is an end but a means to achieve learning outcomes. Schön (1983; 1987) identified two approaches to reflective practice, namely reflectionon-action and reflection-in-action. Reflection on-action can be defined as the self-evaluative thinking that teachers engage in after most lessons. Killen (2007:96) regards reflection on- action as a deliberate attempt by the teacher to understand past events in order to shape future actions. According to Conley et al (2010:5) reflection-in-action-refers to reflection while one is engaged in practice. They refer to this reflection as self-talk because the teacher is silently and Reflective experiences, Page 3
4 continuously engaged in reflective process while teaching. This means that teachers question what they are doing, why they are doing it and the impacts on their learners. Killen (2007:96) maintains that for teachers to reflect in practice they must be able to frame problems almost subconsciously, generate hypotheses and immediately test them. Killen (2007:96) reiterates that both approaches to reflection involve framing and reframing problematic situations and the difference is that they occur at different times. Jacobs et al (2011:59) reiterate that reflective teaching is a process that begins with teaching, choosing one aspect of the lesson that you want to investigate, describe that part in detail, ask yourself why the chosen event happened, reframe events in the light of several theoretical framework, ask yourself what you could have done differently, plan what needs to be done in the next light of analysis and start all over again. The reflective processes as advocated by Jacobs et al (2011:59) are presented in figure 1 below: Figure 1: Reflective cycle Adapted from Jacobs et al (2011:59) Research question The aim of this study was to investigate student teachers reflective experiences during teaching practice. The study will be guided by the following research question: What are the student teachers reflective experiences during teaching practice? Research methodology The study adopted a qualitative research approach to facilitate entry into the participants life-world and to explore their life-experiences or understanding the phenomena from the participants perspective. As Yates (2004:157) points out, qualitative research is concerned with Reflective experiences, Page 4
5 the perspectives of the participants. This involves how participants understand the social world and what meaning it has for those that are under study. Sampling Twenty students were allocated to me to supervise during the teaching practice session of February to December Eight student teachers from the University of South Africa (Unisa) enrolled for a language teaching module in a one-year Post Graduate Certificate in Education (PGCE). This PGCE is an initial teacher education programme for intermediate phase where student teachers were randomly selected to participate in the study. Random sampling method was used in this research to ensure that all the respondents stood the chance of being selected to participate in the study (Mertens 1998:314). This method was also used for convenience as the researcher was visiting students doing their teaching practice at that time. In addition, random sampling allows the researcher to generalise the results beyond the immediate group studied. Student teachers were expected to do ten weeks teaching practice in the schools of their choice. The participants were expected to reflect on their teaching experiences during their teaching practice period. These participants were asked questions such as: 1. What is your impression about the lesson? 2. What would you do differently if you were to teach the same lesson all over again? Data collection instruments Semi-structured interviews were used in order to gain a detailed picture of participants experiences of reflective practice during their teaching practice. Reflective teaching involves teaching and providing answers of why certain events happened through the use the theoretical frameworks to back up the decisions that had be taken. Semi-structured interviews allow more flexibility and the researcher is able to make a follow up to particular interesting avenues that can emerge in the interview (De Vos, Strydom, Fouché and Delport 2011:351). Because the primary data of qualitative interview are verbatim accounts of what transpires in the interview sessions a tape recorder was used to record the interviews. Permission was obtained from the participants to record the interviews on a tape recorder. Neuman (2006:450), states that recording ensures completeness of the verbal interactions and provide material for reliability checks. Student teachers had to present a lesson and were interviewed after that. Data Analysis After data was collected, it was analysed and interpreted. Qualitative analysis process used in this article involved data reduction, data display and conclusion drawing (Miles and Huberman 1984:10). Data reduction refers to the process of selecting, focusing, simplifying, abstracting and transforming the data that appear in written-up field notes or transcriptions, Miles and Huberman (1994:10). This occurs continuously throughout the life of the research project. Data display involves organising information to facilitate drawing of conclusions. Reflective experiences, Page 5
6 Ethical considerations Confidentiality and anonymity Participation in this study was confidential and anonymous. Participants were told that the information they will share will only be treated with confidentiality. Informed consent Participation was voluntary and participants signed a consent form. Participants were also told that they can withdraw from participating if they wish to do so. According to Hakim (2000:143) written informed consent becomes a necessary condition rather than a luxury or an impediment. All the participants signed a consent form containing detailed information of the study. Information Participants were informed of what the data will be used for and were also clarified on why their participation was important. Results and discussion The data collected were consolidated and categorized into themes. Four themes were identified namely: contentment, attitudes towards reflection, use of teaching media and teaching methods. Contentment It is evident from the results that participants were satisfied about their lessons; and this indicates that learners actively participated during the lesson. It should be noted that participants regarded the learners participation as a proof that the lesson went well and that learning has occurred. Loughran (2002), cited in Akbari (2007:195), states that instead of looking for new possibilities and solutions, teachers will try to rationalize their practices and justify the way they teach. Most participants did not acknowledge what they brought to the learning process. They were happy with learners participation and did not indicate how they have contributed in ensuring that the learning outcomes are met or they accomplish their goal. They did not indicate what they have done to get full learner participation. The following are responses of some of the participants about contentment: 1. I felt that the lesson was interesting to my learners because they were cooperating, everything went according to plan. I feel more confident than I had hoped for. The lesson went smoothly and without hitches. 2. The lesson was of a satisfactory standard, I would not change a thing. Reflective experiences, Page 6
7 3. I have been able to incorporate learners prior knowledge in the lesson. This made them active during the lesson also, they participated fully I enjoyed working with them. Most of them seem to be enjoying the lesson. 4. I am very happy about the lesson, I made learners participate and follow the lesson successfully. It went well. Learners enjoyed the game that they played. Only one participant indicated that he was able to incorporate learners prior knowledge during lesson presentation. According to Jacobs et al (2011:217) learning can be meaningful when the information and examples that the teacher presents link up with the learner s previous experiences in a particular field. Teachers need to use what learners know as a starting point and expand that knowledge during lesson presentation. Akbari (2007:195) indicates that the identification of a problem is not an automatic process, and there are many instances where teachers are not able to see what is wrong with their classroom performance. He adds that problem identification needs a trained eye which many teachers lack, especially the novice ones. One can argue that teachers need to be trained to be engaged in critical analysis of their lesson presentations which will lead to improving their practice. Attitudes towards reflection The success of all techniques in reflective teaching is dependent on attitudes (Jacobs et al 2011:58). They contend that teachers need attitudes of open-mindedness and whole-heartedness so that they are able to question their own and other teachers beliefs and practices. They further argue that creation of awareness is the first step towards being a reflective teacher. Teachers need to acknowledge their shortcoming and be prepared to learn from their mistakes. According to Akbar (2007:195) there is no guarantee that teachers who have gone through reflective schemes will teach differently. However, with positive attitude and the preparedness to learn from past experiences, teachers can improve their practice. Teachers need to appreciate the fact that it does not mean they are incompetent or are bad teachers if they acknowledge that there were some mistakes in their lesson presentations. It takes courage and self-introspection to accept that teaching is an art that needs to be perfected on a continuous base regardless of one s previous teaching experiences. Participants were asked what they will do differently if they could teach the same lesson all over again. This was done to give them the opportunity to thoroughly engage in their performance and see if there is any part that needs to be altered. Their responses are presented below: 1. Nothing, I am absolutely happy with the way I have presented the lesson. I believe there is no better way of doing it, I have outdone myself. I am absolutely satisfied and happy with my lesson. 2. I am satisfied with the lesson and will not change a thing if I am to do it again. 3. The lesson was good. It is evident from the interviews that participants could not recognize that there are other possibilities of doing things and that the way they conducted their lessons is not the only way; for example, one participant said: I have outdone myself. Teachers puts a ceiling on their capabilities and do not create a room for exploring other possibilities for lesson presentation. One could argue that participants did not want to critique their own practice. According to Jacobs et al (2011:58) teachers need attitude of open-mindedness and whole-heartedness so that they can be able to question their practices. Killen (2007:93) points out that no matter how well you Reflective experiences, Page 7
8 teach there is always room for presentation improvement. This suggests that teachers need to be open to possibilities. However, open mindedness requires positive attitude and ability to acknowledge that there are alternatives and that a teacher is a life-long learner. In addition, the above utterance indicates that reflective practice is a challenge to participants because they do not have the necessary strategies to use when they are engaged in reflective practice. According to Killen (2007:99) further states that reflection will not be possible if students have not mastered the ability to reflect on their practices. Therefore, student teachers need training on how to reflect as well as the assistance from other individuals such as colleagues to help them to identify defects in their teaching. Weber (1999), cited in Jay and Johnson (2002), argues that reflecting alone increases the possibility of reconstruction of ideas with our own bias. Teachers need colleagues who will work with and assist them in the progressing through the processes of reflective practice. Use of teaching media A teacher need to create a classroom environment that is conducive to learning and stimulate learners curiosity and thinking, Conley et al (2010:128). They add that the teacher needs to bring the remote world out there into the classroom. This can be done through the use of teaching media. Jacobs et al (2011:215) defines teaching media as an object the teacher uses or one that is given to learners to use, to achieve specific teaching and learning outcomes. They add that the use of teaching media places the learner in a better position to use all their senses during learning thus creating the opportunity for learners to become actively involved in the learning process. Conley et al (2011: 128) emphasizes this learning process in that children can discover things through touch, taste, smell, listening and seeing. Teaching media does not replace a teacher, but they enhance learners understanding and motivation. As Jacobs et al (2011:221) mentions teaching media must serve a definite purpose in the lesson and contribute to achieving the lesson outcome. The statements below capture their utterances regarding teaching media as a tool that could improve their lessons: 1. Bring teaching aids to the classroom to enhance learning and teaching. Media helps learners to be part of the lesson. Give more practical work in the lesson and make the lesson interesting. 2. Have a practical assignment where children make their own clocks using cardboards. 3. I will use the chalkboard as well as doing the slide show to demonstrate the use of prepositions. 4. I should have encouraged learners to use the dictionary to check for words they did not understand. The results of the study show that teachers main concern was the use of teaching media. They indicated that the use of teaching aids could have improved and made learning interesting in the learning process. Participants indicated that they could have also used dictionaries to assist learners to understand concepts. As Conley et al (2011:128) media plays an important role in acquiring concepts. Learners learn easily when they are presented with tangible things to assist them to understand what they are being taught. Teaching methods Reflective experiences, Page 8
9 A teaching method is a procedure or a way of teaching in accordance with a definite plan, such as lecturing, questioning or discussing, Jacobs et al (2011:156). This definition suggests that teaching methods need to be planned and varied according to the purpose of the lesson. Therefore, a teacher needs to alternate his/her teaching methods to suite the purpose of the lesson. There are two categories of teaching methods, namely the teacher-directed and the learner-centred methods. The teacher-directed method is defined by Killen (2007:108) as a method in which the teacher delivers academic content in a highly structured format, directing activities of learners and maintaining academic achievement. An example of teacher-directed methods includes the telling method and/or questioning method; whereas the learner-centred method relates to activities such as experimentation, role play and/or discussion. The quotes below represent participants utterances regarding the use of varying teaching methods to improve their lessons: 1. I would allow learners to give more examples of prepositions as well as encourage the learners to create sentences using more than one preposition. The use of slides could have helped other learners to see how prepositions are used as some of them appear to be a bit lost. 2. Read less and allow learners to read and do cooperative learning method. 3. Use power point presentation to show them the different format of letters, both formal and informal letters. The results show that participants believe that varying their teaching method could enhance learners understanding and participation. In addition, the above utterances suggest that participants were using the teacher-directed method of teaching instead of learner-centred method. Participants occupied the centre stage during teaching and directed most of the activities. However, they indicated that they should have used methods that are learner-centred such as a cooperative learning method. Killen (2007:194) indicates that the cooperative learning method teaches students to be less reliant on the teacher and more reliant on their own abilities to think, but seek information from other sources and learn from other students. Cooperative learning method would make learners responsible for their own learning and also stimulate the feeling in them that they too can contribute towards achieving the lesson goals. It is also evident from the results that participants believe that visual presentation through the use of PowerPoint presentation would have added value to their learners learning experiences. This is supported by Jacobs et al (2011:166) that electronic devices can captivate a class and keep learners focused during the presentation. They further indicate that PowerPoint presentations can give a tremendous boost to learners enjoyment of the lesson and appeal to learners sense of adventure as they create a sense of being in a cinema. Visual presentation increases learners motivation. The above discussions suggest that participants acknowledge that they can use different teaching methods to achieve the lesson outcome. This is an indication that reflection is taking place even though at a lower level as they do not indicate their theoretical frameworks that inform their decisions. Larrivee (2008:342) regards this stage as pre-reflection stage. Also, Larrivee (2008:342) indicates that teachers operating at this level at this level focus on strategies and methods used to reach predetermined goals. Participants reflections were not based on their theoretical framework as their reference for making decisions about their lessons. Conclusions Reflective experiences, Page 9
10 The changing demand and responsibilities placed on teachers requires them to be reflective in order to respond appropriately to their changing circumstances (Killen 20007:98). Reflectivity is a complex process that requires student teachers to be adequately prepared to question their actions and change. It is evident that participants had a challenge with reflective teaching. They could not see problems in their teaching. However, they acknowledged that the use of teaching media and variety of teaching methods could enhance their teaching practice. Therefore, positive attitudes on the part of student teachers would assist to ensure that they remain open to learning possibilities to improve their practice. Collaboration among colleagues could also enhance student teachers reflective practices as they will share their experiences and problems during lesson presentation. Teachers deliberate testing and questioning of their practice will assist them in getting a deeper and broader understanding of their practice and enrich their personal theories of teaching and learning. References Akbari, R Reflection on reflection: a critical appraisal of reflective practice in L2 teacher education. System. 35 (2): Braun, J A & Crumpler, TP The social memoir: an analysis of developing reflective ability in pre-service methods course. Teaching and Teacher Education, 20: Conley, L, De Beer, J, Dunbar-Krige, H, Du Plessis, E, Gravett, S, Lomofsky, L., Merckel, V, November, I, Osman, R, Peterson, N, Robinson, M & Van der Merwe, M Becoming a Teacher. Cape Town: Pearson. De Vos, AS, Strydom, H, Fouchѐ, CB & Delport, CSL Research at grass roots: for the social sciences and human service professions. 4th edition. Pretoria: Van Schaik. Griffiths, V The reflective dimension in teacher education. International Journal of Educational Research, 33 (5): Hakim, C Research design: successful designs for social and economic research. New York: Routledge. Jacobs, M, Vakalisa, NCG & Gawe, N Teaching-learning dynamics. Cape Town: Pearson. Jay, JK & Johnson, KL Capturing complexity: a typology of reflective practice for teacher education. Teaching and Teacher Education.18 (1): Killen, R Teaching strategies for outcomes-based education. Cape Town: Juta. Larrivee, B Development of a tool to assess teachers level of reflective practice. Reflective Practice, 9(3): Mertens, DM Research methods in education and psychology: Integrating diversity with qualitative and quantitative approach. Thousand Oaks: Sage. Miles, M & Huberman, A Analyzing qualitative data: a sourcebook of new methods. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage. Neuman, WL Social research methods: qualitative and quantitative approaches. New York: Pearson. Schön, DA The reflective practitioner: how professionals think in action. New York: Basic Books. Schön, DA Educating the reflective practitioner. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. South Africa. Department of Education Norms and standards of educators. Pretoria: Government Printers. Reflective experiences, Page 10
11 South Africa. Department of Education South African Country report: progress on implementation of the National Curriculum Statements. Pretoria: Government Printers. Yang, SH Using blogs to enhance critical reflection and community of practice. Educational Technology and Society, 12(2): Yates, J Doing social science research. London: Sage. Reflective experiences, Page 11
Teaching Beliefs of Graduate Students in Adult Education: A Longitudinal Perspective
 Teaching Beliefs of Graduate Students in Adult Education: A Longitudinal Perspective Edward W. Taylor Penn State University Capital College, USA Abstract This longitudinal study explores the influence
Teaching Beliefs of Graduate Students in Adult Education: A Longitudinal Perspective Edward W. Taylor Penn State University Capital College, USA Abstract This longitudinal study explores the influence
Living and Learning with Technology: Faculty as Reflective Practitioners in the Online Classroom Patricia A. Lawler, Kathleen P. King, Stephen C.
 Living and Learning with Technology: Faculty as Reflective Practitioners in the Online Classroom Patricia A. Lawler, Kathleen P. King, Stephen C. Wilhite Widener University, Fordham University, Widener
Living and Learning with Technology: Faculty as Reflective Practitioners in the Online Classroom Patricia A. Lawler, Kathleen P. King, Stephen C. Wilhite Widener University, Fordham University, Widener
Reflective Practice. Becoming a Teacher Detective and Loving It
 Reflective Practice Hello, my name is Dr. Anne Rodrigue. Today in this keynote presentation, I will define reflective practice - what it involves, how to get started, and how to make reflective practice
Reflective Practice Hello, my name is Dr. Anne Rodrigue. Today in this keynote presentation, I will define reflective practice - what it involves, how to get started, and how to make reflective practice
Exploring Principals Role in Providing Instructional Leadership in Rural High Schools in South Africa
 Kamla-Raj 2013 Stud Tribes Tribals, 11(1): 75-82 (2013) Exploring Principals Role in Providing Instructional Leadership in Rural High Schools in South Africa M. J. Taole Department of Teacher Education,
Kamla-Raj 2013 Stud Tribes Tribals, 11(1): 75-82 (2013) Exploring Principals Role in Providing Instructional Leadership in Rural High Schools in South Africa M. J. Taole Department of Teacher Education,
From What to Why Reflective Storytelling as Context for Critical Thinking
 Fornreris and Campbell, Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning in the Health Sciences, Facione and Facione (eds.), California Academic Press. 1 Measuring Thinking Worldwide This document is a best practices
Fornreris and Campbell, Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning in the Health Sciences, Facione and Facione (eds.), California Academic Press. 1 Measuring Thinking Worldwide This document is a best practices
Mentoring and Coaching Models
 Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Blood, Sweat and Tears: Insights into the Lived Experiences of Graduates of an. Accelerated Undergraduate Degree-Completion Program
 1 Blood, Sweat and Tears: Insights into the Lived Experiences of Graduates of an Accelerated Undergraduate Degree-Completion Program Bonnie Flynn, Ed.D., MPH National-Louis University Abstract: This is
1 Blood, Sweat and Tears: Insights into the Lived Experiences of Graduates of an Accelerated Undergraduate Degree-Completion Program Bonnie Flynn, Ed.D., MPH National-Louis University Abstract: This is
Critical Inquiry in Educational Research and Professional Practice
 DOCTOR IN EDUCATION COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES NEDD 800 Professionalism, Ethics, and the Self This introductory core course will explore and interrogate ideas surrounding professionalism and professionalization.
DOCTOR IN EDUCATION COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES NEDD 800 Professionalism, Ethics, and the Self This introductory core course will explore and interrogate ideas surrounding professionalism and professionalization.
The Role of Reflection in Facilitating Pre-service Primary School Teachers Professional Growth
 The Role of Reflection in Facilitating Pre-service Primary School Teachers Professional Growth Hassan H. Tairab (tairab@uaeu.ac.ae) College of Education United Arab Emirates University Abstract: This paper
The Role of Reflection in Facilitating Pre-service Primary School Teachers Professional Growth Hassan H. Tairab (tairab@uaeu.ac.ae) College of Education United Arab Emirates University Abstract: This paper
OVERCOMING THE BARRIERS TO INTRODUCE LESSON STUDY IN SOUTH AFRICA
 OVERCOMING THE BARRIERS TO INTRODUCE LESSON STUDY IN SOUTH AFRICA Ronél Paulsen University of South Africa paulsr@unisa.ac.za Abstract In this paper I will be looking at the introduction of Outcomes Based
OVERCOMING THE BARRIERS TO INTRODUCE LESSON STUDY IN SOUTH AFRICA Ronél Paulsen University of South Africa paulsr@unisa.ac.za Abstract In this paper I will be looking at the introduction of Outcomes Based
Analyzing Qualitative Data
 Analyzing Qualitative Data The purpose of coding qualitative data is to take an overwhelmingly large amount of words or artifacts and organize them into manageable chunks. Following the steps in this outline
Analyzing Qualitative Data The purpose of coding qualitative data is to take an overwhelmingly large amount of words or artifacts and organize them into manageable chunks. Following the steps in this outline
Doing Phenomenological Research: Connecting Nursing Education, Research, and Professional Practice
 1 Running Head: Doing Phenomenological Research Doing Phenomenological Research: Connecting Nursing Education, Research, and Professional Practice Rebecca S. Sloan, RNCS, Ph.D. Melinda Swenson, RNCS, Ph.D.
1 Running Head: Doing Phenomenological Research Doing Phenomenological Research: Connecting Nursing Education, Research, and Professional Practice Rebecca S. Sloan, RNCS, Ph.D. Melinda Swenson, RNCS, Ph.D.
The Teacher Educator Standards
 The Teacher Educator Standards From the Association of Teacher Educators Winter Conference Standards Clinic New Orleans, LA February, 2008 Facilitators: Dr. Robert Fisher Dr. Barbara Short Dr. Robin McBee
The Teacher Educator Standards From the Association of Teacher Educators Winter Conference Standards Clinic New Orleans, LA February, 2008 Facilitators: Dr. Robert Fisher Dr. Barbara Short Dr. Robin McBee
Characteristics of Effective and Sustainable Teaching Development Programs for Quality Teaching in Higher Education
 Characteristics of Effective and Sustainable Teaching Development Programs for Quality Teaching in Higher Education This presentation will address the following conference aim/question: What are the contextual
Characteristics of Effective and Sustainable Teaching Development Programs for Quality Teaching in Higher Education This presentation will address the following conference aim/question: What are the contextual
Classroom Climate. from the complex transaction of many immediate environmental factors (e.g., physical, material,
 Adelman, H. S. & Taylor, L. (in press). Classroom climate. In S. W. Lee, P. A. Lowe, & E Robinson (Eds.), Encyclopedia of School Psychology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Classroom Climate Classroom climate
Adelman, H. S. & Taylor, L. (in press). Classroom climate. In S. W. Lee, P. A. Lowe, & E Robinson (Eds.), Encyclopedia of School Psychology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Classroom Climate Classroom climate
Students Perceptions of Learning College Algebra Online using Adaptive Learning Technology. Lori Ogden West Virginia University
 Students Perceptions of Learning College Algebra Online using Adaptive Learning Technology Lori Ogden West Virginia University Adaptive learning technology was used in the teaching of an online college
Students Perceptions of Learning College Algebra Online using Adaptive Learning Technology Lori Ogden West Virginia University Adaptive learning technology was used in the teaching of an online college
Paradoxes of social inclusion reflected in a digital story-telling project
 Paradoxes of social inclusion reflected in a digital story-telling project By Janet Condy, Daniela Gachago, Eunice Ivala, Agnes Chigona Cape Peninsula University of Technology Class of 2011 Outline of
Paradoxes of social inclusion reflected in a digital story-telling project By Janet Condy, Daniela Gachago, Eunice Ivala, Agnes Chigona Cape Peninsula University of Technology Class of 2011 Outline of
Study units for the Honours BEd degree
 Study units for the Honours BEd degree (offered by the Department of Educational Studies) Telephone number 012 429 4585 1 Syllabus Old curriculum NB Only students already registered for the old curriculum
Study units for the Honours BEd degree (offered by the Department of Educational Studies) Telephone number 012 429 4585 1 Syllabus Old curriculum NB Only students already registered for the old curriculum
ELTT course 10: Writing Up Qualitative Research (Independent Study version) English Language Teaching Centre
 3 Methodology (In this unit I use the word Methodology as a general term to cover whatever you decide to include in the chapter where you discuss alternative methodological approaches, justify your chosen
3 Methodology (In this unit I use the word Methodology as a general term to cover whatever you decide to include in the chapter where you discuss alternative methodological approaches, justify your chosen
INTEGRATION OF CRITICAL THINKING PRINCIPLES INTO THE CURRICULUM OF SECONDARY SCHOOLS: LITHUANIA S CASE
 INTEGRATION OF CRITICAL THINKING PRINCIPLES INTO THE CURRICULUM OF SECONDARY SCHOOLS: LITHUANIA S CASE Research report Author Daiva Penkauskienė June 2010 Supported by a grant of from Foundation Open Society
INTEGRATION OF CRITICAL THINKING PRINCIPLES INTO THE CURRICULUM OF SECONDARY SCHOOLS: LITHUANIA S CASE Research report Author Daiva Penkauskienė June 2010 Supported by a grant of from Foundation Open Society
Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching
 Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching Contents: Principles of Mentoring and Coaching Mentoring and Coaching: Core Concepts Skills for Mentoring
Mentoring and Coaching CPD Capacity Building Project National Framework for Mentoring and Coaching Contents: Principles of Mentoring and Coaching Mentoring and Coaching: Core Concepts Skills for Mentoring
Standards for Excellence
 THE AUSTRALIAN ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS Standards for Excellence in Teaching Mathematics in Australian Schools 2006 edition These Standards were originally adopted by AAMT Council in 2002 as
THE AUSTRALIAN ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS Standards for Excellence in Teaching Mathematics in Australian Schools 2006 edition These Standards were originally adopted by AAMT Council in 2002 as
IMPROVING QUALITY. Quality criteria for global education school visits
 IMPROVING QUALITY Quality criteria for global education school visits Organisations that have worked on these quality criteria: Pro Ethical Trade Finland Kepa Service Centre for Development Cooperation
IMPROVING QUALITY Quality criteria for global education school visits Organisations that have worked on these quality criteria: Pro Ethical Trade Finland Kepa Service Centre for Development Cooperation
How To Understand The Reactions Of Students Of The Layout And Graphics Design In Computer Course
 THE EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING CYCLE IN VISUAL DESIGN Aysu ARSOY & Bahire Efe ÖZAD Abstract Experiential Learning Cycle has been applied to the Layout and Graphics Design in Computer Course provided by the
THE EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING CYCLE IN VISUAL DESIGN Aysu ARSOY & Bahire Efe ÖZAD Abstract Experiential Learning Cycle has been applied to the Layout and Graphics Design in Computer Course provided by the
Cambridge International Certificate in Educational Leadership 6247 Cambridge International Diploma in Educational Leadership 6248
 Cambridge International Certificate in Educational Leadership 6247 Cambridge International Diploma in Educational Leadership 6248 For examination in 2015 Preface This syllabus sets out the details of the
Cambridge International Certificate in Educational Leadership 6247 Cambridge International Diploma in Educational Leadership 6248 For examination in 2015 Preface This syllabus sets out the details of the
Postgraduate Diploma in Higher Education (PGDHE) Customised for the Ministry of Health
 Postgraduate Diploma in Higher Education (PGDHE) Customised for the Ministry of Health The Training Agency The National Institute of Education (NIE) is Singapore's recognised premier centre for teacher
Postgraduate Diploma in Higher Education (PGDHE) Customised for the Ministry of Health The Training Agency The National Institute of Education (NIE) is Singapore's recognised premier centre for teacher
FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation
 FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation I. Cover Sheet Student Name Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Email (Please Check) Full-time Part-time Field Instructor Work Phone Email Agency Cell Phone Site Address
FOUNDATION YEAR Student Evaluation I. Cover Sheet Student Name Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Email (Please Check) Full-time Part-time Field Instructor Work Phone Email Agency Cell Phone Site Address
What Faculty Learn Teaching Adults in Multiple Course Delivery Formats
 What Faculty Learn Teaching Adults in Multiple Course Delivery Formats Karen Skibba, MA Instructional Design Specialist University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Doctoral Candidate University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
What Faculty Learn Teaching Adults in Multiple Course Delivery Formats Karen Skibba, MA Instructional Design Specialist University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Doctoral Candidate University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
AG418 Public Sector Accounting. Brief description of honours classes 2012/2013. AG424 Accounting Theories
 Brief description of honours classes 2012/2013 AG424 Accounting Theories To offer an advanced course on the historic foundations of, and contemporary theoretical issues in, accounting. The course builds
Brief description of honours classes 2012/2013 AG424 Accounting Theories To offer an advanced course on the historic foundations of, and contemporary theoretical issues in, accounting. The course builds
The Essentials of Critical Care Orientation (ECCO) Program's Impact on New Graduate Nurses' Critical Thinking Development
 The Essentials of Critical Care Orientation (ECCO) Program's Impact on New Graduate Nurses' Critical Thinking Development Sigma Theta Tau International s 21 st International Nursing Research Congress Mahmoud
The Essentials of Critical Care Orientation (ECCO) Program's Impact on New Graduate Nurses' Critical Thinking Development Sigma Theta Tau International s 21 st International Nursing Research Congress Mahmoud
Doctor of Education - Higher Education
 1 Doctor of Education - Higher Education The University of Liverpool s Doctor of Education - Higher Education (EdD) is a professional doctoral programme focused on the latest practice, research, and leadership
1 Doctor of Education - Higher Education The University of Liverpool s Doctor of Education - Higher Education (EdD) is a professional doctoral programme focused on the latest practice, research, and leadership
Effects of Scaffolded Video Analysis on Pre-Service English Teachers Classroom Interactions and Professional Development
 , pp.283-290 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2016.11.3.27 Effects of Scaffolded Video Analysis on Pre-Service English Teachers Classroom Interactions and Professional Development Yoonhee Choe Department
, pp.283-290 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2016.11.3.27 Effects of Scaffolded Video Analysis on Pre-Service English Teachers Classroom Interactions and Professional Development Yoonhee Choe Department
Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]
![Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]](/thumbs/24/3436110.jpg) I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
IDOL Outcomes and Competencies (ibstpi) 2
 Instructional Design for Online Learning (IDOL) Specialization Outcomes and Specialization Competencies Updated January 2008 Table of Contents Outcomes-based curricula at Capella University...3 IDOL MS
Instructional Design for Online Learning (IDOL) Specialization Outcomes and Specialization Competencies Updated January 2008 Table of Contents Outcomes-based curricula at Capella University...3 IDOL MS
Novice Experienced Expert a. Understands the importance of ABE, ASE, and ESOL at the personal and program level. X X X
 Complete Draft 1 through 5 Rhode Island Adult Education Practitioner Standards for Instructors 9-12-12 Definitions: Expert Teachers Expert teachers have the capacity to teach from the heart as well as
Complete Draft 1 through 5 Rhode Island Adult Education Practitioner Standards for Instructors 9-12-12 Definitions: Expert Teachers Expert teachers have the capacity to teach from the heart as well as
Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G
 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines for Primary Schools Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools I N S P E C TO R AT E P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G 2 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines
School Self-Evaluation Guidelines for Primary Schools Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools I N S P E C TO R AT E P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G 2 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines
Pre-Primary Education ( PPE11 )
 FACULTY OF EDUCATION Bachelor s Degree Programmes Pre-Primary Education ( PPE11 ) EDUC180 INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATION This course aims to help students understand the general law of the human education system.
FACULTY OF EDUCATION Bachelor s Degree Programmes Pre-Primary Education ( PPE11 ) EDUC180 INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATION This course aims to help students understand the general law of the human education system.
A. The master of arts, educational studies program will allow students to do the following.
 PROGRAM OBJECTIVES DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DEGREES OFFERED MASTER OF ARTS, EDUCATIONAL STUDIES (M.A.); MASTER OF ARTS, SCIENCE EDUCATION (M.S.); MASTER OF ARTS IN GERMAN WITH TEACHING LICENSURE (M.A.);
PROGRAM OBJECTIVES DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DEGREES OFFERED MASTER OF ARTS, EDUCATIONAL STUDIES (M.A.); MASTER OF ARTS, SCIENCE EDUCATION (M.S.); MASTER OF ARTS IN GERMAN WITH TEACHING LICENSURE (M.A.);
Learning and Teaching
 B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
A Cross-Case Analysis of How Faculty Connect Learning in Hybrid Courses
 A Cross-Case Analysis of How Faculty Connect Learning in Hybrid Courses Karen Skibba University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Keywords: Hybrid Courses, Dimensions of Learning, Case Studies Abstract: This qualitative,
A Cross-Case Analysis of How Faculty Connect Learning in Hybrid Courses Karen Skibba University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Keywords: Hybrid Courses, Dimensions of Learning, Case Studies Abstract: This qualitative,
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd)
 215 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
215 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
Teaching Dossier (2007) LAURA KERR. Queen s University School of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences
 1 Teaching Dossier (2007) Of LAURA KERR Queen s University School of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences 2 CONTENTS 1. Brief Biography 2. Teaching Philosophy 3. Teaching Responsibilities 3.1 Nurs 315 3.2
1 Teaching Dossier (2007) Of LAURA KERR Queen s University School of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences 2 CONTENTS 1. Brief Biography 2. Teaching Philosophy 3. Teaching Responsibilities 3.1 Nurs 315 3.2
The Standards for Registration: mandatory requirements for Registration with the General Teaching Council for Scotland December 2012
 DRIVING FORWARD PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR TEACHERS The Standards for Registration: mandatory requirements for Registration with the General Teaching Council for Scotland December 2012 Contents Page The
DRIVING FORWARD PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR TEACHERS The Standards for Registration: mandatory requirements for Registration with the General Teaching Council for Scotland December 2012 Contents Page The
EAPRIL Best Research and Practice Award
 EAPRIL Best Research and Practice Award GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION 1. Title of project Schools as Sustainable Learning Organizations: Research Based Practice Process of Becoming a Sustainable Learning
EAPRIL Best Research and Practice Award GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION 1. Title of project Schools as Sustainable Learning Organizations: Research Based Practice Process of Becoming a Sustainable Learning
The Process of Integrating Experience with Learning of First Year Social Work Students
 The Process of Integrating Experience with Learning of First Year Social Work Students Shiu-yeu Fok and Fanny Liu City University of Hong Kong A b s t r a c t The student s experience plays an important
The Process of Integrating Experience with Learning of First Year Social Work Students Shiu-yeu Fok and Fanny Liu City University of Hong Kong A b s t r a c t The student s experience plays an important
Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection.
 Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection. Richard Hawkins & Harvey Woolf Greater Manchester AHP/HCS
Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection. Richard Hawkins & Harvey Woolf Greater Manchester AHP/HCS
Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession
 12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
Introduction to Research Methods and Applied Data Analysis Online module
 MODULE SPECIFICATION KEY FACTS Module name Introduction to Methods and Applied Data Analysis Online module Module code HRM011 School School of Health Sciences Department or equivalent Health Services and
MODULE SPECIFICATION KEY FACTS Module name Introduction to Methods and Applied Data Analysis Online module Module code HRM011 School School of Health Sciences Department or equivalent Health Services and
Five Attitudes of Effective Teachers: Implications for Teacher Training. Bonni Gourneau University of North Dakota. Abstract
 Five Attitudes of Effective Teachers: Implications for Teacher Training Bonni Gourneau University of North Dakota Abstract When preservice teachers or teacher candidates are asked, "Why do you want to
Five Attitudes of Effective Teachers: Implications for Teacher Training Bonni Gourneau University of North Dakota Abstract When preservice teachers or teacher candidates are asked, "Why do you want to
College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs)
 College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs) College of PHS Learning Goals PsyD Program Learning Goals
College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs) College of PHS Learning Goals PsyD Program Learning Goals
Running head: FROM IN-PERSON TO ONLINE 1. From In-Person to Online : Designing a Professional Development Experience for Teachers. Jennifer N.
 Running head: FROM IN-PERSON TO ONLINE 1 From In-Person to Online : Designing a Professional Development Experience for Teachers Jennifer N. Pic Project Learning Tree, American Forest Foundation FROM IN-PERSON
Running head: FROM IN-PERSON TO ONLINE 1 From In-Person to Online : Designing a Professional Development Experience for Teachers Jennifer N. Pic Project Learning Tree, American Forest Foundation FROM IN-PERSON
Promoting Learner Autonomy and Language Awareness Through Blogging
 Promoting Learner Autonomy and Language Awareness Through Blogging Paul Dickinson Abstract The benefits of learner Weblogs, or blogs as they are more commonly known, have been reported in various educational
Promoting Learner Autonomy and Language Awareness Through Blogging Paul Dickinson Abstract The benefits of learner Weblogs, or blogs as they are more commonly known, have been reported in various educational
Core Competencies of Clinical Psychology
 Foundational Competencies Core Competencies of Clinical Psychology Graduate Students Must Meet These Competencies at the "Meets Expectations" Level or Better Reflective Practice/Self-Assessment: Practices
Foundational Competencies Core Competencies of Clinical Psychology Graduate Students Must Meet These Competencies at the "Meets Expectations" Level or Better Reflective Practice/Self-Assessment: Practices
The research process with reference to the research method section
 The research process with reference to the research method section Social work theories and methodologies, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 5 11 June 2011 Prof Herman Strydom, North West University, Potchefstroom,
The research process with reference to the research method section Social work theories and methodologies, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 5 11 June 2011 Prof Herman Strydom, North West University, Potchefstroom,
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd)
 247 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
247 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
Using qualitative research to explore women s responses
 Using qualitative research to explore women s responses Towards meaningful assistance - how evidence from qualitative studies can help to meet survivors needs Possible questions Why do survivors of SV
Using qualitative research to explore women s responses Towards meaningful assistance - how evidence from qualitative studies can help to meet survivors needs Possible questions Why do survivors of SV
Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G
 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines for Post-Primary Schools Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools I N S P E C TO R AT E P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G 2 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines
School Self-Evaluation Guidelines for Post-Primary Schools Inspectorate Guidelines for Schools I N S P E C TO R AT E P R O M O T I N G T H E Q U A L I T Y O F L E A R N I N G 2 School Self-Evaluation Guidelines
School Psychology Program Goals, Objectives, & Competencies
 RUTGERS SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM PRACTICUM HANDBOOK Introduction School Psychology is a general practice and health service provider specialty of professional psychology that is concerned with the science
RUTGERS SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM PRACTICUM HANDBOOK Introduction School Psychology is a general practice and health service provider specialty of professional psychology that is concerned with the science
FACULTY PEER ONLINE CLASSROOM OBSERVATIONS AA
 Philosophy Online class observations are meant to facilitate an instructor s professional growth. They will be used to create an opportunity for reflection and stimulate ideas for improvement in the online
Philosophy Online class observations are meant to facilitate an instructor s professional growth. They will be used to create an opportunity for reflection and stimulate ideas for improvement in the online
Abstraction in Computer Science & Software Engineering: A Pedagogical Perspective
 Orit Hazzan's Column Abstraction in Computer Science & Software Engineering: A Pedagogical Perspective This column is coauthored with Jeff Kramer, Department of Computing, Imperial College, London ABSTRACT
Orit Hazzan's Column Abstraction in Computer Science & Software Engineering: A Pedagogical Perspective This column is coauthored with Jeff Kramer, Department of Computing, Imperial College, London ABSTRACT
Wanngam Marakrong Khon Kaen University, Thailand <ao_uki@hotmail.com> Chokchai Yuenyong Khon Kaen University, Thailand <ychok@kku.ac.
 ENHANCING THAI STUDENTS SCIENTIFIC LITERACY IN LEARNING ABOUT WORLD PHENOMENON AND SPACE TECHNOLOGY THROUGH YUENYONG (2006) SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY (STS) APPROACH Wanngam Marakrong Khon Kaen University,
ENHANCING THAI STUDENTS SCIENTIFIC LITERACY IN LEARNING ABOUT WORLD PHENOMENON AND SPACE TECHNOLOGY THROUGH YUENYONG (2006) SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY (STS) APPROACH Wanngam Marakrong Khon Kaen University,
the general concept down to the practical steps of the process.
 Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
Merging Business and Adult Education to Create an Online MBA Degree Program: Concern over Sustaining the Andragogical Approach
 Merging Business and Adult Education to Create an Online MBA Degree Program: Concern over Sustaining the Andragogical Approach Susan Isenberg, Ph.D. Abstract: Merging business and education models for
Merging Business and Adult Education to Create an Online MBA Degree Program: Concern over Sustaining the Andragogical Approach Susan Isenberg, Ph.D. Abstract: Merging business and education models for
Additional Qualification Course Guideline Special Education, Specialist
 Additional Qualification Course Guideline Special Education, Specialist Schedule D Teachers Qualifications Regulation April 2014 Ce document est disponible en français sous le titre Ligne directrice du
Additional Qualification Course Guideline Special Education, Specialist Schedule D Teachers Qualifications Regulation April 2014 Ce document est disponible en français sous le titre Ligne directrice du
Effective Teaching Approaches in Diploma of Business Course
 Abstract: Effective Teaching Approaches in Diploma of Business Course Tsen Tzee Mui Curtin University Sarawak Malaysia tsentm@curtin.edu.my Dr Beena Giridharan Curtin University Sarawak Malaysia beena@curtin.edu.my
Abstract: Effective Teaching Approaches in Diploma of Business Course Tsen Tzee Mui Curtin University Sarawak Malaysia tsentm@curtin.edu.my Dr Beena Giridharan Curtin University Sarawak Malaysia beena@curtin.edu.my
Council on Social Work Education. Curriculum Policy Statement for Baccalaureate Degree Programs in Social Work Education
 Council on Social Work Education Curriculum Policy Statement for Baccalaureate Degree Programs in Social Work Education B1.0 SCOPE AND INTENT OF THE CURRICULUM POLICY STATEMENT B1.1 This document sets
Council on Social Work Education Curriculum Policy Statement for Baccalaureate Degree Programs in Social Work Education B1.0 SCOPE AND INTENT OF THE CURRICULUM POLICY STATEMENT B1.1 This document sets
PROGRAMMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA in LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT (HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE SERVICES)
 PROGRAMMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA in LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT (HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE SERVICES) MA in LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT (HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE SERVICES) 1. Award 2. Route Management (Health and
PROGRAMMME SPECIFICATION FOR MA in LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT (HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE SERVICES) MA in LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT (HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE SERVICES) 1. Award 2. Route Management (Health and
JOB DESCRIPTION. Job Title: Lecturer in Film Production & Cinematography (Ref: J274)
 JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Lecturer in Film Production & Cinematography (Ref: J274) Grade: Lecturer: Unqualified 20,200 to 23,230 pa Qualified 24,240 to 32,320 pa Responsible to: Curriculum Manager Location:
JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Lecturer in Film Production & Cinematography (Ref: J274) Grade: Lecturer: Unqualified 20,200 to 23,230 pa Qualified 24,240 to 32,320 pa Responsible to: Curriculum Manager Location:
Cleveland College of Art & Design BA (Hons) Fashion Enterprise Programme Handbook 2013-2014 1
 Cleveland College of Art & Design BA (Hons) Fashion Enterprise Programme Handbook 2013-2014 1 BA (Hons) Fashion Enterprise Programme Handbook 2013-2014 Your Programme Handbook provides you with a range
Cleveland College of Art & Design BA (Hons) Fashion Enterprise Programme Handbook 2013-2014 1 BA (Hons) Fashion Enterprise Programme Handbook 2013-2014 Your Programme Handbook provides you with a range
ED 666 ~ Advanced Educational Psychology ~ Karen L. Macklin
 UAS CTE graduates will be informed, reflective, and responsive teachers within diverse classroom, school, and community contexts ED S631 Advanced Educational Psychology - Course Syllabus Karen L. Macklin,
UAS CTE graduates will be informed, reflective, and responsive teachers within diverse classroom, school, and community contexts ED S631 Advanced Educational Psychology - Course Syllabus Karen L. Macklin,
REFLECTING ON EXPERIENCES OF THE TEACHER INDUCTION SCHEME
 REFLECTING ON EXPERIENCES OF THE TEACHER INDUCTION SCHEME September 2005 Myra A Pearson, Depute Registrar (Education) Dr Dean Robson, Professional Officer First Published 2005 The General Teaching Council
REFLECTING ON EXPERIENCES OF THE TEACHER INDUCTION SCHEME September 2005 Myra A Pearson, Depute Registrar (Education) Dr Dean Robson, Professional Officer First Published 2005 The General Teaching Council
Health and Physical Education, Intermediate and Senior Specialist
 Additional Qualification Course Guideline Health and Physical Education, Intermediate and Senior Specialist Schedule D Teachers Qualifications Regulation July 2011 Ce document est disponible en français
Additional Qualification Course Guideline Health and Physical Education, Intermediate and Senior Specialist Schedule D Teachers Qualifications Regulation July 2011 Ce document est disponible en français
For examination in 2015
 Cambridge International Certificate in Teaching with Digital Technologies 6224 Cambridge International Diploma in Teaching with Digital Technologies 6225 For examination in 2015 Preface This syllabus sets
Cambridge International Certificate in Teaching with Digital Technologies 6224 Cambridge International Diploma in Teaching with Digital Technologies 6225 For examination in 2015 Preface This syllabus sets
NMBA Registered nurse standards for practice survey
 Registered nurse standards for practice 1. Thinks critically and analyses nursing practice 2. Engages in therapeutic and professional relationships 3. Maintains fitness to practise and participates in
Registered nurse standards for practice 1. Thinks critically and analyses nursing practice 2. Engages in therapeutic and professional relationships 3. Maintains fitness to practise and participates in
How to Encourage Communication Skills in Children and Young People
 Children and Young People s Views What do children and young people think about speech, language and communication skills? What do children and young people think about speech, language and communication
Children and Young People s Views What do children and young people think about speech, language and communication skills? What do children and young people think about speech, language and communication
SES Society for Educational Studies
 Surname: HARGREAVES First name(s): ELEANORE ROSEMARY Title: DR Position and employer: SENIOR LECTURER, INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON Title: How teachers of all disciplines use Masters degree
Surname: HARGREAVES First name(s): ELEANORE ROSEMARY Title: DR Position and employer: SENIOR LECTURER, INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON Title: How teachers of all disciplines use Masters degree
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY. The purpose of this study was to describe which aspects of course design
 CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY The purpose of this study was to describe which aspects of course design and/or instruction are more effective and successful in the online environment than in the face-to-face
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY The purpose of this study was to describe which aspects of course design and/or instruction are more effective and successful in the online environment than in the face-to-face
Human Services Associate Spring 2014 Student SLO Report
 1. What did you like about this program? I loved most of the teachers. One was not that great but I was informed she will not be back so that is good for the new students. I liked how the assignments helped
1. What did you like about this program? I loved most of the teachers. One was not that great but I was informed she will not be back so that is good for the new students. I liked how the assignments helped
CHAPTER 3 : RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 : RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY 3.1 INTRODUCTION The qualitative research design was used in the study. In-depth individual interviews were conducted with lovelife counselors to understand
CHAPTER 3 : RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY 3.1 INTRODUCTION The qualitative research design was used in the study. In-depth individual interviews were conducted with lovelife counselors to understand
Perceptions of participants on the certificate course for distance education practitioners: Botswana Case Study R. K. Masalela, University of Botswana
 Perceptions of participants on the certificate course for distance education practitioners: Botswana Case Study R. K. Masalela, University of Botswana kmasalela@gmail.com Abstract This study qualitatively
Perceptions of participants on the certificate course for distance education practitioners: Botswana Case Study R. K. Masalela, University of Botswana kmasalela@gmail.com Abstract This study qualitatively
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 Programme Specification Section 1: Basic Data Awarding institution/body Teaching institution Faculty responsible for programme University of the West of England University of the West of England Faculty
Programme Specification Section 1: Basic Data Awarding institution/body Teaching institution Faculty responsible for programme University of the West of England University of the West of England Faculty
Standards of proficiency. Arts therapists
 Standards of proficiency Arts therapists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency
Standards of proficiency Arts therapists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency
Teachers' Perspectives about the Effect of Tawjihi English Exam on English Instruction at the Second Secondary Stage in Jordan
 Teachers' Perspectives about the Effect of Tawjihi English Exam on English Instruction at the Second Secondary Stage in Jordan Dr. Mohammad Abd Alhafeez Ali Ta'amneh Assistant Professor of Teaching English
Teachers' Perspectives about the Effect of Tawjihi English Exam on English Instruction at the Second Secondary Stage in Jordan Dr. Mohammad Abd Alhafeez Ali Ta'amneh Assistant Professor of Teaching English
How To Create An Online Learning Community
 19th Annual Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference Las Vegas, Nevada, USA March 5, 2008 Creating Online Learning Communities: A Cross Disciplinary Examination of
19th Annual Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference Las Vegas, Nevada, USA March 5, 2008 Creating Online Learning Communities: A Cross Disciplinary Examination of
Using Evidence in the Classroom for Professional Learning
 Using Evidence in the Classroom for Professional Learning Helen Timperley University of Auckland New Zealand Paper presented to the Ontario Education Research Symposium For teachers to use evidence to
Using Evidence in the Classroom for Professional Learning Helen Timperley University of Auckland New Zealand Paper presented to the Ontario Education Research Symposium For teachers to use evidence to
MODERN TRENDS IN THE USE OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY IN THE CLASSROOM
 MODERN TRENDS IN THE USE OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY IN THE CLASSROOM 1 Dr. (Mrs.) Ann E. Umeh, Dr. (Mrs.) C.C. Nsofor Department of Science Education, Federal University of Technology, Minna Phone No: 08037031358
MODERN TRENDS IN THE USE OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY IN THE CLASSROOM 1 Dr. (Mrs.) Ann E. Umeh, Dr. (Mrs.) C.C. Nsofor Department of Science Education, Federal University of Technology, Minna Phone No: 08037031358
USING NVIVO FOR DATA ANALYSIS IN QUALITATIVE RESEARCH AlYahmady Hamed Hilal Saleh Said Alabri Ministry of Education, Sultanate of Oman
 USING NVIVO FOR DATA ANALYSIS IN QUALITATIVE RESEARCH AlYahmady Hamed Hilal Saleh Said Alabri Ministry of Education, Sultanate of Oman ABSTRACT _ Qualitative data is characterized by its subjectivity,
USING NVIVO FOR DATA ANALYSIS IN QUALITATIVE RESEARCH AlYahmady Hamed Hilal Saleh Said Alabri Ministry of Education, Sultanate of Oman ABSTRACT _ Qualitative data is characterized by its subjectivity,
ANALYSIS OF FOCUS GROUP DATA
 ANALYSIS OF FOCUS GROUP DATA Focus Groups generate a large amount of data which needs to be organized and processed so that the main ideas are elicited. The first step is transcribing the FGs in a way
ANALYSIS OF FOCUS GROUP DATA Focus Groups generate a large amount of data which needs to be organized and processed so that the main ideas are elicited. The first step is transcribing the FGs in a way
Gabrielle Young, Assistant Professor, Memorial University of Newfoundland, gabrielle.young@mun.ca
 Assistive Technology for Students with Learning Disabilities: Perceptions of Students and their Parents Gabrielle Young, Assistant Professor, Memorial University of Newfoundland, gabrielle.young@mun.ca
Assistive Technology for Students with Learning Disabilities: Perceptions of Students and their Parents Gabrielle Young, Assistant Professor, Memorial University of Newfoundland, gabrielle.young@mun.ca
GIS and Cartography at DGUC
 GIS and Cartography at DGUC Short report from an education development project GIS: Just a technical tool for geographers - or a didactical instrument for developing geographical concepts as well? Introduction
GIS and Cartography at DGUC Short report from an education development project GIS: Just a technical tool for geographers - or a didactical instrument for developing geographical concepts as well? Introduction
The role of intuitive feelings as a diagnostic tool in the criminal investigation process
 Study from Interviews with Criminal Investigators from KRIPOS, the national Norwegian unit for fighting organised and other serious crime The role of intuitive feelings as a diagnostic tool in the criminal
Study from Interviews with Criminal Investigators from KRIPOS, the national Norwegian unit for fighting organised and other serious crime The role of intuitive feelings as a diagnostic tool in the criminal
Choosing to do a Doctorate in Education
 01-Burgess-3353.qxd 1/31/2006 7:02 PM Page 1 1 Choosing to do a Doctorate in Education Choosing to study for a professional doctorate is a major decision and, for many, it is often the first step of a
01-Burgess-3353.qxd 1/31/2006 7:02 PM Page 1 1 Choosing to do a Doctorate in Education Choosing to study for a professional doctorate is a major decision and, for many, it is often the first step of a
TEACHER/HIGHER EDUCATION INSPECTION
 TEACHER/HIGHER EDUCATION INSPECTION Education and Training Inspectorate An Inspection Report on the PGCE Early Years Programme, with a focus on Literacy and Numeracy, Stranmillis University College Inspected:
TEACHER/HIGHER EDUCATION INSPECTION Education and Training Inspectorate An Inspection Report on the PGCE Early Years Programme, with a focus on Literacy and Numeracy, Stranmillis University College Inspected:
GUIDE TO EVALUATING INSTITUTIONS
 GUIDE TO EVALUATING INSTITUTIONS A Publication of the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges Western Association of Schools and Colleges JULY 2013 Edition ACCJC/WASC 10 Commercial Blvd.
GUIDE TO EVALUATING INSTITUTIONS A Publication of the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges Western Association of Schools and Colleges JULY 2013 Edition ACCJC/WASC 10 Commercial Blvd.
ACTUAL PROBLEMS AND GOOD PRACTICES IN ACCOUNTANCY TEACHING TO STUDENTS IN ALBANIA
 ACTUAL PROBLEMS AND GOOD PRACTICES IN ACCOUNTANCY TEACHING TO STUDENTS IN ALBANIA Alketa Pasholli (Zheku), PhD Head of Finance and Accounting - Department Faculty of Economy Fan S. Noli University,Korce,
ACTUAL PROBLEMS AND GOOD PRACTICES IN ACCOUNTANCY TEACHING TO STUDENTS IN ALBANIA Alketa Pasholli (Zheku), PhD Head of Finance and Accounting - Department Faculty of Economy Fan S. Noli University,Korce,
COMHAIRLE NAN EILEAN SIAR Roinn an Fhoghlaim is Seirbheisean Chloinne Education and Children s Services Department
 COMHAIRLE NAN EILEAN SIAR Roinn an Fhoghlaim is Seirbheisean Chloinne Education and Children s Services Department Professional Review and Development for Teachers: Self-Evaluation: The Standard for Leadership
COMHAIRLE NAN EILEAN SIAR Roinn an Fhoghlaim is Seirbheisean Chloinne Education and Children s Services Department Professional Review and Development for Teachers: Self-Evaluation: The Standard for Leadership
EUROPEAN RESEARCH IN MATHEMATICS EDUCATION III. Thematic Group 1
 METAPHOR IN YOUNG CHILDREN S MENTAL CALCULATION Chris Bills Oxfordshire Mathematics Centre, Oxford OX4 3DW, UK. Abstract: In this study 7-9 year old children performed mental calculations and were then
METAPHOR IN YOUNG CHILDREN S MENTAL CALCULATION Chris Bills Oxfordshire Mathematics Centre, Oxford OX4 3DW, UK. Abstract: In this study 7-9 year old children performed mental calculations and were then
The Essential Guide to Professional Learning: Leading Culture
 The Essential Guide to Professional Learning: Leading Culture The Australian Charter for the Professional Learning of Teachers and School Leaders (the PL Charter) describes the characteristics of a high
The Essential Guide to Professional Learning: Leading Culture The Australian Charter for the Professional Learning of Teachers and School Leaders (the PL Charter) describes the characteristics of a high
Standards of proficiency. Occupational therapists
 Standards of proficiency Occupational therapists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of
Standards of proficiency Occupational therapists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of
GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS
 GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK All learners whether adult or child acquire the attitudes, skills and knowledge needed for
GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK All learners whether adult or child acquire the attitudes, skills and knowledge needed for
