Source Code Transformations Strategies to Load-balance Grid Applications
|
|
|
- Abigayle Kennedy
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Source Code Transformations Strategies to Load-balance Grid Applications Romaric David, Stéphane Genaud, Arnaud Giersch, Benjamin Schwarz, and Éric Violard LSIIT-ICPS, Université Louis Pasteur, Bd S. Brant, F-674 Illkirch (France) Tel: / Fax: {david,genaud,giersch,schwarz,violard}@icps.u-strasbg.fr Abstract. We present load-balancing strategies to improve the performances of parallel MPI applications running in a Grid environment. We analyze the data distribution constraints found in two scientific codes and propose adapted code transformations to load-balance computations. Experimental results confirm that such source code transformations can improve Grid application performances. 1 Introduction With the growing popularity of middleware dedicated at making so-called Grids of ing and storage resources, network based computing will soon offer to users a dramatic increase in the available aggregate ing power. However, parallel applications have traditionally been designed for parallel computers and their executions on a Grid show poor performances. There are two major reasons for the lack of performance: first, the ors available are heterogeneous and hence the work assigned to ors is often unbalanced, and secondly the network links are orders of magnitude slower on the Grid than in a parallel computer. Much work has been carried out to take into account such heterogeneous environments for distributed computing. However, few research works concern load-balancing strategies specifically guided by the application to be run. The well-known AppLeS project [1] uses information drawn from a specific application to schedule the execution of the application es, but they do not modify the application source code to improve its execution. Thus, our project is original in the sense that we study how source code transformations may impact on the performances obtained when running applications on Grids, and eventually systematically operate these transformations so as to produce programs permanently adapted to heterogeneous environments. To validate our ideas, we work on some real scientific MPI applications. This work is supported by the French Ministry of Research through the ACI-GRID program. M. Parashar (Ed.): GRID 22, LNCS 2536, pp , 22. c Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 22
2 Source Code Transformations Strategies to Load-balance Grid Applications 83 This paper presents preliminary results concerning load-balancing techniques we designed to improve performances of two scientific applications. The two codes differ by their constraints on data distribution. The first one is unconstrained, it is possible to send any chunk of data to any. The second one contains data dependencies, which implies a constrained data distribution. The next two sections describe each of the test applications. We discuss their constraints and expose the code transformation we applied to load-balance computations. We finish with some experimental results. The last section comments on the code transformations operated and discusses future work. 2 Load-Balancing for Unconstrained Data Distribution 2.1 Motivating Example: A Geophysical Application We consider for our first experiment a geophysical code in the seismic tomography field. The parallelization of the application, presented in [2], assumes that all available ors are homogeneous (the implicit target for execution is a parallel computer). Consequently, an MPI_Scatter instruction was used, in which the root distributes equal shares of data to each. We examine two methods of load-balancing this kind of application. The first one, a classical master/slave scheme, is dynamic. Slave es ask a master for a small chunk of the whole data set to compute. After computing it, the slaves ask for a new chunk and repeat this scheme until the master sends a termination message. The second one is static: the root distributes the whole data set in a single communication round, except that it sends unequal shares of data whose sizes are statically computed on the basis of the ors and network performances. We have implemented and tested both program transformations, but we focus in this study on the conditions the application must meet to implement the second load-balancing technique, and which performance results can be obtained with it. 2.2 Static Load-Balancing of Computations and Communications The static load-balancing technique applies for SPMD programs made of rounds of simultaneous communications between all es, followed by local computations ended by a global synchronization (which may be another communication round). Moreover, we must state further assumptions the programmer must verify before the load-balancing may take place. First, the data items in the input data set are independent, and secondly the number of data-items is the only factor in time complexity. Hence, giving any equal-size part of the domain to a given will result in the same computation time. Our objective is to minimize the elapsed time between two synchronization points. We consider the full overlap, single-port model of [3] in which a or node can simultaneously receive data, send data to at most one destination, and
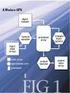
3 84 R. David, S. Genaud, A. Giersch, B. Schwarz, É. Violard perform some computation. As in this model the root sends data to es in turn, a receiving actually begins its communication after all previous es have been served. The root starts its computation after all the es have received their data. This leads to what we call a stair effect. We explain in [4] how to compute, given the ors and network links speeds, the number of data items that should be allocated to each or, so as to reach a load-balanced execution. Once this static load-balance computed, the MPI_Scatter instruction of the original program is replaced with an MPI_Scatterv. 2.3 Experimental Results Our experiment consists in the computation of 827, data units on 16 ors. Processors are heterogeneous and located at two geographically distant sites. All machines run Globus with MPICH-G2 [5]. We made a series of benchmarks to measure or and network performances. The first experiment (fig. 1(a)) evaluates performances of the original program in which each receives an equal. Non-surprisingly the es end times largely differ, thus exhibiting an important imbalance. The second experiment (fig. 1(b)) shows the master/slave version behavior which appears well-balanced after we have finely tuned the size of data chunk sent to slaves 1. Next, we experiment the load-balance of the scatter operation. To assess important parameters, we have first tried to load-balance using the relative ors speed ratings only (fig. 1(c)). Omitting the network parameters leaves important imbalances and gives unsatisfactory results as compared to the master/slave implementation. The last experiment (fig. 1(d)) computes the loadbalance using all parameters. We obtain here the best balance, which confirms the importance of all parameters, especially to take into account the stair effect that clearly appears on figures 1(a,c,d). In the master/slave implementation the total communication time is short as compared to the computation time. We conclude that in the scatter implementations only a small part of the measured is spent in true communications of data. 3 Load-Balancing with Constrained Data Distribution 3.1 Motivating Example: An Application in Plasma Physics Our example is an application devoted to the numerical simulation of problems in Plasma Physics and particle beams propagation. The application implements the PFC resolution method discretizing the Vlasov equation. The parallel code [6] works with any number of ors and uses a classical data decomposition 1 Note that there are only 15 computation es in this implementation since the master only handles data distribution.
4 Source Code Transformations Strategies to Load-balance Grid Applications (a) Uniform distribution (b) Master slave (c) Load-balancing (without network) (d) Load-balancing (with network) Fig. 1. Experimental results (the root is on or ) technique. Matrices are split into blocks of equal size distributed by row on the ors. The code consists in a succession of computation-communication phases where the communication steps are global block matrix transpositions. 3.2 Load-Balancing through Process Emulation In such applications where data structure must be preserved, but computations can still be spread over any number of es, a naive solution to achieve load balancing is to make the operating system run more than one per or on fastest ors. Such a procedure implies a lot of system overhead, due to inter- communications and time-sharing mechanisms. An idea to avoid this, is to rewrite the code in such a way that only one real will compute all data given to the es we intended to run on the given or. In other words we emulate several es by a single one. The original program must meet the following conditions : (i) the code works with any number of ors, (ii) the workload is evenly spread over the ors and (iii) the workload only depends on the to be ed. The emulation of several es by one consists in serializing the computations of the computation phases and changing the communication scheme. The MPI calls have to be modified in order to map emulated es onto real es and perform memory copy instead of communications when sender and receiver are on the same or. Moreover, blocking point-to-point communications such as MPI_Send have to be replaced by their non-blocking versions (e.g. MPI_Isend) in order to avoid
5 86 R. David, S. Genaud, A. Giersch, B. Schwarz, É. Violard deadlock situations. Calls to a collective communication have to be performed only once on a or, no matter the number of emulated es it holds. Some collective communications such as MPI_Barrier do not require any other changes whereas some others do. For example MPI_Scatter instances should be replaced by MPI_Scatterv to distribute chunks of data proportionally to the number of emulated es on each or. A more detailed description of the transformation can be found in [4]. 3.3 Experimental Results For our experiments, we use our code in Plasma Physics and a subset of our test Grid made of four heterogeneous ors. We approximate the number of emulated from speed ratings obtained from benchmarks 2. The results show significant gains in performance. In order to validate our code transformation, we measured the wall clock time of: (a) the initial application with one per or, (b) the initial application with a basic load balancing using the system to run several es on a single or and (c) the transformed application with a load-balancing using emulated es. For (b) and (c), we distributed 11 es on the four ors. Experiments were conducted for 32 4, 48 4, and 64 4 data points. Results are reported in table 1. The modified algorithm is always better than the original one, may there be or not system load-balancing. Table 1. Elapsed Size (a) No load balancing (b) System load balancing (c) Emulated es Related Work The study carried out in [8] compares dynamic versus static load-balancing strategies in an image rendering ray-tracing application. They conclude that no one scheduling strategy is best for all load conditions, and recommend to investigate further the possibilities of switching from static to dynamic loadbalancing. Our experiments confirm that static load-balancing requires precise information about parameters to be efficient whereas the master/slave model naturally adapts to heterogeneous conditions. Therefore, the variance of conditions could be taken into account to request static or dynamic load-balance during execution. Providing a dedicated library to implement load-balancing is also 2 Work is under progress to use theoretical results from [7] so as to find the optimal number of emulated es.
6 Source Code Transformations Strategies to Load-balance Grid Applications 87 proposed by George [9] with the DParLib, who addresses the problem of dynamic load-balancing via array distribution for the class of iterative algorithms with a SPMD implementation. The statistics about load-balance produced dynamically during the execution can be used to redistribute arrays from one iteration to the other. However, the library does not take into account possible communicationcomputation overlaps that we need in our second test application. 5 Conclusion It appears from this study, that the source code must be finely analyzed to choose which load-balancing solution matches best the problem. In the first example, we have put forward influent parameters for static load-balancing. In the second example we have shown that a possible transformation strategy to overcome the constraints on data-distribution and keep a good communication-computation overlap can be the emulation technique. Future work should be done in several directions. We first need to further investigate the communication schemes used in real applications and how they perform in a Grid environment. A classification of the communication types may be used by a software tool to select appropriate transformation strategies. We also believe the programmer should interact with the tool to guide program transformations as he can bring useful information about the application. References [1] Berman, F., Wolski, R., Figueira, S., Schopf, J., Shao, G.: Application-level scheduling on distributed heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of SuperComputing 96. (1996) [2] Grunberg, M., Genaud, S., Mongenet, C.: Parallel seismic ray-tracing in a global earth mesh. In: Proceedings of PDPTA 2. (22) [3] Beaumont, O., Carter, L., Ferrante, J., Legrand, A., Robert, Y.: Bandwidth-centric allocation of independent tasks on heterogeneous platforms. Technical Report 421, INRIA, Rhône-Alpes (21) [4] David, R., Genaud, S., Giersch, A., Schwarz, B., Violard, E.: Source code transformations strategies to load-balance grid applications. Technical Report 2-9, ICPS-LSIIT, University Louis Pasteur, Pôle API, Bd. S. Brant,F-674 Illkirch (22) [5] Foster, I., Karonis, N.: A grid-enabled MPI: Message passing in heterogeneous distributed computing systems. Supercomputing (1998) [6] Violard, E., Filbet, F.: Parallelization of a Vlasov solver by communication overlapping. In: Proceedings of PDPTA 2. (22) [7] Boulet, P., Dongarra, J., Robert, Y., Vivien, F.: Static tiling for heterogeneous computing platforms. Parallel Computing 25 (1999) [8] Shao, G., Wolski, R., Berman, F.: Performance effects of scheduling strategies for master/slave distributed applications. Technical Report CS98-598, UCSD CSE Dept., University of California, San Diego (1998) [9] George, W.: Dynamic load-balancing for data-parallel MPI programs. In: Message Passing Interface developers and users conference. (1999) 95 1
Multi-GPU Load Balancing for Simulation and Rendering
 Multi- Load Balancing for Simulation and Rendering Yong Cao Computer Science Department, Virginia Tech, USA In-situ ualization and ual Analytics Instant visualization and interaction of computing tasks
Multi- Load Balancing for Simulation and Rendering Yong Cao Computer Science Department, Virginia Tech, USA In-situ ualization and ual Analytics Instant visualization and interaction of computing tasks
Characterizing the Performance of Dynamic Distribution and Load-Balancing Techniques for Adaptive Grid Hierarchies
 Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference Parallel and Distributed Computing and Systems November 3-6, 1999 in Cambridge Massachusetts, USA Characterizing the Performance of Dynamic Distribution
Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference Parallel and Distributed Computing and Systems November 3-6, 1999 in Cambridge Massachusetts, USA Characterizing the Performance of Dynamic Distribution
A Performance Study of Load Balancing Strategies for Approximate String Matching on an MPI Heterogeneous System Environment
 A Performance Study of Load Balancing Strategies for Approximate String Matching on an MPI Heterogeneous System Environment Panagiotis D. Michailidis and Konstantinos G. Margaritis Parallel and Distributed
A Performance Study of Load Balancing Strategies for Approximate String Matching on an MPI Heterogeneous System Environment Panagiotis D. Michailidis and Konstantinos G. Margaritis Parallel and Distributed
Load Balancing on a Non-dedicated Heterogeneous Network of Workstations
 Load Balancing on a Non-dedicated Heterogeneous Network of Workstations Dr. Maurice Eggen Nathan Franklin Department of Computer Science Trinity University San Antonio, Texas 78212 Dr. Roger Eggen Department
Load Balancing on a Non-dedicated Heterogeneous Network of Workstations Dr. Maurice Eggen Nathan Franklin Department of Computer Science Trinity University San Antonio, Texas 78212 Dr. Roger Eggen Department
A Robust Dynamic Load-balancing Scheme for Data Parallel Application on Message Passing Architecture
 A Robust Dynamic Load-balancing Scheme for Data Parallel Application on Message Passing Architecture Yangsuk Kee Department of Computer Engineering Seoul National University Seoul, 151-742, Korea Soonhoi
A Robust Dynamic Load-balancing Scheme for Data Parallel Application on Message Passing Architecture Yangsuk Kee Department of Computer Engineering Seoul National University Seoul, 151-742, Korea Soonhoi
Parallel Scalable Algorithms- Performance Parameters
 www.bsc.es Parallel Scalable Algorithms- Performance Parameters Vassil Alexandrov, ICREA - Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Spain Overview Sources of Overhead in Parallel Programs Performance Metrics for
www.bsc.es Parallel Scalable Algorithms- Performance Parameters Vassil Alexandrov, ICREA - Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Spain Overview Sources of Overhead in Parallel Programs Performance Metrics for
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF THREE DYNAMIC LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHMS ON SPMD MODEL
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF THREE DYNAMIC LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHMS ON SPMD MODEL Najib A. Kofahi Associate Professor Department of Computer Sciences Faculty of Information Technology and Computer Sciences
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF THREE DYNAMIC LOAD BALANCING ALGORITHMS ON SPMD MODEL Najib A. Kofahi Associate Professor Department of Computer Sciences Faculty of Information Technology and Computer Sciences
Dynamic Load Balancing for a Grid Application
 Dynamic Load Balancing for a Grid Application Menno Dobber, Ger Koole, and Rob van der Mei Vrije Universiteit, De Boelelaan 1081a, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands {amdobber, koole, mei}@few.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/~amdobber
Dynamic Load Balancing for a Grid Application Menno Dobber, Ger Koole, and Rob van der Mei Vrije Universiteit, De Boelelaan 1081a, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands {amdobber, koole, mei}@few.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/~amdobber
Cellular Computing on a Linux Cluster
 Cellular Computing on a Linux Cluster Alexei Agueev, Bernd Däne, Wolfgang Fengler TU Ilmenau, Department of Computer Architecture Topics 1. Cellular Computing 2. The Experiment 3. Experimental Results
Cellular Computing on a Linux Cluster Alexei Agueev, Bernd Däne, Wolfgang Fengler TU Ilmenau, Department of Computer Architecture Topics 1. Cellular Computing 2. The Experiment 3. Experimental Results
Kommunikation in HPC-Clustern
 Kommunikation in HPC-Clustern Communication/Computation Overlap in MPI W. Rehm and T. Höfler Department of Computer Science TU Chemnitz http://www.tu-chemnitz.de/informatik/ra 11.11.2005 Outline 1 2 Optimize
Kommunikation in HPC-Clustern Communication/Computation Overlap in MPI W. Rehm and T. Höfler Department of Computer Science TU Chemnitz http://www.tu-chemnitz.de/informatik/ra 11.11.2005 Outline 1 2 Optimize
Load Balancing Techniques
 Load Balancing Techniques 1 Lecture Outline Following Topics will be discussed Static Load Balancing Dynamic Load Balancing Mapping for load balancing Minimizing Interaction 2 1 Load Balancing Techniques
Load Balancing Techniques 1 Lecture Outline Following Topics will be discussed Static Load Balancing Dynamic Load Balancing Mapping for load balancing Minimizing Interaction 2 1 Load Balancing Techniques
Parallel Ray Tracing using MPI: A Dynamic Load-balancing Approach
 Parallel Ray Tracing using MPI: A Dynamic Load-balancing Approach S. M. Ashraful Kadir 1 and Tazrian Khan 2 1 Scientific Computing, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden smakadir@csc.kth.se,
Parallel Ray Tracing using MPI: A Dynamic Load-balancing Approach S. M. Ashraful Kadir 1 and Tazrian Khan 2 1 Scientific Computing, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden smakadir@csc.kth.se,
LOAD BALANCING FOR MULTIPLE PARALLEL JOBS
 European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2000 Barcelona, 11-14 September 2000 ECCOMAS LOAD BALANCING FOR MULTIPLE PARALLEL JOBS A. Ecer, Y. P. Chien, H.U Akay
European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS 2000 Barcelona, 11-14 September 2000 ECCOMAS LOAD BALANCING FOR MULTIPLE PARALLEL JOBS A. Ecer, Y. P. Chien, H.U Akay
Resource Allocation Schemes for Gang Scheduling
 Resource Allocation Schemes for Gang Scheduling B. B. Zhou School of Computing and Mathematics Deakin University Geelong, VIC 327, Australia D. Walsh R. P. Brent Department of Computer Science Australian
Resource Allocation Schemes for Gang Scheduling B. B. Zhou School of Computing and Mathematics Deakin University Geelong, VIC 327, Australia D. Walsh R. P. Brent Department of Computer Science Australian
Advances in Smart Systems Research : ISSN 2050-8662 : http://nimbusvault.net/publications/koala/assr/ Vol. 3. No. 3 : pp.
 Advances in Smart Systems Research : ISSN 2050-8662 : http://nimbusvault.net/publications/koala/assr/ Vol. 3. No. 3 : pp.49-54 : isrp13-005 Optimized Communications on Cloud Computer Processor by Using
Advances in Smart Systems Research : ISSN 2050-8662 : http://nimbusvault.net/publications/koala/assr/ Vol. 3. No. 3 : pp.49-54 : isrp13-005 Optimized Communications on Cloud Computer Processor by Using
A Simultaneous Solution for General Linear Equations on a Ring or Hierarchical Cluster
 Acta Technica Jaurinensis Vol. 3. No. 1. 010 A Simultaneous Solution for General Linear Equations on a Ring or Hierarchical Cluster G. Molnárka, N. Varjasi Széchenyi István University Győr, Hungary, H-906
Acta Technica Jaurinensis Vol. 3. No. 1. 010 A Simultaneous Solution for General Linear Equations on a Ring or Hierarchical Cluster G. Molnárka, N. Varjasi Széchenyi István University Győr, Hungary, H-906
A Flexible Cluster Infrastructure for Systems Research and Software Development
 Award Number: CNS-551555 Title: CRI: Acquisition of an InfiniBand Cluster with SMP Nodes Institution: Florida State University PIs: Xin Yuan, Robert van Engelen, Kartik Gopalan A Flexible Cluster Infrastructure
Award Number: CNS-551555 Title: CRI: Acquisition of an InfiniBand Cluster with SMP Nodes Institution: Florida State University PIs: Xin Yuan, Robert van Engelen, Kartik Gopalan A Flexible Cluster Infrastructure
A Comparative Performance Analysis of Load Balancing Algorithms in Distributed System using Qualitative Parameters
 A Comparative Performance Analysis of Load Balancing Algorithms in Distributed System using Qualitative Parameters Abhijit A. Rajguru, S.S. Apte Abstract - A distributed system can be viewed as a collection
A Comparative Performance Analysis of Load Balancing Algorithms in Distributed System using Qualitative Parameters Abhijit A. Rajguru, S.S. Apte Abstract - A distributed system can be viewed as a collection
P013 INTRODUCING A NEW GENERATION OF RESERVOIR SIMULATION SOFTWARE
 1 P013 INTRODUCING A NEW GENERATION OF RESERVOIR SIMULATION SOFTWARE JEAN-MARC GRATIEN, JEAN-FRANÇOIS MAGRAS, PHILIPPE QUANDALLE, OLIVIER RICOIS 1&4, av. Bois-Préau. 92852 Rueil Malmaison Cedex. France
1 P013 INTRODUCING A NEW GENERATION OF RESERVOIR SIMULATION SOFTWARE JEAN-MARC GRATIEN, JEAN-FRANÇOIS MAGRAS, PHILIPPE QUANDALLE, OLIVIER RICOIS 1&4, av. Bois-Préau. 92852 Rueil Malmaison Cedex. France
Using Cloud Computing for Solving Constraint Programming Problems
 Using Cloud Computing for Solving Constraint Programming Problems Mohamed Rezgui, Jean-Charles Régin, and Arnaud Malapert Univ. Nice Sophia Antipolis, CNRS, I3S, UMR 7271, 06900 Sophia Antipolis, France
Using Cloud Computing for Solving Constraint Programming Problems Mohamed Rezgui, Jean-Charles Régin, and Arnaud Malapert Univ. Nice Sophia Antipolis, CNRS, I3S, UMR 7271, 06900 Sophia Antipolis, France
Reliable Systolic Computing through Redundancy
 Reliable Systolic Computing through Redundancy Kunio Okuda 1, Siang Wun Song 1, and Marcos Tatsuo Yamamoto 1 Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil, {kunio,song,mty}@ime.usp.br, http://www.ime.usp.br/ song/
Reliable Systolic Computing through Redundancy Kunio Okuda 1, Siang Wun Song 1, and Marcos Tatsuo Yamamoto 1 Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil, {kunio,song,mty}@ime.usp.br, http://www.ime.usp.br/ song/
Load balancing Static Load Balancing
 Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 349 ISSN 2229-5518
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 349 Load Balancing Heterogeneous Request in DHT-based P2P Systems Mrs. Yogita A. Dalvi Dr. R. Shankar Mr. Atesh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 349 Load Balancing Heterogeneous Request in DHT-based P2P Systems Mrs. Yogita A. Dalvi Dr. R. Shankar Mr. Atesh
Load Balancing and Termination Detection
 Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection 1 Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection 1 Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
Efficient Parallel Execution of Sequence Similarity Analysis Via Dynamic Load Balancing
 Efficient Parallel Execution of Sequence Similarity Analysis Via Dynamic Load Balancing James D. Jackson Philip J. Hatcher Department of Computer Science Kingsbury Hall University of New Hampshire Durham,
Efficient Parallel Execution of Sequence Similarity Analysis Via Dynamic Load Balancing James D. Jackson Philip J. Hatcher Department of Computer Science Kingsbury Hall University of New Hampshire Durham,
walberla: Towards an Adaptive, Dynamically Load-Balanced, Massively Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Fluid Simulation
 walberla: Towards an Adaptive, Dynamically Load-Balanced, Massively Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Fluid Simulation SIAM Parallel Processing for Scientific Computing 2012 February 16, 2012 Florian Schornbaum,
walberla: Towards an Adaptive, Dynamically Load-Balanced, Massively Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Fluid Simulation SIAM Parallel Processing for Scientific Computing 2012 February 16, 2012 Florian Schornbaum,
Scalability and Classifications
 Scalability and Classifications 1 Types of Parallel Computers MIMD and SIMD classifications shared and distributed memory multicomputers distributed shared memory computers 2 Network Topologies static
Scalability and Classifications 1 Types of Parallel Computers MIMD and SIMD classifications shared and distributed memory multicomputers distributed shared memory computers 2 Network Topologies static
Various Schemes of Load Balancing in Distributed Systems- A Review
 741 Various Schemes of Load Balancing in Distributed Systems- A Review Monika Kushwaha Pranveer Singh Institute of Technology Kanpur, U.P. (208020) U.P.T.U., Lucknow Saurabh Gupta Pranveer Singh Institute
741 Various Schemes of Load Balancing in Distributed Systems- A Review Monika Kushwaha Pranveer Singh Institute of Technology Kanpur, U.P. (208020) U.P.T.U., Lucknow Saurabh Gupta Pranveer Singh Institute
?kt. An Unconventional Method for Load Balancing. w = C ( t m a z - ti) = p(tmaz - 0i=l. 1 Introduction. R. Alan McCoy,*
 ENL-62052 An Unconventional Method for Load Balancing Yuefan Deng,* R. Alan McCoy,* Robert B. Marr,t Ronald F. Peierlst Abstract A new method of load balancing is introduced based on the idea of dynamically
ENL-62052 An Unconventional Method for Load Balancing Yuefan Deng,* R. Alan McCoy,* Robert B. Marr,t Ronald F. Peierlst Abstract A new method of load balancing is introduced based on the idea of dynamically
LaPIe: Collective Communications adapted to Grid Environments
 LaPIe: Collective Communications adapted to Grid Environments Luiz Angelo Barchet-Estefanel Thesis Supervisor: M Denis TRYSTRAM Co-Supervisor: M Grégory MOUNIE ID-IMAG Laboratory Grenoble - France LaPIe:
LaPIe: Collective Communications adapted to Grid Environments Luiz Angelo Barchet-Estefanel Thesis Supervisor: M Denis TRYSTRAM Co-Supervisor: M Grégory MOUNIE ID-IMAG Laboratory Grenoble - France LaPIe:
Distributed communication-aware load balancing with TreeMatch in Charm++
 Distributed communication-aware load balancing with TreeMatch in Charm++ The 9th Scheduling for Large Scale Systems Workshop, Lyon, France Emmanuel Jeannot Guillaume Mercier Francois Tessier In collaboration
Distributed communication-aware load balancing with TreeMatch in Charm++ The 9th Scheduling for Large Scale Systems Workshop, Lyon, France Emmanuel Jeannot Guillaume Mercier Francois Tessier In collaboration
Interactive comment on A parallelization scheme to simulate reactive transport in the subsurface environment with OGS#IPhreeqc by W. He et al.
 Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., 8, C1166 C1176, 2015 www.geosci-model-dev-discuss.net/8/c1166/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Geoscientific
Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., 8, C1166 C1176, 2015 www.geosci-model-dev-discuss.net/8/c1166/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Geoscientific
An Empirical Study and Analysis of the Dynamic Load Balancing Techniques Used in Parallel Computing Systems
 An Empirical Study and Analysis of the Dynamic Load Balancing Techniques Used in Parallel Computing Systems Ardhendu Mandal and Subhas Chandra Pal Department of Computer Science and Application, University
An Empirical Study and Analysis of the Dynamic Load Balancing Techniques Used in Parallel Computing Systems Ardhendu Mandal and Subhas Chandra Pal Department of Computer Science and Application, University
Combining Scalability and Efficiency for SPMD Applications on Multicore Clusters*
 Combining Scalability and Efficiency for SPMD Applications on Multicore Clusters* Ronal Muresano, Dolores Rexachs and Emilio Luque Computer Architecture and Operating System Department (CAOS) Universitat
Combining Scalability and Efficiency for SPMD Applications on Multicore Clusters* Ronal Muresano, Dolores Rexachs and Emilio Luque Computer Architecture and Operating System Department (CAOS) Universitat
HPC enabling of OpenFOAM R for CFD applications
 HPC enabling of OpenFOAM R for CFD applications Towards the exascale: OpenFOAM perspective Ivan Spisso 25-27 March 2015, Casalecchio di Reno, BOLOGNA. SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department,
HPC enabling of OpenFOAM R for CFD applications Towards the exascale: OpenFOAM perspective Ivan Spisso 25-27 March 2015, Casalecchio di Reno, BOLOGNA. SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department,
Explicit Spatial Scattering for Load Balancing in Conservatively Synchronized Parallel Discrete-Event Simulations
 Explicit Spatial ing for Load Balancing in Conservatively Synchronized Parallel Discrete-Event Simulations Sunil Thulasidasan Shiva Prasad Kasiviswanathan Stephan Eidenbenz Phillip Romero Los Alamos National
Explicit Spatial ing for Load Balancing in Conservatively Synchronized Parallel Discrete-Event Simulations Sunil Thulasidasan Shiva Prasad Kasiviswanathan Stephan Eidenbenz Phillip Romero Los Alamos National
A Review of Customized Dynamic Load Balancing for a Network of Workstations
 A Review of Customized Dynamic Load Balancing for a Network of Workstations Taken from work done by: Mohammed Javeed Zaki, Wei Li, Srinivasan Parthasarathy Computer Science Department, University of Rochester
A Review of Customized Dynamic Load Balancing for a Network of Workstations Taken from work done by: Mohammed Javeed Zaki, Wei Li, Srinivasan Parthasarathy Computer Science Department, University of Rochester
Introduction to Cloud Computing
 Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Grid Computing Approach for Dynamic Load Balancing
 International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-4, Issue-1 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Grid Computing Approach for Dynamic Load Balancing Kapil B. Morey 1*, Sachin B. Jadhav
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-4, Issue-1 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Grid Computing Approach for Dynamic Load Balancing Kapil B. Morey 1*, Sachin B. Jadhav
Computational grids will provide a platform for a new generation of applications.
 12 CHAPTER High-Performance Schedulers Francine Berman Computational grids will provide a platform for a new generation of applications. Grid applications will include portable applications that can be
12 CHAPTER High-Performance Schedulers Francine Berman Computational grids will provide a platform for a new generation of applications. Grid applications will include portable applications that can be
Cluster, Grid, Cloud Concepts
 Cluster, Grid, Cloud Concepts Kalaiselvan.K Contents Section 1: Cluster Section 2: Grid Section 3: Cloud Cluster An Overview Need for a Cluster Cluster categorizations A computer cluster is a group of
Cluster, Grid, Cloud Concepts Kalaiselvan.K Contents Section 1: Cluster Section 2: Grid Section 3: Cloud Cluster An Overview Need for a Cluster Cluster categorizations A computer cluster is a group of
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines
 Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
Distributed Dynamic Load Balancing for Iterative-Stencil Applications
 Distributed Dynamic Load Balancing for Iterative-Stencil Applications G. Dethier 1, P. Marchot 2 and P.A. de Marneffe 1 1 EECS Department, University of Liege, Belgium 2 Chemical Engineering Department,
Distributed Dynamic Load Balancing for Iterative-Stencil Applications G. Dethier 1, P. Marchot 2 and P.A. de Marneffe 1 1 EECS Department, University of Liege, Belgium 2 Chemical Engineering Department,
Scientific Computing Programming with Parallel Objects
 Scientific Computing Programming with Parallel Objects Esteban Meneses, PhD School of Computing, Costa Rica Institute of Technology Parallel Architectures Galore Personal Computing Embedded Computing Moore
Scientific Computing Programming with Parallel Objects Esteban Meneses, PhD School of Computing, Costa Rica Institute of Technology Parallel Architectures Galore Personal Computing Embedded Computing Moore
Fast Multipole Method for particle interactions: an open source parallel library component
 Fast Multipole Method for particle interactions: an open source parallel library component F. A. Cruz 1,M.G.Knepley 2,andL.A.Barba 1 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk,
Fast Multipole Method for particle interactions: an open source parallel library component F. A. Cruz 1,M.G.Knepley 2,andL.A.Barba 1 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Bristol, University Walk,
A STUDY OF TASK SCHEDULING IN MULTIPROCESSOR ENVIROMENT Ranjit Rajak 1, C.P.Katti 2, Nidhi Rajak 3
 A STUDY OF TASK SCHEDULING IN MULTIPROCESSOR ENVIROMENT Ranjit Rajak 1, C.P.Katti, Nidhi Rajak 1 Department of Computer Science & Applications, Dr.H.S.Gour Central University, Sagar, India, ranjit.jnu@gmail.com
A STUDY OF TASK SCHEDULING IN MULTIPROCESSOR ENVIROMENT Ranjit Rajak 1, C.P.Katti, Nidhi Rajak 1 Department of Computer Science & Applications, Dr.H.S.Gour Central University, Sagar, India, ranjit.jnu@gmail.com
UTS: An Unbalanced Tree Search Benchmark
 UTS: An Unbalanced Tree Search Benchmark LCPC 2006 1 Coauthors Stephen Olivier, UNC Jun Huan, UNC/Kansas Jinze Liu, UNC Jan Prins, UNC James Dinan, OSU P. Sadayappan, OSU Chau-Wen Tseng, UMD Also, thanks
UTS: An Unbalanced Tree Search Benchmark LCPC 2006 1 Coauthors Stephen Olivier, UNC Jun Huan, UNC/Kansas Jinze Liu, UNC Jan Prins, UNC James Dinan, OSU P. Sadayappan, OSU Chau-Wen Tseng, UMD Also, thanks
A Steering Environment for Online Parallel Visualization of Legacy Parallel Simulations
 A Steering Environment for Online Parallel Visualization of Legacy Parallel Simulations Aurélien Esnard, Nicolas Richart and Olivier Coulaud ACI GRID (French Ministry of Research Initiative) ScAlApplix
A Steering Environment for Online Parallel Visualization of Legacy Parallel Simulations Aurélien Esnard, Nicolas Richart and Olivier Coulaud ACI GRID (French Ministry of Research Initiative) ScAlApplix
High Performance Computing. Course Notes 2007-2008. HPC Fundamentals
 High Performance Computing Course Notes 2007-2008 2008 HPC Fundamentals Introduction What is High Performance Computing (HPC)? Difficult to define - it s a moving target. Later 1980s, a supercomputer performs
High Performance Computing Course Notes 2007-2008 2008 HPC Fundamentals Introduction What is High Performance Computing (HPC)? Difficult to define - it s a moving target. Later 1980s, a supercomputer performs
A Load Balancing Tool for Structured Multi-Block Grid CFD Applications
 A Load Balancing Tool for Structured Multi-Block Grid CFD Applications K. P. Apponsah and D. W. Zingg University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS), Toronto, ON, M3H 5T6, Canada Email:
A Load Balancing Tool for Structured Multi-Block Grid CFD Applications K. P. Apponsah and D. W. Zingg University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS), Toronto, ON, M3H 5T6, Canada Email:
APPENDIX 1 USER LEVEL IMPLEMENTATION OF PPATPAN IN LINUX SYSTEM
 152 APPENDIX 1 USER LEVEL IMPLEMENTATION OF PPATPAN IN LINUX SYSTEM A1.1 INTRODUCTION PPATPAN is implemented in a test bed with five Linux system arranged in a multihop topology. The system is implemented
152 APPENDIX 1 USER LEVEL IMPLEMENTATION OF PPATPAN IN LINUX SYSTEM A1.1 INTRODUCTION PPATPAN is implemented in a test bed with five Linux system arranged in a multihop topology. The system is implemented
Research Statement for Henri Casanova
 Research Statement for Henri Casanova Advances in networking technology have made it possible to deploy distributed scientific applications on platforms that aggregate large numbers of diverse and distant
Research Statement for Henri Casanova Advances in networking technology have made it possible to deploy distributed scientific applications on platforms that aggregate large numbers of diverse and distant
Poisson Equation Solver Parallelisation for Particle-in-Cell Model
 WDS'14 Proceedings of Contributed Papers Physics, 233 237, 214. ISBN 978-8-7378-276-4 MATFYZPRESS Poisson Equation Solver Parallelisation for Particle-in-Cell Model A. Podolník, 1,2 M. Komm, 1 R. Dejarnac,
WDS'14 Proceedings of Contributed Papers Physics, 233 237, 214. ISBN 978-8-7378-276-4 MATFYZPRESS Poisson Equation Solver Parallelisation for Particle-in-Cell Model A. Podolník, 1,2 M. Komm, 1 R. Dejarnac,
A Pattern-Based Approach to. Automated Application Performance Analysis
 A Pattern-Based Approach to Automated Application Performance Analysis Nikhil Bhatia, Shirley Moore, Felix Wolf, and Jack Dongarra Innovative Computing Laboratory University of Tennessee (bhatia, shirley,
A Pattern-Based Approach to Automated Application Performance Analysis Nikhil Bhatia, Shirley Moore, Felix Wolf, and Jack Dongarra Innovative Computing Laboratory University of Tennessee (bhatia, shirley,
Overlapping Data Transfer With Application Execution on Clusters
 Overlapping Data Transfer With Application Execution on Clusters Karen L. Reid and Michael Stumm reid@cs.toronto.edu stumm@eecg.toronto.edu Department of Computer Science Department of Electrical and Computer
Overlapping Data Transfer With Application Execution on Clusters Karen L. Reid and Michael Stumm reid@cs.toronto.edu stumm@eecg.toronto.edu Department of Computer Science Department of Electrical and Computer
Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming)
 Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming) Dynamic Load Balancing Dr. Ralf-Peter Mundani Center for Simulation Technology in Engineering Technische Universität München
Praktikum Wissenschaftliches Rechnen (Performance-optimized optimized Programming) Dynamic Load Balancing Dr. Ralf-Peter Mundani Center for Simulation Technology in Engineering Technische Universität München
Performance of Scientific Processing in Networks of Workstations: Matrix Multiplication Example
 Performance of Scientific Processing in Networks of Workstations: Matrix Multiplication Example Fernando G. Tinetti Centro de Técnicas Analógico-Digitales (CeTAD) 1 Laboratorio de Investigación y Desarrollo
Performance of Scientific Processing in Networks of Workstations: Matrix Multiplication Example Fernando G. Tinetti Centro de Técnicas Analógico-Digitales (CeTAD) 1 Laboratorio de Investigación y Desarrollo
Synchronization of sampling in distributed signal processing systems
 Synchronization of sampling in distributed signal processing systems Károly Molnár, László Sujbert, Gábor Péceli Department of Measurement and Information Systems, Budapest University of Technology and
Synchronization of sampling in distributed signal processing systems Károly Molnár, László Sujbert, Gábor Péceli Department of Measurement and Information Systems, Budapest University of Technology and
Mesh Generation and Load Balancing
 Mesh Generation and Load Balancing Stan Tomov Innovative Computing Laboratory Computer Science Department The University of Tennessee April 04, 2012 CS 594 04/04/2012 Slide 1 / 19 Outline Motivation Reliable
Mesh Generation and Load Balancing Stan Tomov Innovative Computing Laboratory Computer Science Department The University of Tennessee April 04, 2012 CS 594 04/04/2012 Slide 1 / 19 Outline Motivation Reliable
An Efficient Hybrid Data Gathering Scheme in Wireless Sensor Networks
 An Efficient Hybrid Data Gathering Scheme in Wireless Sensor Networks Ayon Chakraborty 1, Swarup Kumar Mitra 2, and M.K. Naskar 3 1 Department of CSE, Jadavpur University, Kolkata, India 2 Department of
An Efficient Hybrid Data Gathering Scheme in Wireless Sensor Networks Ayon Chakraborty 1, Swarup Kumar Mitra 2, and M.K. Naskar 3 1 Department of CSE, Jadavpur University, Kolkata, India 2 Department of
Studying Code Development for High Performance Computing: The HPCS Program
 Studying Code Development for High Performance Computing: The HPCS Program Jeff Carver 1, Sima Asgari 1, Victor Basili 1,2, Lorin Hochstein 1, Jeffrey K. Hollingsworth 1, Forrest Shull 2, Marv Zelkowitz
Studying Code Development for High Performance Computing: The HPCS Program Jeff Carver 1, Sima Asgari 1, Victor Basili 1,2, Lorin Hochstein 1, Jeffrey K. Hollingsworth 1, Forrest Shull 2, Marv Zelkowitz
Parallel Processing over Mobile Ad Hoc Networks of Handheld Machines
 Parallel Processing over Mobile Ad Hoc Networks of Handheld Machines Michael J Jipping Department of Computer Science Hope College Holland, MI 49423 jipping@cs.hope.edu Gary Lewandowski Department of Mathematics
Parallel Processing over Mobile Ad Hoc Networks of Handheld Machines Michael J Jipping Department of Computer Science Hope College Holland, MI 49423 jipping@cs.hope.edu Gary Lewandowski Department of Mathematics
Partitioning and Divide and Conquer Strategies
 and Divide and Conquer Strategies Lecture 4 and Strategies Strategies Data partitioning aka domain decomposition Functional decomposition Lecture 4 and Strategies Quiz 4.1 For nuclear reactor simulation,
and Divide and Conquer Strategies Lecture 4 and Strategies Strategies Data partitioning aka domain decomposition Functional decomposition Lecture 4 and Strategies Quiz 4.1 For nuclear reactor simulation,
Performance Monitoring of Parallel Scientific Applications
 Performance Monitoring of Parallel Scientific Applications Abstract. David Skinner National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory This paper introduces an infrastructure
Performance Monitoring of Parallel Scientific Applications Abstract. David Skinner National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory This paper introduces an infrastructure
A Load Balancing Algorithm based on the Variation Trend of Entropy in Homogeneous Cluster
 , pp.11-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ ijgdc.2014.7.2.02 A Load Balancing Algorithm based on the Variation Trend of Entropy in Homogeneous Cluster Kehe Wu 1, Long Chen 2, Shichao Ye 2 and Yi Li 2 1 Beijing
, pp.11-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ ijgdc.2014.7.2.02 A Load Balancing Algorithm based on the Variation Trend of Entropy in Homogeneous Cluster Kehe Wu 1, Long Chen 2, Shichao Ye 2 and Yi Li 2 1 Beijing
Design and Optimization of OpenFOAM-based CFD Applications for Hybrid and Heterogeneous HPC Platforms
 Design and Optimization of OpenFOAM-based CFD Applications for Hybrid and Heterogeneous HPC Platforms Amani AlOnazi, David E. Keyes, Alexey Lastovetsky, Vladimir Rychkov Extreme Computing Research Center,
Design and Optimization of OpenFOAM-based CFD Applications for Hybrid and Heterogeneous HPC Platforms Amani AlOnazi, David E. Keyes, Alexey Lastovetsky, Vladimir Rychkov Extreme Computing Research Center,
An Evaluation of Economy-based Resource Trading and Scheduling on Computational Power Grids for Parameter Sweep Applications
 An Evaluation of Economy-based Resource Trading and Scheduling on Computational Power Grids for Parameter Sweep Applications Rajkumar Buyya, Jonathan Giddy, and David Abramson School of Computer Science
An Evaluation of Economy-based Resource Trading and Scheduling on Computational Power Grids for Parameter Sweep Applications Rajkumar Buyya, Jonathan Giddy, and David Abramson School of Computer Science
EFFICIENT SCHEDULING STRATEGY USING COMMUNICATION AWARE SCHEDULING FOR PARALLEL JOBS IN CLUSTERS
 EFFICIENT SCHEDULING STRATEGY USING COMMUNICATION AWARE SCHEDULING FOR PARALLEL JOBS IN CLUSTERS A.Neela madheswari 1 and R.S.D.Wahida Banu 2 1 Department of Information Technology, KMEA Engineering College,
EFFICIENT SCHEDULING STRATEGY USING COMMUNICATION AWARE SCHEDULING FOR PARALLEL JOBS IN CLUSTERS A.Neela madheswari 1 and R.S.D.Wahida Banu 2 1 Department of Information Technology, KMEA Engineering College,
An approach to grid scheduling by using Condor-G Matchmaking mechanism
 An approach to grid scheduling by using Condor-G Matchmaking mechanism E. Imamagic, B. Radic, D. Dobrenic University Computing Centre, University of Zagreb, Croatia {emir.imamagic, branimir.radic, dobrisa.dobrenic}@srce.hr
An approach to grid scheduling by using Condor-G Matchmaking mechanism E. Imamagic, B. Radic, D. Dobrenic University Computing Centre, University of Zagreb, Croatia {emir.imamagic, branimir.radic, dobrisa.dobrenic}@srce.hr
FPGA area allocation for parallel C applications
 1 FPGA area allocation for parallel C applications Vlad-Mihai Sima, Elena Moscu Panainte, Koen Bertels Computer Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science Delft University
1 FPGA area allocation for parallel C applications Vlad-Mihai Sima, Elena Moscu Panainte, Koen Bertels Computer Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science Delft University
Load Balancing and Termination Detection
 Chapter 7 slides7-1 Load Balancing and Termination Detection slides7-2 Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination
Chapter 7 slides7-1 Load Balancing and Termination Detection slides7-2 Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination
Load Imbalance Analysis
 With CrayPat Load Imbalance Analysis Imbalance time is a metric based on execution time and is dependent on the type of activity: User functions Imbalance time = Maximum time Average time Synchronization
With CrayPat Load Imbalance Analysis Imbalance time is a metric based on execution time and is dependent on the type of activity: User functions Imbalance time = Maximum time Average time Synchronization
Performance of Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms for Unstructured Mesh Calculations
 Performance of Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms for Unstructured Mesh Calculations Roy D. Williams, 1990 Presented by Chris Eldred Outline Summary Finite Element Solver Load Balancing Results Types Conclusions
Performance of Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms for Unstructured Mesh Calculations Roy D. Williams, 1990 Presented by Chris Eldred Outline Summary Finite Element Solver Load Balancing Results Types Conclusions
Dynamic Load Balancing in a Network of Workstations
 Dynamic Load Balancing in a Network of Workstations 95.515F Research Report By: Shahzad Malik (219762) November 29, 2000 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Load Balancing 4 2.1 Static Load Balancing
Dynamic Load Balancing in a Network of Workstations 95.515F Research Report By: Shahzad Malik (219762) November 29, 2000 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Load Balancing 4 2.1 Static Load Balancing
Robust Algorithms for Current Deposition and Dynamic Load-balancing in a GPU Particle-in-Cell Code
 Robust Algorithms for Current Deposition and Dynamic Load-balancing in a GPU Particle-in-Cell Code F. Rossi, S. Sinigardi, P. Londrillo & G. Turchetti University of Bologna & INFN GPU2014, Rome, Sept 17th
Robust Algorithms for Current Deposition and Dynamic Load-balancing in a GPU Particle-in-Cell Code F. Rossi, S. Sinigardi, P. Londrillo & G. Turchetti University of Bologna & INFN GPU2014, Rome, Sept 17th
A Grid for process control
 A Grid for process control Fabrice Sabatier, S u p é l e c, F a b r i c e. S a b a t i e r @m e t z. s u p e l e c. f r Amelia De Vivo, U n i v e r s i t a d i S a l e r n o, a m e d e v @ u n i s a. i
A Grid for process control Fabrice Sabatier, S u p é l e c, F a b r i c e. S a b a t i e r @m e t z. s u p e l e c. f r Amelia De Vivo, U n i v e r s i t a d i S a l e r n o, a m e d e v @ u n i s a. i
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems
 Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems DR.K.P.KALIYAMURTHIE 1, D.PARAMESWARI 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073 1 Asst. Prof. (SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems DR.K.P.KALIYAMURTHIE 1, D.PARAMESWARI 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073 1 Asst. Prof. (SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
How To Balance In Cloud Computing
 A Review on Load Balancing Algorithms in Cloud Hareesh M J Dept. of CSE, RSET, Kochi hareeshmjoseph@ gmail.com John P Martin Dept. of CSE, RSET, Kochi johnpm12@gmail.com Yedhu Sastri Dept. of IT, RSET,
A Review on Load Balancing Algorithms in Cloud Hareesh M J Dept. of CSE, RSET, Kochi hareeshmjoseph@ gmail.com John P Martin Dept. of CSE, RSET, Kochi johnpm12@gmail.com Yedhu Sastri Dept. of IT, RSET,
Performance of the NAS Parallel Benchmarks on Grid Enabled Clusters
 Performance of the NAS Parallel Benchmarks on Grid Enabled Clusters Philip J. Sokolowski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Wayne State University 55 Anthony Wayne Dr., Detroit, MI 4822 phil@wayne.edu
Performance of the NAS Parallel Benchmarks on Grid Enabled Clusters Philip J. Sokolowski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Wayne State University 55 Anthony Wayne Dr., Detroit, MI 4822 phil@wayne.edu
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems
 Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems Dr.K.P.Kaliyamurthie 1, D.Parameswari 2 1.Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073. 2.Asst. Prof.(SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems Dr.K.P.Kaliyamurthie 1, D.Parameswari 2 1.Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073. 2.Asst. Prof.(SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
A Case Study - Scaling Legacy Code on Next Generation Platforms
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 00 (2015) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 24th International Meshing Roundtable (IMR24) A Case Study - Scaling Legacy
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 00 (2015) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 24th International Meshing Roundtable (IMR24) A Case Study - Scaling Legacy
Supercomputing applied to Parallel Network Simulation
 Supercomputing applied to Parallel Network Simulation David Cortés-Polo Research, Technological Innovation and Supercomputing Centre of Extremadura, CenitS. Trujillo, Spain david.cortes@cenits.es Summary
Supercomputing applied to Parallel Network Simulation David Cortés-Polo Research, Technological Innovation and Supercomputing Centre of Extremadura, CenitS. Trujillo, Spain david.cortes@cenits.es Summary
Fast Fluid Dynamics on the Single-chip Cloud Computer
 Fast Fluid Dynamics on the Single-chip Cloud Computer Marco Fais, Francesco Iorio High-Performance Computing Group Autodesk Research Toronto, Canada francesco.iorio@autodesk.com Abstract Fast simulation
Fast Fluid Dynamics on the Single-chip Cloud Computer Marco Fais, Francesco Iorio High-Performance Computing Group Autodesk Research Toronto, Canada francesco.iorio@autodesk.com Abstract Fast simulation
Cloud Friendly Load Balancing for HPC Applications: Preliminary Work
 Cloud Friendly Load Balancing for HPC Applications: Preliminary Work Osman Sarood, Abhishek Gupta and Laxmikant V. Kalé Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana,
Cloud Friendly Load Balancing for HPC Applications: Preliminary Work Osman Sarood, Abhishek Gupta and Laxmikant V. Kalé Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana,
Load Balancing In Concurrent Parallel Applications
 Load Balancing In Concurrent Parallel Applications Jeff Figler Rochester Institute of Technology Computer Engineering Department Rochester, New York 14623 May 1999 Abstract A parallel concurrent application
Load Balancing In Concurrent Parallel Applications Jeff Figler Rochester Institute of Technology Computer Engineering Department Rochester, New York 14623 May 1999 Abstract A parallel concurrent application
MapReduce and Hadoop. Aaron Birkland Cornell Center for Advanced Computing. January 2012
 MapReduce and Hadoop Aaron Birkland Cornell Center for Advanced Computing January 2012 Motivation Simple programming model for Big Data Distributed, parallel but hides this Established success at petabyte
MapReduce and Hadoop Aaron Birkland Cornell Center for Advanced Computing January 2012 Motivation Simple programming model for Big Data Distributed, parallel but hides this Established success at petabyte
Grid Scheduling Dictionary of Terms and Keywords
 Grid Scheduling Dictionary Working Group M. Roehrig, Sandia National Laboratories W. Ziegler, Fraunhofer-Institute for Algorithms and Scientific Computing Document: Category: Informational June 2002 Status
Grid Scheduling Dictionary Working Group M. Roehrig, Sandia National Laboratories W. Ziegler, Fraunhofer-Institute for Algorithms and Scientific Computing Document: Category: Informational June 2002 Status
Performance Evaluation of Mobile Agent-based Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithm
 Performance Evaluation of Mobile -based Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithm MAGDY SAEB, CHERINE FATHY Computer Engineering Department Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport Alexandria,
Performance Evaluation of Mobile -based Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithm MAGDY SAEB, CHERINE FATHY Computer Engineering Department Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport Alexandria,
Feedback guided load balancing in a distributed memory environment
 Feedback guided load balancing in a distributed memory environment Constantinos Christofi August 18, 2011 MSc in High Performance Computing The University of Edinburgh Year of Presentation: 2011 Abstract
Feedback guided load balancing in a distributed memory environment Constantinos Christofi August 18, 2011 MSc in High Performance Computing The University of Edinburgh Year of Presentation: 2011 Abstract
Load Balancing and Termination Detection
 Chapter 7 Slide 1 Slide 2 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination
Chapter 7 Slide 1 Slide 2 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination
Operating System Multilevel Load Balancing
 Operating System Multilevel Load Balancing M. Corrêa, A. Zorzo Faculty of Informatics - PUCRS Porto Alegre, Brazil {mcorrea, zorzo}@inf.pucrs.br R. Scheer HP Brazil R&D Porto Alegre, Brazil roque.scheer@hp.com
Operating System Multilevel Load Balancing M. Corrêa, A. Zorzo Faculty of Informatics - PUCRS Porto Alegre, Brazil {mcorrea, zorzo}@inf.pucrs.br R. Scheer HP Brazil R&D Porto Alegre, Brazil roque.scheer@hp.com
Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection
 Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
Chapter 7 Load Balancing and Termination Detection Load balancing used to distribute computations fairly across processors in order to obtain the highest possible execution speed. Termination detection
AN APPROACH FOR SECURE CLOUD COMPUTING FOR FEM SIMULATION
 AN APPROACH FOR SECURE CLOUD COMPUTING FOR FEM SIMULATION Jörg Frochte *, Christof Kaufmann, Patrick Bouillon Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Bochum University of Applied Science 42579
AN APPROACH FOR SECURE CLOUD COMPUTING FOR FEM SIMULATION Jörg Frochte *, Christof Kaufmann, Patrick Bouillon Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Bochum University of Applied Science 42579
Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments
 Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments Definition of a distributed system Distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single
Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments Definition of a distributed system Distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single
High Performance Computing for Operation Research
 High Performance Computing for Operation Research IEF - Paris Sud University claude.tadonki@u-psud.fr INRIA-Alchemy seminar, Thursday March 17 Research topics Fundamental Aspects of Algorithms and Complexity
High Performance Computing for Operation Research IEF - Paris Sud University claude.tadonki@u-psud.fr INRIA-Alchemy seminar, Thursday March 17 Research topics Fundamental Aspects of Algorithms and Complexity
A Chromium Based Viewer for CUMULVS
 A Chromium Based Viewer for CUMULVS Submitted to PDPTA 06 Dan Bennett Corresponding Author Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Edinboro University of PA Edinboro, Pennsylvania 16444 Phone: (814)
A Chromium Based Viewer for CUMULVS Submitted to PDPTA 06 Dan Bennett Corresponding Author Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Edinboro University of PA Edinboro, Pennsylvania 16444 Phone: (814)
Load Balancing & Termination
 Load Load & Termination Lecture 7 Load and Termination Detection Load Load Want all processors to operate continuously to minimize time to completion. Load balancing determines what work will be done by
Load Load & Termination Lecture 7 Load and Termination Detection Load Load Want all processors to operate continuously to minimize time to completion. Load balancing determines what work will be done by
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
18-742 Lecture 4. Parallel Programming II. Homework & Reading. Page 1. Projects handout On Friday Form teams, groups of two
 age 1 18-742 Lecture 4 arallel rogramming II Spring 2005 rof. Babak Falsafi http://www.ece.cmu.edu/~ece742 write X Memory send X Memory read X Memory Slides developed in part by rofs. Adve, Falsafi, Hill,
age 1 18-742 Lecture 4 arallel rogramming II Spring 2005 rof. Babak Falsafi http://www.ece.cmu.edu/~ece742 write X Memory send X Memory read X Memory Slides developed in part by rofs. Adve, Falsafi, Hill,
Windows Server Performance Monitoring
 Spot server problems before they are noticed The system s really slow today! How often have you heard that? Finding the solution isn t so easy. The obvious questions to ask are why is it running slowly
Spot server problems before they are noticed The system s really slow today! How often have you heard that? Finding the solution isn t so easy. The obvious questions to ask are why is it running slowly
