Nagase s Library of Unnatural Amino Acids
|
|
|
- Theodore Bruce
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 agase s Library of Unnatural Amino Acids August 2012 Ver.17 agase provides unique -mono substituted and, - disubstituted unnatural amino acids which should open new avenues for designing drug candidates and streamlining the production of drugs in the pipeline, which can be supplied in multi-kg and more quantities via stereoselective alkylation of glycine or alanine and which contain no metal so should be safe for API production and should be environmentally friendly. Fmoc Fmoc Fmoc C 2 Bu-t Fmoc Fmoc Fmoc Boc Boc Fmoc Fmoc Fmoc 1
2 ew Service! Di-Peptides synthesized from our Unnatural Amino Acids agase is developing a range di-peptides which are composed of a natural amino acid connected to -terminal of our unnatural, alpha, alpha-di-alkylated amino acids. Fmoc atural Amino Acids Unnatural Amino Acids (, -dialkylated) Usually alpha, alpha-di-alkylated amino acids are not so reactive with other natural amino acids at the -terminal position because of their steric hindrance around the chiral carbon center. That is the reason why you may have obtained a peptide in low yield as a result of incomplete conjugation of the amino acid adjacent to the dialkylated amino acid. As a result agase commissioned certain peptide custom synthesis companies in Japan and China to provide -Fmoc-protected di-peptide which is composed of a natural amino acid and alpha, alpha-di-alkylated amino acid and can be used in solid phase peptide synthesis Examples Fmoc Fmoc Pbf 2 Fmoc-Gly-(S)-Ala(4-Pte)- Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-(S)-Ala(4-Pte)- 2
3 Reactive Amino Acids ( -Alkenyl or -Alkynyl Glycines and Alanines ) -AlkenylAla (S)- -Allylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Allylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (S)--Fmoc- -Allylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 1g $ 760(*) containing 20-50% Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -Allylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 1g $ 760(*) containing 20-50% Methyl tert-butyl ether Fmoc Fmoc (R)--Boc- -Allylalanine Ethyl ester ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 600 [CAS o ] C = Boc C 2 Et (S)--Fmoc- -(4-Pentenyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 500(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,800(*) containing 20-50% of Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -(4-Pentenyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 500(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,800(*) containing 20-50% of Methyl tert-butyl ether Fmoc Fmoc 3
4 (S)- -(4-Pentenyl)alanine tert-butyl ester p-itrobenzoate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) ew [CAS o ] C C 7 5 4= g $ 350 5g $ 1, (R)- -(4-Pentenyl)alanine tert-butyl ester p-itrobenzoate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) ew [CAS o ] C C 7 5 4= g $ 350 5g $ 1,400 C 2 t-bu p- 2 Ph C 2 t-bu p- 2 Ph (S)--Fmoc- -(7-ctenyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 1,000(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,900(*) Containing 10-40% of Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -(7-ctenyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 1,000(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,900(*) Containing 10-40% of Methyl tert-butyl ether Fmoc Fmoc xxxxxx (S)- -(7-ctenyl)alanine tert-butyl ester p-itrobenzoate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) ew [CAS o ] C C 7 5 4= g $ 700 5g $ 1, (R)- -(7-ctenyl)alanine tert-butyl ester p-itrobenzoate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) ew [CAS o ] C C 7 5 4= g $ 700 5g $ 1,500 C 2 t-bu p- 2 Ph C 2 t-bu p- 2 Ph ydrocarbon-stapling of natural peptides enhances helicity, protease resistance, and cell-permeability as well as improves pharmacologic properties. C. E. Schafmeister, et. al. J. Am.Chem.Soc. 2000, 122, L. D. Walensky, et. al. Science 2004, 305, Young-Woo Kim et. al. rg. Lett. 2010, 12,
5 -AlkynylAla (S)- -Propargylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Propargylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (S)--Fmoc- -Propargylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 500(*) [CAS o ] C = containing 20-50% Methyl tert-butyl ether (R) --Fmoc- -Propargylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 500(*) [CAS o ] C = containing 20-50% Methyl tert-butyl ether Fmoc Fmoc (S)--Fmoc- -(4-Pentynyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 800(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 2,400(*) containing 20-50% of Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -(4-Pentynyl)alanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 800(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 2,400(*) containing 20-50% of Methyl tert-butyl ether -AlkenylGly Fmoc Fmoc (S)- -Allylglycine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 5g $ 500 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Allylglycine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 5g $ 500 [CAS o ] C =
6 (R)--Acetyl- -allylglycine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 500 [CAS o ] C = Ac (S)--Boc- -Allylglycine Dicyclohexylamine salt ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 25g $ 800 [CAS o ] C = g $ 2,500 Boc DCA (S)- -Allylglycine Ethyl ester p-toluenesulfonate ( 97.0%, 98.0%ee) 25g $ 800 [CAS o ] C S = g $ 2,500 C 2 Et p-ts Applycation of Allylglycine as the building block for intermediate of pharmaceutical compounds. Rutjes, F. P. J. T. et al. rg. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, Rutjes, F. P. J. T. et al. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, 2000, AlkynylGly (S)- -Propargylglycine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Propargylglycine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = Methyl or -Ethyl derivatives of natural Amino Acids Alanine(Ala) (S)- -Ethylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = g $ (R)- -Ethylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = g $ 800 6
7 (S)--Boc- -Ethylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = g $ (R)--Boc- -Ethylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = g $ 900 Boc Boc (S)--Fmoc- -Ethylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 1,600(*) (refrigerated transport ) (R)--Fmoc- -Ethylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 1,600(*) Fmoc Fmoc Aspartic acid (Asp) (S)- -Methylaspartic acid ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methylaspartic acid ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C = (S)- -Methylaspartic acid-4-tert-butyl ester ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 230 [CAS o ] C = g $ (R)- -Methylaspartic acid-4-tert-butyl ester ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 230 [CAS o ] C = g $ 650 C 2 Bu-t C 2 Bu-t (S)--Fmoc- -Methylaspartic acid-4-tert-butyl ester ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,400(*) containing 10% Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -Methylaspartic acid-4-tert-butyl ester ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 5g $ 1,400(*) containing 10% Methyl tert-butyl ether C 2 t-bu C 2 t-bu Fmoc 7 Fmoc
8 Cysteine (Cys) (R)-L- -Methylcysteine Cl ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C 4 9 2S Cl = g $ 1, (S)-D- -Methylcysteine Cl ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 2,000 [CAS o ] C 4 9 2S Cl = S S Leucine (Leu) (S)- -Methylleucin ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methylleucine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 [CAS o ] C = (S)--Fmoc- - Methylleucine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700(*) [CAS o ] C = (R)--Fmoc- -Methylleucine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700(*) [CAS o ] C = Fmoc Fmoc Lysine (Lys) (S)- -Fmoc- Boc- -Methyllysine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 2,400(*) (R)- -Fmoc- -Boc- -Methyllysine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 2,400(*) Boc Boc Fmoc Fmoc rnithine (rn) (S)- -Fmoc- -Boc- -Methylornithine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 2,000(*) (R)- -Fmoc- -Boc- -Methylornithine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = g $ 2,000(*) 8
9 Boc Boc Fmoc Fmoc Phenylalanine (Phe) Substituted benzene ring derivatives are shown in pp (S)- -Methylphenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = g $ (R)- -Methylphenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = g $ (S)--Fmoc- -Methylphenylalanine 3/2 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C /2 2 = g $ (R)--Fmoc- -Methylphenylalanine 3/2 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C /2 2 = g $ 900 Fmoc Fmoc Proline (Pro) (S)--Boc- -Methylproline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C = g $ 1, (R)--Boc- -Methylproline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C = g $ 1,200 Boc Boc (S)--Fmoc- -Methylproline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 500 [CAS o ] C = g $ 1, (R)--Fmoc- -Methylproline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 500 C = g $ 1,500 Fmoc Fmoc 9
10 Tryptophan (Trp) (S)- -Methyltryptophan 1/2 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700 [CAS o ] C /2 2 = (R)- -Methyltryptophan 1/2 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700 [CAS o ] C /2 2 = (S)--Fmoc- -Boc- -Methyltryptophan ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 200mg $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 1g $ 1,200(*) containing 5% n-eptane (R)--Fmoc- -Boc- -Methyltryptophan ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 200mg $ 600(*) [CAS o ] C = (ET) 1g $ 1,200(*) containing 5% n-eptane Boc Boc Fmoc Fmoc Boyle, S. et al. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 1994, 2, 357. van Megen,. J. et al. Psychophormacology (Berlin) 1997, 129, 243. Dethlof, L. A. et al. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 61. Valerie, A. et al. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, Tyrosine (Tyr) (S)- -Methyl-4-hydroxyphenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 (S)- -Methyltyrosine [ CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methyl-4-hydroxyphenylalanine( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 250 (R)- -Methyltyrosine [ CAS o ] C =
11 (R)-D-m-Tyrosine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 500 [CAS o ] C = (R)-3-Methoxyphenylalanine monohydrate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 700 [CAS o ] C = C 3 Valine (Val) (S)- -Methylvaline( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methylvaline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C = (S)--Fmoc- -Methylvaline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET)1g $ 400(*) [CAS o ] C = containing 10% Methyl tert-butyl ether (R)--Fmoc- -Methylvaline ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) (ET) 1g $ 400(*) [CAS o ] C = containing 10% Methyl tert-butyl ether Fmoc Fmoc -Methyl-substituted-phenylalanines F-Phe (S)- -Fmoc- -Methyl-2-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 25 22F 4 = (R)- -Fmoc- -Methyl-2-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 25 22F 4 = F F Fmoc Fmoc 11
12 (S)- -Methyl-3-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 ew [CAS o ] C 10 12F 2 = g $ 1, (R)- -Methyl-3-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 ew [CAS o ] C 10 12F 2 = g $ 1, (S)- -Methyl-4-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 ew [CAS o ] C 10 12F 2 = g $ (R)- -Methyl-4-fluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 ew [CAS o ] C 10 12F 2 = g $ 900 F F (S)- -Fmoc- -Methyl-2,6-difluorophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C 25 21F 2 4 = Mapelli C. et. al. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, F Fmoc F (R)- -Methyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylalanine ethyl ester hydrochloride monohydrate ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) [CAS o ] C 13 16F 3 2 Cl 2 = g $ 600 CF 3 C 2 C 2 5 Cl (S)- -Methyl-4-trifluoromethoxyphenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 800 ew [CAS o ] C 11 12F 3 3= g $ 3, (R)- -Methyl-4-trifluoromethoxyphenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 800 ew [CAS o ] C 11 12F 3 3= g $ 3,200 CF 3 CF 3 12
13 Br-Phe (S)- -Methyl-2-bromophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $450 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 2 = (R)- -Methyl-2-bromophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 450 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 2 = (S)- -Methyl-3-bromophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 2 = (R)- -Methyl-3-bromophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 2 = (S)- -Methyl-4-bromophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 = (R)- -Methyl-4-bromophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 400 [CAS o ] C 10 12Br 2 = Br Br I-Phe (S)- -Methyl-3-iodophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 350 [CAS o ] C 10 12I 2 2 = (R)- -Methyl-3-iodophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 350 [CAS o ] C 10 12I 2 2 = (S)- -Methyl-4-iodophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 10 12I 2 = (R)- -Methyl-4-iodophenylalanine ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C 10 12I 2 = I I 13
14 2 -Phe (S)- -Methyl-2-nitrophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 200 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methyl-2-nitrophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 200 [CAS o ] C = (S)- -Methyl-3-nitrophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 200 [CAS o ] C = (R)- -Methyl-3-nitrophenylalanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 200 [CAS o ] C = Ph-Phe (S)- -Methyl- -(4-biphenyl)alanine 2 ( 98.0%, 98.0%ee) 1g $ 300 [CAS o ] C =
15 Application of Unnatural Amino Acids for Pharmaceuticals Replacement of the -hydrogen atom of L- -Amino acids with an alkyl substituent, which results in - disubstituted amino acids, has been reported. The modification changes the properties of amino acids as follows: 1) increased chemical stability, 2) increased hydrophobicity, 3) restriction of conformational freedom of side chains in amino acids, 4) restriction of conformational freedom of their peptides, 5) metabolic stability of their peptides. Tanaka, M. Chem. Pharn. Bull. 2007, 55, Examples of investigational API s including -disubstituted amino acids. 2 Br 3 C Cl Cl Chiral Analogue of Single S1P Receptor Albert, R. et al. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, Integrin ab-2 (LFA-1) Antagonist LFA-1/ICAM-1 Interaction Inhibitors Kelly, T.A. et al. J. Immunol, 1999, 163, Me F C 2 K1 Receptor Antagonist Boyle, S.et al. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 1994, 2, 357. Glucagon like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist with Antidiabetic Activity Mapelli, C. et. al. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, Ashwood, V. A. et al. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44,
16 Resistance of a Peptide with -disubstituted Amino Acid against Protease Incubated at 30 deg in 10% DMS/0.1 M Pi buffer (p=8.0) solution A tryptic digestion assay of α-methyl phenylalanine-containing peptide was carried out to investigate the effect of α,α-dialkylamino acid residue on the protease resistance. The introduction of α,α-dialkylamino acid residue (alpha-methylphenylalanine) to the peptide backbone exhibited higher protease resistance in 24 hours than the peptide with α-monoalkyl amino acid (phenylalanine). The peptide with the α,α-dialkylamino acid residue resulted in complete resistance. Reference: Matsuyama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Murakami, S.; Anzai, K. Construction of an unnatural amino acids library through asymmetric alkylation of glycine or alanine ester Shiff-base utilizing Maruoka Catalyst. Presented at the 5th International Peptide Symposium, Kyoto, Japan, December 4-9, 2010; P
17 Asymmetric Phase-Transfer Reaction with Maruoka Catalyst to Synthesize - Monosubstituted and, -Disubstituted Amino Acids. Ikunaka, M. and Maruoka, K. Asymmetric Phase-Transfer Catalysts for the Production of on-proteinogenic alpha-amino Acids in Asymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale 2 nd edition, Blaser, -U. and Federsel,.-J. eds. Wiley-VC Verlag Gmb & Co. KGaA (2010) According to the Maruoka interfacial mechanism, protected -amino acid is converted into the potassium E-enolate. And because of the lipophilic nature of the quaternary ammonium salt, it can move more easily and frequently into the interface layar where cation exchange takes place with the potassium E-enolate. And as the si face of the E-enolate is shielded by the molecular cavity of the catalyst, an alkyl halide is only allowed to approach the re face of the enolate. This is the reason why Maruoka Catalyst shows high reactivity and selectivitiy. Reference: oi, T., Kameda, M., and Maruoka, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, oi, T., Kameda,M., Tannai,., and Maruoka, K. Tetrahedron Lett., 2000, 41, oi, T., Takeuchi.,M., and Maruoka, K. Synthesis 2001, Maruoka, K. rg. Process Research & Development 2008, 12, Patents: USP 6,340,753; 6,441,231; 7,928,224 JP 4,217,085; 4,502,293; 4,605,606 SG 139,249 17
18 General Information: Company Profile: a technology and intelligence oriented company that turns wisdom into business. Mission: Maintain Good and Fair Business Practice agase & Co., Ltd., the nucleus of our group, was established as a dyestuffs wholesaler in Kyoto, Japan in Since then, agase has opened up new markets worldwide together with its customers and accumulated considerable know-how in its role as a technology and intelligence oriented trading company. At the same time, it has enhanced its product offer with new R&D, manufacturing and processing technology. Today, The agase Group is a US$7.9 billion (FY March 2011) company and offers customers trading, marketing, R&D and manufacturing functions in its four strategic areas of Chemicals, Plastics, Electronics and Life Sciences. Sales Information for Unnatural Amino Acids: Prices: All prices are in U.S. dollars. All catalog products are available from inventory in Japan and can be delivered CIP to the designated airport (port of entry) by air within two weeks of confirmed Purchase rder. Prices are subject to change without notice. Products marked with an asterisk (*) mark may require an additional fee for refrigerated transport. rdering: rders (or inquiries) can be placed by , phone or fax with the contact person in your region (see Contacts: below). Inquiries: agase offers a wide range of products not listed in this catalog. If you do not find a product you need in this catalog, please inquire about its availability by , phone, or fax. We will promptly evaluate your request. Bulk Quantities & Custom Manufacturing under cgmp: agase has the technology, know-how, capacity and experience to supply bulk and commercial quantities of products as well as to manufacture items to meet your specific needs. For further information, please feel free to contact our technical representatives by , phone, or fax. ur technical representatives will contact you to discuss your specific needs. R&D and Production Sites of agase Pharmaceutical Group: agase & Co., Ltd. Research & Development Center 2-2-3, Murotani, ishi-ku, Kobe, yogo JAPA agase ChemteX Corporation, Fukuchiyama-2 nd Factory , sadano-cho, Fukuchiyama, Kyoto JAPA ZCL Chemicals Limited A 806/807, 215, Atrium, Chakala, Andheri- Kurla Road, Andheri (E) Mumbai IDIA agase Medicals Co.,Ltd , Senzo, Itami, yogo,
Nagase s Library of Unnatural Amino Acids
 agase s Library of Unnatural Amino Acids September 2014 Ver.20 agase provides unique -mono substituted and, - disubstituted unnatural amino acids which open new avenues for designing drug candidates and
agase s Library of Unnatural Amino Acids September 2014 Ver.20 agase provides unique -mono substituted and, - disubstituted unnatural amino acids which open new avenues for designing drug candidates and
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
BOC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1. Calculating the charge of proteins
 BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
Hamari Chemicals, Ltd.
 amari Chemicals, Ltd. Technology for Life 1 Agenda What amari can offer your company amari s Technology The amari Advantage Core Technology unnatural amino acids and peptides; reduction; chiral technologies;
amari Chemicals, Ltd. Technology for Life 1 Agenda What amari can offer your company amari s Technology The amari Advantage Core Technology unnatural amino acids and peptides; reduction; chiral technologies;
Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Short Peptide Synthesis
 Short Peptide Synthesis Keith ó Proinsias 8 th February 2010 Introduction Amide bond and basic amide synthesis Solution phase peptide synthesis Protecting groups required for peptide synthesis Coupling
Short Peptide Synthesis Keith ó Proinsias 8 th February 2010 Introduction Amide bond and basic amide synthesis Solution phase peptide synthesis Protecting groups required for peptide synthesis Coupling
THE CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PEPTIDES
 TE EMIAL SYTESIS F PEPTIDES Peptides are the long molecular chains that make up proteins. Synthetic peptides are used either as drugs (as they are biologically active) or in the diagnosis of disease. Peptides
TE EMIAL SYTESIS F PEPTIDES Peptides are the long molecular chains that make up proteins. Synthetic peptides are used either as drugs (as they are biologically active) or in the diagnosis of disease. Peptides
2. Couple the two protected amino acids.
 General Considerations The Strategy of Peptide Synthesis Making peptide bonds between amino acids is not difficult. The challenge is connecting amino acids in the correct sequence. andom peptide bond formation
General Considerations The Strategy of Peptide Synthesis Making peptide bonds between amino acids is not difficult. The challenge is connecting amino acids in the correct sequence. andom peptide bond formation
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM
 AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
Introduction to Chemical Biology
 Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
USP's Therapeutic Peptides Expert Panel discusses manufacturing processes and impurity control for synthetic peptide APIs.
 Control Strategies for Synthetic Therapeutic Peptide APIs Part III: Manufacturing Process Considerations By Brian Gregg,Aleksander Swietlow,Anita Y. Szajek,Harold Rode,Michael Verlander,Ivo Eggen USP's
Control Strategies for Synthetic Therapeutic Peptide APIs Part III: Manufacturing Process Considerations By Brian Gregg,Aleksander Swietlow,Anita Y. Szajek,Harold Rode,Michael Verlander,Ivo Eggen USP's
Supporting Information. Minimum active structure of insulin-like. peptide 5 (INSL5)
 Supporting Information Minimum active structure of insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5) Alessia Belgi 1,2, Ross A.D. Bathgate *1,2,3, Martina Kocan *4, Nitin Patil 1,5, Suode Zhang 1, Geoffrey W. Tregear 1,2,
Supporting Information Minimum active structure of insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5) Alessia Belgi 1,2, Ross A.D. Bathgate *1,2,3, Martina Kocan *4, Nitin Patil 1,5, Suode Zhang 1, Geoffrey W. Tregear 1,2,
Benzene Benzene is best represented as a resonance hybrid:
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
1 General introduction
 General introduction Peptides and peptidomimetics _ 1 1 General introduction 1.1 Peptides and peptidomimetics umerous small and large peptides, which are sequence and length-specific polymers composed
General introduction Peptides and peptidomimetics _ 1 1 General introduction 1.1 Peptides and peptidomimetics umerous small and large peptides, which are sequence and length-specific polymers composed
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Outline. Market & Technology Trends. LifeTein Technology Portfolio. LifeTein Services
 1 Outline Market & Technology Trends LifeTein Technology Portfolio LifeTein Services 2 Synthetic Therapeutic Peptides More than 60 synthetic therapeutic peptides under 50 amino acids in size have reached
1 Outline Market & Technology Trends LifeTein Technology Portfolio LifeTein Services 2 Synthetic Therapeutic Peptides More than 60 synthetic therapeutic peptides under 50 amino acids in size have reached
MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012
 Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award
 2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award 2010 Frost & Sullivan 1 We Accelerate Growth Frost & Sullivan s Global Research Platform Frost & Sullivan is entering its 50 th year in
2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award 2010 Frost & Sullivan 1 We Accelerate Growth Frost & Sullivan s Global Research Platform Frost & Sullivan is entering its 50 th year in
CHAPTER 29 AMINO ACIDS, POLYPEPTIDES, AND PROTEINS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin
 Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy
 Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy Jonathan M. Collins, Michael J. Collins, Rebecca C. Steorts CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC 28106-0200, U.S.A. Presented at American
Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy Jonathan M. Collins, Michael J. Collins, Rebecca C. Steorts CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC 28106-0200, U.S.A. Presented at American
Structure and properties of proteins. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE. Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs,
 Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Previous lecture: Today:
 Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers:
 Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
California State Polytechnic University, Pomona. Exam Points 1. Nomenclature (1) 30
 Chem 316 Final Exam Winter, 2008 Beauchamp ame: Topic Total Points Exam Points 1. omenclature (1) 30 Credit 2. Explanation of elative eactivities of Aromatic 20 Compounds or Carbonyl Compounds 3. eactions
Chem 316 Final Exam Winter, 2008 Beauchamp ame: Topic Total Points Exam Points 1. omenclature (1) 30 Credit 2. Explanation of elative eactivities of Aromatic 20 Compounds or Carbonyl Compounds 3. eactions
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 22 Proteins
 hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
The Peptides Vol. 2: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology: Special Methods in Peptide Synthesis
 The Peptides Vol. 2: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology: Special Methods in Peptide Synthesis Download: The Peptides Vol. 2: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology: Special Methods in Peptide Synthesis PDF ebook The Peptides
The Peptides Vol. 2: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology: Special Methods in Peptide Synthesis Download: The Peptides Vol. 2: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology: Special Methods in Peptide Synthesis PDF ebook The Peptides
Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application. Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D.
 Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D. Presentation overview 1 2 3 4 Introduction Peptide Design Basics Advanced Design Strategy Strategy
Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D. Presentation overview 1 2 3 4 Introduction Peptide Design Basics Advanced Design Strategy Strategy
--not necessarily a protein! (all proteins are polypeptides, but the converse is not true)
 00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework
 CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework SHORT ANSWER Consider the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction below to answer the following question(s): 1. Refer to the reaction above. Draw the structure of the electrophilic
CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework SHORT ANSWER Consider the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction below to answer the following question(s): 1. Refer to the reaction above. Draw the structure of the electrophilic
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Fourteen 1
 An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms
 In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 35
 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
8/20/2012 H C OH H R. Proteins
 Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Syllabus. 1. Occurrence and Functions of Peptides in Nature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener,
 Syllabus 1. ccurrence and Functions of Peptides in ature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener, 2. Peptide Synthesis a) Aspartam: Properties of amino acids;
Syllabus 1. ccurrence and Functions of Peptides in ature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener, 2. Peptide Synthesis a) Aspartam: Properties of amino acids;
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway. CHAPTER 14 Substitution Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4 th edition Chapter 14 Homework: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 20, 23, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 41, 46,
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4 th edition Chapter 14 Homework: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 20, 23, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 41, 46,
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms
 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT
 EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
Overview'of'Solid-Phase'Peptide'Synthesis'(SPPS)'and'Secondary'Structure'Determination'by'FTIR'
 verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
Figure 3-1-1: Alkaline hydrolysis (saponification) of oil to make soaps.
 Chapter 3 CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF OILS AND FATS From the fats and oils obtained from natural resources, the majority of them are used directly or just after refinement. While the others are used after
Chapter 3 CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF OILS AND FATS From the fats and oils obtained from natural resources, the majority of them are used directly or just after refinement. While the others are used after
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Application Note. Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples. Summary. Introduction. Category Bio science, food Matrix
 Application Note Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples Category Bio science, food Matrix Baby food Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic amino acids, canonical amino acids,
Application Note Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples Category Bio science, food Matrix Baby food Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic amino acids, canonical amino acids,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(2): 372-380 ISSN No: 0975-7384 Determination of amino acid without derivatization by using
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(2): 372-380 ISSN No: 0975-7384 Determination of amino acid without derivatization by using
SpikeTides TM Peptides for relative and absolute quantification in SRM and MRM Assays
 Protocol SpikeTides TM Peptides for relative and absolute quantification in SRM and MRM Assays Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-6392-7878 Order per fax: +49-30-6392-7888 or e-mail: www: peptide@jpt.com www.jpt.com
Protocol SpikeTides TM Peptides for relative and absolute quantification in SRM and MRM Assays Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-6392-7878 Order per fax: +49-30-6392-7888 or e-mail: www: peptide@jpt.com www.jpt.com
Dedicated Project Management
 Peptides Dedicated Project Management At Lonza, we are committed to our customers success, so it is our mission to help your product reach its full potential. We pride ourselves on delivering high-quality,
Peptides Dedicated Project Management At Lonza, we are committed to our customers success, so it is our mission to help your product reach its full potential. We pride ourselves on delivering high-quality,
The chemistry of insulin
 FREDERICK S ANGER The chemistry of insulin Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1958 It is great pleasure and privilege for me to give an account of my work on protein structure and I am deeply sensitive of the
FREDERICK S ANGER The chemistry of insulin Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1958 It is great pleasure and privilege for me to give an account of my work on protein structure and I am deeply sensitive of the
Dipeptide Synthesis. polarized light (Figure 2).
 Dipeptide Synthesis + Scheme 1: Peptide synthesis without carboxyl activation + 2 Throughout your organic chemistry tenure you have been taught the underlying principles necessary to construct simple organic
Dipeptide Synthesis + Scheme 1: Peptide synthesis without carboxyl activation + 2 Throughout your organic chemistry tenure you have been taught the underlying principles necessary to construct simple organic
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ
 CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Module Title: Topics in Organic Chemistry Module Code: CHEO 7003 School : Science Programme Title: Bachelor of Science in Analytical & Pharmaceutical
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Module Title: Topics in Organic Chemistry Module Code: CHEO 7003 School : Science Programme Title: Bachelor of Science in Analytical & Pharmaceutical
catalogue 2005-2006 of ARGUS Chemicals S.r.l
 Argus Chemicals S.r.l. catalogue 2005-2006 of ARGUS Chemicals S.r.l Rare & fine chemicals Argus Chemicals srl is a Rare & Fine Chemicals company in Vernio (orth of Florence), Italy. The company was started
Argus Chemicals S.r.l. catalogue 2005-2006 of ARGUS Chemicals S.r.l Rare & fine chemicals Argus Chemicals srl is a Rare & Fine Chemicals company in Vernio (orth of Florence), Italy. The company was started
Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines
 1 P a g e Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms ofnh 3 molecule by alkyl/aryl group(s).
1 P a g e Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms ofnh 3 molecule by alkyl/aryl group(s).
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
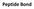 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper
 Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper Writing an effective scientific paper is not easy. A good rule of thumb is to write as if your paper will be read by a person who knows about the field in general
Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper Writing an effective scientific paper is not easy. A good rule of thumb is to write as if your paper will be read by a person who knows about the field in general
T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride
 Technology StrengthS T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride The coupling agent of the future Coupling and water removal are synthesis tools that stand at the cutting edge of purity and cost effective manufacture
Technology StrengthS T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride The coupling agent of the future Coupling and water removal are synthesis tools that stand at the cutting edge of purity and cost effective manufacture
Enzymes reduce the activation energy
 Enzymes reduce the activation energy Transition state is an unstable transitory combination of reactant molecules which occurs at the potential energy maximum (free energy maximum). Note - the ΔG of the
Enzymes reduce the activation energy Transition state is an unstable transitory combination of reactant molecules which occurs at the potential energy maximum (free energy maximum). Note - the ΔG of the
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
ammonium salt (acidic)
 Chem 360 Jasperse Ch. 19 otes. Amines 1 eactions of Amines 1. eaction as a proton base (Section 19-5 and 19-6) amine base -X (proton acid) a X ammonium salt (acidic) Mechanism: equired (protonation) everse
Chem 360 Jasperse Ch. 19 otes. Amines 1 eactions of Amines 1. eaction as a proton base (Section 19-5 and 19-6) amine base -X (proton acid) a X ammonium salt (acidic) Mechanism: equired (protonation) everse
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í
 I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest
 Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica
 PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica 1 Solution phase chemistry -Time consuming: isolation and purification at each step -Low yield: can t drive reaction
PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica 1 Solution phase chemistry -Time consuming: isolation and purification at each step -Low yield: can t drive reaction
N-Methylated Cyclic Peptides: Relationship between Structure and Property. Speaker: Song, Li-Juan Supervisors: Prof. Wu, Yun-Dong Dr.
 N-Methylated Cyclic Peptides: Relationship between Structure and Property Speaker: Song, Li-Juan Supervisors: Prof. Wu, Yun-Dong Dr. Zhang, Xin-Hao 1 Contents Introduction N-methylated cyclic peptides
N-Methylated Cyclic Peptides: Relationship between Structure and Property Speaker: Song, Li-Juan Supervisors: Prof. Wu, Yun-Dong Dr. Zhang, Xin-Hao 1 Contents Introduction N-methylated cyclic peptides
Patrick, An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 4e Chapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions. Pyrrole ring N H
 Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e hapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The pyrrole ring of DU 122290 serves to increase the rigidity
Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e hapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The pyrrole ring of DU 122290 serves to increase the rigidity
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid.
 A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following?
 MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
