AN EXAMPLE FORMAT FOR DESIGN PROJECT REPORTS [ADAPTED FROM ASME GUIDELINES FOR STUDENT DESIGN COMPETITION] TITLE (TIMES NEW ROMAN, 12, BOLD)
|
|
|
- Sharlene Wright
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AN EXAMPLE FORMAT FOR DESIGN PROJECT REPORTS [ADAPTED FROM ASME GUIDELINES FOR STUDENT DESIGN COMPETITION] TITLE (TIMES NEW ROMAN, 12, BOLD) Team Name (Times New Roman, 12) First Author (Times New Roman, 12) Second Author (Times New Roman, 12) Third Author (Times New Roman, 12)...continue to list all authors / team members Date (Times New Roman, 12) Abstract (Times New Roman, 12, justified, placed on title page) The report should start with an abstract of approximately 100 words, summarizing the objective, contents, results, and conclusions of the report as specifically as possible. The heading of the Abstract should be italic. Update the abstract as more sections of the report are competed. [Note: The purpose of the design report is to describe and justify the final design (or for the intermediate reports the current status of the design). The audience is primarily decision makers (technical and business project managers) in your company and internal technical staff. The style (based on guidelines in Style Guide [Shipley and Associates, 1987] and Write to the Top [DiGregorio, 1995] should follow these guidelines: 1) Take the active voice (use first person nouns and direct, forceful verbs); 2) Use pronouns when recommending something, drawing conclusions, or conveying decisions; 3) Write the way you talk - make it easy for the reader to get your point; 4) Keep most sentences and paragraphs short. Formatting Guidelines: The entire body text of the report should be Times New Roman, 12, with 1 inch margins. Major headings should be numbered consecutively, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, etc, typed in bold face with a font size of 16. Sub-headings should be numbered consecutively, 1.1, 1.2, etc, typed in bold face with a font size of 14. Finally, sub-sub-headings should also be numbered consecutively, 1.1.1, 1.1.2, etc., typed in bold face with a size 12 font face. It is not recommended to go beyond three levels of headings.
2 1.0 Introduction (Times New Roman 16, Bold, left) Use the introduction section to provide some background information on the overall design problem domain. This introductory information should come from your literature search Library, Internet, trade magazines, etc. Key points to cover: Set the context: Help the reader understand general information about the problem or need area, including any necessary definitions, statistics, etc. Use pictures and visual images as much as possible. Explain the purpose: why is this work important? Set the scope: How far can you or will you go to solve the problem? State the objectives: In short statements or a bullet list, identify the specific objectives of your work - things that can be assessed at the end of the project to determine if you were successful. Important Note: All sources that are not your own ideas must be referenced. For your reports, please use the parenthetical references: author-date system. A sample reference list addressing each of the five main types of information sources is given at end. These include: websites (Swanson, 1999), journals (Muriru and Daewoo, 2002), books (Zacharia and Daudi, 2001), conference proceedings (Peters et al., 2001) and patents (Wen-Cheng, 1994). For more information on ethical standards for publications (for the example of ASME journals), see Initial Needs Statement (Times New Roman, 14, left) Provide a brief paragraph describing the initial needs statement the needs statement itself is usually given to the design team. Please also include some initial discussion of the need statement, linked to the introductory material. 2.0 Customer Needs Assessment This section describes the iterative FOCUS process for defining the customer (360 degree perspective), developing appropriate interview and observation guides, collecting data, and converting it to customer requirements statements (customer needs). Please show/describe the iterative nature of the process to illustrate how the project was impacted by customer input. This section should include descriptive text and several tables and figures, including: 1. An initial customer needs list obtained from interviews and observations (refer to Table 1). Note that all table captions are placed on top of the tables. Please note that all tables are numbered consecutively. Please make sure that a table is not split between two pages. Move the table to a location where it can fit. If the table is too big to fit, split the table into two separate tables. 2. A table listing the hierarchal design objective list, that has been augmented with constraints and functions (refer to Table 2). Note that the constraints and functions are formatted differently for easy identification. 3. Include the most relevant copy of your interview guide and observation guide in the Appendix, and reference it from this section. 1
3 Table 1. Initial Customer Needs List Obtained from Interviews and Observations (Times New Roman, 12, Bold, Centered) 2
4 Table 2. Hierarchal Customer Needs List (With Weighting factors) (Times New Roman, 12, Bold, Centered) 2.1 Weighting of Customer Needs This section should begin with a brief introduction on the importance of weighting, and then provide a description and/or tables that show how the weights were calculated. The resources for making decisions discussed in class would be a good tool to use here. Figure 1 illustrates the use of one method, the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), to create a weighted hierarchal customer needs list. It is very important to include figures and tables to show how the decisions were made, not just what the decisions are. Like tables, all figures are numbered consecutively. Unlike tables, however, figure captions are typically placed at the bottom of the figure. This section should build on and make reference to the weighted hierarchal customer needs list. 3
5 Portable User Fr. Flexible Durable Total Weighting Portable User Fl Flexible Durable Figure 1. Example of AHP Pair wise Comparison Chart to Determine Weighting for Main Objective Categories 3.0 Revised Needs Statement and Target Specifications Using the initial problem statement and the knowledge gathered from the customer needs, describe a revised needs statement that provides a more concise description of the design problem. Clearly define the target specifications and the design criteria that define the problem (generated from the customer requirements and engineering standards). Include the initial justification for the specifications and the metrics (how meeting the specs will be measured), referring to customer requirements and benchmarking results as appropriate. Also describe how the specifications were checked with the customer to ensure they meet their needs. 4.0 External Search This section should include information gathered from numerous sources about the design problem and the product, process, or system that is at the center of the design problem. Focus primarily on the information that is pertinent to the revised needs statement and target specifications. Sources should include library, internet, magazines, patents, observations of actual products, discussions with experts, etc. You should also perform a patent search to determine the key technologies used in similar designs. Focus on utility patents (looking at function) and not cosmetic patents (focusing on artistic design). Evaluate the patents and information sources, and clearly state what impact they have on the development of your project. Also, summarize your business opportunity, and make reference to your "Business Opportunity Statement" in the Appendix. 4.1 Benchmarking This section should identify all commercially available products, processes, or systems that attempt to address all or a significant part of the needs statement that your project is addressing. Create a benchmarking table that compares numerous applicable features. Note that not all 4
6 systems will have all features. The results should be prefaced with an introductory paragraph and then neatly summarized in a table (see Table 4). In tables, you may reduce the font size to 10 point to allow inclusion of more information per table. Recall a single table should not be split over multiple pages. This section might also include: 1. Figures/pictures of the benchmarked products, systems (if available) 2. Tables listing specs and metrics for benchmarked products, including their performance with respect to the target specifications (if applicable) 3. Sketches clearly indicating dimensions and all relevant features that could be of use in your design. For example, the number, size and location of screw holes. Table 4. Benchmarking of Products Feature Systems 1 System 2 System 3 System 4 Size Weight Cost Flexibility And so on. See the "Intro to Target Specifications" presentation for more information on benchmarking products and metrics. As in the other sections, show some details that illustrate project development but focus on the information that is pertinent to the revised needs statement and target specifications. 4.2 Applicable Patents Each team member should provide at least one applicable patent, and write an evaluation that describes what impact this patent or the ideas therein have on the development of your project. The overall section must describe the results of a thorough patent search in your product area. 4.3 Applicable Standards Search governmental and industry sources for applicable standards, rules, regulations, etc., and record them here. Make sure to consider health and safety, environmental regulations, governmental policies, etc. Also evaluate them and state what impact they have on the development of your project. 4.4 Applicable Constraints Determine what internal (space, budget, expertise, ) and external (market, environment, health and safety, ) constraints are applicable and record them here. Also evaluate them and state what impact they have on the development of your project. 5
7 4.5 Business Opportunity Include a short overview here, and reference the Business Opportunity Statement which should be included in the Appendix. Guidelines for the statement are in Concept Generation In this section describe the processes used to generate creative alternative conceptual designs and do an initial screen for feasibility. Document numerous (>3) feasible alternatives, and discuss the continuing influence of the customer in the design process. 5.1 Problem Clarification Use tools and analytical models to clarify the problem, such as the "Power Flow" Model for Design Concepts, the black-box model or the energy-material-signal model (EMS). 5.2 Concept Generation Briefly describe the process used for concept generation, making note of processes used to enhance creativity and to maximize the number of different system-level and subsystem-level concepts considered. For concept generation various techniques can be used (e.g., brainstorming, C-sketch, TRIZ, etc.). A morphological chart (Figure 2) may help to organize subsystem concepts for each function. Figure 2. Morphological chart 6
8 Include sufficient detail to show the important results of the concept generation process, including (as applicable) brainstorming lists, mind-mapping charts, affinity diagrams, sketches/drawings of concepts (hand sketches or CAD drawings approximately scaled, including users in operating position(s)), etc. Include some discussion of features that may serve as "delighters" - unique or unexpected features that could distinguish your product. 5.3 Initial Screening for Feasibility and Effectiveness Describe the method of concept screening (for possible methods, see Include appropriate evaluation of the alternatives to judge feasibility relative to the specifications and criteria. Document the feasibility of numerous (>3) feasible alternatives. 6. Concept Selection 6.1 Data and Calculations for Feasibility and Effectiveness Analysis Include appropriate Free Body Diagrams (FBD), calculations, simulations, research and other analysis that can be used to more rigorously judge feasibility and effectiveness relative to the specifications and criteria. For example, a vehicle design project would require numerous FBDs, with calculations that show the power requirements to achieve the max speed specification, the torque requirements for the acceleration and gradeability specifications, the energy storage requirements (amp-hour capacity for batteries, fuel tank size,...) for the range specification, etc. 6.2 Concept Screening Describe and show the results of processes used to get feedback from the "customer" with respect to your concepts, the process used to screen the concepts (system-level and subsystem-level if appropriate) and definitions of what feasibility and effectiveness mean with respect to the concept screening, the results (with justification) of the concept screening including how concepts were combined and refined. 6.3 Concept Development, Scoring and Selection Describe the process used to develop and evaluate the final concepts, and describe in detail the concept selected for further refinement, including detailed sketches with the user in operating position(s). See the Concept Evaluation and Selection Presentation for more information. Remember that the goal is not selection but development of the best concept, so combining and refining concepts is highly encouraged. Concept scoring is normally done with Pugh Charts (or other decision-making tools). Explain the scoring method used in the decision matrix. Show detailed feasibility and effectiveness analysis for the selected concept relative to all design specifications. 7
9 7.0 Final Design Discuss details of the design refinement process and the final detailed design. Start with a system level description that flows down to the subsystem and component level. The project must include both thermal and mechanical design aspects, so make sure that both aspects of your project are described. It is suggested that you use FMEA to organize the discussion of how the critical design areas were identified and what methods were used to develop a safe and effective final design. Describe how you did the FMEA and what the results were, and make reference to actual FMEA worksheets included in the appendix. Show highlights of the key analysis that was done to justify design decisions, and include the results and conclusions from the analysis in the body of the report (place the details of any significant analysis in the appendix). For all significant design decisions (items identified by FMEA to be important decisions), provide clear and complete justification that includes all aspects of the decision (to demonstrate that a good design process was followed to achieve a good decision). Acceptable / Supported decisions include most of the following considerations Considerations Impacts / Effects (First, do no harm. Immediate and long term, intended and unintended, local and global impacts of products and production on the environment and society) Professional and ethical standards (Decision and Justification show good judgment and integrity) Function (Research, precedent and vendor info show it should meet the design specifications) FMEA (A failure modes and effects analysis or similar technique is properly used to evaluate the overall system failure modes and hazards and to prioritize risks and focus the design effort. In-Process (Design Refinement) Level Considered for the overall project, and is impacting production and part-level decisions. Demonstrates a commitment to professional standards. Complete and up-to-date All Hazards identified and most significant items evaluated. Completed Decision Level All aspects considered and hard choices and tradeoffs are made as required to limit impacts. Demonstrates a commitment to professional standards. Complete and up-to-date All significant hazards evaluated and RPNs decreased to acceptable values. 8
10 Design Analysis (Sufficient and Correct Analysis for part sizing and material selection to avoid failure; Simulations demonstrate performance of major subsystems in critical operating modes.) Safety (All aspects of project and product safety considered continuously throughout the design process. Design for Safety terminology & approach used.) Economics / Value (Cost/benefit analysis is used to evaluate value, not just immediate cost. A vendor selection process is followed and documented.) Customer (360 degree Customer Input solicited, evaluated and appropriately used.) DFMA (All aspects of Manufacturing and Assembly Considered, including manufacturability of design features, use of manufacturing features, machinability of materials, ) Testing (Mock-ups and experiments used for information and validation) Other (Creativity and initiative are evident in the decision process; Good planning and organizing are demonstrated, including use of decision making tools [Pareto analysis, decision matrices and other prioritizing and organizing tools]; Impacts on design criteria are considered) All critical load cases and failure locations identified and analysis completed and validated for most critical locations. Simulations begun with estimated parameters. Design for safety on a system level is complete. Examples of avoidance and protection are presented. Most significant items have been analyzed for value and a process is used for vendor selection. Significant input has been incorporated from various external and internal customers Manufacturability and assembly of most significant items has been analyzed and improved to appropriate levels. Most mock-ups complete and used appropriately for product development. Other tests are planned. Some other considerations are evident. Analysis completed and validated for all critical locations. Simulation completed with experimentally validated parameters. A comprehensive approach is documented that shows reduction of all hazards (product and production) to low risk. All significant items have been analyzed for value. Good vendor selection process. Usability, marketability and other customer input incorporated from all significant external and internal customers Manufacturability and assembly of all significant items has been analyzed and improved to appropriate levels. Mock-ups and tests were used appropriately for numerous aspects of product development. Most other considerations are evident. 7.1 How does it work? In the best way you can, please explain how your design works. Focus on system-level operational details (how the user would operate the system), but include some technical information that describes how the product actually works. Include instructions for maintenance and service, and any assembly steps that must be completed by the customer. This section should be understandable to the target customer, and should be able to serve as product literature (operating manual). 9
11 7.2 How is it manufactured and assembled, and what does it cost? In either a narrative or step-by-step style, discuss the manufacturability and cost of the final design: A reasonably detailed manufacturing and assembly plan (with pictures and/or figures) must be developed that details how the product will be manufactured (in lots of 5000/yr) and that estimates the per unit production cost (including labor, materials, overhead,...) at that production volume. [Use the recommended cost estimation procedure discussed in class, or an equivalent method] The material, material condition, manufacturing method, surface finish, and tolerances must be specified for the most significant components and justified based on Design for Manufacturing and Assembly principles. Provide some explanation in this section for the tolerances specified in the drawings, and how the dimensions fully control the important part features, and how manufacturing considerations are represented in the drawings. Design Drawings, Parts List and Bill of Materials Include in this section, or in an Appendix or design project file referenced from this section, the assembly-level and part-level drawings that summarize and communicate your design. Please provide a set of drawings with sufficient detail to control manufacture and assembly of the final design (i.e. the drawing set could be sent to a manufacturing shop for the final design to be produced). For this project, assembly and subassembly drawings and parts lists should be complete, but it is acceptable to focus on the most significant part-level drawings (but at least one per team member) to do a good job fully dimensioning and tolerancing them. The assembly drawings should show all parts (purchased and manufactured) with part numbers, and the parts list should identify all parts. The assembly drawing should also include all assembly-level dimensions. Note that detailed drawings are not required for components/subassemblies that are purchased and not modified prior to assembly. These are specified in the parts list and shown with key dimensions to scale in the subassembly/assembly drawings. Supply the best possible purchase information (vendor/part #/part description) for purchased items. o Modification drawings are required for purchased parts that require some manufacturing prior to assembly. o Do not draw details of standard hardware like nuts, bolts, washers, castors, computers, etc.; just specify them in the Bill of Materials. The bill of materials lists: 1) Materials and their specifications (sizes and quantity) necessary to manufacture parts and 2) Off-the-shelf hardware. It may include weights and costs. 10
12 Note: A design project file compiles the drawings and vendor info and all related information, organized by subsystem and part number/part name. It is not a "formal" document like a report, but more like an expanded design notebook organized according to the parts in the assembly. Using a binder with identification tabs is recommended. 7.4 Design validation through test results and operating experience Explain the tests that were used to validate the performance, usability, safety, and other features of your design, including for each test: 1) the need for information (what you needed to know), 2) the design of the test (to control certain factors) and the test apparatus (if required), 3) the metrics (the targets for what needs to be measured or observed), 4) the measurement system, 5) the results, and 6) lessons learned and design changes. Also, discuss the continuing influence of the customer in the design process. 8.0 Conclusions Did your project meet the objective (to design a good solution to the business opportunity and respond to the original needs statement)? Part of the conclusion section should include a specifications table, showing all specification requirements vs. actual values for the final design. Using the performance relative to specs along with performance relative to the design criteria, address the true value of your design. Make sure to highlight the "delighters" and the truly unique features you have added to your design. Also remember to include info on: Environmental: The design (and any fuels or power sources) should be evaluated for total environmental impact, including concerns related to energy use, emissions, and total life cycle issues (environmental impacts of production methods [hazardous materials?] and product retirement [longevity and recyclability]) Political: Identify existing government policies that are supportive of the project. [Note that the following part of the conclusion section will be done individually as part of the executive summary. There is no need to include it in the team report.] This is a technical report, not a sales brochure, so make sure to be brutally honest in your appraisal 11
13 of the overall design and its state of readiness for production. Clearly state whether or not you believe the project should be continued or cancelled (based on your improved understanding of the market, the production costs, and the overall impact that producing this design is likely to have relative to addressing the original needs statement (the current energy situation). Justify your recommendation. If it should be continued but is not ready for production, clearly state (in specific actions, not generalities) what needs to be done to reach the "production-ready" state, and attempt to place a schedule and budget on the remaining work. References (Times New Roman, 16, Bold) Note: That for the author-date system, references are listed in alphabetical order. Muriru, P.K. and Daewoo, R., Prediction of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of a Multi-Flame Injector', Combustion and Flame, vol. 100, no. 2, pp , Peters, L., Johnson, M., and Davidson, K., A Novel Approach to Four-Bar Synthesis', 10 th ASME Design Automation Conference, pp , Pittsburgh, PA, Swanson Inc., Online Users Manual for ANSYS 5.0'', manual, viewed on March Wen-Cheng, C., Electric Bicycle', US Patent no. 5,368,122, November 29, Zacharia, M. and Daudi, P.K., The Effect of Multi-materials on Conventional Finite Element Formulations, New York: Wiley and Sons, Appendices Must include FMEA Worksheets Individual DFMA focus areas Other things that should likely be included Example Calculations FEA details and plots of loads, boundary conditions and results. Include mesh convergence studies, validation calculations, etc. Manufacturing drawings Customer surveys Cost worksheets 12
Imagine Schools Florida Science Fair Guidelines
 DISPLAY BOARD: CLASSROOM CHECK Components Total Points Points Display Board: Neatness/ 20 Appearance Scientific Method: 40 Complete and ordered correctly Thoroughness 25 Earned Comments Conventions: Grammar;
DISPLAY BOARD: CLASSROOM CHECK Components Total Points Points Display Board: Neatness/ 20 Appearance Scientific Method: 40 Complete and ordered correctly Thoroughness 25 Earned Comments Conventions: Grammar;
CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts.
 CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts. As a methodology, it includes descriptions of the typical phases
CRISP-DM, which stands for Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining, is an industry-proven way to guide your data mining efforts. As a methodology, it includes descriptions of the typical phases
Robotics & Automation
 Robotics & Automation Levels: Grades 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.0 CIP Code: 21.0117 Core Code: 38-01-00-00-130 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: 612 COURSE DESCRIPTION Robotics & Automation is a lab-based,
Robotics & Automation Levels: Grades 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.0 CIP Code: 21.0117 Core Code: 38-01-00-00-130 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: 612 COURSE DESCRIPTION Robotics & Automation is a lab-based,
MIS Group Project Guidelines
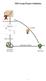 MIS Group Project Guidelines Performance Information Database Feedback Relevant Data Operational Details Transaction Processing Operations 1 A. Report Structure and Content Your section headings should
MIS Group Project Guidelines Performance Information Database Feedback Relevant Data Operational Details Transaction Processing Operations 1 A. Report Structure and Content Your section headings should
Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA
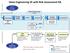 Preparation Conclude & Report Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA yes START Plan for VE and RA Value Engineering Job Plan 1 2 Function Information Analysis 3 Creative 4 Evaluation 5 Develop recommendations
Preparation Conclude & Report Value Engineering VE with Risk Assessment RA yes START Plan for VE and RA Value Engineering Job Plan 1 2 Function Information Analysis 3 Creative 4 Evaluation 5 Develop recommendations
Student Writing Guide. Fall 2009. Lab Reports
 Student Writing Guide Fall 2009 Lab Reports The manuscript has been written three times, and each rewriting has discovered errors. Many must still remain; the improvement of the part is sacrificed to the
Student Writing Guide Fall 2009 Lab Reports The manuscript has been written three times, and each rewriting has discovered errors. Many must still remain; the improvement of the part is sacrificed to the
Prosthetic Arm Challenge 2.0
 MESA USA NATIONAL ENGINEERING DESIGN COMPETITION 2015-2016 R E S O U R C E D O C U M E N T Contents Itemized Budget Sheet Sample... 2 Budget Documentation Examples... 3 Technical Paper... 4 Academic Poster
MESA USA NATIONAL ENGINEERING DESIGN COMPETITION 2015-2016 R E S O U R C E D O C U M E N T Contents Itemized Budget Sheet Sample... 2 Budget Documentation Examples... 3 Technical Paper... 4 Academic Poster
AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CIVIL ENGINEERS. Standards Writing Manual for ASCE Standards Committees. Prepared by ASCE Codes and Standards Committee
 AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CIVIL ENGINEERS Standards Writing Manual for ASCE Standards Committees Prepared by ASCE Codes and Standards Committee Revised August 20, 2010 Contents Section Page 1.0 Scope, purpose,
AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CIVIL ENGINEERS Standards Writing Manual for ASCE Standards Committees Prepared by ASCE Codes and Standards Committee Revised August 20, 2010 Contents Section Page 1.0 Scope, purpose,
SOE GUIDELINES FOR APA STYLE FOR PAPERS, THESES AND DISSERTATIONS. School of Education Colorado State University
 SOE GUIDELINES FOR APA STYLE SOE PD 32 FOR PAPERS, THESES AND DISSERTATIONS School of Education Colorado State University This document has three major sections: differences between APA and SOE styles,
SOE GUIDELINES FOR APA STYLE SOE PD 32 FOR PAPERS, THESES AND DISSERTATIONS School of Education Colorado State University This document has three major sections: differences between APA and SOE styles,
NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture. Version 3.0
 NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture Version 3.0 October 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SOLUTION ARCHITECTURE...1 Introduction...1 Benefits...3 Link to Implementation Planning...4 Definitions...5
NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture Version 3.0 October 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SOLUTION ARCHITECTURE...1 Introduction...1 Benefits...3 Link to Implementation Planning...4 Definitions...5
MSIE Engineering Management Capstone Description. Project Title: Knowledge Preservation in University Physical Plant Operations COMMITTEE
 MSIE Engineering Management Capstone Description Candidate: Project Title: Knowledge Preservation in University Physical Plant Operations COMMITTEE Advisor: Member: Member: Problem Statement: (What is
MSIE Engineering Management Capstone Description Candidate: Project Title: Knowledge Preservation in University Physical Plant Operations COMMITTEE Advisor: Member: Member: Problem Statement: (What is
How To Write A Thesis
 Thesis and Dissertation Formatting by Office of Graduate Studies Deadlines for Graduation Check the Office of Graduate Studies website (grad.mst.edu) for the deadline dates for the semester you plan on
Thesis and Dissertation Formatting by Office of Graduate Studies Deadlines for Graduation Check the Office of Graduate Studies website (grad.mst.edu) for the deadline dates for the semester you plan on
UNDERGRADUATE SENIOR PROJECT MANUAL
 Independent University, Bangladesh UNDERGRADUATE SENIOR PROJECT MANUAL Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Copyright Dept. of EEE, IUB Guidelines for senior project These guidelines may serve
Independent University, Bangladesh UNDERGRADUATE SENIOR PROJECT MANUAL Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Copyright Dept. of EEE, IUB Guidelines for senior project These guidelines may serve
Design & Drafting Services
 Design & Drafting Services 1. Mechanical CAD Services 1. Mechanical CAD Services Mechanical Design Services: Custom machine design Packaging machine design Mechanism design Machine tool design Material
Design & Drafting Services 1. Mechanical CAD Services 1. Mechanical CAD Services Mechanical Design Services: Custom machine design Packaging machine design Mechanism design Machine tool design Material
COURSE DELIVERY METHOD
 Public Safety Management Degree Program Syllabus for Community Risk Reduction for the Fire and Emergency Services UST 427, 3 Credit Hour Course, Spring Term 2014 PROFESSOR Bernard W. Becker, III, MS, EFO,
Public Safety Management Degree Program Syllabus for Community Risk Reduction for the Fire and Emergency Services UST 427, 3 Credit Hour Course, Spring Term 2014 PROFESSOR Bernard W. Becker, III, MS, EFO,
This alignment chart was designed specifically for the use of Red River College. These alignments have not been verified or endorsed by the IIBA.
 Red River College Course Learning Outcome Alignment with BABOK Version 2 This alignment chart was designed specifically for the use of Red River College. These alignments have not been verified or endorsed
Red River College Course Learning Outcome Alignment with BABOK Version 2 This alignment chart was designed specifically for the use of Red River College. These alignments have not been verified or endorsed
Universal Design Principles Checklist
 Universal Design Principles Checklist The concept of Universal Design was developed by people who worked on designing equipment and environments for people with a disability. They saw that it was more
Universal Design Principles Checklist The concept of Universal Design was developed by people who worked on designing equipment and environments for people with a disability. They saw that it was more
WRITING EFFECTIVE REPORTS AND ESSAYS
 WRITING EFFECTIVE REPORTS AND ESSAYS A. What are Reports? Writing Effective Reports Reports are documents which both give a reader information and ask the reader to do something with that information.
WRITING EFFECTIVE REPORTS AND ESSAYS A. What are Reports? Writing Effective Reports Reports are documents which both give a reader information and ask the reader to do something with that information.
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP ) - Practice Standard and Certification Overview
 PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP ) - Practice Standard and Certification Overview Sante Torino PMI-RMP, IPMA Level B Head of Risk Management Major Programmes, Selex ES / Land&Naval Systems Division
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP ) - Practice Standard and Certification Overview Sante Torino PMI-RMP, IPMA Level B Head of Risk Management Major Programmes, Selex ES / Land&Naval Systems Division
How To Develop Software
 Software Engineering Prof. N.L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture-4 Overview of Phases (Part - II) We studied the problem definition phase, with which
Software Engineering Prof. N.L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture-4 Overview of Phases (Part - II) We studied the problem definition phase, with which
Guidelines and Requirements for Writing a Research Paper
 Guidelines and Requirements for Writing a Research Paper Professor Hossein Saiedian Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science School of Engineering University of Kansas saiedian@eecs.ku.edu
Guidelines and Requirements for Writing a Research Paper Professor Hossein Saiedian Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science School of Engineering University of Kansas saiedian@eecs.ku.edu
Sustainable Energy Design Project (SEDP) Information
 Sustainable Energy Design Project (SEDP) Information Introduction Today, the call for a focused effort to research and design alternative means of energy production in the United States and the rest of
Sustainable Energy Design Project (SEDP) Information Introduction Today, the call for a focused effort to research and design alternative means of energy production in the United States and the rest of
MIDLANDS STATE UNIVERSITY
 MIDLANDS STATE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT.../.../2011 Preamble Students are expected to produce a fully functional Dissertation projects
MIDLANDS STATE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT.../.../2011 Preamble Students are expected to produce a fully functional Dissertation projects
A Guide to the ABAG Grant Proposal Format
 A Guide to the ABAG Grant Proposal Format The following document is not a form to be completed, but an outline and advice for writing a grant proposal developed by a task force of grantmakers and nonprofit
A Guide to the ABAG Grant Proposal Format The following document is not a form to be completed, but an outline and advice for writing a grant proposal developed by a task force of grantmakers and nonprofit
UNIT 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN GAME DESIGN
 UNIT 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN GAME DESIGN UNIT 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN GAME DESIGN 2.A: Unit Overview 2.B: Instructional Resource Guide 2.C: Learning Activities Guide 2.D: Standards Alignment Guide 2.E:
UNIT 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN GAME DESIGN UNIT 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN GAME DESIGN 2.A: Unit Overview 2.B: Instructional Resource Guide 2.C: Learning Activities Guide 2.D: Standards Alignment Guide 2.E:
Higher Degree by Research Thesis Presentation - Guidelines
 Higher Degree by Research Thesis Presentation - Guidelines Introduction These Guidelines apply to theses prepared for Higher Degrees by Research (HDR). HDR candidates at the University of the Sunshine
Higher Degree by Research Thesis Presentation - Guidelines Introduction These Guidelines apply to theses prepared for Higher Degrees by Research (HDR). HDR candidates at the University of the Sunshine
PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY SECTION 3 -- PLANNING PHASE
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY SECTION 3 -- PLANNING PHASE Table of Contents Introduction...3-1 Overview...3-1 The Process and the Project Plan...3-1 Project Objectives and Scope...3-1 Work Breakdown Structure...3-1
PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY SECTION 3 -- PLANNING PHASE Table of Contents Introduction...3-1 Overview...3-1 The Process and the Project Plan...3-1 Project Objectives and Scope...3-1 Work Breakdown Structure...3-1
Continuous Risk Management Guidebook
 Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute Continuous Guidebook Audrey J. Dorofee Julie A. Walker Christopher J. Alberts Ronald P. Higuera Richard L. Murphy Ray C. Williams The ideas and findings in
Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute Continuous Guidebook Audrey J. Dorofee Julie A. Walker Christopher J. Alberts Ronald P. Higuera Richard L. Murphy Ray C. Williams The ideas and findings in
Revised 4/2/09. Practicum Guidelines
 Revised 4/2/09 Practicum Guidelines Practicum Overview Purpose The practicum provides a structured public health practice experience whereby students can take a population based approach to a public health
Revised 4/2/09 Practicum Guidelines Practicum Overview Purpose The practicum provides a structured public health practice experience whereby students can take a population based approach to a public health
Product Design and Technology 21 st March 12 th July 2015
 Product Design and Technology 21 st March 12 th July 2015 School Assessed Task -SAT Design folio Production and Record of Progress Evaluation report, Care label & Presentation Contributes to 50% of Unit
Product Design and Technology 21 st March 12 th July 2015 School Assessed Task -SAT Design folio Production and Record of Progress Evaluation report, Care label & Presentation Contributes to 50% of Unit
For <Project> Version 1.0
 Oklahoma Department of Human Services Data Services Division Enterprise Single Sign-On System Implementation Plan For Version 1.0 Enterprise Single Sign-On System Implementation
Oklahoma Department of Human Services Data Services Division Enterprise Single Sign-On System Implementation Plan For Version 1.0 Enterprise Single Sign-On System Implementation
(Note: Each of the above sections in your report should begin on a new page.)
 MY ENGINEERING DESIGN REPORT TEMPLATE 1) Title Page 2) Table of Contents 3) The Engineering Problem 4) Evaluation of Alternative Designs 5) The Design 6) Prototype 7) Test Data 8) Analysis & Conclusions
MY ENGINEERING DESIGN REPORT TEMPLATE 1) Title Page 2) Table of Contents 3) The Engineering Problem 4) Evaluation of Alternative Designs 5) The Design 6) Prototype 7) Test Data 8) Analysis & Conclusions
GUIDELINES FOR MASTER OF SCIENCE INTERNSHIP THESIS
 GUIDELINES FOR MASTER OF SCIENCE INTERNSHIP THESIS Dear Participant of the MScIS Program, If you have chosen to follow an internship, one of the requirements is to write a Thesis. This document gives you
GUIDELINES FOR MASTER OF SCIENCE INTERNSHIP THESIS Dear Participant of the MScIS Program, If you have chosen to follow an internship, one of the requirements is to write a Thesis. This document gives you
Answers to Review Questions
 Tutorial 2 The Database Design Life Cycle Reference: MONASH UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA Faculty of Information Technology FIT1004 Database Rob, P. & Coronel, C. Database Systems: Design, Implementation & Management,
Tutorial 2 The Database Design Life Cycle Reference: MONASH UNIVERSITY AUSTRALIA Faculty of Information Technology FIT1004 Database Rob, P. & Coronel, C. Database Systems: Design, Implementation & Management,
GUIDE TO BUSINESS REPORT WRITING
 F - PURPOSE OF BUSINESS REPORTS A business report conveys information to assist in business decision-making. The business report is the medium in which to present this information. Some reports might present
F - PURPOSE OF BUSINESS REPORTS A business report conveys information to assist in business decision-making. The business report is the medium in which to present this information. Some reports might present
System Engineering Plan
 Project Documentation Document SPEC-0064 Revision A System Engineering Plan Rob Hubbard, Jeremy Wagner, Larry Daggert, Larry Stepp, Christoph Keller Systems Engineering / Project Management 5 October 2006
Project Documentation Document SPEC-0064 Revision A System Engineering Plan Rob Hubbard, Jeremy Wagner, Larry Daggert, Larry Stepp, Christoph Keller Systems Engineering / Project Management 5 October 2006
Finding the Right People for Your Program Evaluation Team: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions
 : Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
Writing Reports BJECTIVES ONTENTS. By the end of this section you should be able to :
 Writing Reports By the end of this section you should be able to : O BJECTIVES Understand the purposes of a report Plan a report Understand the structure of a report Collect information for your report
Writing Reports By the end of this section you should be able to : O BJECTIVES Understand the purposes of a report Plan a report Understand the structure of a report Collect information for your report
FORMAT OF THE PROPOSAL FOR A THESIS Revised and adapted from Practical Guide to Research Methods by Lang and Heiss.
 THESIS PROPOSAL The proposal should describe what you propose to do for your research study. It should include: (a) your name; (b) date submitted; (c) a tentative title; (d) the problem; (e) the purpose
THESIS PROPOSAL The proposal should describe what you propose to do for your research study. It should include: (a) your name; (b) date submitted; (c) a tentative title; (d) the problem; (e) the purpose
Mechanical Design/Product Design Process
 Mechanical Design/Product Design Process Several Major Steps: Define project and its planning Identify customers (users) and their needs Evaluate existing similar products (benchmarking) Generate engineering
Mechanical Design/Product Design Process Several Major Steps: Define project and its planning Identify customers (users) and their needs Evaluate existing similar products (benchmarking) Generate engineering
Nine Probation Officer Competencies. Alberta Justice & Solicitor General
 Nine Probation Officer Competencies 2014 Officer 1. Managing Information & People The ability to interact with others to access, retrieve, input analyze, apply, interpret and process information for investigative
Nine Probation Officer Competencies 2014 Officer 1. Managing Information & People The ability to interact with others to access, retrieve, input analyze, apply, interpret and process information for investigative
Develop Project Charter. Develop Project Management Plan
 Develop Charter Develop Charter is the process of developing documentation that formally authorizes a project or a phase. The documentation includes initial requirements that satisfy stakeholder needs
Develop Charter Develop Charter is the process of developing documentation that formally authorizes a project or a phase. The documentation includes initial requirements that satisfy stakeholder needs
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM
 APPROVED BY Protocol No. 18-02-2016 Of 18 February 2016 of the Studies Commission meeting REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Vilnius 2016-2017 1 P a g e
APPROVED BY Protocol No. 18-02-2016 Of 18 February 2016 of the Studies Commission meeting REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Vilnius 2016-2017 1 P a g e
CATIA Drafting TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Drafting...2 Drawing Screen...3 Pull-down Menus...4 File...4 Edit...5 View...6 Insert...7 Tools...8 Drafting Workbench...9 Views and Sheets...9 Dimensions and Annotations...10
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Drafting...2 Drawing Screen...3 Pull-down Menus...4 File...4 Edit...5 View...6 Insert...7 Tools...8 Drafting Workbench...9 Views and Sheets...9 Dimensions and Annotations...10
STUDENT S PACKET FOR THE SCIENCE FAIR PROJECT
 STUDENT S PACKET FOR THE SCIENCE FAIR PROJECT SCIENCE PROJECT STEPS 1. Choose a topic. Be sure it interests you. Don t pick one because you think it will be easy. Talk it over with your parents and when
STUDENT S PACKET FOR THE SCIENCE FAIR PROJECT SCIENCE PROJECT STEPS 1. Choose a topic. Be sure it interests you. Don t pick one because you think it will be easy. Talk it over with your parents and when
Appendix E. A Guide to Writing an Effective. Executive Summary. Navy and Marine Corps Public Health Center Environmental Programs
 Appendix E A Guide to Writing an Effective Executive Summary Navy and Marine Corps Public Health Center Environmental Programs MISSION Ensure Navy and Marine Corps readiness through leadership in prevention
Appendix E A Guide to Writing an Effective Executive Summary Navy and Marine Corps Public Health Center Environmental Programs MISSION Ensure Navy and Marine Corps readiness through leadership in prevention
Design for Six Sigma +Lean Toolset
 Stephan Lunau (Ed.) Christian Staudter Jens-Peter Mollenhauer Renata Meran Olin Roenpage Clemens von Hugo Alexis Hamalides Design for Six Sigma +Lean Toolset Implementing Innovations Successfully 4y Springer
Stephan Lunau (Ed.) Christian Staudter Jens-Peter Mollenhauer Renata Meran Olin Roenpage Clemens von Hugo Alexis Hamalides Design for Six Sigma +Lean Toolset Implementing Innovations Successfully 4y Springer
2. SUMMER ADVISEMENT AND ORIENTATION PERIODS FOR NEWLY ADMITTED FRESHMEN AND TRANSFER STUDENTS
 Chemistry Department Policy Assessment: Undergraduate Programs 1. MISSION STATEMENT The Chemistry Department offers academic programs which provide students with a liberal arts background and the theoretical
Chemistry Department Policy Assessment: Undergraduate Programs 1. MISSION STATEMENT The Chemistry Department offers academic programs which provide students with a liberal arts background and the theoretical
Running head: RESEARCH PROPOSAL GUIDELINES: APA STYLE. APA Style: An Example Outline of a Research Proposal. Your Name
 Research Proposal Guidelines: APA Style - 1 Running head: RESEARCH PROPOSAL GUIDELINES: APA STYLE APA Style: An Example Outline of a Research Proposal Your Name School of Health & Applied Human Sciences
Research Proposal Guidelines: APA Style - 1 Running head: RESEARCH PROPOSAL GUIDELINES: APA STYLE APA Style: An Example Outline of a Research Proposal Your Name School of Health & Applied Human Sciences
ME2110 Lecture 9 : Concept Evaluation (ctnd.) Technical Design Presentations (ctnd.)
 ME2110 Lecture 9 : Concept Evaluation (ctnd.) Technical Design Presentations (ctnd.) GIT Outline 1. Review Design Phases Covered Problem Understanding, Design Specification 2. Concept Generation (review)
ME2110 Lecture 9 : Concept Evaluation (ctnd.) Technical Design Presentations (ctnd.) GIT Outline 1. Review Design Phases Covered Problem Understanding, Design Specification 2. Concept Generation (review)
BUSINESS WRITING: LETTERS, E-MAILS, REPORTS, CASES, AND PRESENTATIONS
 BUSINESS WRITING: LETTERS, E-MAILS, REPORTS, CASES, AND PRESENTATIONS WHY IS EXCELLENT PROFESSIONAL WRITING SO IMPORTANT TO YOU? Hiring a new employee is expensive, and companies often evaluate their recruiters
BUSINESS WRITING: LETTERS, E-MAILS, REPORTS, CASES, AND PRESENTATIONS WHY IS EXCELLENT PROFESSIONAL WRITING SO IMPORTANT TO YOU? Hiring a new employee is expensive, and companies often evaluate their recruiters
M PHIL IN CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO GUIDELINE FOR DISSERTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 M PHIL IN CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO GUIDELINE FOR DISSERTATION Below are prescribed guidelines to follow when presenting your dissertation towards the
M PHIL IN CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO GUIDELINE FOR DISSERTATION Below are prescribed guidelines to follow when presenting your dissertation towards the
Example of Tollgate-Based Project Management Template from Industry
 Example of Tollgate-Based Project Management Template from Industry Tollgate Project Management Process: Define tollgates and checklist items to be completed for each tollgate Project reviews are based
Example of Tollgate-Based Project Management Template from Industry Tollgate Project Management Process: Define tollgates and checklist items to be completed for each tollgate Project reviews are based
Technical writing tutorial
 Technical writing tutorial Purpose: To learn how to communicate technical information in writing. Importance: The main modes of communication are written, verbal, and visual. As a scientist or engineer,
Technical writing tutorial Purpose: To learn how to communicate technical information in writing. Importance: The main modes of communication are written, verbal, and visual. As a scientist or engineer,
The Grant Writing Game
 101 Ways to Win The Grant Writing Game by Steve Price, Ed.D. and Stephen Price, M.A. Introduction In this brief ebook, Dr. Steve Price and Stephen Price share 101 strategies for successful grant writing
101 Ways to Win The Grant Writing Game by Steve Price, Ed.D. and Stephen Price, M.A. Introduction In this brief ebook, Dr. Steve Price and Stephen Price share 101 strategies for successful grant writing
MULTIPLE-OBJECTIVE DECISION MAKING TECHNIQUE Analytical Hierarchy Process
 MULTIPLE-OBJECTIVE DECISION MAKING TECHNIQUE Analytical Hierarchy Process Business Intelligence and Decision Making Professor Jason Chen The analytical hierarchy process (AHP) is a systematic procedure
MULTIPLE-OBJECTIVE DECISION MAKING TECHNIQUE Analytical Hierarchy Process Business Intelligence and Decision Making Professor Jason Chen The analytical hierarchy process (AHP) is a systematic procedure
A Case Study in Software Enhancements as Six Sigma Process Improvements: Simulating Productivity Savings
 A Case Study in Software Enhancements as Six Sigma Process Improvements: Simulating Productivity Savings Dan Houston, Ph.D. Automation and Control Solutions Honeywell, Inc. dxhouston@ieee.org Abstract
A Case Study in Software Enhancements as Six Sigma Process Improvements: Simulating Productivity Savings Dan Houston, Ph.D. Automation and Control Solutions Honeywell, Inc. dxhouston@ieee.org Abstract
National Education Technology Standards
 National Education Technology Standards Objectives Satisfied by Each Deliverable in the Program 1 Basic operations and concept Students demonstrate a sound understanding of the nature and operation of
National Education Technology Standards Objectives Satisfied by Each Deliverable in the Program 1 Basic operations and concept Students demonstrate a sound understanding of the nature and operation of
TECHNICAL REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES
 TECHNICAL REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES Prepared by LEAH M. AKINS and JEFFERSON H. AKINS for TECHNICAL/ENGINEERING STUDENTS ABSTRACT This document specifies the recommended format to be used when submitting
TECHNICAL REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES Prepared by LEAH M. AKINS and JEFFERSON H. AKINS for TECHNICAL/ENGINEERING STUDENTS ABSTRACT This document specifies the recommended format to be used when submitting
Using the Thesis and Dissertation Templates
 Using the Thesis and Dissertation Templates For use with Microsoft Word on Windows and Macintosh computers January 2011 Graduate School e-mail: bpenman@austin.utexas.edu 2011 Graduate School Revised January
Using the Thesis and Dissertation Templates For use with Microsoft Word on Windows and Macintosh computers January 2011 Graduate School e-mail: bpenman@austin.utexas.edu 2011 Graduate School Revised January
BOOK REVIEW A REVIEW OF THE SECOND EDITION OF SCHOLARLY WRITING FOR LAW STUDENTS: SEMINAR PAPERS, LAW REVIEW NOTES, AND LAW REVIEW COMPETITION PAPERS
 BOOK REVIEW A REVIEW OF THE SECOND EDITION OF SCHOLARLY WRITING FOR LAW STUDENTS: SEMINAR PAPERS, LAW REVIEW NOTES, AND LAW REVIEW COMPETITION PAPERS David S. Romantz * Most legal educators would agree
BOOK REVIEW A REVIEW OF THE SECOND EDITION OF SCHOLARLY WRITING FOR LAW STUDENTS: SEMINAR PAPERS, LAW REVIEW NOTES, AND LAW REVIEW COMPETITION PAPERS David S. Romantz * Most legal educators would agree
<name of project> Software Project Management Plan
 The document in this file is adapted from the IEEE standards for Software Project Management Plans, 1058-1998, which conforms to the requirements of ISO standard 12207 Software Life Cycle Processes. Tailor
The document in this file is adapted from the IEEE standards for Software Project Management Plans, 1058-1998, which conforms to the requirements of ISO standard 12207 Software Life Cycle Processes. Tailor
Continuous Improvement Toolkit
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Mind Mapping Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholder Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost Benefit Analysis PEST PERT/CPM
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Mind Mapping Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholder Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost Benefit Analysis PEST PERT/CPM
Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Language Arts Curriculum and Assessment Alignment Form Rewards Intermediate Grades 4-6
 Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Language Arts Curriculum and Assessment Alignment Form Rewards Intermediate Grades 4-6 4 I. READING AND LITERATURE A. Word Recognition, Analysis, and Fluency The student
Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Language Arts Curriculum and Assessment Alignment Form Rewards Intermediate Grades 4-6 4 I. READING AND LITERATURE A. Word Recognition, Analysis, and Fluency The student
FINAL-YEAR PROJECT REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES
 FINAL-YEAR PROJECT REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES Expected Content...2 Content summary... 4 Example Layout...5 Report Format... 6 Stylistic And Grammar Advice... 9 Useful Web Based Resources... 10 FINAL-YEAR
FINAL-YEAR PROJECT REPORT WRITING GUIDELINES Expected Content...2 Content summary... 4 Example Layout...5 Report Format... 6 Stylistic And Grammar Advice... 9 Useful Web Based Resources... 10 FINAL-YEAR
Value to the Mission. FEA Practice Guidance. Federal Enterprise Architecture Program Management Office, OMB
 Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
Guidelines for the master s thesis
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Guidelines for the master s thesis 1. Introduction Every master s degree requires the fulfillment of a master s thesis. The master s thesis consists of a personal and original manuscript
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Guidelines for the master s thesis 1. Introduction Every master s degree requires the fulfillment of a master s thesis. The master s thesis consists of a personal and original manuscript
Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development. John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE
 Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE Overview Introduction and Definitions Part 1: Lean Product Development Lean vs. Traditional Product Development Key Elements
Ensuring Reliability in Lean New Product Development John J. Paschkewitz, P.E., CRE Overview Introduction and Definitions Part 1: Lean Product Development Lean vs. Traditional Product Development Key Elements
AMERICAN SOCIETY OF CIVIL ENGINEERS COMMENTARY. For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010
 COMMENTARY For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010 Purpose This document has been prepared by the ASCE Committee on Curriculum and Accreditation (CC&A). The purpose of this document
COMMENTARY For Architectural Engineering Programs Draft of September 2010 Purpose This document has been prepared by the ASCE Committee on Curriculum and Accreditation (CC&A). The purpose of this document
Process Models and Metrics
 Process Models and Metrics PROCESS MODELS AND METRICS These models and metrics capture information about the processes being performed We can model and measure the definition of the process process performers
Process Models and Metrics PROCESS MODELS AND METRICS These models and metrics capture information about the processes being performed We can model and measure the definition of the process process performers
QAD Business Intelligence Dashboards Demonstration Guide. May 2015 BI 3.11
 QAD Business Intelligence Dashboards Demonstration Guide May 2015 BI 3.11 Overview This demonstration focuses on one aspect of QAD Business Intelligence Business Intelligence Dashboards and shows how this
QAD Business Intelligence Dashboards Demonstration Guide May 2015 BI 3.11 Overview This demonstration focuses on one aspect of QAD Business Intelligence Business Intelligence Dashboards and shows how this
Guidelines for Writing An APA Style Lab Report
 Guidelines for Writing An APA Style Lab Report Research articles in psychology follow a specific format as set forth by the American Psychological Association (APA Style). The following sections describe
Guidelines for Writing An APA Style Lab Report Research articles in psychology follow a specific format as set forth by the American Psychological Association (APA Style). The following sections describe
I E 361. Jennifer Tapke Allyson Muller Greg Johnson Josh Sieck. House of Quality. Steps in Understanding the House of Quality
 I E 361 Jennifer Tapke Allyson Muller Greg Johnson Josh Sieck House of Quality Steps in Understanding the House of Quality House of Quality Steps in Understanding the House of Quality Introduction Every
I E 361 Jennifer Tapke Allyson Muller Greg Johnson Josh Sieck House of Quality Steps in Understanding the House of Quality House of Quality Steps in Understanding the House of Quality Introduction Every
Step 6: Report Your PHDS-PLUS Findings to Stimulate System Change
 Step 6: Report Your PHDS-PLUS Findings to Stimulate System Change Sharing information from the PHDS-PLUS can help you launch or strengthen partnerships and efforts to improve services, policies, and programs
Step 6: Report Your PHDS-PLUS Findings to Stimulate System Change Sharing information from the PHDS-PLUS can help you launch or strengthen partnerships and efforts to improve services, policies, and programs
Liberty High School Science Department Lab Report Format
 Liberty High School Science Department Lab Report Format General Information: 12 pt Times New Roman font Double Spaced 1 inch margins Always write in third person Write in Full Sentences except for the
Liberty High School Science Department Lab Report Format General Information: 12 pt Times New Roman font Double Spaced 1 inch margins Always write in third person Write in Full Sentences except for the
MStM Reading/Language Arts Curriculum Lesson Plan Template
 Grade Level: 6 th grade Standard 1: Students will use multiple strategies to read a variety of texts. Grade Level Objective: 1. A.6.1: compare/contrast the differences in fiction and non-fiction text.
Grade Level: 6 th grade Standard 1: Students will use multiple strategies to read a variety of texts. Grade Level Objective: 1. A.6.1: compare/contrast the differences in fiction and non-fiction text.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PROGRAMMER/ANALYST
 JOB DESCRIPTION MICHIGAN CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION JOB SPECIFICATION INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PROGRAMMER/ANALYST Employees in this job function as information technology professionals, participating in or
JOB DESCRIPTION MICHIGAN CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION JOB SPECIFICATION INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PROGRAMMER/ANALYST Employees in this job function as information technology professionals, participating in or
System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology. Approval CISSCO Program Director
 System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology Subject Type Standard Approval CISSCO Program Director A. PURPOSE This standard specifies content and format requirements for a Physical
System Development and Life-Cycle Management (SDLCM) Methodology Subject Type Standard Approval CISSCO Program Director A. PURPOSE This standard specifies content and format requirements for a Physical
Thesis and Dissertation Digital Handbook
 North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University Thesis and Dissertation Digital Handbook This style guide outlines the thesis/dissertation formatting requirements at NC A&T. The Graduate School
North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University Thesis and Dissertation Digital Handbook This style guide outlines the thesis/dissertation formatting requirements at NC A&T. The Graduate School
The Psychology Lab Checklist By: Danielle Sclafani 08 and Stephanie Anglin 10; Updated by: Rebecca Behrens 11
 The Psychology Lab Checklist By: Danielle Sclafani 08 and Stephanie Anglin 10; Updated by: Rebecca Behrens 11 1. Title Page My title is informative, mentioning both the independent and dependent variable(s).
The Psychology Lab Checklist By: Danielle Sclafani 08 and Stephanie Anglin 10; Updated by: Rebecca Behrens 11 1. Title Page My title is informative, mentioning both the independent and dependent variable(s).
The IFPUG Counting Practices On-Going Effort in Sizing Functional Requirements. Janet Russac
 The IFPUG Counting Practices On-Going Effort in Sizing Functional Requirements Janet Russac 2009 IFPUG s method for function point analysis is an ISO standard and must be conformant to ISO/IEC 14143-1:2007.
The IFPUG Counting Practices On-Going Effort in Sizing Functional Requirements Janet Russac 2009 IFPUG s method for function point analysis is an ISO standard and must be conformant to ISO/IEC 14143-1:2007.
Style Guide for Writing Online Custom Courses
 Style Guide for Writing Online Custom Courses 2 Introduction Web-based learning has become an integral component of most training programs because it is scalable and provides an economic advantage over
Style Guide for Writing Online Custom Courses 2 Introduction Web-based learning has become an integral component of most training programs because it is scalable and provides an economic advantage over
ANNA UNIVERSITY COIMBATORE
 ANNA UNIVERSITY COIMBATORE FORMAT FOR PREPARATION OF PROJECT REPORT FOR M.E/M.Tech /MCA/M.Sc/MBA CONTENTS 1. GENERAL 2. NUMBER OF COPIES TO BE SUBMITTED 3. SIZE OF PROJECT REPORT 4. ARRANGEMENT OF CONTENTS
ANNA UNIVERSITY COIMBATORE FORMAT FOR PREPARATION OF PROJECT REPORT FOR M.E/M.Tech /MCA/M.Sc/MBA CONTENTS 1. GENERAL 2. NUMBER OF COPIES TO BE SUBMITTED 3. SIZE OF PROJECT REPORT 4. ARRANGEMENT OF CONTENTS
Information Technology Systems 2012 Sample unit of work
 Information Technology Systems 2012 Sample unit of work Learning experiences Learning experiences support the educational goals of the subject and align with assessment. Learning experiences are student-based
Information Technology Systems 2012 Sample unit of work Learning experiences Learning experiences support the educational goals of the subject and align with assessment. Learning experiences are student-based
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Content Outline
 PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Content Outline Project Management Institute PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Content Outline Published by: Project Management Institute,
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Content Outline Project Management Institute PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP) Exam Content Outline Published by: Project Management Institute,
Standardized Technology Evaluation Process (STEP) User s Guide and Methodology for Evaluation Teams. Sarah Brown May 2007
 Standardized Technology Evaluation Process (STEP) User s Guide and Methodology for Evaluation Teams Sarah Brown May 2007 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Purpose 4 1.2 Background 5 1.3 Intended
Standardized Technology Evaluation Process (STEP) User s Guide and Methodology for Evaluation Teams Sarah Brown May 2007 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Purpose 4 1.2 Background 5 1.3 Intended
ISA CERTIFIED AUTOMATION PROFESSIONAL (CAP ) CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
 ISA CERTIFIED AUTOMATION PROFESSIONAL (CAP ) CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM Domain I: Feasibility Study - identify, scope and justify the automation project Task 1: Define the preliminary scope through currently
ISA CERTIFIED AUTOMATION PROFESSIONAL (CAP ) CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM Domain I: Feasibility Study - identify, scope and justify the automation project Task 1: Define the preliminary scope through currently
HOW TO WRITE A TECHNICAL REPORT. by Alan Smithee. A report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for. ME 000 Some Course
 HOW TO WRITE A TECHNICAL REPORT by Alan Smithee A report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for ME 000 Some Course Department of Mechanical Engineering Fictitious Institute of Technology
HOW TO WRITE A TECHNICAL REPORT by Alan Smithee A report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for ME 000 Some Course Department of Mechanical Engineering Fictitious Institute of Technology
Standards and progression point examples
 Design, Creativity and Technology In Design, Creativity and Technology, standards for assessing and reporting on student achievement are introduced at Level 3. The learning focus statements for Levels
Design, Creativity and Technology In Design, Creativity and Technology, standards for assessing and reporting on student achievement are introduced at Level 3. The learning focus statements for Levels
THESIS AND DISSERTATION FORMATTING GUIDE GRADUATE SCHOOL
 THESIS AND DISSERTATION FORMATTING GUIDE GRADUATE SCHOOL A Guide to the Preparation and Submission of Thesis and Dissertation Manuscripts in Electronic Form August 2015 Revised Fort Collins, Colorado 80523-1005
THESIS AND DISSERTATION FORMATTING GUIDE GRADUATE SCHOOL A Guide to the Preparation and Submission of Thesis and Dissertation Manuscripts in Electronic Form August 2015 Revised Fort Collins, Colorado 80523-1005
Information Technology Systems (2012)
 Information Technology Systems (2012) Sample work program April 2012 Information Technology Systems (2012) Sample work program Compiled by the Queensland Studies Authority April 2012 This work program
Information Technology Systems (2012) Sample work program April 2012 Information Technology Systems (2012) Sample work program Compiled by the Queensland Studies Authority April 2012 This work program
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_engineering/software_engineering_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these Software Engineering
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_engineering/software_engineering_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these Software Engineering
G102 Graphic Design MTCU Code 61820 MTCU Program Name- Advanced Graphic Design Program Learning Outcomes
 G102 Graphic Design MTCU Code 61820 MTCU Program Name- Advanced Graphic Design Program Learning Outcomes Synopsis of the Vocational Learning Outcomes* The graduate has reliably demonstrated the ability
G102 Graphic Design MTCU Code 61820 MTCU Program Name- Advanced Graphic Design Program Learning Outcomes Synopsis of the Vocational Learning Outcomes* The graduate has reliably demonstrated the ability
GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION, CONTENT & EVALUATION OF TECHNICAL REPORTS
 GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION, CONTENT & EVALUATION OF TECHNICAL REPORTS OBJECTIVE This document is intended to aid in the preparation and review of Technical reports prepared by applicants to CTTAM as required
GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION, CONTENT & EVALUATION OF TECHNICAL REPORTS OBJECTIVE This document is intended to aid in the preparation and review of Technical reports prepared by applicants to CTTAM as required
Guidelines for Preparing an Undergraduate Thesis Proposal Department of Agricultural Education and Communication University of Florida
 Guidelines for Preparing an Undergraduate Thesis Proposal Department of Agricultural Education and Communication University of Florida What is a thesis? In our applied discipline of agricultural education
Guidelines for Preparing an Undergraduate Thesis Proposal Department of Agricultural Education and Communication University of Florida What is a thesis? In our applied discipline of agricultural education
Certified Software Quality Engineer (CSQE) Body of Knowledge
 Certified Software Quality Engineer (CSQE) Body of Knowledge The topics in this Body of Knowledge include additional detail in the form of subtext explanations and the cognitive level at which the questions
Certified Software Quality Engineer (CSQE) Body of Knowledge The topics in this Body of Knowledge include additional detail in the form of subtext explanations and the cognitive level at which the questions
APPENDIX T: GUIDELINES FOR A THESIS RESEARCH PROPOSAL. Masters of Science Clinical Laboratory Sciences Program
 APPENDIX T: GUIDELINES FOR A THESIS RESEARCH PROPOSAL Masters of Science Clinical Laboratory Sciences Program Name of Candidate:..... Name of Thesis Director:. Track :... I. Topic of research proposal
APPENDIX T: GUIDELINES FOR A THESIS RESEARCH PROPOSAL Masters of Science Clinical Laboratory Sciences Program Name of Candidate:..... Name of Thesis Director:. Track :... I. Topic of research proposal
For <Project> Version 1.0
 Oklahoma Department of Human Services Data Services Division Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) For Version 1.0 Table of Contents 1. Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) Scope...
Oklahoma Department of Human Services Data Services Division Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) For Version 1.0 Table of Contents 1. Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) Scope...
Software Project Management Plan (SPMP)
 Software Project Management Plan (SPMP) The basic template to be used is derived from IEEE Std 1058-1998, IEEE Standard for Software Project Management Plans. The following is a template for the SPMP.
Software Project Management Plan (SPMP) The basic template to be used is derived from IEEE Std 1058-1998, IEEE Standard for Software Project Management Plans. The following is a template for the SPMP.
Business Plan Template Telling the story of your business
 Business Plan Template Telling the story of your business Business focus: Retention driven 1 Business Plan Template Introduction The big day is here! You are about to begin the writing of your business
Business Plan Template Telling the story of your business Business focus: Retention driven 1 Business Plan Template Introduction The big day is here! You are about to begin the writing of your business
