Understanding and Treating Heart Failure
|
|
|
- Ronald Lyons
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL CARDIOVASCULAR CENTER Understanding and Treating Heart Failure A Guide for Patients and Families
2 This guide was written by the members of the Advanced Heart Disease Program at Brigham and Women s Hospital to help you understand heart failure. We hope the information will help you care for yourself. Be sure to discuss any questions or concerns you may with your care providers as you read through this guide. TAKE HEART AND TAKE CHARGE. You will feel better if you, in partnership with your doctor or nurse, take charge of your heart failure.
3 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure Table of Contents Understanding Heart Failure...2 What is heart failure? How does the normal heart work? What happens in heart failure? What causes heart failure? What are the symptoms of heart failure? Diagnosing Heart Failure...4 How does your doctor know if you have heart failure? Tests you may have Treating Heart Failure...6 How is heart failure treated? Take your medication Eat low sodium (low salt) food Watch fluid intake Exercise every day Make lifestyle changes Looking Ahead...11 New Treatments
4 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure 2 Understanding Heart Failure What is heart failure? Heart failure is often misunderstood. Many people think heart failure means that their heart will stop beating. If you have heart failure, it means that your heart has lost some of its ability to pump blood. There are two kinds of heart failure. In the first kind, the heart muscle has weakened and cannot pump enough blood out with each beat. This is called systolic heart failure. In the second kind, the heart pumps normally but the heart muscle has become stiff. Your heart has lost its ability to relax and does not completely fill with blood. This is called diastolic heart failure. Don t be discouraged by the word failure. For most patients, heart failure cannot be cured, but you can help to keep it from getting worse or even make it better by taking your medicine, eating the right foods, watching your fluids and exercising. If you take care of your heart, you can feel better and enjoy life more. How does the normal heart work? The heart is a muscle. It has four chambers that pump blood. The upper two chambers are called the atria and the lower two chambers are called the ventricles. The heart is really two pumps that work together to move blood through the body. The right-sided pump fills with blood returning from the body and pumps it to the lungs to receive oxygen. This rightsided pump is a thinner muscle than the left-sided pump because it only has to pump blood to the lungs. The left side of the heart receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to all parts of the body. This left-sided pump is a thick, strong muscle. The heart has an electrical system that sends impulses to tell the heart muscle when to pump. What happens in heart failure? Right atrium From upper body From lower body To upper body Right ventricle To lower body To lungs Left atrium From lungs If you have heart failure, your heart may not pump enough blood to the lungs and other parts of the body during activity. This causes a shortage of oxygen and nutrients in the blood that may make you feel weak and tired. When the heart is not pumping well, it can cause a backup of blood. This backup of blood causes fluid to leak from the blood vessels into the tissues. This is called congestion. In the lungs, congestion may lead to difficulty breathing. In the ankles and legs, the congestion or backup of fluid causes swelling. In the belly, congestion may cause fullness or loss of appetite. Left ventricle
5 What causes heart failure? Any disease that weakens the heart muscle can lead to heart failure. The most common causes of heart failure are: Blockages in the blood vessels that may lead to a heart attack High blood pressure that may cause diastolic heart failure Disease of the heart valves Diabetes Infections of the heart muscle Cancer drugs Genetic abnormalities that run in families In many cases, the cause is never known. When the cause cannot be found, it is called Idiopathic Cardiomyopathy. (i-dee-o-path ik CAR-dee-o-my-OP-a-thee) What is the cause of my heart failure? Heart Lungs Kidneys & Bladder What are the symptoms of heart failure? Many of the symptoms of heart failure can also be symptoms of other medical problems. Do you have any of the following symptoms? Weight gain of more than 2 pounds overnight or 5 pounds in a week Shortness of breath after climbing a flight of stairs or getting dressed Difficulty breathing when lying down Cough Weakness or tiredness Swelling in your ankles or legs Loss of appetite Belly pain and fullness Swelling in ankles or legs If you develop any of these symptoms or they are getting worse, call your doctor or nurse. 3
6 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure Diagnosing Heart Failure How does your doctor know if you have heart failure? The first clues of heart failure are shortness of breath or feeling weak with activity. If your doctor thinks you have heart failure, some tests may be needed. These tests help your doctor find out the cause of your symptoms and decide the best treatment for you. Tests you may have Electrocardiogram (ee-lek-tro-kar-dee-o-gram), also called EKG or ECG, records the electrical activity of your heart. It may show irregular beats or abnormal areas of the heart. Echocardiogram (eh-ko-kar-dee-o-gram), often called Echo, is an ultrasound of your heart. It uses sound waves to measure the heart s size and shape and looks at your heart valves. It also looks at how well your heart fills with blood and how well it pumps. This is known as the ejection fraction. Your ejection fraction is the percentage or amount of blood pumped with each heartbeat. The normal ejection fraction is between 55% and 70%. This number is often lower in patients who have heart failure. Chest X-ray is a picture of your heart and lungs. Your doctor can see if your heart is enlarged or if there is a lot of fluid in your lungs. MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mag-net-ik REZ-o-nans IM-a-jing) uses a combination of radio waves in a magnetic field to produce a three-dimensional picture of your heart. The doctor can see the blood vessels and chambers of your heart in more detail. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (KAR-dee-o-PULL-moan-air-e) is a kind of stress test. This test measures the ability of your heart and lungs to deliver oxygen to the tissues of your body while you exercise. During this stress test, you will pedal a bicycle or walk on a treadmill and use a mouthpiece to breathe. MIBI Stress Test (mi-bee) is another type of stress test. This is a test to find out how well your heart muscle is supplied with blood when you are at rest and when you exercise. PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scan (POZ-e-tron e-mish-un tom-og-rafee) is another test to measure the blood flow to the heart muscle and to look for signs of blockages in the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. This test also looks for small areas of the heart that need oxygen and may be damaged but are still alive. Blood Tests may be taken to find out possible causes of your heart failure. 4
7 Heart Catheterization is done under sterile conditions in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory (also called the Cath Lab ), which looks very much like an operating room. There are two kinds of heart catheterization: Right heart catheterization - a small plastic tube called a catheter is inserted into a vein in your neck or leg. The doctor can measure blood pressures and blood flow in the right side of your heart. Sometimes a small piece of tissue called a biopsy is taken from the heart during the procedure and examined to determine a possible cause of your heart failure. Left heart catheterization a small plastic tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery in your groin or wrist. Dye is then injected into your coronary arteries. Coronary arteries are blood vessels located around the outside of your heart that supply oxygen to the heart muscle itself. The dye outlines the coronary arteries so your doctor can see them on x-ray and check for blockages. Left coronary artery Right coronary artery Circumflex artery Left anterior descending artery Posterior descending artery 5
8 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure Treating Heart Failure How is heart failure treated? There is no cure for heart failure, but you can prevent your heart failure from getting worse and often help it get better. Here are some things that you can do to feel better. Take your medication Eat low sodium (low salt) food Watch your fluid intake Exercise Make lifestyle changes Weigh yourself every day Quit smoking Avoid alcohol Go to your doctor s appointments Take Your Medication Medication can control your heart failure symptoms such as difficulty breathing, weakness and swelling in your ankles and legs. Your doctor may prescribe some of the following medications. By taking your medication you will feel better and help prevent your symptoms from getting worse. Diuretics --- also called water pills When you take diuretics or water pills, you urinate more frequently. Diuretics help your kidneys remove salt and water from your bloodstream and decrease the water in your body. Three good things happen when you lower extra water in your body: It makes your breathing more comfortable. It makes the swelling in your ankles, legs, and belly go down. It makes it easier for your heart to pump. If too much water is lost you will become dehydrated. You may feel dizzy and weak as a result. 6 There are many different kinds of diuretics. Which diuretic or water pill are you taking? (furosemide) Lasix (torsemide) Demadex (bumetanide) Bumex (metolazone) Zaroxolyn (hydrochlorothiazide) HCTZ (spironolactone) Aldactone
9 Medicines that may help you live longer ACE Inhibitors ---- (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors) ACE Inhibitors help to prevent weakening and scarring of the heart, and may also protect your kidneys and blood vessels. These medications vasodilate or relax your blood vessels and may lower your blood pressure. Two good things happen when you lower your blood pressure: Your heart does not have to work as hard Your heart failure may not get worse and may even get better Are you taking an ACE Inhibitor? (enalapril) Vasotec (captopril) Capoten (ramipril) Altace (lisinopril) Prinivil, Zestril (quinapril) Accupril Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) Angiotensin Receptor Blockers are similar to ACE inhibitors and also may lower your blood pressure. Your doctor may order ARBs if you are unable to take an ACE inhibitor usually due to a cough. Are you taking an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB)? (losartan) Cozaar (valsartan) Diovan (irbesartan) Avapro (candesartan) Atacand Beta Blockers Beta Blockers help to protect the heart after injury and may improve heart function. By slowing your heart rate, beta blockers also give your heart more rest time between beats. Are you taking a Beta Blocker? (metoprolol) Lopressor, Toprol XL (carvedilol) Coreg 7
10 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure 8 Things you can do about your medication: Know the names of your medicines and what they do Know how often to take them Always carry your medication card with you Take your pills Call your doctor or nurse if You are about to run out of pills You are not able to take your pills You have side effects from your pills You start any new medication Eat Low Sodium (Low Salt) Food Sodium is a mineral that is used by the body in small amounts. Most people get most of their sodium from salt, which is contained in almost every food. When you eat sodium or salt, your body holds on to water, which can make your heart failure worse. Eating low sodium (low salt) food can make you feel better. A low sodium diet means eating between 2,000-3,000 milligrams (mg) of sodium per day. Ask your doctor or nurse what is right for you. Things you can do: Read food labels for the sodium amounts Choose foods low in sodium Eat: o Fresh fruit o Fresh vegetables o Fresh meat o Fresh fish This is an example of a high sodium food Things not to do: Do not eat any more than milligrams (mg) of sodium per day Do not put salt on your food Do not eat: o Cheese o Deli meat o Canned foods o Salted snack foods o Mixed spices with hidden sodium (salt) Your doctor, nurse, or dietician can help you choose foods that are low in sodium. They can help you change your favorite meals and recipes to be lower in sodium. Nutrition Facts Serving Size 1 pretzel (about 25g) Servings Per Container 20 Amount Per Serving Calories 90 Calories from Fat 0 % Daily Value* Total Fat 0g 0% Saturated Fat 0g 0% Cholesterol 0mg 0% Sodium 470mg 20% Total Carbohydrate 19g 6% Dietary Fiber less than 1g 4% Protein 1g Vitamin A Vitamin C Calcium Iron * Contains less than 2% of the Daily Value of these nutrients * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs: Calories 2, Total Fat Less than 45g 80g Sat Fat Less than 20g 25g Cholesterol Less than 300mg 300mg Sodium Less than 2,400mg 2,400mg Total Carbohydrate 300g 375g Dietary Fiber 25g 30g
11 Watch Fluid Intake You may need to limit your fluid intake to 2 liters / 2 quarts per day. If you need high doses of diuretics to get rid of fluid, it is important not to take in too much liquid. This will help prevent difficulty with breathing or swelling in your ankles or feet. Your doctor or nurse may want you to measure all of the fluids that you drink including anything that becomes liquid at room temperature. If it melts, like ice cream, it is a liquid. Ask your doctor or nurse what your fluid limit is. Things you can do if you need to limit fluids: Measure drinks in a measuring cup before you drink them Use gum or sugar free mints to quench your thirst Chill drinks to make them more refreshing Limit your fluids to Exercise Every Day Just because you were diagnosed with heart failure does not mean you should not exercise. In fact, your heart is a muscle and like any other muscle it needs to work to stay healthy. Exercise helps to strengthen your body. You should exercise every day. Talk to your doctor about your exercise plan before you start. The goal for most people with heart failure is to do 30 minutes of exercise each day. Remember to start slowly. Start by exercising 5 to 10 minutes a day. Increase the time of your exercise until you reach 30 minutes a day. When you have finished exercising, you should feel like you could still do more. If you feel wiped out, then you have done too much. Great ways to exercise are: Walking o Take a friend with you for company o During bad weather try walking at a mall Biking o Try a stationary bike Swimming o Join water aerobics at a health club or your community pool In the beginning, you may feel anxious about starting physical activities or you may feel too weak or tired to exercise. However, once you begin regular exercise, you will begin to feel better. By keeping active, you may be able to do more of the things you enjoy. Call your doctor or nurse if: You plan to start any kind of exercise program You are short of breath at rest or with mild activity You are tired for more than a day after a lot of activity 9
12 UNDERSTANDING AND TREATING Heart Failure Make Lifestyle Changes Choosing a heart healthy lifestyle means maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking and avoiding alcohol. Record Your Weight Every Day Weigh yourself every morning and write it down. Weight gain may signal that your body is holding on to water. This means your heart failure is getting worse. Things you can do: Weigh yourself every morning at the same time Write your weight on a calendar or chart Call your doctor or nurse if you gain more than two pounds overnight or more than five pounds in a week Quit Smoking Smoking is bad for everyone, but it is especially bad for people with heart failure. Smoking may make your heart failure worse. Quitting can be difficult, but you can do it! Things you can do if you smoke: Ask your doctor or nurse about the BWH Quit Smoking Program. Join a program in your community. You can visit or call TRY-TO-STOP ( ) for listings of services throughout New England. Avoid Alcohol Most doctors say avoid drinking alcohol if you have heart failure. Ask your doctor what is best for you. Follow-up with your Doctor and Nurse One of the best ways to take care of your heart is to keep in contact with your doctor or nurse. By closely watching your symptoms and calling your doctor or nurse with any changes, you may be able to prevent a hospital stay. 10 Things you can do: Keep in contact with your doctor or nurse. TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEART FAILURE!!!
13 Looking Ahead New Treatments There have been many new developments in treating heart failure. If medication and lifestyle changes are not enough to control your symptoms, your doctor may suggest: Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) A normal heart sends electrical signals to both lower chambers or ventricles of the heart to make them pump at the same time. Sometimes in heart failure patients, the two chambers do not pump together. A special pacemaker called CRT is a small battery-powered device that is placed under the skin that helps make the two sides of the heart beat together. It has special wires called leads that send tiny electrical signals to the heart telling the heart muscle when to pump. CRT is a pacemaker that tells both ventricles to pump at the same time, so it has leads on the right and left side of the heart. CRT can reduce your heart failure symptoms and increase your ability to exercise and be more active. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Some patients with heart failure have dangerously fast heartbeats called ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. This fast heartbeat can cause serious symptoms such as fainting or even death. An ICD is like a pacemaker that can be inserted under your skin. It can recognize a dangerous heart beat and send an electrical signal to the heart and return the heart back to a normal heartbeat. If your heart needs both a CRT and an ICD, they can be placed at the same time using one device. Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) A Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) is a mechanical pump inserted into your body to improve blood flow. If you have severe heart failure, your heart is unable to pump enough blood to your body s organs and tissues, and a VAD may be needed. You will need open heart surgery to implant the mechanical pump. The VAD works together with your own heart to pump more effectively. VADs can stabilize your heart condition and allow you to become stronger and feel better. This option may not be possible for everyone. Heart Transplantation Heart transplantation is an operation to replace a diseased heart with a healthy heart. Heart transplantation is a treatment used for severe heart failure when a patient may be at risk of dying. This is an option only for a few people who, except for their heart problem, are otherwise in very good health. Research and Clinical Studies Medical research is ongoing to discover new treatments, especially for heart failure. New surgical procedures are currently being done. In addition, research using stem cells and artificial hearts are in the early stages. There are several clinical studies involving drugs and mechanical devices that are underway which may bring new treatments in the future. Brigham and Women s Hospital participates in many clinical studies that are ongoing. If you are interested, you should ask your doctor or nurse about possibly enrolling in one of them. 11
14
15 Important Phone Numbers CALL WHO WHEN 911 Emergency If you are having a life threatening emergency Doctor: Nurse: If you have any of the following symptoms: Weight gain of 2 lbs. overnight Increased shortness of breath Difficulty breathing when lying down Increased weakness/tiredness Increased swelling in your legs and feet Loss of appetite Belly pain and fullness Brigham Medical Specialties To make or change appointments
16 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL 75 Francis Street Boston, MA (617)
SYMPTOMS Heart failure symptoms may vary and can be hard to detect. Symptoms may include:
 Heart Failure Heart failure is a condition in which the heart has trouble pumping blood. This means your heart does not pump blood efficiently for your body to work well. In some cases of heart failure,
Heart Failure Heart failure is a condition in which the heart has trouble pumping blood. This means your heart does not pump blood efficiently for your body to work well. In some cases of heart failure,
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PATIENT TEACHING
 CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PATIENT TEACHING What is Heart Failure? Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the heart loses its ability to pump enough blood to meet the body s needs. Because the heart is not
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PATIENT TEACHING What is Heart Failure? Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the heart loses its ability to pump enough blood to meet the body s needs. Because the heart is not
The Basics of Congestive Heart Failure...1. CHF & Medications...1. Nutrition and CHF...2. Worrying Symptoms of CHF...4
 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Basics of Congestive Heart Failure...1 CHF & Medications...1 Nutrition and CHF...2 Worrying Symptoms of CHF...4 Living with CHF: How to Stay Healthy and Avoid a Hospital Stay...4
TABLE OF CONTENTS The Basics of Congestive Heart Failure...1 CHF & Medications...1 Nutrition and CHF...2 Worrying Symptoms of CHF...4 Living with CHF: How to Stay Healthy and Avoid a Hospital Stay...4
CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet
 What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Congestive Heart Failure
 Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
COMPARING TWO KINDS OF BLOOD PRESSURE PILLS:
 COMPARING TWO KINDS OF BLOOD PRESSURE PILLS: ACEIs and ARBs A Guide for Adults Fast Facts ACEIs and ARBs are two of the many kinds of blood pressure pills. Both kinds of pills (ACEIs and ARBs) do a good
COMPARING TWO KINDS OF BLOOD PRESSURE PILLS: ACEIs and ARBs A Guide for Adults Fast Facts ACEIs and ARBs are two of the many kinds of blood pressure pills. Both kinds of pills (ACEIs and ARBs) do a good
CARDIOLOGIST What does a cardiologist do? A cardiologist is a doctor who specializes in caring for your heart and blood vessel health.
 YOUR TREATMENT TEAM CARDIOLOGIST What does a cardiologist do? A cardiologist is a doctor who specializes in caring for your heart and blood vessel health. To become a cardiologist, a doctor completes additional
YOUR TREATMENT TEAM CARDIOLOGIST What does a cardiologist do? A cardiologist is a doctor who specializes in caring for your heart and blood vessel health. To become a cardiologist, a doctor completes additional
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
 Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
A Patients Guide to Heart Failure
 A Patients Guide to Heart Failure Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Heart Failure The term heart failure means that your heart is weakened and is having difficulty in pumping as hard as it would
A Patients Guide to Heart Failure Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Heart Failure The term heart failure means that your heart is weakened and is having difficulty in pumping as hard as it would
Atrial Fibrillation Centre
 About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
LIVING WELL WITH HEART FAILURE
 JOHN MUIR HEALTH How Does a Healthy Heart Work? What is Heart Failure (HF)? Summary of How Heart Failure Develops How is Heart Failure Diagnosed? Ejection Fraction and Its Importance Is There a Cure for
JOHN MUIR HEALTH How Does a Healthy Heart Work? What is Heart Failure (HF)? Summary of How Heart Failure Develops How is Heart Failure Diagnosed? Ejection Fraction and Its Importance Is There a Cure for
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes:
 Prepared in collaboration with High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes: Are you at risk? Updated 2012 People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure. What is blood pressure? The force
Prepared in collaboration with High Blood Pressure in People with Diabetes: Are you at risk? Updated 2012 People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure. What is blood pressure? The force
Diabetes and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? TESTS TO DETECT OR DIAGNOSE KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR KIDNEY DISEASE
 Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Atrial Fibrillation. Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation. The Beat Goes On. Living with AFib. Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices.
 Atrial Fibrillation The Beat Goes On Living with AFib Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices. What is AFib? This booklet is for you if you have AFib, or if you are at risk for AFib. This booklet
Atrial Fibrillation The Beat Goes On Living with AFib Know Your Heart. Live Your Life. Know Your Choices. What is AFib? This booklet is for you if you have AFib, or if you are at risk for AFib. This booklet
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Let s talk about: Stroke
 Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
High blood pressure and stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk High blood pressure and stroke High blood pressure usually has no symptoms but it is the biggest risk factor for stroke. Both lifestyle changes and
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk High blood pressure and stroke High blood pressure usually has no symptoms but it is the biggest risk factor for stroke. Both lifestyle changes and
Cardiac Catheterization
 Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
About High Blood Pressure
 About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
How To Treat Dilated Cardiomyopathy
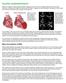 DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY Dilated or congestive cardiomyopathy (DCM) is diagnosed when the heart is enlarged (dilated) and the pumping chambers contract poorly (usually left side worse than right). A diagram
DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY Dilated or congestive cardiomyopathy (DCM) is diagnosed when the heart is enlarged (dilated) and the pumping chambers contract poorly (usually left side worse than right). A diagram
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Angioplasty and Stenting
 Understanding Angioplasty and Stenting Coronary Artery Disease Angioplasty and Stenting Procedures Risk Factor Management Help for Heart Problems You have been given this booklet because you have symptoms
Understanding Angioplasty and Stenting Coronary Artery Disease Angioplasty and Stenting Procedures Risk Factor Management Help for Heart Problems You have been given this booklet because you have symptoms
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Failure Clinical Pathway
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Heart Failure Clinical Pathway www.nshealth.ca Heart Failure Clinical Pathway Your hospital stay will follow a written care plan called a Clinical Pathway. The pathway is a
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Heart Failure Clinical Pathway www.nshealth.ca Heart Failure Clinical Pathway Your hospital stay will follow a written care plan called a Clinical Pathway. The pathway is a
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Treatment Approximately 5 million people about 2 percent of the U.S. population are affected by heart failure. Diabetes affects 20.8 million Americans and 65 million Americans
Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Treatment Approximately 5 million people about 2 percent of the U.S. population are affected by heart failure. Diabetes affects 20.8 million Americans and 65 million Americans
Cardiac Catheterization
 Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure From Heart Failure to Heart Success Understanding Heart Failure Table of Contents What is Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)? 4 (Part I) Symptoms of Heart Failure. Signs of Heart Failure.
Congestive Heart Failure From Heart Failure to Heart Success Understanding Heart Failure Table of Contents What is Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)? 4 (Part I) Symptoms of Heart Failure. Signs of Heart Failure.
www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND
 www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND Cardiomyopathy Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have cardiomyopathy. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart
www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND Cardiomyopathy Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have cardiomyopathy. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION. sacubitril/valsartan film-coated tablets
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr ENTRESTO TM sacubitril/valsartan film-coated tablets Read this carefully before you start taking ENTRESTO TM and
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr ENTRESTO TM sacubitril/valsartan film-coated tablets Read this carefully before you start taking ENTRESTO TM and
Heart Healthy Living
 Heart Healthy Living Objectives Understand basic functioning of the heart Understand cardiac risk factors Learn how to keep your heart healthy 2 How the Heart Works Muscular organ that pumps blood to your
Heart Healthy Living Objectives Understand basic functioning of the heart Understand cardiac risk factors Learn how to keep your heart healthy 2 How the Heart Works Muscular organ that pumps blood to your
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Managing your blood pressure
 Managing your blood pressure What is blood pressure? Blood pressure measures the force of blood against your artery walls. This pressure allows your blood to push out to other parts of your body for circulation.
Managing your blood pressure What is blood pressure? Blood pressure measures the force of blood against your artery walls. This pressure allows your blood to push out to other parts of your body for circulation.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Blood Pressure: Aim Low. inside this issue
 managingdiabetes fall 2012 inside this issue BE MINDFUL OF YOUR MEDICATIONS...3 PROTECT YOURSELF FROM STROKE...4 Blood Pressure: Aim Low As many as two out of three adults with diabetes also have high
managingdiabetes fall 2012 inside this issue BE MINDFUL OF YOUR MEDICATIONS...3 PROTECT YOURSELF FROM STROKE...4 Blood Pressure: Aim Low As many as two out of three adults with diabetes also have high
Supportive Cardiology: Living with Advanced Heart Failure A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES
 Supportive Cardiology: Living with Advanced Heart Failure A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES Table of contents Contact information...1 Advanced heart failure care at North York General Hospital...2 What
Supportive Cardiology: Living with Advanced Heart Failure A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES Table of contents Contact information...1 Advanced heart failure care at North York General Hospital...2 What
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Ventricular Assist Device Program. Patient Education Brochure
 Ventricular Assist Device Program Patient Education Brochure TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. How the Heart Works 3. Heart Disease and VADs 4. Alternative Treatments 5. The Implantation Procedure 6.
Ventricular Assist Device Program Patient Education Brochure TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. How the Heart Works 3. Heart Disease and VADs 4. Alternative Treatments 5. The Implantation Procedure 6.
Living with. Atrial Fibrillation
 Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
You may continue to use your old manuals by writing in the detailed changes below:
 STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation
 A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
IRISH HEART FOUNDATION. Living well with. Heart Failure
 IRISH HEART FOUNDATION Living well with Heart Failure Living Well with Heart Failure produced by the Irish Heart Foundation. This booklet is one of the publications in our Patient Information series. For
IRISH HEART FOUNDATION Living well with Heart Failure Living Well with Heart Failure produced by the Irish Heart Foundation. This booklet is one of the publications in our Patient Information series. For
HEART FAILURE ROBERT SOUFER, M.D.
 CHAPTER 14 HEART FAILURE ROBERT SOUFER, M.D. The heart s primary function is to pump blood to all parts of the body, bringing nutrients and oxygen to the tissues and removing waste products. When the body
CHAPTER 14 HEART FAILURE ROBERT SOUFER, M.D. The heart s primary function is to pump blood to all parts of the body, bringing nutrients and oxygen to the tissues and removing waste products. When the body
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women
 What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Your Results. For more information visit: www.sutton.gov.uk/healthchecks. Name: Date: In partnership with
 Your Results Name: Date: For more information visit: www.sutton.gov.uk/healthchecks In partnership with Introduction Everyone is at risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, stroke and
Your Results Name: Date: For more information visit: www.sutton.gov.uk/healthchecks In partnership with Introduction Everyone is at risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, stroke and
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
Myth vs. Reality: Diabetes Related
 Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1
 Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS
 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Surgery Scheduling Process
 Pre-op Instructions Our surgery scheduler will contact you within one week of leaving our office. Your availability for surgery will be determined during that phone call. Our scheduler will then call the
Pre-op Instructions Our surgery scheduler will contact you within one week of leaving our office. Your availability for surgery will be determined during that phone call. Our scheduler will then call the
Exercise. Good Weight A PT E R. Staying Healthy
 Eat Healthy Foods Keep at a Good Weight Exercise Don t Smoke Get Regular Checkups Take Care of Stress A PT E R CH Staying Healthy 6 81 How Can I Stay Healthy? You can do many things to prevent poor health
Eat Healthy Foods Keep at a Good Weight Exercise Don t Smoke Get Regular Checkups Take Care of Stress A PT E R CH Staying Healthy 6 81 How Can I Stay Healthy? You can do many things to prevent poor health
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The kidneys play a key
High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The kidneys play a key
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
(Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know
 Afib (Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know BRING THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR NEXT DOCTOR S VISIT. Getting Started This guide will: 1. Provide you with information to help you and your family
Afib (Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know BRING THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR NEXT DOCTOR S VISIT. Getting Started This guide will: 1. Provide you with information to help you and your family
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
DIABETES MELLITUS. By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria
 DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
