Netfilter / IPtables
|
|
|
- Randolph Ball
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Netfilter / IPtables Stateful packet filter firewalling with Linux Antony Stone [email protected]
2 Netfilter / IPtables Quick review of TCP/IP networking & firewalls Netfilter & IPtables components How packets pass through the system Netfilter matches & targets Standard security policy Network Address Translation + problems New & interesting netfilter matches & targets What can go wrong / debugging
3 Review of TCP/IP & Firewalls HTTP requests and responses Packaged into TCP packet, with TCP header Source & destination port numbers TCP flags Sequence & acknowledgement numbers TCP packaged into IP packet with IP header Source & destination IP addresses IP packets travel across the Internet Routed by destination address
4 Review of TCP/IP & Firewalls Early Internet - everyone trusted - no firewalls Public access - firewalls restrict: External access to internal resources Internal access to external services Internal access to sensitive data Basic principle: Keep the engineers out of the personnel database Firewalls are routers which can say no. Firewall rules based on organisation's security policy
5 Types of firewalls Packet filters vs. proxy firewalls Packet filters look at IP addresses, TCP/UDP port numbers - header information only Proxies look at IP addresses, TCP/UDP port numbers, plus content of datastream Stateful vs. non-stateful Stateful packet filters understand 'connections' Reply packets can be handled securely Rulesets are simpler and easier to understand
6 Netfilter & iptables Netfilter is the kernel component which processes the packets IPtables is the userspace application which manages the ruleset Netfilter terminology: Chains - eg: INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT Tables - eg: filter, nat, mangle, raw Rule matches - eg: protocol, address, port etc. Rule targets - eg: ACCEPT, REJECT, LOG etc.
7 Netfilter chains & tables PREROUTING chain all packets entering an interface (eg: eth, lo, ppp...) INPUT chain all packets addressed to the firewall FORWARD chain all packets being routed through the firewall OUTPUT chain all packets generated from the firewall POSTROUTING chain all packets leaving an interface (eg: eth, lo, ppp...)
8 Netfilter chains & tables filter table nat table Filtering operations :-) ACCEPT, REJECT, DROP Also LOG Network Address Translation SNAT, DNAT, MASQUERADE Also ACCEPT can be useful for exceptions
9 Netfilter chains & tables mangle table raw table Packet (header) mangling Change TTL Change TOS / DSCP Set MARKs Change routing (interfaces, gateway) access to packets before connection tracking
10 Path of packets PREROUTING POSTROUTING R FORWARD R INPUT OUTPUT
11 Path of packets PREROUTING POSTROUTING In to THIS system R FORWARD R From THIS system INPUT OUTPUT
12 Path of packets PREROUTING Routed through this system POSTROUTING R FORWARD R INPUT OUTPUT
13 Path of packets - even more detail PREROUTING chain raw ---> mangle ---> nat POSTROUTING chain mangle ---> nat INPUT & FORWARD chains mangle ---> filter OUTPUT chain raw ---> mangle ---> nat ---> filter
14 Netfilter rule matches Match means which packets does this rule apply to? -p tcp - all TCP packets -d a.b.c.d/n - destination address = a.b.c.d/n --dport x - destination port number = x --length - number of bytes in packet --mac-source - MAC address of sending device -i, -o - input / output interface for packet
15 Netfilter rule targets Target means what happens to the packets which match? ACCEPT - packet is accepted DROP - packet is dropped / discarded DNAT - destination address is changed LOG - packet is logged to syslog (processing continues) REJECT - packet is dropped, reject returned MARK - mark a packet, useful in later processing MIRROR - reverse source & destination :-) UKUUG Leeds 2004 Netfilter / IPtables Antony Stone
16 User-defined chains User-defined chains can be created in addition to the five built-in chains iptables -N mychain iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j mychain iptables -A mychain -s j LOG iptables -A mychain -j ACCEPT RETURN target returns from user-defined chain to the calling chain (useful for exceptions)
17 Standard security policy Everything is blocked, except that which is explicitly allowed Default DROP policy on filter tables (NEVER set default DROP on nat or mangle!) Individual rules allow packets which are wanted LOG packets which get blocked?
18 Example ruleset 1 iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -A INPUT -i eth1 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j ACCEPT
19 Stateful filtering What does this mean? -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED ESTABLISHED matches any packets with source/destination addresses/ports matching an entry in the connection tracking table Source/destination match forward & reverse Conntrack table entries are automatically created when a packet is ACCEPTed
20 Stateful filtering RELATED matches packets which netfilter identifies as being related to an entry in the conntrack table FTP data channel is RELATED to the control channel ICMP responses (eg: host unreachable, TTL exceeded) are RELATED to the packets they're in response to
21 Network Address Translation SNAT / MASQUERADE Changes the source address of packets leaving a network - usually so that the reply packets can get back again DNAT Changes the destination address of packets so that they go to a different machine than they were originally addressed to
22 Network Address Translation SNAT / MASQUERADE Usually used to 'hide' a network of machines using private (RFC1918) internal addresses behind one or more publicly routable IP addresses DNAT Usually used to provide publicly-accessible services from machines on a privately-addressed network
23 Network Address Translation Some people regard NAT as evil - because it breaks protocols such as FTP, H.323 Some people regard protocols such as FTP, H.323 as evil - because they embed IP addresses and port numbers in application layer communications NAT also breaks IPsec transport mode (AH), which has a checksum involving the addresses
24 Example ruleset 2 iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -A INPUT -i eth1 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j ACCEPT iptables -A POSTROUTING -t nat -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
25 Network Address Translation I have DNAT working fine from the Internet to a machine on my network, but why can't clients on my network access its public IP address? Request goes through firewall (NAT) Reply goes directly across network (no NAT) Client sends to a.b.c.d, gets reply from w.x.y.z I would be very happy if nobody ever asked this question again on the netfilter mailing list!
26 More netfilter matches & targets Recent versions of netfilter (currently ) have introduced many interesting and less-often used (less-often explained?) matches and targets No longer just packet header information Also netfilter internal information eg: MARK, CONNMARK, rate limits, helpers Also external packet characteristics eg: owner, route, time, random matches
27 Interesting new rule matches addrtype condition connmark UNICAST, LOCAL, BROADCAST, ANYCAST, MULTICAST, BLACKHOLE, UNREACHABLE, PROHIBIT, THROW, NAT, XRESOLVE checks content of / proc/net/ipt_condition/filename matches packets in marked connections like the mark match, but applies to replies too
28 Interesting new rule matches conntrack dstlimit allows detailed matching of packet against connection tracking table data: original source/destination address reply source/destination address internal conntrack state (EXPECTED, SEEN_REPLY, ASSURED etc) expiry time remaining allows rate limiting per IP address like the limit match, but per IP
29 Interesting new rule matches helper owner physdev matches packets according to a particular connection tracking helper module (eg: FTP, IRC) for locally-generated packets, match for the process which generated the packet: UID, GID, PID, SID, command name allows matching of interfaces when bridging
30 Interesting new rule targets BALANCE CLASSIFY DNAT to several addresses using round-robin set priority value for classifying packets into CBQ (Class-Based-Queuing) classes CBQ is used for allocating bandwidth pools CLUSTERIP distributes connections to a cluster of machines sharing IP & MAC addresses
31 Interesting new rule targets CONNMARK NETMAP NOTRACK Assign a numeric mark to packets, for later matching, but match on reply packets too map a range of addresses to a second range of addresses (can be 1:1, can map to a smaller range using a mask) (SNAT & DNAT) Disables connection tracking for selected packets (good for avoiding DoS attacks)
32 Interesting new rule targets ROUTE TCPMSS Changes routing information about a packet input interface name output interface name next hop gateway address Control Maximum Segment Size of TCP packets (usually to match the Maximum Transmission Unit of a particular link) TTL Change the Time To Live value of a packet
33 Extensions to netfilter Patch-o-matic Various experimental, unofficial or esoteric extensions to netfilter Applies patches to netfilter (in the kernel source code) and iptables (userspace application) - need to recompile both Currently still stabilising after being adapted to kernel 2.6 (as well as kernel 2.4)
34 Extensions to netfilter OSF Operating System Fingerprinting Adapted from BSD pf code PSD Port Scan Detection TARPIT Accepts incoming TCP connections, causing the remote system to get stuck in a minute timeout, without allowing connection closure
35 Extensions to netfilter XOR Simplistic encryption of TCP / UDP packet contents using XOR operation COMMENT Allows comments to be added to netfilter rules connbytes CuSeeMe Matches against number of bytes transferred NAT helper for CuSeeMe protocol
36 Extensions to netfilter drop table (and DROPPED chain) Adds a new table for packets which are being dropped, enabling them to be logged goto Alternative to jump, returns to parent chain QUAKE3 instead of this chain Adds conntracking & nat support for Quake III
37 Conntrack technical details Connection tracking table ~300 bytes of RAM needed per conntrack entry Default conntrack table size = RAM (Mbytes) x 64 (min 128, max 65536) eg: 256Mbyte machine: connections This allocates 2% of system RAM for conntrack Dedicated firewall has not much use for most of the remaining 98% RAM Manually adjust: /proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max
38 Conntrack technical details Connection tracking table can fill up! No more new connections will be accepted Common causes: Solution: SYN flood (DoS attack) Worm-infected PC on internal network Add rule to block offending IP (or unplug PC) Increase conntrack table size Wait for old connections to timeout
39 Conntrack technical details Connection tracking is entirely based on: Source & destination IP addresses Source & destination TDP/UDP ports Connection tracking does not use: TCP sequence / acknowledgement numbers /proc/net/ip_conntrack lists current entries useful first indication of a worm on your network
40 Firewall debugging Client cannot connect when firewall ruleset is in place; client can connect with no ruleset How to debug? ACCEPT packets which are wanted DROP packets which are known and unwanted LOG packets which get this far DROP remainder using default policy iptables -L -nvx Shows packet & byte counters for each rule
41 Traps for the unwary iptables -L does not list all the rules The filter table is assumed by default If you want the nat or mangle tables, you must specify them: iptables -L -t nat DNAT is not working ensure that the FORWARD rule allows the new (translated) address, not the original address LOG logs to the console, not /var/log/messages use -j LOG --log-level=6 and check /etc/syslogd.conf
42 Traps for the unwary DNAT sends packets to my server, but nobody can connect check return route from server - must go through firewall for reverse NAT Passive FTP works fine, but not active FTP When doing NAT, active FTP requires the FTP NAT helper module loaded, or compiled into kernel Looks for the FTP PORT command in the datastream and adds a RELATED conntrack table entry
43 Traps for the unwary LOG in the nat table records almost no packets Only the first packet of a connection goes through the rules in the nat tables - all subsequent packets (both ways) are processed automagically in the background DNAT works fine for packets routed through the firewall, but not for packets originating on the firewall machine itself PREROUTING is only for packets entering the machine The OUTPUT chain has a nat table for DNATting locallygenerated packets
44 Netfilter tricks Rules do not have to have a target iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport 22 is a perfectly valid rule Useful for packet counting! can be used to mean anything except... iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport! 22 -j LOG Will LOG all packets except SSH (TCP 22)
45 Netfilter tricks How to handle two (or more) exceptions? User-defined chain iptables -N mychain iptables -A mychain -d a.b.c.d -j RETURN iptables -A mychain -d w.x.y.z -j RETURN iptables -A mychain -j LOG User-defined chains can also have nat and mangle table rules eg: SNAT all packets except from these three IP addresses
46 Networking words of wisdom 90% of all networking problems are routing problems. 9 of the remaining 10% are routing problems, but in the other direction. The final 1% might be something else, but check the routing anyway.
Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall
 Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall Linux Kernel Firewall Kernel provides Xtables (implemeted as different Netfilter modules) which store chains and rules x_tables is the name of the kernel module carrying
Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall Linux Kernel Firewall Kernel provides Xtables (implemeted as different Netfilter modules) which store chains and rules x_tables is the name of the kernel module carrying
+ iptables. packet filtering && firewall
 + iptables packet filtering && firewall + what is iptables? iptables is the userspace command line program used to configure the linux packet filtering ruleset + a.k.a. firewall + iptable flow chart what?
+ iptables packet filtering && firewall + what is iptables? iptables is the userspace command line program used to configure the linux packet filtering ruleset + a.k.a. firewall + iptable flow chart what?
Firewalls. Chien-Chung Shen [email protected]
 Firewalls Chien-Chung Shen [email protected] The Need for Firewalls Internet connectivity is essential however it creates a threat vs. host-based security services (e.g., intrusion detection), not cost-effective
Firewalls Chien-Chung Shen [email protected] The Need for Firewalls Internet connectivity is essential however it creates a threat vs. host-based security services (e.g., intrusion detection), not cost-effective
Main functions of Linux Netfilter
 Main functions of Linux Netfilter Filter Nat Packet filtering (rejecting, dropping or accepting packets) Network Address Translation including DNAT, SNAT and Masquerading Mangle General packet header modification
Main functions of Linux Netfilter Filter Nat Packet filtering (rejecting, dropping or accepting packets) Network Address Translation including DNAT, SNAT and Masquerading Mangle General packet header modification
Linux firewall. Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users
 Linux firewall Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users Linux firewall Linux is a open source operating system and any firewall
Linux firewall Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users Linux firewall Linux is a open source operating system and any firewall
Linux Routers and Community Networks
 Summer Course at Mekelle Institute of Technology. July, 2015. Linux Routers and Community Networks Llorenç Cerdà-Alabern http://personals.ac.upc.edu/llorenc [email protected] Universitat Politènica de
Summer Course at Mekelle Institute of Technology. July, 2015. Linux Routers and Community Networks Llorenç Cerdà-Alabern http://personals.ac.upc.edu/llorenc [email protected] Universitat Politènica de
Track 2 Workshop PacNOG 7 American Samoa. Firewalling and NAT
 Track 2 Workshop PacNOG 7 American Samoa Firewalling and NAT Core Concepts Host security vs Network security What is a firewall? What does it do? Where does one use it? At what level does it function?
Track 2 Workshop PacNOG 7 American Samoa Firewalling and NAT Core Concepts Host security vs Network security What is a firewall? What does it do? Where does one use it? At what level does it function?
Firewall. IPTables and its use in a realistic scenario. José Bateira ei10133 Pedro Cunha ei05064 Pedro Grilo ei09137 FEUP MIEIC SSIN
 Firewall IPTables and its use in a realistic scenario FEUP MIEIC SSIN José Bateira ei10133 Pedro Cunha ei05064 Pedro Grilo ei09137 Topics 1- Firewall 1.1 - How they work? 1.2 - Why use them? 1.3 - NAT
Firewall IPTables and its use in a realistic scenario FEUP MIEIC SSIN José Bateira ei10133 Pedro Cunha ei05064 Pedro Grilo ei09137 Topics 1- Firewall 1.1 - How they work? 1.2 - Why use them? 1.3 - NAT
Linux Firewall Wizardry. By Nemus
 Linux Firewall Wizardry By Nemus The internet and your server So then what do you protect your server with if you don't have a firewall in place? NetFilter / Iptables http://www.netfilter.org Iptables
Linux Firewall Wizardry By Nemus The internet and your server So then what do you protect your server with if you don't have a firewall in place? NetFilter / Iptables http://www.netfilter.org Iptables
Chapter 7. Firewalls http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/enterprise/rhel-4-manual/security-guide/ch-fw.html
 Red Hat Docs > Manuals > Red Hat Enterprise Linux Manuals > Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4: Security Guide Chapter 7. Firewalls http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/enterprise/rhel-4-manual/security-guide/ch-fw.html
Red Hat Docs > Manuals > Red Hat Enterprise Linux Manuals > Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4: Security Guide Chapter 7. Firewalls http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/enterprise/rhel-4-manual/security-guide/ch-fw.html
Building a Home Gateway/Firewall with Linux (aka Firewalling and NAT with iptables )
 Building a Home Gateway/Firewall with Linux (aka Firewalling and NAT with iptables ) Michael Porkchop Kaegler [email protected] http://www.nic.com/~mkaegler/ Hardware Requirements Any machine capable of
Building a Home Gateway/Firewall with Linux (aka Firewalling and NAT with iptables ) Michael Porkchop Kaegler [email protected] http://www.nic.com/~mkaegler/ Hardware Requirements Any machine capable of
Linux Firewalls (Ubuntu IPTables) II
 Linux Firewalls (Ubuntu IPTables) II Here we will complete the previous firewall lab by making a bridge on the Ubuntu machine, to make the Ubuntu machine completely control the Internet connection on the
Linux Firewalls (Ubuntu IPTables) II Here we will complete the previous firewall lab by making a bridge on the Ubuntu machine, to make the Ubuntu machine completely control the Internet connection on the
CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls
 CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls Professor Kevin Butler Fall 2015 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire, heat
CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls Professor Kevin Butler Fall 2015 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire, heat
Protecting and controlling Virtual LANs by Linux router-firewall
 Protecting and controlling Virtual LANs by Linux router-firewall Tihomir Katić Mile Šikić Krešimir Šikić Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing University of Zagreb Unska 3, HR 10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Protecting and controlling Virtual LANs by Linux router-firewall Tihomir Katić Mile Šikić Krešimir Šikić Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing University of Zagreb Unska 3, HR 10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Linux Firewall. Linux workshop #2. www.burningnode.com
 Linux Firewall Linux workshop #2 Summary Introduction to firewalls Introduction to the linux firewall Basic rules Advanced rules Scripting Redundancy Extensions Distributions Links 2 Introduction to firewalls
Linux Firewall Linux workshop #2 Summary Introduction to firewalls Introduction to the linux firewall Basic rules Advanced rules Scripting Redundancy Extensions Distributions Links 2 Introduction to firewalls
CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls
 CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls Professor Patrick Traynor Spring 2015 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
CS 5410 - Computer and Network Security: Firewalls Professor Patrick Traynor Spring 2015 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
TECHNICAL NOTES. Security Firewall IP Tables
 Introduction Prior to iptables, the predominant software packages for creating Linux firewalls were 'IPChains' in Linux 2.2 and ipfwadm in Linux 2.0, which in turn was based on BSD's ipfw. Both ipchains
Introduction Prior to iptables, the predominant software packages for creating Linux firewalls were 'IPChains' in Linux 2.2 and ipfwadm in Linux 2.0, which in turn was based on BSD's ipfw. Both ipchains
CSC574 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls
 CSC574 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Prof. William Enck Spring 2013 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
CSC574 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Prof. William Enck Spring 2013 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
Linux Networking: IP Packet Filter Firewalling
 Linux Networking: IP Packet Filter Firewalling David Morgan Firewall types Packet filter Proxy server 1 Linux Netfilter Firewalling Packet filter, not proxy Centerpiece command: iptables Starting point:
Linux Networking: IP Packet Filter Firewalling David Morgan Firewall types Packet filter Proxy server 1 Linux Netfilter Firewalling Packet filter, not proxy Centerpiece command: iptables Starting point:
Netfilter. GNU/Linux Kernel version 2.4+ Setting up firewall to allow NIS and NFS traffic. January 2008
 Netfilter GNU/Linux Kernel version 2.4+ Setting up firewall to allow NIS and NFS traffic January 2008 Netfilter Features Address Translation S NAT, D NAT IP Accounting and Mangling IP Packet filtering
Netfilter GNU/Linux Kernel version 2.4+ Setting up firewall to allow NIS and NFS traffic January 2008 Netfilter Features Address Translation S NAT, D NAT IP Accounting and Mangling IP Packet filtering
1:1 NAT in ZeroShell. Requirements. Overview. Network Setup
 1:1 NAT in ZeroShell Requirements The version of ZeroShell used for writing this document is Release 1.0.beta11. This document does not describe installing ZeroShell, it is assumed that the user already
1:1 NAT in ZeroShell Requirements The version of ZeroShell used for writing this document is Release 1.0.beta11. This document does not describe installing ZeroShell, it is assumed that the user already
Network security Exercise 9 How to build a wall of fire Linux Netfilter
 Network security Exercise 9 How to build a wall of fire Linux Netfilter Tobias Limmer Computer Networks and Communication Systems Dept. of Computer Sciences, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany 14.
Network security Exercise 9 How to build a wall of fire Linux Netfilter Tobias Limmer Computer Networks and Communication Systems Dept. of Computer Sciences, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany 14.
How To Understand A Firewall
 Module II. Internet Security Chapter 6 Firewall Web Security: Theory & Applications School of Software, Sun Yat-sen University Outline 6.1 Introduction to Firewall What Is a Firewall Types of Firewall
Module II. Internet Security Chapter 6 Firewall Web Security: Theory & Applications School of Software, Sun Yat-sen University Outline 6.1 Introduction to Firewall What Is a Firewall Types of Firewall
Optimisacion del ancho de banda (Introduccion al Firewall de Linux)
 Optimisacion del ancho de banda (Introduccion al Firewall de Linux) Christian Benvenuti [email protected] Managua, Nicaragua, 31/8/9-11/9/9 UNAN-Managua Before we start... Are you familiar
Optimisacion del ancho de banda (Introduccion al Firewall de Linux) Christian Benvenuti [email protected] Managua, Nicaragua, 31/8/9-11/9/9 UNAN-Managua Before we start... Are you familiar
Computer Firewalls. The term firewall was originally used with forest fires, as a means to describe the
 Pascal Muetschard John Nagle COEN 150, Spring 03 Prof. JoAnne Holliday Computer Firewalls Introduction The term firewall was originally used with forest fires, as a means to describe the barriers implemented
Pascal Muetschard John Nagle COEN 150, Spring 03 Prof. JoAnne Holliday Computer Firewalls Introduction The term firewall was originally used with forest fires, as a means to describe the barriers implemented
Firewalls, NAT and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS)
 Firewalls, NAT and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS) Internet (In)Security Exposed Prof. Dr. Bernhard Plattner With some contributions by Stephan Neuhaus Thanks to Thomas Dübendorfer, Stefan
Firewalls, NAT and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS) Internet (In)Security Exposed Prof. Dr. Bernhard Plattner With some contributions by Stephan Neuhaus Thanks to Thomas Dübendorfer, Stefan
Internet Protocol: IP packet headers. vendredi 18 octobre 13
 Internet Protocol: IP packet headers 1 IPv4 header V L TOS Total Length Identification F Frag TTL Proto Checksum Options Source address Destination address Data (payload) Padding V: Version (IPv4 ; IPv6)
Internet Protocol: IP packet headers 1 IPv4 header V L TOS Total Length Identification F Frag TTL Proto Checksum Options Source address Destination address Data (payload) Padding V: Version (IPv4 ; IPv6)
Linux: 20 Iptables Examples For New SysAdmins
 Copyrighted material Linux: 20 Iptables Examples For New SysAdmins Posted By nixcraft On December 13, 2011 @ 8:29 am [ 64 Comments ] L inux comes with a host based firewall called
Copyrighted material Linux: 20 Iptables Examples For New SysAdmins Posted By nixcraft On December 13, 2011 @ 8:29 am [ 64 Comments ] L inux comes with a host based firewall called
Firewalls. Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected]
 Firewalls Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected] 1 Definition A firewall is a network device that separates two parts of a network, enforcing a policy for all traversing traffic. 2 Fundamental requirements
Firewalls Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected] 1 Definition A firewall is a network device that separates two parts of a network, enforcing a policy for all traversing traffic. 2 Fundamental requirements
Network Security Exercise 10 How to build a wall of fire
 Network Security Exercise 10 How to build a wall of fire Tobias Limmer, Christoph Sommer, David Eckhoff Computer Networks and Communication Systems Dept. of Computer Sciences, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
Network Security Exercise 10 How to build a wall of fire Tobias Limmer, Christoph Sommer, David Eckhoff Computer Networks and Communication Systems Dept. of Computer Sciences, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
How To Set Up An Ip Firewall On Linux With Iptables (For Ubuntu) And Iptable (For Windows)
 Security principles Firewalls and NAT These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) Host vs Network
Security principles Firewalls and NAT These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) Host vs Network
Worksheet 9. Linux as a router, packet filtering, traffic shaping
 Worksheet 9 Linux as a router, packet filtering, traffic shaping Linux as a router Capable of acting as a router, firewall, traffic shaper (so are most other modern operating systems) Tools: netfilter/iptables
Worksheet 9 Linux as a router, packet filtering, traffic shaping Linux as a router Capable of acting as a router, firewall, traffic shaper (so are most other modern operating systems) Tools: netfilter/iptables
Packet filtering with Linux
 LinuxFocus article number 289 http://linuxfocus.org Packet filtering with Linux by Vincent Renardias About the author: GNU/Linux user since 1993, Vincent Renardias started to
LinuxFocus article number 289 http://linuxfocus.org Packet filtering with Linux by Vincent Renardias About the author: GNU/Linux user since 1993, Vincent Renardias started to
How to Turn a Unix Computer into a Router and Firewall Using IPTables
 How to Turn a Unix Computer into a Router and Firewall Using IPTables by Dr. Milica Barjaktarovic Assistant Professor of Computer Science at HPU Lecture from CENT370 Advanced Unix System Administration
How to Turn a Unix Computer into a Router and Firewall Using IPTables by Dr. Milica Barjaktarovic Assistant Professor of Computer Science at HPU Lecture from CENT370 Advanced Unix System Administration
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 02 NAT and DHCP Tópicos Avançados de Redes
 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 1 1 Dynamic Assignment of IP addresses Dynamic assignment of IP addresses is desirable for several reasons: IP addresses are assigned on-demand Avoid manual IP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 1 1 Dynamic Assignment of IP addresses Dynamic assignment of IP addresses is desirable for several reasons: IP addresses are assigned on-demand Avoid manual IP
ipchains and iptables for Firewalling and Routing
 ipchains and iptables for Firewalling and Routing Jeff Muday Instructional Technology Consultant Department of Biology, Wake Forest University The ipchains utility Used to filter packets at the Kernel
ipchains and iptables for Firewalling and Routing Jeff Muday Instructional Technology Consultant Department of Biology, Wake Forest University The ipchains utility Used to filter packets at the Kernel
Firewalls. Firewall types. Packet filter. Proxy server. linux, iptables-based Windows XP s built-in router device built-ins single TCP conversation
 Firewalls David Morgan Firewall types Packet filter linux, iptables-based Windows XP s built-in router device built-ins single TCP conversation Proxy server specialized server program on internal machine
Firewalls David Morgan Firewall types Packet filter linux, iptables-based Windows XP s built-in router device built-ins single TCP conversation Proxy server specialized server program on internal machine
Packet Filtering Firewall
 Packet Filtering Firewall Page 1 of 9 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP NAT & IP Masquerade Packet Filters vs Proxy Servers Firewalls make a simple decision: accept or deny communication. There are two
Packet Filtering Firewall Page 1 of 9 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP NAT & IP Masquerade Packet Filters vs Proxy Servers Firewalls make a simple decision: accept or deny communication. There are two
Managing Multiple Internet Connections with Shorewall
 Managing Multiple Internet Connections with Shorewall Tom Eastep Linuxfest Northwest April 24-25, 2010 http://www.shorewall.net Agenda Introduction Routing Refresher Introduction to Policy Routing Policy
Managing Multiple Internet Connections with Shorewall Tom Eastep Linuxfest Northwest April 24-25, 2010 http://www.shorewall.net Agenda Introduction Routing Refresher Introduction to Policy Routing Policy
CSE543 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls
 CSE543 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Professor Trent Jaeger Fall 2010 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
CSE543 - Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Professor Trent Jaeger Fall 2010 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed to limit the spread of fire,
Internet Firewall CSIS 3230. Internet Firewall. Spring 2012 CSIS 4222. net13 1. Firewalls. Stateless Packet Filtering
 Internet Firewall CSIS 3230 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 8.8: Packet filtering, firewalls, intrusion detection Ch
Internet Firewall CSIS 3230 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 8.8: Packet filtering, firewalls, intrusion detection Ch
Definition of firewall
 Internet Firewalls Definitions: firewall, policy, router, gateway, proxy NAT: Network Address Translation Source NAT, Destination NAT, Port forwarding NAT firewall compromise via UPnP/IGD Packet filtering
Internet Firewalls Definitions: firewall, policy, router, gateway, proxy NAT: Network Address Translation Source NAT, Destination NAT, Port forwarding NAT firewall compromise via UPnP/IGD Packet filtering
Load Balancing Trend Micro InterScan Web Gateway
 Load Balancing Trend Micro InterScan Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.7 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...
Load Balancing Trend Micro InterScan Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.7 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...
Linux Cluster Security Neil Gorsuch NCSA, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois.
 Linux Cluster Security Neil Gorsuch NCSA, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois. Abstract Modern Linux clusters are under increasing security threats. This paper will discuss various aspects of cluster
Linux Cluster Security Neil Gorsuch NCSA, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois. Abstract Modern Linux clusters are under increasing security threats. This paper will discuss various aspects of cluster
VENKATAMOHAN, BALAJI. Automated Implementation of Stateful Firewalls in Linux. (Under the direction of Ting Yu.)
 ABSTRACT VENKATAMOHAN, BALAJI. Automated Implementation of Stateful Firewalls in Linux. (Under the direction of Ting Yu.) Linux Firewalls are the first line of defense for any Linux machine connected to
ABSTRACT VENKATAMOHAN, BALAJI. Automated Implementation of Stateful Firewalls in Linux. (Under the direction of Ting Yu.) Linux Firewalls are the first line of defense for any Linux machine connected to
Linux Networking Basics
 Linux Networking Basics Naveen.M.K, Protocol Engineering & Technology Unit, Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 12. Outline Basic linux networking commands Servers
Linux Networking Basics Naveen.M.K, Protocol Engineering & Technology Unit, Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 12. Outline Basic linux networking commands Servers
Компјутерски Мрежи NAT & ICMP
 Компјутерски Мрежи NAT & ICMP Riste Stojanov, M.Sc., Aleksandra Bogojeska, M.Sc., Vladimir Zdraveski, B.Sc Internet AS Hierarchy Inter-AS border (exterior gateway) routers Intra-AS interior (gateway) routers
Компјутерски Мрежи NAT & ICMP Riste Stojanov, M.Sc., Aleksandra Bogojeska, M.Sc., Vladimir Zdraveski, B.Sc Internet AS Hierarchy Inter-AS border (exterior gateway) routers Intra-AS interior (gateway) routers
Load Balancing Sophos Web Gateway. Deployment Guide
 Load Balancing Sophos Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.0.9 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Sophos Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.0.9 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Module: Firewalls. Professor Patrick McDaniel Spring 2009. CMPSC443 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CMPSC443 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Professor Patrick McDaniel Spring 2009 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed
CMPSC443 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Firewalls Professor Patrick McDaniel Spring 2009 1 Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed
Stateful Firewalls. Hank and Foo
 Stateful Firewalls Hank and Foo 1 Types of firewalls Packet filter (stateless) Proxy firewalls Stateful inspection Deep packet inspection 2 Packet filter (Access Control Lists) Treats each packet in isolation
Stateful Firewalls Hank and Foo 1 Types of firewalls Packet filter (stateless) Proxy firewalls Stateful inspection Deep packet inspection 2 Packet filter (Access Control Lists) Treats each packet in isolation
CIS 433/533 - Computer and Network Security Firewalls
 CIS 433/533 - Computer and Network Security Firewalls Professor Kevin Butler Winter 2011 Computer and Information Science Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed
CIS 433/533 - Computer and Network Security Firewalls Professor Kevin Butler Winter 2011 Computer and Information Science Firewalls A firewall... is a physical barrier inside a building or vehicle, designed
Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security. by Avi Kak ([email protected])
 Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak ([email protected]) April 26, 2012 1:41am c 2012 Avinash Kak, Purdue University Goals: Packet-filtering
Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak ([email protected]) April 26, 2012 1:41am c 2012 Avinash Kak, Purdue University Goals: Packet-filtering
Firewalls N E T W O R K ( A N D D ATA ) S E C U R I T Y 2 01 5 / 2 01 6 P E D R O B R A N D Ã O M A N U E L E D U A R D O C O R R E I A
 Firewalls N E T W O R K ( A N D D ATA ) S E C U R I T Y 2 01 5 / 2 01 6 P E D R O B R A N D Ã O M A N U E L E D U A R D O C O R R E I A Slides are based on slides by Dr Lawrie Brown (UNSW@ADFA) for Computer
Firewalls N E T W O R K ( A N D D ATA ) S E C U R I T Y 2 01 5 / 2 01 6 P E D R O B R A N D Ã O M A N U E L E D U A R D O C O R R E I A Slides are based on slides by Dr Lawrie Brown (UNSW@ADFA) for Computer
Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter. Deployment Guide
 Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.8 Copyright 2002 2016 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...4 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.8 Copyright 2002 2016 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...4 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 Loadbalancer.org
21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) 21.4.1 NAT concept
 21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) This section explains Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is also known as IP masquerading. It provides a mapping between internal IP addresses and officially
21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) This section explains Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is also known as IP masquerading. It provides a mapping between internal IP addresses and officially
Firewalls (IPTABLES)
 Firewalls (IPTABLES) Objectives Understand the technical essentials of firewalls. Realize the limitations and capabilities of firewalls. To be familiar with iptables firewall. Introduction: In the context
Firewalls (IPTABLES) Objectives Understand the technical essentials of firewalls. Realize the limitations and capabilities of firewalls. To be familiar with iptables firewall. Introduction: In the context
Netfilter s connection tracking system
 PABLO NEIRA AYUSO Netfilter s connection tracking system Pablo Neira Ayuso has an M.S. in computer science and has worked for several companies in the IT security industry, with a focus on open source
PABLO NEIRA AYUSO Netfilter s connection tracking system Pablo Neira Ayuso has an M.S. in computer science and has worked for several companies in the IT security industry, with a focus on open source
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering ENG 224 Information Technology Laboratory 6: Internet Connection Sharing Objectives: Build a private network that
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering ENG 224 Information Technology Laboratory 6: Internet Connection Sharing Objectives: Build a private network that
Network Security. Routing and Firewalls. Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Autumn 2014
 Network Security Routing and Firewalls Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 A short recap IP spoofing by itself is easy Typically used in conjunction with other attacks, e.g.: DOS attacks
Network Security Routing and Firewalls Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 A short recap IP spoofing by itself is easy Typically used in conjunction with other attacks, e.g.: DOS attacks
IP Address: the per-network unique identifier used to find you on a network
 Linux Networking What is a network? A collection of devices connected together Can use IPv4, IPv6, other schemes Different devices on a network can talk to each other May be walls to separate different
Linux Networking What is a network? A collection of devices connected together Can use IPv4, IPv6, other schemes Different devices on a network can talk to each other May be walls to separate different
Load Balancing McAfee Web Gateway. Deployment Guide
 Load Balancing McAfee Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.4 Copyright 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing McAfee Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.4 Copyright 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode
 Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode Ralf Spenneberg, [email protected] Revision : 1.5 Abstract Firewalling using packet filters is usually performed by a router. The packet filtering software
Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode Ralf Spenneberg, [email protected] Revision : 1.5 Abstract Firewalling using packet filters is usually performed by a router. The packet filtering software
Virtual private network. Network security protocols VPN VPN. Instead of a dedicated data link Packets securely sent over a shared network Internet VPN
 Virtual private network Network security protocols COMP347 2006 Len Hamey Instead of a dedicated data link Packets securely sent over a shared network Internet VPN Public internet Security protocol encrypts
Virtual private network Network security protocols COMP347 2006 Len Hamey Instead of a dedicated data link Packets securely sent over a shared network Internet VPN Public internet Security protocol encrypts
About Firewall Protection
 1. This guide describes how to configure basic firewall rules in the UTM to protect your network. The firewall then can provide secure, encrypted communications between your local network and a remote
1. This guide describes how to configure basic firewall rules in the UTM to protect your network. The firewall then can provide secure, encrypted communications between your local network and a remote
Firewall Configuration and Assessment
 FW Firewall Configuration and Assessment Goals of this lab: v v Get hands- on experience implementing a network security policy Get hands- on experience testing a firewall REVISION: 1.4 [2014-01- 28] 2007-2011
FW Firewall Configuration and Assessment Goals of this lab: v v Get hands- on experience implementing a network security policy Get hands- on experience testing a firewall REVISION: 1.4 [2014-01- 28] 2007-2011
GregSowell.com. Mikrotik Security
 Mikrotik Security IP -> Services Disable unused services Set Available From for appropriate hosts Secure protocols are preferred (Winbox/SSH) IP -> Neighbors Disable Discovery Interfaces where not necessary.
Mikrotik Security IP -> Services Disable unused services Set Available From for appropriate hosts Secure protocols are preferred (Winbox/SSH) IP -> Neighbors Disable Discovery Interfaces where not necessary.
Firewalls. October 23, 2015
 Firewalls October 23, 2015 Administrative submittal instructions answer the lab assignment s questions in written report form, as a text, pdf, or Word document file (no obscure formats please) email to
Firewalls October 23, 2015 Administrative submittal instructions answer the lab assignment s questions in written report form, as a text, pdf, or Word document file (no obscure formats please) email to
IPv6 Security from point of view firewalls
 IPv6 Security from point of view firewalls János Mohácsi 09/June/2004 János Mohácsi, Research Associate, Network Engineer NIIF/HUNGARNET Contents Requirements IPv6 firewall architectures Firewalls and
IPv6 Security from point of view firewalls János Mohácsi 09/June/2004 János Mohácsi, Research Associate, Network Engineer NIIF/HUNGARNET Contents Requirements IPv6 firewall architectures Firewalls and
Firewall implementation and testing
 Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE
 SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION MTAT.08.021 LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE Prepared By: Amnir Hadachi and Artjom Lind University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science [email protected] / [email protected]
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION MTAT.08.021 LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE Prepared By: Amnir Hadachi and Artjom Lind University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science [email protected] / [email protected]
How to protect your home/office network?
 How to protect your home/office network? Using IPTables and Building a Firewall - Background, Motivation and Concepts Adir Abraham [email protected] Do you think that you are alone, connected from
How to protect your home/office network? Using IPTables and Building a Firewall - Background, Motivation and Concepts Adir Abraham [email protected] Do you think that you are alone, connected from
FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a
 FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a COMPSCI 726 Network Defence and Countermeasures Muhammad Rizwan Asghar August 3, 2015 Source of most of slides: University of Twente FIREWALL An integrated collection of security
FIREWALL AND NAT Lecture 7a COMPSCI 726 Network Defence and Countermeasures Muhammad Rizwan Asghar August 3, 2015 Source of most of slides: University of Twente FIREWALL An integrated collection of security
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems. Firewalls
 CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Firewalls Topics 1. What is a firewall? 2. Types of Firewalls 1. Packet filters (stateless) 2. Stateful firewalls 3. Proxy servers 4. Application layer firewalls 3. Configuring
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Firewalls Topics 1. What is a firewall? 2. Types of Firewalls 1. Packet filters (stateless) 2. Stateful firewalls 3. Proxy servers 4. Application layer firewalls 3. Configuring
Load Balancing Web Proxies Load Balancing Web Filters Load Balancing Web Gateways. Deployment Guide
 Load Balancing Web Proxies Load Balancing Web Filters Load Balancing Web Gateways Deployment Guide rev. 1.4.9 Copyright 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Appliances
Load Balancing Web Proxies Load Balancing Web Filters Load Balancing Web Gateways Deployment Guide rev. 1.4.9 Copyright 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide... 3 Appliances
Fault tolerant stateful firewalling with GNU/Linux. Pablo Neira Ayuso <[email protected]> Proyecto Netfilter <[email protected]> University of Sevilla
 Fault tolerant stateful firewalling with GNU/Linux Pablo Neira Ayuso Proyecto Netfilter University of Sevilla Outline Introduction: Stateless and stateful firewalls
Fault tolerant stateful firewalling with GNU/Linux Pablo Neira Ayuso Proyecto Netfilter University of Sevilla Outline Introduction: Stateless and stateful firewalls
Load Balancing Smoothwall Secure Web Gateway
 Load Balancing Smoothwall Secure Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.7 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Smoothwall Secure Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.7 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Clearswift Secure Web Gateway
 Load Balancing Clearswift Secure Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.8 Copyright 2002 2016 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Clearswift Secure Web Gateway Deployment Guide rev. 1.1.8 Copyright 2002 2016 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. 1 Table of Contents About this Guide...3 Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...3 Loadbalancer.org
Linux Network Security
 Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
NAT & IP Masquerade. Internet NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION INTRODUCTION. NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5. Internal PC 192.168.0.25
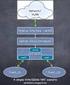 NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
Linux 2.4 stateful firewall design
 Linux 2.4 stateful firewall design Presented by developerworks, your source for great tutorials Table of Contents If you're viewing this document online, you can click any of the topics below to link directly
Linux 2.4 stateful firewall design Presented by developerworks, your source for great tutorials Table of Contents If you're viewing this document online, you can click any of the topics below to link directly
iptables: The Linux Firewall Administration Program
 CHAPTER 3 iptables: The Linux Firewall Administration Program Chapter 2, Packet-Filtering Concepts, covers the background ideas and concepts behind a packet-filtering firewall. Each built-in rule chain
CHAPTER 3 iptables: The Linux Firewall Administration Program Chapter 2, Packet-Filtering Concepts, covers the background ideas and concepts behind a packet-filtering firewall. Each built-in rule chain
10.4. Multiple Connections to the Internet
 10.4. Multiple Connections to the Internet Prev Chapter 10. Advanced IP Routing Next 10.4. Multiple Connections to the Internet The questions summarized in this section should rightly be entered into the
10.4. Multiple Connections to the Internet Prev Chapter 10. Advanced IP Routing Next 10.4. Multiple Connections to the Internet The questions summarized in this section should rightly be entered into the
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems. Firewalls
 CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Firewalls Topics 1. What is a firewall? 2. Types of Firewalls 1. Packet filters (stateless) 2. Stateful firewalls 3. Proxy servers 4. Application layer firewalls 3. Configuring
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Firewalls Topics 1. What is a firewall? 2. Types of Firewalls 1. Packet filters (stateless) 2. Stateful firewalls 3. Proxy servers 4. Application layer firewalls 3. Configuring
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 6 Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs. Agenda. Nomadic Services. Agenda. Nomadic Services Functions
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 6 Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs Describe the role of nomadic services in mobile networking Describe the objectives
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 6 Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs Describe the role of nomadic services in mobile networking Describe the objectives
IP Network Layer. Datagram ID FLAG Fragment Offset. IP Datagrams. IP Addresses. IP Addresses. CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security. by Avi Kak ([email protected])
 Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak ([email protected]) March 24, 2015 3:44pm c 2015 Avinash Kak, Purdue University Goals: Packet-filtering
Lecture 18: Packet Filtering Firewalls (Linux) Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak ([email protected]) March 24, 2015 3:44pm c 2015 Avinash Kak, Purdue University Goals: Packet-filtering
Linux as an IPv6 dual stack Firewall
 Linux as an IPv6 dual stack Firewall Presented By: Stuart Sheldon [email protected] http://www.actusa.net http://www.stuartsheldon.org IPv6 2001:0DB8:0000:0000:021C:C0FF:FEE2:888A Address format: Eight 16
Linux as an IPv6 dual stack Firewall Presented By: Stuart Sheldon [email protected] http://www.actusa.net http://www.stuartsheldon.org IPv6 2001:0DB8:0000:0000:021C:C0FF:FEE2:888A Address format: Eight 16
Network and Services Discovery
 A quick theorical introduction to network scanning January 8, 2016 Disclaimer/Intro Disclaimer/Intro Network scanning is not exact science When an information system is able to interact over the network
A quick theorical introduction to network scanning January 8, 2016 Disclaimer/Intro Disclaimer/Intro Network scanning is not exact science When an information system is able to interact over the network
Chapter 13 Internet Protocol (IP)
 Chapter 13 Internet Protocol (IP) Introduction... 13-5 IP Packets... 13-5 Addressing... 13-7 Subnets... 13-8 Assigning an IP Address... 13-9 Multihoming... 13-11 Local Interfaces... 13-11 Address Resolution
Chapter 13 Internet Protocol (IP) Introduction... 13-5 IP Packets... 13-5 Addressing... 13-7 Subnets... 13-8 Assigning an IP Address... 13-9 Multihoming... 13-11 Local Interfaces... 13-11 Address Resolution
IPv6 Firewalls. ITU/APNIC/MICT IPv6 Security Workshop 23 rd 27 th May 2016 Bangkok. Last updated 17 th May 2016
 IPv6 Firewalls ITU/APNIC/MICT IPv6 Security Workshop 23 rd 27 th May 2016 Bangkok Last updated 17 th May 2016 1 Acknowledgements p Contains material from n Stallings and Brown (2015) n Ian Welch (Victoria
IPv6 Firewalls ITU/APNIC/MICT IPv6 Security Workshop 23 rd 27 th May 2016 Bangkok Last updated 17 th May 2016 1 Acknowledgements p Contains material from n Stallings and Brown (2015) n Ian Welch (Victoria
How To Set Up A Network Map In Linux On A Ubuntu 2.5 (Amd64) On A Raspberry Mobi) On An Ubuntu 3.5.2 (Amd66) On Ubuntu 4.5 On A Windows Box
 CSC-NETLAB Packet filtering with Iptables Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Date Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...2 2 Introduction...3 3 Getting started...3 4 Connecting to the virtual hosts...3
CSC-NETLAB Packet filtering with Iptables Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Date Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...2 2 Introduction...3 3 Getting started...3 4 Connecting to the virtual hosts...3
19531 - Telematics. 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P
 19531 - Telematics 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P Bastian Blywis Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 10. February, 2011 Institute of Computer Science Telematics
19531 - Telematics 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P Bastian Blywis Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 10. February, 2011 Institute of Computer Science Telematics
Focus on Security. Keeping the bad guys out
 Focus on Security Keeping the bad guys out 3 ICT Security Topics: Day 1: General principles. Day 2: System hardening and integrity. Day 3: Keeping the bad guys out. Day 4: Seeing the invisible; what's
Focus on Security Keeping the bad guys out 3 ICT Security Topics: Day 1: General principles. Day 2: System hardening and integrity. Day 3: Keeping the bad guys out. Day 4: Seeing the invisible; what's
Firewalls with IPTables. Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems
 Firewalls with IPTables Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Host-based Firewalls with IPTables 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Concepts...............................
Firewalls with IPTables Jason Healy, Director of Networks and Systems Last Updated Mar 18, 2008 2 Contents 1 Host-based Firewalls with IPTables 5 1.1 Introduction.............................. 5 1.2 Concepts...............................
OpenBSD in the wild...a personal journey
 OpenBSD in the wild......a personal journey Avik Sengupta Chief Technology Officer Itellix Software Solutions Pvt Ltd 2006 Avik Sengupta. Licensed under Creative Commons by-nc-nd. 1 Agenda OpenBSD Why
OpenBSD in the wild......a personal journey Avik Sengupta Chief Technology Officer Itellix Software Solutions Pvt Ltd 2006 Avik Sengupta. Licensed under Creative Commons by-nc-nd. 1 Agenda OpenBSD Why
