Can October Surprise? A Natural Experiment Assessing Late Campaign Effects
|
|
|
- Damon Todd
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Can Otober Surprise? A Natural Experiment Assessing Late Campaign Effets Mar Meredith and Neil Malhotra* * Visiting Leturer, Department of Politial Siene, MIT, mmeredit@mit.edu and Assistant Professor, Graduate Shool of Business, Stanford University, neilm@stanford.edu.
2 Abstrat One onsequene of the proliferation of vote-by-mail (VBM) in ertain areas of the United States is the opportunity for voters to ast ballots weeks before Eletion Day. Understanding the ensuing effets of VBM on late ampaign information loss has important impliations for both the study of ampaign dynamis and publi poliy debates on the expansion of onveniene voting. Unfortunately, the self-seletion of voters into VBM makes it diffiult to asually identify the effet of VBM on eletion outomes. We overome this identifiation problem by exploiting a natural experiment, in whih some preints are assigned to be VBM-only based on an arbitrary threshold of the number of registered voters. We assess the effets of VBM on andidate performane in the 2008 California presidential primary via a regression disontinuity design. We show that VBM both inreases the probability of seleting andidates who withdrew from the rae in the interval after the distribution of ballots but before Eletion Day and affets the relative performane of andidates remaining in the rae. Thus, we find evidene of late ampaign information loss, pointing to the influene of ampaign events and momentum in Amerian politis, as well as the unintended onsequenes of onveniene voting. 2
3 On the evening of September 30, 2004, George W. Bush and John Kerry met for the first of their three presidential debates. A Newsweek poll of registered voters wathing the debate found that Kerry won; 61 perent said he did a better job ompared to only 17 perent who seleted Bush. Prior to the debate, Bush was leading Kerry 54%- 43% in the poll; after the debate, Kerry had taken a 47%-45% lead, a substantial elevenpoint swing. However, Kerry s debate vitory ould not help him win the votes of ertain individuals living in battleground states like Iowa and Ohio who ast their ballots prior to the debate. These early voters are part of the growing segment of the United States eletorate that asts votes using onveniene voting, defined as any form of voting other than traditional polling plae voting, of whih vote-by-mail (VBM) and early inperson voting are most ommon. 1 Thirty-four states allow voters to ast no-exuse VBM or early in-person ballots, and the remainder allow VBM if voters have ertain exuses for why they annot vote in-person. 2 In a number of these states onveniene voters make-up an inreasingly substantial portion of the eletorate; in California, for example, the perent of mail voters in the presidential primary inreased from less than ten perent in 1988 to 23.4, 34.3, and 41.7 perent in 2000, 2004, and 2008 respetively. 3 Distributing mail ballots weeks before Eletion Day gives voters the opportunity to make hoies in the absene of a signifiant amount of ampaign information, suh as the debates. In the weeks leading up to Eletion Day, advertisements and eletion overage are pervasive in the mass media. During the penultimate and final weeks of the 2004 presidential ampaign, the ampaigns and their surrogates ombined to spend more 1 Some past work has referred to mandatory mail balloting as vote-by-mail (VBM) and individuals seleting a mail ballot as absentee voting. In this paper we use the term vote-by-mail to refer jointly to both forms of mail ballots. 2 Retrieved from laws.php on 9/23/ Retrieved from on 9/23/
4 than $37 and $60 million dollars, respetively, on television ads alone (Anderson 2004; MCormik 2004). Moreover, in 2004, most major newspaper endorsements were announed in the final three weeks of ampaign. Our researh question in this paper is whether the ability to ast VBM ballots prior to Eletion Day auses a differential effet of late ampaign information on the hoies of VBM and polling plae voters. As disussed below, our findings enrih our understanding of several important debates in politial siene, inluding those on ampaign dynamis and the poliy impliations of onveniene voting. Our analysis fouses on differenes in the andidate hoies of VBM and polling plae voters in the 2008 California presidential primary. This rae has two appealing features for the purposes of addressing our researh question. First, there are several identifiable and temporally isolated ampaign events. Speifially, three major andidates John Edwards, Rudy Giuliani, and Fred Thompson abandoned their bids for their parties nomination in the interval between the distribution of VBM ballots and Eletion Day. Examining how VBM affets the performane of these withdrawn andidates provides us with a straightforward test of late ampaign information loss. These results help inform us of the potential effet of more traditionally studied aspets of the ampaign suh as debates and onventions. Seond, a number of primary eletions and auuses took plae in the interval between the distribution of VBM ballots and Eletion Day that affeted the relative standing of andidates remaining in the rae. In partiular, Mike Hukabee went from being the reent vitor of the Iowa auus when ballots were distributed to having almost no hane of winning the Republian nomination by Eletion Day. Hene, the 4
5 effet of VBM on Hukabee s performane provides insight into the importane of momentum in determining primary eletion hoies. Estimating the ausal effet of VBM on andidate hoie is ompliated by a seletion problem. Beause people who hoose to vote more onveniently prior to Eletion Day may differ in fundamental ways both observable and non-observable from people who vote at the polling plae, we annot ausally asribe differenes in andidate preferenes to the tehnology. 4 In this study, we address this identifiation problem by taking advantage of a natural experiment in California whih produes exogenous differenes aross preints in the number of VBM voters. 5 Briefly, the California Eletion Code permits ounty eletions offiials to delare preints with 250 or fewer registered voters as mail-only preints. Further, beause California often has several overlapping distrits and onsequently a plethora of ballot forms these small preints are often in dense urban areas, along with more rural portions of the state. Our analysis leverages this disontinuity by testing how differenes in the use of VBM in preints with slightly more than 250 voters versus preints with slightly less than 250 voters translate into differenes in andidate performane. Beause this speifi utoff is arbitrary (it ould have easily been seleted to be 200 or 300, for example), restriting our analysis to preints in the narrow region of the aliper around the disontinuity approximates the ideal of random assignment. This researh design produes two main results. First, we show that withdrawn andidates perform both statistially and substantively better when using VBM, 4 Previous researh has generally shown that preint day voters are younger, less eduated, and less partisan (Patterson and Caldeira 1985; Dubin and Kalsow 1996; Stein 1998; Baretto et al. 2006, though see Neeley and Rihardson 2001 for an alternate aount). 5 This natural experiment was previously identified by Kousser and Mullin (2008) in their study of the effets of mandated VBM on turnout. 5
6 suggesting that VBM does ause late ampaign information loss. On the Demorati side, John Edwards reeived about four to five perentage points more votes on VBM ballots. On the Republian side, Rudi Giuliani and Fred Thompson eah reeived about two to three perentage points more votes on VBM ballots. Seond, we show that VBM affets the relative performane of andidates that remain in the rae. Mike Hukabee, for example, outperformed John MCain and Mitt Romney among VBM voters relative to polling plae voters. This result is onsistent with Hukabee reeiving a strong, albeit brief, boune of momentum following his vitory in the Iowa auuses. These findings shed important light on three major debates in politial siene. First, they provide evidene that events during the ampaign signifiantly influene vote hoie, thereby rejeting the minimal effets hypotheses. Importantly, this paper presents evidene from a ausally-identified naturalisti ontext, supplementing and supporting previous literature that has used surveys, laboratory experiments, or observational studies to demonstrate omparable effets (e.g. Hillygus and Jakman 2003; Holbrook 1996; Iyengar and Kinder 1987). Seond, our results present empirial support again from a naturalisti ontext for theoretial models and empirial explorations of sequential primaries that highlight the importane of past ontests on future eletion results (Aldrih 1980a, 1980b; Abramson et al. 1992; Ali and Kartik 2008; Callander 2007; Klumpp and Polborn 2006), and the entral role of momentum in determining eletion outomes (e.g. Bartels 1988; Kenney and Rie 1994; Knight and Shiff 2007). 6 Third, the findings speak diretly to publi poliy onerns about the effets of onveniene voting, whih have been touted as a mehanism for making voting easier 6 For an exellent overview of this literature, see Norrander (1996). 6
7 and enhaning partiipation. 7 Whereas existing researh has foused on turnout impliations (e.g. Southwell and Burhett 2000; Berinsky et al. 2005; Kousser and Mullin 2008) or the partisan impats (e.g. Stein 1998; Baretto et al. 2006; Dyk and Gimpel 2005; Berinsky 2005), this paper addresses a totally unexplored question: Does onveniene voting adversely affet itizen deision making by eliminating late ampaign information? We find that itizens who were not exposed to later information potentially wasted their votes by seleting andidates no longer in the rae. Additionally, people presumably voted sub-optimally without aess to late information, suh as the results of the South Carolina primary or the Demorati debate that took plae in Los Angeles a few days before the eletion. As voting moves earlier and earlier, it is important for poliymakers to be aware of these unintended onsequenes. The paper proeeds as follows. Setion I presents a theoretial overview to motivate the analyses. Setion II details the 2008 California presidential primary and desribes the natural experiment. The following two setions present our prinipal hypotheses and disuss the eonometri methods to test them. The final two setions present the results and disuss their impliations. I. Bakground and Coneptual Overview A major question in the study of eletions has been: Do ampaigns matter? The early researh on the topi hypothesized that ampaigns had minimal effets on voter attitudes and behavior, as the primary determinants of vote hoie were presumed to be fixed demographi harateristis suh as religion and ethniity (Berelson et al. 1954) and itizens long-standing party attahments (Campbell et al. 1960). Additionally, 7 A survey of the literature on onveniene voting is provided by Gronke et al. (2008). 7
8 other sholars argued that maroeonomi onditions outside the ontrol of the andidates during the short time period of the ampaign were powerful preditors of vote hoie (e.g., Kramer 1971; Fiorina 1981). Conurrent with these advanes in sholarship, researh on politial psyhology ontended that itizens were not politial ideologues and did not pay lose attention to politial events or possess strongly held attitudes on issues (Converse 1964). Modern empirial researh provided support to these onjetures (Bartels 1993; Gelman and King 1993), arguing that the publi s inattention as well as balaned spending by both sides mitigate the influene of ampaigns. Reent sholarship has alled this earlier researh into question by leveraging advanes in methodology and researh design. Many sholars have taken advantage of both survey and laboratory experiments in addition to onduting more detailed observational studies with riher data to isolate the ausal impats of speifi politial events. Several features of ampaigns have been found to substantially influene voters attitudes and evaluations of the andidates inluding politial advertising (Ansolabehere and Iyengar 1995; Freedman and Goldstein 1999; Geer and Lau 2006; Shaw 1999), media overage (Iyengar and Kinder 1987; Holbrook 1996), andidate appearanes (Shaw 1999), raial ues (Mendleberg 2001; Valentino et al. 2004), party onventions, and debates (Holbrook 1996; Drukman 2003). Additionally, field experiments by Gerber and Green (2000, 2008) and others have demonstrated the powerful impat of mobilization efforts that take plae during ampaigns. Additionally, advanes in data olletion methods have produed more nuaned results. The ability to ondut multiple interviews over short time periods has made it muh more possible to identify the influenes of speifi events. Johnston et al. s (1992) 8
9 pioneering study of the 1987 Canadian national eletion utilized a rolling ross-setion design to find a substantial impat of a debate over free trade in boosting support for the liberal party. Using multiple interviews of the same group of respondents in an Internet panel, Hillygus and Jakman (2003) found that onventions and debates signifiantly affeted itizens support for andidates in the 2000 presidential eletion, and that moderates and Independents were the most likely to be moved by suh events. More broadly, the authors found that voters hange their minds often during the ampaign, and that these swithes are systematially linked to ampaign events. This paper advanes the study of ampaign effets by presenting a novel methodology to identify their existene in a naturalisti setting. We exploit temporal variation in when VBM and polling plae voters make their hoies to study the effets of late ampaign events on vote hoie. Moreover, we take advantage of a natural experiment to aount for seletion issues in the types of voters using VBM and traditional polling plaes. In doing so, we hope to address some of the limitations of previous methodologies. Whereas laboratory and survey experiments an identify ausal effets of treatments, they are limited in terms of external validity. In addition to the treatment often not having ampaign analogues, respondents behavior may hange if they know they are being monitored, the effets may wear off over time, and partiipants in experiments are self-seleted volunteers. Rolling-ross setion and panel designs also address ausality, but the response variable is still an attitude or survey response, not an atual behavior. Finally, the analysis of observational data from the field is subjet to ommon ritiisms of non-experimental work inluding omitted variable bias, simultaneity, and unobserved heterogeneity. 9
10 The natural experiment desribed in this study has two main advantages. First, we are able to identify the ausal effets of the ampaign beause some voters are quasirandomly assigned to VBM or at a polling plae. Seond, the response variable we are measuring is the atual votes ast by itizens, not the survey responses or intended vote hoies of respondents who have self-seleted into an experiment. Hene, we are able to assess whether the ampaign effets identified in the lab and in surveys extend to a naturalisti ontext. However, beause our assignment mehanism is exogenous, we are able to interpret our findings as ausal. This is not to say that our approah does not have its own limitations. The priniple one is that the time period in whih the treatment is administered is somewhat long. Moreover, sine our subjets are not in a ontrolled laboratory setting, we are not able to attribute hanges in behavior to a single treatment. Rather, we an only say that a group of events that took plae during a given time period during the ampaign influened vote hoie, and simply infer as to what those speifi events were. Nevertheless, our findings in onjuntion with those found in other settings by other sholars advane the literature on ampaign effets by onfirming speifi findings in a more general naturalisti setting. II. The 2008 California Presidential Primary The 2008 California presidential primary took plae on February 5, 2008, ommonly known as Super Tuesday. California was one of the twenty-four states holding at least one primary or a auus on this day. On the Demorati side, eight andidates appeared on the ballot: Mike Gravel, John Edwards, Joe Biden, Barak 10
11 Obama, Chris Dodd, Hillary Clinton, Bill Rihardson, and Dennis Kuinih, although only Obama, Clinton, and Gravel remained in the rae. Clinton edged Obama 51.5 to 43.2 perent, netting her approximately 55 perent of the Demorati onvention delegates. On the Republian side, eleven andidates appeared on the ballots: Mike Hukabee, Dunan Hunter, Tom Tanredo, Fred Thompson, Rudy Giuliani, Sam Brownbak, John Cox, John MCain, Mitt Romney, Ron Paul, and Alan Keyes, although only Hukabee, MCain, Romney, Paul, and Keyes remained in the rae. John MCain won the Republian rae with 42.3 perent of the vote and nearly all of the available Republian onvention delegates, with Mitt Romney and Mike Hukabee finishing seond and third with 34.6 and 11.7 perent of the vote, respetively. Figure 1 provides a timeline of the important events leading up to the California primary. On November 6, 2007, 88 days before the primary, the total number of voters registered in a preint determined the eligibility of a preint for mail-ballot only status. The first primary votes were ast in both the Demorati and Republian raes in the Iowa auuses on January 3, Four days later, one day before the New Hampshire primary, California ounties began distributing VBM ballots to both registered voters hoosing to vote-by-mail and to all registered votes in mail-ballot only preints. These VBM ballots required reeipt by ounty offiials by 8 pm on Eletion Day to be ounted and ould be returned either via mail or dropped off at any polling plae in the ounty. The andidates positions in the rae hange onsiderably from when VBM ballots were mailed out to Eletion Day. The top panel of Figure 2 shows how the pries of ontrats from the Iowa Eletroni Market paying $1 if Hillary Clinton and Barak Obama won the Demorati nomination respetively varied over the period after the first 11
12 reeipt of ballots and the California primary. The figure suggests that Clinton gained some advantage over Obama following her 51 perent to 45 perent vitory in the Nevada Cauus, whih Obama largely took bak after his larger than expeted 55 perent to 27 perent vitory over Clinton in the South Carolina primary. After finishing third with eighteen and fourteen perent of the vote in South Carolina and Florida respetively, John Edwards dropped out of the rae on January 31, 2008, one day prior to Clinton and Obama squaring off in the California Demorati debate in Los Angeles, and six days prior to the California primary. Hene, there were numerous events that took plae in the month prior to Eletion Day, and VBM and polling plae voters may have been exposed to different levels of information. The Republian ontest was similarly dynami. The bottom panel of Figure 2 shows how the pries of similar ontrats paying $1 if John MCain, Mitt Romney, and Mike Hukabee won the Republian nomination varied over the same time interval. The figure indiates that John MCain s vitories in South Carolina and Florida primaries made him the overwhelming favorite to win the Republian nomination prior to the California primary. Romney s vitories in the Mihigan primary and the Nevada auus left him as the only other andidate with a non-trivial hane of winning the nomination. Mike Hukabee, who won the initial auus in Iowa, failed to win any primary or auus in this interval, whih aused the value of his ontrat to drop from about $0.20 when VBM ballots were distributed to less than $0.01 on Eletion Day. Also noteworthy over this interval was the withdrawal of Fred Thompson and Rudy Giuliani from the rae seventeen and six days before the California primary, respetively. 12
13 III. Hypotheses We expet that voters using VBM will ast ballots earlier in the eletion yle than is optimal for full information aggregation. A well established literature in psyhology shows that people tend to be overonfident in deision making (see Tversky and Kahneman (1974) for a summary). As a result, voters may underestimate the likelihood that they will want to swith their votes prior to Eletion Day. This may be more likely in primaries beause voters annot rely on party ues. Moreover, previous researh in behavioral eonomis has shown that people tend to be risk-averse (see also Tversky and Kahneman 1974), and onsequently may meet deadlines early to absolutely ensure that their ballot reahes on time. For instane, people tend to pay of redit ard bills far before the deadline even though the payment an arue interest for the onsumer before it is due. Finally, to the extent voting provides onsumptive rather than investment benefits, individuals may hoose to onsume the at of voting as soon as possible and be exited to express their viewpoints (Fiorina 1976). In sum, many voters will be tempted to send in their ballot far before Eletion Day. Holding all else equal, we therefore expet a vote ast using VBM will be less likely to apture late ampaign information than a vote ast at a traditional polling plae. We first investigate whether VBM affets the vote share of the major andidates that withdrew from the rae in the interval between the distribution of ballots and the primary. We predit that late ampaign information loss will ause John Edwards, Rudy Giuliani, and Fred Thompson to perform better among VBM voters. This is not to say that some voters do not prefer to vote for withdrawn andidates under full information as a protest or expressive vote; indeed John Edwards got more than seven perent of the 13
14 vote in the West Virginia primary on May 13, 2008, months after he withdrew from the rae. Instead, we attribute any signifiant inrease in support for withdrawn andidates when using VBM instead of polling plae as evidene of late ampaign information loss. We also investigate the effet of VBM on the relative performane of andidates remaining in the rae. We predit that momentum hanges in the interval between the distribution of ballots and the primary will be inorporated less into VBM ballots. In this ase, Mike Hukabee lost the momentum he gained from winning the Iowa auus when he failed to win any additional primaries or auuses prior to Super Tuesday; Figure 2 indiates that he went from being a top ontender for the nomination when ballots were distributed to having almost no hane for the nomination by the day of the California primary. We therefore expet that California voters asting ballots earlier will be more likely to support Hukebee, whih will result in Hukabee outperforming John MCain and Mitt Romney on VBM relative to polling plae ballots. IV. Desription of the Natural Experiment Our analysis uses preint-level data from the 2008 February Presidential Primary for 48 of the 58 ounties in California. 8 We supplement our preint-level vote totals with preint-level demographi data onstruted by aggregating individual voting reords from the California Statewide Voter File. Using orrespondenes obtained either from the Berkeley Statewide Voter Database or diretly from the ounties, we were able 8 We were unable to obtain preint-level data for Trinity County. We exluded data from San Diego, Monterey, Tulare, San Luis Obispo, Nevada, Sutter, and Inyo ounties from the analysis beause results were reported at a different level of aggregation than what is used to assign mail-only preints. We also exluded data from Tuolumne and Calaveras ounties beause the number of absentee and polling plae votes were unavailable at the rae level. In San Mateo and Orange ounties, we were unable to ollet preint-level data on the number VBM and polling plae votes. For these ounties, we assume that all non mail-only preints have a VBM perentage equal to the ounty average VBM perentage in a given rae. Results are nearly idential if we exlude these ounties from the analysis. 14
15 to map individuals voter file preints (e.g. home preints) to individuals onsolidated preints (e.g. preints from whih mail-only status is assigned and eletion results are reported). We dropped data from those preints in whih we were unable to math any registrants from the voter file. The diffiulty with studying the effets of VBM on eletion outomes is that individuals generally either selet into VBM or the entire eletorate is fored to VBM (for example, in Oregon). Beause those individuals that selet into VBM are not randomly seleted from the eletorate, differenes in observed eletion outomes between VBM and polling plae voters will likely onfound the effets of VBM with differenes aused by seletion bias. Conversely, when the entire eletorate is fored to VBM it is diffiult to onstrut the ounterfatual outome that would have ourred if the eletorate had voted at polling plaes. One ould examine hanges over time as states adopt VBM, but differenes in the politial environment and the harateristis of the eletorate between t and t+1 are potential onfounders. To address this identifiation problem, we take advantage of a natural experiment in California that results in a small subset of the state being fored to VBM, while the remainder of the state is allowed to hoose between VBM and polling plae voting. Setion 3003 of the California Eletion Code speifies that a preint an be ategorized as a VBM-only preint if 88 days prior to an eletion there are fewer than 250 registrants. In these preints everyone uses VBM, instead of the mix of VBM and traditional polling plae voting in a normal preint. A preint is a geographi grouping of registered voters that onsists of no more than 1000 voters that use the same ballot 15
16 form. 9 Setion 3003 also states that preints are not allowed to be divided in order to onform to the 250 registrant requirement. A onsequene of this law is that two otherwise similar types of preints that fall on either side of the mail-only threshold are assigned different treatment statuses. Figure 3 illustrates the effet of preint size on the use of mail-only preints by graphing the perentage of mail-only preints by the number of registrants on Eletion Day. There is a sizeable derease in the perentage of mail-only preints when the number of registrants is just above versus just below the 250-registrant threshold. Figure 3 also shows two unexpeted features. First, beause we observe registration on Eletion Day rather than November 6, 2007, when mail-only status is determined, there appears to be a number of mail-only preints just above the 250- registrant threshold that were likely below the threshold on November 6, Seond, independent of this measurement error there are observations above the threshold that are mail-only and observations below the threshold that are polling plaes; gains or losses in registration between November and February annot explain a mail-only preint in La Quinta in Riverside County with 702 registrants on Eletion Day or a polling plae preint in Baker in San Bernardino County with 140 registrants. In order to determine the soure of these disrepanies, we interviewed eletion offiials from many ounties in our dataset, inluding all of the disrepant ounties. The eletion offiials provided us with a number of fators that may affet whether a preint is mail-only. A number of ounties (Butte, El Dorado, Mered, Napa, Riverside, Santa Clara) told us that they did not ount permanent absentee voters in determining whether a 9 Beause of new registrants entering existing preints, there are more than 1000 registrants in some preints. 16
17 preint was eligible to be mail-only. 10 The logi here is that inluding permanent VBM voters would be double ounting sine they are not expeted to visit the polling plae on Eletion Day. A number of other ounties make military bases VBM regardless of the registration due to seurity onerns. Finally, some preints with fewer than 250 registrants were still made into traditional polling plae preints. County eletions offiials ited the availability of a polling plae loation as an important determinant of whether a preint with fewer than 250 registrants was left as a traditional polling plae. Beause mail-only preints are not purely randomly seleted from the universe of preints, as they would be in a laboratory experiment, we annot assess the effets of VBM by simply omparing the eletion outomes in mail-only preints against traditional polling plae preints. Kousser and Mullin (2008) deal with this non-random seletion by using propensity sore mathing to reate a ontrol group of traditional polling plaes with nearly idential ensus bloks harateristis as mail-only preints. Mathing only produes unbiased estimates if all relevant variables used to determine mail-only status are inluded in the mathing speifiation. Beause there are likely to be unobservable fators (like polling plae availability) that affet the hoie of whether to make a preint mail-only, mathing is unlikely to produe unbiased estimates (Areneaux et al. 2006). 11 However, Figure 3 shows that the 250-registrant threshold generates a fuzzy disontinuity in the probability that a preint is mail-only. Conditional on the effet of preint size being ontinuous on eletion outomes, this implies that being above versus below the 250-registrant threshold is a valid instrument for the perentage of VBM ballots ast in a preint (Hahn, Todd, and Van der Klaauw, 10 Riverside also said that it used 350 registrants rather than 250 registrants as its threshold. 11 For example, Butte, El Dorado, Napa, and Riverside are inluded in Kousser and Mullin s sample, but the perent of permanent absentee voters is not one of the mathed variables. 17
18 2001). 12 Put another way, Figure 3 suggests that we an simulate a quasi-random experiment by omparing outomes in preints just above versus just below the arbitrary 250-registrant threshold. V. Methods In this setion, we develop our identifiation strategy, whih we oneptually illustrate in Figure 4. The top panel of Figure 4 shows how the perentage of total ballots that were VBM in the Demorati primary varies with the number of registrants in the preint. The perentage of VBM ballots dereases as the preint size inreases above 250; although even in preints far above the threshold there still are a substantial perentage of votes who selet into VBM. For example, in preints with 201 to 250 registrants, 95.8 perent of ballots were VBM, ompared to only 63.9 perent of ballots in preints with 251 to 300 registrants. The bottom panel of Figure 3 gives the vote share of John Edwards by the size of the preint on Eletion Day. The figure shows that Edwards vote share delines as preint size inreases above 250 registrants. For example, in preints with 201 to 250 registrants that John Edwards reeived about 7.5 perent of the vote, as ompared to 6.0 perent of the vote in preints with 251 to 300. To estimate edwards, the perentage point inrease in the likelihood of voting for Edwards from asting a VBM ballot, we divided the differene in eletion performane by the differene in the treatment onentration: edwards , or about 4.7 perentage points The solution is analogous to Gerber and Green (2000) using treatment assignment as an instrument for treatment status in their experimental study of GOTV ativity, in whih seletion into the treatment (i.e., being home when the anvasser visits or alls) is nonrandom. 18
19 We next hek for balane around the disontinuity. Table 1 ompares the demographis of registered voters in preints just above and just below the 250- registrant threshold. Table 1 shows that there are some small demographi imbalanes between the two groups. Preints just below the 250-registrant threshold are slightly more Republian than those just above the arbitrary 250-registrant threshold. In addition, preints just below the 250-registrant threshold ontain a higher perentage of older and male registered voters. When we turn to regression analysis we estimate models that inlude these ovariates to ensure that our oeffiients estimates are robust to these demographi imbalanes. In most ases, we find that our estimates are unaffeted when we inlude these ovariates. Model We use two different types of instrumental variables (IV) regression speifiations to formally test the effets of VBM on vote hoie. Equations (1) and (2) represent the first and seond stage regressions, respetively, in the first type of IV speifiation: % (1) VBM p, 1( ') ( registrants p, utoff ) p, ' % (2) y p, 1( ') (% VBM p, ) p, where %VBM p, is the perentage of vote-by-mail ballots in preint p in ounty, registrants p, is the number of registrants on Eletion Day in preint p in ounty, utoff is the utoff for being a mail ballot preint in ounty, %y p, is andidate y s vote share in preint p in ounty, and p, and p, represent stohasti disturbanes. In 19
20 this speifiation we limit the sample to preints where utoff K registrant sp, utoff K, where K = {50, 75, or 100} and we do not weight observations beause they are approximately equally sized. 13 Equations (3) and (4) define the seond type of IV speifiation: % VBM p, ( registrants z p, z 1( zip p, utoff z) K) ( registrants ( registrants p, p, utoff utoff ) K) X p, p, (3) % y p, z ( registrants z 1( zip p, p, utoff z) K) (% VBM p, ) ( registrants p, utoff K) X p, p, (4) where zip p, is the zip ode that ontains a plurality of the registrants in preint p in ounty and X p, is a vetor of ontrol variables that ontains the perent of registered voters in preint p who are registered Demorats, registered Republians, age 18 29, age 30 44, age 45 64, male, and unknown gender. In this speifiation we inlude all preints in the dataset and weight observations by the number of votes ast in andidate y s rae. The main differene between the two sets of equations is that (1) and (2) inlude ounty fixed effets that are estimated from points only within K registrants of the threshold, whereas (3) and (4) inlude zip ode fixed effets estimated using the entire dataset. Both types of speifiations have their relative advantages. Beause we estimate equations (1) and (2) using only data near the threshold, the estimates annot be ontaminated if preints far from the disontinuity are different in some fundamental way. Equations (3) and (4) also identify the effets of VBM using information from 13 Note that even if our disontinuity wasn t fuzzy, we still wouldn t expet that π would equal 1, beause individuals still have the option to self-selet into VBM in non-vbm-only preints. 20
21 preints with a total number of registrants within K of the disontinuity. However, they also use information from preints far away from the disontinuity to identify the effets of the other ovariates, potentially making Equations (3) and (4) more effiient. Both speifiations rely on the exlusion restritions that preints with a total number of registrants between utoff K and K are the same as preints with a total number of registrants between K and utoff + K onditional on the other ovariates. 14 The reason that the variable utoff is inluded in the above speifiations is so that we an inlude information from ounties that exlude permanent VBM registrants in our regressions. In ounties that do not exlude permanent VBM registrants, utoff is set equal to 250. In ounties that do exlude permanent VBM registrants, we first alulate the perentage of all voters in the ounty that are permanent VBM registrants, %PVBM. In Butte, El Dorado, Mered, Napa, and Santa Clara ounties we set utoff equal to 250 / (1 - %PVBM ). Beause Riverside County told us they use as utoff of 350 rather than 250, we instead set utoff equal to 350 / (1 - %PVBM ). VI. Results Assessing Campaign Effets with Withdrawn Candidates We find that andidates who withdrew from the eletion in the days before Super Tuesday reeived greater support among VBM voters, suggesting late ampaign information loss. In other words, many of these people ast their ballots without knowing these andidates were no longer in the rae, and potentially wasted their vote by not swithing to a remaining andidate. Table 2a presents the effets of VBM on John 14 We estimate a number of additional speifiations that inlude various polynomials or splines of total registrants that are available from the authors upon request. The results of these alterative speifiations are substantively similar to those reported here. 21
22 Edwards vote share. As a baseline for omparison, we first estimate equation (2) naively using ordinary least squares (OLS), prediting Edwards vote share simply with the perentage of mail-in ballots in the preint, along with ounty fixed-effets. As shown in olumn (1) of Table 2a, the estimate of is.083, meaning that in a preint that is wholly VBM, John Edwards reeived, on average, 8.3 more perentage points of the vote as ompared to a preint that entirely onsists of polling plae voters. In olumns (2)-(4), we present IV estimates of equation (2) using a variety of different bandwidths (K) around the disontinuity. For instane, when K = 50, we restrit our analysis to preints within 50 registered voters of utoff, and use whether the number of registered voters is greater than utoff as an instrument for the perentage of VBM ballots. We obtain point estimates between 4.2 and 5.3 perentage points depending on the size of K, all of whih are highly statistially signifiant at onventional levels (p<.001, two-tailed). This result is highly robust; our estimates of late ampaign information loss remain highly signifiant aross a number of speifiations. We use zip ode fixed effets in plae of ounty fixed effets in olumns (5)-(8). The three IV regressions find similar estimates ranging from 4.4 to 5.1 perentage points with substantially redued standard errors. Inluding demographi ovariates (x p ) and estimating equations (3) and (4) also produes similar results, alleviating onerns of omitted variable bias. As shown in olumns (10)-(12), the point estimates range between 4.0 and 4.7 perentage points. Thus, we find that VBM were less likely to inorporate information about Edwards exit from the rae into their vote hoie. This indiates that the opportunity to submit votes early aused a substantial number of Demorati primary voters to essentially waste their votes. As mentioned above, beause of our identifiation strategy, this differene 22
23 an be ausally attributed to the timing of the vote, not to unobserved harateristis of VBM voters. Similar results were observed in the Republian primary, with Giuliani and Thompson reeiving signifiantly greater support among VBM voters. Tables 2b and 2 present estimates from an analogous set of regressions to those presented in Table 2a. Similar to Edwards, we find that Giuliani and Thompson reeived a signifiantly higher share of votes from VBM ompared to polling plae voters. Depending on the speifiation, we find that moving from a preint with no VBM ballots to all VBM ballots inreases both Giuliani and Thompson s vote shares by two to three perentage points. Again these results are robust to the inlusion of zip ode fixed effets and demographi ovariates. Although the effet on Thompson s performane is highly signifiant aross all speifiations, the effet on Giuliani s vote share is only marginally signifiant in the narrowest window. When interpreting our results, it is important to onsider the loal average treatment effet (LATE) property of RD estimation (Hahn, Todd, Van der Klaauw, 2001). RD gives the effet of the treatment for those observations whose treatment status is affeted by the disontinuity. In this ase, these are voters who would hoose to vote in a polling plae if they were not fored to VBM. The IV results do not provide any insight about whether similar patterns would hold for those voters who hoose to VBM. However, the ross-setional orrelations between mail voting and the seletion of Edwards, Giuliani, and Thompson suggest that similar effets likely hold for voters seleting to VBM. 23
24 We would like to know what these results tell us more generally about voters responses to late ampaign information. To assess this, we would ideally estimate what perentage of Edwards, Giuliani, and Thompson supporters did not inorporate information about their exit when asting VBM ballots. To make this alulation, we need to know the baseline level of support that Edwards, Giuliani, and Thompson had prior to dropping out of the rae. While our eonometri model annot provide these diretly, we an approximate what they likely were using previous eletion results and polling data. The California Field Poll, taken between January 13th and January 20th, found Edwards reeiving about 10 perent of the vote on the Demorati side, while Giuliani and Thompson reeived about 11 and 9 perent of the vote on the Republian side respetively. These levels of support are broadly onsistent with other polls and primary eletion results observed over this period. If we assume that eah andidate had about ten perentage points of support between when VBM ballots were mailed and their exit from the rae, our estimates of suggest that about 40 to 50 perent of Edwards supporters (i.e., 4-5 divided by 10) and 20 to 30 perent of Giuliani s and Thompson s supporters would have voted differently if they had not been using VBM. To speulate about what these results tell us about VBM and ampaign effets more generally, note that Thompson exited the rae sixteen days before Eletion Day and Edwards and Giuliani exited six days before Eletion Day. Therefore, our results suggest that around 25 perent of VBM voters did not inorporate information that ourred two weeks before an eletion into their voting deision, while up to 50 perent of VBM voters did not inorporate information that happens in the final week on the ampaign. Given that potentially relevant ampaign information has ome out in the last week of reent 24
25 presidential ampaigns, onveniene voting may have important effets on general eletoral outomes. For instane, in the 2000 eletion, Karl Rove s internal data suggested that George W. Bush lost 4 million evangelial votes due to the news of his DUI onvition, whih Bush aknowledged five days before the eletion (Denton 2005). Additionally, internal analyses by Kerry advisors Mary Beth Cahill and Mark Mellman suggested that the release of an al Qaeda tape featuring Osama bin Laden three days before the 2004 eletion primed terrorism in voters minds, reduing Kerry s vote share (Harvard Institute of Politis 2006). Our results suggest that a signifiant proportion of the eletorate will be unable to inorporate potentially important late ampaign information as a onsequene of onveniene voting. Assessing Momentum with Remaining Candidates We find that Mike Hukabee performed signifiantly better among VBM voters, suggesting that he reeived a burst of momentum following his surprise Iowa auus vitory, whih had dissipated by the time of Super Tuesday a month later. Table 3a presents regression results of the effet of VBM on the differene between Hukabee s vote share in the preint and the winner MCain s share. The naive OLS regression in olumn (1) shows a large negative orrelation between Hukabee s relative performane and the use of VBM. Note that this estimate does not represent a treatment effet beause ounties with high perentages of VBM voters have other harateristis orrelated with support for Hukabee. However, onsistent with our momentum loss hypothesis, the sign flips when we isolate the effet around the disontinuity and inlude zip-ode speifi fixed effets. In olumns (6) (8), we find marginally signifiant positive effets that 25
26 range between 3.7 and 8.8 perentage points when we instead estimate equations (3) and (4) exluding X p. When we inlude X p in olumns (10) (12) this effet grows to be between 5.6 and 11.4 perentage points. This inrease when X p is inluded ours beause preints below the 250-registrant threshold are slightly more Republian, older, and more male than preints above the threshold, all of whih negatively orrelate with Hukabee s relative performane to MCain in a preint. Our finding that Hukabee s support was signifiantly greater when voters were not exposed to late ampaign information builds upon existing literature on momentum in sequential eletions suh as presidential primaries. This literature suggests that performane in early ontests provides andidates with momentum that affets them in later eletions. California voters reeived their ballots on January 7 th, only four days after Hukabee s vitory in the Iowa auus. Thus, VBM voters had the opportunity to ast ballots immediately after the Iowa vitory and before a number of subsequent eletions in whih Hukabee performed poorly. Consistent with past results in the laboratory and on surveys, we show that observing these poor eletion performanes aused a signifiant redution in the likelihood of supporting Hukabee. One alternative explanation for Hukabee s worse performane relative to MCain among polling plae voters is that former Giuliani and Thompson voters disproportionately swithed to voting for MCain. To assess this, we also examined the vote share of Mitt Romney relative to John MCain. If Giuliani and Thompson supporters went predominantly for MCain, we expet that Romney would also perform relatively better than MCain among VBM voters. However, unlike what we observed in the Table 3a, Table 3b demonstrates small and insignifiant positive estimates of the 26
27 effet VBM on Romney s relative performane to MCain. Thus, while former Giuliani and Thompson voters may explain some portion of the gap between Hukabee and MCain on VBM ballots (e.g. Romney and MCain split their support), the magnitudes of the oeffiients in Table 3a are suh that it annot explain it entirely. Table 3 examines how VBM affeted the relative performane of Barak Obama and Hillary Clinton in the Demorati primary. We have no ex ante preditions about how their relative performane should be affeted by VBM. As Figure 2 demonstrates, there were relatively small hanges in momentum in the interval between the distribution of ballots and Eletion Day. Moreover, it is unlear whih andidate benefited more from Edwards exit from the rae. In addition, both ampaigns advertised heavily in California, whih may have affeted their relative standings. The point estimates in Table 3 suggest Clinton performed relatively better than Obama on VBM ballots. The naïve OLS speifiation show a large negative orrelation between the relative performane of Obama and the usage of VBM. The IV speifiations ontinue to show this negative relationship, although the size and signifiane of the estimate is sensitive to the window around the disontinuity. The point estimates range between a 2.0 and 9.9 perentage point redution in Obama s vote share on VBM ballots depending of speifiation. There are a number of potential explanations for the negative effet of VBM on Obama s performane. Figure 2 suggests that Obama may have gained some momentum following his vitory in the South Carolina primary that was lost on some VBM voters. Obama may have been more likely to gain the support of Edwards former supporters. Campaign advertising or debates may also have affeted the relative standing of Clinton 27
28 and Obama. Any or all of these explanations are potential mehanisms for the results observed in Table VI. Conlusion Hopeful of inreasing turnout and dereasing ost, eletions offiials around the ounty have been greatly inreasing their use of onveniene voting in reent years. Most of the resistane to this inrease has been based on the grounds that VBM and inperson early voting jeopardize the sense of ommunity generated by Eletion Day and inrease the potential for voter fraud. In this paper we doument an additional phenomenon not often disussed when onsidering the adoption of onveniene voting: the potential for late ampaign information loss. Using a RD design we doument that withdrawn andidates perform signifiantly better in the 2008 California presidential primary in preints where VBM ballots are mandated. What are the impliations of these findings for our study of ampaign effets? We find that voters signifiantly altered their preferenes in response to a major hange in the ampaign the exit of andidates. Although the result is not partiularly surprising (i.e., voters withdraw support for andidates who drop out), it is the first ausal evidene that we know of showing that events during the ampaign influening the behavior of eletion outomes. In future work we hope to extend the methodology developed here to onsider whether other major ampaign events suh as advertising, debates, and Otober surprises ause differential affets between VBM and polling plae voters. 15 One additional aveat to these results is that unlike with Hukabee, it is not lear how the demographi imbalanes aross the VBM threshold might affet our results. Registered voters in preints below the VBM threshold tended to be slightly older whih favored Clinton, but also slightly more Republian and male whih favored Obama. 28
29 Moreover, our findings have important impliations for publi poliy, espeially as early voting proliferates throughout the United States. We observed that a signifiant portion of Amerians were affeted by information emerging late in the ampaign, and some without aess to this information essentially wasted their votes. Hene, onveniene voting may be damaging the eletoral proess by dereasing the impat of traditionally important events suh as debates, ampaign advertisements, and mobilization drives. We believe that our results have important impliations for the design of eletoral systems. Conveniene voting began as early as late September in a number of states in 2008 presidential eletion. In some states this will result in the first votes being ast prior to the first presidential debate. Given the patterns observed in this paper, we think that eletions offiials need to have greater disussions about when to begin early voting, inorder to balane information loss and onveniene. This may be partiularly important in primaries, where momentum plays suh an important omponent in affeting voter hoie. States might want to wait until loser to Eletion Day to send out mail ballots. States also may onsider instruting people on ballots to make sure to wait until they are ready to make a deision before voting. To this end, we hope more researh is done in the future on this subjet to help guide this disussion. 29
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Effectiveness of a law to reduce alcohol-impaired driving in Japan
 Effetiveness of a law to redue alohol-impaired driving in Japan T Nagata, 1,2 S Setoguhi, 3 D Hemenway, 4 M J Perry 5 Original artile 1 Takemi Program, Department of International Health, Harvard Shool
Effetiveness of a law to redue alohol-impaired driving in Japan T Nagata, 1,2 S Setoguhi, 3 D Hemenway, 4 M J Perry 5 Original artile 1 Takemi Program, Department of International Health, Harvard Shool
Retirement Option Election Form with Partial Lump Sum Payment
 Offie of the New York State Comptroller New York State and Loal Retirement System Employees Retirement System Polie and Fire Retirement System 110 State Street, Albany, New York 12244-0001 Retirement Option
Offie of the New York State Comptroller New York State and Loal Retirement System Employees Retirement System Polie and Fire Retirement System 110 State Street, Albany, New York 12244-0001 Retirement Option
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship
 From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship Marianne Bertrand, University of Chiago, Center for Eonomi Poliy Researh, and National Bureau
From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship Marianne Bertrand, University of Chiago, Center for Eonomi Poliy Researh, and National Bureau
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
Table of Contents. Appendix II Application Checklist. Export Finance Program Working Capital Financing...7
 Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST
 Poliy/Certifiate Number(s) BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST *L2402* *L2402* Setion 1: Insured First Name Middle Name Last Name Permanent Address: City, State, Zip Code Please hek if you would like the address
Poliy/Certifiate Number(s) BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST *L2402* *L2402* Setion 1: Insured First Name Middle Name Last Name Permanent Address: City, State, Zip Code Please hek if you would like the address
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effect: New Evidence from Norway 1
 Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effet: New Evidene from Norway 1 Qinglei Dai Universidade Nova de Lisboa September 2005 1 Aknowledgement: I would like to thank Kristian Rydqvist at Binghamton
Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effet: New Evidene from Norway 1 Qinglei Dai Universidade Nova de Lisboa September 2005 1 Aknowledgement: I would like to thank Kristian Rydqvist at Binghamton
Motivations for swap-covered foreign currency borrowing
 Motivations for swap-overed foreign urreny borrowing Anella Munro and Philip Wooldridge 1 1. Introdution Borrowing denominated in foreign urrenies soared during the s. 2 Gross issuane of foreign urreny
Motivations for swap-overed foreign urreny borrowing Anella Munro and Philip Wooldridge 1 1. Introdution Borrowing denominated in foreign urrenies soared during the s. 2 Gross issuane of foreign urreny
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre
 Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Research Data Management ANONYMISATION
 ANONYMISATION Sensitive Data Sensitive Data is information overing: The raial or ethni origin of the Data Subjet Politial opinions Religious or other beliefs of a similar nature Membership of trade unions
ANONYMISATION Sensitive Data Sensitive Data is information overing: The raial or ethni origin of the Data Subjet Politial opinions Religious or other beliefs of a similar nature Membership of trade unions
MEMBER. Application for election MEMBER, NEW GRADUATE. psychology.org.au. April 2015
 MEMBER Appliation for eletion MEMBER, NEW GRADUATE April 2015 psyhology.org.au MEMBER Belonging to the Australian Psyhologial Soiety (APS) means you are part of an ative, progressive organisation whih
MEMBER Appliation for eletion MEMBER, NEW GRADUATE April 2015 psyhology.org.au MEMBER Belonging to the Australian Psyhologial Soiety (APS) means you are part of an ative, progressive organisation whih
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
Dynamic and Competitive Effects of Direct Mailings
 Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
Paid Placement Strategies for Internet Search Engines
 Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS. Discussion Paper No. 475. The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism
 RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
Optimal Health Insurance for Multiple Goods and Time Periods
 Preliminary draft for review only 0R.P. Ellis, S. Jiang, and W.G.Manning MultipleGood_ 00630.dox June 30, 0 Optimal Health Insurane for Multiple Goods and Time Periods Randall P. Ellis a,, Shenyi Jiang
Preliminary draft for review only 0R.P. Ellis, S. Jiang, and W.G.Manning MultipleGood_ 00630.dox June 30, 0 Optimal Health Insurane for Multiple Goods and Time Periods Randall P. Ellis a,, Shenyi Jiang
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012
 i e AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Gambling Duty At 2012 Index i e GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Index Setion Page PART 1 INTRODUCTORY 5 1 Short title... 5 2 Commenement... 5 3 General interpretation...
i e AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Gambling Duty At 2012 Index i e GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Index Setion Page PART 1 INTRODUCTORY 5 1 Short title... 5 2 Commenement... 5 3 General interpretation...
BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW WORKING PAPER SERIES, LAW & ECONOMICS WORKING PAPER NO. 00-03 AN ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION MODEL OF LITIGATION KEITH N. HYLTON This paper an be downloaded without harge at:
BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW WORKING PAPER SERIES, LAW & ECONOMICS WORKING PAPER NO. 00-03 AN ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION MODEL OF LITIGATION KEITH N. HYLTON This paper an be downloaded without harge at:
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
A Theoretical Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia *
 A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
A Theoretial Analysis of Credit Card Reform in Australia * by Joshua S. Gans and Stephen P. King Melbourne Business Shool University of Melbourne First Draft: 12 th May, 2001 This Version: 5 th May, 2003
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
THE TAX EXCLUSION FOR EMPLOYER-SPONSORED HEALTH INSURANCE
 National Tax Journal, June 2,64 (2, Part 2), 5-53 THE TAX EXCLUSION FOR EMPLOYER-SPONSORED HEALTH INSURANCE Jonathan Gruber This paper reviews the issues raised by and the impats of the tax exlusion for
National Tax Journal, June 2,64 (2, Part 2), 5-53 THE TAX EXCLUSION FOR EMPLOYER-SPONSORED HEALTH INSURANCE Jonathan Gruber This paper reviews the issues raised by and the impats of the tax exlusion for
The Optimal Deterrence of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits
 The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
The Basics of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment
 The Basis of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment Alberto Isgut, Ganesan Ravishanker, and Tanya Rosenblat * Wesleyan University Abstrat We introdue a simple web-based lassroom experiment in whih
The Basis of International Trade: A Classroom Experiment Alberto Isgut, Ganesan Ravishanker, and Tanya Rosenblat * Wesleyan University Abstrat We introdue a simple web-based lassroom experiment in whih
Information Security 201
 FAS Information Seurity 201 Desktop Referene Guide Introdution Harvard University is ommitted to proteting information resoures that are ritial to its aademi and researh mission. Harvard is equally ommitted
FAS Information Seurity 201 Desktop Referene Guide Introdution Harvard University is ommitted to proteting information resoures that are ritial to its aademi and researh mission. Harvard is equally ommitted
i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006
 i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Employment At 2006 Index i e EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Index Setion Page PART I DISCRIMINATION AT RECRUITMENT ON TRADE UNION GROUNDS 9 1 Refusal of employment on grounds
i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Employment At 2006 Index i e EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Index Setion Page PART I DISCRIMINATION AT RECRUITMENT ON TRADE UNION GROUNDS 9 1 Refusal of employment on grounds
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Working Paper Deriving the Taylor principle when the central bank supplies money
 eonstor www.eonstor.eu Der Open-Aess-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtshaft The Open Aess Publiation Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Eonomis Davies, Ceri; Gillman,
eonstor www.eonstor.eu Der Open-Aess-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtshaft The Open Aess Publiation Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Eonomis Davies, Ceri; Gillman,
SupermarketPricingStrategies
 SupermarketPriingStrategies PaulB.Ellikson Duke University SanjogMisra University of Rohester November 13, 2006 Abstrat Most supermarket firms hoose to position themselves by offering either Every Day
SupermarketPriingStrategies PaulB.Ellikson Duke University SanjogMisra University of Rohester November 13, 2006 Abstrat Most supermarket firms hoose to position themselves by offering either Every Day
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
WINSTON-SALEM STATE UNIVERSITY
 FRESHMEN TRANSFER STUDENTS NON-WSSU SECOND DEGREE STUDENTS NON-DEGREE & SUMMER SCHOOL TEACHER CERTIFICATION/LICENSURE READMISSION UNDERGRADUATE INTERNATIONAL WINSTON-SALEM STATE UNIVERSITY MAIL COMPLETED
FRESHMEN TRANSFER STUDENTS NON-WSSU SECOND DEGREE STUDENTS NON-DEGREE & SUMMER SCHOOL TEACHER CERTIFICATION/LICENSURE READMISSION UNDERGRADUATE INTERNATIONAL WINSTON-SALEM STATE UNIVERSITY MAIL COMPLETED
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
The B.E. Journal of Macroeconomics
 The B.E. Journal of Maroeonomis Contributions Volume 7, Issue 2007 Artile 9 Nominal Debt Dynamis, Credit Constraints and Monetary Poliy Liam Graham Stephen Wright University College London, liam.graham@ul.a.uk
The B.E. Journal of Maroeonomis Contributions Volume 7, Issue 2007 Artile 9 Nominal Debt Dynamis, Credit Constraints and Monetary Poliy Liam Graham Stephen Wright University College London, liam.graham@ul.a.uk
An exploration of student failure on an undergraduate accounting programme of study
 Aounting Eduation 11 (1), 93 107 (2002) An exploration of student failure on an undergraduate aounting programme of study LOUISE GRACIA* and ELLIS JENKINS University of Glamorgan, S Wales, UK Reeived:
Aounting Eduation 11 (1), 93 107 (2002) An exploration of student failure on an undergraduate aounting programme of study LOUISE GRACIA* and ELLIS JENKINS University of Glamorgan, S Wales, UK Reeived:
The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurance Plan Exclusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurance Company of America (Prudential)
 Plan Basis The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane Plan Exlusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurane Company of Ameria (Prudential) What does it over? The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane
Plan Basis The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane Plan Exlusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurane Company of Ameria (Prudential) What does it over? The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane
Night Work and Breast Cancer Risk Among Norwegian Nurses: Assessment by Different Exposure Metrics
 Amerian Journal of Epidemiology Advane Aess published Marh 31, 2011 Amerian Journal of Epidemiology ª The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg Shool
Amerian Journal of Epidemiology Advane Aess published Marh 31, 2011 Amerian Journal of Epidemiology ª The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg Shool
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Caught in the Crossfire: The Effects of a Peer-based Intervention Program for Violently Injured Youth
 JOURNAL OF ADOLESCENT HEALTH 2004;34:177 183 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Caught in the Crossfire: The Effets of a Peer-based Intervention Program for Violently Injured Youth MARLA G. BECKER, M.P.H., JEFFERY S. HALL,
JOURNAL OF ADOLESCENT HEALTH 2004;34:177 183 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Caught in the Crossfire: The Effets of a Peer-based Intervention Program for Violently Injured Youth MARLA G. BECKER, M.P.H., JEFFERY S. HALL,
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Strategies for Development and Adoption of ERR in German Ambulatory Care
 Strategies for Development and Adoption of ERR in German Ambulatory Care Sebastian Duennebeil 1, Ali Sunyaev 1, Jan Maro Leimeister 2, Helmut Krmar 1 1 Department of Informatis 1 Tehnishe Universitat MUnhen
Strategies for Development and Adoption of ERR in German Ambulatory Care Sebastian Duennebeil 1, Ali Sunyaev 1, Jan Maro Leimeister 2, Helmut Krmar 1 1 Department of Informatis 1 Tehnishe Universitat MUnhen
Market power and banking failures
 International Journal of Industrial Organization 20 (2002) 1341 1361 www.elsevier.om/ loate/ eonbase a Market power and banking failures Ramon Caminal *, Carmen Matutes a, a,b Institut d Analisi ` Eonomia
International Journal of Industrial Organization 20 (2002) 1341 1361 www.elsevier.om/ loate/ eonbase a Market power and banking failures Ramon Caminal *, Carmen Matutes a, a,b Institut d Analisi ` Eonomia
Monetary Policy, Leverage, and Bank Risk-Taking
 Monetary Poliy, Leverage, and Bank Risk-Taking Giovanni Dell Ariia IMF and CEPR Lu Laeven IMF and CEPR Otober 200 Robert Maruez Boston University Abstrat We provide a theoretial foundation for the laim
Monetary Poliy, Leverage, and Bank Risk-Taking Giovanni Dell Ariia IMF and CEPR Lu Laeven IMF and CEPR Otober 200 Robert Maruez Boston University Abstrat We provide a theoretial foundation for the laim
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System
 DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
Health Savings Account Application
 Health Savings Aount Appliation FOR BANK USE ONLY: ACCOUNT # CUSTOMER # Health Savings Aount (HSA) Appliation ALL FIELDS MUST BE COMPLETED. Missing fields may delay the aount opening proess and possibly
Health Savings Aount Appliation FOR BANK USE ONLY: ACCOUNT # CUSTOMER # Health Savings Aount (HSA) Appliation ALL FIELDS MUST BE COMPLETED. Missing fields may delay the aount opening proess and possibly
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Product Warranties and Double Adverse Selection
 rodut Warranties and Double Adverse eletion David A. oberman Assistant rofessor of Marketing INEAD Boulevard de Constane 77305 Fontainebleau Cede, Frane The author thanks rofessors Andy Mithell, Jak Mintz,
rodut Warranties and Double Adverse eletion David A. oberman Assistant rofessor of Marketing INEAD Boulevard de Constane 77305 Fontainebleau Cede, Frane The author thanks rofessors Andy Mithell, Jak Mintz,
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Board Building Recruiting and Developing Effective Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations
 Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Globalization, Jobs, and Welfare: The Roles of Social Protection and Redistribution 1
 Globalization, Jobs, and Welfare: The Roles of Soial Protetion and Redistribution Priya Ranjan University of California - Irvine pranjan@ui.edu Current Draft Otober, 04 Abstrat This paper studies the welfare
Globalization, Jobs, and Welfare: The Roles of Soial Protetion and Redistribution Priya Ranjan University of California - Irvine pranjan@ui.edu Current Draft Otober, 04 Abstrat This paper studies the welfare
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Account Contract for Card Acceptance
 Aount Contrat for Card Aeptane This is an Aount Contrat for the aeptane of debit ards and redit ards via payment terminals, on the website and/or by telephone, mail or fax. You enter into this ontrat with
Aount Contrat for Card Aeptane This is an Aount Contrat for the aeptane of debit ards and redit ards via payment terminals, on the website and/or by telephone, mail or fax. You enter into this ontrat with
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS
 SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS UNDER SECTION 48 OF THE SCHOOL STANDARDS AND FRAMEWORK ACT 1998 DfE Approved - Marh 1999 With amendments Marh 2001, Marh 2002, April 2003, July 2004, Marh 2005, February 2007,
SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS UNDER SECTION 48 OF THE SCHOOL STANDARDS AND FRAMEWORK ACT 1998 DfE Approved - Marh 1999 With amendments Marh 2001, Marh 2002, April 2003, July 2004, Marh 2005, February 2007,
NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology
 NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology January 2016 1 P a g e 1. Introdution... 5 1.1 Index Types... 5 1.2 Index History... 5 1.3 Index Curreny... 5 1.4 Index Family... 6 1.5 NQCI Index Setors... 6 2. Definitions...
NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology January 2016 1 P a g e 1. Introdution... 5 1.1 Index Types... 5 1.2 Index History... 5 1.3 Index Curreny... 5 1.4 Index Family... 6 1.5 NQCI Index Setors... 6 2. Definitions...
Design Implications for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trace Analysis
 Design Impliations for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trae Analysis Yanpei Chen, Kiran Srinivasan, Garth Goodson, Randy Katz University of California, Berkeley, NetApp In. {yhen2, randy}@ees.berkeley.edu,
Design Impliations for Enterprise Storage Systems via Multi-Dimensional Trae Analysis Yanpei Chen, Kiran Srinivasan, Garth Goodson, Randy Katz University of California, Berkeley, NetApp In. {yhen2, randy}@ees.berkeley.edu,
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939
 i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 The Personal Injuries (Emergeny Provisions) At 1939 Index i e THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 Index Setion
i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 The Personal Injuries (Emergeny Provisions) At 1939 Index i e THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 Index Setion
THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING. NURS 6390-004 Introduction to Genetics and Genomics SYLLABUS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING NURS 6390-004 Introdution to Genetis and Genomis SYLLABUS Summer Interession 2011 Classroom #: TBA and 119 (lab) The University of Texas at Arlington
THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING NURS 6390-004 Introdution to Genetis and Genomis SYLLABUS Summer Interession 2011 Classroom #: TBA and 119 (lab) The University of Texas at Arlington
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Chapter 1: Introduction
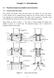 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Iatrogenic Specification Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1093 Iatrogeni Speifiation Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data Christopher R. Bollinger Amitabh Chandra Marh 2004 Forshungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1093 Iatrogeni Speifiation Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data Christopher R. Bollinger Amitabh Chandra Marh 2004 Forshungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
Are Rates of Psychiatric Disorders in the Homeless Population Changing?
 Are Rates of Psyhiatri Disorders in the Homeless Population Changing? Carol S. North, MD, MPE, Karin M. Eyrih, MSW, MPE, David E. Pollio, PhD, and Edward L. Spitznagel, PhD Objetives. We examined the prevalene
Are Rates of Psyhiatri Disorders in the Homeless Population Changing? Carol S. North, MD, MPE, Karin M. Eyrih, MSW, MPE, David E. Pollio, PhD, and Edward L. Spitznagel, PhD Objetives. We examined the prevalene
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
 Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
