Home Care for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
|
|
|
- Virgil Lloyd
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Home Care for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury Printed in USA Arcadia Home Care & Staffing
2 What is Traumatic Brain Injury? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is most often an injury caused by a blow or a jolt to the head or by a penetration to the skull, and disrupts the normal functioning of a healthy brain. However, brain injuries can also be the result of strokes, brain bleeds from ruptured arteries, infections (e.g., meningitis), tumors, or oxygen deprivation. The degree of injury may range from mild to severe, which will determine the length of time necessary to recover. Key Demographics and Statistics about TBI Industry research tells us that currently, approximately 1.7 million Americans sustain some form of TBI every year, and the numbers will continue to climb. These TBIs occur either singularly or in conjunction with other injuries. Additionally: Approximately 75% of the TBIs that occur in the United States each year are concussions or other forms of mild TBIs. TBI is a factor in approximately 30% of all injury-related deaths in the United States. The populations most likely to suffer a TBI include children between the ages of 0 to 4 years old, adolescents between 15 and 19 years old and older adults (65+ years). Adults 75 years and older have the highest rates of TBI-related hospitalization and death. In sheer numbers, across all age groups, males are the most likely to sustain a TBI. Child abuse, warfare, professional sports (football, baseball, boxing, etc.) are major causes of this type of brain damage. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 1
3 Types of Brain Injuries There are many degrees of brain injuries some are mild and an individual can recover with no long-lasting effects, and some are so severe that the individual will require lifelong 24/7 care. Some of the more common brain injuries include the following: Aneurysm (a blood-filled sac formed by a diseaserelated or hereditary condition that weakens and stretches the wall of an artery or blood vessel) Anoxic/Hypoxic Encephalopathy (absence or shortage of oxygen in the brain) Arterial Dissections (severed or torn arteries in the neck) Concussion (injury from a blow or bump to the head) Contusion (bruising of the brain tissue) Hemorrhage/hematoma (damage to blood vessels in the brain, causing heavy bleeding, seepage or accumulation of blood in the brain) Hydrocephalus (excess fluid in the brain) Seizures (brain irritation or injury that interferes with communication between parts of the brain) Shearing (damage to the tissue and nerve cells of the brain) Skull Fracture (penetrating wound to the brain with broken skull bones) Stroke (a blood clot blocks the flow of blood to the brain and the brain cannot receive new oxygen or important nutrients) Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 2
4 Assessing the Damage When a brain injury occurs, especially a severe one, getting medical help as soon as possible is vital to lessening further damage to the brain. Health professionals will first act to maintain an adequate supply of oxygen to the brain, ensure blood pressure is at an acceptable level, obtain all the facts about the injury, and otherwise stabilize the individual. Various diagnostic tools specific to the brain and its functioning are used to determine the nature and severity of the brain injury. These include x-rays, CT and PET scans, MRIs, EEGs, and other related tests as well as frequent blood and urine testing. Glasgow Coma Scale After an individual has been stabilized, transfer to the ICU (intensive care unit) for further treatment and ongoing assessment is usually the next step. Doctors typically use the Glasgow Coma Scale to evaluate injuries to the brain and thus to classify them as mild, moderate or severe. The Scale has three levels of response that indicate the severity of brain impairment: 1. Eye opening test reveals the level of functioning of the brain s activity centers. 2. Best verbal response test identifies the condition of the central nervous system. 3. Best motor response test measures the ability to move arms and legs. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 3
5 Vital Signs Continuous monitoring and assessment of vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, breathing rate, pupil response to light, and grip strength) is an integral part of care for the individual with a brain injury. This is because a change in any one vital sign can be the first indication of a change in the overall condition of the individual. For example, a fever could indicate that an infection may be starting or lack of responsiveness could indicate increasing pressure on the brain. From Intensive Care to Inpatient Hospitalization to Rehabilitation Once vital signs are stable for a defined period or time, and there are no risks for other medical problems or surgical needs, the individual is transferred to an acute care setting or to a brain injury rehabilitation setting. At this time, further evaluation and treatment is conducted. For those who sustained neurological damage from which they have not recovered, the Rancho Los Amigos Scale of Cognitive Functioning is used to assist rehabilitation professionals in determining the individual s behavioral and psychological capabilities. The Scale has eight levels of functioning against which the individual is evaluated, ranging from no response (Level 1) to showing a purposeful and appropriate response to their environment (Level 8). As the individual shows improvement at every level, the healthcare team (with support from the family) will begin activities and treatment to help the individual develop successive skills and encourage appropriate behavior. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 4
6 Physical Changes In addition to the physical injuries that occur at the time of a TBI, there are many physical changes that may result from this type of injury some temporary, and some permanent and disabling. Headaches, pain, loss of hearing, speech or vision, recurring seizures, loss of mobility, (e.g., being confined to a wheelchair), paralysis or amputation of a limb these are examples of the physical changes an individual with a TBI may have to contend with during recovery and beyond, when trying to return to as normal a life as possible. Behavioral Changes A brain injury, even a mild one, can bring changes in behavior. While some of these may be temporary, it is very likely that when a serious brain injury occurs, there will be a range of emotional, psychological, and intellectual impairments that are longer term or permanent. For example, inability to reason, memory loss, poor attention span, and difficulty reading, writing, and speaking are all known issues with brain injuries. However, some of the most difficult issues to address (for the individual and their family) are those associated with the personality changes that often result from a TBI. For example, an individual who had previously been quiet and calm can become loud, aggressive, and impatient. Conversely, a previously friendly, gregarious individual who suffers a TBI can become withdrawn, sad, and quiet. Typically, whatever personality changes do occur will become pronounced, and may include mood swings that happen without warning and an inability to control emotions. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 5
7 Much of this behavior is emotionally fueled by the frustration, worry, and confusion the individual is experiencing, and can result in depression, anxiety, anger, irritability, and restlessness. Teamwork to Find Answers Finding solutions to the physical and behavioral issues that confront an individual with a TBI requires the combined efforts and dedicated teamwork of various healthcare professionals working with the individual and their family. It is often a long process and one in which outcomes are measured in small steps rather than larger milestones. Impact on Family Members When a loved one suffers a traumatic injury of any kind, understandably, the family is traumatized too. And when the injury involves the brain, the stress and worry are compounded. Depending on the circumstances of the injury, family members may feel a host of emotions: panic, fear, anger, guilt, anxiety, confusion, isolation, fatigue, and hopelessness about the outcome for their loved one. It is an overwhelming situation by any measure. To help the family through this crisis and beyond, the healthcare team should educate them on what to expect (depending on the diagnosis and condition of their loved one) at every phase of recovery. Some things to consider: There will be good days and bad days during the recovery and rehabilitation periods. Progress can take the form of fits and starts of moving forward and taking a step backward. The healthcare team should work together to explain what is happening to the individual at any point on the continuum of care. Planning for post-discharge care is critical and should begin while the individual is still hospitalized. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 6
8 Care for the TBI Patient after the Hospital/ Rehabilitation Facility Once the individual and family know what the expected outcome of the TBI will be, together they can plan for post-discharge care. An in-depth discussion with the doctor/healthcare team should identify the options for the individual. Whether the team believes that home care is a good next step or if the recommendation is for a long-term care facility, the doctor should initiate the referral and discharge planning process to begin the transition of care. Home Care for Individuals with TBI The goal of rehabilitation is to help the individual safely function as independently as possible. A home care program can support the rehabilitation program established by the doctor to help the body and the brain heal, and to (re)learn critical activities. Recovery from a brain injury is different for everyone no two brain injuries are exactly alike. It is usually a lengthy process and may take anywhere from several months to several years. The activities of daily living, including a home care program, must be carefully monitored by both professional caregivers as well as family members. The home care nurse and other members of the home care team (physical, occupational, and speech therapists, as well as behavioral therapists, home health aides, et al) will work with the doctor to develop an appropriate plan of care and implement and monitor the individual s progress. One very important element will be educating the individual and the family on the home-based rehabilitation process, including the following: Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 7
9 Teaching healthy habits to establish and maintain as part of the recovery, including: Get enough rest energy levels are still recovering too, and it is easy to become fatigued. Avoid any activities or behavior that could cause another blow or injury to the head. Discuss with the doctor a timetable for driving a car, riding a bike, playing sports, using any kind of heavy equipment, lawn mowers, etc. Take medication as prescribed. Do not use drugs or alcohol. Keep a list of things to help with memory loss. Discuss with the doctor other rehabilitation services that might help and ask for a referral to receive those services. Helping the family understand how the individual s disabilities (short- or long-term) will affect behavior and activities of daily living, and involve them in the day-to-day rehabilitation process whenever possible. Suggesting practical ways the family can help the individual compensate for the loss of abilities, whether temporary or permanent. Ensuring the individual has a room ready at the time of arrival at home, and that it is arranged so the individual can function as independently as possible. For example, dresser drawers may be labeled to describe the contents (socks, underwear, pajamas, etc.) The nightstand next to the bed may have a tray meant just for eyeglasses, phone, wallet, pens, etc. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 8
10 Establishing a consistent home care schedule that encourages as much activity as the individual can manage without becoming fatigued. This schedule will take into account any in-home as well as outpatient rehabilitation activities, doctor s appointments, social contact, etc. Addressing (along with the family) any other issues that existed before the injury (e.g., alcohol or drug abuse). While in the rehabilitation phase, this is an excellent time to educate and reinforce to the individual the importance of maintaining good health by avoiding drugs and alcohol, especially if prescription medications are being administered. Mixing alcohol or other drugs with prescription medication is dangerous. Teaching the importance of cueing by using lists, notes, cue cards or similar tools to help the individual compensate for memory loss while increasing selfconfidence and promoting independence. Emphasizing the importance of consistency and structure in the home environment. This strategy helps provide a sense of security because the individual knows what to expect day in and day out. Maintaining ongoing communication with the doctor and with the family especially if changes in behavior are seen. For example, silent seizures may develop after a TBI, and while the individual may not show any outward signs (i.e., no convulsions) this can create changes in behavior. Other symptoms may include restlessness, pacing, complaining of changes in smell or taste, even hallucinations. Monitoring the individual s progress in all aspects of their home care program. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 9
11 The Role of Family/Friends When a loved one is recovering from a traumatic injury, the help and support of friends and family can make a significant difference in their rehabilitation. Here are some suggestions for ways to support a loved one who is in recovery whether in a facility or at home: During visits, especially in the early days of the injury, direct verbal communication may not be possible; sit quietly, hold their hand, let them know you are there. Because other senses (e.g., hearing, smell, taste) may be intact, you might bring a sample of their favorite perfume, or read to them from one of their favorite books, or arrange for them to listen to music they previously enjoyed. If they are able to speak, limit the length of the conversation and discuss topics that will not over-stimulate or stress the individual. Use familiar names for things consistently to help orient the individual to their environment. Be consistent in your approach during every contact; stay calm during emotional outbursts or behavior that is extreme. Give step-by-step directions that the individual can follow when carrying out tasks, especially those associated with their rehabilitation program. Don t remind them of their past abilities; they may not be able to do the things they did before the injury. Use age appropriate language; don t talk down to the individual, and allow them time to respond; their condition may slow down response times. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 10
12 Keep a sense of humor; this can help everyone cope Praise the individual as they progress in their recovery and rehabilitation program; this encourages and reinforces the effort they are making. Tips for Managing Stress Even as their loved one is undergoing treatment and receiving intensive care for a TBI, family members need care, too. More times than not, the family suffers along with the individual. Some things that may help family members during this very difficult time include: Maintain good nutrition; eat well-balanced meals at regular intervals. Get as much rest as possible; have family members and friends take turns visiting the individual. Let others help. Share your feelings with a professional. This can help relieve feelings of guilt and worry. Join a support group. Often hospitals or community organizations sponsor these for family and friends. Try to get some regular exercise. See friends, maintain social connections. Role of Community Resources As part of an ongoing home care program for the individual with a TBI, a daytime rehabilitation program may be an option. Day treatment programs may provide rehabilitation activities for partial or full days, and the individual can return to their home later in the day. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 11
13 Behavior management programs can also be an important part of a rehabilitation plan. These are usually community-based programs that teach techniques for selfcontrol and other socially appropriate behaviors. The hospital or treatment facility should be able to arrange referrals to these resources. There are national organizations that also support TBI survivors and their families. Contacting them for information and practical assistance can be very helpful, no matter where the individual is in the treatment or recovery processes. Please see Additional Resources at the back of this booklet for more Web sites and contact information. Research on Traumatic Brain Injury The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) has long been a major resource for research on TBI. Key findings from their research include the following: One of the most pervasive types of injury is shearing damage to the brain s tissue and nerve cells. Shearing sets off a chain reaction of chemicals in the brain that also damages other healthy brain cells and can lead to cell death. This typically occurs within the first hours after the TBI. Research has demonstrated that: there are special chemicals that can be used to counteract shearing; using a substance called cyclosporin A can protect the nerve cells in the brain; and inducing a state of low body temperature (hypothermia) can slow down brain cell death. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 12
14 After a TBI the brain tries to heal itself. It is a very delicate process and it can be interrupted by any of a number of things, such as low oxygen levels and low blood flow to the brain. Therefore, researchers are trying to learn more about the brain's natural recovery process and the factors that control it. Trauma to the frontal lobes of the brain can damage specific chemical messengers in the brain the dopaminergic system. This system is a group of nerve cells in the brain that uses dopamine, an important chemical messenger. Ongoing research is trying to determine how the dopaminergic system responds after a TBI. Use of stem cells to repair or replace damaged brain tissue. A neural stem cell can normally develop into several different cell types found within the central nervous system. Research is focusing on the ability of stem cells to develop into neurotransmitterproducing neurons, specifically dopamine-producing cells. Clinical Trials Research In addition to the research described above, the clinical scientific community is also working on a wider variety of TBI research involving actual TBI patients, including: Study of the brain s plasticity (ability to adapt to injury) after a trauma. The brain s plasticity as well as its ability to rewire its nerve connections enables another part of the brain to take on the functions of the damaged area. Creation of new and better rehabilitation programs for those with disabilities resulting from a TBI. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 13
15 Lowering the body temperature (hypothermia) in TBI patients within 8 hours of the trauma. Research has already shown that while this treatment did not improve outcome overall, it did demonstrate that patients younger than 45 years old who were admitted to the hospital already in a hypothermic state fared better if they were kept cool than if they were brought back to normal body temperature. Other ongoing clinical trials include the use of hypothermia for severe TBI in children, the use of magnesium sulfate to protect nerve cells after TBI, and the effects of lowering ICP and increasing cerebral blood flow. Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 14
16 Glossary of Terms Associated with TBI Aneurysm - a blood-filled sac formed by disease-related stretching of an artery or blood vessel Anoxia lack of oxygen to an organ's tissues leading to cell death Aphasia - difficulty understanding and/or producing spoken and written language Brain death - an irreversible cessation of measurable brain function Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) - the fluid that bathes and protects the brain and spinal cord Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Brain damage caused by repetitive head injury (often associated with professional sports such as boxing, football, baseball, etc.) Closed head injury - an injury that occurs when the head suddenly and violently hits an object but the object does not break through the skull Coma - a state of profound unconsciousness caused by disease, injury, or poison Computed Tomography (CT) - a scan that creates a series of cross-sectional X-rays of the head and brain; also called CAT scan Concussion - injury to the brain caused by a hard blow or violent shaking, resulting in a sudden and temporary impairment of brain function, such as a loss of consciousness or disturbance of vision and equilibrium Contusion - distinct area of swollen brain tissue mixed with blood released from broken blood vessels Deep vein thrombosis - formation of a blood clot deep within a vein Depressed skull fracture - a fracture occurring when pieces of broken skull press into the tissues of the brain Hematoma - heavy bleeding into or around the brain caused by damage to a major blood vessel in the head Hypoxia - decreased oxygen levels in an organ, such as the brain; less severe than anoxia Immediate seizures - seizures that occur within 24 hours of a traumatic brain injury Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 15
17 Intracranial pressure build-up of pressure in the brain as a result of injury Locked-in syndrome - a condition in which an individual is aware and awake, but cannot move or communicate due to complete paralysis of the body Penetrating head injury - a brain injury in which an object pierces the skull and enters the brain tissue Persistent vegetative state - an ongoing state of severely impaired consciousness, in which the individual is incapable of voluntary movement Plasticity - ability of the brain to adapt to injury Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) - a complex problem that may cause headache after head injury; in most cases, there is no memory of the event that caused the concussion and of the time prior to the injury Post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) - confusion due to a traumatic brain injury, including difficulty with perception, thinking, remembering, and concentration Post-traumatic dementia - mental deterioration and emotional apathy following trauma Shaken Baby Syndrome - a severe form of head injury that occurs when an infant or small child is shaken forcibly enough to cause the brain to bounce against the skull; symptoms include irritability, lethargy, tremors, or vomiting, seizures, coma, stupor, or death Stupor - a state of impaired consciousness in which the individual is unresponsive but can be aroused briefly by a strong stimulus Thrombosis or thrombus the forming of a blood clot at the site of an injury Vasospasm - exaggerated, persistent contraction of the walls of a blood vessel Vegetative state - a condition in which individuals are unconscious and unaware of their surroundings, but continue to have a sleep/wake cycle and can have periods of alertness Ventriculostomy - a surgical procedure that drains cerebrospinal fluid from the brain Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 16
18 Additional Resources Brain Injury Association of America, Inc Spring Hill Road, Suite 110 Vienna, VA Phone: / Fax: National Brain Injury Information Center (Brain Injury Information Only) Brain Trauma Foundation 7 World Trade Center/34th Floor 250 Greenwich St. New York, NY Phone: National Rehabilitation Information Center 8400 Corporate Drive, Suite 500 Landover, MD Phone: 800/ (V) 301/ (TTY) 301/ (Fax) Arcadia Home Care & Staffing 17
19 Arcadia Health Services, Inc.
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
BINSA Information on Brain Injury
 Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3.
 Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and
 Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol
 Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol Returning to play following a concussion involves a stepwise progression once the individual is symptom free. There are many risks to premature return to play
Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol Returning to play following a concussion involves a stepwise progression once the individual is symptom free. There are many risks to premature return to play
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI)
 Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit
 Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit D Legal Guide Simple Step-By-Step Guide to Your Brain & Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [Type text] Distributed By: www.downtownlalw.com A Simple Step-by-Step Guide to your
Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit D Legal Guide Simple Step-By-Step Guide to Your Brain & Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [Type text] Distributed By: www.downtownlalw.com A Simple Step-by-Step Guide to your
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
brain injury take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest.
 take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
Brain Injury Education
 Memorial Hermann mischer neuroscience institute Brain Injury Education texas medical center Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 What Is a Brain Injury? 4 Types of Brain Injury 6 Meet Our Directors and Attending
Memorial Hermann mischer neuroscience institute Brain Injury Education texas medical center Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 What Is a Brain Injury? 4 Types of Brain Injury 6 Meet Our Directors and Attending
Injury Law Center HEAD INJURY. Head injuries can be caused by car crashes, sports injuries, falls, workplace injuries and assaults.
 Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. Description
Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. Description
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
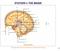
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Head Injury in Children
 Head Injury in Children The worst fear of every parent is to receive news that your child has been injured in an accident. Unfortunately, in our society, accidental injuries have become the leading threat
Head Injury in Children The worst fear of every parent is to receive news that your child has been injured in an accident. Unfortunately, in our society, accidental injuries have become the leading threat
EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY
 Traumatic brain injury EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common neurological condition that can have significant emotional and cognitive consequences.
Traumatic brain injury EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common neurological condition that can have significant emotional and cognitive consequences.
B U R T & D A V I E S PERSONAL INJURY LAWYERS
 TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY An Information Guide BRAIN INJURY REHABILITATION SERVICE CONCUSSION CLINIC BURWOOD HOSPITAL TABLE OF CONTENTS AN INFORMATION GUIDE... 3 WHAT HAPPENS IN A TRAUMATIC
RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY An Information Guide BRAIN INJURY REHABILITATION SERVICE CONCUSSION CLINIC BURWOOD HOSPITAL TABLE OF CONTENTS AN INFORMATION GUIDE... 3 WHAT HAPPENS IN A TRAUMATIC
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 1 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WHAT IS IT? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is caused by impact to the head in turn causes damage to the brain. TBI can happen at the time of the impact or later on. The injury may
1 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WHAT IS IT? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is caused by impact to the head in turn causes damage to the brain. TBI can happen at the time of the impact or later on. The injury may
Mild Brain Injury Recovery
 2011 Mild Brain Injury Recovery Mild Brain Injury Recovery What is a mild brain injury? A brain injury is often caused by trauma to the head for any reason. If you had a change in your level of consciousness,
2011 Mild Brain Injury Recovery Mild Brain Injury Recovery What is a mild brain injury? A brain injury is often caused by trauma to the head for any reason. If you had a change in your level of consciousness,
Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3. Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6. Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9
 Table of Contents Brain Injury: Basic Facts... 1 Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3 Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6 Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9 Questions Families Should Ask Their...
Table of Contents Brain Injury: Basic Facts... 1 Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3 Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6 Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9 Questions Families Should Ask Their...
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Revised 10-4-10 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes
 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
Recovering from Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion. A Guide for Patients and Their Families
 Recovering from Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion A Guide for Patients and Their Families Recovering From Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion: A Guide for Patients and Their Families This booklet
Recovering from Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion A Guide for Patients and Their Families Recovering From Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion: A Guide for Patients and Their Families This booklet
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury
 A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Methamphetamine. Like heroin, meth is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Meth is a highly addictive drug.
 Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Addressing Family Needs
 Addressing Family Needs FAMILIES How Can I Build Stronger Family Ties? Everyone in the family is affected by TBI. * Your role within the family has changed and the role of your family member with TBI may
Addressing Family Needs FAMILIES How Can I Build Stronger Family Ties? Everyone in the family is affected by TBI. * Your role within the family has changed and the role of your family member with TBI may
BINSA Information on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury
 Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury The consequences of a brain injury on any individual, family or relationship are far reaching. A brain injury not only impacts
Memory, Behaviour, Emotional and Personality Changes after a Brain Injury The consequences of a brain injury on any individual, family or relationship are far reaching. A brain injury not only impacts
How To Understand The Effects Of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Updated, July 2014 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She also hit her
Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Updated, July 2014 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She also hit her
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Resources updated, March 2011 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She
Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Resources updated, March 2011 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE
 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE Women who are abused often suffer injury to their head, neck, and face. The high potential for women who are abused to have mild to severe Traumatic Brain Injury
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE Women who are abused often suffer injury to their head, neck, and face. The high potential for women who are abused to have mild to severe Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury. Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community.
 Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
THE MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION IN AUSTRALIAN FOOTBALL
 THE MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION IN AUSTRALIAN FOOTBALL AFL Research board AFL MEDICAL OFFICERS' ASSOCIATION THE MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION IN AUSTRALIAN FOOTBALL This document has been published by the AFL
THE MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION IN AUSTRALIAN FOOTBALL AFL Research board AFL MEDICAL OFFICERS' ASSOCIATION THE MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION IN AUSTRALIAN FOOTBALL This document has been published by the AFL
TBI TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WITHIN THE MILITARY/VETERAN POPULATION
 TBI TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WITHIN THE MILITARY/VETERAN POPULATION What is TBI? An external force that disrupts the normal function of the brain. Not all blows or jolts to the head result in a TBI. The
TBI TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WITHIN THE MILITARY/VETERAN POPULATION What is TBI? An external force that disrupts the normal function of the brain. Not all blows or jolts to the head result in a TBI. The
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. A Fact Sheet for School Nurses
 A Fact Sheet for School Nurses Assess the situation Be alert for signs and symptoms Contact a health care professional The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. * Most concussions occur without loss of
A Fact Sheet for School Nurses Assess the situation Be alert for signs and symptoms Contact a health care professional The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. * Most concussions occur without loss of
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Cocaine. Like heroin, cocaine is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Cocaine is a commonly abused drug.
 Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]
![SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]](/thumbs/27/9667060.jpg) SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
Head Injury. Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI
 Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME:
 SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME: A SAFETY MANUAL FOR HAND IN HAND CHILD CARE SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME BACKGROUND: The dangers of shaking a baby are becoming more and more apparent, often with disastrous results. The
SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME: A SAFETY MANUAL FOR HAND IN HAND CHILD CARE SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME BACKGROUND: The dangers of shaking a baby are becoming more and more apparent, often with disastrous results. The
Population Health: Veterans. Humble Beginnings
 Population Health: Veterans Randy Moore, MSN, RN VA Nursing Academy partnership with UAB SON; Clinical Instructor Humble Beginnings Colonial Period From the beginning, the English colonies in North America
Population Health: Veterans Randy Moore, MSN, RN VA Nursing Academy partnership with UAB SON; Clinical Instructor Humble Beginnings Colonial Period From the beginning, the English colonies in North America
Facts about Concussion and Brain Injury
 Facts about Concussion and Brain Injury W H E R E T O G E T H E L P About Concussion Signs and Symptoms Getting Better Where to Get Help Resources U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for
Facts about Concussion and Brain Injury W H E R E T O G E T H E L P About Concussion Signs and Symptoms Getting Better Where to Get Help Resources U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for
Understanding. Spinal Cord Injury. Tasha, injured in 1997.
 Understanding Spinal Cord Injury Tasha, injured in 1997. What Is Spinal Cord Injury? The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system that contains the body s longest nerve fibers. It serves as
Understanding Spinal Cord Injury Tasha, injured in 1997. What Is Spinal Cord Injury? The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system that contains the body s longest nerve fibers. It serves as
Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services
 Brain injury and neuro-rehabilitation services focused on recovery. Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services Milwaukee Center for Independence Nexday programs provide a continuum of care for people recovering
Brain injury and neuro-rehabilitation services focused on recovery. Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services Milwaukee Center for Independence Nexday programs provide a continuum of care for people recovering
Mental health issues in the elderly. January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca
 Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Brain Tumours Understanding your diagnosis
 Brain Tumours Understanding your diagnosis Brain Tumours Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have a brain tumour you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Brain Tumours Understanding your diagnosis Brain Tumours Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have a brain tumour you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Understanding. Depression. The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself. Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members
 TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
The faster a person gets medical care after a stroke, the better the chances are that some or all damage from the stroke can be reversed.
 What is a Stroke? A stroke or brain attack occurs when blood flow to the brain is cut off or reduced. Brain cells die or are damaged. There are two types of stroke: One type happens when a blood clot blocks
What is a Stroke? A stroke or brain attack occurs when blood flow to the brain is cut off or reduced. Brain cells die or are damaged. There are two types of stroke: One type happens when a blood clot blocks
Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery
 Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery Recovery after brain injury is a process that occurs in stages. Some people move quickly through the stages, while others make slow, but steady gains. The Rancho Los Amigos'
Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery Recovery after brain injury is a process that occurs in stages. Some people move quickly through the stages, while others make slow, but steady gains. The Rancho Los Amigos'
Psychological First Aid Red Cross Preparedness Academy 2014
 Caring for Survivors of Trauma and Disaster: An Introduction to Psychological First Aid Biographical Information Rev. William F. Engfehr III LutheranChurch MissouriSynod DisasterResponseChaplain Senior
Caring for Survivors of Trauma and Disaster: An Introduction to Psychological First Aid Biographical Information Rev. William F. Engfehr III LutheranChurch MissouriSynod DisasterResponseChaplain Senior
acbis Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury
 acbis Academy for the Certification of Brain Injury Specialists Certification Exam Preparation Course Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury Module Objectives Describe the incidence, prevalence and epidemiology
acbis Academy for the Certification of Brain Injury Specialists Certification Exam Preparation Course Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury Module Objectives Describe the incidence, prevalence and epidemiology
Table of Contents. Credits. New Terms You May Hear. Introduction. Brain Injury 101. Recovery From Traumatic Brain Injury
 Table of Contents Credits New Terms You May Hear Introduction Brain Injury 101 Recovery From Traumatic Brain Injury What To Expect In The Intensive Care Unit What You Can Do What To Expect In The Rehab
Table of Contents Credits New Terms You May Hear Introduction Brain Injury 101 Recovery From Traumatic Brain Injury What To Expect In The Intensive Care Unit What You Can Do What To Expect In The Rehab
NEUROPSYCHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE. (Please fill this out prior to your appointment and bring it with you.) Name: Date of appointment: Home address:
 NEUROPSYCHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE (Please fill this out prior to your appointment and bring it with you.) Name: Date of appointment: Date of birth: Age: _ Home address: _ Home phone: Cell phone: Work phone:
NEUROPSYCHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE (Please fill this out prior to your appointment and bring it with you.) Name: Date of appointment: Date of birth: Age: _ Home address: _ Home phone: Cell phone: Work phone:
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR:
 PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department
 Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department *This document should be used as a framework for a successful concussion management program but is not intended to replace
Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department *This document should be used as a framework for a successful concussion management program but is not intended to replace
Brain Injury 102 The Basics
 Brain Injury 102 The Basics Brain Injury 102 1 After completion of this module, the learner will be able to: Identify: the basic types of brain injuries. the types of insults to the brain s anatomy. the
Brain Injury 102 The Basics Brain Injury 102 1 After completion of this module, the learner will be able to: Identify: the basic types of brain injuries. the types of insults to the brain s anatomy. the
Comprehensive Special Education Plan. Programs and Services for Students with Disabilities
 Comprehensive Special Education Plan Programs and Services for Students with Disabilities The Pupil Personnel Services of the Corning-Painted Post Area School District is dedicated to work collaboratively
Comprehensive Special Education Plan Programs and Services for Students with Disabilities The Pupil Personnel Services of the Corning-Painted Post Area School District is dedicated to work collaboratively
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older
 Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
E x p l a i n i n g Stroke
 Explaining Stroke Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
Explaining Stroke Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
Rainy River District School Board SECTION 4
 Rainy River District School Board SECTION 4 Students STUDENT CONCUSSION PROTOCOL PROCEDURE PURPOSE 4.74 The Rainy River District School Board is committed to the safety of all students. In the interests
Rainy River District School Board SECTION 4 Students STUDENT CONCUSSION PROTOCOL PROCEDURE PURPOSE 4.74 The Rainy River District School Board is committed to the safety of all students. In the interests
Non-epileptic seizures
 Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Coma & impaired consciousness after brain injury. A guide for relatives and carers
 Coma & impaired consciousness after brain injury A guide for relatives and carers About the guide Contents A guide for relative s and carers Written by Dr Martin Coleman, Impaired Consciousness Research
Coma & impaired consciousness after brain injury A guide for relatives and carers About the guide Contents A guide for relative s and carers Written by Dr Martin Coleman, Impaired Consciousness Research
HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2
 HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2 LET S TALK ABOUT BRAIN INJURIES! Traumatic head injury affects more than 1.7 million people in
HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2 LET S TALK ABOUT BRAIN INJURIES! Traumatic head injury affects more than 1.7 million people in
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Understanding. Brain Tumors. Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul.
 Understanding Brain Tumors Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul. What Is a Brain Tumor? A brain tumor, like other tumors, is a collection of cells that multiply at a rapid rate. The tumor may
Understanding Brain Tumors Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul. What Is a Brain Tumor? A brain tumor, like other tumors, is a collection of cells that multiply at a rapid rate. The tumor may
Neurology. A stroke, what to do? Een beroerte en dan? Ward:: Subject:
 Ward:: Subject: Neurology? Een beroerte en dan? 1 The brain and its function The brain and the spinal cord together form the central nervous system. This system compares well to a telephone exchange. Through
Ward:: Subject: Neurology? Een beroerte en dan? 1 The brain and its function The brain and the spinal cord together form the central nervous system. This system compares well to a telephone exchange. Through
Table of contents Topic Page
 Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
20 Questions (and answers) about Traumatic Brain Injury
 20 Questions (and answers) about Traumatic Brain Injury for insurance claims adjusters, case managers, attorneys, and health-care providers by Dennis P. Swiercinsky, Ph.D. 1. What is traumatic brain injury
20 Questions (and answers) about Traumatic Brain Injury for insurance claims adjusters, case managers, attorneys, and health-care providers by Dennis P. Swiercinsky, Ph.D. 1. What is traumatic brain injury
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
USVH Disease of the Week #1: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
 USVH Disease of the Week #1: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Effects of Traumatic Experiences A National Center for PTSD Fact Sheet By: Eve B. Carlson, Ph.D. and Josef Ruzek, Ph.D. When people find
USVH Disease of the Week #1: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Effects of Traumatic Experiences A National Center for PTSD Fact Sheet By: Eve B. Carlson, Ph.D. and Josef Ruzek, Ph.D. When people find
Presently, there are no means of preventing bipolar disorder. However, there are ways of preventing future episodes: 1
 What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
Common Questions and Answers About Severe Brain Injury
 Common Questions and Answers About Severe Brain Injury What you should know about severe brain injuries The purpose of this publication is to provide you with information about severe brain injuries. Such
Common Questions and Answers About Severe Brain Injury What you should know about severe brain injuries The purpose of this publication is to provide you with information about severe brain injuries. Such
Alzheimer s disease. What is Alzheimer s disease?
 Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
75-09.1-08-02. Program criteria. A social detoxi cation program must provide:
 CHAPTER 75-09.1-08 SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION ASAM LEVEL III.2-D Section 75-09.1-08-01 De nitions 75-09.1-08-02 Program Criteria 75-09.1-08-03 Provider Criteria 75-09.1-08-04 Admission and Continued Stay Criteria
CHAPTER 75-09.1-08 SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION ASAM LEVEL III.2-D Section 75-09.1-08-01 De nitions 75-09.1-08-02 Program Criteria 75-09.1-08-03 Provider Criteria 75-09.1-08-04 Admission and Continued Stay Criteria
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
PHYSICAL/MEDICAL ISSUES
 PHYSICAL/MEDICAL ISSUES Tutorial: Fatigue WHAT IS FATIGUE? Two importantly different concepts are suggested by the word, fatigue. The first is sleepiness or drowsiness; the second is a more pervasive feeling
PHYSICAL/MEDICAL ISSUES Tutorial: Fatigue WHAT IS FATIGUE? Two importantly different concepts are suggested by the word, fatigue. The first is sleepiness or drowsiness; the second is a more pervasive feeling
Sleep Difficulties. Insomnia. By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD
 Sleep Difficulties By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD For most people, night is a time of rest and renewal; however, for many people with Parkinson s disease nighttime is a struggle to get the
Sleep Difficulties By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD For most people, night is a time of rest and renewal; however, for many people with Parkinson s disease nighttime is a struggle to get the
A Depression Education Toolkit
 A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
HEAD INJURIES & CONCUSSION PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL
 HEAD INJURIES & CONCUSSION PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL Policy Statement In order to effectively and consistently manage head injuries, the Brooke Charter School has established the following protocol
HEAD INJURIES & CONCUSSION PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL Policy Statement In order to effectively and consistently manage head injuries, the Brooke Charter School has established the following protocol
Concussion Guidance for the General Public
 CONCUSSION FACTS A concussion is a brain injury. All concussions are serious. Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness. All athletes with any symptoms following a head injury must be removed
CONCUSSION FACTS A concussion is a brain injury. All concussions are serious. Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness. All athletes with any symptoms following a head injury must be removed
9/11Treatment Referral Program How to Get Care
 9/11Treatment Referral Program How to Get Care Health 9/11 Treatment Referral Program The 9/11 Treatment Referral Program was created to help enrollees and others find care for WTC-related health problems.
9/11Treatment Referral Program How to Get Care Health 9/11 Treatment Referral Program The 9/11 Treatment Referral Program was created to help enrollees and others find care for WTC-related health problems.
Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories
 23 Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories In this chapter you will: learn the different special education categories 24 IDEA lists different disability categories under which children may be eligible for services.
23 Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories In this chapter you will: learn the different special education categories 24 IDEA lists different disability categories under which children may be eligible for services.
Are you feeling... Tired, Sad, Angry, Irritable, Hopeless?
 Are you feeling... Tired, Sad, Angry, Irritable, Hopeless? I feel tired and achy all the time. I can t concentrate and my body just doesn t feel right. Ray B. I don t want to get out of bed in the morning
Are you feeling... Tired, Sad, Angry, Irritable, Hopeless? I feel tired and achy all the time. I can t concentrate and my body just doesn t feel right. Ray B. I don t want to get out of bed in the morning
The Thirteen Special Education Classifications. Part 200 Regulations of the Commissioner of Education, Section 4401(1)
 The Thirteen Special Education Classifications Part 200 Regulations of the Commissioner of Education, Section 4401(1) Student With a Disability: A student as defined in section 4401(1), who has not attained
The Thirteen Special Education Classifications Part 200 Regulations of the Commissioner of Education, Section 4401(1) Student With a Disability: A student as defined in section 4401(1), who has not attained
Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Carol A. Waldmann, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/ deceleration forces, is common in the general population. Homeless persons
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Carol A. Waldmann, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/ deceleration forces, is common in the general population. Homeless persons
WHY CAN POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER LEAD TO SUBSTANCE ADDICTION? 3 WAYS TO MANAGE YOUR POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER WITHOUT RELYING ON DRUGS
 Take Charge of Substance Abuse Related to Your Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Prepared by: Coping with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can be overwhelming at times and it is so easy to become dependent
Take Charge of Substance Abuse Related to Your Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Prepared by: Coping with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can be overwhelming at times and it is so easy to become dependent
